Abstract
Soft pneumatic actuators with a channel network (pneu-net) based on thermoplastic elastomers are compatible with fused deposition modeling (FDM). However, conventional filament-based fused deposition modeling (FDM) printers are not well suited for thermoplastic elastomers with a shore hardness (Sh < 70A). Therefore, in this study, a pellet-based FDM printer was used to print pneumatic actuators with a shore hardness of Sh18A. Additionally, the method allowed the in situ integration of soft piezoresistive sensing elements during the fabrication. The integrated piezoresistive elements were based on conductive composites made of three different styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS) thermoplastic elastomers, each with a carbon black (CB) filler with a ratio of 1:1. The best sensor behavior was achieved by the SEBS material with a shore hardness of Sh50A. The dynamic and quasi-static sensor behavior were investigated on SEBS strips with integrated piezoresistive sensor composite material, and the results were compared with TPU strips from a previous study. Finally, the piezoresistive composite was used for the FDM printing of soft pneumatic actuators with a shore hardness of 18 A. It is worth mentioning that 3 h were needed for the fabrication of the soft pneumatic actuator with an integrated strain sensing element. In comparison to classical mold casting method, this is faster, since curing post-processing is not required and will help the industrialization of pneumatic actuator-based soft robotics.
1. Introduction
Soft robotics are increasing in popularity compared to their rigid counterparts and can be used in applications that require the careful manipulation of sensitive objects, safe interaction with the user and complex motion [1,2]. Pneumatic soft actuators are a type of soft robot modules in which the inflation of hollow sections, which are connected through a channel system (pneu-net), results in a bending of the elastomeric structure [3]. Very large deformations are exerted on the elastic inflatable actuators and to avoid high pressure, elastomers with low shore hardness, such as silicone elastomers, are preferred [4].
The most widespread method for the production of pneumatic actuators is mold casting [5,6,7,8]. However, the method is time consuming because it involves multiple steps and is not easy to scale up for production lines, especially if there is the embedding of soft sensors involved [4,9]. It is a simple technique and it is compatible with elastomers of low shore hardness such as silicone elastomers, which are the most widespread elastomers used for pneumatic actuators [10,11]. The rise of additive manufacturing (AM) methods provide an interesting alternative to molding. It can lead to the production of samples with good reproducibility and flexibility in the design of the actuator device [12]. Extrusion-based AM and stereolithographic-based AM (SLA) are methods compatible with elastomers of low shore hardness. SLA, especially, can be used for the fabrication of soft pneumatic actuators from silicone elastomers [13], but unfortunately, higher cost and fabrication time are required [14]. Similar to the casting method, it is difficult to integrate soft sensors. Multi-material printing is state-of-the-art for extrusion-based AM and soft sensor elements can be integrated in situ during printing process [15].
From the extrusion-based AM methods, the most widespread for the printing of soft robotic pneumatic actuators is Direct Ink Writing (DIW) [16,17,18,19]. However, there are significant disadvantages related to restrictions from the rheological properties of the elastomers and the additional step of curing that is required after the printing [20,21]. Fused deposition modeling (FDM), or fused filament fabrication (FFF), is an extrusion-based method of AM for thermoplastics. The polymers are extruded through a heated hot-end and deposited as threads, layer by layer, on a moving platform to build up a 3D structure [22]. FDM is known for its cost efficiency, compatibility with large scale production and the fact that the produced parts can be recycled [15,23]. The resolution of the method has been reported to be 100 µm [24,25]. There have been some attempts in producing pneumatic actuators with FDM based on thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers, such as NinjaFlex [26,27] and eSUN eFLEX [28], and it was shown that the method can be used to fabricate airtight pneumatic structures [29]. Unfortunately, the shore hardness was limited to materials with a shore hardness above 70A, which is significantly higher than most silicone elastomers. The conventional FDM printers have a gear system that causes a jamming of the filament if the shore hardness of the material is too low.
