Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Gastric Biopsies of Pediatric Patients with Dyspepsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Clinical Samples
2.2. EBV Genome Quantification
2.3. Helicobacter Pylori PCR Determination
2.4. Serologic Determination of Anti-EBV VCA and Anti-Hp Antibodies
2.5. Histopatological Examination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
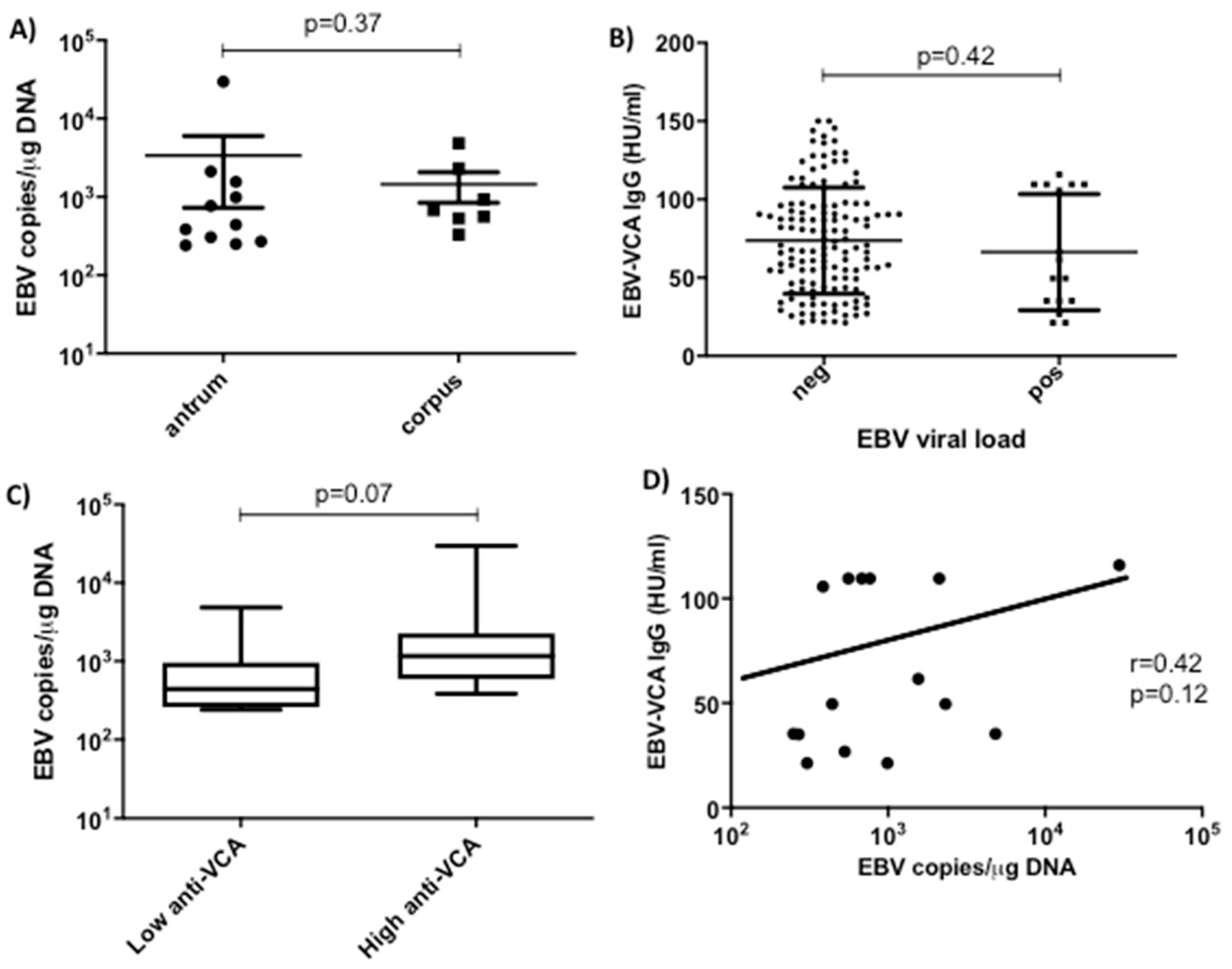
3.1. Screening of EBV DNA in Gastric Biopsies and Comparison with Systemic Anti-EBV Antibodies
3.2. Evaluation of Immune Cell Infiltration in EBV Positive Biopsies
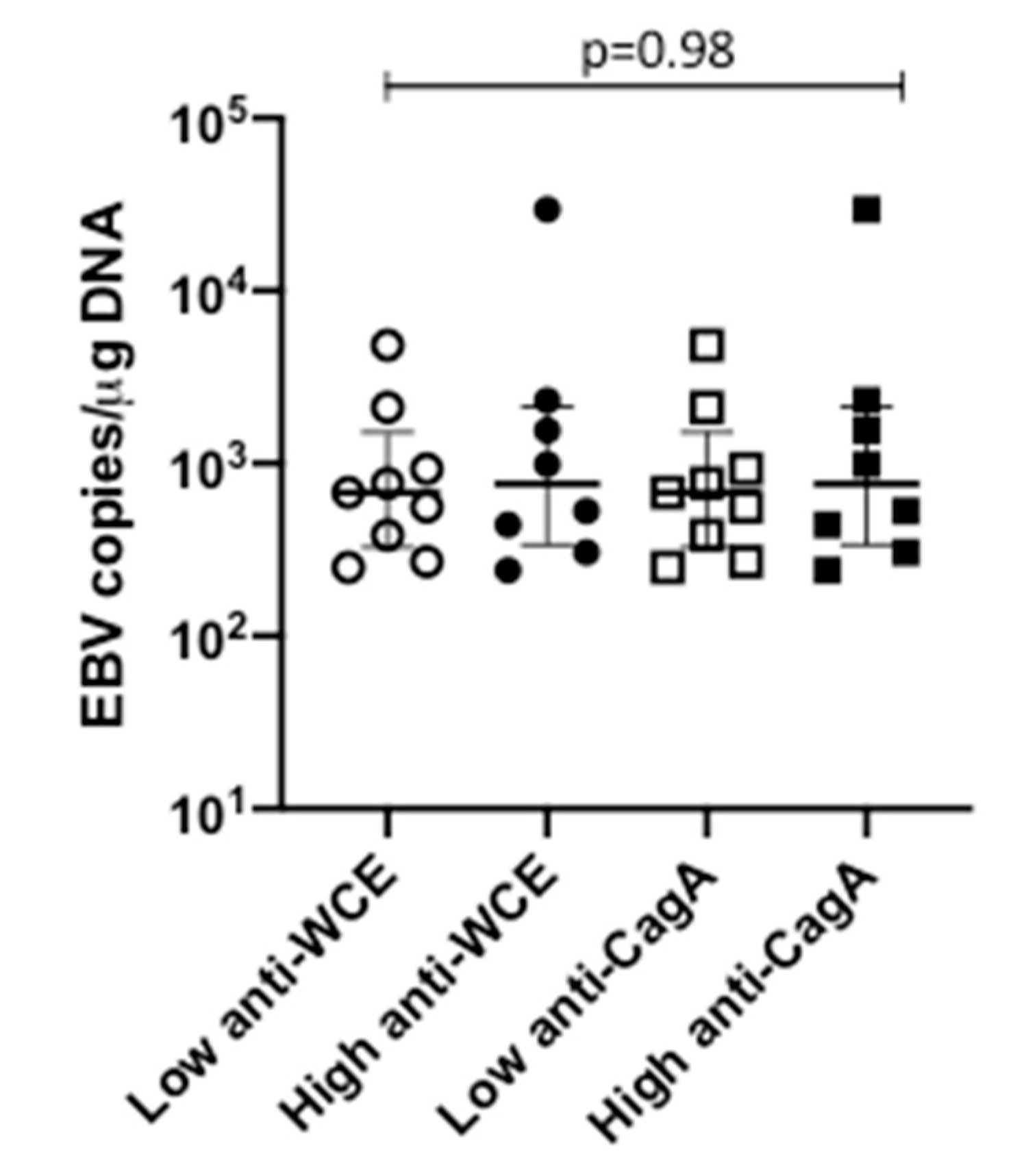
3.3. Hp Antibody Evaluation in Patients with EBV-Positive vs. Negative Gastric Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Correa, P.; Haenszel, W.; Cuello, C.; Tannenbaum, S.; Archer, M. A model for gastric cancer epidemiology. Lancet 1975, 2, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laichalk, L.L.; Hochberg, D.; Babcock, G.J.; Freeman, R.B.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. The dispersal of mucosal memory B cells: Evidence from persistent EBV infection. Immunity 2002, 16, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Mondragon, M.G.; Carreon-Talavera, R.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Gomez-Delgado, A.; Torres, J.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M. Epstein Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori co-infection are positively associated with severe gastritis in pediatric patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Mondragon, M.G.; Torres, J.; Flores-Luna, L.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Carreon-Talavera, R.; Gomez-Delgado, A.; Kasamatsu, E.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M. Case-control study of Epstein-Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori serology in Latin American patients with gastric disease. Br. J. Cancer 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Mondragon, M.G.; Torres, J.; Flores-Luna, L.; Carreon-Talavera, R.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M. Epstein-Barr virus association with peptic ulcer disease. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2015, 2015, 164840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Ponce, Y.; Varela-Fascinetto, G.; Romo-Vazquez, J.C.; Lopez-Martinez, B.; Sanchez-Huerta, J.L.; Parra-Ortega, I.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M.; Morales-Sanchez, A. Simultaneous Detection of Beta and Gamma Human Herpesviruses by Multiplex qPCR Reveals Simple Infection and Coinfection Episodes Increasing Risk for Graft Rejection in Solid Organ Transplantation. Viruses 2018, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Almaali, H.M.; Al-Khatabi, H.A.; Nasr-Allah, H.A.; Al-Khafaji, Z.M. Duplex PCR primers for detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA directly from gastric biopsy samples. Karbala J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2012, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Torres, J.; Perez-Perez, G.; Leal-Herrera, Y.; Gonzalez-Ortiz, B.; de la Madrazo Garza, A.; Gomez, A.; Munoz, O. Validation of a serologic test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and the immune response to urease and CagA in children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, S.K.