Experimental Evaluation of Modified Groundhook Car Suspension with Fast Magnetorheological Damper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
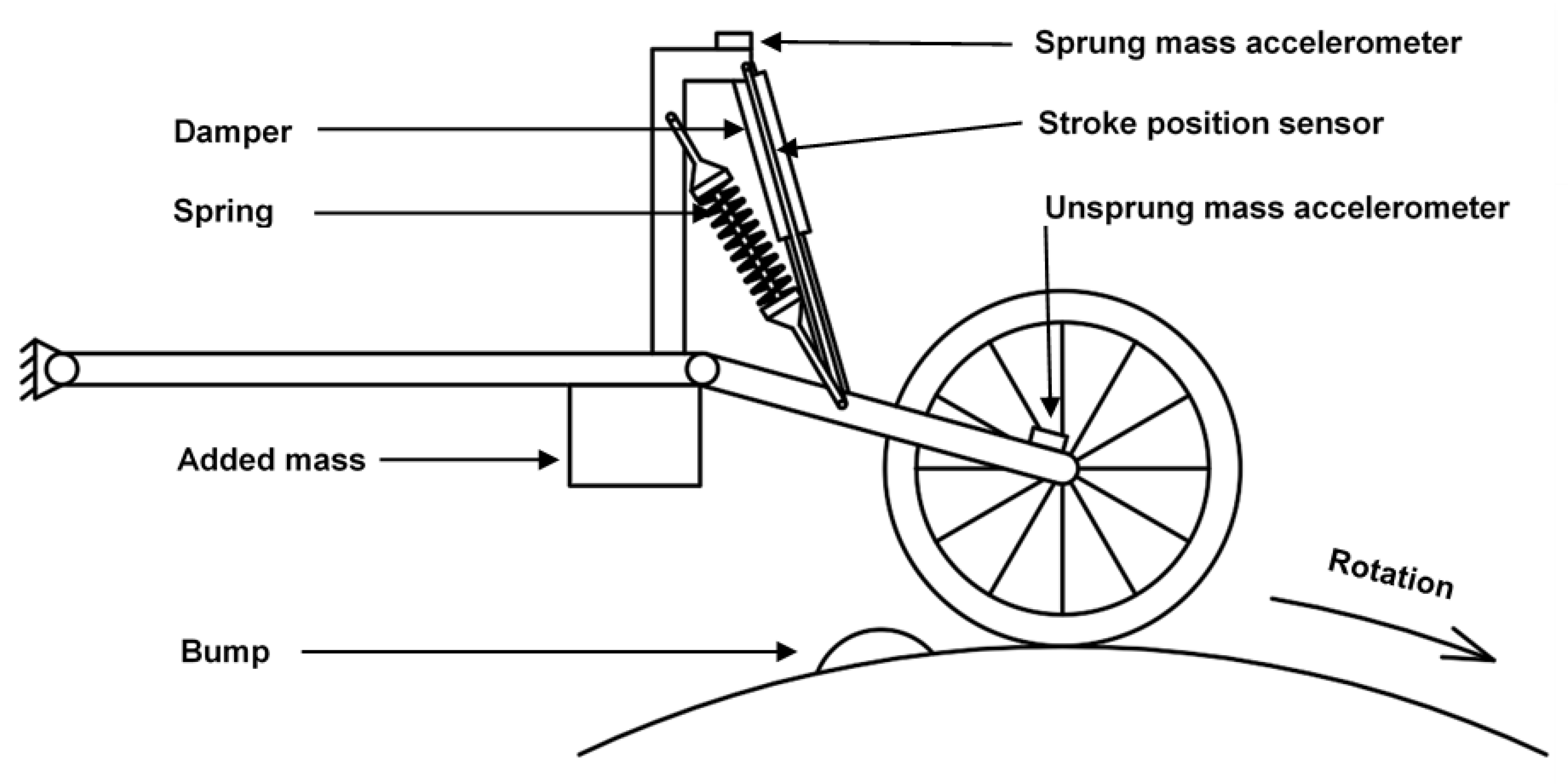
2.1. Experimental Test Rig
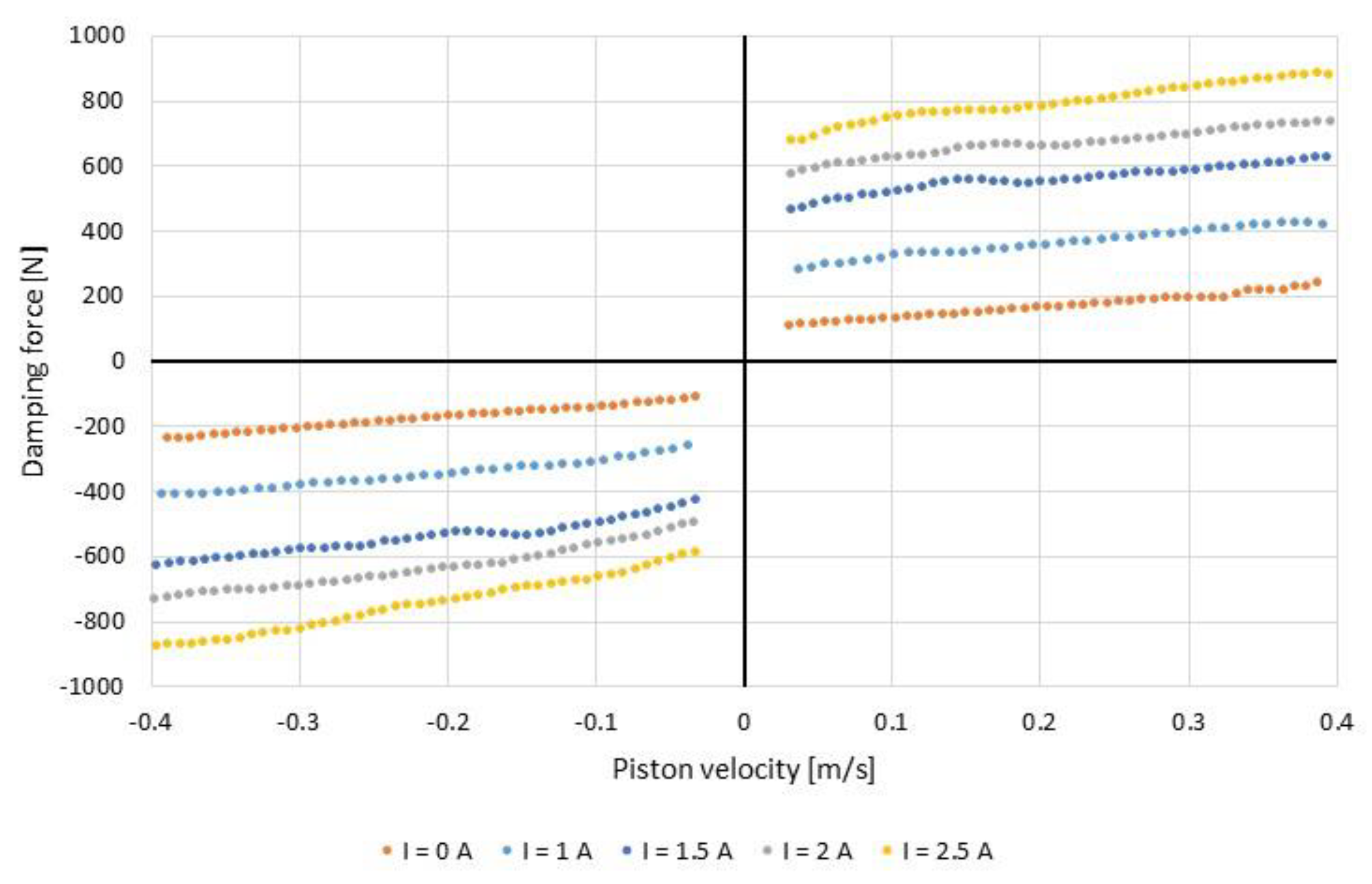
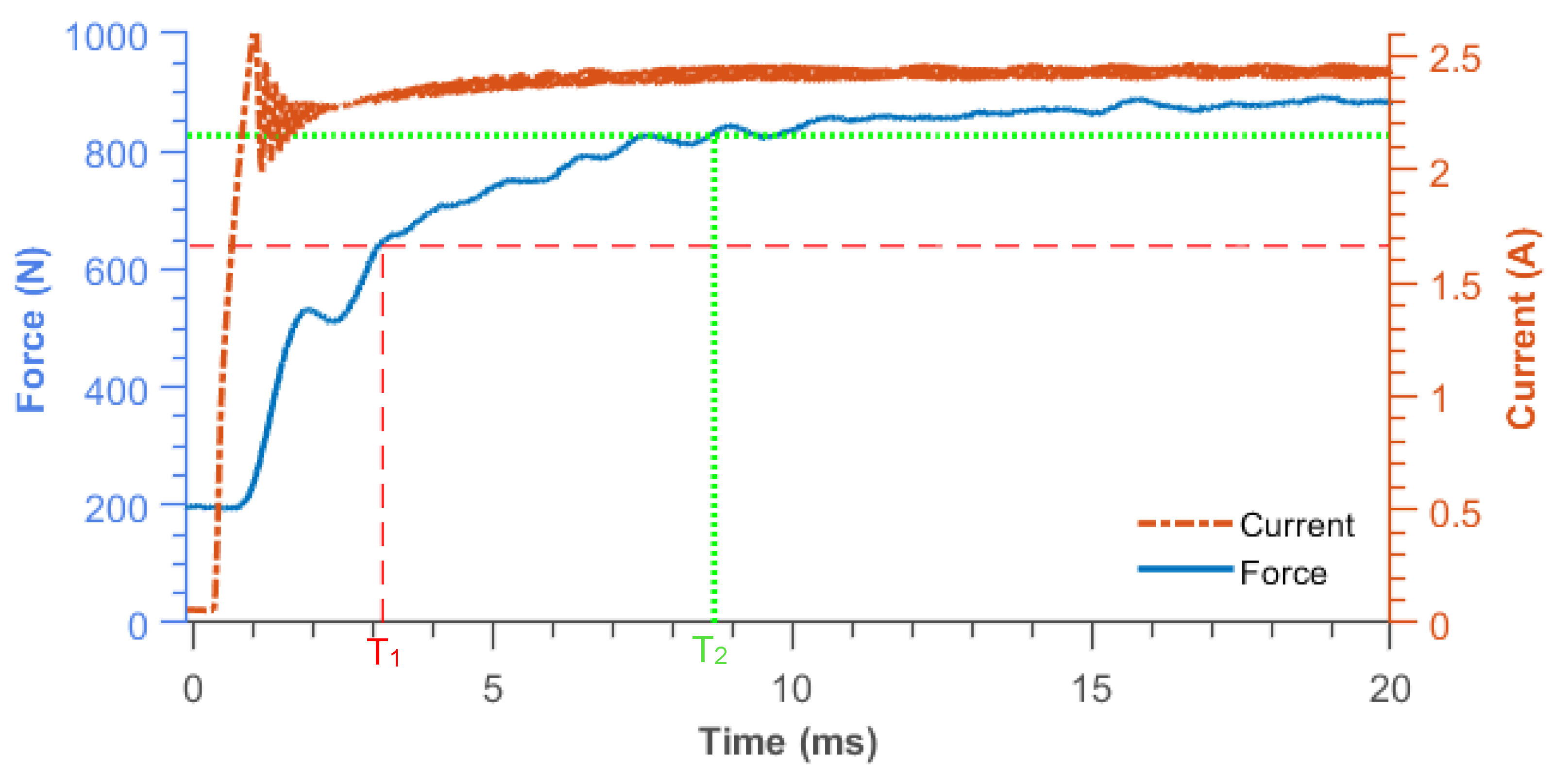
2.2. Magnetorheological Damper
2.3. Groundhook Algorithm Selection
2.4. Ride Quality Evaluation
2.5. Dynamic Model
- Method—ode4 (Runge–Kutta);
- Step size—fixed to 0.0002 s (5000 steps/s)
3. Results
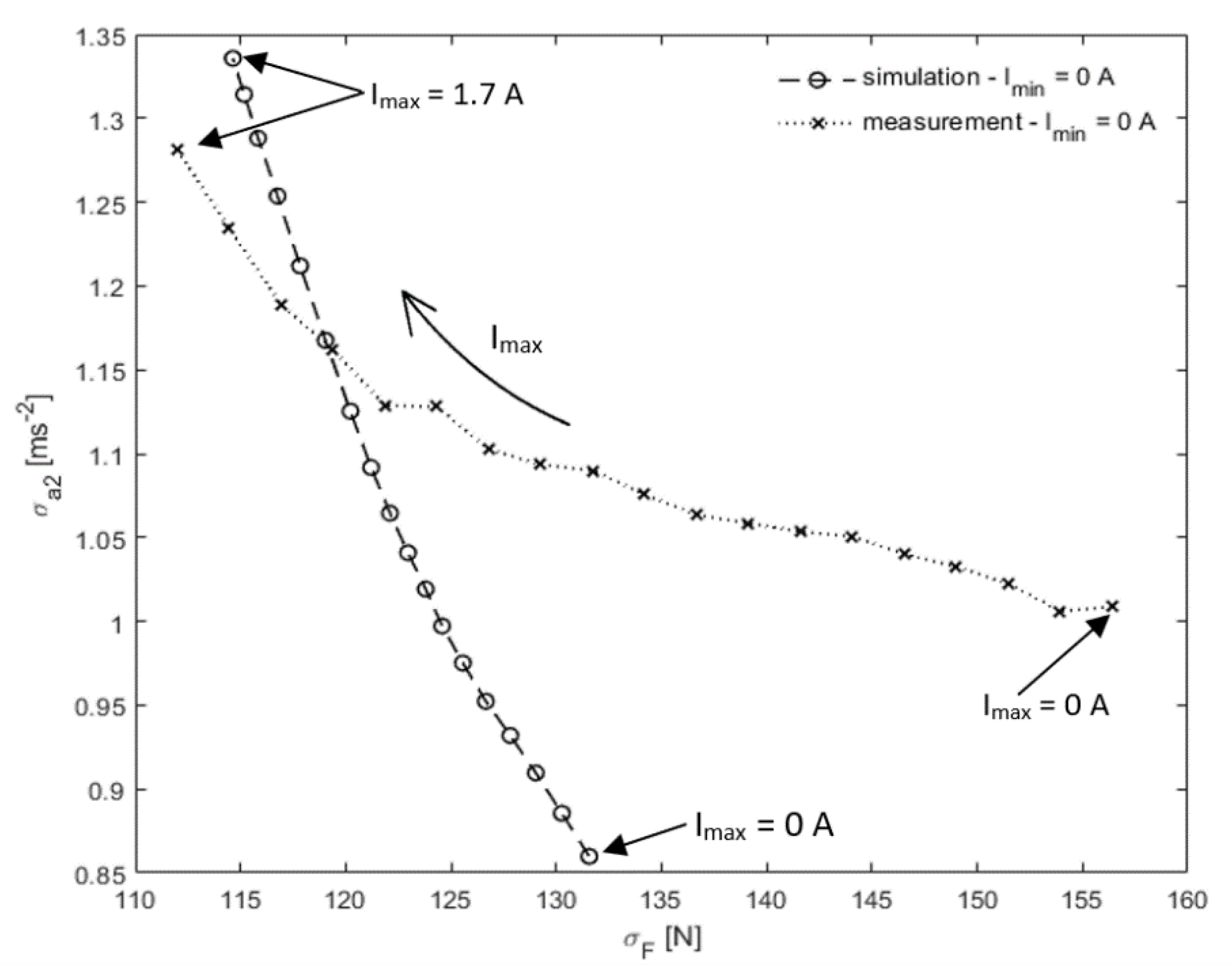
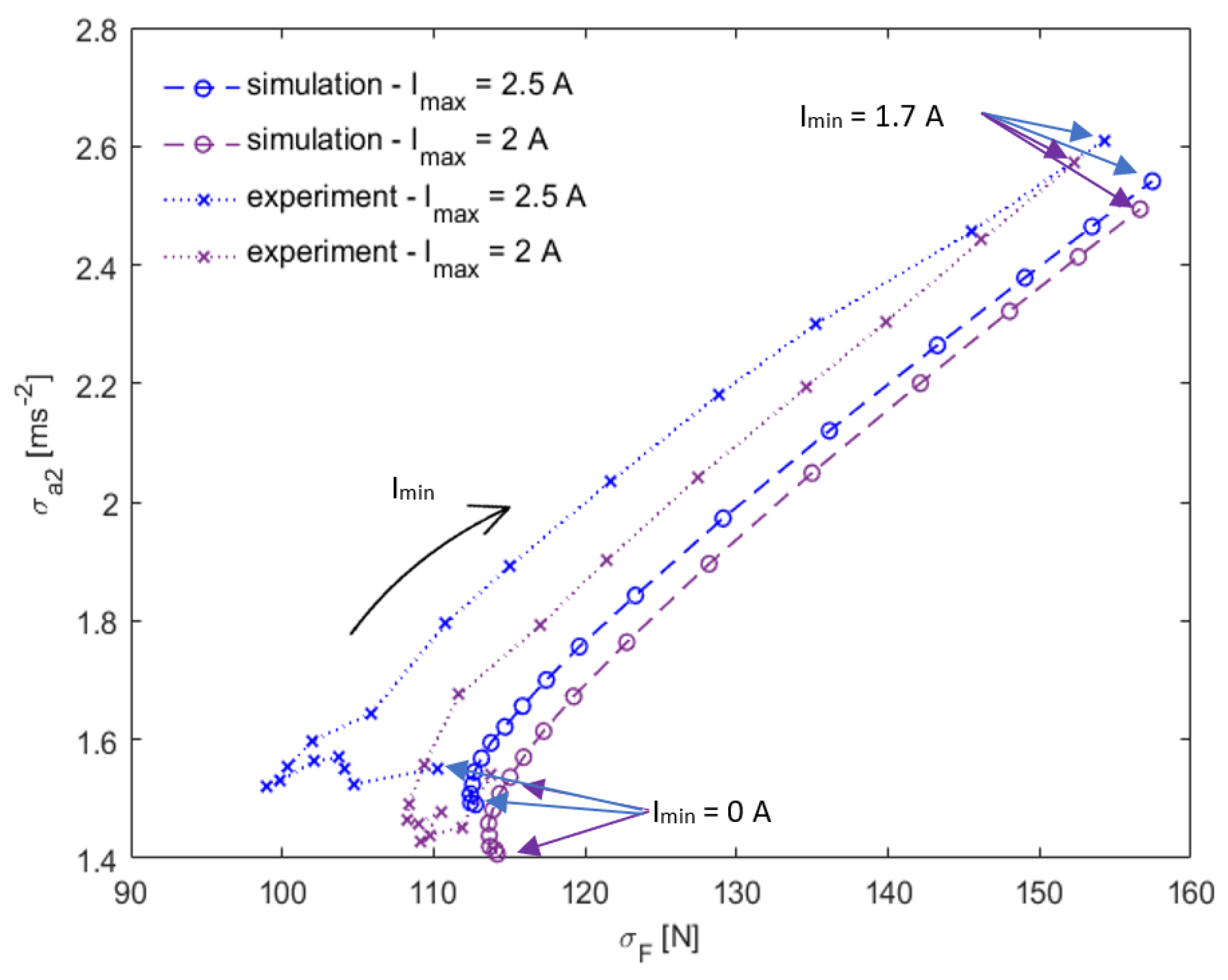
3.1. Comparison of Groundhook Settings
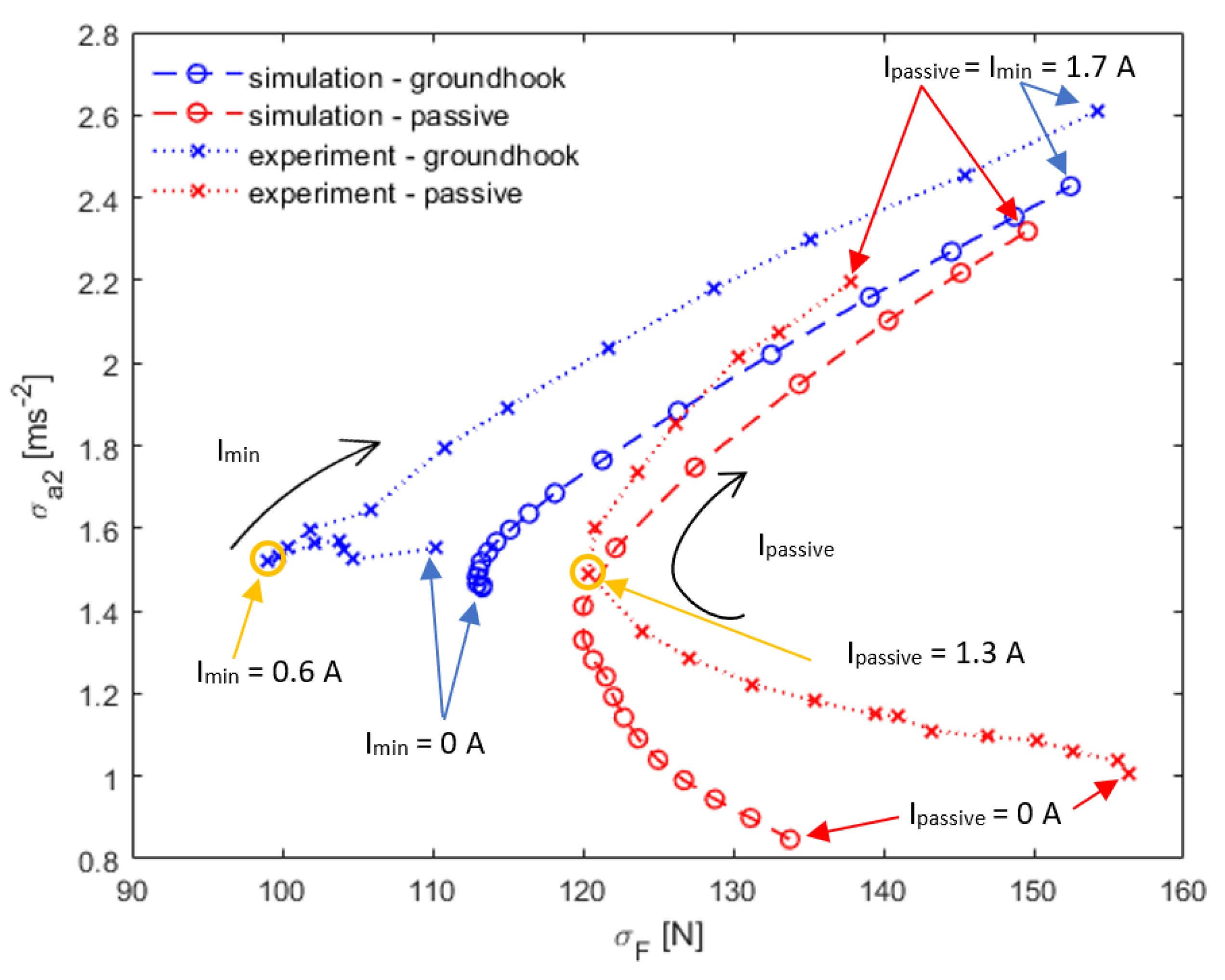
3.2. Comparison of Passive and Semiactive Mode
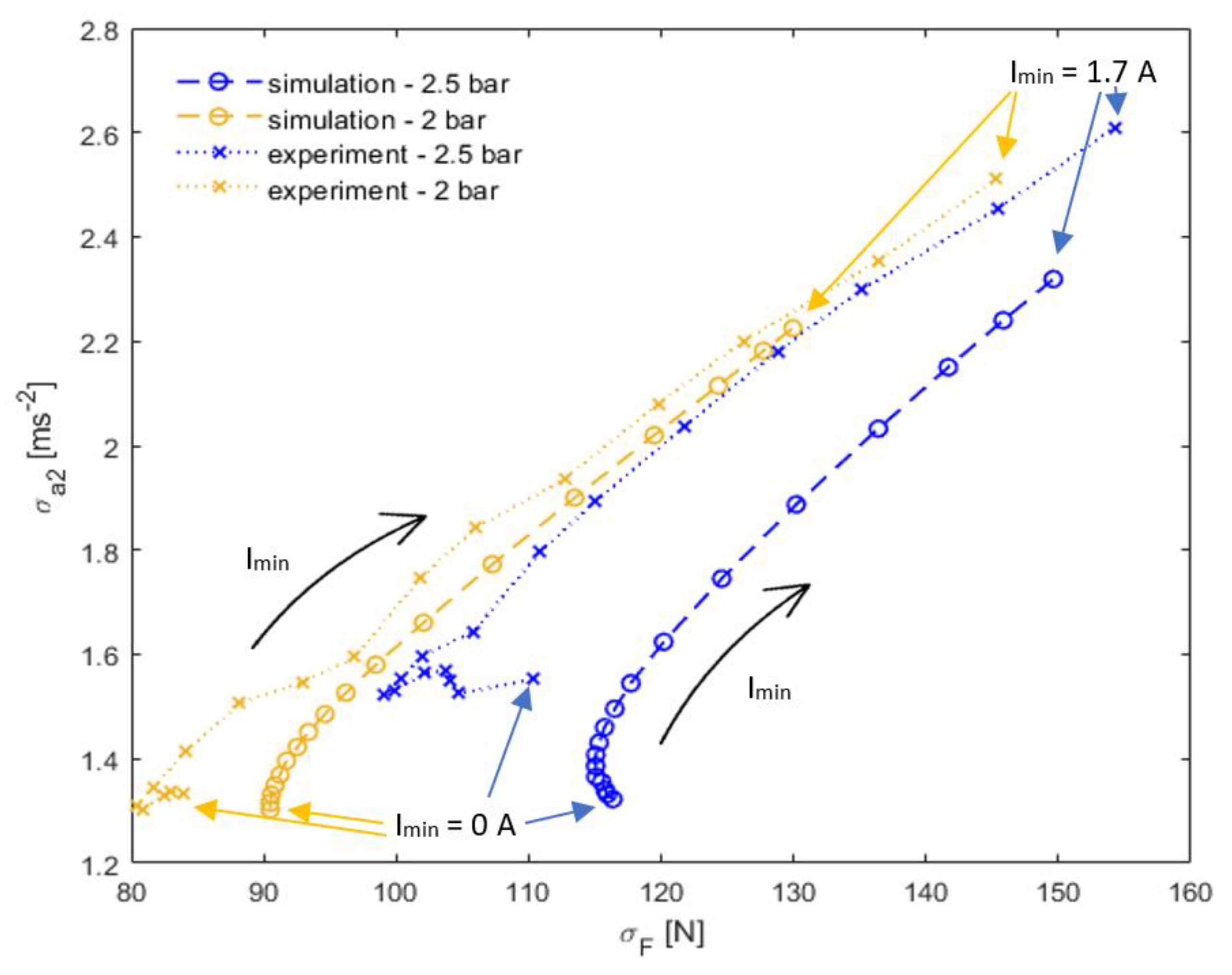
3.3. Effect of Tire Stiffness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The dynamic range of the damper should be as high as possible
- The non-activated state should be uniquely set for the vehicle
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeyasenthil, R.; Yoon, D.; Choi, S.; Kim, G. Robust Semiactive Control of a Half-car Vehicle Suspension System with Magnetorheological Dampers: Quantitative Feedback Theory Approach with Dynamic Decoupler. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 1418–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPlante, J.A.; Larkins, W.T. Semi-Active Shock Absorber Control System. US20040254701, 16 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Eslaminasab, N.; Golnaraghi, M.F. The Effect of Time Delay of the Semi-Active Dampers on the Performance of On-Off Control Schemes. In Proceedings of the ASME 2007 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Volume 9: Mechanical Systems and Control, Parts A, B, and C, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 November 2007; pp. 1911–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Bica, I.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Physical Characteristics of Magnetorheological Suspensions and Their Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetskiy, S.; Kermani, M. High-Performance Magneto-Rheological Clutches for Direct-Drive Actuation: Design and Development. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 2582–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Du, H. Design and Experimental Evaluation of a Magnetorheological Brake. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 21, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yao, P.; Xiao, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, T.; Zhao, L.; Deng, M.; Liu, C.; Ling, P. Tribology International Friction and Wear Maps of Copper Metal Matrix Composites with Different Iron Volume Content. Tribol. Int. 2019, 132, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdasz, J.; Sapiński, B. Insight into Magnetorheological Shock Absorbers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783319132334. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sehgal, R.; Wani, M.F.; Sharma, M.D. Stabilization and Tribological Properties of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluids: A Review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 538, 168295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, M.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Ghaffari, A. A Review on the Magnetorheological Fluid Preparation and Stabilization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jing, X.; Cheng, L. Magnetorheological Fluid Dampers: A Review on Structure Design and Analysis. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 839–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, O.; Kubik, M.; Novák, P. A New Method of Magnetorheological Damper Quality Evaluation. Eng. Mech. 2017, 2017, 594–597. [Google Scholar]
- Goldasz, J. Magnetostatic Study of a Dual-Gap MR Valve. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM), Wels, Austria, 23–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Fatah, A.Y.; Mazlan, S.A.; Koga, T.; Zamzuri, H.; Imaduddin, F. Design of Magnetorheological Valve Using Serpentine Flux Path Method. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 50, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.-H.; Goncalves, F.D.; Ahmadian, M. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Response Time of MR Dampers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Guo, P.; Ou, J. Study of the Response Time of MR Dampers. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Weihai, China, 8–11 July 2009; p. 74930U. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Xu, H.P.; Liao, C.R.; Deng, Z.X. Dynamic Response of Magnetorheological Fluid Damper for Automotive Suspension and the Influence by Long-Time Standing-Still. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 105–107, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, Z.; Jeniš, F.; Kubík, M.; Macháček, O.; Choi, S.B. Novel Approaches to the Design of an Ultra-Fast Magnetorheological Valve for Semi-Active Control. Materials 2021, 14, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubík, M.; Goldasz, J. Multiphysics Model of an MR Damper Including Magnetic Hysteresis. Shock Vib. 2019, 2019, 3246915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubík, M.; Šebesta, K.; Strecker, Z.; Jeniš, F.; Goldasz, J.; Mazůrek, I. Hydrodynamic Response Time of Magnetorheological Fluid in Valve Mode: Model and Experimental Verification. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubík, M.; Válek, J.; Žáček, J.; Jeniš, F.; Borin, D.; Strecker, Z.; Mazůrek, I. Transient Response of Magnetorheological Fluid on Rapid Change of Magnetic Field in Shear Mode. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F.D.; Ahmadian, M.; Carlson, J.D. Investigating the Magnetorheological Effect at High Flow Velocities. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, Z.; Mazůrek, I.; Roupec, J.; Klapka, M. Influence of MR Damper Response Time on Semiactive Suspension Control Efficiency. Meccanica 2015, 50, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, L.; Jancirani, J. An Investigation on Semi-Active Suspension Damper and Control Strategies for Vehicle Ride Comfort and Road Holding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2012, 226, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnopp, D.; Crosby, M.J.; Harwood, R.A. Vibration Control Using Semi-Active Force Generators. ASME Pap. 1973, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.A.; Kaldas, M.M.S. Semi-Active Suspension Systems from Research to Mass-Market—A Review. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2021, 40, 1005–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.S.; Sohn, H.C.; Hedrick, J.K. Modified Skyhook Control of Semi-Active Suspensions: A New Model, Gain Scheduling, and Hardware-in-the-Loop Tuning. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. Trans. ASME 2002, 124, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, S.B.; Park, Y.G. An Analytical Approach to Optimally Design of Electrorheological Fluid Damper for Vehicle Suspension System. Meccanica 2012, 47, 1633–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, W.G.; Salem, A.M. Semi-Active Control of Tracked Vehicle Suspension Incorporating Magnetorheological Dampers. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2017, 55, 626–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Jeon, K.; Kim, G.W.; Choi, S.B. Dynamic Analysis of Semi-Active MR Suspension System Considering Response Time and Damping Force Curve. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, H. Passive Skyhook Suspension Reduction for Improvement of Ride Comfort in an Off-Road Vehicle. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150710–150719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze, P. Skyhook Control of Front and Rear Magnetorheological Vehicle Suspension; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Valášek, M.; Kortüm, W.; Šika, Z.; Magdolen, L.; Vaculín, O. Development of Semi-Active Road-Friendly Truck Suspensions. Control Eng. Pract. 1998, 6, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poussot-Vassal, C.; Spelta, C.; Sename, O.; Savaresi, S.M.; Dugard, L. Survey and Performance Evaluation on Some Automotive Semi-Active Suspension Control Methods: A Comparative Study on a Single-Corner Model. Annu. Rev. Control 2012, 36, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Goncalves, F.D.; Sandu, C. An Experimental Analysis of Suitability of Various Semiactive Control Methods for Magneto Rheological Vehicle Suspensions. Smart Struct. Mater. 2005 Damping Isol. 2005, 5760, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze, P.; Kasprzyk, J.; Kozyra, A.; Rzepecki, J. Experimental Analysis of Vibration Control Algorithms Applied for an Off-Road Vehicle with Magnetorheological Dampers. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018, 37, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, Z.; Roupec, J.; Mazurek, I.; Machacek, O.; Kubik, M.; Klapka, M. Design of Magnetorheological Damper with Short Time Response. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cường, Đ.M.; Hong, Z.S.; Hùng, Đ.V.; Ngọc, N.T. Study on the Vertical Stiffness and Damping Coefficient of Tractor Tire Using Semi-Empirical Model. Hue Univ. J. Sci. Agric. Rural Dev. 2013, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Samin, P.M.; Hishamuddin, J.; Abd Rahman, R.; Burhaumudin, M.S. Groundhook Control of Semi-Active Suspension for Heavy Vehicle. Int. J. Reasearch Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yerrawar, R.N.; Arakerimath, R.R. Performance Assessment and Control Policies for Semiactive Suspension Using SIMSCAPE. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Techniques (ICACDOT), Pune, India, 9–10 September 2016; pp. 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


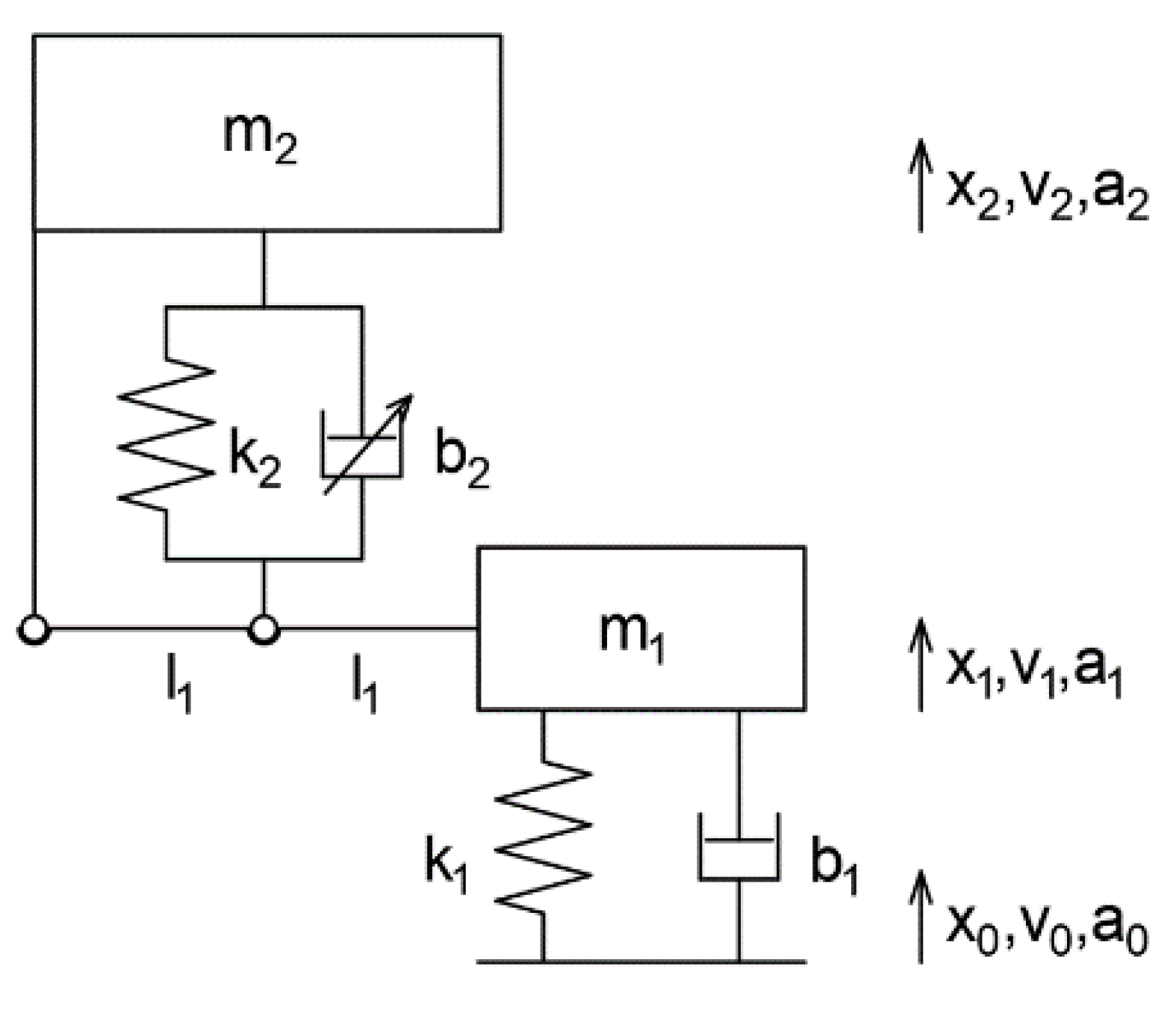