In this study, a pneumatic bending actuator with a shore hardness of Sh18A was printed with in situ integrated sensing elements by FDM. The FDM printer was equipped with a screw extruder that allowed the use of material in the form of pellets instead of the conventional filament. For the sensing element, three different styrene-butadiene-styrene (SEBS) thermoplastic elastomers with a carbon black filler content (CB) of 50 wt.% were investigated. Clemens et al. reported that when using a high CB filler content, the piezoresistive sensor properties of SEBS composites could be improved [30]. After the selection of the right piezoresistive sensor material, SEBS strips (Sh18A) with an integrated piezoresistive element were characterized by dynamic and quasi-static tensile testing in order to investigate the potential of the sensor, in comparison to TPU strips reported in literature [15]. The sensor performance was also assessed on the pneumatic bending actuators. This study allows for expanding the applicability of thermoplastic elastomer materials for the fabrication of soft pneumatic actuators.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Piezoresistive Sensing Material
For the development of piezoresistive sensing material, styrene-based tri-block co-polymers by Kraiburg TPE (Waldkraiburg, Germany), with a shore hardness of Sh25A, Sh50A and Sh70A were used. As a conductive filler, carbon black obtained from TIMCAL (Bodio, Switzerland) was used. The two components were mixed in a 1:1 mass ratio, using torque rheometer HAAKE Polylab Rheomix 600 from Thermofisher (Karlsruhe, Germany). After mixing, the filaments were extruded, using a capillary rheometer RH7 from NETZSCH (Selb, Germany). To achieve a homogeneous granule size, manual cutting was performed using filaments with a diameter of 1.75 mm. Finally, the electrically conductive filament was cut into 3 mm pellets.
Sensor fibers with a diameter of 0.6 mm were extruded using pellet printer Voladora NX+ (International Technology 3D Printers, S.L., Valencia, Spain). For the extrusion, the temperature of 250 °C was used.
2.2. Printing of the SEBS Structures with Integrated Sensing Elements Using Pellet-Based FDM
For the printing of SEBS-based soft pneumatic structures, a thermoplastic elastomer with a shore hardness of Sh18A (Kraiburg TPE, Waldkraiburg, Germany) was used. In order to compare the electrical sensor behavior with TPU reported results [15,31], strip-like structures were printed (Figure 1a). The design of the pneumatic actuator (Figure 1b) was performed using a CAD software based on an open-source design for molds of a pneu-net bending actuator [32]. The dimensions of the actuator were derived from the design of the mold that is traditionally used for casting silicone rubber. The width of the actuator was 25 mm, the length 108 mm and the height 18 mm. One segment of the actuator had the length of 8 mm and the size of the trench between the different segments was 0.2 mm. To produce the bending actuator with the in situ integrated strain sensor, first the sensing element was printed and on top of it the bending actuator (Figure 1c).
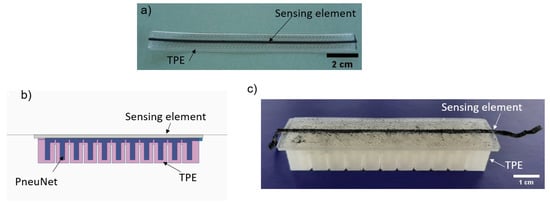
Figure 1.
(a) The SEBS-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) strip with the integrated sensing element fabricated with a pellet-based FDM printer; (b) the CAD design of the bending actuator; (c) the bending actuator with the integrated sensing element fabricated with a pellet-based FDM printer.
The printer was equipped with a rotating screw that was controlled by a stepper motor. The printing parameter, extrusion multiplier is linked with the speed of the stepper motor. The extrusion chamber was heated with two different heating elements and separated into two heating zones, as seen in Figure 2. The printing parameters for the strip-like structure and the soft robotic actuator are listed in Table 1.
