Abstract
The soft robots actuated by pressure, cables, thermal, electrosorption, combustion and smart materials are usually faced with the problems of poor portability, noise, weak load capacity, small deformation and high driving voltages. In this paper, a novel pneumatic generator for soft robots based on the gas-liquid reversible transition is proposed, which has the advantages of large output force, easy deformation, strong load capacity and high flexibility. The pressure of the pneumatic generator surges or drops flexibly through the reversible transformation between liquid and gas phase, making the soft actuator stretch or contract regularly, without external motors, compressors and pressure-regulating components. The gas-liquid reversible-transition actuation process is modeled to analyze its working mechanism and characteristics. The pressure during the pressurization stage increases linearly with a rate regulated by the heating power and gas volume. It decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a quadratic function of time at the fast depressurization stage, while with the exponential term as a linear function of time at the slow depressurization stage. The drop rate can be adjusted by changing the gas volume and cooling conditions. Furthermore, effectiveness has been verified through experiments of the prototype. The pressure reaches 25 bar with a rising rate of +3.935 bar/s when 5 mL weak electrolyte solution is heated at 800 W, and the maximum depressurization rate in air cooling is –3.796 bar/s. The soft finger actuated by the pneumatic generator can bend with an angular displacement of 67.5°. The proposed pneumatic generator shows great potential to be used for the structure, driving and sensing integration of artificial muscles.
1. Introduction
Soft robots can deform continuously, which feature high flexibility and good human-machine-object interaction security [1]. Some soft robots imitate caterpillars, earthworms and fishes to realize crawling, rolling, jumping and swimming movement, while others focus on manipulation such as grabbing, bending, extension, contraction and twisting like an octopus, elephant trunk and human arm [2,3]. As the basis of soft robots, actuators play a key role in improving the robot working performance and broadening their application, which has attracted a great deal of research by scholars for decades. The existing soft robots are mainly actuated by pressure, cables, smart materials induced by magnetism or light, thermal, combustion and electrosorption.
Traditional pneumatic, hydraulic or cable-driven soft robots are most prevalent. For example, Xie et al. [4,5] proposed octopus-arm-inspired pneumatic actuators with vacuum-actuated suckers. Lin et al. [6] developed a vacuum-powered cube-shaped artificial muscle embedded with controllable stiffness origami “skeletons”. Jiang et al. [7] presented a manipulator based on the honeycomb pneumatic network structure, that showed potential in achieving balance between flexibility and load bearing capacity. Yan et al. [8] designed a torsional soft actuator module based on spiral chambers with pneumatic driving. Xie et al. [9,10] proposed a 3D-printed pipe-climbing robot actuated by the flat modular pneumatic artificial muscle consisting of thin-film cylinder modules. Preechayasomboon et al. [11] presented a hybrid bellows-style sensor-actuator with salt water inside. Gravagne et al. [12] studied a class of cable-driven robot manipulators termed continuum robots such as the Clemson tentacle manipulator, consisting of two independent sections on a continuous backbone with a thin elastic rod. Yang et al. [13] developed a symmetrical 6-cable-driven spherical joint module for modular manipulators, with three cables regulating stiffness and the others simultaneously regulating position. Li et al. [14] proposed a wire-driven multi-section flexible robot, consisting of three sections made up of several identical vertebras, that were articulated by both spherical joints and a flexible backbone. However, the soft actuators mentioned above often rely on external motors, compressors and pressure-regulating components, having disadvantages such as complex hoses, cables, high noise and poor portability of untethered applications including bionic frogs, fishes and birds.
Smart materials have recently been applied to the actuation of soft robots. Liu et al. [15] developed a soft-rigid hybrid actuator, based on pressure control for large output force and fiber-reinforced dielectric elastomer (DE) for accurate tuning. Li et al. [16] proposed an untethered soft robot with flapping fins actuated by the DE material for deep-sea exploration. Ekbatani et al. [17] presented ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) actuators with feedback control using adaptive full-order recursive terminal sliding mode. Kotikian et al. [18] printed soft robotic matter composed of a liquid crystal elastomer (LCE) bilayer with orthogonal director alignment and different nematic-to-isotropic transition temperatures to form active hinges that interconnected polymeric tiles. The printed LCE hinges exhibited a large, reversible bending response to thermal stimuli, which were programmed by varying the chemistry and printed architecture. Lee et al. [19] proposed a magnetically actuated walking soft robot based on a chained magnetic-microparticle-embedded polymer actuator that was controlled using an external magnetic field. Zhang et al. [20] developed a remotely controlled soft transformer based on a shape memory hydrogel system embedding Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles into a poly-gelatin double network structure, which deformed on navigation in the magnetic field. The deformed shape was fixed and recovered by the assistance of light irradiation. Chu et al. [21] described a unipolar stroke carbon nanotube yarn muscle in which the stroke substantially increased with the increasing potential scan rate. Wang et al. [22] proposed a bioartificial muscle based on functional carboxylated bacterial cellulose and polypyrrole nanoparticles, with a bending strain of 0.93% under an ultralow voltage for soft robots. However, the soft actuators above generally have weak load capacity, small deformation or high driving voltages, and the complex or bulky external equipment for generating magnetism and light is always necessary.
