Abstract
Twisted polymer fibre actuators provide high torsional rotation from stimulated volume expansion, induced either by chemical fuelling, thermal stimulation, or electrochemical charging. One key limitation of these actuators is the irreversibility of torsional stroke that limits their feasibility when considering real-life smart applications. Moreover, scaling the torsional stroke of these actuators becomes difficult when these are integrated into practically usable systems such as smart textiles, due to the external and variable opposing torque that is applied by the adjacent non-actuating fibres. Herein, a simple composite type torsional actuator made of hydrogel coated commercial textile cotton multifilament fibre is demonstrated. This novel actuator is of high moisture responsiveness, given that hydrogels are capable of providing huge volume expansion and twisting the overall system can transform the volumetric expansion to fibre untwisting based torsional actuation. Theoretical treatment of torsional actuation is also demonstrated based on the change in torsional stiffness of dry and wet fibres as well as a few externally applied torques. The agreement between experimental measurements and theoretical estimation is found reasonable, and the investigation allows the near-appropriate estimation of torsional stroke before integrating an actuator into a smart system.
1. Introduction
Soft stimuli-responsive materials are capable of providing many smart applications as they can mimic movements that are available in natural muscles [1,2]. Soft actuators based on this principle are of growing interest, converting the chemical or physical potential into a mechanical response [3,4]. The use of soft polymeric materials can potentially provide devices with appropriate mechanical, chemical, and biological properties that are famously known as artificial muscles [5,6].
Up until now, many materials have been used as soft actuators including elastomers [7], conducting polymers [8], carbon nanotube yarns [9,10], graphene/polymer fibres [11], highly oriented thermoplastic fibres [11,12], and hydrogels [13]. Of them, stimuli-responsive hydrogels are capable of accommodating large amounts of water and provide the possibility for designing soft actuators sensitive to environmental stimuli. The primary advantage of hydrogels is represented by their three-dimensional covalently crosslinked polymer networks, providing three-dimensional volume expansion capability [14].
The extraordinary hydrophilic volume expansion property of hydrogels can be transformed into different actuation movements such as linear [15], torsional [16], and bending [17], depending on the configured structures. Still, there are inadequate reports on torsional actuation studies due to the slow and brittle nature of hydrogels that potentially limit their applicability in real world smart systems. Motivated by lessons from nature, a few twisted fibres-based torsional actuators which respond to solvents and vapours were also reported [18,19,20]. Hydrogels have shown that they can undergo huge deformations due to moisture swelling, and a twisted fibrous hydrogel can provide torsional actuation as discussed in single helix mechanism studies [21]. Of interest, twisted fibre torsional actuators can be prompted to overtwisting which form helical coils of such kind. These coiled actuators can mimic the movements of natural contractile muscles which make them suitable to call artificial muscles. The potential applications of artificial muscles are versatile including in soft and wearable robotics, assistive prosthetics, and self-functioning smart devices.
However, the macroscopic applications of hydrogels are limited in some cases due to their high torsional stiffness when dry [22], and they might not be able to withstand torsional deformation when making twisted actuators. One useful idea is to use a flexible and torsionally stable core material within a hydrogel shell. In this work, a simple method to fabricate hydrogel coated multifilament cotton fibres and further configure them into twisted fibres is demonstrated. Due to the hydrophilic volume expansion driven fibre untwisting/retwisting, these fibres can reversibly rotate when moisture is introduced and removed. However, the extent of reversibility has still been a concern for the first few actuation cycles as the dynamic moment of inertia plays a vital role during fibre untwisting [23]. This inertia allows moisture driven fibre to untwist much more than it has the capability of drying-assisted retwisting. Use of a return spring fibre can eventually solve this reversibility issue, as they can accommodate a twisting torque when the actuating fibre is being moisture driven untwisted and apply that torque to the retwisting fibre when being dried. When a stimulus is applied to the actuating fibre with a return spring, the external torque from the spring acting against the actuator gradually increases [24]. This is a practically feasible approach such as for using the actuating fibres in smart textiles, as there are external and variable opposing torques available from the adjacent non-actuating fibres [25]. Supposedly, these non-actuating fibres are to act as the return springs, accommodating a twisting torque when the actuating fibres untwist and apply that torque to the retwisting fibre.
