Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Mango Grey Leaf Spot Disease in Sinaloa, Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
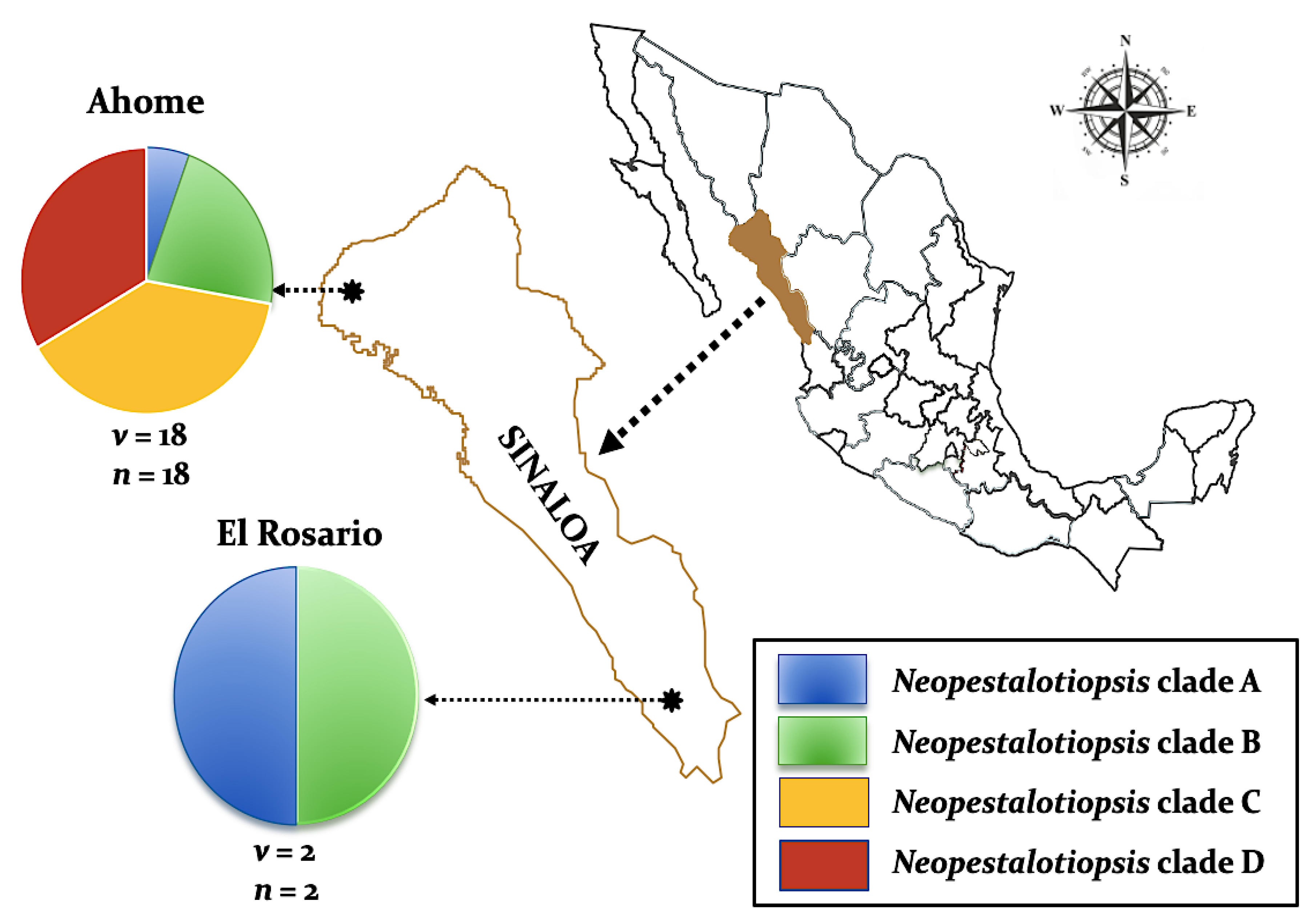
2.1. Fungal Isolates
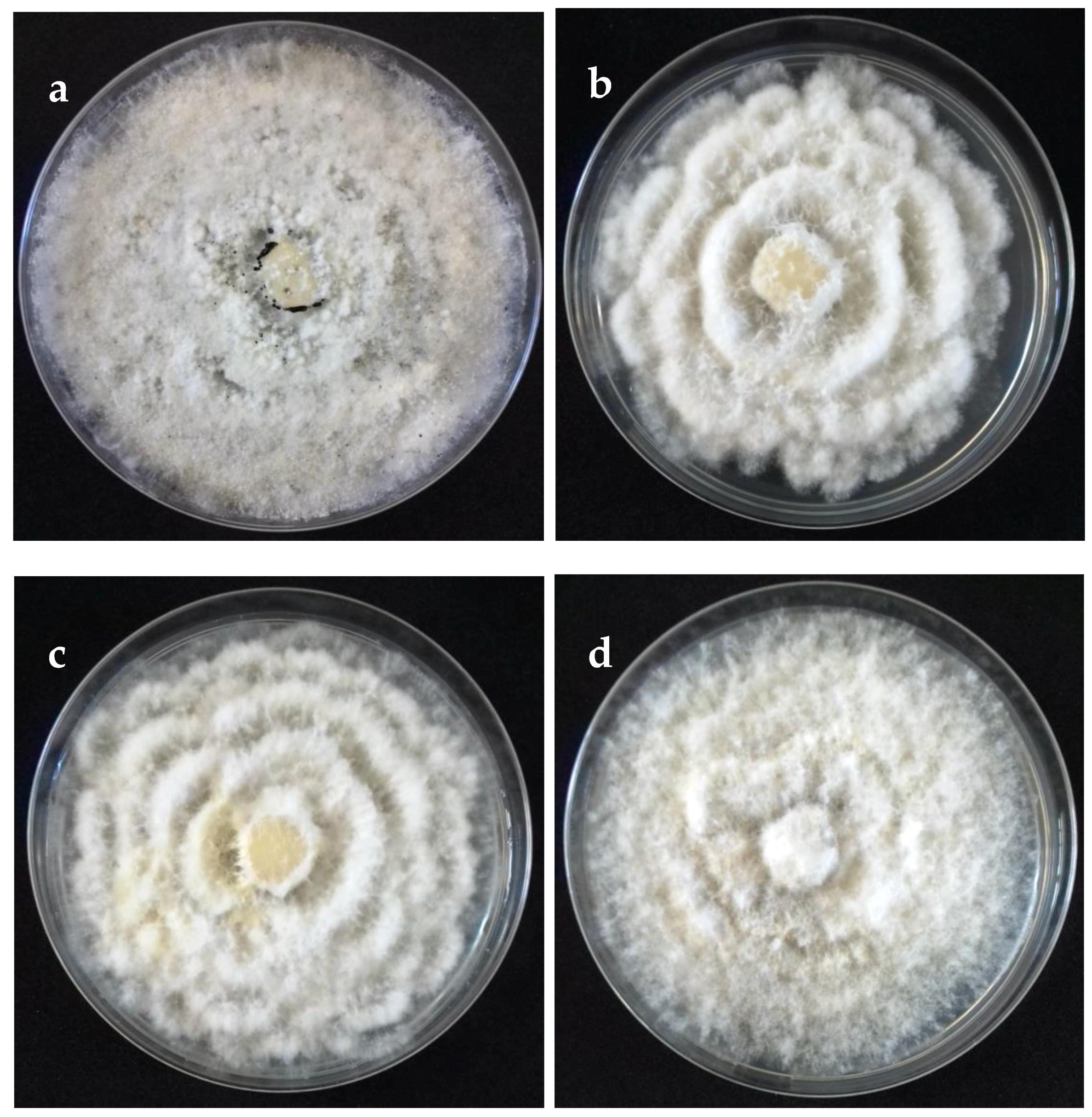
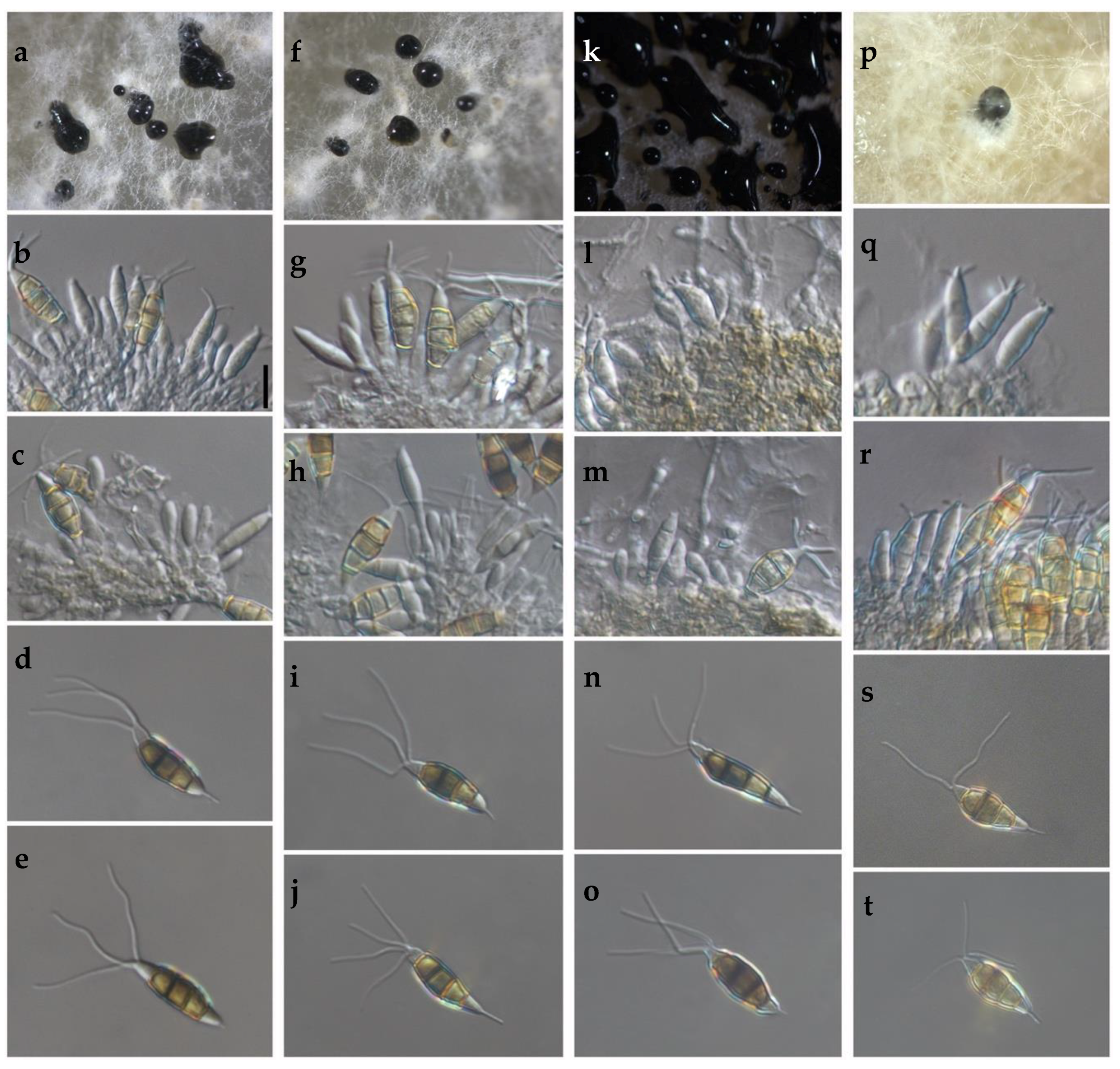
2.2. Morphological and Cultural Characteristics
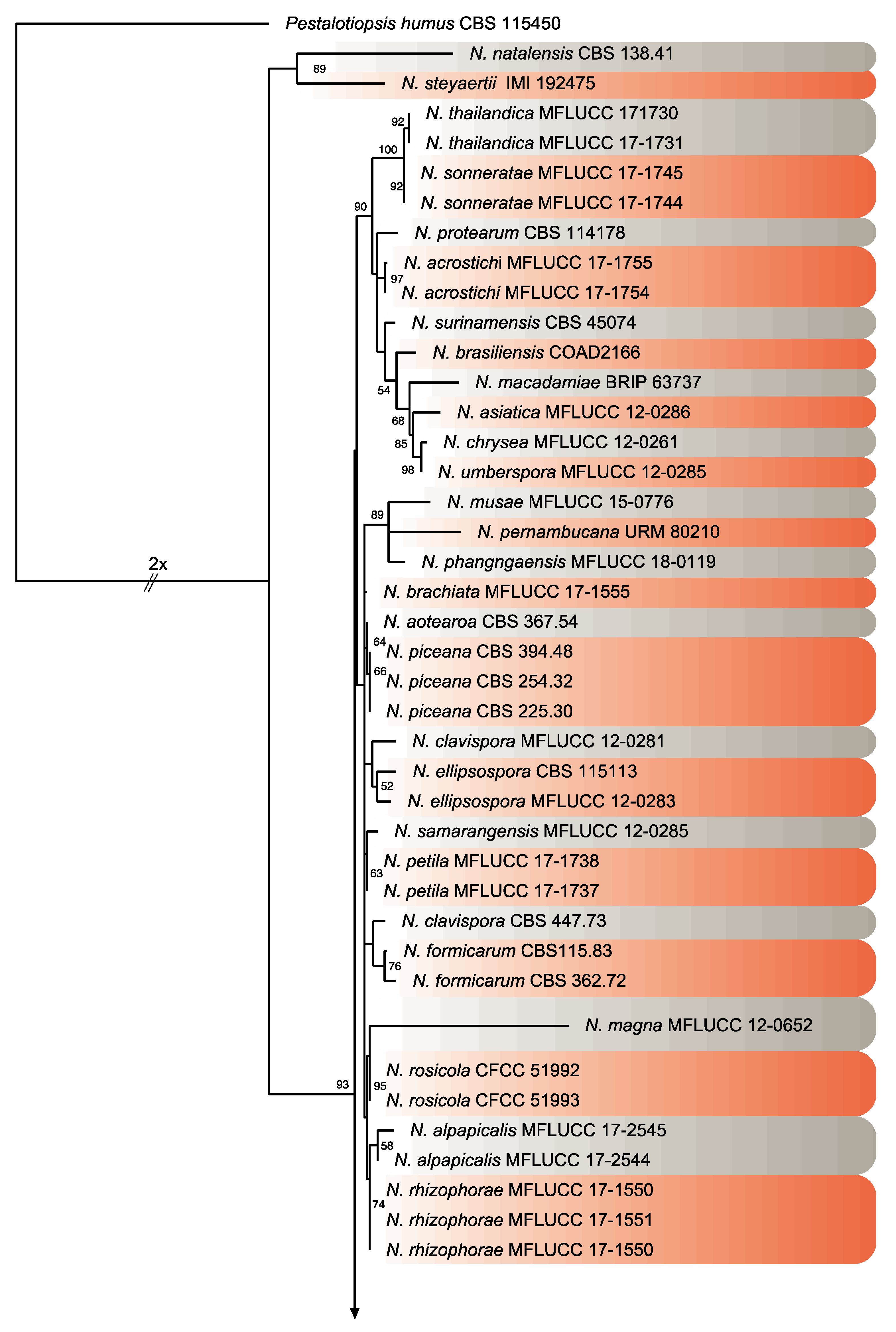
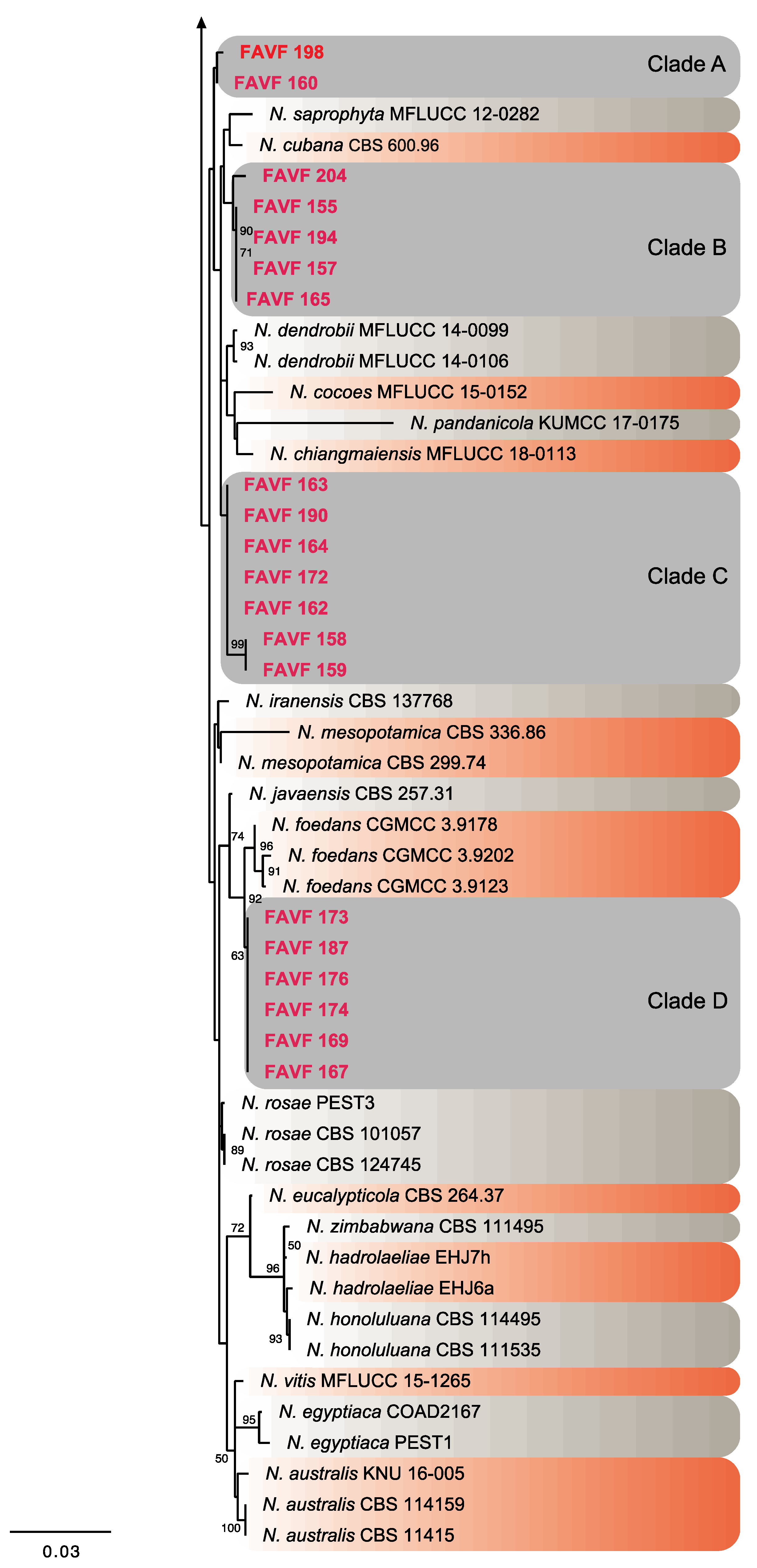
2.3. Phylogeny
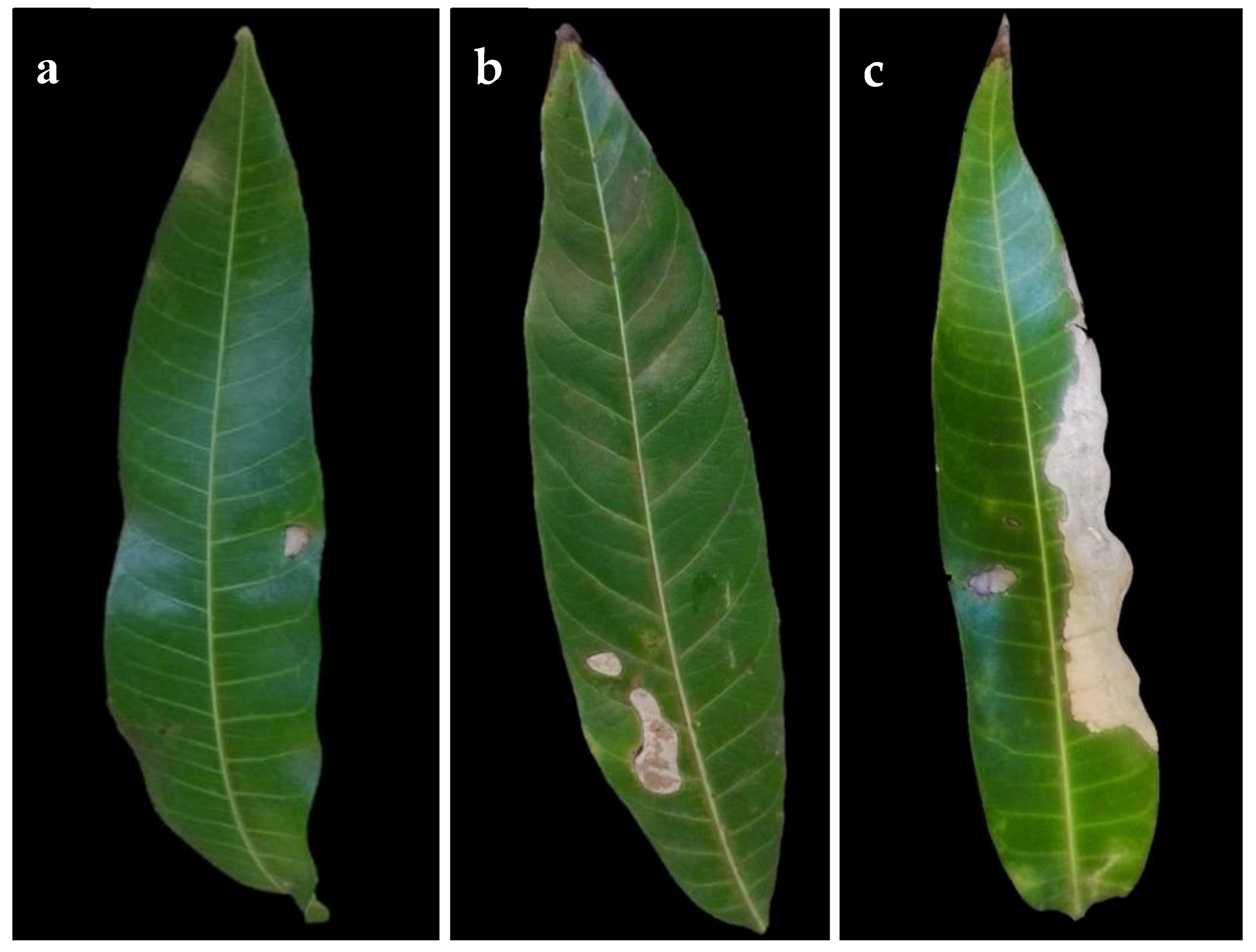
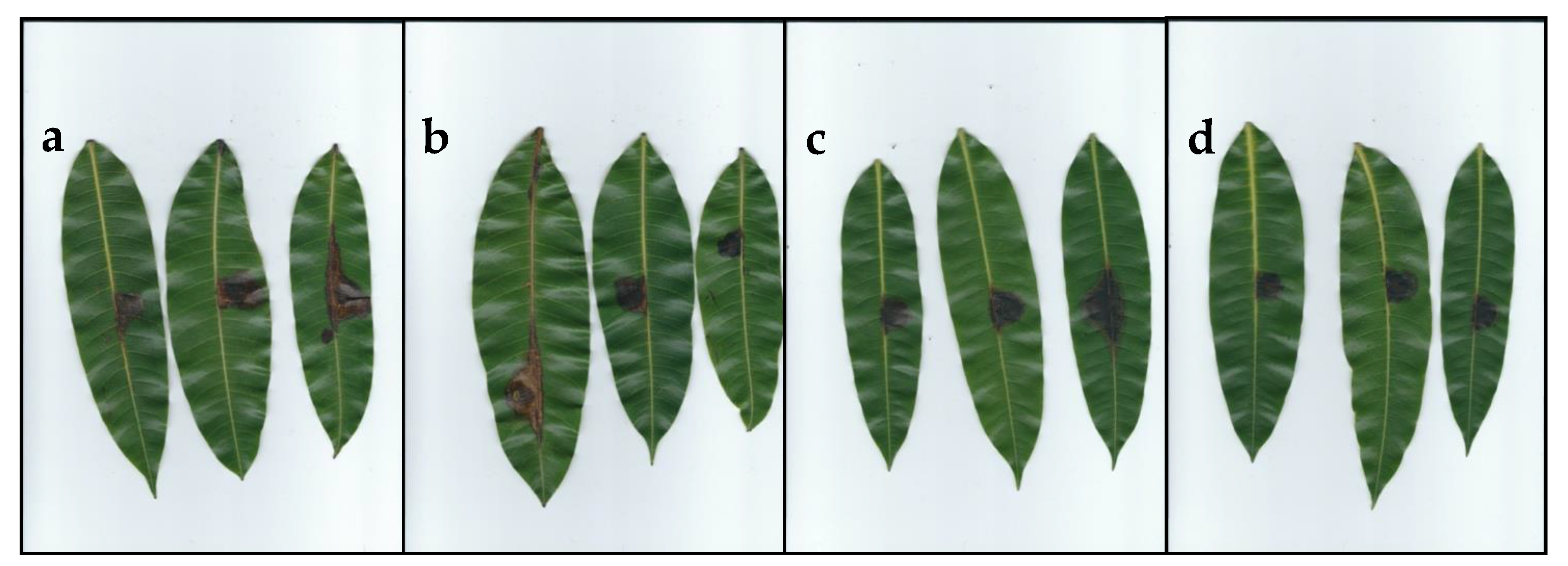