Thermal-activated actuators are capable of outputting large force. Haines et al. [23] demonstrated that the high-strength thermal polymer fibers used for fishing line and sewing thread could be easily transformed by twist insertion to provide tensile and torsional muscles. Cianchetti et al. [24] proposed an artificial muscular hydrostat for soft robots with longitudinal actuators consisting of cables driven by servomotors and transverse actuators driven by the shape memory alloys (SMA) in the form of helical springs. Yang et al. [25] presented a continuum robot with a generic rod-driven structure and a variable stiffness mechanism powered by a set of SMA springs. Zhang et al. [26] introduced a stiffness-tunable pneumatic soft actuator with a shape memory polymer layer via hybrid multimaterial 3D printing. Miriyev et al. [27,28] developed a self-contained soft actuator in which ethanol underwent a thermally-induced phase change accompanying the liquid-vapor transition. Mirvakili et al. [29] proposed a pneumatic artificial muscle using magnetically induced liquid-to-gas phase transitions via inductively heating the ferromagnetic material in the liquid. However, the response speed is slow due to the poor controllability of temperature.
Combustion-powered soft robots can provide high-speed response and large pressure. Bartlett et al. [30] designed an untethered jumping robot powered by the combustion of butane and oxygen. Shepherd et al. [31] demonstrated a rapid actuation for soft robots using the combustion of methane to generate explosive bursts of pressure. Loepfe et al. [32] developed a fully untethered and combustion-actuated soft robot powered by nitrous oxide-propane/butane gas mixtures. However, it is a challenging issue to accurately control the pressure generated by combustion.
Soft actuators based on the electrosorption of electrodes are easy to control. Must et al. [33] demonstrated reversible osmotic stiffening and actuation of a tendril-like soft robot based on the electrosorption of ions on the flexible porous carbon electrodes driven at low input voltages. Acome et al. [34,35] proposed hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators, which harnessed a mechanism coupling electrostatic and hydraulic forces to achieve a variety of actuation modes. Tang et al. [36] introduced a class of fully soft electronic pumps that utilized electrical energy to pump liquid through electrons and ions migration mechanism. However, the actuators commonly need high driving voltages as well.
In this paper, a novel pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots is proposed. The pressure of the pneumatic generator surges or drops through the reversible transition between liquid and gas phase, yielding extension or contraction of the actuator. Soft robots actuated by it feature large output force, easy deformation, strong load capacity and high flexibility, yet without external motors, compressors, pressure-regulating components and high-voltage power. Based on the theory of convective mass transfer, thermodynamics, conservation of mass, phase and state equilibrium, the gas-liquid reversible-transition actuation process is then modeled to analyze its working mechanism and characteristics. Furthermore, effectiveness of the pneumatic generator is validated through prototype fabrication and experimental research of the pressure control and soft finger actuation.
The paper proceeds as follows. The mechanical and electric control system is described in Section 2. Section 3 establishes the model of the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition and analyzes the factors affecting the pressure control characteristics. The prototype and main parameters of the pneumatic generator are drawn in Section 4. The experimental setup and results are presented in Section 5. Finally, the conclusions are given in Section 6.
2. Design Concept of the Novel Pneumatic Generator
The pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots is proposed. The pressure of the pneumatic generator surges or drops through the reversible transition between liquid and gas phase, yielding extension or contraction of the actuator. The characteristics of the weak electrolyte solution such as ammonia are utilized so that it is easily decomposed into gas under heating, while soluble in water when cooled. The volume of the gas released and the pressure in the cavity is regulated by adjusting the temperature of the self-contained generator with ammonia inside through the heater and cooler, to achieve fluid power without external pneumatic and hydraulic compressors as shown in Figure 1. The pneumatic generator is primarily composed of the closed container, heater, temperature sensor, weak electrolyte solution and gas, and connected to the soft finger via interfaces such as hoses and blocks. The structure diagram of the pneumatic generator connected with a soft gripper is illustrated in Figure 2. When the heater is turned on, the weak electrolyte solution is decomposed into gas leading to the pressure surge in the closed cavity, which forces the soft finger connected to bend. On the contrary, when the heater is turned off, the decomposition of the weak electrolyte into gas stops leads to the pressure drop and restoration of the soft finger. Therefore, the soft finger can be actuated by changing the heating status of the pneumatic generator without external compressors.
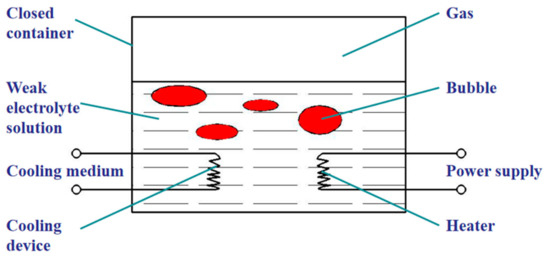
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition.
