Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Improvement Using Plasma Actuator with Discretized Encapsulated Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
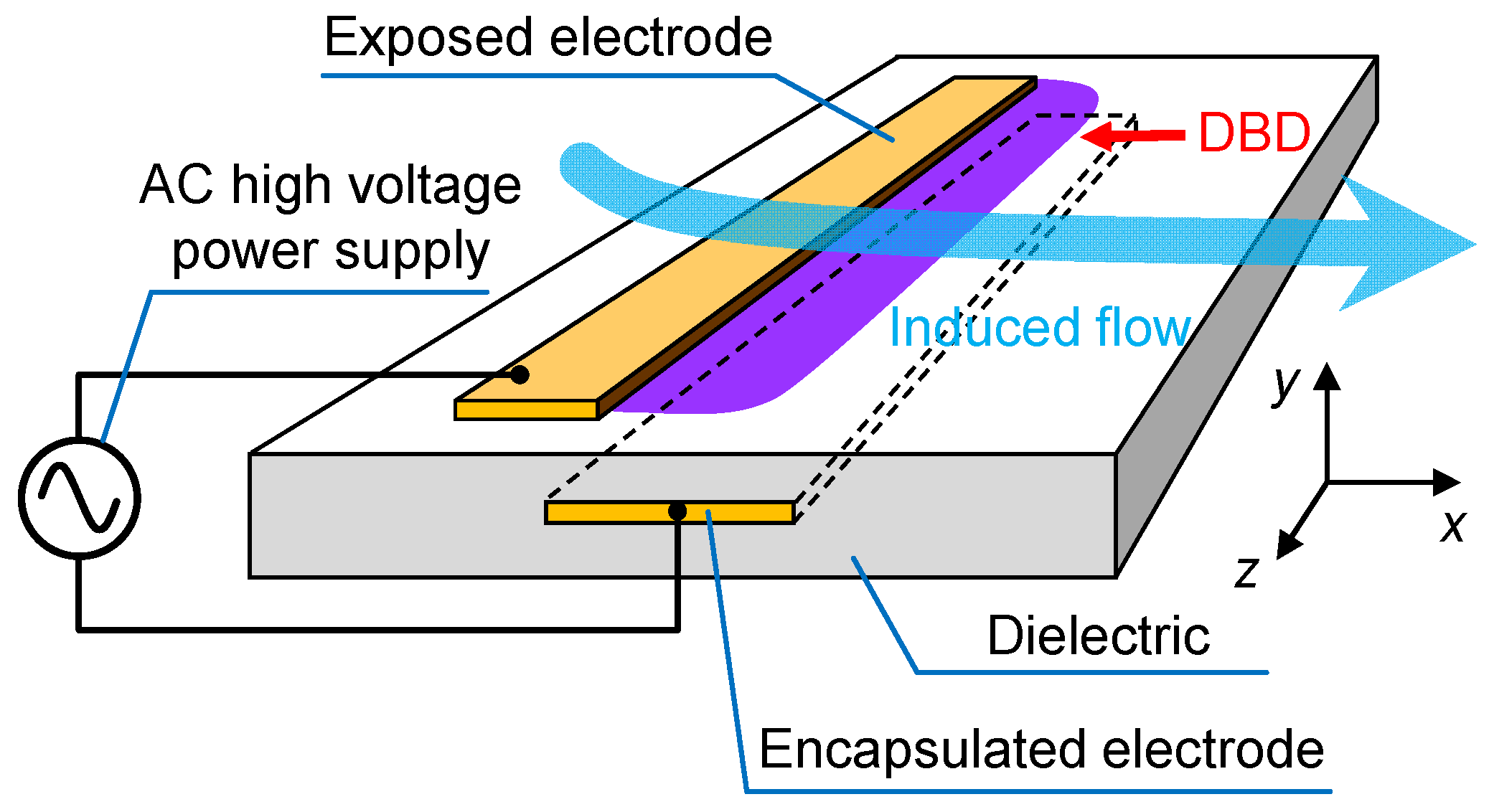
2. Experimental Setup
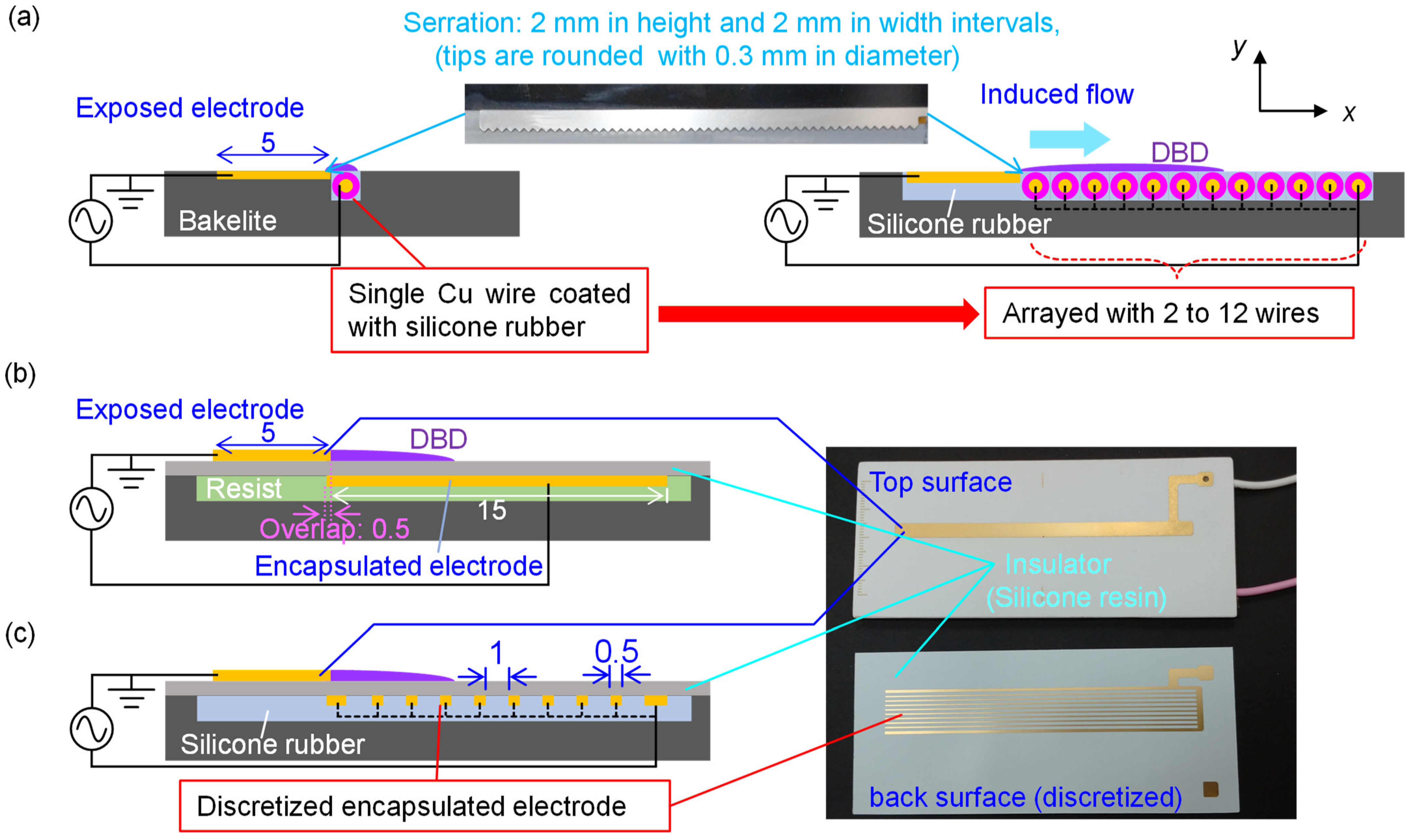
2.1. Specifications of the Three Types of Plasma Actuators
2.2. Experimental System for Evaluating Flow and Electrical Characteristics
3. Results
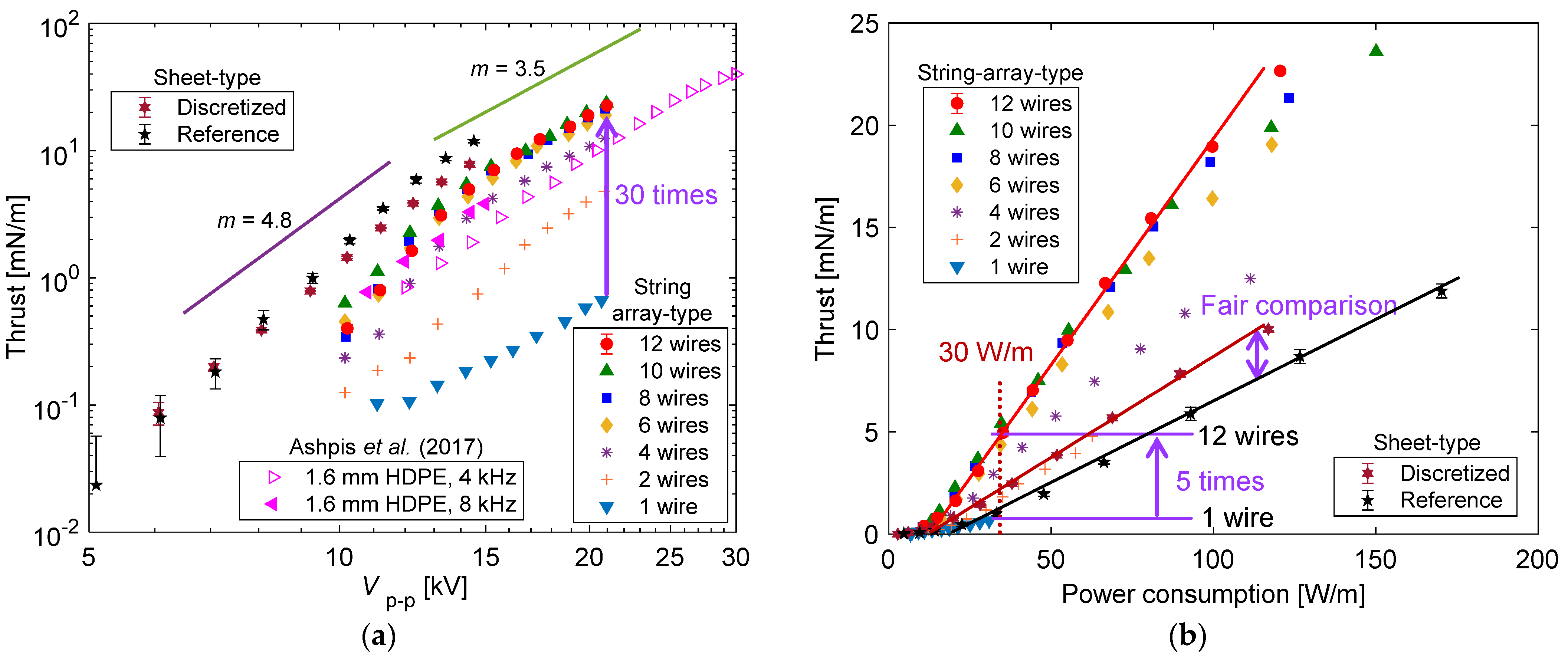
3.1. Performance Comparison between String-Type and Sheet-Type PAs without and with a Discretized Encapsulated Electrode
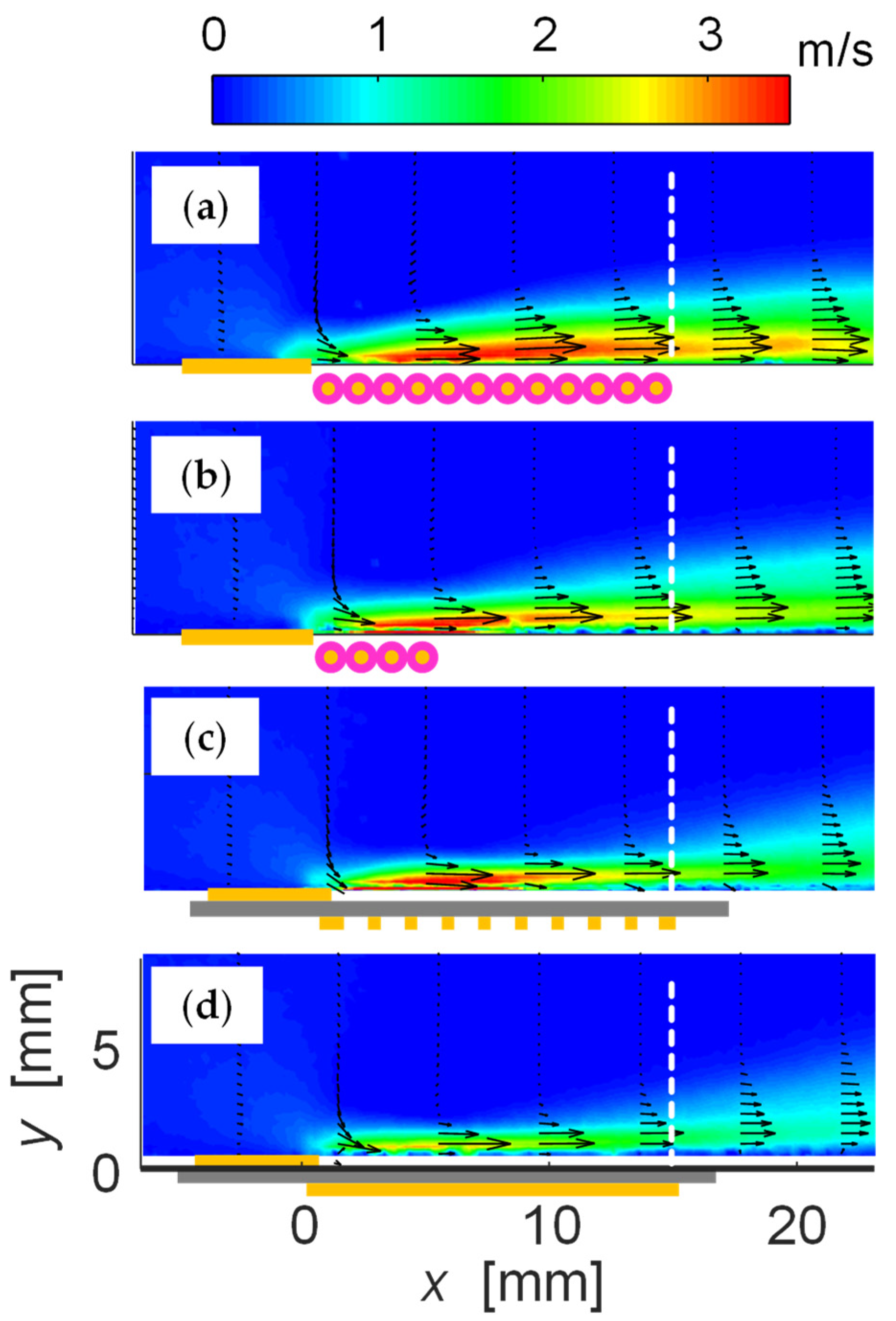
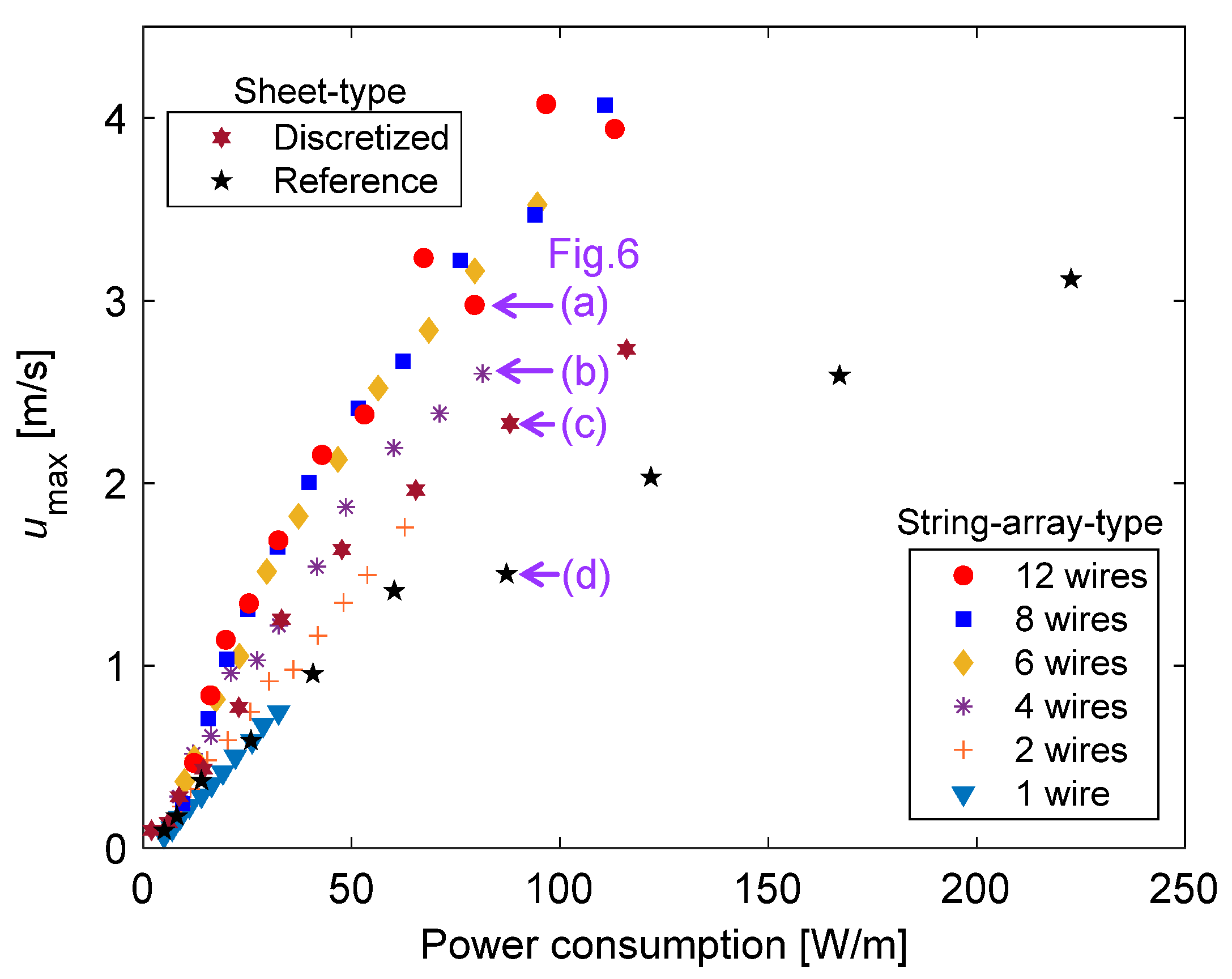
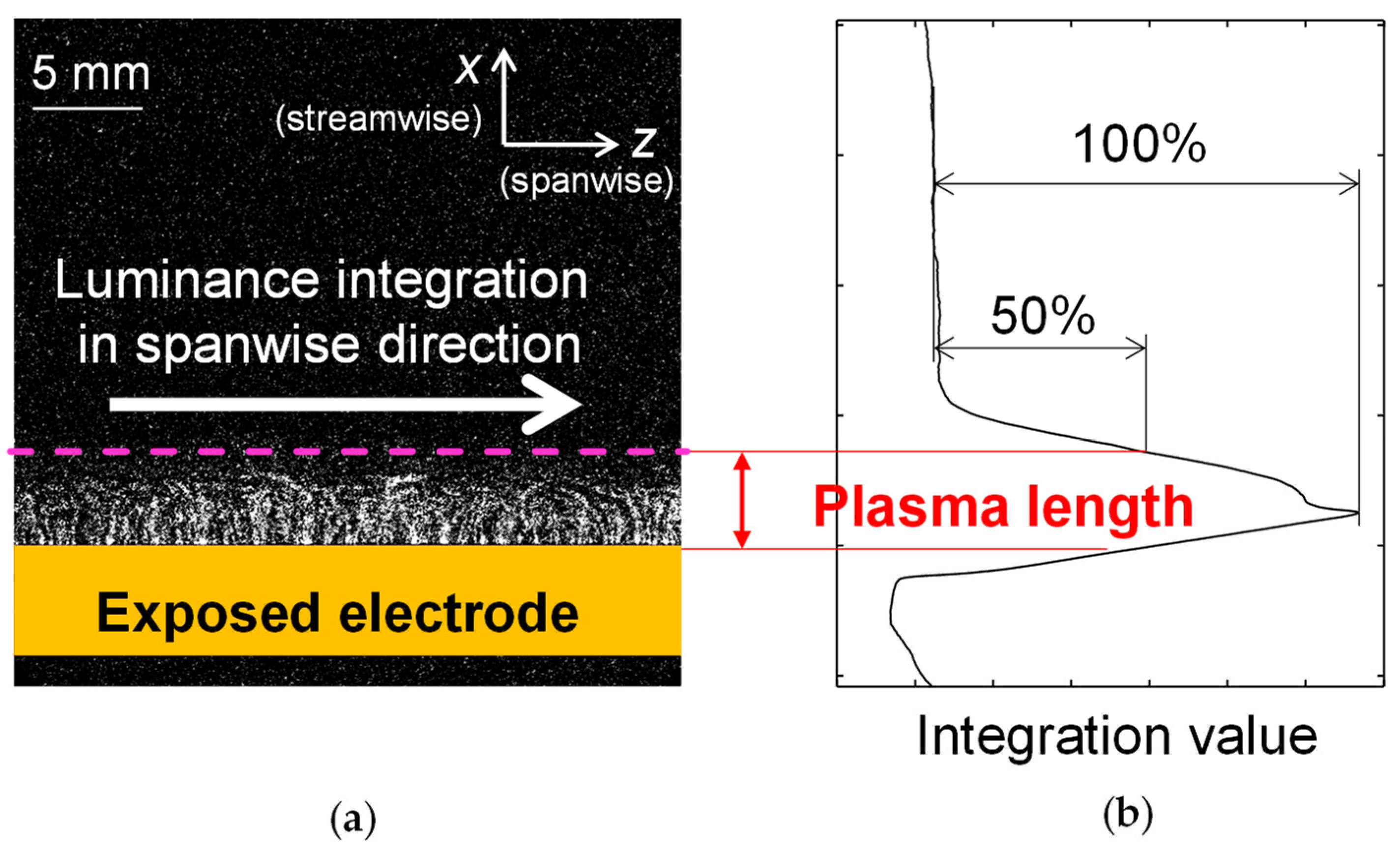
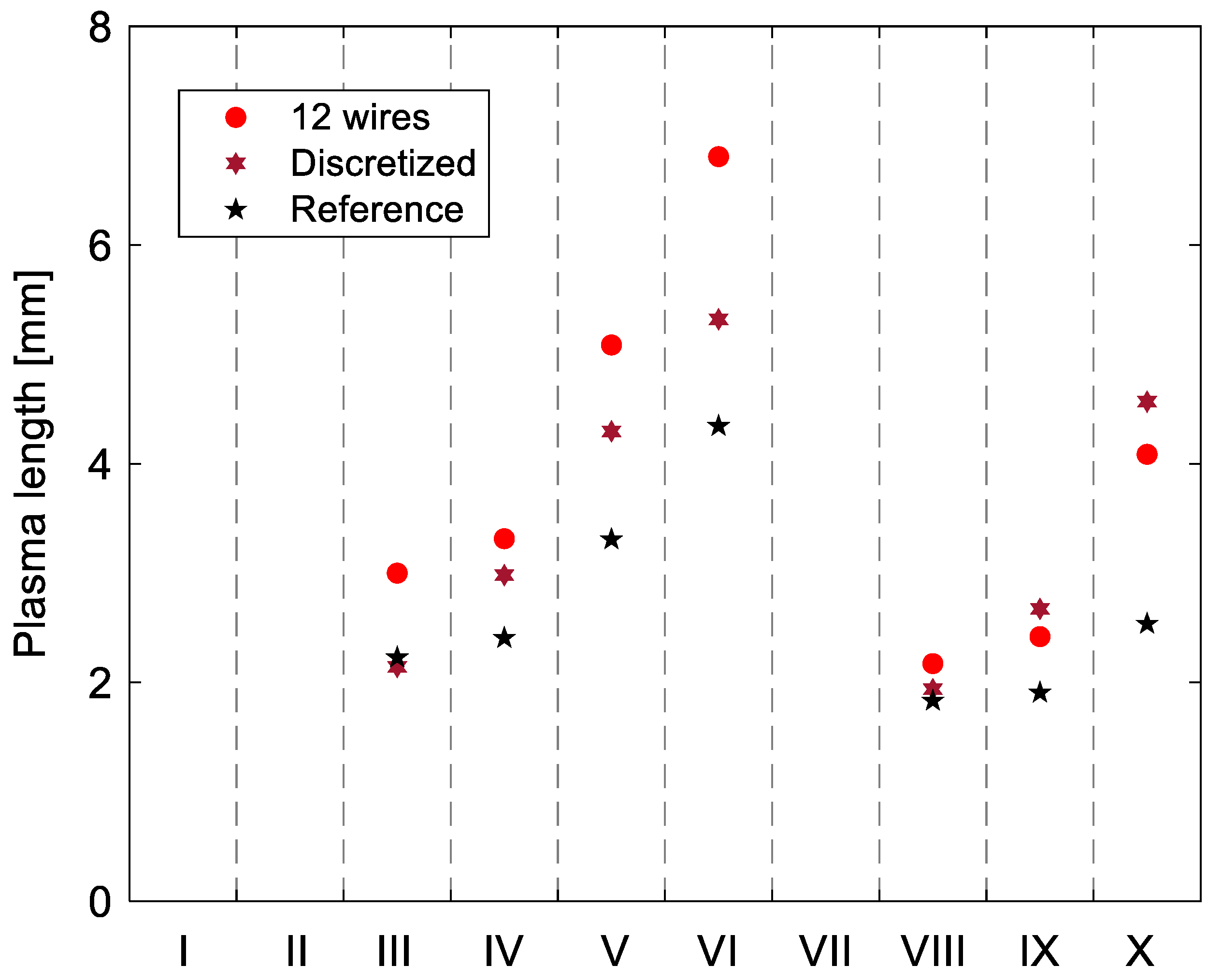
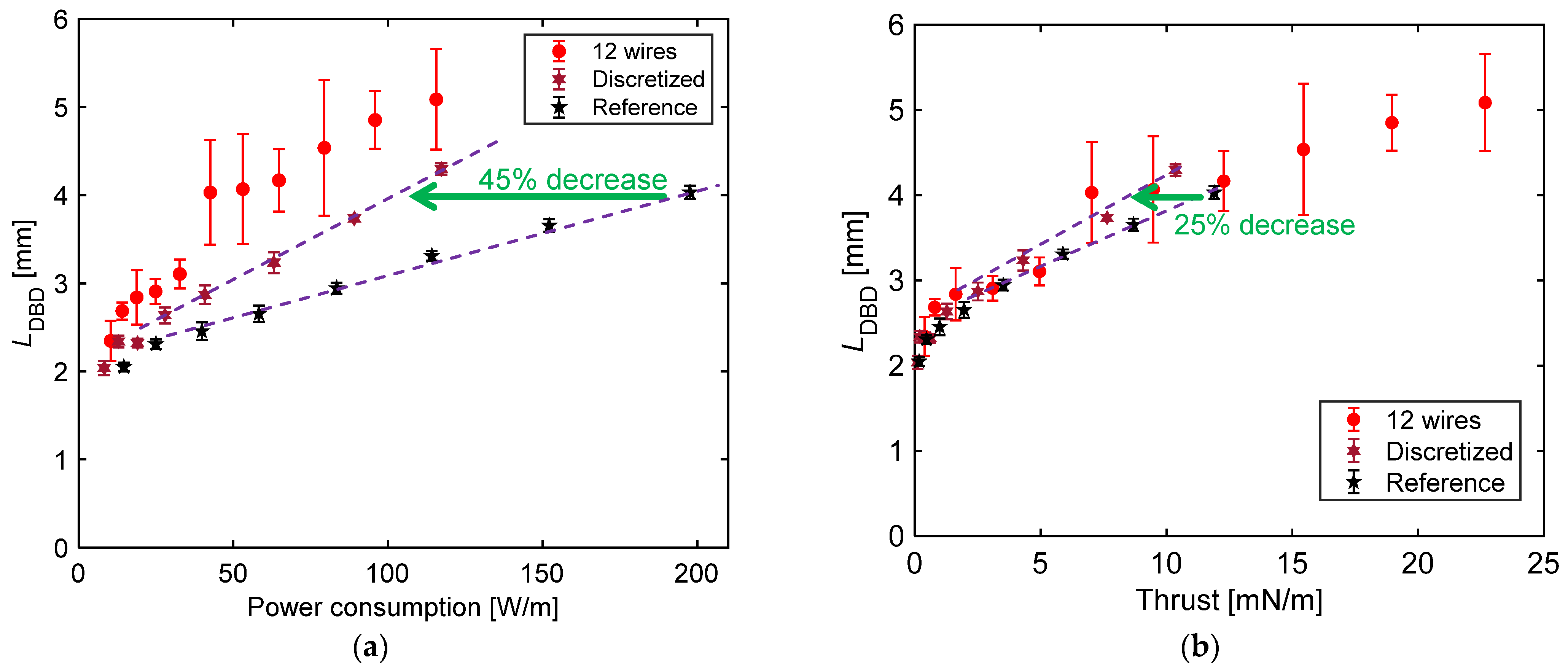
3.2. Changes in Plasma Extension Length with Respect to Power Consumption and Thrust
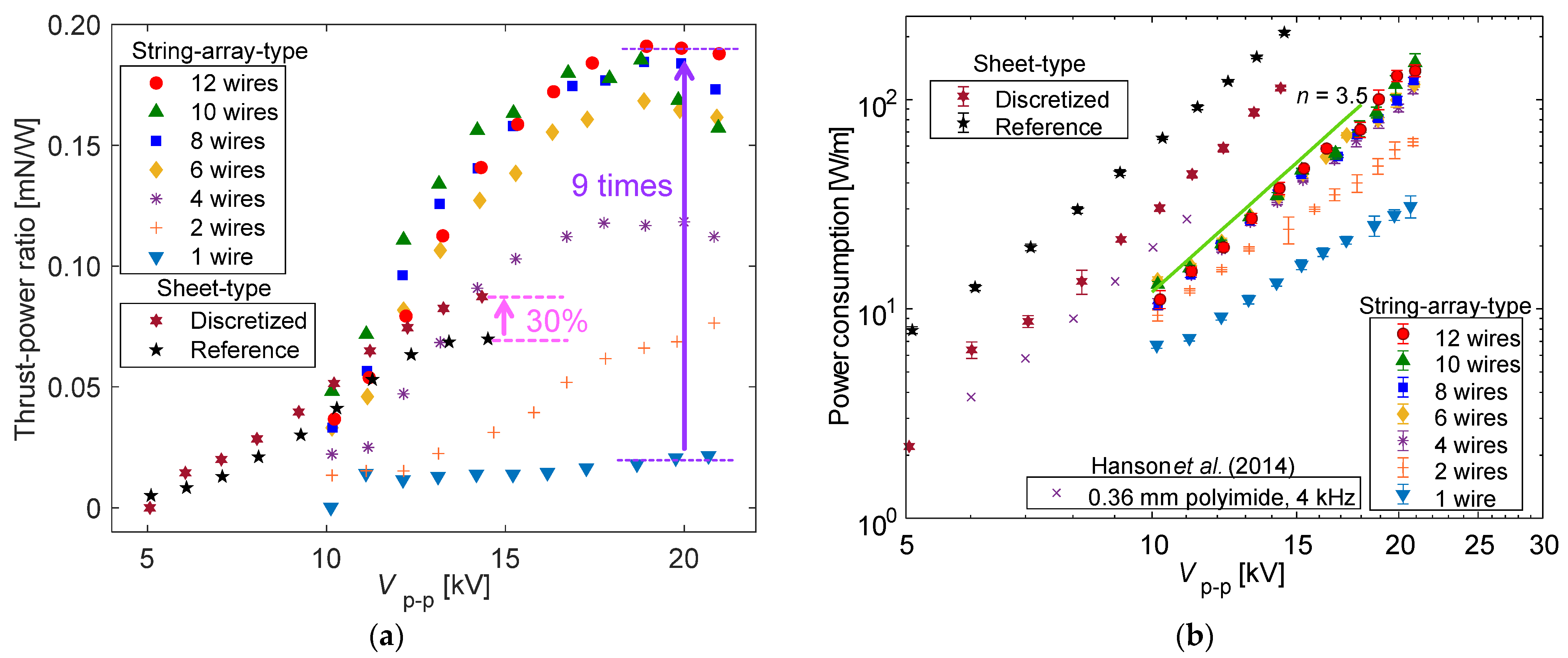
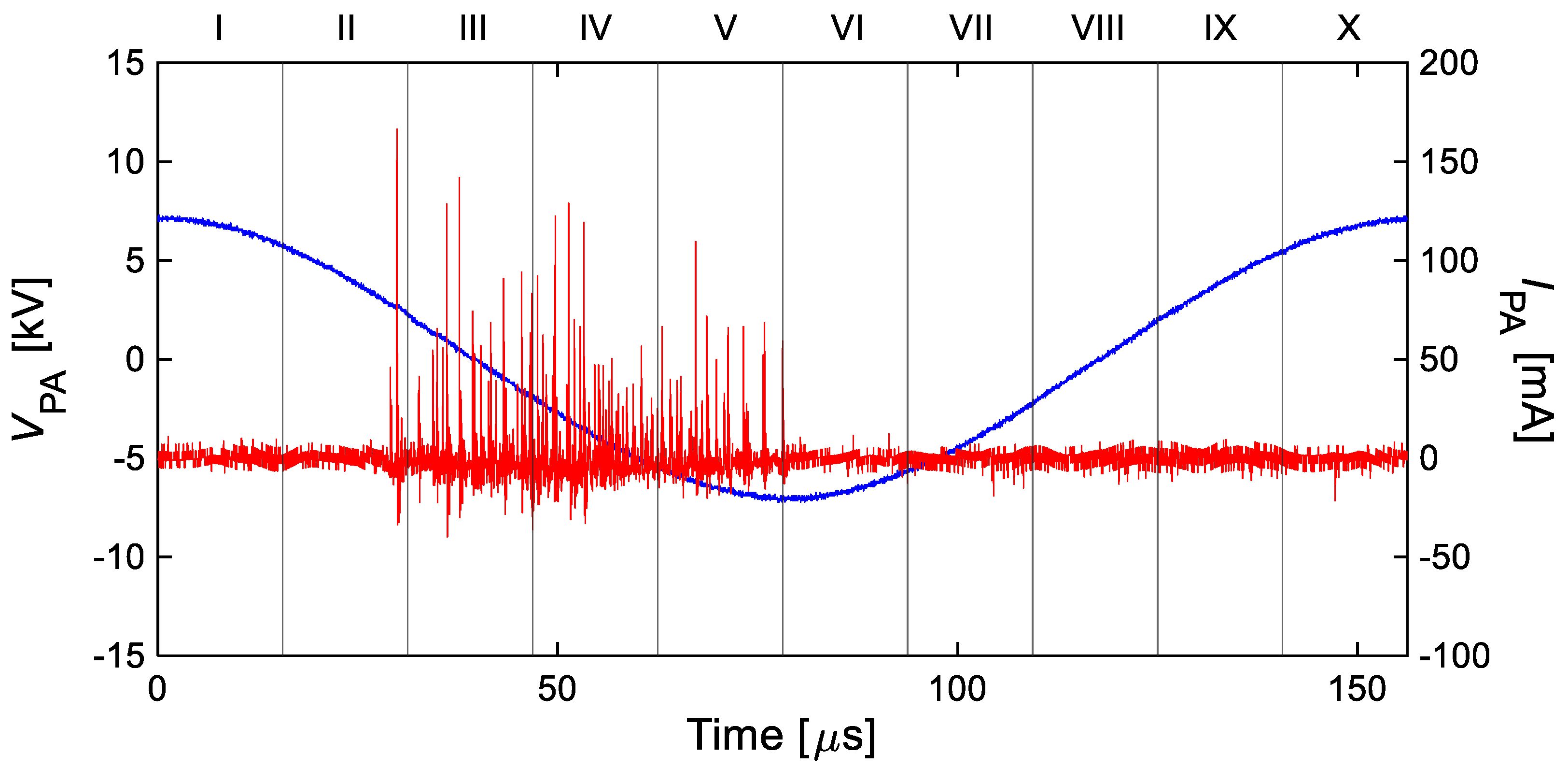
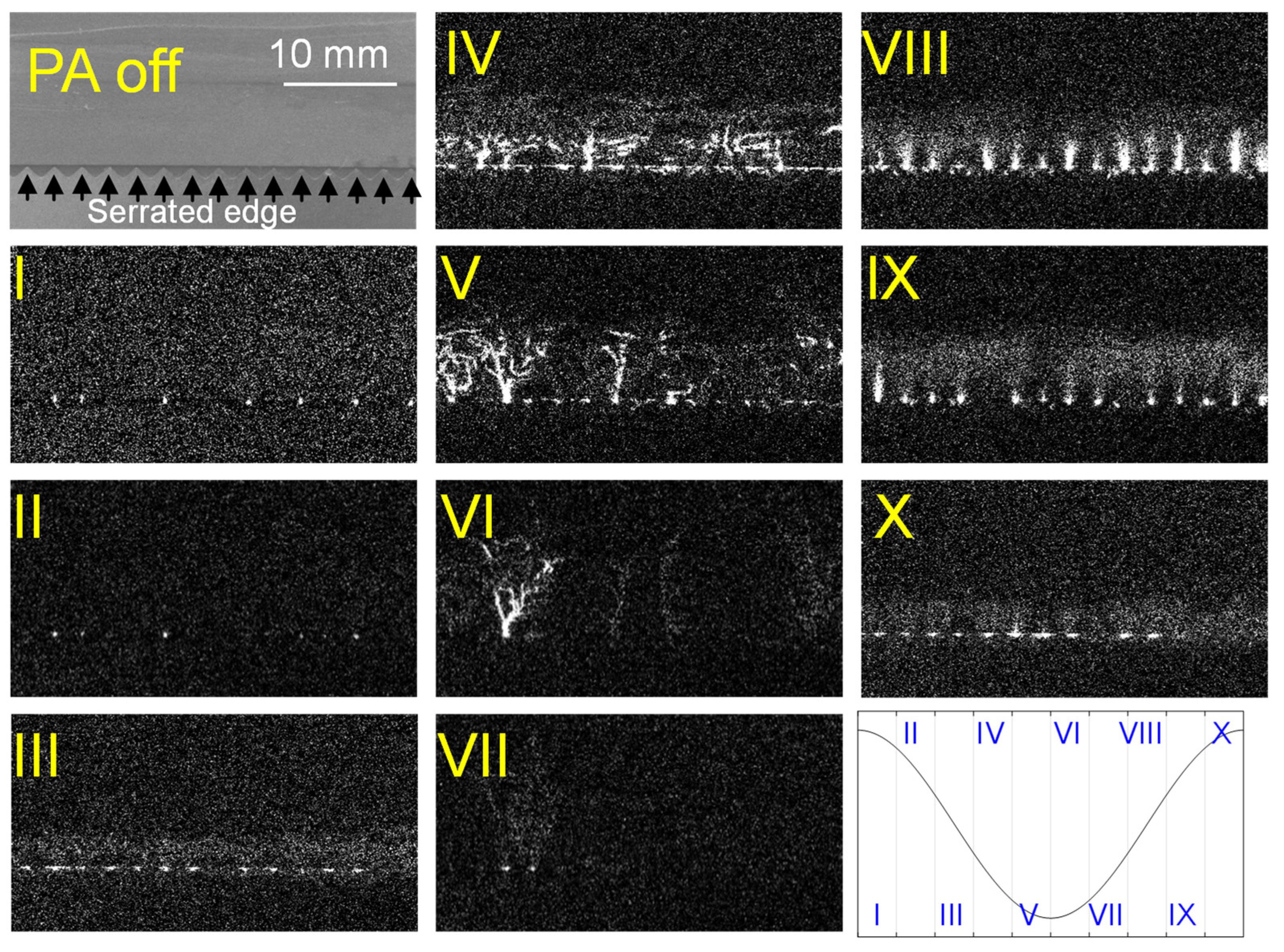
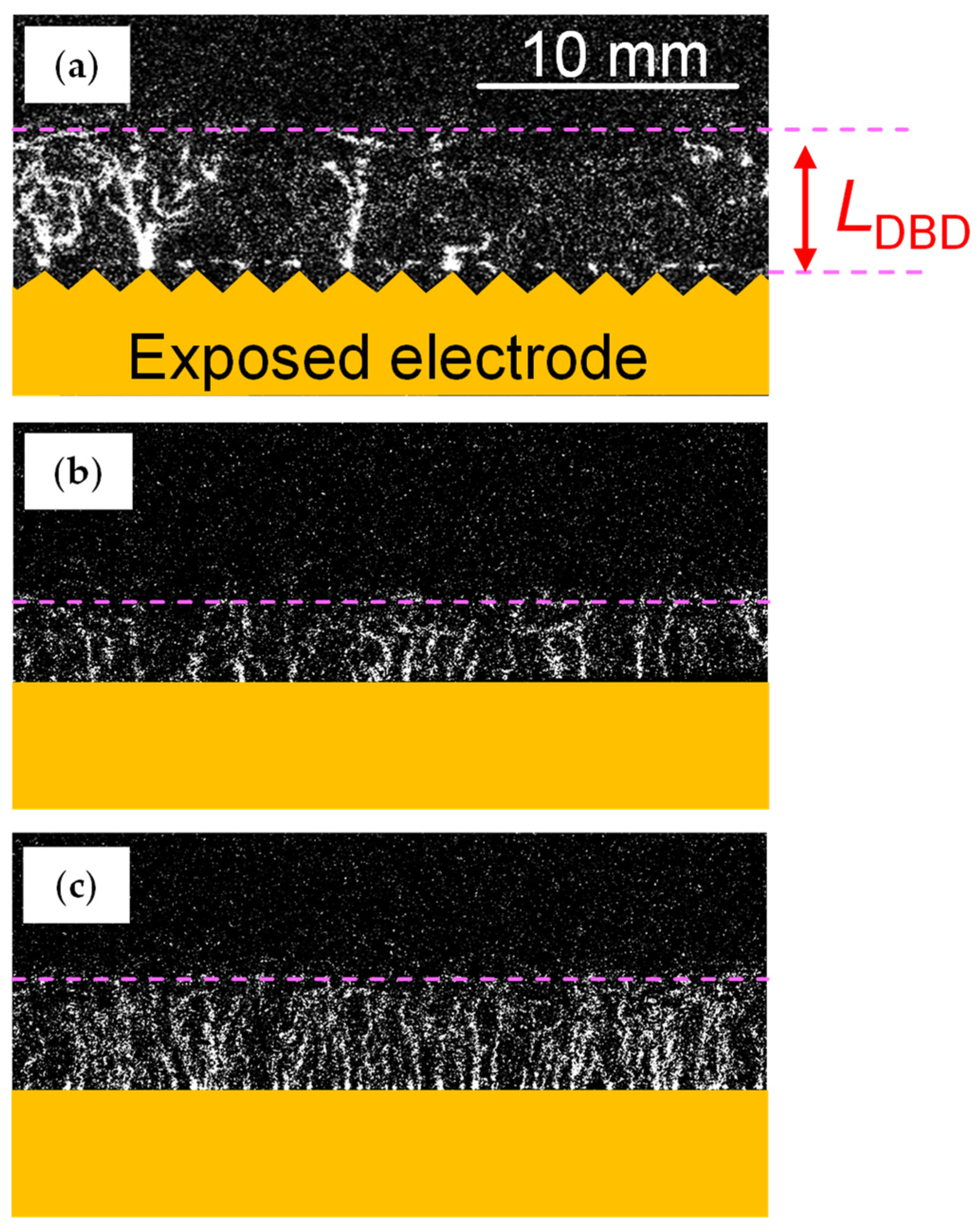
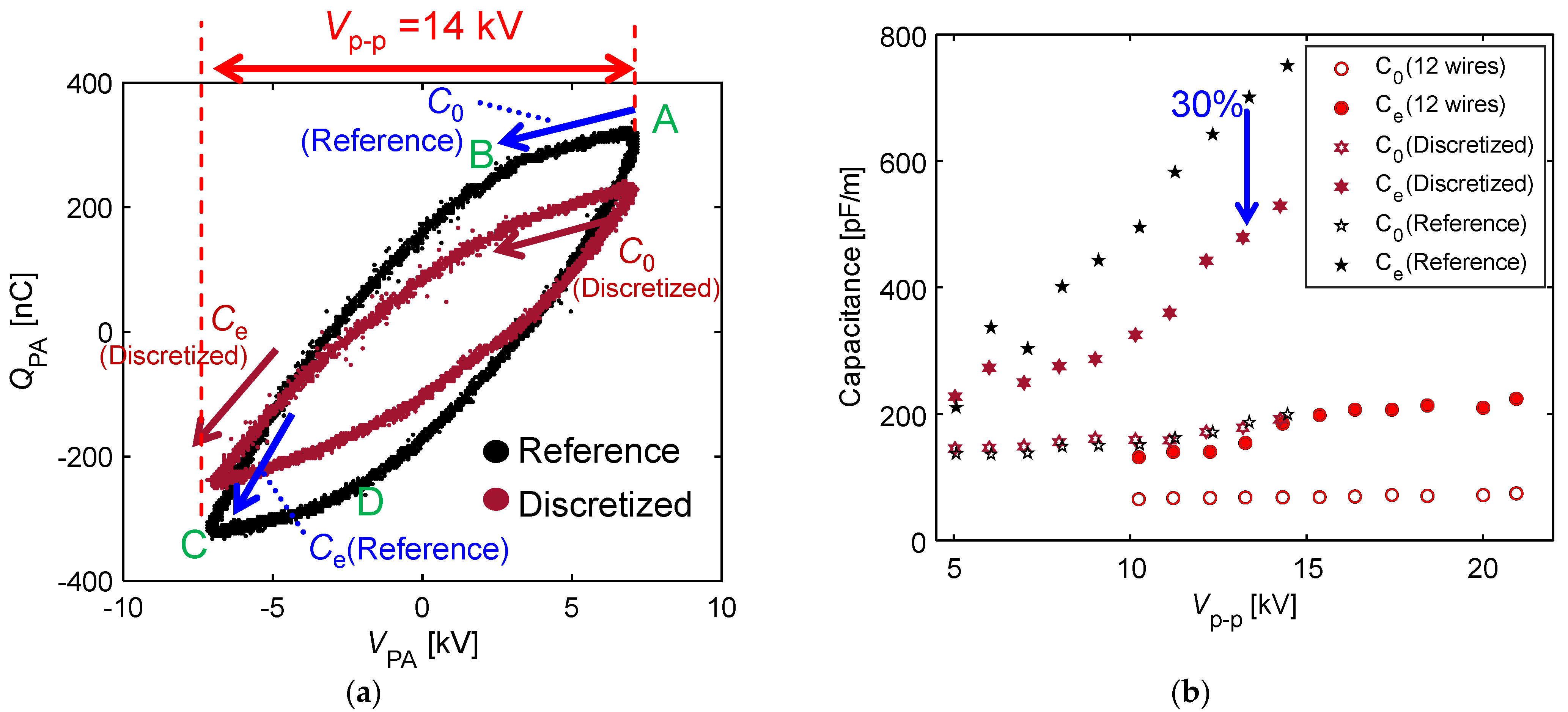
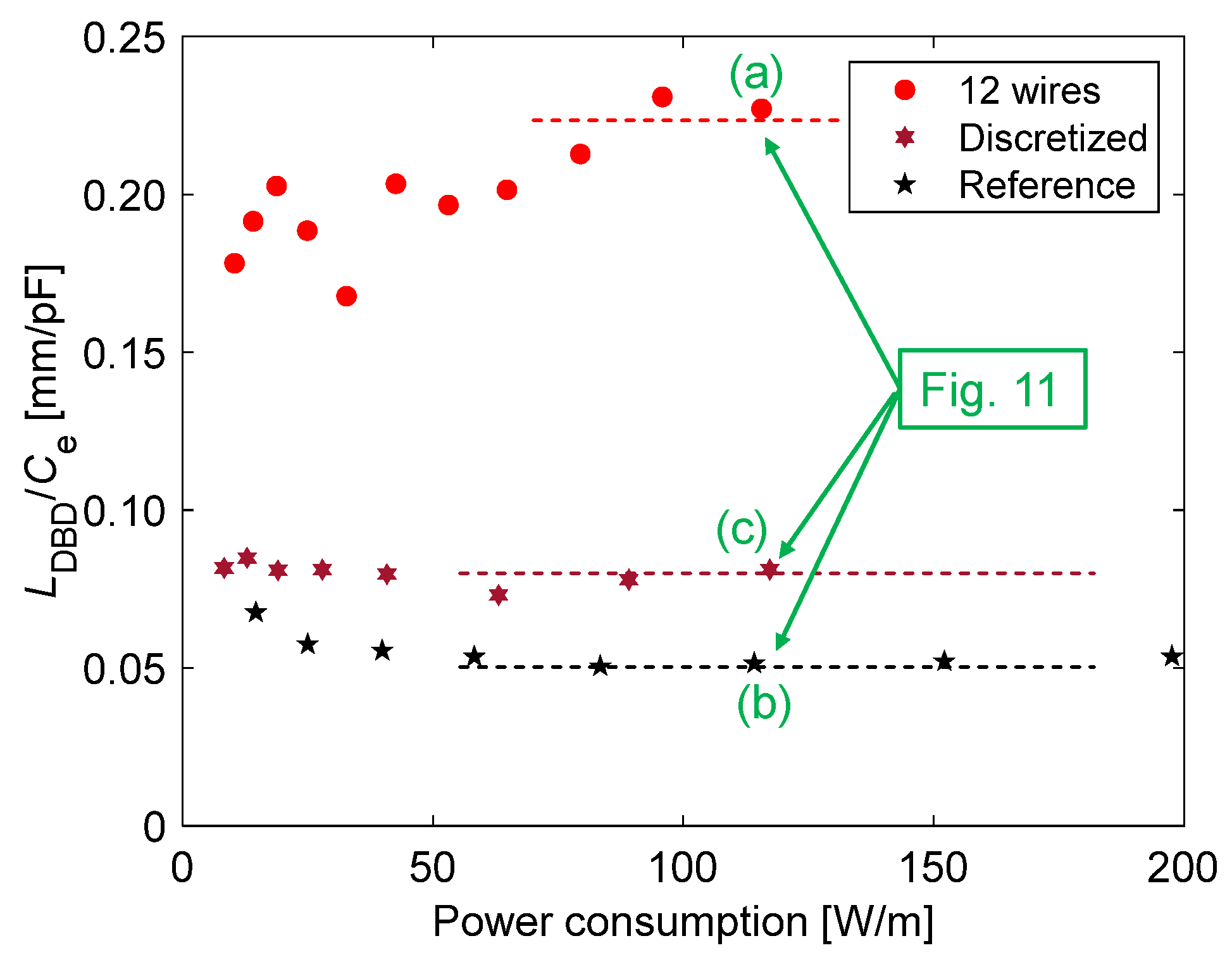
3.3. Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Increase by Discretizing Encapsulated Electrode
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The developed string-array-type PAs not only increased the thrust and induced flow velocity but also led to a nine-fold increase in the thrust–power ratio for eight or more wires, as compared with that when using a single wire, in the case of Vp-p ≥ 18 kV. This is likely due to both the substantial increase in the encapsulated electrode width by increasing the number of insulation-coated conductive wires and the discretization effect of the encapsulated electrode structure.