2.4. Pathogenicity and Virulence on Mango Leaves
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation and Purification
4.3. Morphological Characterization and Growth Rate
4.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
4.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
4.6. Pathogenicity and Virulence
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguirre-Güitrón, L.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Bautista-Rosales, P.U.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Application of powder formulation of Meyerozyma caribbica for postharvest control of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in mango (Mangifera indica L.). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 113, 108271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Karimi, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, A. Effects of postharvest polyamine application and edible coating on maintaining quality of mango (Mangifera indica L.) cv. Langra during cold storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Yang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Khan, A.; Cao, J.; Cheng, G. Purification and characterization of four benzophenone derivatives from Mangifera indica L. leaves and their antioxidant, immunosuppressive and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Garza, I.P.; Ramos-Parra, A.P.; Hernández-Brenes, C.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A. Effects of postharvest ripening on the nutraceutical and physicochemical properties of mango (Mangifera indica L. cv Keitt). Postharvest Biol. Tech. 2015, 103, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, G.; Abeywickrama, K.; Daranagama, A.; Kannangara, S. Morphological characterization and molecular identification of stem-end rot associated fungal species isolated from ‘Karutha Colomban’ mango fruits in Sri Lanka. J. Agric. Sci-Sri Lanka 2019, 14, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organizations of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca5692en/CA5692EN.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2019).