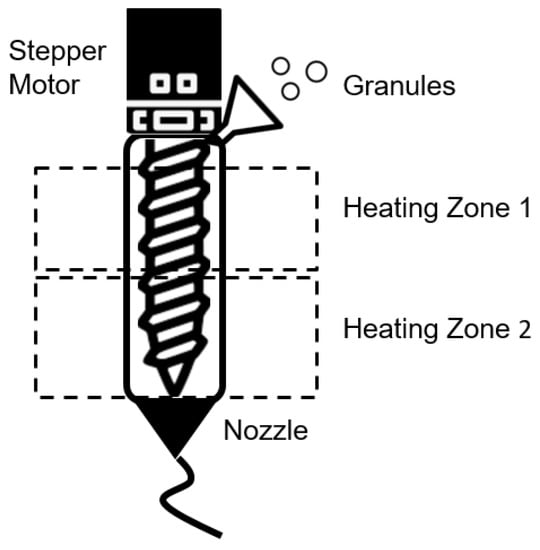
Figure 2.
Pellet-based FDM extruder head. The extruder is equipped with a rotating screw and stepper motor and has two separate heating zones.

Table 1.
Processing parameters used for AM of the TPS strips with integrated sensing elements using pellet-based FDM printer.
For the actuation of the pneumatic actuator, a vacuum pump was used from SparkFun Electronics (Boulder, CO, USA). The vacuum pump was controlled with an arduino microcontroller. A pressure of 220 kPa was used.
2.3. Tensile Testing
For the investigation of the piezoresistive behavior of the sensors, a tensile testing with simultaneous measurement of the electrical sensor signal was performed. For the tensile testing, a Zwick Roell Z005 tensile testing machine from Zwick Roell GmbH & Co. (Ulm, Germany) was used. The tensile machine was equipped with pneumatic clamps with a pressure of 4 bar and a 200 N load cell to avoid slipping behavior during the tensile testing. A crosshead speed of 200 mm/min was applied during all the different tensile experiments. The electrical signal was measured using a Keithley 2450 multimeter (Keithley Instruments, Solon, OH, USA) with a data recording frequency of 10 Hz. Based on Georgopoulou et al., tensile tests were performed up to the point of fracture, under dynamic and quasi-static conditions [33].
The relative resistance (Rrel) was calculated using the following formula:
where R is the value of the resistance during certain strain and Ro the initial resistance value of the printed strip.
To define the sensitivity of the sensor, the gauge factor (GF) was calculated by the following equation:
where Δε is the range of strain in which the Rrel is measured.
The drift of the resistance value between different tensile cycles was calculated at maximal as the percentage difference between the values of the relative resistance, at the same level of strain between different cycles of the dynamic tensile testing. Finally, the relaxation of the resistance between the beginning and the end of a dwell time of 60 s during the quasi-static test was investigated. Finally, the relaxation of the mechanical stress and electrical resistance was calculated using the percentage difference of the resistance at the beginning and the end of a dwell time, during the quasi-static test. For the bending actuator a stepwise test was performed, where the value of the electrical resistance was recorded in different bending angles of the pneumatic actuator with the integrated sensing element. With the same actuator, a dynamic test was performed with a dwell time of 4 s at angles 0° and 90°.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FDM-Printed Sensing Fibers
FDM-printed sensor fibers were produced using thermoplastic elastomer (SEBS) as a matrix material. Based on literature, in all three cases, the carbon black concentration was fixed to 50 wt.% (1:1 mass ratio). A tensile test up to the point of fracture, with a simultaneous recording of the electrical resistance, was performed for the three different filaments (Figure 3).
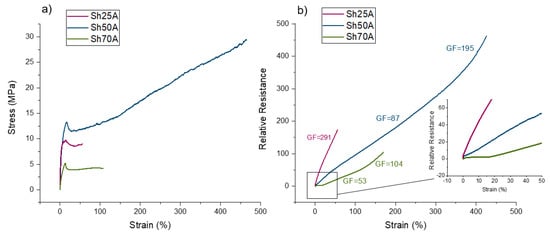
Figure 3.
(a) Stress-strain and (b) relative electrical resistance-strain response for FDM extruded sensor filaments made of SEBS-based TPEs with three different shore hardness (Sh25A, Sh50A, Sh70A).
