Identification of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication Proteins in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
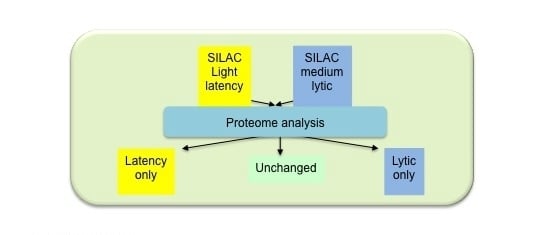
2.1. Isolation of Proteins in Cells Undergoing EBV Lytic Cycle
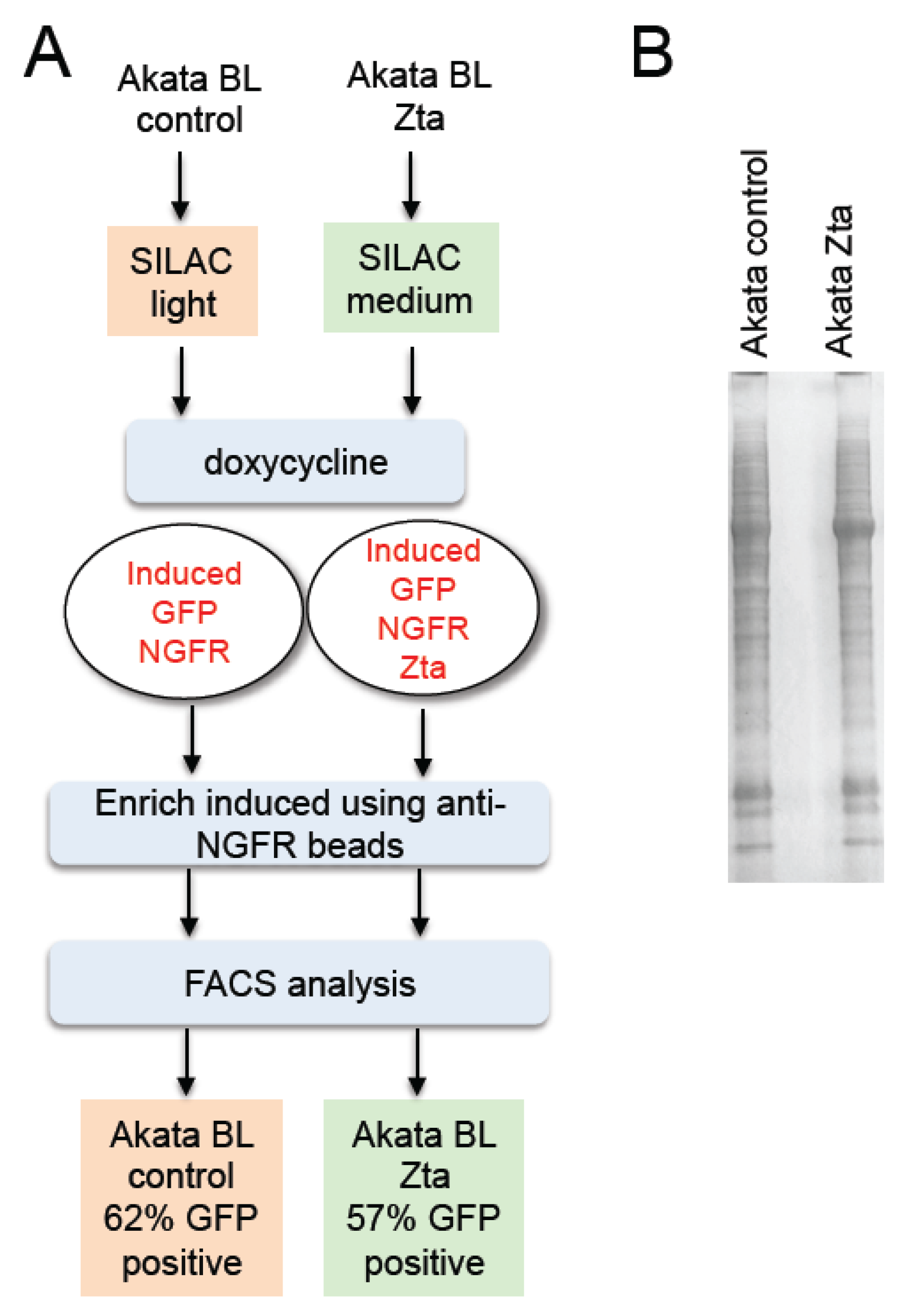
2.2. Identification of Proteins in Cells Undergoing EBV Lytic Cycle
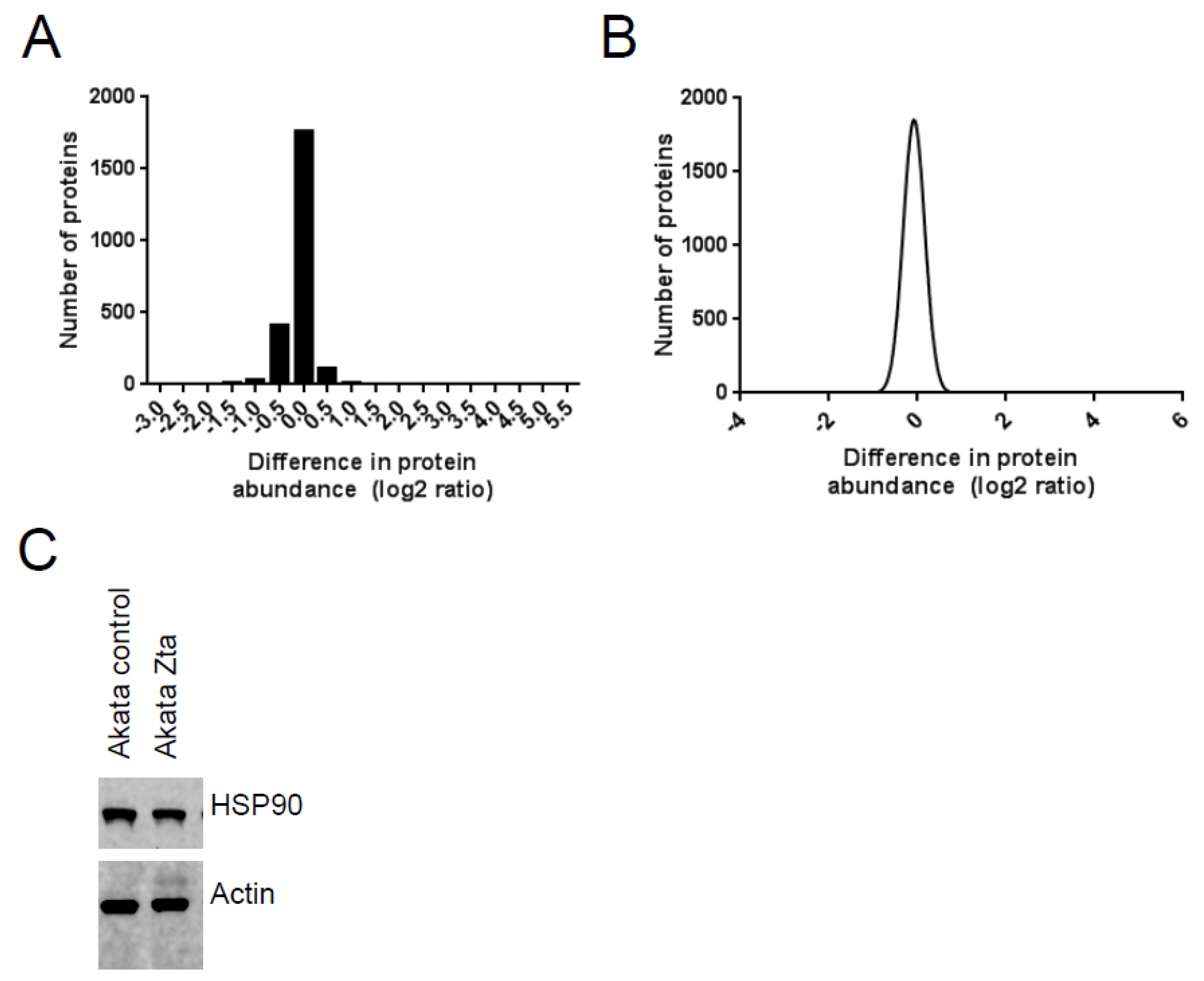
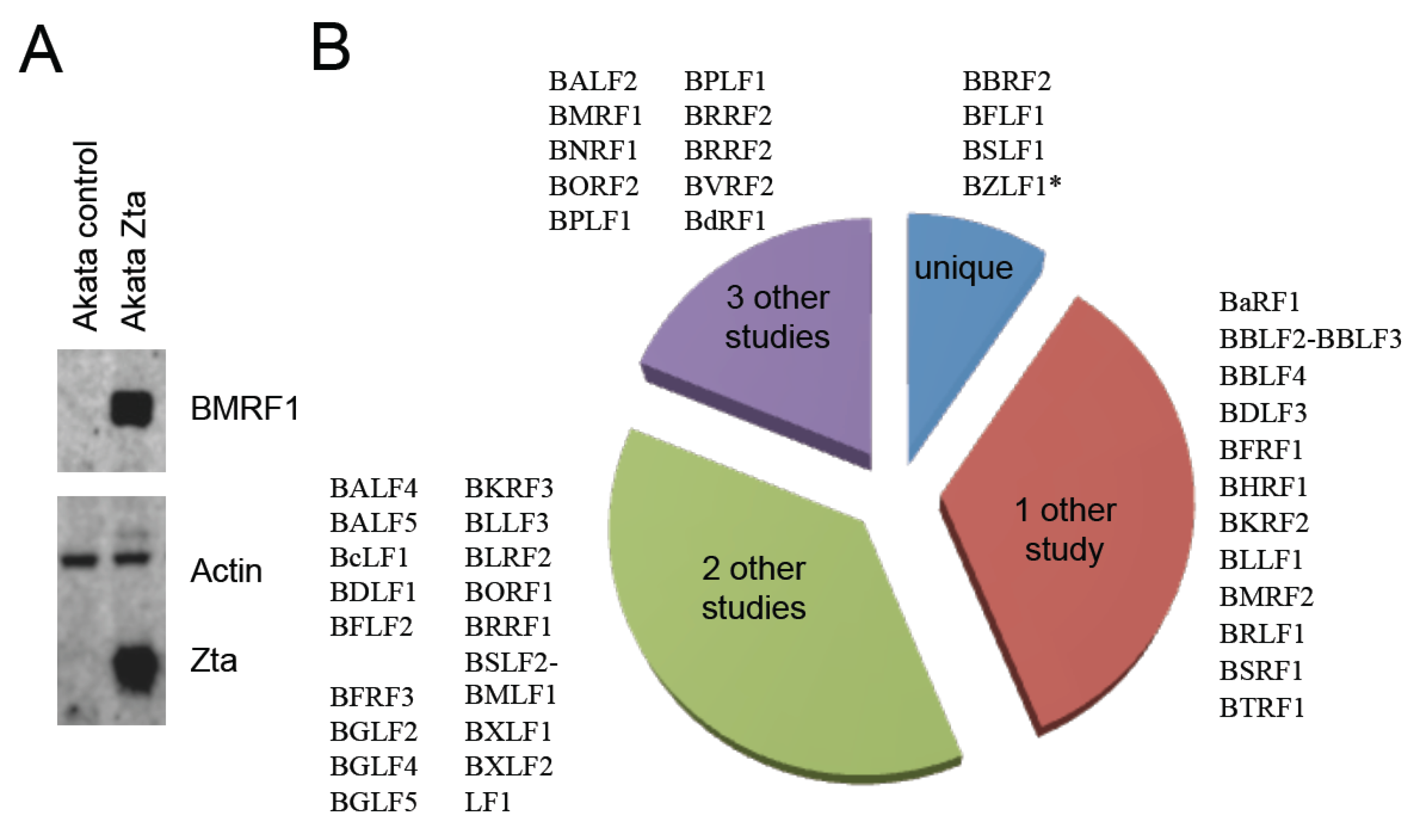
2.3. Identification of EBV Proteins
| Gene | Function |
|---|---|
| BALF2 | Major DNA-binding protein |
| BALF4 | Envelope glycoprotein B |
| BALF5 | DNA polymerase catalytic subunit |
| BaRF1 | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase small chain |
| BBLF2-BBLF3 | primase protein |
| BBLF4 | DNA replication helicase |
| BBRF2 | Virion egress protein UL7 homolog |
| BcLF1 | Major capsid protein |
| BDLF1 | Triplex capsid protein VP23 homolog |
| BFLF1 | Packaging protein UL32 homolog |
| BFLF2 | Virion egress protein |
| BFRF1 | Virion egress protein UL34 homolog |
| BFRF3 | Capsid protein VP26 |
| BGLF2 | Capsid-binding protein |
| BGLF4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| BGLF5 | Shutoff alkaline exonuclease |
| BHRF1 | Apoptosis regulator |
| BKRF3 | Uracil-DNA glycosylase |
| BLLF3 | Deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase |
| BLRF2 | Tegument protein |
| BSLF2-BMLF1 | mRNA export factor ICP27 homolog |
| BMRF1 | DNA polymerase processivity factor |
| BNRF1 | Major tegument protein |
| BORF2 | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase large subunit |
| BPLF1 | Deneddylase |
| BRRF1 | Transcriptional activator |
| BRRF2 | Tegument protein |
| BSRF1 | Tegument protein UL51 homolog |
| BTRF1 | Uncharacterized protein BTRF1 |
| BVRF2 | Capsid scaffolding protein |
| BdRF1 | |
| BXLF1 | Thymidine kinase |
| BZLF1 * | Trans-activator protein |
| BDLF3 | pg85 |
| BLLF1 | gp350 |
| BMRF2 | Protein BMRF2 |
| BORF1 | Triplex capsid protein |
| BPLF1 | deneddylase |
| BRLF1 | Replication and transcription factor |
| BRRF2 | tegument protein |
| BSLF1 | DNA primase |
| gH | gH |
| gL | gL |
| LF1 | LF1 |
| Gene Name | Modification | pep_seq | aa of EBV Protein | Residue of Modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BALF5 | N terminal acetylation | [ac]SGGLFYNPFLRPNK | 2–15 | 2 |
| BLLF3 | N terminal acetylation | [ac]MEACPHIR | 9–16 | 9 |
| BLRF2 | Phosphorylation | GQPS[ph]PGEGTRPR | 124–135 | 127 |
| BMRF1 | 2 Phosphorylation | HTVS[ph]PSPS[ph]PPPPPR | 330–343 | 333 and 337 |
| BMRF2 | N terminal acetylation | [ac]METTQTLR | 1–8 | 1 |
| BORF1 | Phosphorylation | RLNIS[ph]R | 26–31 | 30 |
| BORF2 | N terminal acetylation | [ac]ATTSHVEHELLSK | 2–14 | 2 |
