Abstract
High-temperature superconducting (HTS) magnetic levitation (maglev) trains for designed high speed need a non-contact braking method that can produce stable and sufficient braking forces to ensure the safety of the train during emergency braking. In order to study the braking effects of permanent magnet eddy current braking (PMECB) used in HTS maglev vehicles and its effects on the levitation performance of HTS maglev vehicles, an equivalent two-dimensional simulation model of PMECB for a HTS maglev test vehicle under different working air gaps of 5 mm, 10 mm, 15 mm and 20 mm was established in Maxwell software. Then, a 6 degree of freedom dynamic model of the vehicle was established in Universal Mechanism software. In the dynamic simulation, the normal force of PMECB was not considered, and only the detent force of PMECB was taken as the excitation of the vehicle. The simulation results show that PMECBs can reduce the vehicle to relatively low speed in a few seconds. During the operation of PMECBs, the levitation height and levitation force of the maglev Dewar will be affected, and maximum variations in levitation heights and levitation forces occur on the Dewars at both ends of the vehicle. These help us to understand the braking and levitation performance of HTS maglev vehicles under the action of PMECBs and enrich the design idea of braking and levitation systems of HTS maglev vehicles equipped with PMECBs.
1. Introduction
Eddy current braking (ECB) technology overcomes many defects such as the low friction coefficient and insufficient heat capacity of adhesive braking. The braking force of ECB changes smoothly in the high-speed range. Therefore, the application of ECB technology in the fields of high-speed trains is increasing [1,2,3,4]. According to the excitation mode, ECB can be divided into electromagnetic eddy current braking (EECB) [5,6] and permanent magnet eddy current braking (PMECB) [7,8,9,10,11]. There are three typical applications of ECB in rail vehicles [12,13]. One of them uses the electromagnet or permanent magnet installed on the bogie frame to generate an induced eddy current on the surface of the disk on the axle to produce a braking effect, which includes the EECB and PMECB systems. Another one uses the electromagnet installed on the frame to generate an induced eddy current on the track surface to produce a braking effect, which belongs to the EECB system. The last one is based on the electromagnet or permanent magnet mounted on the bogie or levitation frame to produce eddy currents on the metal plate surface to produce a braking effect, which includes EECB and PMECB systems. Compared with the EECB system, the PMECB is seldom used in railway trains. The PMECB system is composed of a Halbach permanent magnet array [14,15,16,17] and metal induction plates. The PMECB has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple structure and no electric excitation, but its braking force is difficult to control. Choi et al. designed the magnetization pattern of the eddy current brake system of a permanent magnet type where the design aim is to maximize the braking force. The analysis of brake systems is based on the two-dimensional finite element analysis [18]. Jin et al. developed an analytical model of a permanent magnet linear eddy current brake considering lateral edge effects. The braking force of the eddy current brake is then calculated while taking the dynamic transverse edge effect into consideration [19]. Chen et al. designed a double-sided linear permanent magnet Halbach array that can brake at a very high speed within a short time or a short distance [20].
HTS maglev vehicles have an advantage of inherent stability both in the lateral and vertical directions. And there is no inherent magnetic resistance force in the forward direction. In 2000, the first manned HTS maglev experimental vehicle “Century” was developed in China [21]. In 2013, the group further developed an HTS maglev ring test line with a running speed of 50 km/h [22]. In 2021, the HTS high-speed maglev engineering prototype rolled off in Chengdu, China and its design speed was 620 km/h [23]. The HTS maglev vehicle does not consume electricity for levitation and guidance, so it does not need to be powered by a pantograph or a third rail, which makes it suitable for a PMECB without electrical excitation. Currently, the study of HTS maglev vehicles is at the engineering stage. It is of significance to study the braking effects of PMECBs used in HTS maglev vehicles. Meanwhile, it is necessary to study the levitation, guidance and other dynamic performances of the vehicles under the action of PMECBs. Figure 1 shows an HTS maglev test vehicle equipped with a PMECB system. The study of this paper is based on it.