Based on the stress-strain curve (Figure 3a), it was seen that for all the different fibers, there was a characteristic necking around the yield point. This response has been seen before for composites based on TPE with high carbon black concentration [30] and it is worth mentioning that such a high loading is needed to achieve sufficient sensor properties [30]. Comparing the fibers, the main difference can be observed for the strain at the point of fracture. For the Sh25A, the fiber broke already at 55% strain. This is insufficient for applications with deformations above 30% strain, even if the sensor fibers have the highest GF (291). Obviously, the mechanical and electrical behavior do not correlate with the shore hardness of the SEBS matrix. A possible explanation could be found in the carbon black distribution inside the SEBS. It has been reported that the preferential location of CB is in the hard rather than the soft phase of the TPE [34]. A common way to tune the shore hardness of the TPE is to change the ratio of the hard and soft phases of the TPE and the oil content [35]. The distribution of the CB filler in the TPE is affected by the shore hardness. However, we assume that the additional oil content in the TPE explains the non-correlation between the shore hardness and the mechanical and electrical properties of the three different composites. For the Sh70A, up to 18% strain, almost no change in resistance occurs and then the relative resistance sharply increases. The sensor responds monotonically, with a GF of 53 between 18% and 140% strain and 104 from 140% and up to the point of fracture. Using a pre-straining concept above 18% strain, this sensor can be used for strain sensing applications. However, pre-straining of 3D-printed pneumatic actuators is difficult. Therefore, it can be concluded that good performance in terms of sensing without pre-straining, high GF and maximal elasticity can be achieved with the Sh50A TPE material. The slope, in this case, changes at 50% and 340% strain.
For further validation, piezoresistive lines, based on Sh50A and Sh70A, were printed on a heated printer bed with a pellet extruder-based FDM printer. Looking on the printed sensor lines made of piezoresistive Sh50A composite (Figure 4a), two lines without interruptions and a constant width can be observed. For the Sh70A (Figure 4b), the printed lines were interrupted and not smooth. Individual dots were visible and indicated an inhomogeneous flow of the material through the nozzle.

Figure 4.
Three-dimensional-printed piezoresistive lines using (a) Sh50A and (b) Sh70A SEBS-based composites.
Based on the printing results, the Sh50A piezoresistive composite was used for the fabrication of the strips and soft pneumatic actuators with in situ-printed piezoresistive strain sensing elements.
3.2. FDM-Printed Strip with Sh18A SEBS and Integrated Strain Sensing Element
It is the first time that low shore hardness SEBS-based TPE (Sh18A) was printed with a pellet-based FDM extruder. Therefore, before printing pneumatic actuator structures with integrated strain sensors, strips with an in situ-printed sensing element were printed and investigated by dynamic and quasi-static tensile testing [15]. It is worth mentioning that for the later application, the integrated sensor is bent under compression mode. However, it was decided to use tensile testing method to be able to compare the sensor behavior with 3D-printed TPU strips, based on commercial filaments, published by Georgopoulou et al. [14]. Figure 5 shows the mechanical and piezoresistive response of the SEBS-based TPE strips with the integrated sensing elements up to the point of fracture.
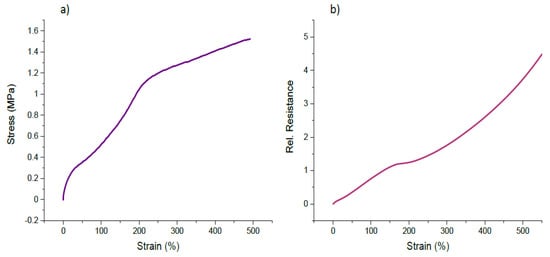
Figure 5.
(a) Stress-strain and (b) relative electrical resistance-strain response for the SEBS-based TPE strips (Sh18A) with integrated sensing elements Sh50A.
From the stress-strain curve (Figure 5a), it can be seen that the SEBS strips can endure large elongations of up to 500%. The Young’s modulus of 1 MPa was calculated from the elastic region of the stress-strain curve. As expected, Young’s modulus of the printed elastomer structure is much lower than the reported TPU strips (34 MPa) [15]. Silicone-based pneumatic actuators typically have a Young’s modulus between 0.1 and 10 MPa [4], and therefore it can be expected that SEBS-based printed structures could replace silicone easily, if needed for future applications. The relative resistance increased monotonically, up to the point of fracture (Figure 5b). For previous TPU-based printed strips, such a monotonic increase in resistance behavior cannot be achieved. For low strain values, a negative piezoresistive effect can be observed [15]. Dynamic tensile testing (cyclic) was performed between the strains 0–50% (Figure 6).