Here, a set of multifilament cotton yarns are sequentially dip coated into polyether-based hydrophilic polyurethane (PEPU) and alginate hydrogels, followed by torsionally deforming them into twisted fibres. These twisted fibres are characterised to evaluate the mechanical, microscopic, and torsional actuation properties. However, free rotation actuators (by clamping the fibre at one end and measuring the torsional stroke of the free end) mostly provide irreversible torsional stroke at the initial actuation cycles, owing to the dynamic moment of inertia and the stress relaxation phenomenon of core twisted structures. To aid the reversibility of such systems, we use a return spring based torsional stroke mechanism where the actuating fibre is attached to a non-actuating fibre, both ends are tethered, and the rotation is measured at the attachment point of two fibres. We further utilise the torsional stiffness of actuating and non-actuating fibres to theoretically predict the torsional stroke of gel/fibre actuators under different external torque conditions. By carefully choosing return springs of certain torsional stiffness, controlled actuation can be obtained from such systems that are practically important if these actuators are to be used as the building blocks of smart textiles. As the developed actuating fibres are moisture activated, specific future applications could include sweat responsive smart textiles that alter breathability by altering filament gaps during fibre swelling and twisting. As the torsionally actuating twisted fibres can be transformed into a linear actuator when the fibres are formed into coils, these coiled actuators could be used to operate window shutters that will robotically close the shutter when swollen in the presence of rain [26].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Open source textile cotton fibre was used in this study. Granular polyether-based polyurethane (PEPU) was obtained from AdvanSource Biomaterials (Wilmington, MA, USA). Sodium alginate (alginic acid sodium salt) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Australia. Deionised (DI) water was used in all experimental works.
2.2. Preparation of Gel Solutions
Initially, 5 w/v% PEPU granules were dissolved with diluted ethanol (95 vol% in water) at 60 °C for 48 h, which formed a transparent PEPU gel solution. The lid of the glass bottle was kept tightened to avoid ethanol evaporation. The transparent PEPU was then stored at room temperature for further usage. To prepare alginate solution, 1.9 w/v% alginate powder was stir-mixed (Wiggens Stirrer WH220-HT, Straubenhardt, Germany) in DI water at 50 rpm for 48 h. The dissolved alginate solution then was stored at 4 °C.
2.3. Fabrication and Characterisation of Gel/Fibre Actuator
The textile cotton fibre was dip coated within PEPU gel solution for 5 min to ensure complete adherence of PEPU gel to the fibre. Once removed from the gel, the coated fibre was hung for 1 h for natural drying. This PEPU gel coated fibre was further dip coated within alginate solution for 5 min followed by natural drying for 24 h. After two times of dip coating, the fibre formed a hierarchical structure. The gel coated fibre was vertically suspended from an overhead motor (Heidolph RZR2020, Schwabach, Germany) rotating at 60 rpm to form a twisted gel/fibre while applying 5 MPa of axial stress to the fibre. However, the bottom end of the fibre was not allowed to rotate torsionally, to accommodate twisting within the fibre. The process was continued until the gel/fibre became highly twisted (at the onset when more twisting of the fibre resulted in the formation of coils), and this highly twisted fibre could then act as a torsional actuator. Figure 1 shows the schematic drawing of the gel/fibre torsional actuator making method. The gel/fibre actuator was then placed in an air oven (Labec Laboratory Equipment, Marrickville, NSW, Australia) at 60 °C for 10 min to stabilise the twisted shape. The gel/fibre actuator was then removed from the oven and was ready for characterisation and actuation tests.
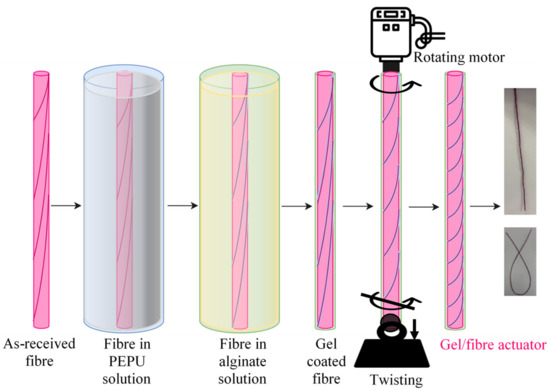
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of fabricating twisted gel/fibre torsional actuator.