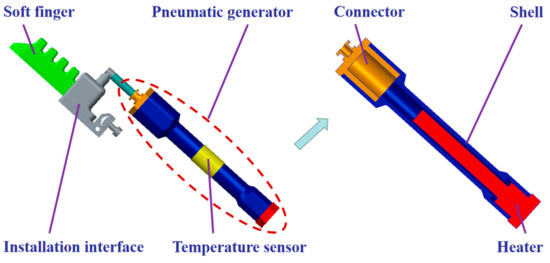
Figure 2.
Structure diagram of the pneumatic generator connected with a soft gripper.
3. Modeling
According to the experiments and theory of convective mass transfer, thermodynamics, conservation of mass, phase and state equilibrium, the process of pressure buildup and actuation based on gas-liquid reversible transition can be divided into three stages, including the pressurization, fast and slow depressurization stage. The working conditions and characteristics of each stage are different. The pressurization and fast depressurization stage featuring convective mass transfer, and slow depressurization stage changing into molecular diffusion need to be modeled respectively.
3.1. Basic Equations
According to the energy conservation law, the temperature of the gas-liquid mixture in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator at work satisfies the following equation [37].
where is the mass of the gas-liquid, is the specific heat capacity, is the equivalent temperature, is the ambient temperature, is the heating power, is the coefficient of heat transfer (related to the equivalent temperature (), exposed area () and cooling conditions), and is time.
Assuming the gas in the pneumatic generator is ideal, the state equation can be expressed as
where is the pressure of the gas, is the temperature, is the volume, is the mass, is the molar mass, and is the gas constant.
The mass of the gas in the pneumatic generator is
where is the thermal coefficient of evaporation and is the dissolution rate of gas.
In addition, suppose the volume of gas in the closed cavity is approximately constant. Differentiating both sides of Equation (2) with respect to time (t), we obtain
where , and denote the time derivatives of , and with respect to time (t), respectively.
Equation (5) is similarly derived from Equation (3).
Substituting Equation (5) into (4) yields
3.2. Pressurization Stage
During the pressurization stage, the weak electrolyte solution in the pneumatic generator is heated, making the pressure in the closed cavity surge. Assuming the solution is sufficient, the heating power is large enough and the heating time is very short, the temperature of the gas changes little. Equation (6) can be written as
The total solution concentration is
where is the average density of the gas-liquid mixture and is the average molar mass.
Mol fractions of the solute in liquid phase are
where is the solution concentration in liquid phase.
Equilibrium mol fractions of the solute in gas phase corresponding to that in liquid phase are
where is the phase equilibrium constant and is the Henry’s constant.
Suppose the total mass transfer coefficient driven by the mol fraction difference in gas phase is defined as
where is the mass transfer coefficient driven by the mol fraction difference in liquid phase, is the mass transfer coefficient driven by the mol fraction difference in gas phase, is the mass transfer coefficient driven by the solution concentration difference in liquid phase and is the mass transfer coefficient driven by the fractional pressure difference in gas phase.
The rate of interphase mass transfer can be represented by
where is the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase.
The gas-liquid equilibrium characteristics play an important role in the resistance of each mass transfer process when the gas dissolves. The phase equilibrium constant () of the easily dissolved gas with high solubility (such as ammonia and hydrogen chloride) is small, and the dissolution process depends on the resistance in gas. Assuming the resistance of mass transfer in gas is much larger than that in liquid (), we write
Therefore, the dissolution rate of gas can be obtained as
where is the equivalent contact area between the gas and liquid.
Substituting Equations (12)–(14) into (7) leads to
Though the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase are related to the initial mass of gas, the dissolution rate and the content of other gases (such as the air and water vapor) is continuous and varies little. Assuming the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase is a linear function of time, it can be expressed as
where is the initial mol fraction of the solute in gas phase and is the growth rate.
Making the substitution of Equation (16) into (15), we get
Suppose the weak electrolyte solution in the pneumatic generator is heated with constant power (). The pressure in the closed cavity can be computed as
Since the growth rate is relatively small compared with other items, Equation (18) can be simplified as
The pressure is therefore
where is the initial pressure of the gas, and are coefficients.
Since the coefficient is close to zero and the time of this stage is short, Equation (20) can be approximated as
The formula above indicates that the pressure increases linearly with a rate, which can be adjusted by changing the heating power and the volume of gas in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator.
3.3. Fast Depressurization Stage
When the heater is turned off, the pressure in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator no longer rises but falls down. The gas continues to dissolve quickly in the surrounding low-temperature solution due to the inhomogeneity of temperature distribution at this moment, that is defined as the fast depressurization stage with short duration. Assuming the solution is sufficient, the temperature of gas changes little at this stage. Equation (6) can be written as
Since the dissolution characteristics of the gas at the fast depressurization stage are similar to that at the pressurization stage featuring convective mass transfer, the dissolution rate of gas conforms to Equation (14). Substituting it into (22) leads to
Though the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase are related to the initial mass of the gas, the dissolution rate and the content of the other gas (such as the air and water vapor) is continuous and varies little. Assuming the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase is a linear function of time, it can be expressed as
where is the initial mol fraction of the solute in gas phase and is the decrease rate.
Substituting Equation (24) into (23) yields
Then we can solve for the pressure as
where is the initial pressure of the gas, , and are coefficients.
