Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part III: Impingement Flow Field and Cooling Characteristics of Vectoring Dual Synthetic Jets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Device and Methods
2.1. Experimental Device
2.2. Vectoring Evaluation Method of Impinging DSJ
2.3. Cooling Performance Evaluation Method of Impinging DSJ
3. Results and Discussion
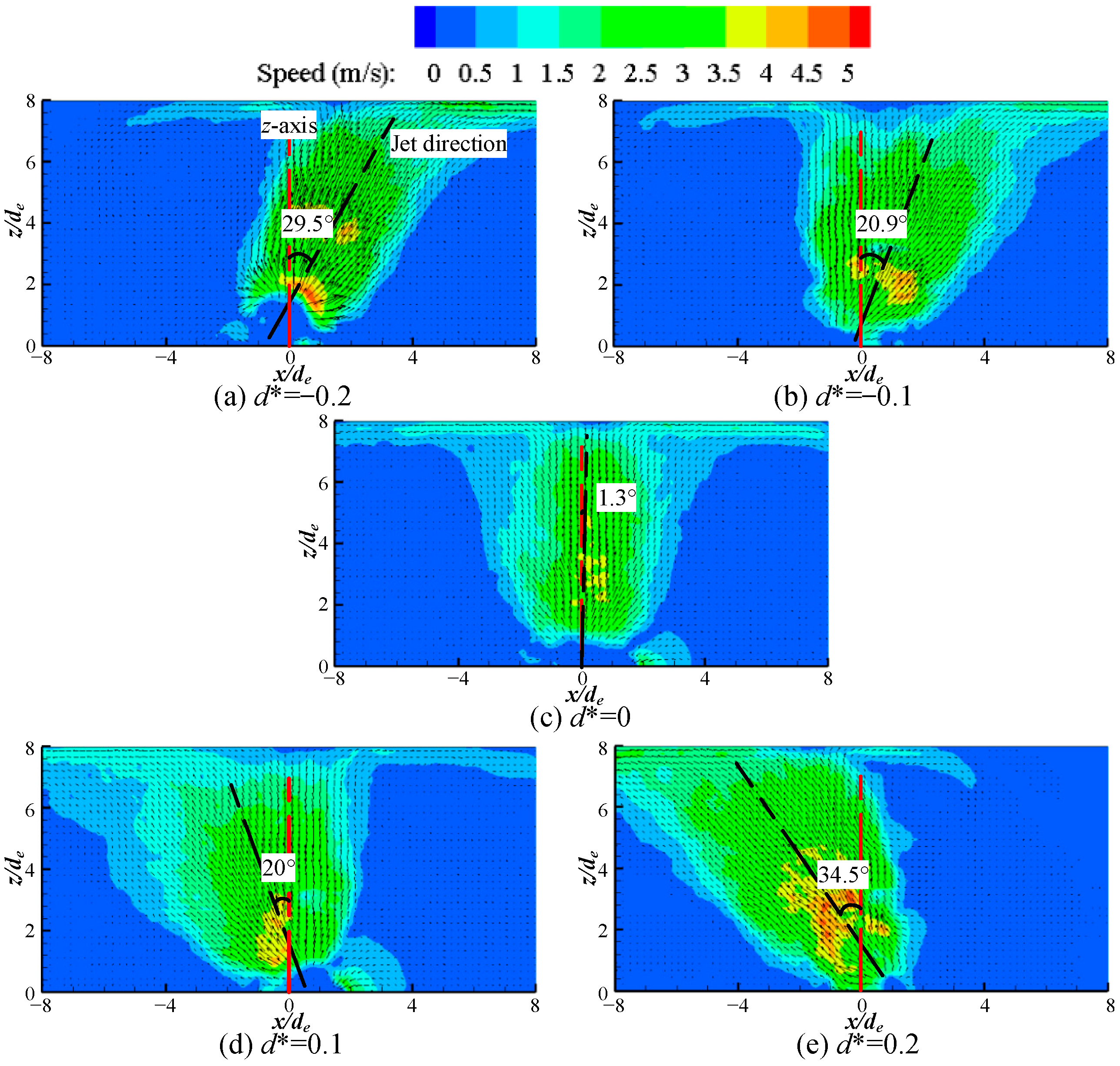
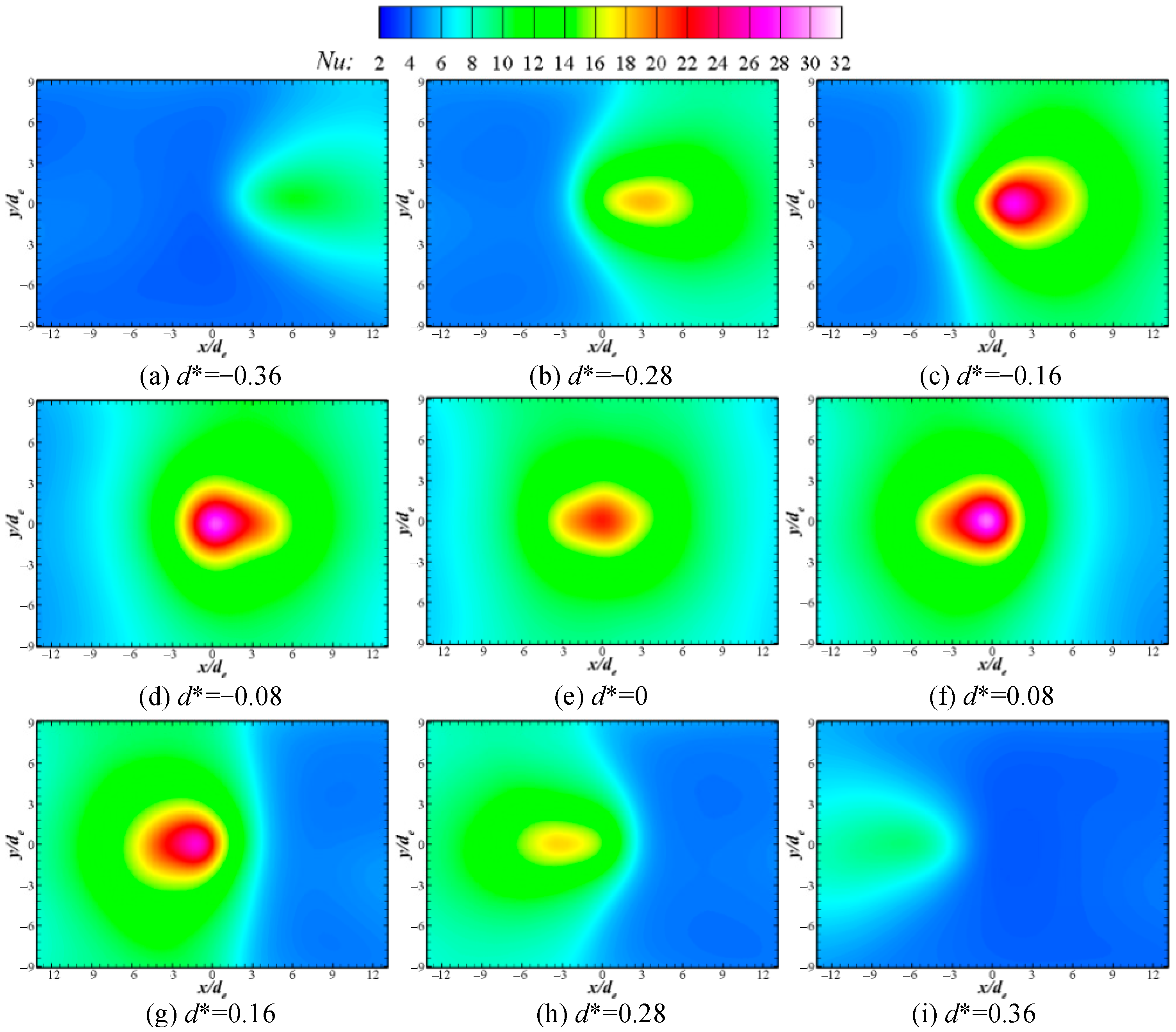
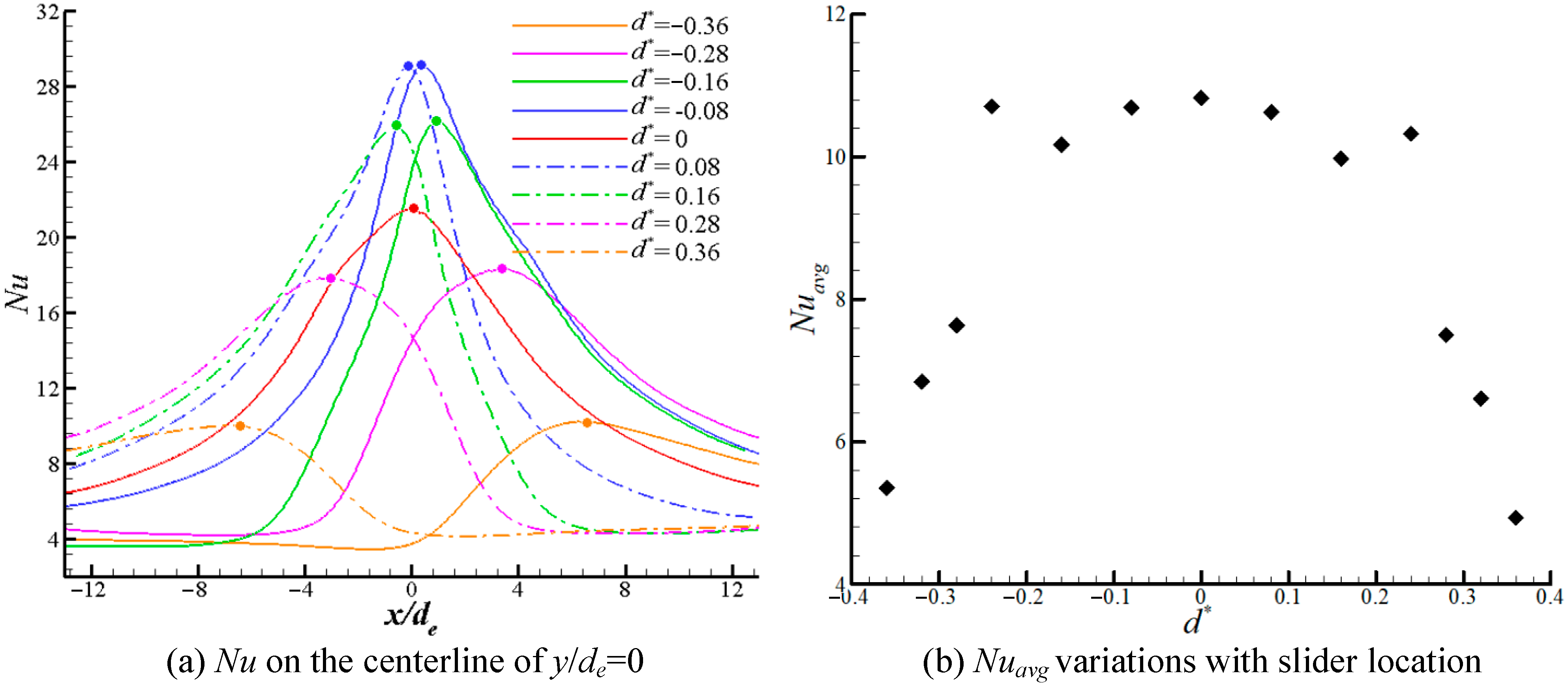
3.1. Effect of Slider Location
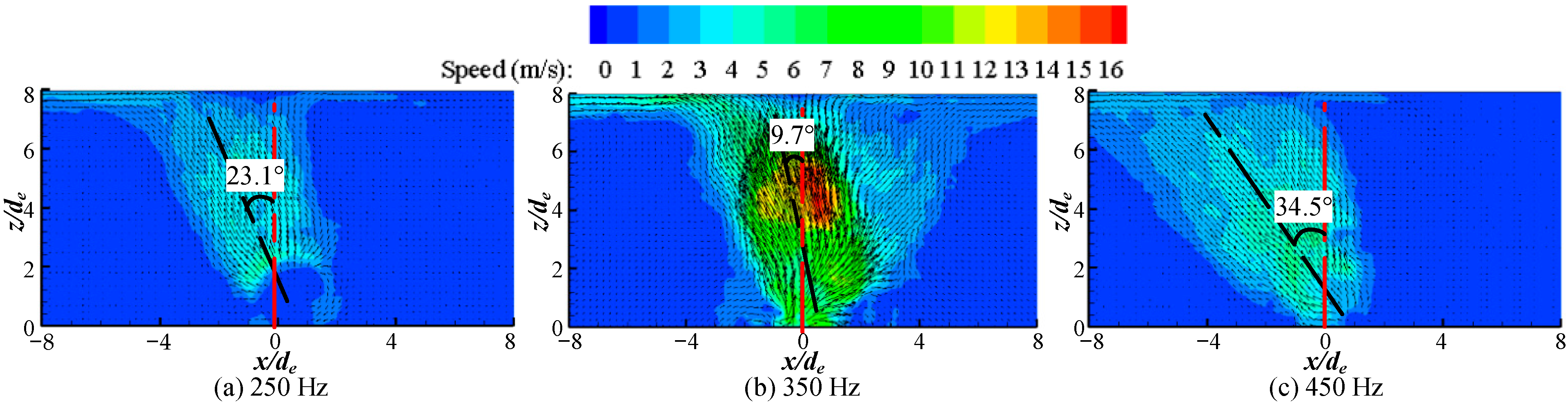
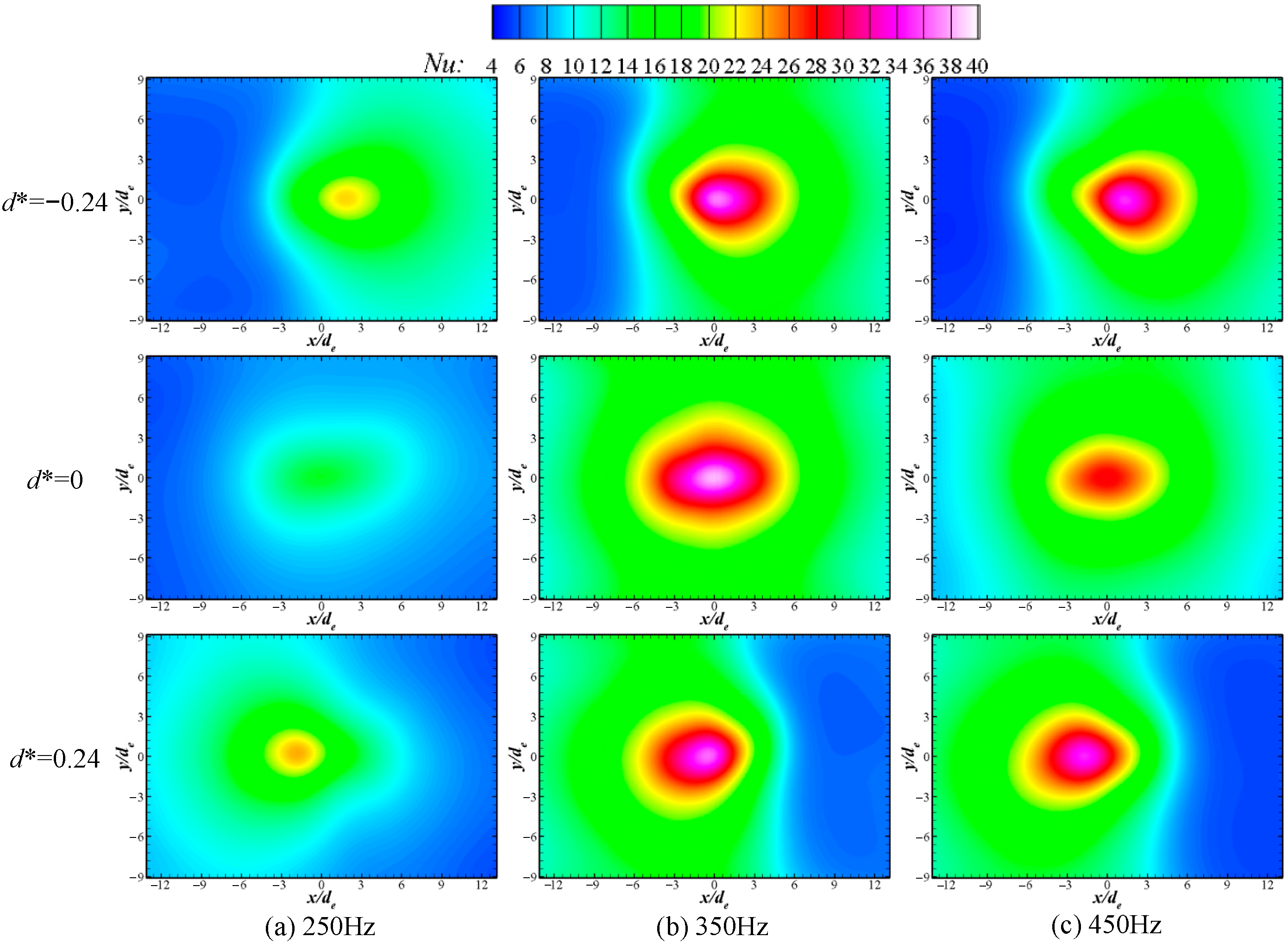
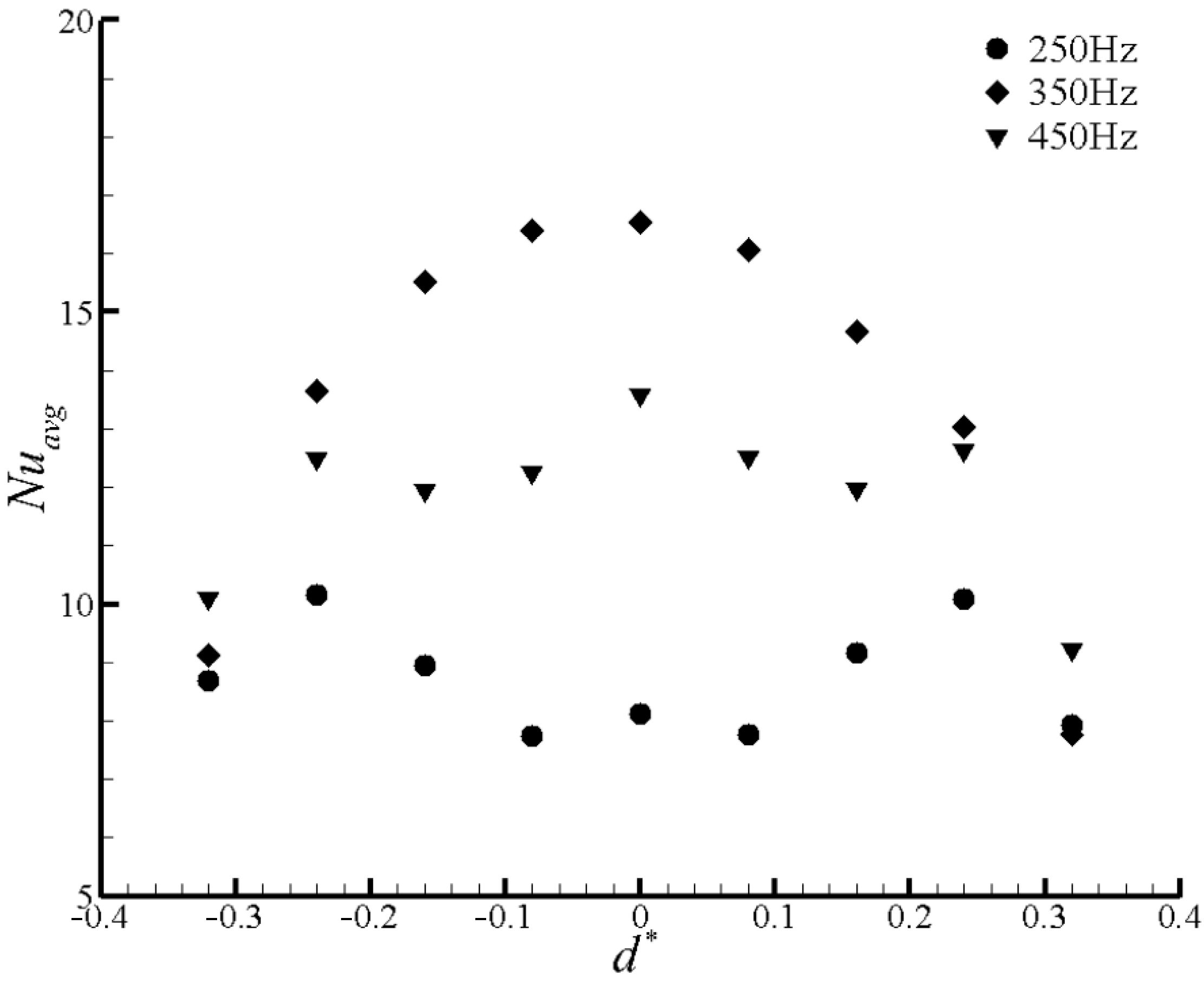
3.2. Effect of Driving Frequency
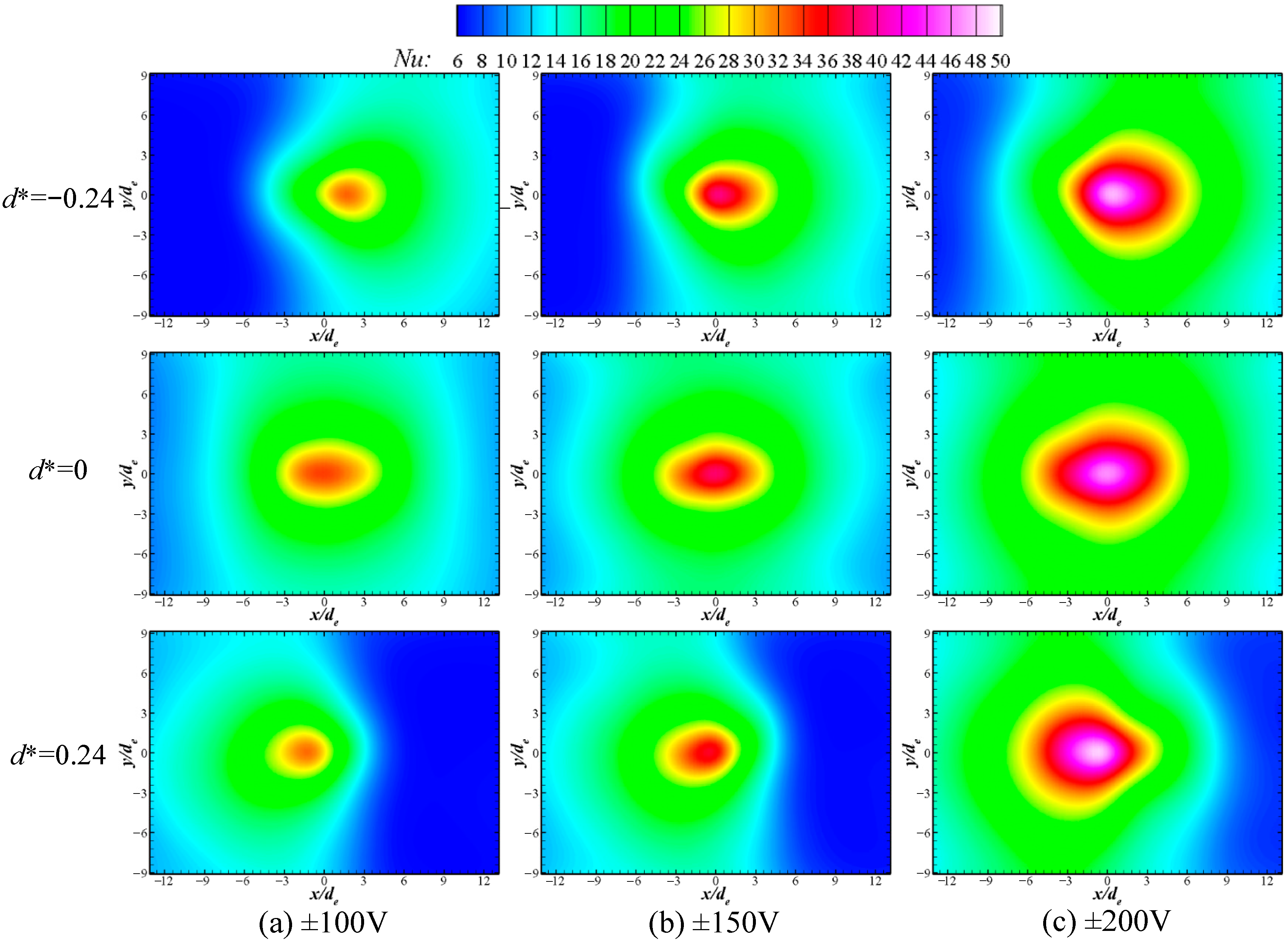
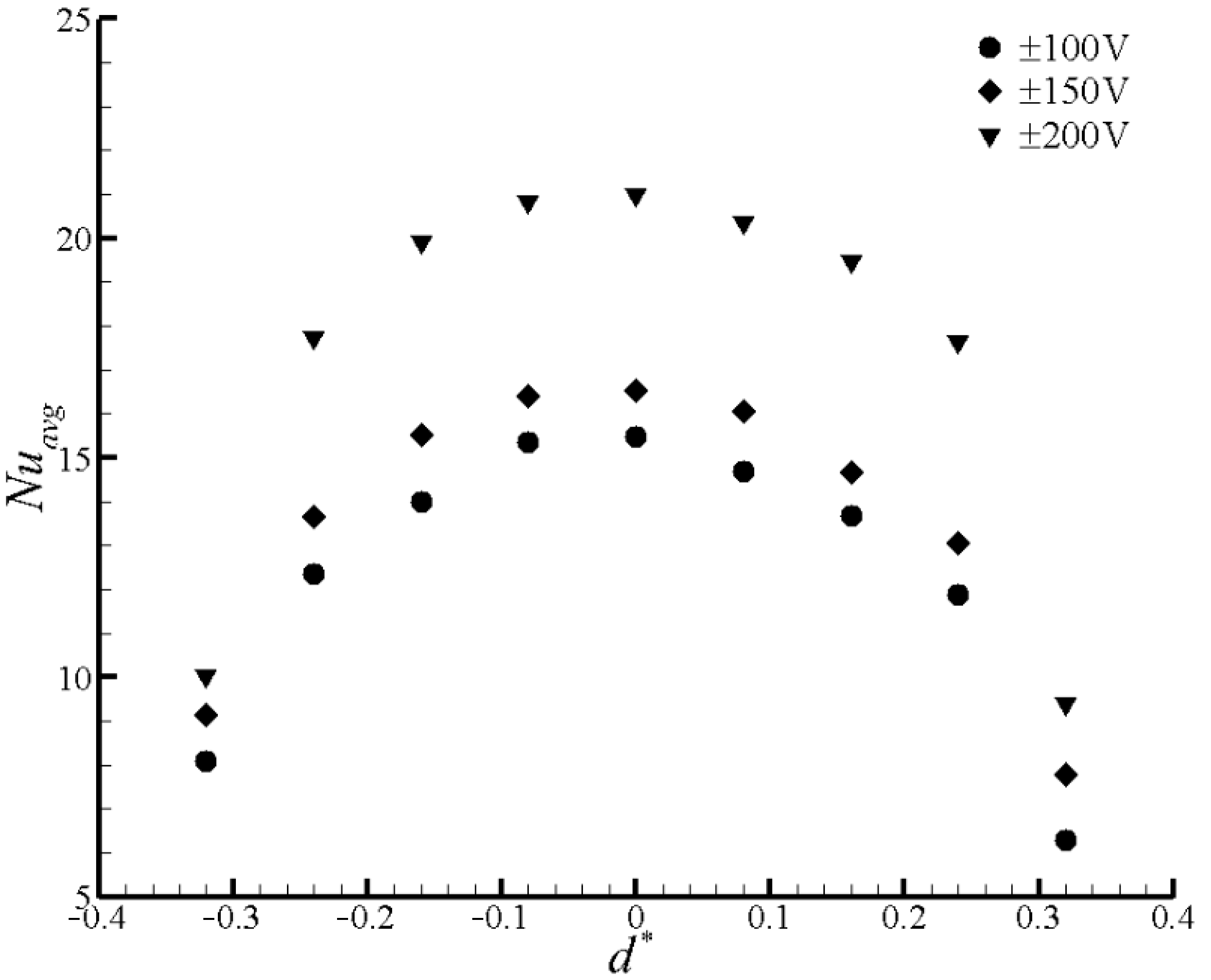
3.3. Effect of Driving Voltage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | effectively heated area (mm2) |
| AΩ | integration area (mm2) |
| d | slot location (mm) |
| d1, d2 | width of two slots (mm) |
| de | characteristic length (mm) |
| d* | slot dimensionless location |
| eθ | unit vector along the projected line |
| h | convective heat transfer W/(m2K) |
| I | current through the foil (A) |
| Ma | Mach number |
| Nu | local Nusselt number |
| Nuavg | area-averaged Nusselt number |
| Qele, Qloss | input power and heat loss (W) |
| qnet | net removed heat flux (W/m2) |
| So | objection function (m/s) |
| ui, wi | velocity components along x, z axis |
| Ts, Tj | impingement surface and jet |
| temperature (°C) | |