Figure 1.
An HTS maglev test vehicle equipped with PMECBs: (a) the test vehicle; (b) the PMECB composed of Halbach permanent magnet array fixed on both sides of the vehicle; (c) the metal induction plates.
2. The Detent Force Model
It can be seen from Figure 2a that the bogie is equipped with four sets of PMECBs, which are installed on two sides of the bogie symmetrically. When PMECBs move relative to the metal conductor plates, eddy currents will be induced in the plates and the vehicle will slow down.
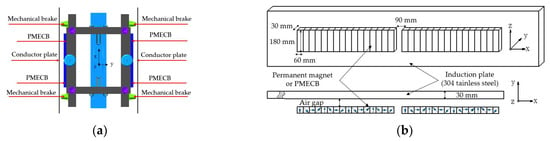
Figure 2.
Schematic of (a) the arrangement of four PMECBs and (b) the equivalent two-dimensional unilateral simulation model of two PMECBs.
Figure 2b shows an equivalent two-dimensional unilateral simulation model, which consists of two PMECBs. In other words, the simulated detent force and normal force are the sum of the two sets of PMECBs. The magnetization angle of the permanent magnets is represented by a series of arrows, and the relevant parameters of the permanent magnet and the metal induction plates are shown in Figure 2b. There are several modeling assumptions in the model as follows:
- (1)
- The magnetic induction intensity in the Z direction is 0.
- (2)
- The edge effect is ignored.
- (3)
- The frictional resistance and aerodynamic resistance are also ignored.
The relationships between the detent force, the normal force and initial speed under the working air gaps of 5 mm, 10 mm, 15 mm, and 20 mm are studied respectively. The results in Figure 3a–d are obtained from electromagnetic simulation results in Maxwell software.
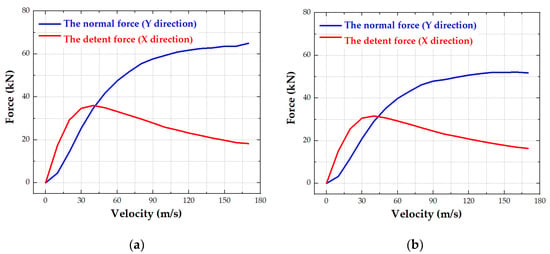
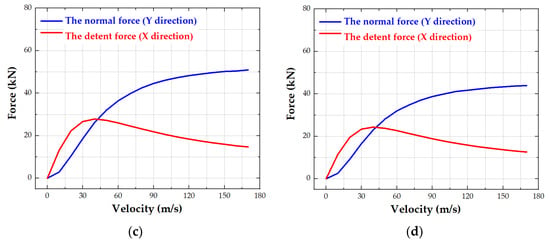
Figure 3.
Relationship between the detent force, the normal force and velocity of the vehicle under different working air gaps: (a) under 5 mm air gap, (b) under 10 mm air gap, (c) under 15 mm air gap, (d) under 20 mm air gap.
It can be seen form Figure 3a–d that the normal force increases with the increase in the running velocity of the vehicle, whose increasing trend becomes slow. At the same initial speed, the smaller the air gap, the greater the normal force. The detent force increases continuously with the increase in velocity under different air gaps. The detent force reaches its maximum value around 40 m/s (144 km/h) under different air gaps. After that, it gradually decreases with the increase in velocity. At the same initial speed, the smaller the air gap, the greater the detent force. Table 1 lists the maximum detent force under different air gaps.

Table 1.
The maximum detent force under different air gaps.
In addition, Figure 3a–d shows that in the low-speed range (about 0–40 m/s), the detent force is large, and the normal force is small. When the speed increases, the normal force is greater than the detent force. In the high-speed range (about 90–170 m/s), the changes in detent force and normal force with speed tend to be gentle, which is conducive to high-speed movement.