- SIAP. Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera. Producción Agrícola. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/siap/acciones-y-programas/produccion-agricola-33119 (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Ploetz, R.; Freeman, S. Foliar, floral and soilborne diseases. In The Mango: Botany, Production and Uses, 2nd ed.; Litz, R., Ed.; CAB International: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 209, 231–302. [Google Scholar]
- Otero-Colina, G.; Rodríguez-Alvarado, G.; Fernández-Pavía, S.; Maymon, S.M.; Ploetz, R.C.; Aoki, T. Identification and characterization of a novel etiological agent of mango malformation disease in Mexico, Fusarium mexicanum sp. nov. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Gastélum, R.; Herrera-Rodríguez, G.; Martínez-Valenzuela, C.; Longoria-Espinoza, R.M.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Espinosa-Matías, S. First report of powdery mildew (Pseudoidium anacardii) of mango trees in Sinaloa, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Sánchez, M.; Nieto-Ángel, D.; Sandoval-Islas, J.; Téliz-Ortiz, D.; Orozco-Santos, M.; Silva-Rojas, H.V. Fungi associated to stem-end rot and dieback of mango (Mangifera indica L.). Agrociencia 2013, 47, 1405–3195. [Google Scholar]
- Noriega-Cantú, D.; Téliz-Ortiz, D.; Mora-Aguilera, A.; Mora-Aguilera, G. Enfermedades del mango. In El Mango: Su Cultivo, Fitosanidad y Comercialización; Mora-Aguilera, G., Noriega-Cantú, D., Pérez-Barraza, M., Eds.; Colegio de Postgraduados: Texcoco, Edo. México, Mexico, 2017; pp. 146–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Pedraza, J.M.; Mora-Aguilera, J.A.; Nava-Díaz, C.; Lima, N.B.; Michereff, S.J.; Sandoval-Islas, J.S.; Leyva-Mir, S.G. Distribution and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species associated with mango anthracnose in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordue, J.E.M. Pestalotiopsis Mangiferae; Descriptions of pathogenic fungi and bacteria; Commonwealth Mycological Institute: Kew Bridge, UK, 1980; Volume 676, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.; Yao, K.; Chen, C.; Lin, C. First report of gray leaf spot of mango (Mangifera indica) caused by Pestalotiopsis mangiferae in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Cirvilleri, G.; Polizzi, G. Characterization and pathogenicity of Pestalotiopsis uvicola and Pestalotiopsis clavispora causing grey leaf spot of mango (Mangifera indica L.) in Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 135, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Laringnonl, P.; Hyde, K.D.; Al-Sady, A.; Liu, Z. Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Truncatella species associated with grapevine trunk diseases in France. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2016, 55, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Nilsson, R.H.; Alias, S.A.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Blair, J.E.; Cai, L.; Gorczak, M. One stop shop: Backbones trees for important phytopathogenic genera: I (2014). Fungal Divers. 2014, 67, 21–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; McKenzie, E.H.; Jeewon, R.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Perera, R.H.; Tennakoon, D.S. One stop shop III: Taxonomic update with molecular phylogeny for important phytopathogenic genera: 51–75 (2019). Fungal Divers. 2019, 98, 77–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Hyde, K.D. Identification and characterization of Pestalotiopsis-like fungi related to grapevine diseases in China. Fungal Biol. 2015, 119, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, N.; Soleimani, M.J. Morphological and molecular identification of Neopestalotiopsis asiatica causing leaf spot on sweet almond. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 98, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M.; Aguado, A.; De los Santos, B. First report of root and crown rot caused by Pestalotiopsis clavispora (Neopestalotiopsis clavispora) on strawberry in Spain. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Chen, M.; Zhong, C. First report of Pestalotiopsis microspora causing postharvest rot of kiwifruit in Hubei province, China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanmi, O.; Nisa, S.; Jeff-Ego, O.; Shivas, R.; Drenth, A. Dry flower disease of Macadamia in Australia caused by Neopestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. and Pestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. Plant Dis. 2017, 10, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarte, F.; Muñoz, C.G.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Álvarez, E. Diversity of Neopestalotiopsis and Pestalotiopsis spp., causal agents of guava scab in Colombia. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Ariyawansa, H.A. Molecular phylogeny, morphology and pathogenicity of Pseudopestalotiopsis species on Ixora in Taiwan. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okigbo, R.; Osuinde, M. Fungal leaf spot diseases of mango (Mangifera indica L.) in southeastern Nigeria and biological control with Bacillus subtilis. Plant Protect. Sci. 2003, 39, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis anacardiacearum sp. 29. nov. (Amphisphaeriaceae) has an intricate relationship with Penicillaria jocosatrix, the mango tip borer. Phytotaxa 2013, 99, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Wingfield, M.J.; Le Roux, J.J.; Richardson, D.M.; Strasberg, D.; Shivas, R.G.; Sonawane, M.S. Fungal Planet description sheets: 371–399. Persoonia 2015, 35, 264–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Cai, L.