The surface and inter-facial morphology of the prepared fibres were initially examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM; Hitachi SU3500-A, Tokyo, Japan). The SEM images allow understanding of the torsional actuation mechanism in terms of inter-filament and intra-filament structures. The torsional stiffness () of the gel/fibre actuator was evaluated by using a torsion test set up comprising horizontally placed gel/fibre, tethered on both sides with two free rotating metal shafts. Torsion was applied to the gel/fibre by wrapping a flexible cotton fibre around the metal shaft that was eventually loaded by gradually increasing the pulling force (). Application of torque () torsionally rotated the gel/fibre, and the torque was related to the metal shaft radius (), as provided in Equation (1) [27]. The inverse slope of the torsional rotation/torque curve defined the torsional stiffness [24]. The measured torsional stiffnesses was used to predict the torsional stroke of gel/fibre actuators using a single helix based geometrical model.
2.4. Actuation Test Method
The free torsional stroke of the gel/fibre actuator was first evaluated. The gel/fibre actuator was vertically suspended from a fixed frame, and the bottom of the actuator was linked with a rotation indicator (one side marked with ink). Spray water was used for moisture-driven torsional actuation tests, while the bottom of the actuator was held fixed during water spraying. Once the surface of the actuator became wet, water spraying was ceased and the fibre was released to rotate freely. An optical video camera was used to record the torsional actuation, and the recorded video was later analysed to determine the magnitude of the torsional stroke (Figure 2A). The recorded video was converted into inter-frame intervals of 2 s and the angular displacement (stroke in degree) relevant to the fibre axis was measured by using the ImageJ image processing program.
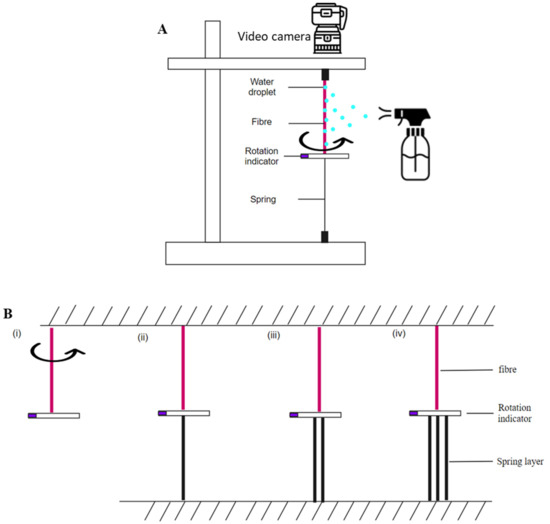
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the actuation test method: (A) A complete test set up; (B) comparative test methods considering free rotation and rotation against return springs.
For torsional actuation of gel/fibre actuator against a return spring, commercially available spandex-made yarn (sourced from Spotlight Pty Ltd., QLD, Brisbane, Australia) springs were connected to the bottom of the actuator that acted as rotation resistance. The number of springs was increased from 1 to 3, to apply higher resistance to the actuating fibre, and probably assist in better reversibility (Figure 2B). The key objective was to obtain ~100% reversibility of the system, and an optimisation study was conducted based on different number of return springs used, i.e., torsional stiffnesses.
For all the experiments, a 10 cm long gel/fibre actuator and 10 cm long return spring were used. Each test was repeated for 5 cycles, and each cycle was approximately 45 min. The rotation was recorded corresponding to the time.