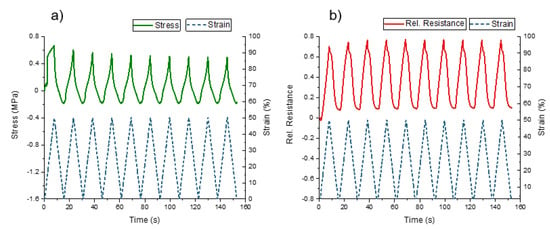
Figure 6.
(a) Stress-strain and (b) relative electrical resistance-strain response for the SEBS-based TPE strips (Sh18A) with integrated sensing elements Sh50A under dynamic testing between 0% and 50% strain.
From the response of the stress (Figure 6a), it was seen that below 14% strain, the mechanical stress became negative. This response is known as buckling and it can be linked with the viscoelasticity of the thermoplastic elastomer matrix. The buckling behavior can be confirmed by visual inspection during the experiment (Figure S1). For the relative electrical resistance, a positive piezoresistive response can be observed. This is in good agreement with the tensile test shown in Figure 5b. For the strips, an initial resistance of 3 ± 0.6 kΩ was measured. The small deviation shows the good consistency in quality that can be achieved with additive manufacturing as a fabrication method. The sensor signal response at 50% strain, between cycle number 2 and 10, had a drift of 1%. The drift was smaller in comparison to FDM-printed TPU strips (8%), reported by Georgopoulou et al. [15]. A hysteresis of 2% of the electrical signal was calculated. The value was calculated at 10% strain, to compare with another study that reported values for the hysteresis between 1.2% and 16% for the different composites at 10% strain [36]. Therefore, it is assumed that the hysteresis of 2% in the current study was at the lower part of the reported range. The SEBS-based TPE strips exhibited a positive piezoresistive response without a plateau or uncertainty in the sensor behavior; however, a change in the slope at low strains during unloading can be observed.
Another important aspect of the sensor characterization is cycling testing with a dwell time at the maximum and minimum strain, called “quasi-static” cycling test (Figure 7). For that reason, a quasi-static test between 0% and 50% strain with a dwell time of 60 s at maximum and minimum strain was performed.
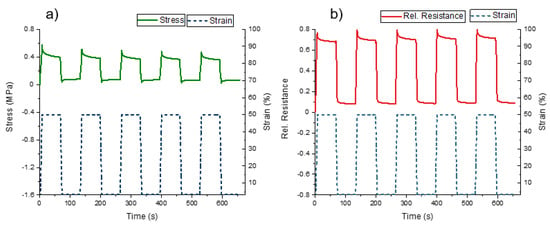
Figure 7.
(a) Stress-strain and (b) relative electrical resistance-strain response for the SEBS-based strips (Sh18A) with integrated sensing elements Sh50A under quasi-static testing between 0% and 50% strain and a dwell time of 60 s.
For the mechanical and electrical relaxation, a value of 88% and 13% was calculated at 0% strain, respectively. The larger value of the mechanical relaxation can be linked with the buckling behavior observed at strains below 14% during the dynamic tensile testing (Figure 6). At 50% strain, values of 29% and 32% can be detected for the mechanical and electrical relaxation, respectively. For TPU strips, relaxation values of 20% and 25% were reported for the mechanical and electrical analysis, respectively, at 30% strain [14]. It is worth mentioning that the TPU strips are limited to 30% strain. Above this strain, viscoelastic effects increased significantly (high drift) and secondary peak appeared during unloading phases [37]. There was no drift observed between the second and fifth cycles.