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Granato, C.F.H.; Rohr, M.; Artigiani Neto, R.; Kawakami, E. Development and validation of a whole-cell ELISA for serologically diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection in Brazilian children and adults: A diagnostic accuracy study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2018, 136, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Neuhierl, B.; Baldwin, G.; Rickinson, A.; Delecluse, H.-J. Resting B cells as a transfer vehicle for Epstein–Barr virus infection of epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Young, L.; Niedobitek, G.; Dawson, C.; Birkenbach, M.; Wang, F.; Rickinson, A. Epstein–Barr virus infection and replication in a human epithelial cell system. Nature 1992, 356, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; Pang, P.S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, H.; Lo, K.W. The Biology of EBV Infection in Human Epithelial Cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Aviles-Jimenez, F.; Cabrera, L.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Munoz, O.; Soza, J.; Torres, J. Intensity of inflammation, density of colonization and interleukin-8 response in the gastric mucosa of children infected with Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2003, 8, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Perez-Perez, G.; Munoz, L.; Munoz, O. Specific serum immunoglobulin G response to urease and CagA antigens of Helicobacter pylori in infected children and adults in a country with high prevalence of infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Camargo, M.C.; Murphy, G.; Koriyama, C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Kim, W.H.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Corvalan, A.H.; Carrascal, E.; Abdirad, A.; Anwar, M.; et al. Determinants of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer: An international pooled analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, M.; Land, C.E.; Uemura, Y.; Tokudome, T.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, E. Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, H.; Nishikawa, J.; Mizugaki, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Takada, K.; Matsusaki, K.; Toda, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tada, M.; Okita, K. Endoscopic and pathologic features of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1997, 45, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lopez, J.L.; Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Mantilla, A.; Leal, Y.A.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M. Evidence of Epstein-Barr virus association with gastric cancer and non-atrophic gastritis. Viruses 2014, 6, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morilla, A.; Melon, S.; Alvarez-Arguelles, M.E.; Armesto, E.; Villar, H.; de Ona, M. Utility of normalized genome quantification of Helicobacter pylori in gastric mucosa using an in-house real-time polymerase chain reaction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, A.P.; Godfroid, E.; Fauconnier, A.; Burette, A.; Butzler, J.P.; Bollen, A.; Glupczynski, Y. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection by PCR: Comparison with other invasive techniques and detection of cagA gene in gastric biopsy specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton-Key, M.; Diss, T.C.; Isaacson, P.G. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in gastric biopsy and resection specimens. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syahniar, R.; Wahid, M.H.; Syam, A.F.; Yasmon, A. Detecting the Helicobacter pylori 16S rRNA Gene in Dyspepsia Patients Using Real-Time PCR. Acta Med. Indones. 2019, 51, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Qi, D.; Kang, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, W.; Hou, P.; Lu, J. Efficacy of real-time PCR-based detection of Helicobacter pylori infection and genotypic resistance-guided quadruple therapy as the first-line treatment for functional dyspepsia with Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur. J. Gastroen. Hepat. 2015, 27, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinette, K.M.; Gibney, K.M.; Proujansky, R.; Fawcett, P.T. Comparison of PCR and clinical laboratory tests for diagnosing H. pylori infection in pediatric patients. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oksanen, K.; Kainulainen, H.; Ruuska, T.; Maki, M.; Ashorn, M. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in Finnish children. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 1999, 28, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura-Etoh, J.; Gotoh, K.; Sato, R.; Ogata, M.; Kaku, N.; Fujioka, T.; Nishizono, A. Helicobacter pylori-associated oxidant monochloramine induces reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in gastric epithelial cells latently infected with EBV. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saju, P.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Hayashi, T.; Senda, Y.; Nagase, L.; Noda, S.; Matsusaka, K.; Funata, S.; Kunita, A.; Urabe, M.; et al. Host SHP1 phosphatase antagonizes Helicobacter pylori CagA and can be downregulated by Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Jha, H.C.; Shukla, S.K.; Shirley, M.K.; Robertson, E.S. Epigenetic Regulation of Tumor Suppressors by Helicobacter pylori Enhances EBV-Induced Proliferation of Gastric Epithelial Cells. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jha, H.C. Status of Epstein-Barr Virus Coinfection with Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2017, 2017, 3456264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.F.; Wang, D.K.; Yu, Y.L.; Guo, Y.Q.; Liang, J.S.; Cheng, W.M.; Zong, Y.S.; Chan, K.H.; Ng, S.P.; Wei, W.I.; et al. Sustained elevation of Epstein-Barr virus antibody levels preceding clinical onset of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachiroh, J.; Paramita, D.K.; Hariwiyanto, B.; Harijadi, A.; Dahlia, H.L.; Indrasari, S.R.; Kusumo, H.; Zeng, Y.S.; Schouten, T.; Mubarika, S.; et al. Single-assay combination of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) EBNA1- and viral capsid antigen-p18-derived synthetic peptides for measuring anti-EBV immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA antibody levels in sera from nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: Options for field screening. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.P.; Liao, X.C.; Qin, X. Diagnostic value of Epstein-Barr virus capsid antigen-IgA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, P.H.; Stemmermann, G.; Lennette, E.T.; Hildesheim, A.; Shibata, D.; Nomura, A. Elevated antibody titers to Epstein-Barr virus prior to the diagnosis of Epstein-Barr-virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 60, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A.J.; You, W.C.; Lennette, E.T.; Gail, M.T.; Rabkin, C.S. Association of Epstein-Barr virus antibody levels with precancerous gastric lesions in a high-risk cohort. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, L.; Camorlinga, M.; Hernandez, R.; Giono, S.; Ramon, G.; Munoz, O.; Torres, J. Immune and proliferative cellular responses to Helicobacter pylori infection in the gastric mucosa of Mexican children. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, C.R.; de Oliveira, K.S.; Ferraz, J.J.; Leal, M.F.; Calcagno, D.Q.; Seabra, A.D.; Khayat, A.S.; Montenegro, R.C.; Alves, A.P.; Assumpcao, P.P.; et al. Occurrence of Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infection in endoscopic and gastric cancer patients from Northern Brazil. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.E.; Kim, K.M.; Jung, H.L.; Shim, J.W.; Kim, D.S.; Shim, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.K. Acute Gastritis and Splenic Infarction Caused by Epstein-Barr Virus. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2018, 21, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Song, C.W.; Song, K.S.; Kim, J.Y. Acute gastritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in a child. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, S68–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Pang, A.; Chan, E.C.; Chu, K.M.; Shek, T.W.; Kwong, Y.L. Epstein-Barr virus-Related gastric adenocarcinoma: An early secondary cancer post hemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age (Years) Median (IQR) | 10 (6–13) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex N (%) | Male 93 (39.4%) Female 143 (60.6%) 1 | |||
| Positive Samples N (%) | p Value *** | Genome Copies/μg DNA Median (IQR) | ||
| EBV viral load in stomach * | Total | 18 (7.6) | 545 (311–975) | |
| Antrum | 11 (4.7) | 412.5 (265–1131) | ||
| Corpus | 7 (2.9) | 0.85 | 620 (480–1279) | |
| Hp PCR Positivity | Total | 50 (22.8) | ND | |
| Antrum | 34 (15.5) | ND | ||
| Corpus | 16 (7.3) | 0.42 | ND | |
| Positive samples N (%) | Antibody titers Median (IQR) | |||
| EBV Serology ** | VCA IgG | 95 (69.8) | 67 (42.8–95.2) | |
| VCA IgM | 10 (7.4) | <0.01 | ND | |
| Hp Serology ** | WCE IgG | 71 (52.2) | 1.53 (1.06–2.5) | |
| CagA IgG | 44 (32.3) | p = 0.03 | 3.76 (2.1–7.6) | |
| Gastric Tissues | Antrum n = 107 | Corpus n = 84 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV Viral Load Status in Gastric Mucosa | EBV Neg n = 100 | EBV Pos n = 7 | p Value ** | EBV Neg n = 81 | EBV Pos n = 3 | p Value ** | |
| Mononuclear cell Infiltration * N (%) | Absent | 6 (6) | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | ||