- (2)
- A direct performance comparison was achieved using reference and discretized sheet-type PAs with the same configuration, except for a discretized encapsulated electrode, and a 30% increase in the thrust–power ratio was confirmed due to the discretization effect. The velocity distributions of the induced flow, analyzed using PIV, revealed that the trend of the maximum velocity at x = 15 mm downstream of the exposed electrode edge as a function of the power consumption was consistent with the relationship between the thrust and power consumption characteristics.
- (3)
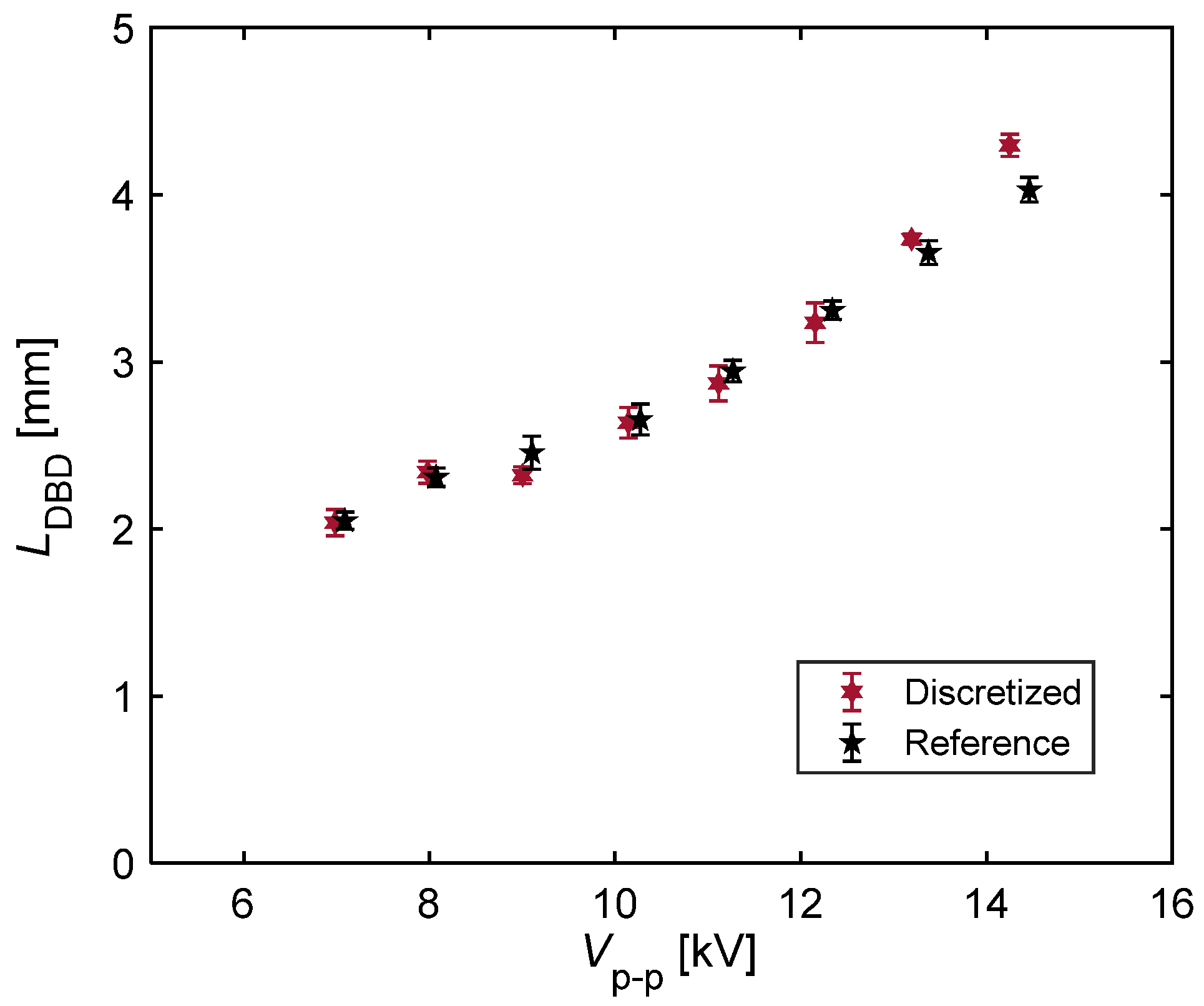
- A comparative analysis of the plasma extension lengths (LDBD) revealed that there was no significant difference in the LDBD of the reference and discretized PAs at the same Vp-p. Decreases of 25% in the thrust and 45% in the power consumption, respectively, under the same LDBD = 4 mm conditions using the discretized PA led to a 30% increase in the thrust–power ratio compared to the reference PA. The significant reduction in the power consumption, which contributed toward the increase in the thrust–power ratio, was caused by the decrease in capacitance during discharge at all peak-to-peak voltages as verified by voltage–charge (V–Q) Lissajous measurements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, J.R.; Sherman, D.M.; Wilkinson, S.P. Boundary layer flow control with a one atmosphere uniform glow discharge surface plasma. In Proceedings of the 36th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 