In the study of the vehicle’s levitation performance, the normal force of the PMECB is ignored. On the one hand, the normal force is transverse (Y direction), which mainly affects the guidance performance of the vehicle, and does not affect the vertical levitation performance. On the other hand, in an ideal model, the normal force acts on both sides of the vehicle, which cancels out without considering the test line and other factors. Compared with the effects of several polynomial fittings, the sixth-order polynomial with the best fitting effect is finally selected. The relationships between the detent force (or braking force) and speed under different working air gaps are calculated in Equation (1).
where Fdetent is the detent force of two PMECBs; v is the initial speed; a, b, c, d, e, s, t are the coefficients. As shown in Table 2, their values vary with different working air gaps. Although the coefficients s and t in Equation (1) and Table 2 are small, when v = 100 m/s, 110 m/s, v5 and v6 are very large, the influence of this item on the result cannot be omitted.

Table 2.
Coefficient of braking force fitting curves under different working air gaps.
3. The HTS Maglev Test Vehicle Model
Figure 4 shows the principle and layout of the HTS maglev test vehicle system. The levitation force and the guidance force (together called the flux pinning force) are derived from the interaction between the HTS bulks in maglev Dewars and the permanent magnet guidance (PMG). The driving function is achieved by the long stator coil to pull the on-board mover to realize a high-speed operation. The PMECB is used to realize a braking function in the high-speed case and the mechanical brake is used in the low-speed case.
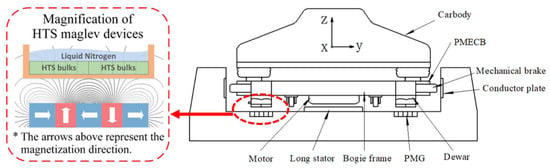
Figure 4.
Schematic of principle and layout of the HTS maglev test vehicle system.
Li and Wang [24,25,26] proposed separately a levitation force model based on an exponential function combining formula deriving and the experimental measurement. These mathematical models describe the relation between the levitation force and levitation height of the single maglev Dewar, but the Dewar here is not primarily used for engineering or as a test vehicle Dewar. The research group to which the author belongs then obtained a new and more accurate levitation force model through the maglev Dewar experiments. Figure 5 shows the relationship between the levitation force and the levitation height of a single Dewar used in the based test vehicle. The mathematical model of the Dewar’s guidance force is represented by the spring-damper module that comes with UM, which is not used in this paper.
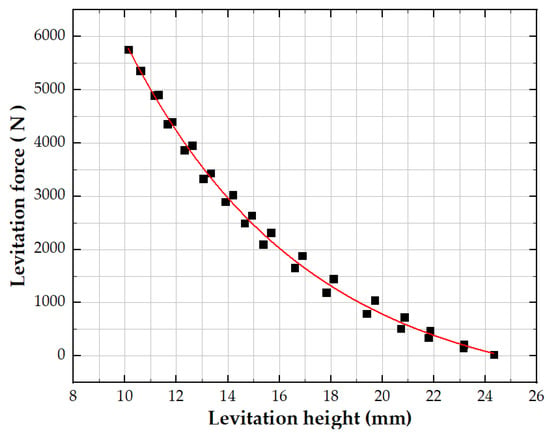
Figure 5.
The relationship between levitation force and levitation height of single maglev Dewar used in the test vehicle.
After fitting the data curves in Figure 5, the following levitation force model can be obtained:
where Flev represents the levitation force of a single Dewar used in the test vehicle; h represents the levitation height of the Dewar; Vz represents the vertical vibration speed of Dewars, which is a transient variable, and the Vz of each Dewar can be retrieved from the electromagnetic module of the UM software; Cp is defined as the damping force of the Dewar, which is 30 N·s/m [26].
Figure 6 shows the installation location and number of Dewars. Dewars are installed symmetrically, so only Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3, and No. 4 are taken as the objects of study. Figure 7 shows the dynamic model of the HTS maglev test vehicle. The vehicle itself has a primary suspension because of the flux pinning force. The secondary suspension is provided by rubber springs and air springs. The detent force Fdetent in Equation (1) is evenly distributed to two sets of PMECBs, which is done by Fbreak. The main parameters related to the vehicle can be seen in Table 3.