3.3. FDM-Printed Pneumatic Bending Actuators with Integrated Sensing Element
An airtight pneumatic-based actuator with an integrated sensing element can be successfully printed with a pellet-based FDM printer. The printed actuators can be inflated by an external air pump. Even though FDM is based on layer-by-layer deposition of the material to form the 3D structure, airtight structure can be successfully achieved. A printing time of 3 h was needed for the fabrication of the soft pneumatic actuator with the integrated strain-sensing element. Therefore, in comparison to the classical mold casting method, the pellet-based FDM method is significantly faster.
As already mentioned, the pneumatic soft actuator module deforms under bending and the piezoresistive element acts under compression. Therefore, the electrical signal was evaluated under different bending angles (Figure 8).
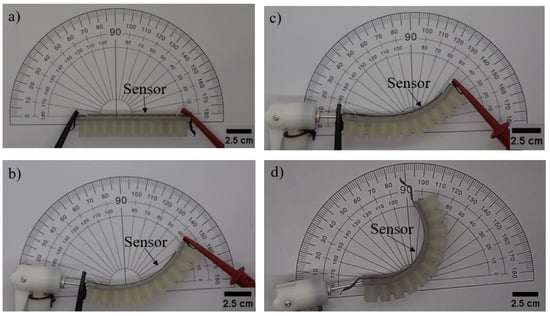
Figure 8.
FDM-printed bending actuator with the integrated piezoresistive sensor under deformation angles of (a) 0°, (b) 30°, (c) 50° and (d) 90°.
In order to assess the sensor performance, two different tests were performed. First, the value was recorded for different deformation angles (Figure 9a); second, a cycling bending test between 0° and 90° was performed (Figure 9b).
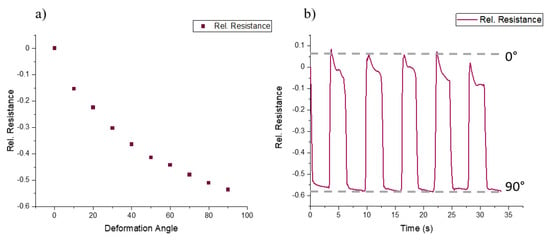
Figure 9.
(a) The change in electrical sensor signal during stepwise bending of FDM-printed pneumatic actuator and (b) the sensor signal during quasi-static cycling measurement (with a dwell time of 4 s at 0° and 90° angles).
From Figure 9a, it is seen that the resistance decreased when the bending angle increased. In comparison to tensile testing experiments (Figure 5), inverse behavior was expected due to compression mode. Nonetheless, the sensing element exhibited good sensing response (Figure 9a) and it was possible to distinguish between the different values of the angle of the bending actuator.
As for the quasi-static cycling test (Figure 9b), relaxation in the sensor signal was observed, especially at minimum deformation (60%). There was an overshoot (e.g., positive relative resistance value) when the sensor returned to the initial state (0° angle). At 90°, a relaxation of 4% can be observed. At 90°, the relaxation is lower than what was measured during the quasi-static testing of the strips. Additionally, there is a small drift between the different cycles (2%). This drift was not observed during the quasi-static testing of the strips and may possibly be associated with the fixation of the actuator. Based on the results, it can be concluded that the piezoresistive Sh50A composite can be used to monitor the bending of soft actuators. The bending angle can be measured in situ and used in the future for closed-loop controlling of the bending actuator module.
4. Conclusions
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is a cost-efficient extrusion method of AM and can be used for fabricating multi-material structures. Using an FDM printer equipped with a screw extruder, pellets can be used instead of filaments. Pellet-based FDM is compatible with elastomers of low shore hardness, and a soft pneumatic bending actuator with a shore hardness of Sh18A and an integrated piezoresistive sensing element were successfully fabricated with FDM. For the sensing element, SEBS thermoplastic elastomers with three different shore hardness (Sh25A, Sh50A, Sh70A) were mixed with 50 wt.% CB and based on the good elastic, sensitive and printing properties of the Sh50A piezoresistive composite, it was embedded in the soft pneumatic actuator.
The SEBS-based TPE strips with integrated sensing elements exhibited a positive piezoresistive response, even at low strains, and very small drift was observed. Even though the strain sensor embedded in the bending actuator was used under compression mode, dynamic and quasi-static tensile testing were performed to be able to compare the strip properties with literature.