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wu, W.P.; Sun, X.; Hyde, K.D. A multi-locus backbone tree for Pestalotiopsis, with a polyphasic characterization of 14 new species. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hou, L.; Raza, M.; Cai, L. Pestalotiopsis and allied genera from Camellia, with description of 11 new species from China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozawa, S.; Seto, Y.; Watanabe, K. First report of leaf blight caused by Pestalotiopsis chamaeropis and Neopestalotiopsis sp. in Japanese andromeda. J. Gen. Plant. Pathol. 2019, 85, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Q.; Hao, H.; Zheng, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y. Diversity of Pestalotiopsis-like species causing gray blight disease of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in China, including two novel Pestalotiopsis species, and analysis of their pathogenicity. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2548–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belisário, R.; Aucique-Pérez, C.E.; Abreu, L.M.; Salcedo, S.S.; Oliveira, W.M.; Furtado, G.Q. Infection by Neopestalotiopsis spp. occurs on unwounded eucalyptus leaves and is favoured by long periods of leaf wetness. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Giraud, T.; Zhang, N.; Begerow, D.; Cai, G.; Shivas, R.G. The evolution of species concepts and species recognition criteria in plant pathogenic fungi. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Yu, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Tang, L.; Luo, S. Identification and characterization of pestalotioid fungi causing leaf spots on mango in southern China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.A.; Mehta, B.P.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Bavalgave, V.G. Fungicides for the management of gray leaf blight (Pestalotia anacardii) of mango. Int. J. Econ. Plants. 2019, 6, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaochan, N.; Pornsuriya, C.; Chairin, T.; Sunpapao, A. Roles of systemic fungicide in antifungal activity and induced defence responses in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) against leaf fall disease caused by Neopestalotiopsis cubana. Physiol. Mol. Plant P. 2020, 111, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippeshi, L.C.; Suryanarayana, V.; Naik, S.T. Survey and management of Pestalotiopsis leaf blight of Jatropha – a destructive new disease in Karnataka. Indian Phytopath. 2010, 63, 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevakumar, S.; Janardhana, G.R. First report of Pestalotiopsis species causing leaf spot of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in India. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevakumar, S.; Janardhana, G.R. First report on the association of Pestalotiopsis mangiferae with leaf blight disease of Canthium dicoccum in India. For. Pathol. 2014, 44, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Q.; Zhu, H.; Yu, F.Y.; Tang, Q.H.; Song, W.W.; Liu, L.; Qin, W.Q. First report of Pestalotiopsis menezesiana causing leaf blight of coconut in Hainan, China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.F.; Yang, X.; Gu, C.Y.; Kyaw, E.P. First report of Pestalotiopsis clavispora causing twig blight on highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) in Anhui province of China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, L.; Hughes, G.; van den Bosch, F. The Study of Plant Disease Epidemics; APS Press/American Phytopathological Society: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2007; No. SB731.M32. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, S.; Katan, T.; Shabi, E. Characterization of Colletotrichum species responsible for anthracnose disease of various fruits. Plant Dis. 1998, 82, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Hyde, K.D. A novel species of Pestalotiopsis causing leaf spots of Trachycarpus fortunei. Cryptogamie Mycol. 2012, 33, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, G.; Philippoussis, A.; Ioannidou, S.; Diamantopoulou, P. Mycelium growth kinetics and optimal temperature conditions for the cultivation of edible mushroom species on lignocellulosic substrates. Folia Microbiol. 2001, 46, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rienzo, J.A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, G.; González, L.; Tablada, M.; Robledo, W. InfoStat, Versión 2014; Grupo InfoStat.; FCA; Universidad Nacional de Córdoba: Córdoba, Argentina, 2014; Available online: http://www.infostat.com.ar (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- White, T.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M., Gelfand, D., Sninsky, J., White, T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, D.; Michalak, I. raxmlGUI: A graphical front-end for RAxML. Org. Divers. Evol. 2012, 12, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauceda-Acosta, C.P.; Lugo-García, G.A.; Villaseñor-Mir, H.E.; Partida-Ruvalcaba, L.; Reyes-Olivas, A. Un método preciso para medir severidad de roya de la hoja (Puccinia triticina Eriksson) en trigo. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2015, 38, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxon | Culture Code | Cultivar | Location | GeneBank Accession Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | TUB | TEF | ||||