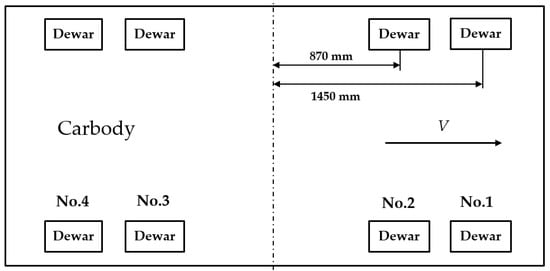
Figure 6.
Schematic of location and number of maglev Dewars.
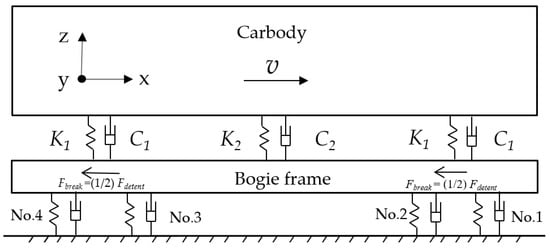
Figure 7.
Schematic of dynamic model of the HTS maglev test vehicle.

Table 3.
The main parameters related to the test vehicle.
4. Results and Analysis
Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the change process in the braking force (or detent force), the velocity of the vehicle and braking distance under the action of PMECBs, which are obtained from the simulation results in UM software.
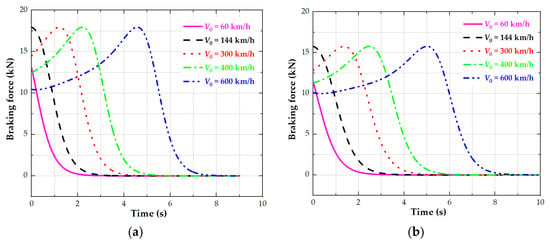
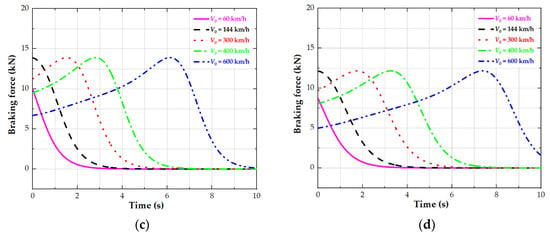
Figure 8.
The change process of braking force of single PMECB at initial speeds of V0 = 60 km/h, 144 km/h, 300 km/h, 400 km/h and 600 km/h under different air gaps: (a) under 5 mm air gap, (b) under 10 mm air gap, (c) under 15 mm air gap, (d) under 20 mm air gap.
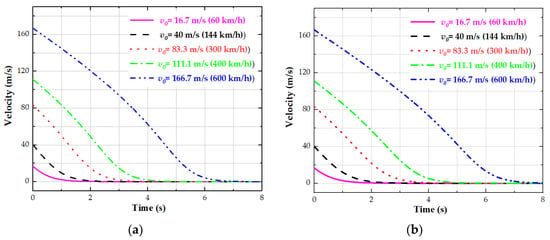
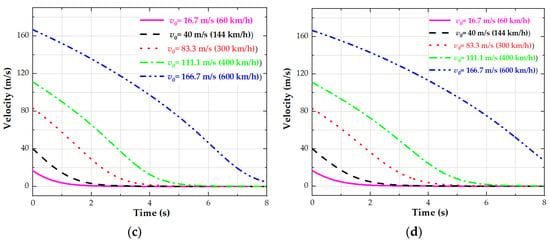
Figure 9.
The change process of the vehicle’s velocity at initial speeds of V0 = 60 km/h, 144 km/h, 300 km/h, 400 km/h and 600 km/h under different air gaps: (a) under 5 mm air gap, (b) under 10 mm air gap, (c) under 15 mm air gap, (d) under 20 mm air gap.