2.5. Method of Predicting Torsional Actuation
Theoretically, torsional stroke () of a fibre actuator adopts that a stimulus induced free rotation increases linearly with the length. The real torsional rotation differs linearly with distance taken from the fixed end of the actuating fibre, and the torsional stroke at the free end () of a free rotating fibre of length is:
When the actuating fibre is attached to a non-actuating return spring of torsional stiffness , the torsional stroke () at the junction between actuating fibre and return spring can be determined from the torque balance equation, as reported previously [27]:
Here, is the torsional stiffness of the gel/fibre in actuated state (wet) after the moisture is applied. The estimation of free and return spring integrated torsional stroke will be useful to scale the amount of actuation needed in practical applications.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Gel/Fibre Actuator
The microscopic morphology of gel/fibre was investigated considering both the surface and fibre-gel interface (Figure 3). As seen from Figure 3A, the as-received cotton yarn is much bulky, capable of accommodating materials that are compatible with their surface. When dip coated with PEPU, the gel materials were impregnated within the inter-filament spaces, producing a much solid structure. PEPUs are highly flexible when dried; however, they are not of high water adsorption, and cannot be used as a high performing torsional actuator. Further dip coating the fibre by alginate gave high water uptake capability, and this multi-materials coated fibre can be actuated via introducing moisture. As shown in Figure 3C, the coating of alginate only formed on the outer surface of PEPU coated fibre (the claim also confirmed via cross sectional imaging), therefore the actuation is only operated from the surface. Highly twisting the gel/fibre gave a uniform helical structure of the fibre surface (Figure 3D) that is crucial to obtain high torsional actuation. The single helix-based model is well suited for such twisted structures as the surface helices are the key to understanding the torsion mechanics when volume change triggers the torsional rotation. Considering the twisted fibre as a helix of equal diameter and twist angle provides the insight for torsional stroke being dependent on the number of inserted twists [28]. The number of twists inserted within the gel/fibre actuator was ~330 twists/m of initial fibre length, while the final twist angle was found to be ~29 degrees.
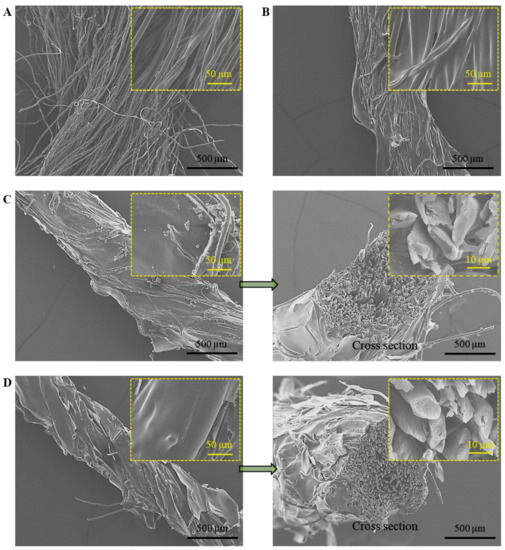
Figure 3.
SEM images of gel/fibre composite actuators (insets show high-magnification images): (A) As-received multifilament cotton fibre; (B) PEPU coated untwisted fibre; (C) PEPU and alginate coated untwisted fibre; (D) gel/fibre twisted actuator (left side image showing surface morphology and right side image showing cross section of the twisted actuator).
Incorporation of PEPU gel as the second core material might give lower torsional stiffness to the gel/fibre actuator, which is unavailable from a solely alginate coated fibre. Alginate hydrogels are highly brittle when dried due to the aggregation of polymer chains [29]. These dehydrated polymer chains act like amorphous material and are the subject of cracking when torsion is applied. Low stiff materials are of the great advantage of flexible smart textiles [30], assistive prosthetics [31], and soft robotic operations in confined spaces [32,33].
3.2. Torsional Stiffness
Torsional stiffnesses of the gel/fibre actuator and the return spring were evaluated from the torque-rotation curves (Figure 4). The torsional stiffness of the dry and wet gel/fibre actuator calculated from relevant torque-rotation curves was ~3.75 and ~2.68 µN.m/rad, respectively (Figure 4A). Relevant to hydrogel materials, stiffnesses of the conducting polymer actuators were smaller in the swollen state compared with the dry state [34]. The difference in stiffness of dry and wet (hydrogel) fibres represents the possible extent of moisture driven torsional actuation, with a greater difference triggering a higher actuation performance. As seen from Figure 4B, the torsional stiffness of the return spring became higher when the fibre diameter increased (related to the number of springs used). The torsional stiffnesses of 1, 2 and 3 springs were measured to be ~0.43, ~0.88 and ~2.68 µN.m/rad, respectively. These stiffnesses are much lower than that of the actuating gel/fibre, confirming that the opposing spring torque will not be above the threshold of blocking the actuator rotation.