12–15 January 1998; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Corke, T.C.; Jumper, E.J.; Post, M.L.; Orlov, D.; McLaughlin, T.E. Application of weakly-ionized plasmas as wing flow-control devices. In Proceedings of the 40th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 14–17 January 2002; p. 350. [Google Scholar]
- Corke, T.C.; Enloe, C.L.; Wilkinson, S.P. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators for flow control. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 2010, 42, 505–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.O.; Corke, T.C.; Iqbal, M.; Kozlov, A.; Schatzman, D. Optimization of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators for active aerodynamic flow control. AIAA J. 2009, 47, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giepman, R.H.M.; Kotsonis, M. On the mechanical efficiency of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 221504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, N.; Moreau, E. Electrical and mechanical characteristics of surface ac dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators applied to airflow control. Exp. Fluids 2014, 55, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, T.; Suzuki, D.; Fujino, T.; Jukes, T.; Matsunuma, T. Feedback control of flow separation using plasma actuator and FBG sensor. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 2016, 8648919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Shima, Y.; Aono, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Segawa, T. Effects of jet induced by string-type plasma actuator on flow around three-dimensional bluff body and drag force. Energies 2020, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Jolibois, J.; Pons, J.; Moreau, E.; Touchard, G.; Cazalens, M. Optimization of a dielectric barrier discharge actuator by stationary and non-stationary measurements of the induced flow velocity: Application to airflow control. Exp. Fluids 2007, 43, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussot, R.; Leroy, A.; Weber, R.; Rabat, H.; Loyer, S.; Hong, D. Plasma morphology and induced airflow characterization of a DBD actuator with serrated electrode. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komuro, A.; Ogura, N.; Ito, M.; Nonomura, T.; Asai, K.; Ando, A. Visualization of density variations produced by alternating-current dielectric-barrier-discharge plasma actuators using the background-oriented schlieren method. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunuma, T.; Segawa, T. Effects of input voltage and freestream velocity on active flow control of passage vortex in a linear turbine cascade using dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. Energies 2020, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonomura, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Ibuki, T.; Nankai, K.; Komuro, A.; Nishida, H.; Kotsonis, M.; Kubo, N.; Kawabata, H. Single-pixel particle image velocimetry for characterization of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators. AIAA J. 2020, 58, 4952–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nishida, H.; Tagawa, Y. Background-oriented schlieren measurement of near-surface density field in surface dielectric-barrier-discharge. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, A.; Podlinski, J.; Mizeraczyk, J. Elongated DBD with floating interelectrodes for actuators. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 55, 13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.P.; Siochi, E.J.; Sauti, G.; Xu, T.; Meador, M.A.; Guo, H. Evaluation of dielectric-barrier-discharge actuator substrate materials. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014; p. 2810. [Google Scholar]
- Geuns, R.; Goekce, S.; Plyushchev, G.; Leyland, P.; Pimentel, R.; Champlain, A.; Jean, Y. Understanding SDBD actuators: An experimental study on plasma characteristics. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014; p. 2811. [Google Scholar]
- Ashpis, D.E.; Laun, M.C. Characterization of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators: Logarithmic thrust–voltage quadratic relationship. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegseis, J.; Möller, B.; Grundmann, S.; Tropea, C. Capacitance and power consumption quantification of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma actuators. J. Electrostat. 2011, 69, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, N.D.; Xu, H.; Gomez-Vega, N.; Barrett, S.R.H. A model of surface dielectric barrier discharge power. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashpis, D.E.; Laun, M.C.; Griebeler, E.L. Progress toward accurate measurement of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator power. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 2254–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.E.; Houser, N.M.; Lavoie, P. Dielectric material degradation monitoring of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 043301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegseis, J.; Grundmann, S.; Tropea, C. Power consumption, discharge capacitance and light emission as measures for thrust production of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 013305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, N.; Moreau, E. Role of the electric waveform supplying a dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 110, 193503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsonis, M.; Ghaemi, S. Performance improvement of plasma actuators using asymmetric high voltage waveforms. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 045204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A.; Nishida, H. The effect of the voltage waveform on performance of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 116, 173303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangina, R.S.; Enloe, C.L.; Font, G.I. Dielectric barrier discharge-based plasma actuator operation in artificial atmospheres for validation of modeling and simulation. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, E.; Cazour, J.; Benard, N. Influence of the air-exposed active electrode shape on the electrical, optical and mechanical characteristics of a surface dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. J. Electrostat. 2018, 93, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nishida, H.; Tagawa, Y. Visualization of the electrohydrodynamic and thermal effects of AC-DBD plasma actuators of plate and wire-exposed electrodes. Actuators 2021, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, R.; Zare-Behtash, H.; Hale, C.; Kontis, K. Development of DBD plasma actuators: The double encapsulated electrode. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 109, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, R.; Erfani, T.; Utyuzhnikov, S.V.; Kontis, K. Optimisation of multiple encapsulated electrode plasma actuator. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 26, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelis, T.; Kotsonis, M. Flow control on a transport truck side mirror using plasma actuators. J. Fluid Eng-Trans. ASME 2015, 137, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet, J.A.; Örlü, R.; Söderblom, D.; Elofsson, P.; Alfredsson, P.H. Plasma streamwise vortex generators for flow separation control on trucks. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2018, 100, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.; Nagano, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Nishioka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Nakano, M. Demonstration of knock intensity mitigation through dielectric barrier discharge reformation in an RCEM. Combust. Flame 2020, 216, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starostin, S.A.; Premkumar, P.A.; Creatore, M.; van Veldhuizen, E.M.; de Vries, H.; Paffen, R.M.J.; de Sanden, M.C.M. On the formation mechanisms of the diffuse atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge in CVD processes of thin silica-like films. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18, 045021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, J.-F.; Kafle, B.; Saint-Cast, P.; Brunet, P.; Magnan, R.; Hernandez, E.; Pouliquen, S.; Massines, F. Efficient silicon nitride SiNx:H antireflective and passivation layers deposited by atmospheric pressure PECVD for silicon solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. 2019, 27, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershman, S.; Harreguy, M.B.; Yatom, S.; Raitses, Y.; Efthimion, P.; Haspel, G. A low power flexible dielectric barrier discharge disinfects surfaces and improves the action of hydrogen peroxide. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shima, Y.; Imai, R.; Ishikawa, H.; Segawa, T. Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Improvement Using Plasma Actuator with Discretized Encapsulated Electrodes. Actuators 2022, 11, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11100296
Shima Y, Imai R, Ishikawa H, Segawa T. Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Improvement Using Plasma Actuator with Discretized Encapsulated Electrodes. Actuators. 2022; 11(10):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11100296
Chicago/Turabian StyleShima, Yoshiki, Ryuya Imai, Hitoshi Ishikawa, and Takehiko Segawa. 2022. "Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Improvement Using Plasma Actuator with Discretized Encapsulated Electrodes" Actuators 11, no. 10: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11100296
APA StyleShima, Y., Imai, R., Ishikawa, H., & Segawa, T. (2022). Mechanism of Thrust–Power Ratio Improvement Using Plasma Actuator with Discretized Encapsulated Electrodes. Actuators, 11(10), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11100296