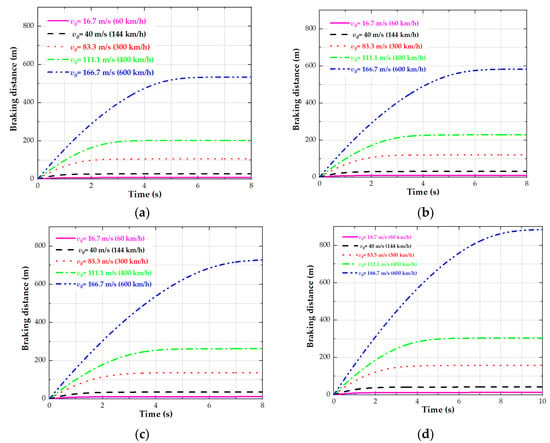
Figure 10.
The change process in the braking distance at initial speeds of V0 = 60 km/h, 144 km/h, 300 km/h, 400 km/h and 600 km/h under different air gaps: (a) under 5 mm air gap, (b) under 10 mm air gap, (c) under 15 mm air gap, (d) under 20 mm air gap.
Figure 8a–d show the change process in the braking force (or Fbreak) of a single PMECB at different initial speeds and under different air gaps. At the initial speed of the vehicle V0 = 144 km/h, the braking force of the single PMECB is the largest when PMECBs start working. That is to say, the braking force of the whole vehicle (4 * Fbreak) reaches its maximum value. The braking force then decreases until it is close to zero. At the initial speed of the vehicle V0 > 144 km/h, the braking force of the whole vehicle will first increase and then decrease rapidly after reaching the peak value. At the initial speed of the vehicle V0 < 144 km/h, the braking force of the whole vehicle reaches its maximum at the moment when the PMECBs start working, but it is not the maximum value of the vehicle system. Thereafter, the braking force decreases until it approaches zero. These variations are consistent with the relationship between the detent force and velocity in Figure 3a–d, which proves the accuracy of the vehicle dynamics modeling.
Figure 9a–d shows the change process in the vehicle’s running velocity at different initial speeds, under different air gaps. The larger the initial speed and air gap, the longer it takes the vehicle to come to a standstill. It can be seen from the blue curves that when the vehicle running speed is V0 > 40 m/s (144 km/h), the absolute value of this curve’s slope (representing acceleration) increases; that is, the braking force increases. When V0 < 40 m/s (144 km/h), the absolute value of this curve’s slope decreases gradually; that is, the braking force becomes smaller and smaller. These variations are consistent with the relationship between the detent force and velocity in Figure 3a–d.
Figure 10a–d shows the change process in the vehicle’s braking distance at different initial speeds, under different air gaps. The slope of curves represents the magnitude of the vehicle’s velocity. It can be seen from the blue curves that the slope is becoming ever smaller, and the velocity is becoming ever slower, which is consistent with the change process of the vehicle’s velocity in Figure 9a–d.
Table 4 shows the braking effect on the vehicle of PMECBs at the initial speed of 60 km/h and 600 km/h and under different air gaps. It can be seen from the table that when the vehicle runs at the initial speed of 600 km/h and under the air gap of 10mm, the maximum braking force of the whole vehicle is about 62 k N, the braking time of the vehicle is about 8 s, and the braking distance of the vehicle is about 580 m. The braking effect of the PMECB is obvious.

Table 4.
Braking effects under different air gaps.
Figure 11a,c shows the change process in the levitation heights of Dewars when V0 is 60 km/h and 600 km/h under the braking air gap of 10 mm, respectively. It can be seen from these two figures that when the PMECBs are not working, the stable levitation heights of all Dewars are about 15.3 mm.
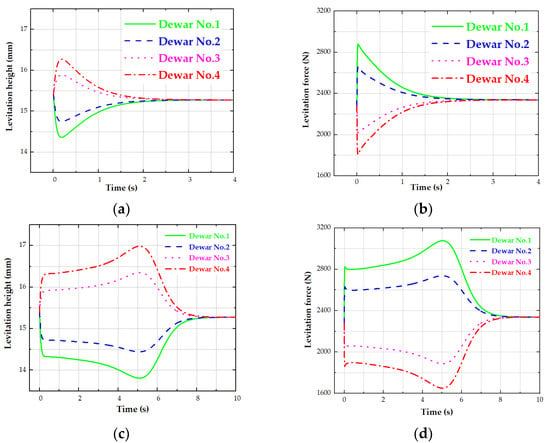
Figure 11.