| Mild | 69 (69) | 4 (57) | 71 (88) | 3 (100) | |||
| Moderate | 17 (17) | 3 (43) | 8 (10) | 0 (0) | |||
| Severe | 8 (8) | 0(0) | 0.42 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| Polymorphonuclear cell Infiltration * N (%) | Absent | 71 (71) | 4 (57) | 67 (83) | 3 (100) | ||
| Mild | 15 (15) | 2 (29) | 12 (15) | 0 (0) | |||
| Moderate | 9 (9) | 1 (14) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | |||
| Severe | 5 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.51 | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| Anti-Hp Whole Extract (N) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | OR * (95% CI) | ||
| EBV viral load (N) | Neg | 87 | 92 | 1.6 (0.15–1.60) p = 0.20 |
| Pos | 11 | 6 | ||
| Anti-CagA (N) | ||||
| EBV viral load (N) | Neg | 88 | 91 | 0.68 (0.21–2.07) p = 0.45 |
| Pos | 10 | 7 | ||
| Biopsy | EBV Copies/μg DNA | EBV-VCA IgG (HU/mL) | Hp PCR | Hp-WCE IgG | Hp-CagA IgG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 240 | neg | pos | neg | neg |
| 2 a | 250 | 35.26 | neg | neg | neg |
| 3 | 270 | 35 | neg | neg | neg |
| 4 | 305 | 21.26 | pos | 1.2607 | 3.7933 |
| 5 | 330 | unknown | neg | neg | neg |
| 6 | 385 | 105.67 | neg | neg | neg |
| 7 b | 440 | 49.59 | neg | 1.9366 | neg |
| 8 | 530 | 26.8 | neg | neg | 1.816 |
| 9 c | 560 | 109.58 | neg | neg | neg |
| 10 d | 680 | 109.55 | neg | neg | neg |
| 11 c | 765 | 109.58 | neg | neg | neg |
| 12 | 930 | neg | neg | neg | neg |
| 13 | 990 | 21.31 | neg | 1.086 | neg |
| 14 | 1555 | 61.61 | pos | 1.3151 | 2.126 |
| 15 d | 2115 | 109.55 | neg | neg | neg |
| 16 b | 2325 | 49.59 | neg | 1.9366 | neg |
| 17 a | 4830 | 35.26 | neg | neg | neg |
| 18 | 29685 | 115.9 | pos | 2.2 | 2.935 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Sánchez, A.; Torres, J.; Cardenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Romo-González, C.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Flores-Luna, L.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Gastric Biopsies of Pediatric Patients with Dyspepsia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080623
Morales-Sánchez A, Torres J, Cardenas-Mondragón MG, Romo-González C, Camorlinga-Ponce M, Flores-Luna L, Fuentes-Pananá EM. Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Gastric Biopsies of Pediatric Patients with Dyspepsia. Pathogens. 2020; 9(8):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080623
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Sánchez, Abigail, Javier Torres, María G. Cardenas-Mondragón, Carolina Romo-González, Margarita Camorlinga-Ponce, Lourdes Flores-Luna, and Ezequiel M. Fuentes-Pananá. 2020. "Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Gastric Biopsies of Pediatric Patients with Dyspepsia" Pathogens 9, no. 8: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080623
APA StyleMorales-Sánchez, A., Torres, J., Cardenas-Mondragón, M. G., Romo-González, C., Camorlinga-Ponce, M., Flores-Luna, L., & Fuentes-Pananá, E. M. (2020). Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Gastric Biopsies of Pediatric Patients with Dyspepsia. Pathogens, 9(8), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080623





