Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control Based on Ultra-Local Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
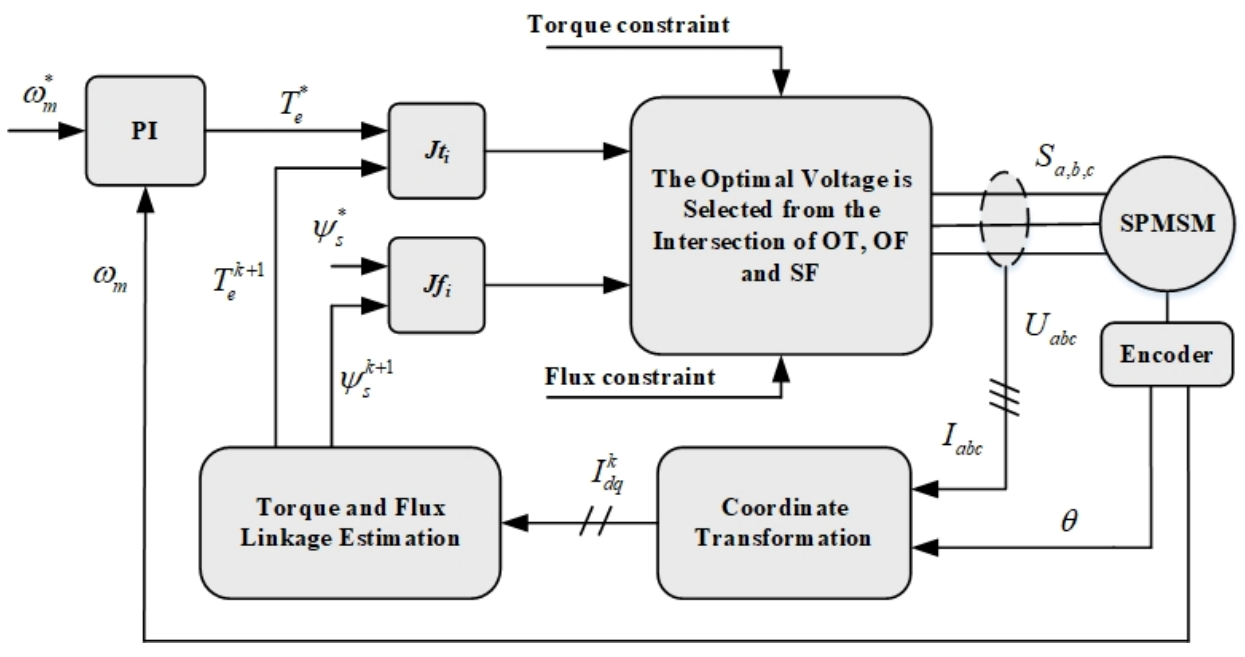
2. Principle of Conventional Parallel Predictive Torque Control
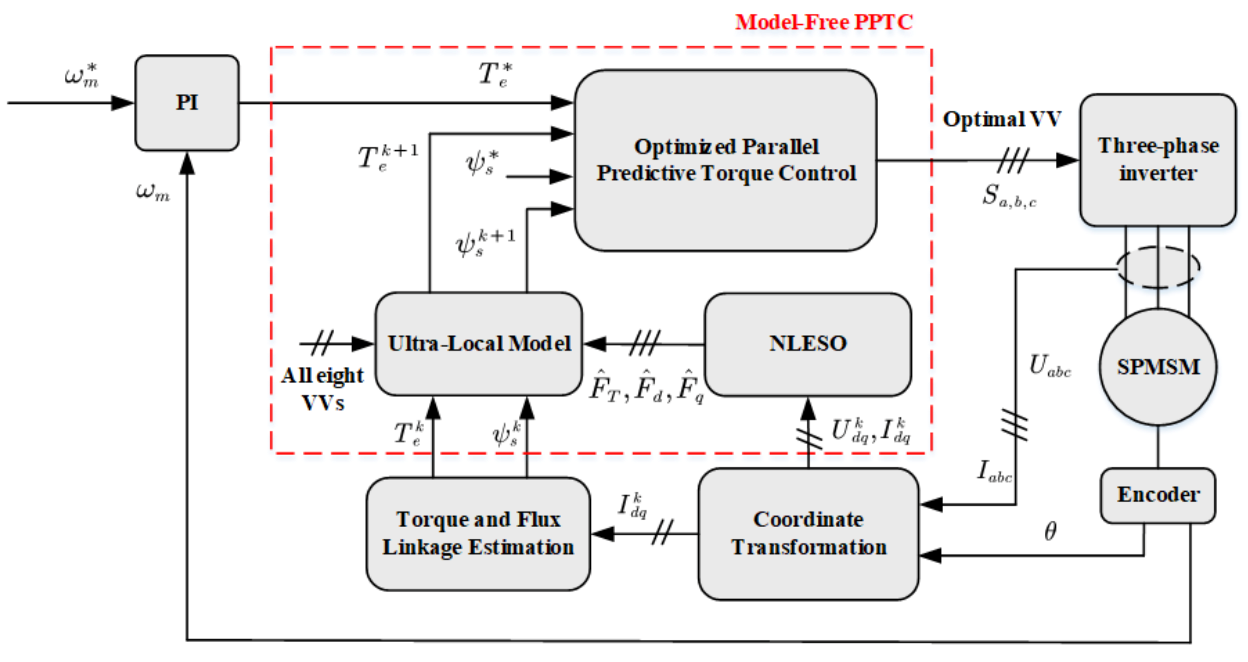
3. Principle of Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control
3.1. Model Free Control Based on UL Model
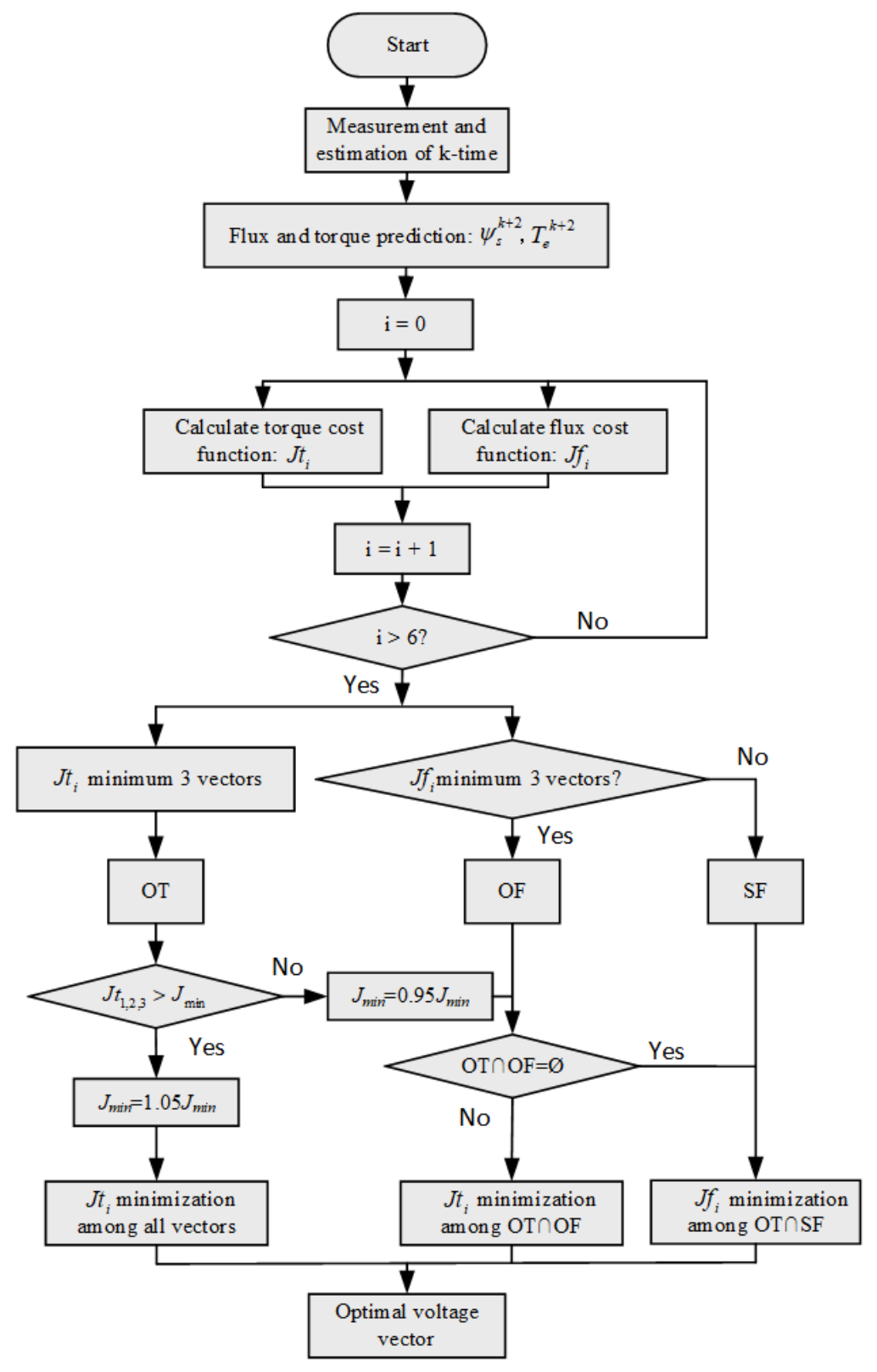
3.2. Optimized Parallel Predictive Torque Control
4. Performance Evaluation Simulation
4.1. Simulation with Precise Parameters
4.2. Simulation with Mismatched Parameters
4.3. Simulation with Mismatched Parameters under Steady State
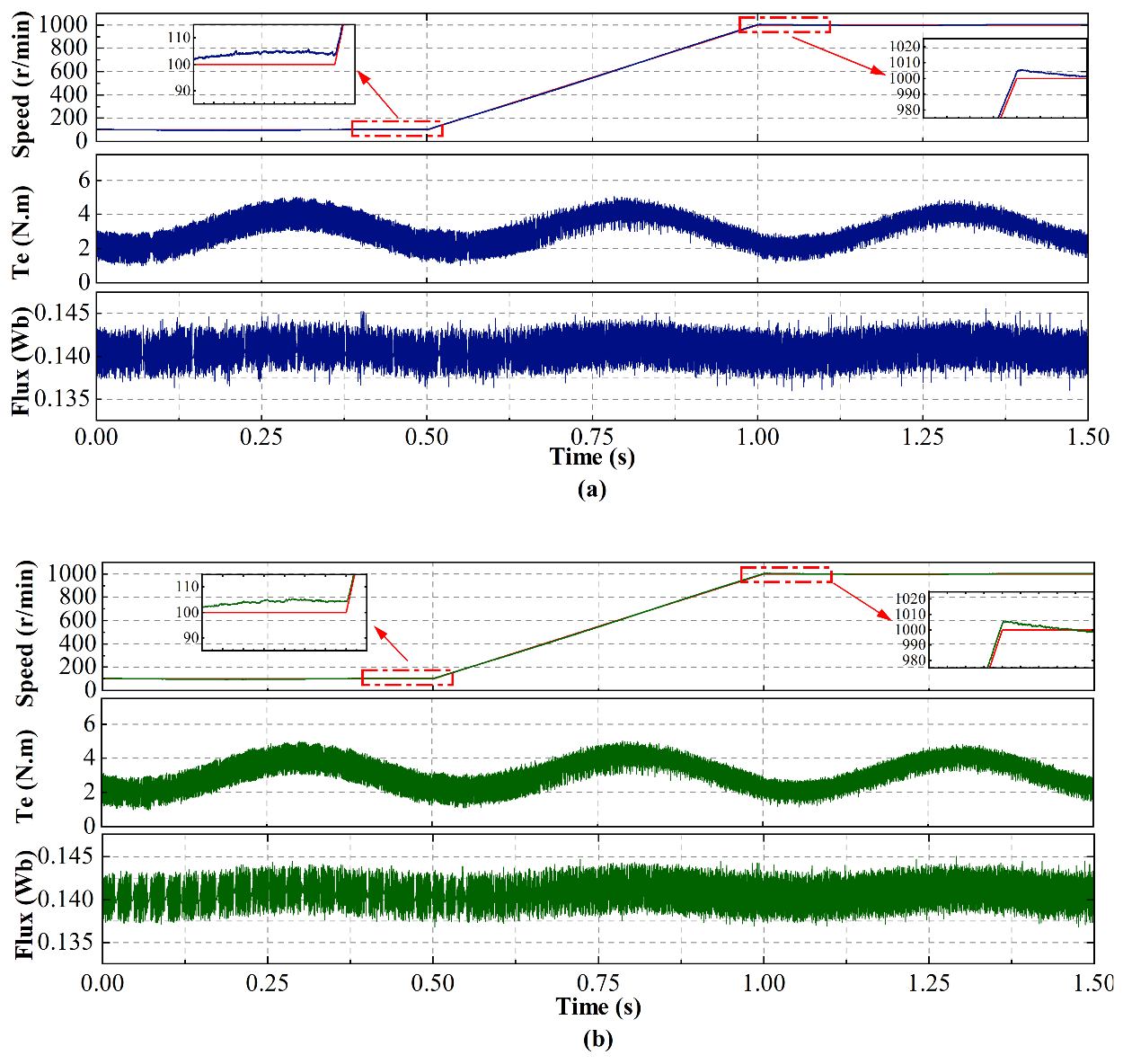
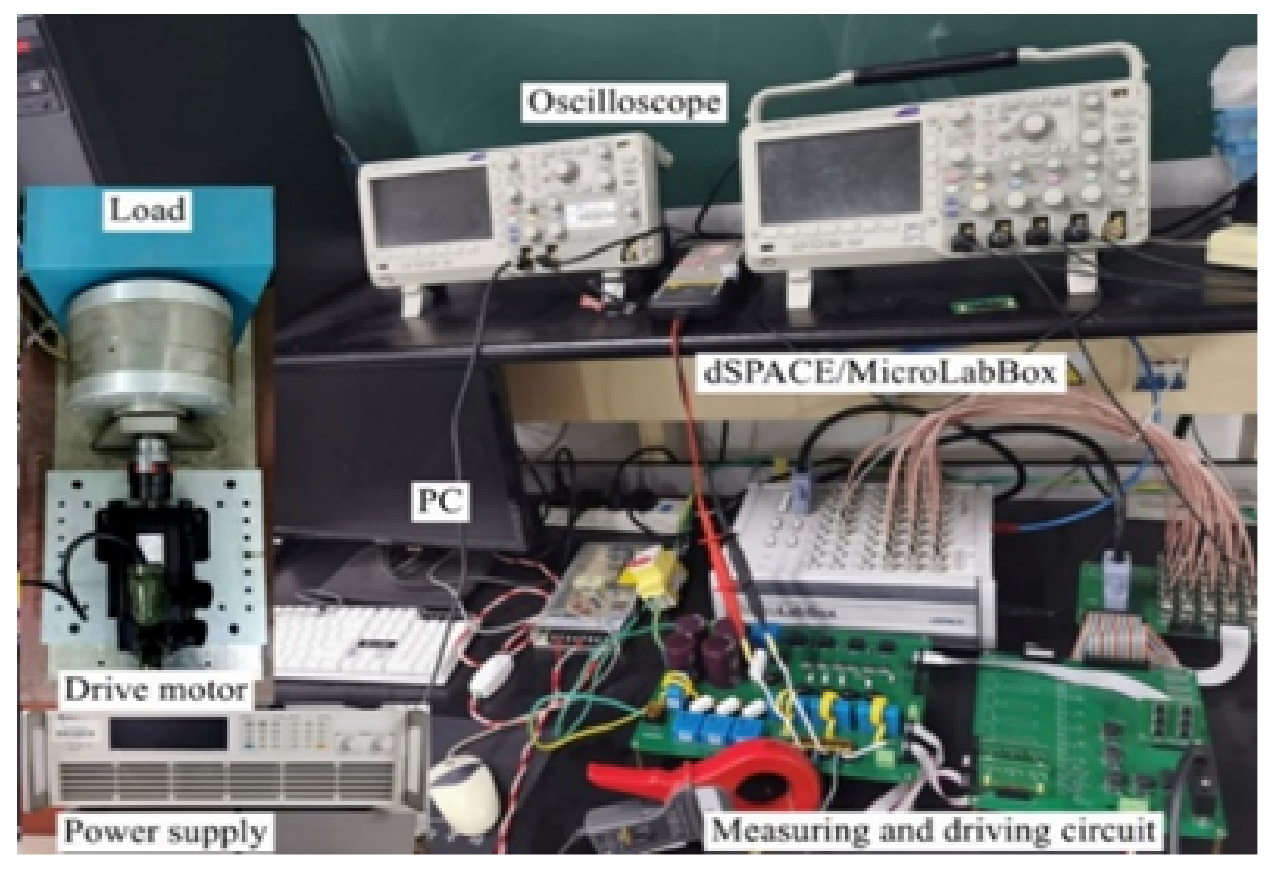
5. Performance Evaluation Experiment
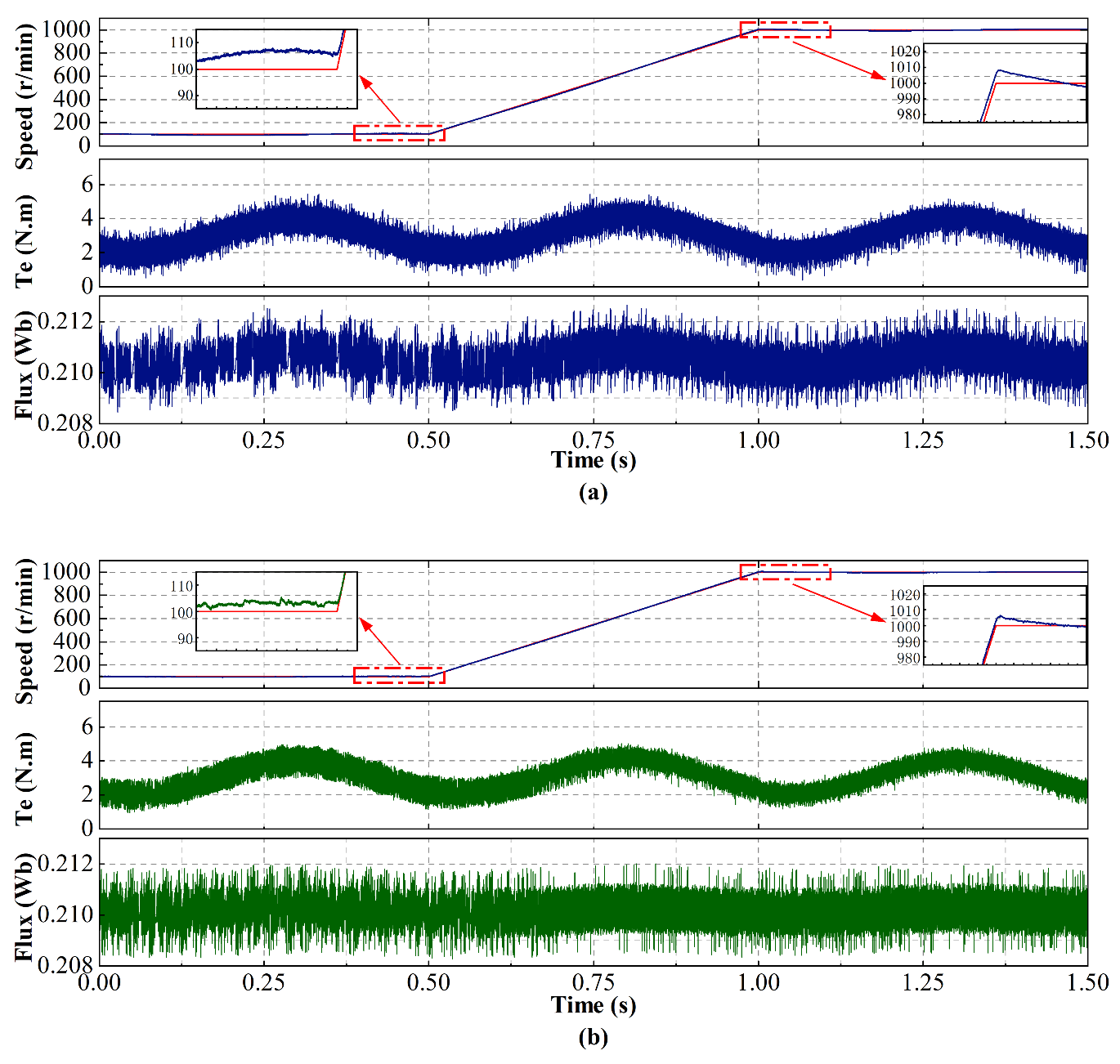
5.1. No-Load Start-Up Experiment of Proposed MF-PPTC
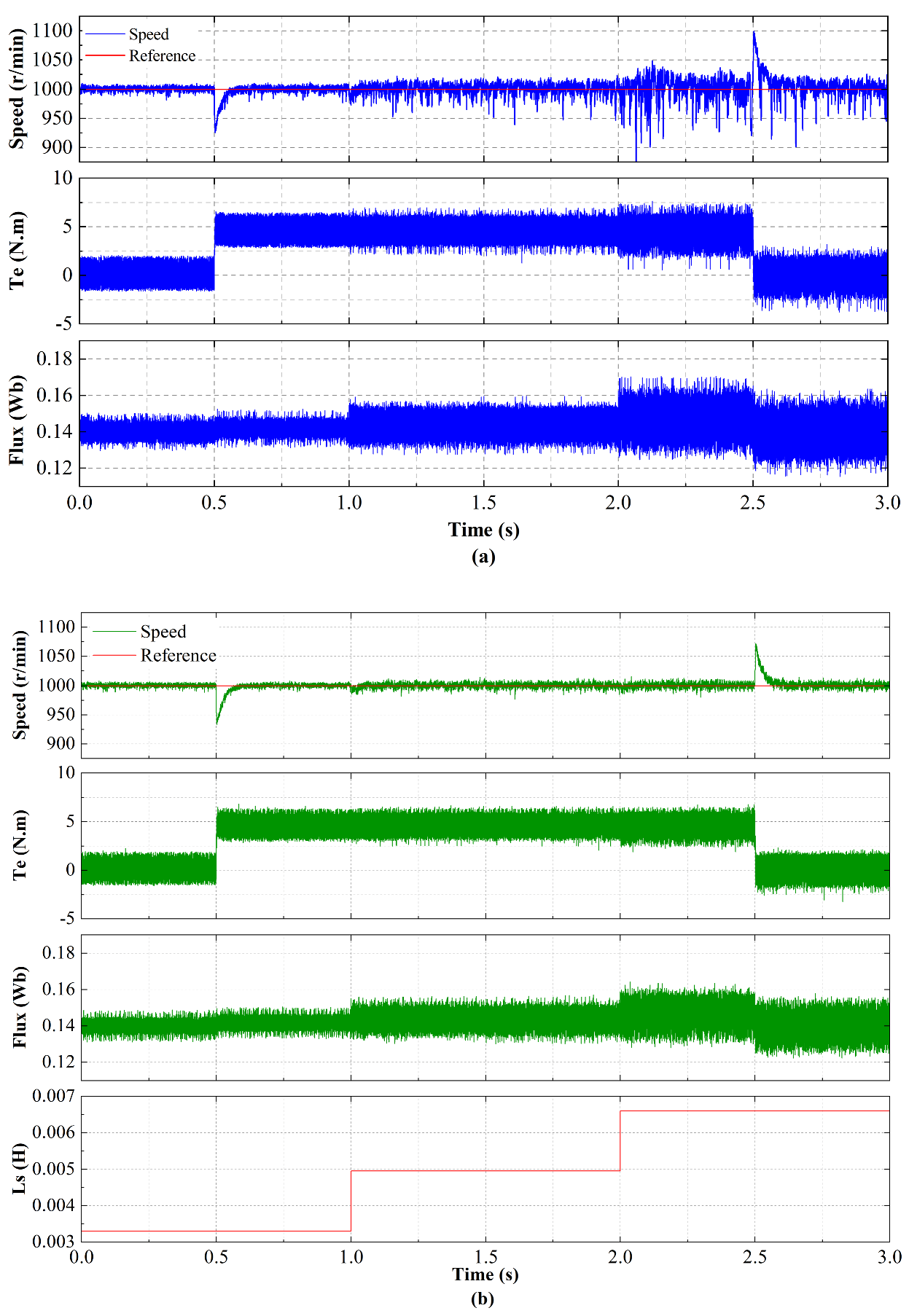
5.2. Experimental Evaluation of Stator Inductance Mismatch
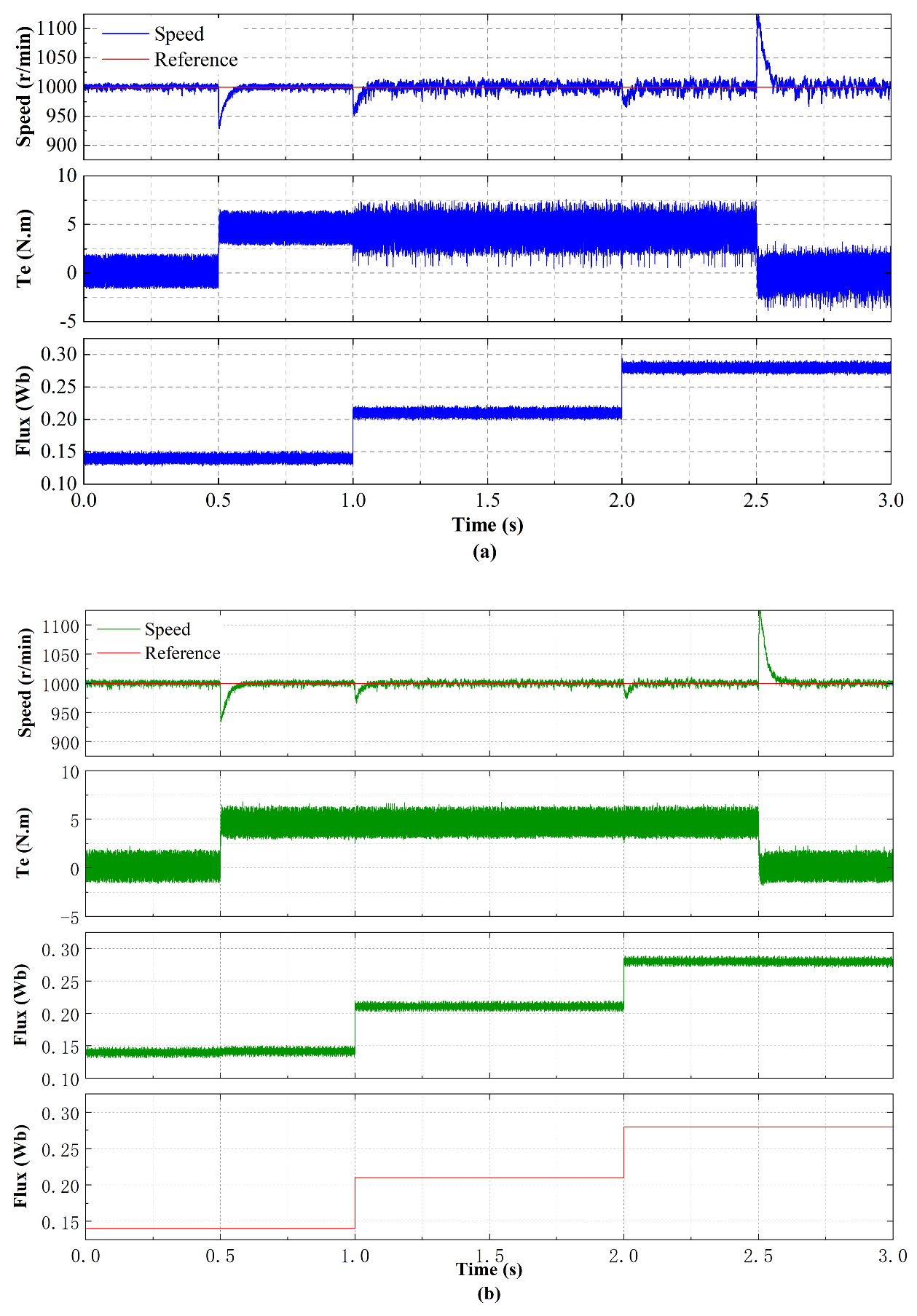
5.3. Experimental Evaluation of Rotor Flux Mismatch
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FCS-MPTC | Infinite control set model predictive torque control |
| MPCC | Model predictive current control |
| PPTC | parallel predictive torque control |