Effect of the detent force on the levitation performance of the vehicle: (a) change process of levitation heights of Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 at V0 = 60 km/h under 10 mm air gap, (b) change process of levitation forces of Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 at V0 = 60 km/h under 10 mm air gap, (c) change process of levitation heights of Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 at V0 = 600 km/h under 10 mm air gap, (d) change process of levitation forces of Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 at V0 = 600 km/h under 10 mm air gap.
Figure 11b,d shows the change process in the levitation forces of the Dewar when V0 is 60 km/h and 600 km/h under the braking air gap of 10 mm, respectively. It can be seen from these two figures that when the PMECBs are not running, the stable levitation forces of all Dewars are about 2340 N.
When V0 exceeds 144 km/h, the braking forces of the PMECB have the same peak value. In this case, the impact on the suspension system is roughly the same. In order not to make the content redundant, this part only gives the above two working conditions (V = 60 km/h, 600 km/h).
In detail, Figure 11a shows that under the V0 = 60 km/h and 10 mm air gap, the actual minimum levitation heights of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 are about 14.3 mm and 14.8 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces are about 2880 N and 2650 N (shown in Figure 11b), respectively. Compared with the stable state, the levitation heights of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 decrease by about 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces increase by about 540 N and 310 N, respectively. While the actual maximum levitation heights of Dewar No. 4 and No. 3 increase by about 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces decrease by about 530 N and 330 N, respectively. The relevant data above are listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Variation in the levitation heights and levitation forces of Dewar under V0 = 60 km/h and 10 mm air gap.
Figure 11c shows that under V0 = 600 km/h and the 10 mm air gap, the actual minimum levitation heights of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 are about 13.8 mm and 14.5 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces are about 3080 N and 2750 N (shown in Figure 11d), respectively. Compared with the stable state, the levitation heights of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 decrease by about 1.5 mm and 0.8 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 increase by about 740 N and 590 N, respectively. While the actual maximum levitation heights of Dewar No. 4 and No. 3 increase by about 1.5 mm and 0.8 mm, respectively, and the corresponding levitation forces of Dewar No. 4 and No. 3 decrease by about 740 N and 590 N, respectively. The relevant data above are listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Variation in the levitation heights and levitation forces of Dewar under V0 = 600 km/h and 10 mm air gap.
The analysis shows that the detent forces of the PMECBs may not be on the same level as the system centroid. Under the action of the PMECBs, the bogie has a nodding motion, and the nodding angle (β) is shown in Figure 12. As a result, the levitation heights of Dewar No. 1 and No. 2 decreased, while the levitation heights of Dewar No. 3 and No. 4 increased.
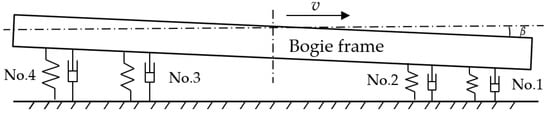
Figure 12.
Schematic of the nodding motion of the HTS maglev test vehicle.
Figure 13 shows the change in the nodding angle of the bogie at different initial speeds and under 10 mm air gaps. Other working conditions under different air gaps will not be repeated here. It can be seen from this figure that at 600 km/h, 400 km/h, 300 km/h and 144 km/h, the nodding angle (β) of the bogie reaches the maximum value. It is because when V0 is 144 km/h, the detent force (or braking force) reaches the maximum value (shown in Figure 3). The maximum nodding angle is about 0.0630. Combined with the dimensional data in Figure 6, through Equation 3, it can be calculated that the levitation height (Δh1) of Dewar No. 1 reduced by 1.594 mm, and through Equation (4), it can be calculated that the levitation height (Δh2) of Dewar No. 2 reduced by 0.957 mm. These calculated results are basically consistent with the results in Table 6.