As expected, the sensor embedded in the bending actuator showed a reverse piezoresistive behavior, with the relative resistance decreasing when the bending deformation increased. Quasi-static cycling experiments of the soft actuator revealed small drift between each cycle. Overall, the use of pellet-based FDM for the fabrication of soft robotic actuator modules with integrated sensing elements was successfully demonstrated. The method is an alternative low-cost fabrication process for design studies and it can lead to the manufacture of large soft robot structures.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/act10050102/s1, Figure S1: The strip with the integrated sensing element (a) before and (b) after the dynamic tensile testing. The length did not return to the original value after the test and this phenomenon is described as buckling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C.; data curation, A.G. and F.C.; formal analysis, A.G. and L.E.; funding acquisition, B.V. and F.C.; investigation, A.G. and L.E.; methodology, A.G., L.E. and F.C.; project administration, F.C.; supervision, B.V. and F.C.; validation, A.G., L.E. and F.C.; visualization, A.G. and L.E.; writing—original draft, A.G.; writing—review & editing, B.V. and F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 828818 (SHERO Project).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and comply with the research integrity guidelines of EMPA (https://www.empa.ch/web/empa/integrity, accessed on 10 May 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Thomas Wagner from Kraiburg Holding GmbH & Co. KG and Lenorplastics Zug AG for supplying the SEBS materials used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gu, G.; Wang, D.; Ge, L.; Zhu, X. Analytical Modeling and Design of Generalized Pneu-Net Soft Actuators with Three-Dimensional Deformations. Soft Robot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Walsh, C.J. Towards a Soft Pneumatic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics That Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, B.; Reynaerts, D.; Konishi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Kim, J.-W.; Volder, M.D. Elastic Inflatable Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, S.; Suzumori, K.; Ogura, K. Miniature Pneumatic Curling Rubber Actuator Generating Bidirectional Motion with One Air-Supply Tube. Adv. Robot. 2011, 25, 1311–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, T.; Nafea, M.; Faudzi, A.A.; Saleh, T.; Ali, M.S.M. PDMS-Based Dual-Channel Pneumatic Micro-Actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.H.; King, E.; Lee, E.H.; Sardesai, A.N.; Chen, Y.; Obuz, S.E.; Graf, Y.; Ma, T.; Chow, D.Y.; Fu, T.; et al. Soluble Polymer Pneumatic Networks and a Single-Pour System for Improved Accessibility and Durability of Soft Robotic Actuators. Soft Robot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terryn, S.; Roels, E.; Brancart, J.; Van Assche, G.; Vanderborght, B. Self-Healing and High Interfacial Strength in Multi-Material Soft Pneumatic Robots via Reversible Diels–Alder Bonds. Actuators 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.K.; Yeow, R.C.H. A Novel Fold-Based Design Approach toward Printable Soft Robotics Using Flexible 3D Printing Materials. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, L.; Balland, P.; Lindenroth, L.; Petrou, F.; Kontovounisios, C.; Bello, F. Toward a Common Framework and Database of Materials for Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, S.; Majidi, C.; LeDuc, P.; Hsia, K.J. Bio-Inspired Soft Robotics: Material Selection, Actuation, and Design. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, G.; Percoco, G. Additive Manufacturing Aimed to Soft Robots Fabrication: A Review. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 42, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, M.; Faber, J.A.; Pianegonda, L.; Ruhs, P.A.; Coulter, F.; Studart, A.R. 3D Printing of Robotic Soft Actuators with Programmable Bioinspired Architectures. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D Printing of Polymer Matrix Composites: A Review and Prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Vanderborght, B.; Clemens, F. Multi-Material 3D Printing of Thermoplastic Elastomers for Development of Soft Robotic Structures with Integrated Sensor Elements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Additive Manufacturing in Products and Applications, Zurich, Switzerland, 1–3 September 2020; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Skylar-Scott, M.A.; Mueller, J.; Visser, C.W.; Lewis, J.A. Voxelated Soft Matter via Multimaterial Multinozzle 3D Printing. Nature 2019, 575, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.; Yirmibeşoğlu, O.D.; Daalkhaijav, U.; Mengüç, Y. 14—Additive manufacturing of soft robots. In Robotic Systems and Autonomous Platforms; Walsh, S.M., Strano, M.S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing in Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 335–359. ISBN 978-0-08-102260-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yirmibesoglu, O.D.; Morrow, J.; Walker, S.; Gosrich, W.; Cañizares, R.; Kim, H.; Daalkhaijav, U.; Fleming, C.; Branyan, C.; Menguc, Y. Direct 3D Printing of Silicone Elastomer Soft Robots and Their Performance Comparison with Molded Counterparts. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Valentine, A.D.; Busbee, T.A.; Boley, J.W.; Raney, J.R.; Chortos, A.; Kotikian, A.; Berrigan, J.D.; Durstock, M.F.; Lewis, J.A. Hybrid 3D Printing of Soft Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zou, B.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, H. A Survey of Design Methods for Material Extrusion Polymer 3D Printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 15, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-M.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Lee, D.; Lin, Y.-T.; Lin, S.-H.; Lee, T.-Y.; Liu, S.-J.; Ito, H. A Robust Experimental Model to Explore the Three-Dimensional Printing of Polylactide Parts: Solution versus Melt Extrusion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.K.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Advanced Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion Coupled with Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D Printing for Personalised Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woern, A.L.; Byard, D.J.; Oakley, R.B.; Fiedler, M.J.; Snabes, S.L.; Pearce, J.M. Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials’ Optimization and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daminabo, S.C.; Goel, S.; Grammatikos, S.A.; Nezhad, H.Y.; Thakur, V.K. Fused Deposition Modeling-Based Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Techniques for Polymer Material Systems. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 16, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentijn, G.I.J.; Oomen, P.E.; Grajewski, M.; Verpoorte, E. Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing for (Bio)Analytical Device Fabrication: Procedures, Materials, and Applications. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7053–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, C.-H. High-Force Soft Printable Pneumatics for Soft Robotic Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalia, L.; Ang, B.W.-K.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Geometry-Based Customization of Bending Modalities for 3D-Printed Soft Pneumatic Actuators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, W.; Ritonga, A.S.; Prastowo, A. Design and Fabrication in the Loop of Soft Pneumatic Actuators Using Fused Deposition Modelling. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 298, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohimer, C.J.; Petrossian, G.; Ameli, A.; Mo, C.; Pötschke, P. 3D Printed Conductive Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Carbon Nanotube Composites for Capacitive and Piezoresistive Sensing in Soft Pneumatic Actuators. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, F.; Koll, B.; Graule, T.; Watras, T.; Binkowski, M.; Mattmann, C.; Silveira, I. Development of Piezoresistive Fiber Sensors, Based on Carbon Black Filled Thermoplastic Elastomer Compounds, for Textile Application. Smart Interact. Text. 2013, 80, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Michel, S.; Vanderborght, B.; Clemens, F. Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Based on Silicone Elastomers for the Monitoring of the Position of a Robot Arm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 318, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PneuNets Bending Actuators. Available online: https://softroboticstoolkit.com/book/pneunets-bending-actuator (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Georgopoulou, A.; Clemens, F. Piezoresistive Elastomer-Based Composite Strain Sensors and Their Applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 1826–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchoudakov, R.; Breuer, O.; Narkis, M.; Siegmann, A. Conductive Polymer Blends with Low Carbon Black Loading: High Impact Polystyrene/Thermoplastic Elastomer (Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene). Polym. Eng. Sci. 1997, 37, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Bhowmick, A.K. HIGH-TEMPERATURE THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMERS FROM RUBBER–PLASTIC BLENDS: A STATE-OF-THE-ART REVIEW. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Clemens, F. Effect of the Elastomer Matrix on Thermoplastic Elastomer-Based Strain Sensor Fiber Composites. Sensors 2020, 20, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, J.F.; Aliheidari, N.; Ameli, A.; Pötschke, P. 3D Printed Highly Elastic Strain Sensors of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).