| MF-PPTC | Model-Free parallel predictive torque control |
| PMSM | Permanent magnet synchronous machine |
| TSEKF | two-stage extended Kalman filter |
| NLESO | Nonlinear extended state observer |
| FOC | Field-oriented control |
| DTC | Direct torque control |
| VV | Voltage Vector |
| OT | Optimal torque |
| OF | Optimal flux |
| SF | Suboptimal flux |
| ITAE | Integrated time and absolute error |
References
- Pillay, P.; Krishnan, R. Modeling, simulation, and analysis of permanent-magnet motor drives. I. The permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1989, 25, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, D.; Profumo, F.; Serra, G.; Tani, A. FOC and DTC: Two viable schemes for induction motors torque control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dini, P.; Saponara, S. Cogging Torque Reduction in Brushless Motors by a Nonlinear Control Technique. Energies 2019, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dini, P.; Saponara, S. Design of an Observer-Based Architecture and Non-Linear Control Algorithm for Cogging Torque Reduction in Synchronous Motors. Energies 2020, 13, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubare, P.; Ingole, D.; Sonawane, D. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of BLDC Motor with State Estimation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Rahman, M.; Hu, W.; Lim, K. Analysis of direct torque control in permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1997, 12, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qi, H.; Guo, X. Prediction Horizons Optimized Nonlinear Predictive Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Position System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 9153–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preindl, M.; Bolognani, S. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control with Finite Control Set for PMSM Drive Systems, Part 1: Maximum Torque Per Ampere Operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, W.; Kennel, R.M.; Gerling, D.; Lorenz, R.D. Finite-Control-Set Model Predictive Torque Control with a Deadbeat Solution for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Qi, H.; Wei, Y. A Modified Model Predictive Torque Control with Parameters Robustness Improvement for PMSM of Electric Vehicles. Actuators 2021, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. An improved two-vectors-based model predictive torque control without weighting factors for induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 2766–2772. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Norambuena, M.; Rodriguez, J. Generalized Sequential Model Predictive Control of IM Drives with Field-Weakening Ability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8944–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, H.; Chen, Q.; Davari, S.A.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Parallel Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machines without Weighting Factors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, F.; He, Y.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R. Encoderless Parallel Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Using A Robust Model Reference Adaptive System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Robust Predictive Current Control With Online Disturbance Estimation for Induction Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 4663–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junejo, A.K.; Xu, W.; Mu, C.; Ismail, M.M.; Liu, Y. Adaptive Speed Control of PMSM Drive System Based a New Sliding-Mode Reaching Law. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12110–12121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Mu, C.; Liu, Y. Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Combined Sliding Mode Strategy for PMSM Drive System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwasilu, F.; Nguyen, H.T.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.W. Finite Set Model Predictive Control of Interior PM Synchronous Motor Drives With an External Disturbance Rejection Technique. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, K. Robust Current Controller for IPMSM Drives Based on Explicit Model Predictive Control with Online Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 45898–45910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Galassini, A.; Buticchi, G.; Degano, M. Improved Model Predictive Current Control for SPMSM Drives Using Current Update Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Han, Z.; Lu, S. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines with Closed-Form Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 5018–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Dou, M.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Robustness Improvement of FCS-MPTC for Induction Machine Drives Using Disturbance Feedforward Compensation Technique. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, F.; Dou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Kennel, R.; Rodríguez, J. Active Disturbance-Rejection-Based Speed Control in Model Predictive Control for Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Offline Parameter Self-Learning Method for General-Purpose PMSM Drives with Estimation Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 11103–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.Q.; Rafaq, M.S.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.W. Online Parameter Estimation Technique for Adaptive Control Applications of Interior PM Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.K.; Liu, T.H.; Yu, J.T.; Fu, L.C.; Hsiao, C.F. Model-Free Predictive Current Control for Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on Current Difference Detection Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustin, C.A.; Yu, J.T.; Cheng, Y.S.; Lin, C.K.; Huang, H.Q.; Lai, Y.S. Model-Free Predictive Current Control for SynRM Drives Based on Optimized Modulation of Triple-Voltage-Vector. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 130472–130483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlet, P.G.; Tinazzi, F.; Bolognani, S.; Zigliotto, M. An Effective Model-Free Predictive Current Control for Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fliess, M.; Join, C. Model-free control. Int. J. Control 2013, 86, 2228–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Yao, H. Model-free control of surface mounted PMSM drive system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–17 March 2016; pp. 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Jiao, J. Model-Free Predictive Current Control of DFIG Based on an Extended State Observer Under Unbalanced and Distorted Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 8130–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Active disturbance rejection control: From an enduring idea to an emerging technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo), Poznan, Poland, 6–8 July 2015; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 1 | |
| Rated speed | 1000 | |
| Rated torque | 4.5 | |
| p | Number of pole pairs | 4 |
| Stator resistance | 1.35 | |
| Stator inductance | 3.17 | |
| Rotor magnet flux | 0.14 |
| Observer Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|
| observer parameters | 900 | 200,000 |
| observer parameters | 800 | 160,000 |
| observer parameters | 800 | 160,000 |
| Feature | PPTC | MF-PPTC |
|---|---|---|
| Start-up phase rise time (ms) | - | 187 |
| Speed overshoot with load disturbance variation (r/min) | 73 | 69 |
| Maximum speed ripple for pu (r/min) | 48 | 12 |
| Maximum speed ripple for pu (r/min) | 20 | 9 |
| Maximum Torque ripple for pu (N.m) | 3.14 | 2.26 |
| Maximum Torque ripple for pu (N.m) | 3.06 | 2.18 |
| Parameter sensitivity | High | Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Gao, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Qi, H.; Wei, Y. Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control Based on Ultra-Local Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. Actuators 2022, 11, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11020031
Lv M, Gao S, Wei Y, Zhang D, Qi H, Wei Y. Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control Based on Ultra-Local Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. Actuators. 2022; 11(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Manping, Siyu Gao, Yanjun Wei, Di Zhang, Hanhong Qi, and Yao Wei. 2022. "Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control Based on Ultra-Local Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine" Actuators 11, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11020031
APA StyleLv, M., Gao, S., Wei, Y., Zhang, D., Qi, H., & Wei, Y. (2022). Model-Free Parallel Predictive Torque Control Based on Ultra-Local Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. Actuators, 11(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11020031