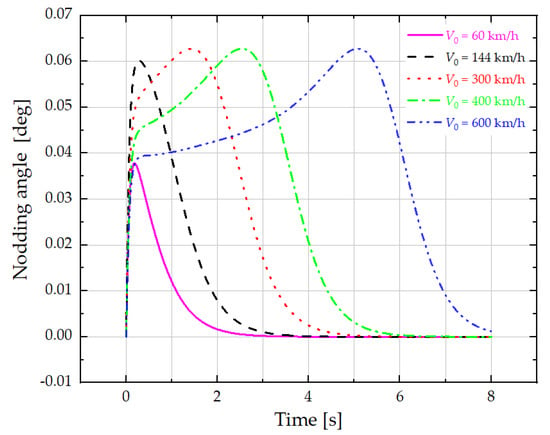
Figure 13.
The change process in the nodding angle (β) of the bogie at initial speeds of V0 = 60 km/h, 144 km/h, 300 km/h, 400 km/h and 600 km/h and under 10 mm air gaps.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the mathematical models of the detent forces of PMECBs installed on an HTS maglev test vehicle are fitted, and on this basis, their effects on the braking and levitation performance of the vehicle are studied.
The results of the simulation show that the detent forces of PMECBs reach their maximum value around 40 m/s (144 km/h) under different air gaps. Under the 10mm air gap, the detent force of the two sets of PMECBs on one side reaches a maximum value of 31 KN (shown in Figure 3d and Table 1).
The braking effects of PMECBs used in the test vehicle are remarkable. Under the 10 mm air gap and V0 = 600 km/h, the maximum braking force of the single PMECB is about 15.5 kN (shown in Figure 8b); the braking time of the vehicle is about 8 s (shown in Figure 9b); the braking distance of the vehicle is about 580 m.
The results also show that the stable levitation heights and levitation forces of all Dewars are about 15.3 mm and 2340 N, respectively. Under the 10 mm air gap and V0 = 600 km/h, the maximum nodding angle produced by the bogie is about 0.0630. Then the changes in levitation heights of Dewar No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 are about −1.5 mm, −0.8 mm, +0.8 mm and +1.5 mm, respectively. The corresponding changes in levitation forces are about +740 N, +590 N, −540 N and −700 N, respectively. It can be considered that the PMECBs will affect the levitation heights and forces of the maglev Dewars. The levitation heights and forces of the Dewars at both ends of the bogie change most obviously. In fact, a significant reduction in levitation height can happen when the vehicle stable levitation height is low, and the braking force is very large.
Because the normal force of the PMECB will not cancel out when it is working, the normal force exists in actual operation all the time. In the future, the levitation and guidance of the HTS maglev test vehicle under the combined actions of the detent force and the normal force of the PMECB will be further studied.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z. and J.Z.; Methodology, P.L.; Software, Y.Y.; Validation, G.Z. and L.W.; Investigation, Y.L., Y.X. and L.W.; Writing—original draft preparation, G.Z.; Writing—review and editing, J.Z., Y.L., Y.X.; Supervision, Z.D. and J.L. and L.L.; Project administration, Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52022086), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (22CXTD0070), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2682022ZT051).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data reported in this manuscript is accessible based on reasonable requests to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ren, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J. Characteristic Analysis and Control of a Rotary Electromagnetic Eddy Current Brake. Appl. Comput. Electrom. 2021, 36, 806–815. [Google Scholar]
- Valderas, D.; Mesa, I.; Adín, I.; Lehmann, H.; Lancaster, G.; Stark, O.; Baldauf, W.; del Portillo, J. 2014 Modeling Eddy Current Brake Emissions for Electromagnetic Compatibility with Signaling Devices in High-Speed Railways. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 9743–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Peng, T.; Chen, Q.; Cao, Q.-L.; Ji, K.; Shuang, B.; Ye, J.-J.; Li, L. 3-D Nonlinear Transient Analysis and Design of Eddy Current Brake for High-speed Trains. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2012, 40, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chiueh, S. Analysis of Eddy-Current Brakes for High Speed Railway. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1998, 34, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Chen, J. Efficiency Analysis of Eddy Current Braking Based on Electromagnetic Field Shape Adjustment. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 48, 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Braking Torque Analysis and Control Method of a New Motor with Eddy-Current Braking and Heating System for Electric Vehicle. Int. J. Autot. Tech-Kor. 2021, 22, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, G.; Kumar, K. Experimental Investigation of Influence of Various Parameters on Permanent Magnet Eddy Current Braking System. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, G. Design and Analysis of Magnetic Circuit of Permanent Magnet Eddy Current Brake. Vibroengineering Procedia 2019, 28, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Sun, Q. Characteristic and Thermal Analysis of Permanent Magnet Eddy Current Brake. CMES—Comp. Model. Eng. 2021, 126, 1011–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, M.; Aydin, M.; Nerg, J. Analysis of an Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet-Assisted Eddy-Current Brake at High-Temperature Working Conditions. IEEE Trans. 2021, 68, 5112–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, D.; Shi, J.; Gao, Z. A Performance Prediction Model for Permanent Magnet Eddy-Current Couplings Based on the Air-Gap Magnetic Field Distribution. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha, K.; Sathish, K. Investigation on Eddy Current Braking Systems-A Review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 592–594, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-M.; Park, H.-J.; Cho, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.-W. Analysis of Multiple Factor of the Eddy Current Brake for Railway Application. Trans. Korean. Inst. Elect. Eng. 2015, 64, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S. The Application of Linear Halbach Array to Eddy Current Rail Brake System. Magnetics 2001, 37, 2627–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, G.; Guo, L.; Mu, Y.; Gao, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, K. Design and Optimization of Halbach Permanent Magnet Array with Rectangle Section and Trapezoid Section. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Xia, C.; Zheng, J. Optimization Study of the Halbach Permanent Magnetic Guideway for High Temperature Superconducting Magnetic Levitation. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2020, 33, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, W.; Xue, M. Design and Optimization of a Novel HTS Flux-Modulated Linear Motor Using Halbach Permanent Magnet Arrays. IEEE. Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2021, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-S.; Yoo, J.-H. Optimal Array Design of the Permanent Magnet in an Eddy Current Brake. T. Kor. Soc. Mec. Eng. A 2009, 33, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kou, B.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Pan, D.; Song, K. Analytical Model for a Permanent Magnet Eddy-Current Brake with Transverse Edge Effect. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 61170–61179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tan, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Mareels, I. Design of Double-Sided Linear Permanent Magnet Eddy Current Braking System. Prog. Electroma. Res. M 2017, 61, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, H.; Luo, F.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Lin, G.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Z.; et al. The first man-loading high temperature superconducting Maglev test vehicle in the world. Phys. C 2002, 378, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Wang, B.; Ren, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J. A High-temperature Superconducting Maglev-evacuated Tube Transport (HTS Maglev-ETT) Test System. IEEE. Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2017, 27, 3602008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 600+ Per Hour! The World’s First HTS High Speed Maglev Engineering Prototype Vehicle Goes Offline. Available online: https://finance.sina.com.cn/tech/2021-01-14/doc-ikftpnnx6900907.shtml (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, B.; Huang, H.; Deng, Z. Nonlinear vibration behaviors of high-Tc superconducting bulks in an applied permanent magnetic array field. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 243901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Xia, C.; Gou, Y.; Wang, C.; Zheng, J. Subharmonic Resonance in Magnetic Levitation of the High-Temperature Superconducting Bulks YBa2Cu3O7-x Under Harmonic Excitation. IEEE. Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 3600908. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Deng, Z.; Ma, S.; Sun, R.; Li, H.; Li, J. Dynamic Simulation of the HTS Maglev Vehicle-Bridge Coupled System Based on Levitation Force Experiment. IEEE. Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 3601606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).