When the mol fractions of the solute in gas phase is equal to the equilibrium value, the fast depressurization stage ends. The moment at the inflection point is
The corresponding pressure is
Equation (26) indicates that the pressure at the fast depressurization stage decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a quadratic function of time, and the descending rate can be regulated by changing the gas volume. According to Equation (28), the pressure at the inflection point is positively correlated with the initial pressure and the volume of the gas in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator.
3.4. Slow Depressurization Stage
After the convective mass transfer in fast depressurization stage, the temperature of the gas-liquid mixture tends to be uniform and the solution is close to saturation. Though the solubility is generally related to the pressure and temperature, the pressure at this stage is small and varies little. The pressure of the pneumatic generator decreases slowly due to the increasing solubility of the gas with decreasing temperature, that is defined as the slow depressurization stage. Assuming the solubility of the gas is a linear function of temperature, it can be given by
where is initial solubility and is the slope coefficient.
Furthermore, the mass of the gas can be achieved
where is the initial mass of this stage, is the mass of the weak electrolyte solution and is the initial temperature of the gas.
Making substitution of Equation (30) into (2), we obtain
Therefore, the pressure can be determined
Since the heating power at this stage is zero, Equation (1) can be written as
Assuming the coefficient of heat transfer is influenced little by temperature and regarded as a constant, the following equation can be obtained by integration of the formula above.
Substituting Equation (34) into (32), we have
where , , , and are coefficients.
The formula above indicates that the pressure at the slow depressurization stage decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a linear function of time, and the drop rate can be adjusted by changing the gas volume and cooling conditions.
4. Prototype
Based on the principle and modeling analysis mentioned above, a prototype of the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots has been designed and manufactured as shown in Figure 3. The main parameters of the core components such as the heater, shell, weak electrolyte solution (ammonia), pressure and temperature sensors are shown in Table 1. Metallic material (7075 aluminum alloy) featuring high hardness and light weight is applied to the shell of the prototype to prevent fluid-solid coupling between the gas-liquid mixture and the housing.
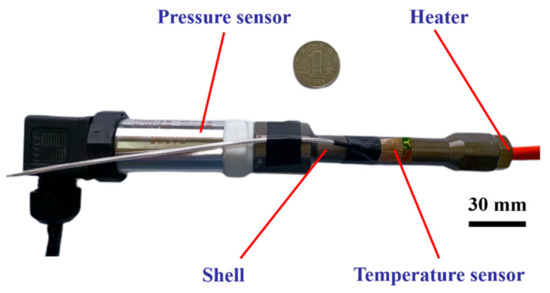
Figure 3.
Prototype of the pneumatic generator.

Table 1.
Main parameters of the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for robots.
5. Experimental Investigations
5.1. Experimental Setup
In order to test the performance and verify the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots, the experimental platform and testing system have been set up. Then the pressure control experiments of the prototype have been conducted on it. The pneumatic generator is controlled by the electric control system, which consists of the controller, communication module, industrial computer, interface module, heater, pressure sensor, temperature sensor and power supply as shown in Figure 4. The DS1007 PPC processor board produced by the dSPACE company is employed as the real-time controller with the sampling time of 10 ms, as it is compatible with the Matlab/Simulink package. It communicates with the industrial computer through the communication module. The interface module primarily realizes the isolation, protection and analog-to-digital conversion of the input and output signals, including the digital input (DI), digital output (DO), analog input (AI) and analog output (AO). The heater converts electric energy into thermal energy to heat the weak electrolyte solution. The pressure and temperature are acquired through the corresponding sensors by signal filtering, amplification and transmission. The power of the heater and sensor is supplied separately to reduce the influence of high-power circuits on signal loops. The software platform mainly includes Matlab/Simulink and ControlDesk. The control and test programs are designed and compiled in the former, and then imported into the latter for target parameter selection and human machine interface design. The control program is mainly composed of the control signal module, conversion and processing module for the pressure and temperature signals, and runs on the dSPACE real-time system.
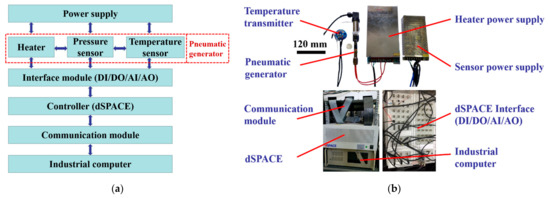
Figure 4.
Pressure characteristics experimental platform of the pneumatic generator: (a) Schematic diagram of the electric control system; (b) Physical system.
The soft finger actuation experiment has also been conducted on the platform and testing system above. The soft finger is connected to the pneumatic generator via the interfaces such as hoses and blocks, and forced to bend through controlling the heating power as shown in Figure 5. A commercial soft finger (FM-B5V5/LS1) produced by Suzhou Rochu Robotics Co., LTD., located in Suzhou, China, is employed in the experiment, that is made of soft materials without rigid skeletons and suitable for the manipulation of soft and fragile objects. The main parameters of it are shown in Table 2. It bends and realizes the grab action when filled with compressed gas or liquid, featuring good compliance with the environment. The output force of the single soft finger at zero displacement is 0.5 N, 1.2 N and 1.9 N under the pressure 0.4 bar, 0.8 bar and 1.2 bar, respectively, and rises to 2 N, 3 N and 3.9 N as the displacement increases to 12.8 mm [38].
