Modulation of the Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Fasciola gigantica Thioredoxin Peroxidase In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
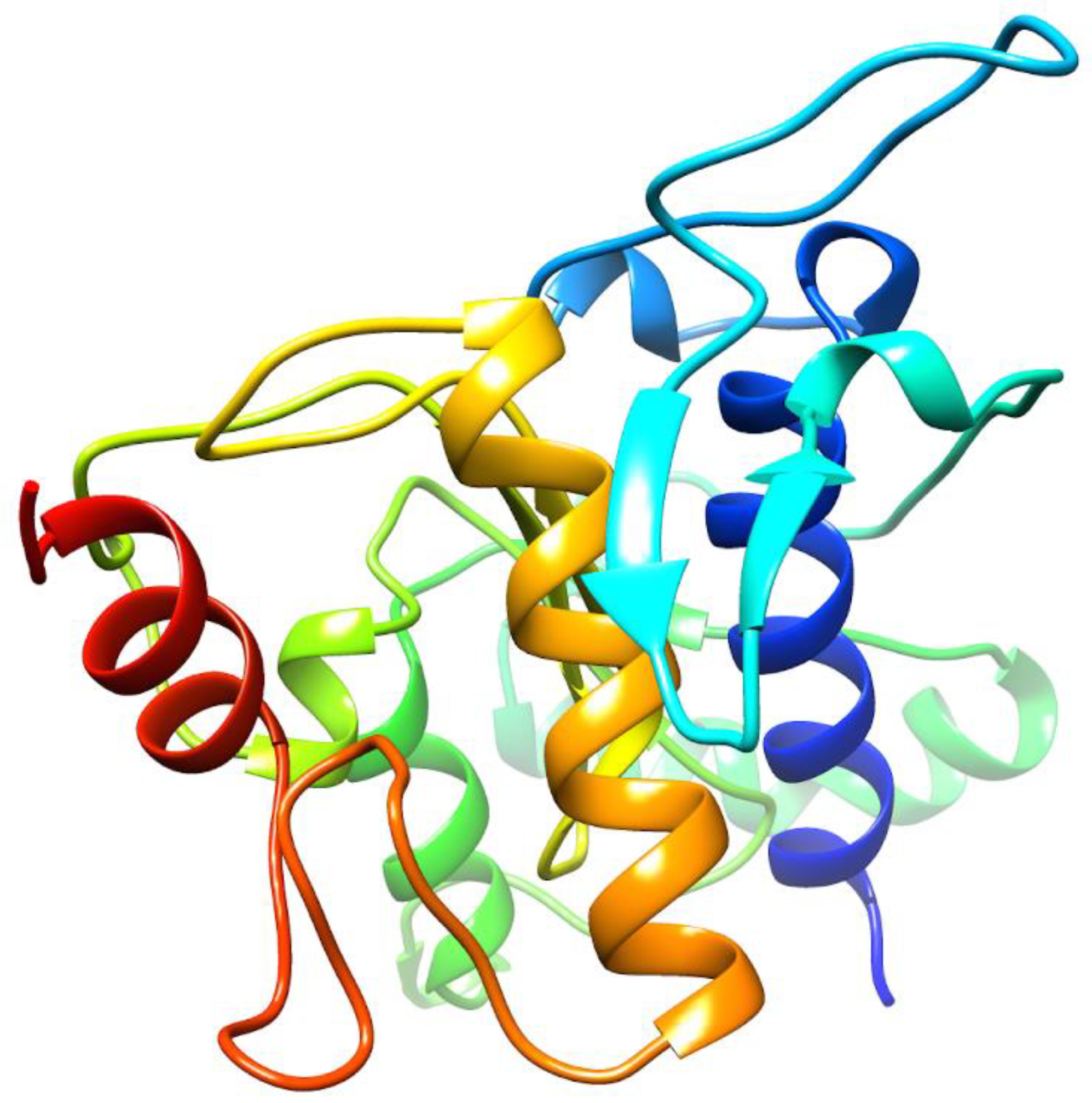
2.1. De Novo Prediction of FgTPx Protein
2.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of FgTPx
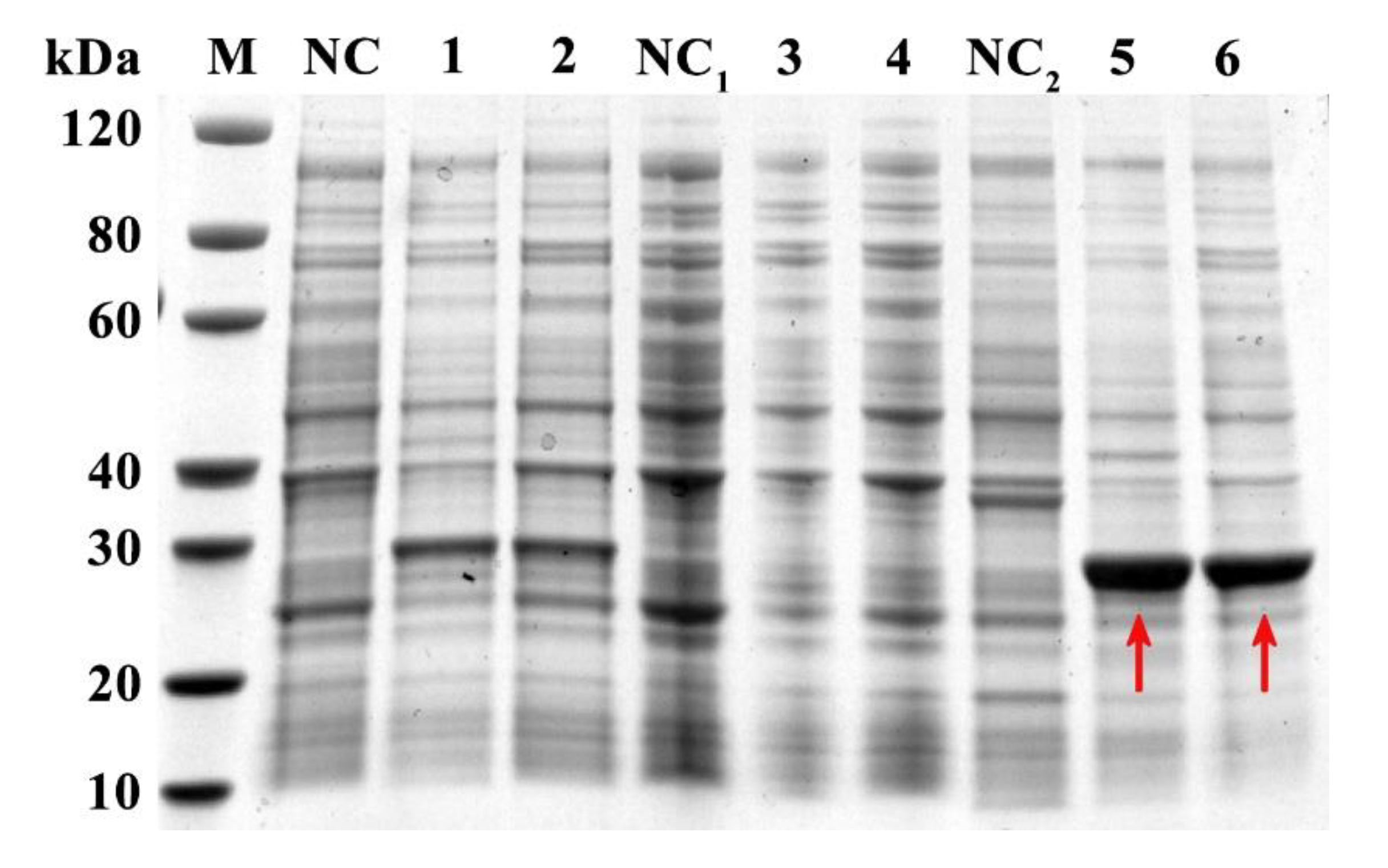
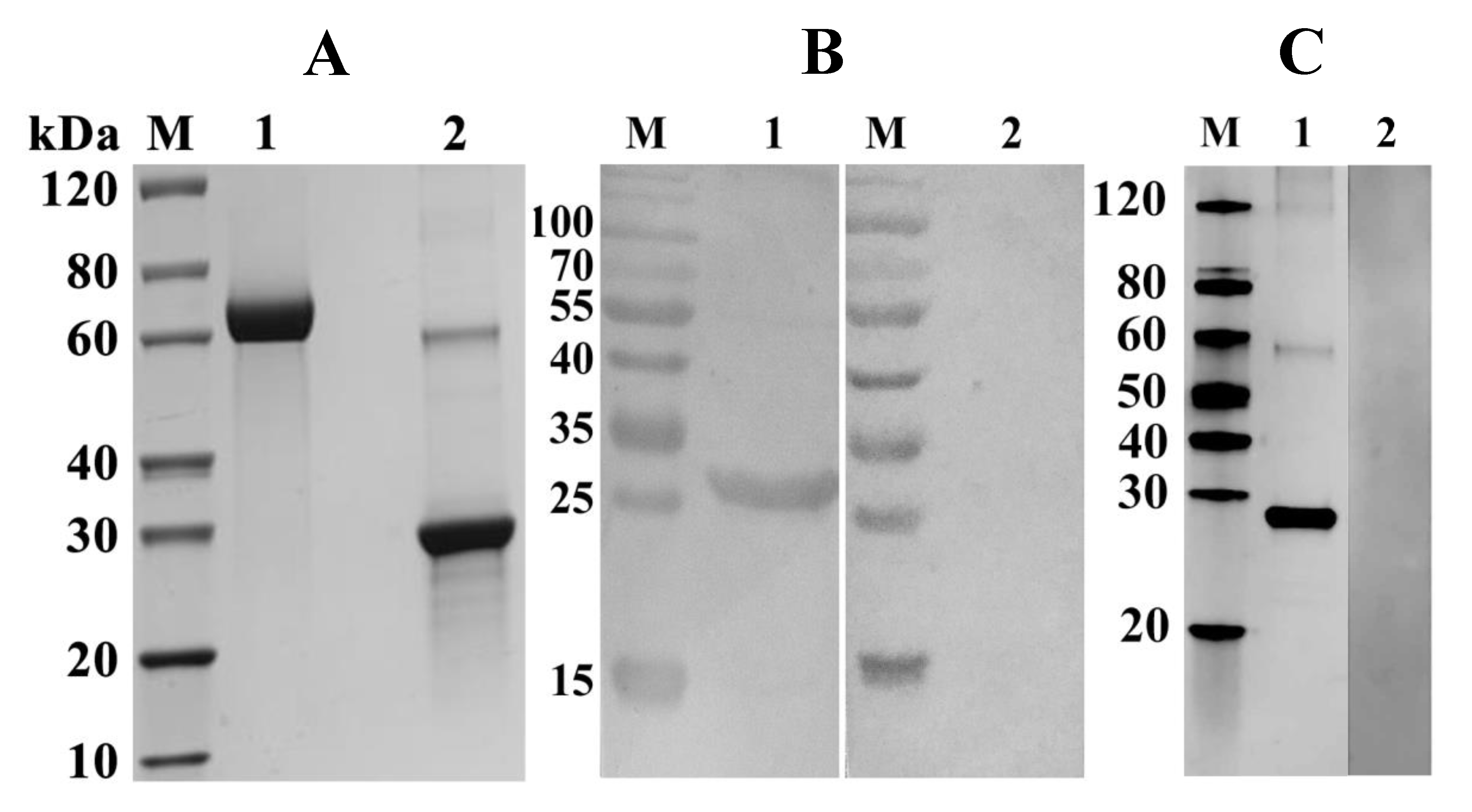
2.3. Expression, Purification, and Detection of rFgTPx
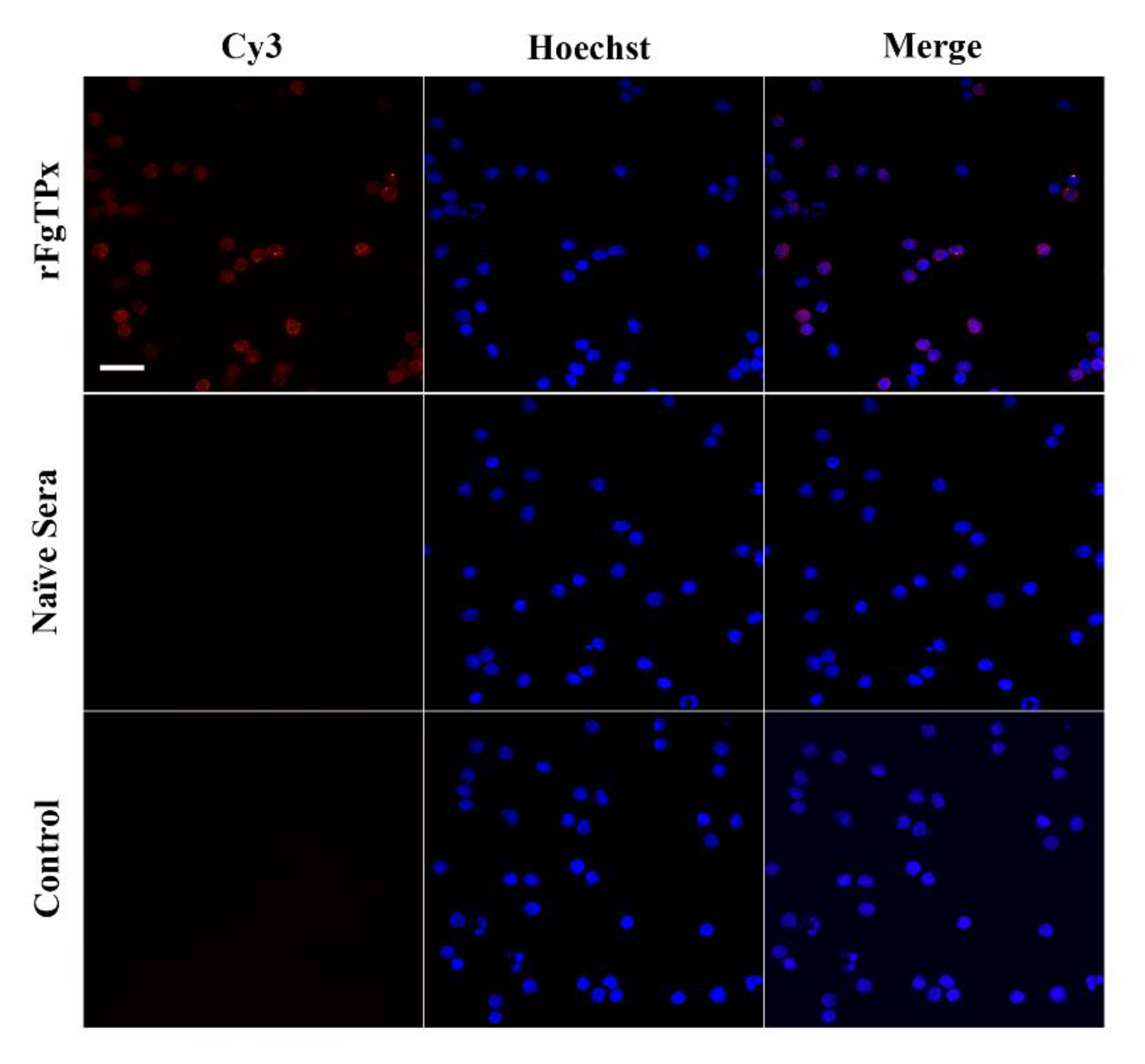
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay
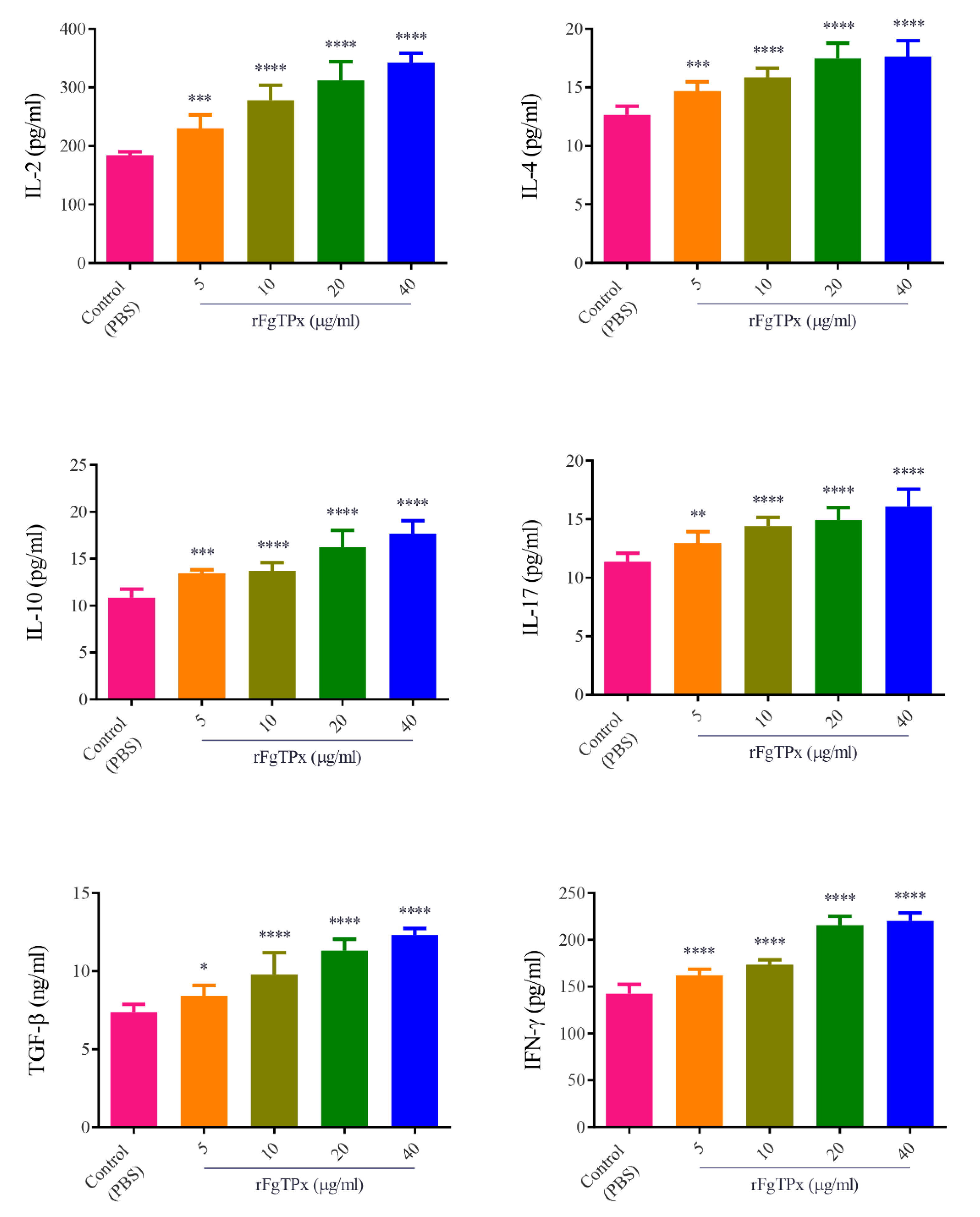
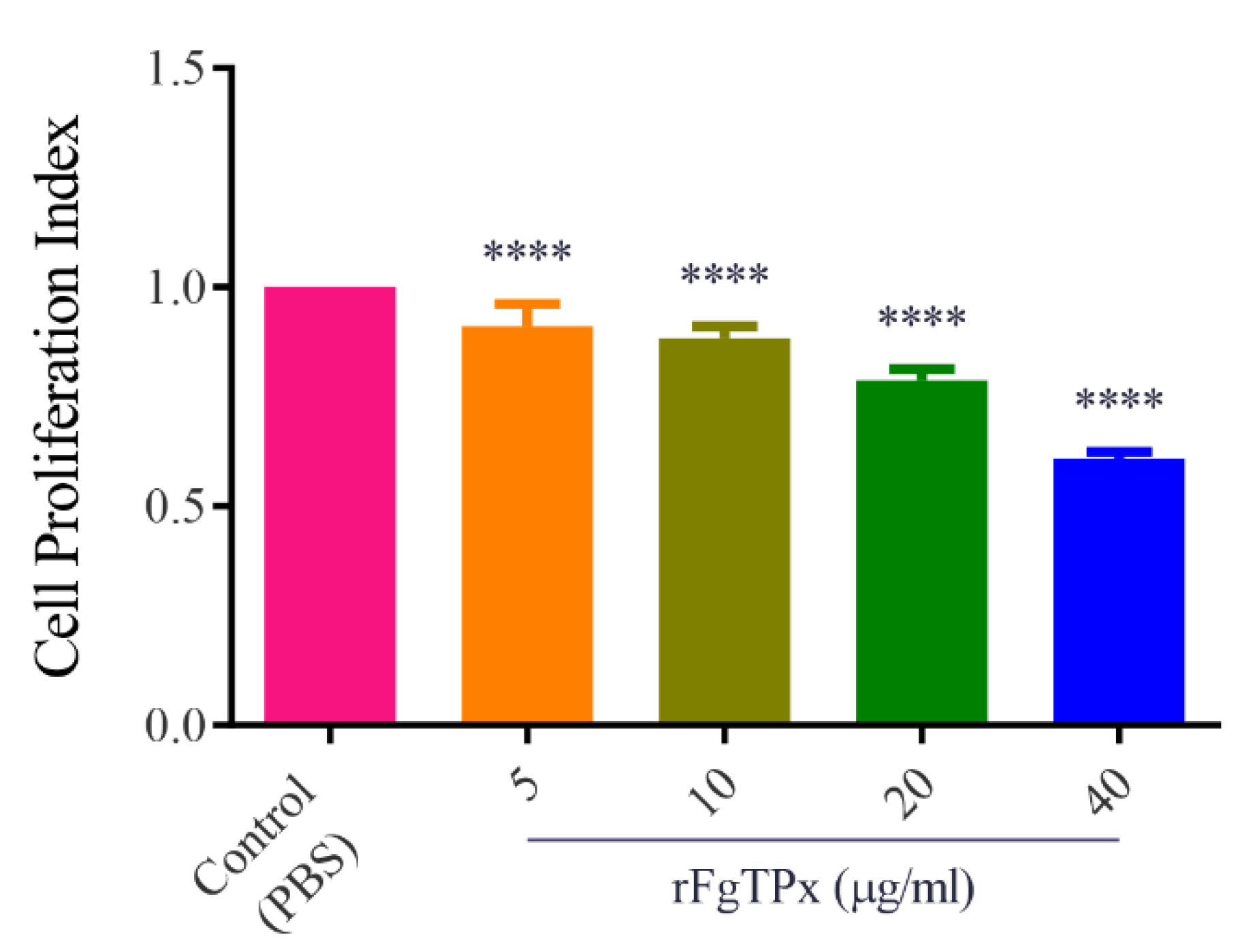
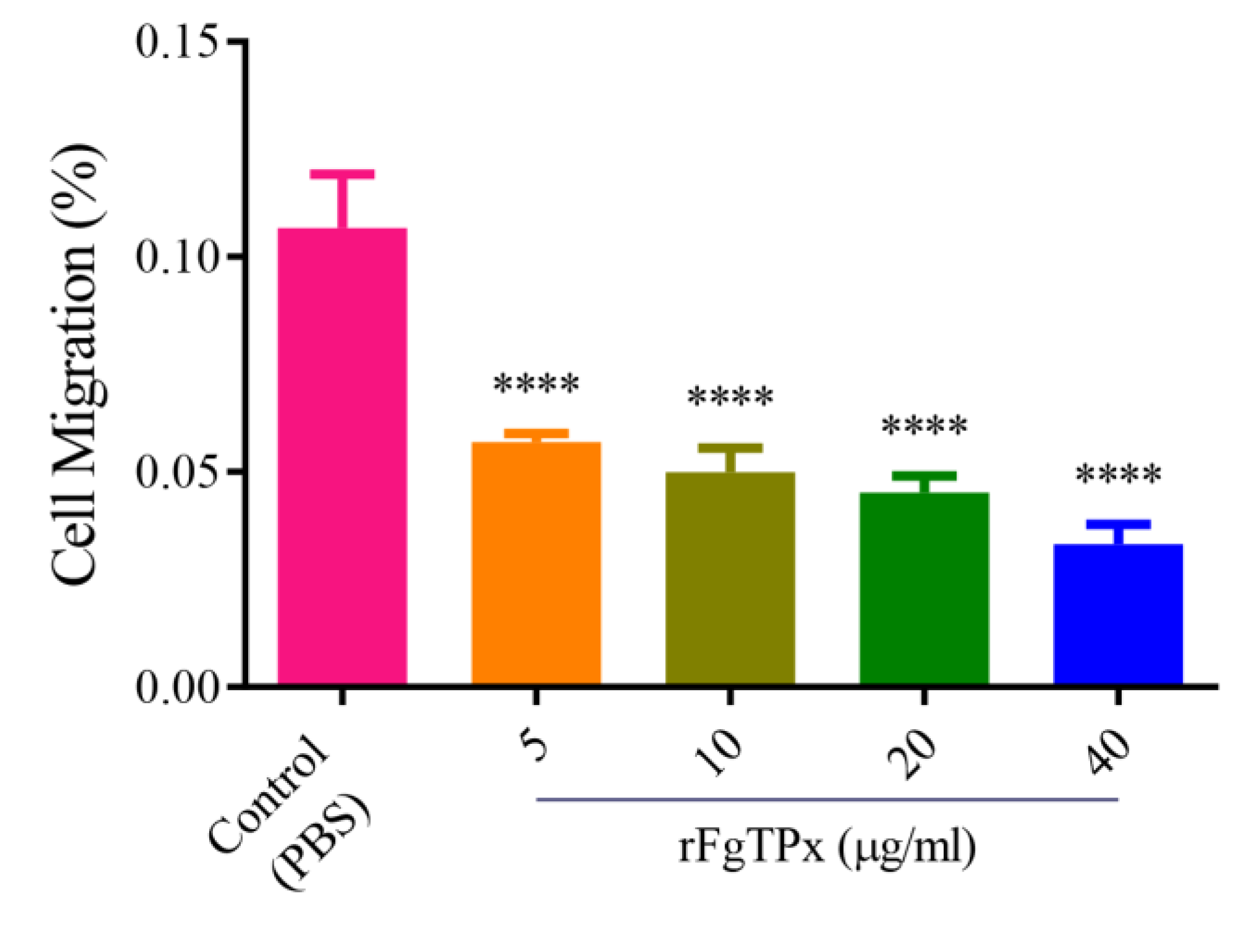
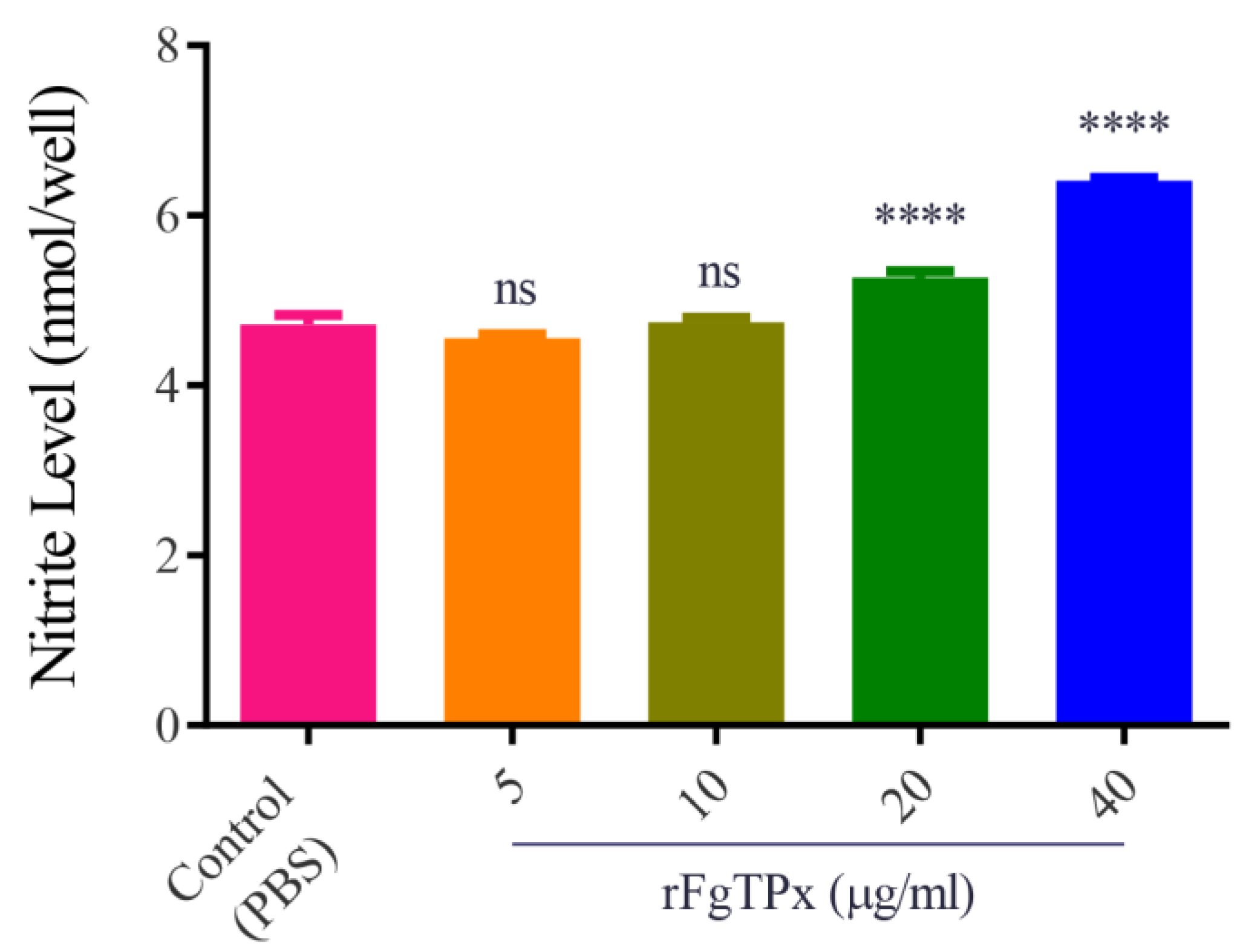
2.5. Cytokine Production, Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Production of NO
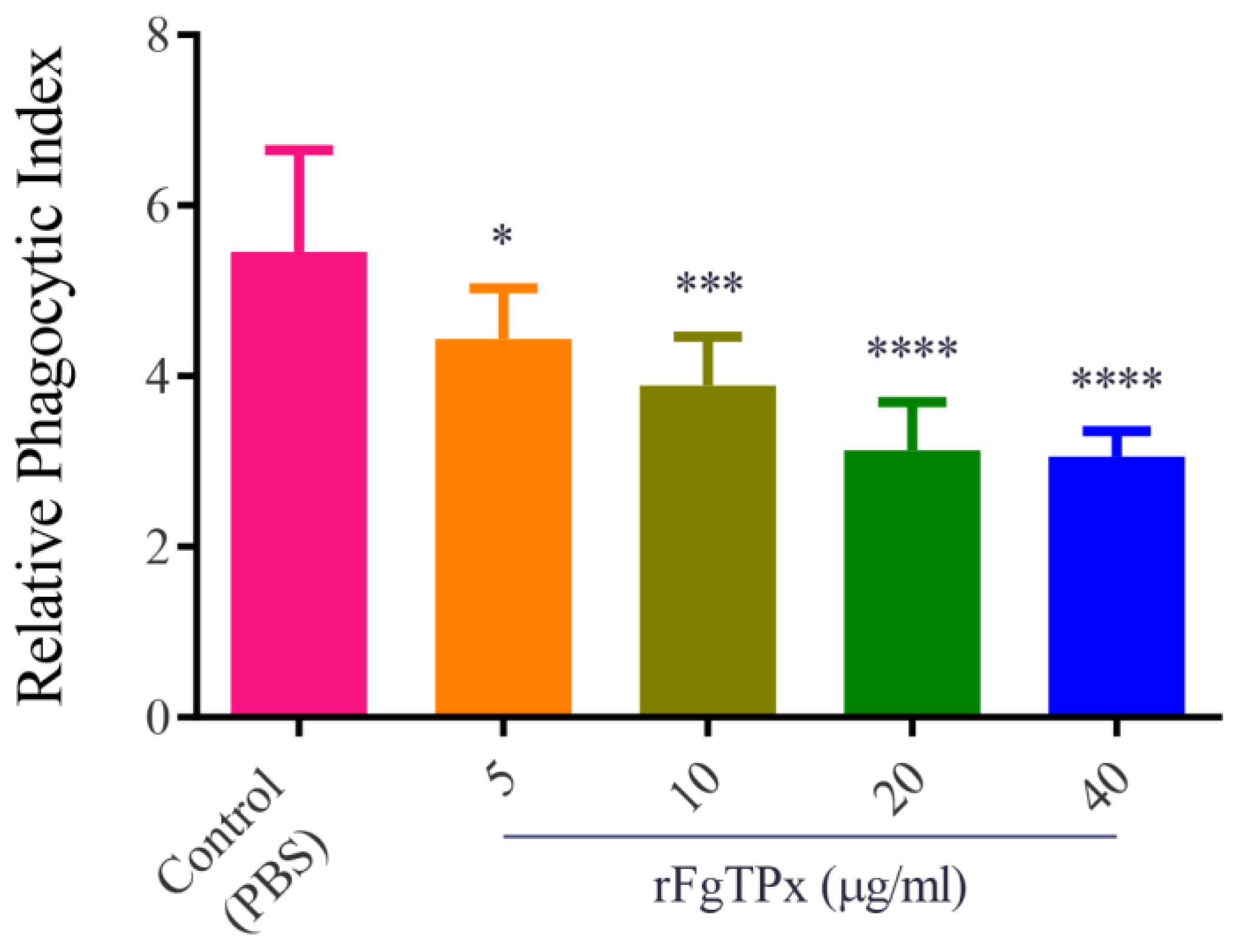
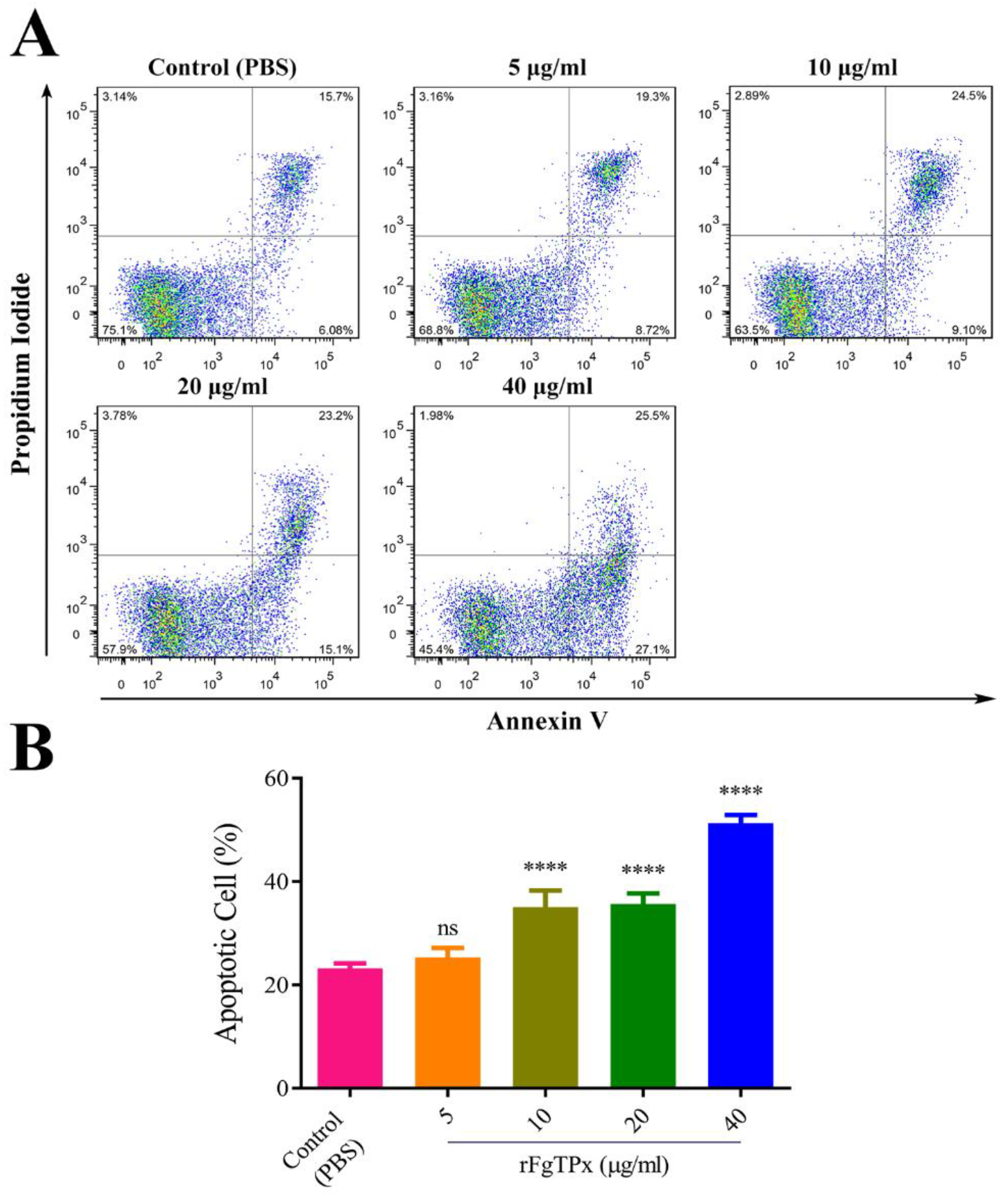
2.6. Monocyte Phagocytosis and Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approval
4.2. Parasites and Animals
4.3. Bioinformatis Analysis
4.4. Construction of Prokaryotic Expression Vector of FgTPx
4.5. Expression and Purification of Recombinant FgTPx (rFgTPx)
4.6. Generation of Antibodies
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Isolation and Culture of Goat PBMCs and Monocytes
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
4.11. Cell Proliferation Analysis
4.12. Cell Migration Assay
4.13. Measurement of Total Nitric Oxide (NO) Production
4.14. Determination of Phagocytic Activity
4.15. Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alasaad, S.; Soriguer, R.C.; Abu-Madi, M.; El Behairy, A.; Jowers, M.J.; Banos, P.D.; Piriz, A.; Fickel, J.; Zhu, X.Q. A TaqMan real-time PCR-based assay for the identification of Fasciola spp. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedrafita, D.; Spithill, T.W.; Smith, R.E.; Raadsma, H.W. Improving animal and human health through understanding liver fluke immunology. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Report of the WHO Informal Meeting on Use of Triclabendazole in Fascioliasis Control; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The “Neglected” Neglected Worms. Action against Worms; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation—Executive Summary; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meemon, K.; Sobhon, P. Juvenile-specific cathepsin proteases in Fasciola spp.: Their characteristics and vaccine efficacies. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, U.; Redman, E.M.; Raman, M.; Gilleard, J.S. Genetic evidence for the spread of a benzimidazole resistance mutation across southern India from a single origin in the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Vidyashankar, A.N. An inconvenient truth: Global worming and anthelmintic resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, K.M.; Bowdridge, S.A.; Kanevsky-Mullarky, I.; Zajac, A.M.; Notter, D.R. Gene expression profiles of hair and wool sheep reveal importance of Th2 immune mechanisms for increased resistance to. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, G.; Bauomy, I.R.; Hemyeda, Z.M.; Sakran, T.F. Evaluation of a 14.5 kDa-Fasciola gigantica fatty acid binding protein as a diagnostic antigen for human fascioliasis. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Santiago, O.; Delgado, B.; Espino, A.M. Fasciola hepatica saposin-like protein-2-based ELISA for the serodiagnosis of chronic human fascioliasis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.G.; Le, T.H.; De, N.V.; Doan, T.T.; Dao, T.H.; Vercruysse, J.; Dorny, P. Assessment of a 27-kDa antigen in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of fasciolosis in Vietnamese patients. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2010, 15, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkham, C.; Tantrawatpan, C.; Intapan, P.M.; Maleewong, W.; Wongkham, S.; Nakashima, K. Evaluation of immunoglobulin G subclass antibodies against recombinant Fasciola gigantica cathepsin L1 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of human fasciolosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukli, N.M.; Delgado, B.; Ricaurte, M.; Espino, A.M. Fasciola hepatica and Schistosoma mansoni: Identification of common proteins by comparative proteomic analysis. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, J.R.; Campbell, A.M.; van Rossum, A.J.; Barrett, J.; Brophy, P.M. Proteomic analysis of Fasciola hepatica excretory-secretory products. Proteomics 2001, 1, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P.; O’Brien, B.A.; Donnelly, S. Fasciola hepatica: The therapeutic potential of a worm secretome. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P. Zoonotic helminth infections with particular emphasis on fasciolosis and other trematodiases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2763–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Apisawetakan, S.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. Identification and expression of Fasciola gigantica thioredoxin. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preyavichyapugdee, N.; Sahaphong, S.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Grams, R.; Viyanant, V.; Sobhon, P. Fasciola gigantica and Schistosoma mansoni: Vaccine potential of recombinant glutathione S-transferase (rFgGST26) against infections in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.L.; Lu, M.; Calderon-Mantilla, G.; Petsalaki, E.; Dottorini, T.