| BXLF1 | Phosphorylation | TQAAVTSNTGNS[ph]PGSR | 86–101 | 97 |
| BZLF1 | N terminal acetylation | [ac]MMDPNSTSEDVK | 1–12 | 1 |
2.4. Identification of Post-Translational Modifications of EBV Proteins
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. FACS Analysis
3.3. Western Blot Analysis
3.4. Mass Spectrometry Collection and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longnecker, R.; Kieff, E.; Cohen, J.I. Epstein-barr virus/replication and Epstein-Barr virus. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Lippencott, Williams, Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, M.; Kelly, G.L.; Bell, A.I.; Rickinson, A.B. Burkitt’s lymphoma: The rosetta stone deciphering Epstein-Barr virus biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, M.J.; Xu, G.; Coco, J.; Baribault, C.; Vinay, D.S.; Lacey, M.R.; Strong, A.L.; Lehman, T.A.; Seddon, M.B.; Lin, Z.; et al. Differences in gastric carcinoma microenvironment stratify according to EBV infection intensity: Implications for possible immune adjuvant therapy. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Z.; Chen, H.; Castro, F.A.; Hu, J.K.; Brenner, H. Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review. Medicine 2015, 94, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kunita, A.; Fukayama, M. Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppers, R. The biology of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vockerodt, M.; Cader, F.Z.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Murray, P. Epstein-barr virus and the origin of Hodgkin lymphoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, M.A. Acute effects of inhaled sulphur dioxide on pig nasal vascular and airway resistances. Acta physiol. Sinica 2014, 66, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.T. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. ESMO 2010, 21, vii308–vii312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R.; Bankier, A.T.; Biggin, M.D.; Deninger, P.D.; Farrell, P.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Hatfull, G.; Hudson, G.S.; Satchwell, S.C.; Seguin, C.; et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 1984, 310, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grady, T.; Cao, S.; Strong, M.J.; Concha, M.; Wang, X.; Splinter Bondurant, S.; Adams, M.; Baddoo, M.; Srivastav, S.K.; Lin, Z.; et al. Global bidirectional transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus genome during reactivation. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, M.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Baddoo, M.; Fewell, C.; Lin, Z.; Hulme, W.; Hedges, D.; McBride, J.; Flemington, E.K. Identification of new viral genes and transcript isoforms during Epstein-Barr virus reactivation using RNA-Seq. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, R.J.; Shannon-Lowe, C.D.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Bell, A.I.; Rowe, M. Unexpected patterns of Epstein-Barr virus transcription revealed by a high throughput PCR array for absolute quantification of viral mrna. Virology 2015, 474, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Ramos, J.C.; Mian, A.M.; Toomey, N.L.; Cabral, L.; Whitby, D.; Barber, G.N.; Dittmer, D.P.; Harrington, W.J., Jr. Azidothymidine inhibits nf-kappab and induces Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2005, 106, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.J. Epstein-barr virus genome. In Epstein-Barr Virus; Robertson, E.S., Ed.; Caister: Wymondham, UK, 2005; pp. 263–288. [Google Scholar]
- Feederle, R.; Kost, M.; Baumann, M.; Janz, A.; Drouet, E.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Delecluse, H.J. The Epstein-Barr virus lytic program is controlled by the co-operative functions of two transactivators. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruffat, H.; Batisse, J.; Pich, D.; Neuhierl, B.; Manet, E.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Sergeant, A. Epstein-Barr virus mrna export factor eb2 is essential for production of infectious virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9635–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhierl, B.; Delecluse, H.J. The Epstein-Barr virus bmrf1 gene is essential for lytic virus replication. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5078–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.; Feederle, R.; Raffa, S.; Gonnella, R.; Santarelli, R.; Frati, L.; Angeloni, A.; Torrisi, M.R.; Faggioni, A.; Delecluse, H.J. Bfrf1 of Epstein-Barr virus is essential for efficient primary viral envelopment and egress. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3703–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, M.; Feederle, R.; Farina, A.; Gonnella, R.; Santarelli, R.; Hub, B.; Faggioni, A.; Delecluse, H.J. Deletion of Epstein-Barr virus bflf2 leads to impaired viral DNA packaging and primary egress as well as to the production of defective viral particles. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, S.; Feederle, R.; Gartner, K.; Fuchs, W.; Granzow, H.; Delecluse, H.J. An Epstein-Barr virus mutant produces immunogenic defective particles devoid of viral DNA. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Isomura, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Toyama, S.; Sato, Y.; Nakayama, S.; Kudoh, A.; Iwahori, S.; Kanda, T.; Tsurumi, T. Efficient production of infectious viruses requires enzymatic activity of Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase. Virology 2009, 389, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guindy, A.; Lopez-Giraldez, F.; Delecluse, H.J.; McKenzie, J.; Miller, G. A locus encompassing the Epstein-Barr virus bglf4 kinase regulates expression of genes encoding viral structural proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feederle, R.; Bannert, H.; Lips, H.; Muller-Lantzsch, N.; Delecluse, H.J. The Epstein-Barr virus alkaline exonuclease bglf5 serves pleiotropic functions in virus replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4952–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feederle, R.; Mehl-Lautscham, A.M.; Bannert, H.; Delecluse, H.J. The Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase bglf4 and the exonuclease bglf5 have opposite effects on the regulation of viral protein production. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10877–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, A.; Oezel, M.; Kurzeder, C.; Mautner, J.; Pich, D.; Kost, M.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Delecluse, H.J. Infectious Epstein-Barr virus lacking major glycoprotein bllf1 (gp350/220) demonstrates the existence of additional viral ligands. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10142–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feederle, R.; Neuhierl, B.; Baldwin, G.; Bannert, H.; Hub, B.; Mautner, J.; Behrends, U.; Delecluse, H.J. Epstein-Barr virus bnrf1 protein allows efficient transfer from the endosomal compartment to the nucleus of primary B lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9435–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhierl, B.; Feederle, R.; Adhikary, D.; Hub, B.; Geletneky, K.; Mautner, J.; Delecluse, H.J. Primary B-cell infection with a deltabalf4 Epstein-Barr virus comes to a halt in the endosomal compartment yet still elicits a potent cd4-positive cytotoxic T-cell response. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4616–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, N.P.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Bell, A.I.; Horst, D.; Kremmer, E.; Ressing, M.E.; Wiertz, E.J.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Rowe, M.; Rickinson, A.B.; et al. Stage-specific inhibition of mhc class i presentation by the Epstein-Barr virus bnlf2a protein during virus lytic cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Tsurumi, T. Genome guardian p53 and viral infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsen, E.; Luftig, M.; Chase, M.R.; Weicksel, S.