| Variable | Meaning | Model Setting |
|---|---|---|
| m1 | Unsprung mass | 6.7 kg |
| m2 | Sprung mass | 42.2 kg |
| k1 | Tire stiffness | 50,190 N m−1 |
| k2 | Main spring stiffness | 7380 N m−1 |
| b1 | Tire damping coefficient | 100 Ns m−1 |
| b2 | MR damper coefficient | Figure 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Žáček, J.; Šebesta, K.; Mohammad, H.; Jeniš, F.; Strecker, Z.; Kubík, M. Experimental Evaluation of Modified Groundhook Car Suspension with Fast Magnetorheological Damper. Actuators 2022, 11, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120354
Žáček J, Šebesta K, Mohammad H, Jeniš F, Strecker Z, Kubík M. Experimental Evaluation of Modified Groundhook Car Suspension with Fast Magnetorheological Damper. Actuators. 2022; 11(12):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120354
Chicago/Turabian StyleŽáček, Jiří, Karel Šebesta, Housam Mohammad, Filip Jeniš, Zbyněk Strecker, and Michal Kubík. 2022. "Experimental Evaluation of Modified Groundhook Car Suspension with Fast Magnetorheological Damper" Actuators 11, no. 12: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120354
APA StyleŽáček, J., Šebesta, K., Mohammad, H., Jeniš, F., Strecker, Z., & Kubík, M. (2022). Experimental Evaluation of Modified Groundhook Car Suspension with Fast Magnetorheological Damper. Actuators, 11(12), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11120354