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade A | FAVF 198 | Tommy Atkins | El Rosario | MT774584 | MT782088 | MT782108 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade A | FAVF 160 | Kent | Ahome | MT774581 | MT782085 | MT782105 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B | FAVF 204 | Kent | El Rosario | MT774583 | MT782087 | MT782107 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B | FAVF 155 | Kent | Ahome | MT774586 | MT782090 | MT782110 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B | FAVF 194 | Ataulfo | Ahome | MT774585 | MT782089 | MT782109 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B | FAVF 157 | Kent | Ahome | MT774587 | MT782091 | MT782111 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B | FAVF 165 | Ataulfo | Ahome | MT774582 | MT782086 | MT782106 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 163 | Kent | Ahome | MT774577 | MT782081 | MT782101 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 190 | Kent | Ahome | MT774579 | MT782083 | MT782103 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 164 | Kent | Ahome | MT774576 | MT782080 | MT782100 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 172 | Ataulfo | Ahome | MT774580 | MT782084 | MT782104 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 162 | Ataulfo | Ahome | MT774574 | MT782078 | MT782098 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 158 | Kent | Ahome | MT774575 | MT782079 | MT782099 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C | FAVF 159 | Kent | Ahome | MT774578 | MT782082 | MT782102 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 173 | Tommy Atkins | Ahome | MT774572 | MT782076 | MT782096 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 187 | Kent | Ahome | MT774568 | MT782072 | MT782092 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 176 | Kent | Ahome | MT774569 | MT782073 | MT782093 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 174 | Kent | Ahome | MT774570 | MT782074 | MT782094 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 169 | Kent | Ahome | MT774571 | MT782075 | MT782095 |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D | FAVF 167 | Kent | Ahome | MT774573 | MT782077 | MT782097 |
| Average Size (µm) of Conidia and Appendages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species w | Origin | Colony Type x | Length | Width | Length of Apical Appendages | Length of Basal Appendage | Number of Apical Appendages | Average Growth (mm day−1) y |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade A (FAVF 160 and FAVF 198) | Ahome, El Rosario | 1, 2 | 21.78 ± 1.61 A | 7.23 ± 0.55 A | 17.81 ± 2.54 A | 5.81 ± 1.31 B | 2–3 | 2.77 ± 0.06 B |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade B (FAVF 155, FAVF 157, FAVF 165, FAVF 194, and FAVF 204) | Ahome, El Rosario | 1, 4 | 20.93 ± 1.86 A | 7.71 ± 0.80 B | 18.95 ± 3.68 A | 6.89 ± 1.66 C | 2–3 | 2.12 ± 0.16 A |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade C (FAVF 158, FAVF 159, FAVF 162, FAVF 163, FAVF 164, FAVF 172 and FAVF 190) | Ahome | 1, 3 | 21.20 ± 1.92 A | 7.81 ± 0.99 B | 21.21 ± 4.71 B | 4.77 ± 1.36 A | 2–4 | 2.40 ± 0.23 AB |
| Neopestalotiopsis sp. Clade D (FAVF 167, FAVF 169, FAVF 173, FAVF 174, FAVF 176 and FAVF 187) | Ahome | 1, 2, 4 | 23.29 ± 2.09 B | 7.13 ± 0.61 A | 18.35 ± 3.35 A | 5.24 ± 1.06 B | 2–4 | 2.48 ± 0.19 AB |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerardo-Lugo, S.S.; Tovar-Pedraza, J.M.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Apodaca-Sánchez, M.A.; Correia, K.C.; Sauceda-Acosta, C.P.; Camacho-Tapia, M.; Hyde, K.D.; Marraiki, N.; Elgorban, A.M.; et al. Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Mango Grey Leaf Spot Disease in Sinaloa, Mexico. Pathogens 2020, 9, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100788
Gerardo-Lugo SS, Tovar-Pedraza JM, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Apodaca-Sánchez MA, Correia KC, Sauceda-Acosta CP, Camacho-Tapia M, Hyde KD, Marraiki N, Elgorban AM, et al. Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Mango Grey Leaf Spot Disease in Sinaloa, Mexico. Pathogens. 2020; 9(10):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100788
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerardo-Lugo, Saida S., Juan M. Tovar-Pedraza, Sajeewa S. N. Maharachchikumbura, Miguel A. Apodaca-Sánchez, Kamila C. Correia, Carlos P. Sauceda-Acosta, Moisés Camacho-Tapia, Kevin D. Hyde, Najat Marraiki, Abdallah M. Elgorban, and et al. 2020. "Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Mango Grey Leaf Spot Disease in Sinaloa, Mexico" Pathogens 9, no. 10: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100788
APA StyleGerardo-Lugo, S. S., Tovar-Pedraza, J. M., Maharachchikumbura, S. S. N., Apodaca-Sánchez, M. A., Correia, K. C., Sauceda-Acosta, C. P., Camacho-Tapia, M., Hyde, K. D., Marraiki, N., Elgorban, A. M., & Beltrán-Peña, H. (2020). Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Mango Grey Leaf Spot Disease in Sinaloa, Mexico. Pathogens, 9(10), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100788