| V | voltage across the foil (V) |
| Vc | critical velocity (m/s) |
| Greek symbols | |
| θ | oblique angle of projected line (°) |
| θ0 | vectoring angle (°) |
| λ | thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
| Subscripts | |
| avg | spatially-averaged |
| net | net |
| elc | electric |
| j | jet |
| loss | heat radiation loss |
| max | maximum value |
| s | surface |
| Ω | integral domain |
| Acronyms | |
| CCD | charge-coupled device |
| DSJ | dual synthetic jet |
| PIV | particle image velocimetry |
References
- Glezer, A. Some aspects of aerodynamic flow control using synthetic-jet actuation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.; Amitay, M. Dynamic stall process on a finite span model and its control via synthetic jet actuators. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 077104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L. Role of synthetic jet control in energy harvesting capability of a semi-active flapping airfoil. Energy 2020, 208, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G.; Gibbons, M.; Persoons, T. Combined Passive/Active Flow Control of Drag and Lift Forces on a Cylinder in Crossflow Using a Synthetic Jet Actuator and Porous Coatings. Actuators 2022, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Zheng, M.; Yang, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, S. Novel roll effector based on zero-mass-flux dual synthetic jets and its flight test. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Salunkhe, P.; Zheng, Y.; Du, J.; Wu, Y. On the use of synthetic jet actuator arrays for active flow separation control. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, Q. Parametric analyses for synthetic jet control on separation and stall over rotor airfoil. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y. Interaction of twin synthetic jets in attached and separated boundary layers: Effects of yaw angle and phase difference. J. Vis. 2018, 21, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathay, N.; Amitay, M. Interaction of synthetic jets with a massively separated three-dimensional flow field. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2022, 7, 034702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhong, S. Enhancement of inline mixing with lateral synthetic jet pairs at low Reynolds numbers: The effect of fluid viscosity. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 53, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Li, T. Characteristics and mechanism of mixing enhancement for noncircular synthetic jets at low Reynolds number. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 98, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Dong, J. Experimental Study of Coaxial Jets Mixing Enhancement Using Synthetic Jets. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Glezer, A. Jet vectoring using synthetic jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 458, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-B.; Xia, Z.