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Illanes, D.; Sarracino, D.; Kieff, E. Proteins of purified Epstein-Barr virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16286–16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresang, L.R.; Teuton, J.R.; Feng, H.; Jacobs, J.M.; Camp, D.G., 2nd; Purvine, S.O.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Li, Z.; Smith, R.D.; Sugden, B.; et al. Coupled transcriptome and proteome analysis of human lymphotropic tumor viruses: Insights on the detection and discovery of viral genes. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koganti, S.; Clark, C.; Zhi, J.; Li, X.; Chen, E.I.; Chakrabortty, S.; Hill, E.R.; Bhaduri-McIntosh, S. Cellular stat3 functions via pcbp2 to restrain ebv lytic activation in B lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5002–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.M.; Thomas, W.A.; Haigh, T.A.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Long, H.M.; Hislop, A.D.; Taylor, G.S.; Rowe, M. Epstein-barr virus evades cd4(+) t cell responses in lytic cycle through bzlf1-mediated downregulation of cd74 and the cooperation of vbcl-2. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasubramanyan, S.; Osborn, K.; Al-Mohammad, R.; Naranjo Perez-Fernandez, I.B.; Zuo, J.; Balan, N.; Godfrey, A.; Patel, H.; Peters, G.; Rowe, M.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor zta acts through distal regulatory elements to directly control cellular gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 3563–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, W.S. Mass spectrometrists should search only for peptides they care about. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Lau, R.; Rowe, M.; Niedobitek, G.; Packham, G.; Shanahan, F.; Rowe, D.T.; Greenspan, D.; Greenspan, J.S.; Rickinson, A.B.; et al. Differentiation-associated expression of the Epstein-Barr virus bzlf1 transactivator protein in oral hairy leukoplakia. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, V.C.; Barker, G.; Heesom, K.J.; Fan, J.; Bessant, C.; Matthews, D.A. De novo derivation of proteomes from transcriptomes for transcript and protein identification. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thermo Scientific. Xcalibur Software v2.1. Available online: http://www.thermoscientific.com/content/tfs/en/product/xcalibur-software.html (accessed on 23 October 2015).