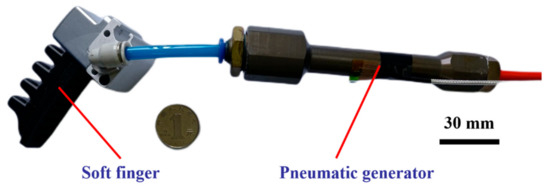
Figure 5.
Experimental device for bending actuation of soft finger.

Table 2.
Main parameters of the soft finger.
In order to achieve the inherent dynamic characterizations of the soft finger, the bending experiment actuated by the compressed air is conducted on the platform as shown in Figure 6. The pressure of the compressed air from the pneumatic compressor is regulated by the integrated passive control unit, which forces the soft finger to bend as required. The finger bends with an angular displacement reducing from 86.5 to 56.5° in 1/20 s under the pressure of 1.2 bar with an average velocity of –600°/s as shown in Figure 7. On the contrary, the finger recovers from 55.5 to 88.5° in 1/20 s with an average velocity of +660°/s when it is released.

Figure 6.
Experimental device for the soft finger actuated by the compressed air.
Figure 7.
Soft finger actuated by the compressed air: (a) t = 1/60 s; (b) t = 1/30 s; (c) t = 1/20 s; (d) t = 1/15 s; (e) t = 1/12 s; (f) t = 1/10 s; (g) t = 7/60 s and (h) t = 2/15 s.
5.2. Results
The pressure control characteristics and soft finger actuation experiments of the prototype have been conducted on the platform mentioned above. The curves of the pressure control and temperature characteristics of the pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition, and the bending effectiveness of the soft finger actuated by it are presented in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12.
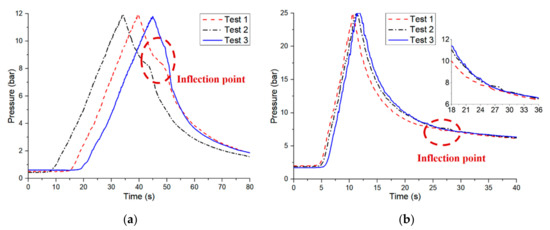
Figure 8.
Pressure control characteristics of the pneumatic generator under different working conditions: (a) 200 W heating power in water cooling and (b) 800 W heating power in air cooling.
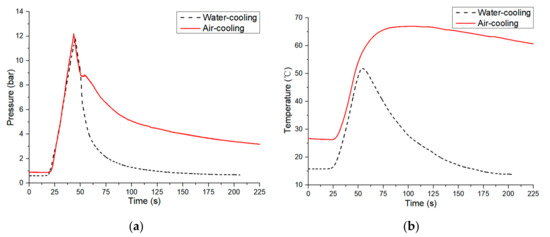
Figure 9.
Pressure and temperature characteristics of the pneumatic generator under different cooling conditions: (a) Pressure characteristics and (b) temperature characteristics.
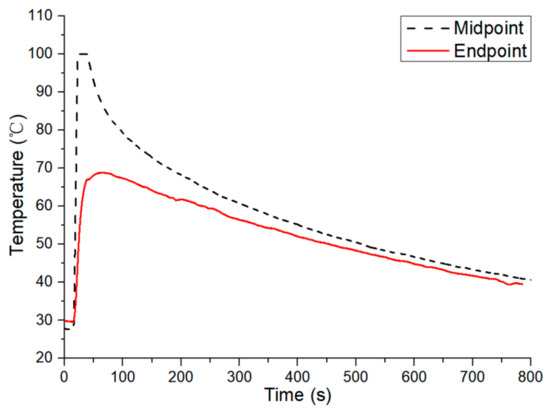
Figure 10.
Temperature characteristics at different measuring points of the pneumatic generator.
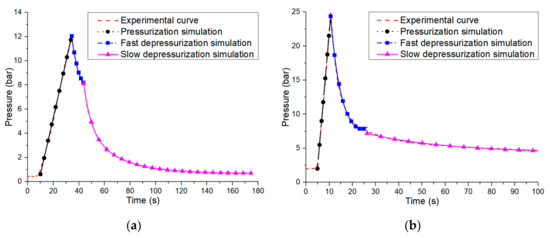
Figure 11.
Simulation and experimental pressure control characteristics of the pneumatic generator under different working conditions: (a) 200 W heating power in water cooling and (b) 800 W heating power in air cooling.
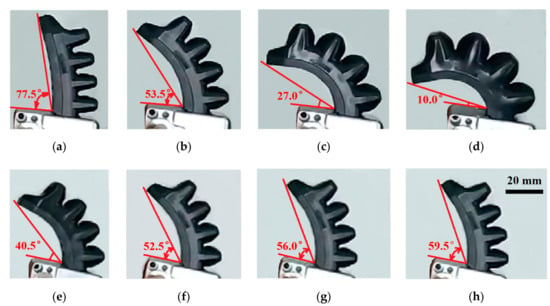
Figure 12.