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Hou, J.L.; Li, X.; et al. A recombinant Fasciola gigantica 14-3-3 epsilon protein (rFg14-3-3e) modulates various functions of goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, F.K.; Calderon-Mantilla, G.; Petsalaki, E.; Tian, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; et al. The pervasive effects of recombinant Fasciola gigantica Ras-related protein Rab10 on the functions of goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Hutchinson, A.T.; Dalton, J.P.; Donnelly, S. Peroxiredoxin: A central player in immune modulation. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Jewhurst, H.; McVeigh, P.; Barbour, T.; Maule, A.G.; Tort, J.; O’Neill, S.M.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.; Dalton, J.P. Infection by the helminth parasite Fasciola hepatica requires rapid regulation of metabolic, virulence, and invasive factors to adjust to its mammalian host. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2018, 17, 792–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, S.; Stack, C.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Sayed, A.A.; Williams, D.L.; Dalton, J.P. Helminth 2-Cys peroxiredoxin drives Th2 responses through a mechanism involving alternatively activated macrophages. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4022–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Phoinok, N.; Yencham, C.; Sobhon, P.; Kueakhai, P. Vaccine potential of recombinant cathepsinL1G against Fasciola gigantica in mice. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 226, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Raina, O.K.; Nagar, G.; Prakash, V.; Jacob, S.S. Th1 and Th2 cytokine gene expression in primary infection and vaccination against Fasciola gigantica in buffaloes by real-time PCR. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.K.; Guo, A.J.; Hou, J.L.; Sun, M.M.; Sheng, Z.A.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, W.Y.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Serum levels of cytokines in water buffaloes experimentally infected with Fasciola gigantica. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 244, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenken, J.A.; Poschenrieder, A.J. Bioanalytical chemistry of cytokines--a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Cloning and characterization of a selenium-independent glutathione peroxidase (HC29) from adult Haemonchus contortus. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 13, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Weng, I.C.; Li, C.S.; Wan, L.; Liu, F.T. Examination of galectins in phagocytosis. Methods. Mol. Biol. 2015, 1207, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli, R.T.; Oswald, I.P.; James, S.L.; Sher, A. IL-10 inhibits parasite killing and nitrogen oxide production by IFN-gamma-activated macrophages. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Wandurska-Nowak, E. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in parasitic infections. Wiad Parazytol. 2004, 50, 665–678. [Google Scholar]
- Cervi, L.; Rossi, G.; Cejas, H.; Masih, D.T. Fasciola hepatica-induced immune suppression of spleen mononuclear cell proliferation: Role of nitric oxide. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 87, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasanti, M.; Gradoni, L.; Mattu, M.; Persichini, T.; Salvati, L.; Venturini, G.; Ascenzi, P. Molecular bases for the anti-parasitic effect of NO (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 9, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroux, C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Andreoletti, O.; Prevot, F.; Grisez, C.; Bergeaud, J.P.; Gruner, L.; Brunel, J.C.; Francois, D.; Dorchies, P.; et al. Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) infection in lambs elicits an unequivocal Th2 immune response. Vet. Res. 2006, 37, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Hurtado, F.; Munoz-Guzman, M.A. Immune responses associated with resistance to haemonchosis in sheep. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 162158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, E.; Chauvin, A. Immunity against helminths: Interactions with the host and the intercurrent infections. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 428593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallig, H.D. Immunological responses of sheep to Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology 2000, 120, S63–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla, A.; Perez-Caballero, R.; Zafra, R.; Bautista, M.J.; Pacheco, I.L.; Ruiz, M.T.; Martinez-Cruz, M.S.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Molina-Hernandez, V.; Perez, J. Apoptosis of peritoneal leucocytes during early stages of Fasciola hepatica infections in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 238, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzowska, M.; Guzik, K.; Barczyk, K.; Ernst, M.; Flad, H.D.; Pryjma, J. Increased IL-10 production during spontaneous apoptosis of monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voll, R.E.; Herrmann, M.; Roth, E.A.; Stach, C.; Kalden, J.R.; Girkontaite, I. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature 1997, 390, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Frank, M.E.; Jin, W.; Wahl, S.M. TGF-beta released by apoptotic T cells contributes to an immunosuppressive milieu. Immunity 2001, 14, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadok, V.A.; Bratton, D.L.; Konowal, A.; Freed, P.W.; Westcott, J.Y.; Henson, P.M. Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, S.; O’Neill, S.M.; Sekiya, M.; Mulcahy, G.; Dalton, J.P. Thioredoxin peroxidase secreted by Fasciola hepatica induces the alternative activation of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serradell, M.C.; Guasconi, L.; Cervi, L.; Chiapello, L.S.; Masih, D.T. Excretory-secretory products from Fasciola hepatica induce eosinophil apoptosis by a caspase-dependent mechanism. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.K.; Zhang, X.X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; He, J.J.; Sheng, Z.A.; Zheng, W.B.; Ma, J.G.; Huang, W.Y.; Guo, A.J.; Zhu, X.Q. Transcriptomic responses of water buffalo liver to infection with the digenetic fluke Fasciola gigantica. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Wei, Z.Y.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhang, F.K.; Sheng, Z.A.; Lu, K.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Dynamic expression of cytokine and transcription factor genes during experimental Fasciola gigantica infection in buffaloes. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, G.; Umemura, M. Interleukin-17 as an effector molecule of innate and acquired immunity against infections. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.M.; Kohler, G.; Holscher, C.; Iwakura, Y.; Alber, G. IL-17A is produced by Th17, gammadelta T cells and other CD4- lymphocytes during infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis and has a mild effect in bacterial clearance. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- States, D.J.; Gish, W. Combined use of sequence similarity and codon bias for coding region identification. J. Comput. Biol. 1994, 1, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conchúir, O.C.; Barlow, K.A.; Pache, R.A.; Ollikainen, N.; Kundert, K.; O’Meara, M.J.; Smith, C.A.; Kortemme, T. A web resource for standardized benchmark datasets, metrics, and Rosetta protocols for macromolecular modeling and design. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paclik, D.; Werner, L.; Guckelberger, O.; Wiedenmann, B.; Sturm, A. Galectins distinctively regulate central monocyte and macrophage function. Cell Immunol. 2011, 271, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, A.-L.; Tian, X.; Chen, D.; Lu, M.; Calderón-Mantilla, G.; Yuan, X.-D.; Li, X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.-Q. Modulation of the Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Fasciola gigantica Thioredoxin Peroxidase In Vitro. Pathogens 2020, 9, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090758
Tian A-L, Tian X, Chen D, Lu M, Calderón-Mantilla G, Yuan X-D, Li X, Elsheikha HM, Zhu X-Q. Modulation of the Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Fasciola gigantica Thioredoxin Peroxidase In Vitro. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090758
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Ai-Ling, Xiaowei Tian, Dan Chen, Mingmin Lu, Guillermo Calderón-Mantilla, Xiao-Dan Yuan, Xiangrui Li, Hany M. Elsheikha, and Xing-Quan Zhu. 2020. "Modulation of the Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Fasciola gigantica Thioredoxin Peroxidase In Vitro" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090758
APA StyleTian, A.-L., Tian, X., Chen, D., Lu, M., Calderón-Mantilla, G., Yuan, X.-D., Li, X., Elsheikha, H. M., & Zhu, X.-Q. (2020). Modulation of the Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Fasciola gigantica Thioredoxin Peroxidase In Vitro. Pathogens, 9(9), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090758