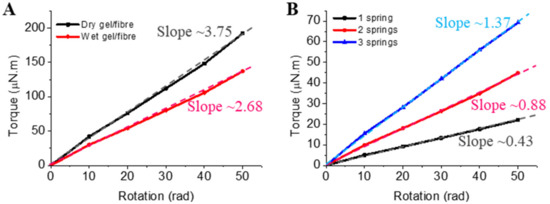
Figure 4.
Torque-rotation curves: (A) gel fibre actuator; (B) return springs. (The slopes of the curves define the torsional stiffness of relevant fibre.)
3.3. Torsional Actuation Test Results
The initial actuation test was conducted to evaluate the effect of twisting on the torsional actuation performance (Figure 5A). Highly twisted 10 cm long gel/fibre actuator provided a torsional stroke ~3.7 times higher than the untwisted fibre of similar length. The actuation response was found to be reversible in a free operating condition, providing an insight into how the gel materials are well-adhered to the multifilament cotton fibres. This is considered as a basis for showing the importance of twist insertion, but no optimisation studies were conducted in the current project. Thus far, the complete focus was given to obtaining high reversibility of torsional stroke. Figure 5B shows the actuation stroke of a 10 cm long gel/fibre actuator, operated against 10 cm long return springs comprising one, two, and three spandex yarns. As demonstrated in previous research papers, the application of increasing opposed torque from the return springs allows the actuating fibres to untwist less [16,24]. However, the use of a return spring allowed for a high reversibility of torsional stroke that was unavailable from the free rotating fibre. For instance, when first introduced to moisture, a free rotating 10 cm long gel/fibre actuator provided ~3680 degrees of torsional untwisting with only ~22% of retwisting reversibility. On the other hand, with similar fibre length and moisture swelling conditions, the actuator with two return springs gave ~975 degrees of torsional untwisting with >100% of reversibility.
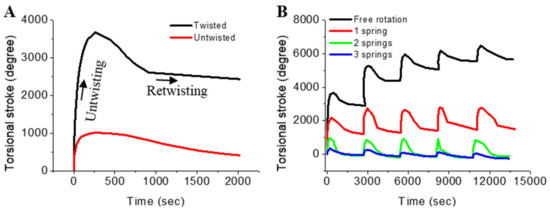
Figure 5.
Torsional stroke results of gel/fibre actuators: (A) comparative stroke found from untwisted twisted fibres; (B) comparative stroke when the actuator was operated freely or against return springs.
When the gel/fibre actuator was operated against a return spring, the spring yarn was twisted as the actuator torsionally deformed, producing a restoring torque inside the return spring yarn. The rotation at the junction point of the gel/fibre and return spring was smaller than that at the free torsional stroke, so a residual torque was preserved within the actuating gel/fibre. The residual torque in the actuating gel/fibre was cancelled by the restoring torque produced in the return spring when the system reached equilibrium. Optimum actuation performance with adequate reversibility is crucial for making the torsional actuators suitable for real world applications. In this context, the return spring mechanism is well accepted and simple to utilise in an integrated actuating system.
3.4. Theoretical Prediction of Torsional Actuation
The initial data required for the theoretical prediction of torsional stroke against opposing torque were the stiffnesses of the actuating fibres and the return springs. The free torsional stroke was used as the basis, and the relevant stroke against return springs of certain stiffnesses was calculated by using Equation (3). As can be seen from Figure 6A, the magnitude of torsional stroke decreases almost linearly with gradually higher opposing torque from the return spring. This linear correlation of torsional stroke and opposing torque supports the development of scalable systems inspired by current investigative results. The predictive results show close agreement with the experimentally measured ones, indicating that the theoretical estimation based on torsion mechanics of return spring involved systems is a reasonable method for evaluating torsional stroke in twisted fibres. Insignificant discrepancies were found in lower opposing torque conditions that might be attributed to the inherent dynamic moment of inertia and stress relaxation phenomenon of core twisted structures. At higher opposing torque, appropriate balancing occurs between those inherent properties and the torque from spring, providing a highly reversible torsional actuator system.