Soft finger under the bending actuation experiment: (a) t = 1 s; (b) t = 3 s; (c) t = 5 s; (d) t = 7 s; (e) t = 9 s; (f) t = 11 s; (g) t = 13 s and (h) t = 15 s.
5.2.1. Pressure Control Characteristics
The pressure of the generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition is measured under different heating powers (such as 200 W and 800 W) and cooling conditions, which can be divided into three stages, including the pressurization, fast and slow depressurization stage. The experiments conducted have demonstrated good stability and consistency of the pressure control characteristics as shown in Figure 8. The pressure increases approximately in proportion to time with a constant heating power. It increases linearly from 0.4 to 12 bar at a rate of +0.469 bar/s when 3 mL weak electrolyte solution is heated at 200 W. Similarly, it increases linearly from 2 to 25 bar at a rate of +3.935 bar/s when 5 mL weak electrolyte solution is heated at 800 W. The rising rate of the pressure is positively correlated with the heating power and inversely proportional to the volume of gas, that verifies the modeling and theoretical analysis above. Therefore, the duration of the pressurization stage can be shortened through enlarging the heating power or reducing the volume of gas. When the heater is turned off, the pressure in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator no longer rises but falls down. The gas continues to dissolve quickly in the surrounding low-temperature solution due to the inhomogeneity of temperature distribution in the fast depressurization stage before the inflection point, and the pressure decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a quadratic function of time. The maximum depressurization rate of the 3 mL weak electrolyte solution heated at 200 W and cooled in water is –0.595 bar/s, while that of the 5 mL weak electrolyte solution heated at 800 W and cooled in air is –3.796 bar/s. The temperature of the gas-liquid mixture at the slow depressurization stage after the inflection point tends to be uniform and the solution is close to saturation. The pressure of the pneumatic generator decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a linear function of time due to the increasing solubility of the gas with decreasing temperature. The depressurization rate of it is much less than before, and decreases over time.
When the generator is heated, the pressure surges. The efficiency can be expressed as
where is volume of the closed cavity and and are the voltage and current of the heater, respectively.
Substituting the parameters of the generator obtained from pressure characteristics experiment yields the efficiency. They are 0.16% and 0.33% under conditions of 200 W heating power with water cooling and 800 W heating power in air cooling, respectively. As the efficiency is positively correlated with the heating power , and negatively correlated with the thermal coefficient of evaporation and the mass transfer coefficient , it can be improved by increasing the heating power, reducing the heat dissipation power at the pressurization stage, and employing material with low heat capacity. Though the efficiency of the pneumatic generator is low for the current design, it is comparable to the other thermally activated artificial muscles such as polyethyelene, nylon fibers and nanoparticle-based actuators (less than 1%) [39,40]. In addition, the pneumatic generator has the advantages of relatively large output strain, stress and high flexibility without external motors, compressors and pressure-regulating components.
In order to compare and analyze the pressure control characteristics of the pneumatic generator under different cooling conditions, the 3 mL weak electrolyte solution heated at 200 W is cooled in water and air, respectively. The results are shown in Figure 9. The pressure increases at a similar rate of +0.469 bar/s and +0.529 bar/s. When the heater is turned off, the pressure decreases at a similar rate of –0.595 bar/s in water and –0.557 bar/s in air. However, it is significantly different at the slow depressurization stage. The maximum depressurization rate reaches –0.358 bar/s in water in contrast to –0.118 bar/s in air. The reason is the temperature in water decreases much faster than that in air, leading to quicker dissolution and depressurization of the gas. Therefore, the depressurization rate can be greatly increased through improving the cooling condition.
In order to study the temperature characteristics at different measuring points of the pneumatic generator, the midpoint and endpoint temperature of it heated at 800 W is measured respectively as shown in Figure 10, including the heating and cooling stage. The temperature of the midpoint close to the heater increases linearly from 27.7 to 100 °C with a large rate of +10.856 °C/s due to a large amount of heat delivered directly here. However, the temperature of the endpoint increases slowly from 29.7 to 68.9 °C with an average rate of +0.772 °C/s due to the long heat transfer path. When the heater is turned off, the temperature of the midpoint and endpoint decreases exponentially from 100 °C and 68.9 °C, respectively, with the exponential term as a linear function of time, and converges at last. Therefore, the temperature and dissolution characteristics at different measuring points of the pneumatic generator differ from each other, leading to the phenomenon mentioned above that the gas dissolves quickly into the surrounding low-temperature solution at the fast depressurization stage.
Based on the model of the pneumatic generator and experiments conducted above, the pressure of it under different heating power and cooling conditions has been measured and shown in Figure 11 compared with that of simulation. They coincide with each other well. It is verified that the pressure in the closed cavity at the pressurization stage increases linearly at a rate, , that is positively correlated with the heating power and inversely proportional to the volume of gas. The pressure at the fast depressurization stage before the inflection point decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a quadratic function of time. The coefficient affecting the shape of the descent curve, , is negatively correlated with the volume of the gas, and the depressurization rate can be enhanced through reducing it. The pressure of the inflection point at the depressurization stage is positively correlated with the initial pressure and the volume of the gas. The pressure at the slow depressurization stage after the inflection point decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a linear function of time. The depressurization rate is correlated with the cooling conditions and tends to zero over time.