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Rios, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. Proteomexchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roller, R.J.; Fetters, R. The herpes simplex virus 1 ul51 protein interacts with the ul7 protein and plays a role in its recruitment into the virion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, C.; Weller, S.K. The herpes simplex virus type 1 cleavage/packaging protein, ul32, is involved in efficient localization of capsids to replication compartments. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fixman, E.D.; Hayward, G.S.; Hayward, S.D. Trans-acting requirements for replication of Epstein-Barr virus ori-lyt. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fixman, E.D.; Hayward, G.S.; Hayward, S.D. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus orilyt: Lack of a dedicated virally encoded origin-binding protein and dependence on Zta in cotransfection assays. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2998–3006. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnesen, T. Towards a functional understanding of protein N-terminal acetylation. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.W.; Chang, S.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Chao, Y.H.; Chen, M.R. Effect of phosphorylation on the transactivation activity of Epstein-Barr virus bmrf1, a major target of the viral bglf4 kinase. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traylen, C.; Ramasubramanyan, S.; Zuo, J.; Rowe, M.; Almohammad, R.; Heesom, K.; Sweet, S.M.M.; Matthews, D.A.; Sinclair, A.J. Identification of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication Proteins in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells. Pathogens 2015, 4, 739-751. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4040739
Traylen C, Ramasubramanyan S, Zuo J, Rowe M, Almohammad R, Heesom K, Sweet SMM, Matthews DA, Sinclair AJ. Identification of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication Proteins in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells. Pathogens. 2015; 4(4):739-751. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4040739
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraylen, Chris, Sharada Ramasubramanyan, Jianmin Zuo, Martin Rowe, Rajaei Almohammad, Kate Heesom, Steve M. M. Sweet, David A. Matthews, and Alison J. Sinclair. 2015. "Identification of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication Proteins in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells" Pathogens 4, no. 4: 739-751. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4040739
APA StyleTraylen, C., Ramasubramanyan, S., Zuo, J., Rowe, M., Almohammad, R., Heesom, K., Sweet, S. M. M., Matthews, D. A., & Sinclair, A. J. (2015). Identification of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication Proteins in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells. Pathogens, 4(4), 739-751. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4040739