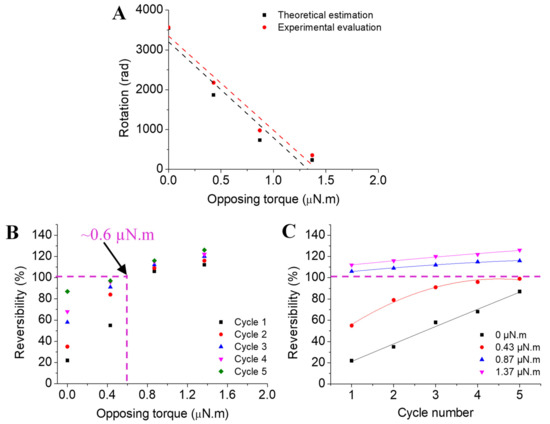
Figure 6.
Graphical representation of the method to obtain high reversibility of torsional stroke: (A) agreement between theoretically estimated and experimentally measured results; (B) reversibility in terms of experimental opposing torque applied by the return spring; (C) number of cycles before achieving full reversibility.
Figure 6B shows the reversibility obtained in terms of opposing torque applied by the return spring. As shown by extrapolating intersected dashed lines, full reversibility of gel/fibre actuation can be obtained when a return spring of ~0.6 µN.m/rad stiffness is used. However, a few training cycles should still be performed before reaching full reversibility, due to the previously discussed inherent dynamic inertia and stress relaxation of core twisted fibre. For instance, our gel/fibre actuator gave almost full reversibility at the fourth cycle and further improved at the fifth cycle (Figure 6C). In this current circumstance, it is preferable to train the gel/fibre actuators for three cycles before integrating them into a torsionally actuating smart system.
4. Conclusions
In this manuscript, a new type of torsional actuator made of hydrogel coated cotton multifilament fibre was developed. The extraordinary volume expansion property of moisture swollen hydrogel was transformed into torsional rotation of the overall actuator system. We used alginate as the moisture swelling material, while polyurethane hydrogel was used as the second core material in between alginate and cotton fibre. This multilayered structure gave lower torsional stiffness to the gel/fibre actuator, which is unavailable from a solely alginate coated fibre. Low stiff materials are of the great advantage of flexible smart textiles, assistive prosthetics, and soft robotic operations in confined spaces.
The limitation relating to the reversibility of torsional stroke was noticed from the free rotating gel/fibre actuator. When moisture was applied, the first actuating cycle of a free rotating gel/fibre actuator provided ~368 degrees/cm of torsional untwisting with only ~22% of retwisting reversibility. To aid the reversibility of actuation, a return spring-based method was used and optimised, and a moisture driven gel/fibre actuator gave ~97.5 degrees/cm of torsional untwisting with full reversibility. Theoretical treatment of torsional actuation was also demonstrated based on the change in torsional stiffness of dry and wet fibres as well as a few externally applied torques. The agreement between experimental measurements and theoretical estimation was found reasonable, and the investigation allows the near-appropriate estimation of torsional stroke before integrating an actuator into a complex and integrated system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, X.Z. and B.S.; methodology, X.Z., J.Z. and B.S.; software, X.Z. and J.Z.; validation, B.S., S.G., S.A. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, B.S. and S.A.; investigation, X.Z. and S.A.; resources, Z.Z.; data curation, X.Z. and S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., J.Z., B.S., S.G., S.A. and Z.Z.; visualisation, X.Z., B.S. and S.A.; supervision, S.A. and Z.Z.; project administration, Z.Z.; funding acquisition, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Z. Zhu would like to thank the support from Australian Research Council Discovery Projects DP190101782 and DP200101397.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors also acknowledge the facilities, and the scientific and technical assistance, of the Australian Microscopy & Microanalysis Research Facility at the Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, The University of Queensland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.S.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M.; et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Espinosa, L.M.; Meesorn, W.; Moatsou, D.; Weder, C. Bioinspired Polymer Systems with Stimuli-Responsive Mechanical Properties. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12851–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriyev, A. A Focus on Soft Actuation. Actuators 2019, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ariano, P.; Accardo, D.; Lombardi, M.; Bocchini, S.; Draghi, L.; De Nardo, L.; Fino, P. Polymeric materials as artificial muscles: An overview. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2015, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Lee, P.S. Recent Progress in Artificial Muscles for Interactive Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ikeda, T. Soft actuators based on liquid-crystalline elastomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5416–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.; Martinez, J.G.; Salahuddin, B.; Persson, N.K.; Jager, E.W. Fast and High-Strain Electrochemically Driven Yarn Actuators in Twisted and Coiled Configurations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2008959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Martinez, J.G.; Foroughi, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Jager, E.W. Artificial Muscles from Hybrid Carbon Nanotube-Polypyrrole-Coated Twisted and Coiled Yarns. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Aziz, S.; Mirabedini, A.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Wallace, G.G.; Kozlov, M.E.; Baughman, R.H. Knitted carbon-nanotube-sheath/spandex-core elastomeric yarns for artificial muscles and strain sensing. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9129–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, C.; Jang, H.; Lim, T.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.R.; Hao, Y.; Suk, J.W. Enhanced dynamic performance of twisted and coiled soft actuators using graphene coating. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 178, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Villacorta, B.; Naficy, S.; Salahuddin, B.; Gao, S.; Baigh, T.A.; Sangian, D.; Zhu, Z. A microwave powered polymeric artificial muscle. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, B.; Warren, H.; Spinks, G.M. Thermally actuated hydrogel bead based braided artificial muscle. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 055042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Jing, L.; Yang, H.; Machnicki, C.E.; Fu, X.; Li, K.; Wong, I.; Chen, P.-Y. Multifunctional soft machines based on stimuli-responsive hydrogels: From freestanding hydrogels to smart integrated systems. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 8, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Kim, J. Hydrogel-Based Artificial Muscles: Overview and Recent Progress. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.; Spinks, G.M. Torsional artificial muscles. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 7, 667–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, L. Hydrogel-based actuators: Possibilities and limitations. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabedini, A.; Aziz, S.; Spinks, G.M.; Foroughi, J. Wet-spun biofiber for torsional artificial muscles. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, L. Moisture-activated torsional graphene-fiber motor. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2909–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, T. Graphene Oxide/Alginate Hydrogel Fibers with Hierarchically Arranged Helical Structures for Soft Actuator Application. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 5079–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Oh, J.; Kozlov, M.E.; Fang, S.; Mirfakhrai, T.; Madden, J.D.W.; Shin, M.K.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Torsional carbon nanotube artificial muscles. Science 2011, 334, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voo, W.-P.; Ooi, C.-W.; Islam, A.; Tey, B.-T.; Chan, E.-S. Calcium alginate hydrogel beads with high stiffness and extended dissolution behaviour. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Kao, Y.-C.; Shiang, T.-Y. Effects of training with a dynamic moment of inertia bat on swing performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.; Naficy, S.; Foroughi, J.; Brown, H.R.; Spinks, G.M. Twist-coil coupling fibres for high stroke tensile artificial muscles. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 283, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, T.L.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Functional fibers for robotic fabrics. Multifunct. Mater. 2018, 1, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.S.; Li, N.; Spinks, G.M.; Aliev, A.E.; Di, J.; Baughman, R.H. New twist on artificial muscles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11709–11716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.; Naficy, S.; Foroughi, J.; Brown, H.R.; Spinks, G.M. Characterisation of torsional actuation in highly twisted yarns and fibres. Polym. Test. 2015, 46, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.; Naficy, S.; Foroughi, J.; Brown, H.R.; Spinks, G.M. Controlled and scalable torsional actuation of twisted nylon 6 fiber. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, L. Design of mechanically strong and tough alginate hydrogels based on a soft-brittle transition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, Z. Flexible actuators. In Handbook of Smart Textiles; Springer: Singapore, 2015; pp. 381–410. [Google Scholar]
- Maziz, A.; Concas, A.; Khaldi, A.; Stålhand, J.; Persson, N.-K.; Jager, E.W.H. Knitting and weaving artificial muscles. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Flexible actuators for soft robotics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 2, 1900077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.; Zidek, T.; Harbel, C.; Yoon, S.; Strickland, F.S.; Kumar, S.; Shin, M. Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators. Actuators 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spinks, G.M.; Campbell, T.E.; Wallace, G.G. Force generation from polypyrrole actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).