5.2.2. Soft Finger Actuation Experiment
In order to validate the effectiveness of the pneumatic generator as a power source for soft robots, it is connected to the soft finger via interfaces such as hoses and blocks, and actuated to bend in the experiment. When the pneumatic generator is heated at 800 W, the pressure in the closed cavity of it surges and the finger bends with an angular displacement reducing from 77.5 to 10° in 6 s as shown in Figure 12a–d. The bending velocity increases at first and decreases later due to the nonlinearity of the soft finger. The average angular velocity is –11.25°/s. When the heater is turned off, the gas in the closed cavity of the pneumatic generator and soft finger dissolves quickly in the surrounding low-temperature solution due to the inhomogeneity of temperature distribution at the fast depressurization stage. The pressure falls down and the soft finger stretches out rapidly in the meanwhile. Then the temperature of the gas-liquid mixture tends to be uniform and the solution is close to saturation, the pressure of the pneumatic generator decreases slowly due to the increasing solubility of the gas with decreasing temperature. The soft finger recovers from 40.5 to 59.5° in 6 s with an average velocity of +3.17°/s at the depressurization stage as shown in Figure 12e–h. Though the angular velocity is smaller than the inherent dynamic characterizations of the soft finger due to the characteristics of the pneumatic generator, the bending diaplacement is large enough for the application such as grab and other clamping manipulation. The pneumatic generator can actuate the soft finger to bend with a large deformation, which verifies the effectiveness of the power supply based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes a novel pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots. The pressure of the pneumatic generator can surge or drop flexibly through the reversible transformation between liquid and gas phase, making the soft actuator stretch or contract regularly. Soft robots actuated by the pneumatic generator feature large output force, easy deformation, strong load capacity and high flexibility, yet without external motors, compressors, pressure-regulating components and high-voltage power. The gas-liquid reversible-transition actuation process is modeled to analyze its working mechanism and characteristics. The pressure during the pressurization stage increases approximately in proportion to time with a rate regulated by the heating power and gas volume. The pressure at the fast depressurization stage decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a quadratic function of time, and the descending rate increases as the gas volume decreases, while the pressure at the inflection point is positively correlated with its initial pressure. The pressure at the slow depressurization stage decreases exponentially with the exponential term as a linear function of time, and the drop rate can be adjusted by changing the gas volume and cooling conditions. Furthermore, a prototype of the pneumatic generator has been fabricated and the experimental system has also been built up. The pressure control characteristics and soft finger actuation experiments of the prototype have been conducted. The experimental results of the pressure under different heating power and cooling conditions coincide with that of simulation, verifying the effectiveness of the model. The feasibility of the power supply based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots is validated through the bending with a large deformation of the soft finger actuated by the pneumatic generator. The proposed pneumatic generator shows great potential to be used for the structure, driving and sensing integration of artificial muscles and soft robots.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z., G.Y. and Y.D.; methodology, G.Z., G.Y., T.Z. and Z.F.; theoretical analysis, G.Z.; validation, G.Z.; investigation, G.Z., H.Z. and X.J.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z.; writing—review and editing, G.Z. and G.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant numbers: 2017YFB1300400), the General Research Project of Education of Zhejiang Province of China (Grant number: Y202043544), the Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (Grant number: 2019A610114), the Ningbo Key Project of Scientific and Technological Innovation 2025 (Grant numbers: 2018B10058, 2018B10069), the National-Zhejiang Joint Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: U1909215), and the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang (Grant number: 2019C01043).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the first author or corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Blumenschein, L.H.; Greer, J.D.; Okamura, A.M. A soft robot that navigates its environment through growth. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Xie, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Wen, L. Design, fabrication and kinematic modeling of a 3D-motion soft robotic arm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Domel, A.G.; An, N.; Green, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, T.; Knubben, E.M.; Weaver, J.C.; Bertoldi, K.; Wen, L. Octopus Arm-Inspired Tapered Soft Actuators with Suckers for Improved Grasping. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.A.; Walker, I.D. Kinematics for multisection continuum robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, G.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Qian, D.; Yang, H.; Zou, J. Controllable Stiffness Origami “Skeletons” for Lightweight and Multifunctional Artificial Muscles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X. Design and simulation analysis of a soft manipulator based on honeycomb pneumatic networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J. Design and test on a new spiral driven pure torsional soft actuator. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications 2017, Wuhan, China, 16–18 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Zuo, S.; Liu, J. A novel flat modular pneumatic artificial muscle. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 065013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Liu, J.; Kang, R.; Zuo, S. Fully 3D-Printed Modular Pipe-Climbing Robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preechayasomboon, P.; Rombokas, E. Sensuator: A Hybrid Sensor–Actuator Approach to Soft Robotic Proprioception Using Recurrent Neural Networks. Actuators 2021, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravagne, I.; Rahn, C.; Walker, I. Large deflection dynamics and control for planar continuum robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2003, 8, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Wang, C. Study on Stiffness-Oriented Cable Tension Distribution for a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Mechanism. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Du, R. Design and analysis of a bio-inspired wire-driven multi-section flexible robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, P. A bio-inspired soft-rigid hybrid actuator made of electroactive dielectric elastomers. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B.; Yin, S.; et al. Self-powered soft robot in the Mariana Trench. Nature 2021, 591, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekbatani, R.Z.; Shao, K.; Khawwaf, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X.; Nikzad, M. Control of an IPMC Soft Actuator Using Adaptive Full-Order Recursive Terminal Sliding Mode. Actuators 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotikian, A.; Mcmahan, C.; Davidson, E.C.; Muhammad, J.M.; Weeks, R.D.; Daraio, C.; Lewis, J.A. Untethered soft robotic matter with passive control of shape morphing and propulsion. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-U.; Lee, I.-S.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Hoang, M.C.; Hong, A.; Choi, E.; Park, J.-O.; Kim, C.-S. Wireless Walking Paper Robot Driven by Magnetic Polymer Actuator. Actuators 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Jian, Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, H.; Lu, H.; Wei, S.; Wu, S.; Xue, Q.; Chen, T. Multi-Field Synergy Manipulating Soft Polymeric Hydrogel Transformers. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 3, 2000208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Mu, J.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; Fang, S.; Haines, C.S.; Park, J.W.; Qin, S.; et al. Unipolar stroke, electroosmotic pump carbon nanotube yarn muscles. Science 2021, 371, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Park, J.-O.; Zheng, S.; Choi, E. Ultralow voltage high-performance bioartificial muscles based on lonically crosslinked polypyrrole-coated functional carboxylated bacterial cellulose for soft robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 12, 2007749. [Google Scholar]
- Haines, C.S.; Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; Spinks, G.M.; Foroughi, J.; Madden, J.D.W.; Kim, S.H.; Fang, S.; De Andrade, M.J.; Göktepe, F.; et al. Artificial Muscles from Fishing Line and Sewing Thread. Science 2014, 343, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Follador, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Dario, P.; Laschi, C. Design and development of a soft robotic octopus arm exploiting embodied intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 28 June 2012; pp. 5271–5276. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Geng, S.; Walker, I.; Branson, D.T.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.S.; Kang, R. Geometric constraint-based modeling and analysis of a novel continuum robot with Shape Memory Alloy initiated variable stiffness. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, N.; Hingorani, H.; Ding, N.; Wang, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, B.; Gu, G.; GE, Q. Fast-response, stiffness-tunable soft actuator by hybrid multimaterial 3D printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriyev, A.; Stack, K.; Lipson, H. Soft material for soft actuators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartolano, M.; Xia, B.; Miriyev, A.; Lipson, H. Conductive Fabric Heaters for Heat-Activated Soft Actuators. Actuators 2019, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvakili, S.M.; Sim, D.; Hunter, I.W.; Langer, R. Actuation of untethered pneumatic artificial muscles and soft robots using magnetically induced liquid-to-gas phase transitions. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eaaz4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.W.; Tolley, M.T.; Overveld, J.T.B.; Weaver, J.C.; Mosadegh, B.; Bertoldi, K.; Whitesides, G.M.; Wood, R.J. A 3D-printed, functionally graded soft robot powerd by combustion. Science 2015, 349, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Stokes, A.A.; Freake, J.; Barber, J.; Snyder, P.W.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Cademartiri, L.; Morin, S.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Using Explosions to Power a Soft Robot. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 2892–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loepfe, M.; Schumacher, C.M.; Lustenberger, U.B.; Stark, W.J. An Untethered, Jumping Roly-Poly Soft Robot Driven by Combustion. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Must, I.; Sinibaldi, E.; Mazzolai, B. A variable-stiffness tendril-like soft robot based on reversible osmotic actuation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acome, E.; Mitchell, S.K.; Morrissey, T.G.; Emmett, M.B.; Benjamin, C.; King, M.; Radakovitz, M.; Keplinger, C. Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 2019, 359, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellaris, N.; Venkata, V.G.; Smith, G.M.; Mitchell, S.K.; Keplinger, C. Peano-HASEL actuators: Muscle-minetic, electrohydraulic transducers that linearly contract on activation. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Wei, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; et al. Customizing a self-healing soft pump for robot. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, F.; Wu, L.; Tadesse, Y. Modeling of One-ply and Two-ply Twisted and Coiled Polymer (TCP) Artificial Muscles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2021, 26, 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Suzhou Rochu Robotics Co., LTD. Rochu Catalog V2.6[EB/OL]. Available online: https://en.rochu.com/catalogusermanuals/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Mirvakili, S.M.; Hunter, I.W. Artificial Muscles: Mechanisms, Applications, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zarrouk, D.; Seo, J.-W.T.; Cheng, J.C.; Buchan, A.D.; Takei, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ager, J.W.; et al. Photoactuators and motors based on carbon nanotubes with selective chirality distributions. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).