-X.; Xie, Y.-G. Jet Vectoring Control Using a Novel Synthetic Jet Actuator. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2007, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryota, K.; Yuki, W.; Yu, T.; Koichi, N.; Donghyuk, K.; Kotaro, S. Jet vectoring using secondary Coanda synthetic jets. Mech. Eng. J. 2020, 7, 20-00215. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Simon, T.W.; Zhang, M.; Yeom, T.; North, M.T.; Cui, T. Enhancing heat transfer in air-cooled heat sinks using piezoelectrically-driven agitators and synthetic jets. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 68, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, T.; Simon, T.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Cui, T. Active heat sink with piezoelectric translational agitators, piezoelectric synthetic jets, and micro pin fin arrays. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 99, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Smyk, E.; Gałek, R.; Przeszłowski, Ł. Thermal, flow and acoustic characteristics of the heat sink integrated inside the synthetic jet actuator cavity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 170, 107171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, J.; Salehi, F.; Lee, A.; Brandt, L. Nanofluid heat transfer in a microchannel heat sink with multiple synthetic jets and protrusions. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabie, H.M. Heat transfer intensification of jet impingement using exciting jets—A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, A.; Amitay, M. Synthetic jets. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2002, 34, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.S.; Cardone, G.; Soria, J. On the behaviour of impinging zero-net-mass-flux jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 810, 25–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, A.; Amitay, M. Electronic Cooling Using Synthetic Jet Impingement. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, S.L.; Alfonso, O. Vortex dynamics and mechanisms of heat transfer enhancement in synthetic jet impingement. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 112, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, C.S.; Paolillo, G.; Ianiro, A.; Cardone, G.; de Luca, L. Effects of the stroke length and nozzle-to-plate distance on synthetic jet impingement heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 117, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.-L.; Hu, W.-J.; Wu, C.-J.; Chen, W.-F. Flow and heat transfer characteristics in a microchannel with a circular synthetic jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 164, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.-W.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Tan, J.-W.; Shan, Y. Impingement heat transfer on flat and concave surfaces by piston-driven synthetic jet from planar lobed orifice. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 167, 120832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, G.; Mohammadpour, J.; Lee, A. Cooling performance of an impinging synthetic jet in a microchannel with nanofluids: An Eulerian approach. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 188, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.J. Experimental investigation on flow characteristics and unsteady heat transfer of noncircular impinging synthetic jets. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2022, 190, 122760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Renganathan, M.; Yadav, H.; Sahu, S.K.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Agrawal, A. An experimental investigation of the flow-field and thermal characteristics of synthetic jet impingement with different waveforms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 187, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Glezer, A. The formation and evolution of synthetic jets. Phys. Fluids 1998, 10, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-B.; Xia, Z.-X.; Liu, B. New Generation of Synthetic Jet Actuators. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Xia, Z.-X.; Luo, Z.-B.; Li, Y.-J. Vector-Adjusting Characteristic of Dual-Synthetic-Jet Actuator. AIAA J. 2015, 53, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Wangw4, L.; Xia, Z. Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part I: PIV Measurements and Comparison to Synthetic Jet Actuator. Actuators 2022, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Luo, Z.; Xia, Z.; Gong, W.; Wang, L. Active-passive combined and closed-loop control for the thermal management of high-power LED based on a dual synthetic jet actuator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 132, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Luo, Z.-B.; Xia, Z.-X.; Gong, W.-J. Experimental investigation on the flow regime and impingement heat transfer of dual synthetic jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Luo, Z.-B.; Deng, X.; Xia, Z.-X. Experimental investigation on the performance of a novel dual synthetic jet actuator-based atomization device. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 142, 118406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Luo, Z.-B.; Deng, X.; Peng, W.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-J. Experimental investigation on the vectoring spray based on a novel synthetic jet actuator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 179, 115677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-B.; Deng, X.; Xia, Z.-X.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.-J. Flow field and heat transfer characteristics of impingement based on a vectoring dual synthetic jet actuator. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 102, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-B.; Xia, Z.-X. The mechanism of jet vectoring using synthetic jet actuators. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 19, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas, Q.; Holman, R.; Nishida, T.; Carroll, B.; Sheplak, M.; Cattafesta, L. Lumped Element Modeling of Piezoelectric-Driven Synthetic Jet Actuators. AIAA J. 2003, 41, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, X.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Q.; Peng, C.; He, W.; Luo, Z. Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part III: Impingement Flow Field and Cooling Characteristics of Vectoring Dual Synthetic Jets. Actuators 2022, 11, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120376
Deng X, Dong Z, Liu Q, Peng C, He W, Luo Z. Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part III: Impingement Flow Field and Cooling Characteristics of Vectoring Dual Synthetic Jets. Actuators. 2022; 11(12):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120376
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Xiong, Zhaofeng Dong, Qiang Liu, Can Peng, Wei He, and Zhenbing Luo. 2022. "Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part III: Impingement Flow Field and Cooling Characteristics of Vectoring Dual Synthetic Jets" Actuators 11, no. 12: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120376
APA StyleDeng, X., Dong, Z., Liu, Q., Peng, C., He, W., & Luo, Z. (2022). Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part III: Impingement Flow Field and Cooling Characteristics of Vectoring Dual Synthetic Jets. Actuators, 11(12), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120376






