Abstract
Worldwide, colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most common cancer and the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths. The inflammatory response initiated by pathogens, environmental and dietary factors, and inflammatory bowel diseases can promote the formation of colorectal tumors. The hygiene hypothesis proposes an inverse link between inflammatory diseases and early childhood exposure to pathogens, with a significant negative correlation between chronic inflammatory diseases and helminth infections. On the other hand, it is also known that several pathogens may influence or even cause the development of cancer, including helminth infections. How do helminth infections influence CRC outcomes? The existing literature presents two different perspectives. Experimental studies in CRC models suggest that helminths may accelerate disease progression and lead to worse outcomes (such as Schistosoma and Trichuris sp.), while others indicate that helminths could help reduce tumor burden (such as Taenia sp.). This review focuses on helminths’ pro- and anti-tumorigenic effects and their derivatives, specifically in CRC. We provide a comprehensive understanding of how helminths impact the macroscopic, histopathological, immunological, and molecular aspects of CRC.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks as the third-most common cancer globally and stands as the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The incidence of CRC is rising among individuals younger than 50, particularly in high-income countries. This increase is associated with some risk factors, such as obesity, sedentary habits, and the consumption of antibiotics, red meats, alcohol, and tobacco. Another important factor is gut inflammation, such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC), that represent up to 18% increased risk of developing CRC [1,2].
The etiological origin of CRC can be categorized into three main types: hereditary cases, which account for 10% of all occurrences; familial history-related cases, comprising 25%; and sporadic cases, which represent 65% [3]. Currently, five genetic risk factors have been identified for hereditary CRC cases. These include early-onset CRC, a family history of cancer, deficient mismatch repair, multiple primary CRC tumors, and primary hereditary cancer syndrome associated with extra-colonic cancer. Each of these factors predisposes individuals to specific germline mutations, which can affect the clinicopathological phenotype, the family cancer spectrum, cancer penetrance, and long-term prognosis [4].
Colorectal tumors are classified in four consensus molecular subtypes (CMSs): (1) CMS1: hypermutated tumors characterized by microsatellite instability and strong immune activation, (2) CMS2: tumors exhibiting high levels of somatic copy number mutations and activation of the wingless-related integration site (WNT) and myelocytomatosis (MYC) signaling pathways, (3) CMS3: tumors demonstrating metabolic deregulation, and (4) CMS4: tumors associated with a mesenchymal phenotype, stromal infiltration, angiogenesis, activation of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway, and a strong inflammatory response [5].
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of cancer that drives tumorigenesis and tumor progression [6]. The inflammatory response initiated by pathogens, environmental and dietary factors, and IBD can promote the formation of colorectal tumors [7,8,9]. The accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) released by immune infiltrating cells, particularly neutrophils, leads to DNA mutations in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) [10]. Furthermore, the disruption of the intestinal barrier and the invasion of microbiota activate inflammatory factors associated with tumor progression, including the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB), interleukin (IL) 6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2)/prostaglandin E2, and IL-23/T helper (Th) 17 signaling pathways [11].
The hygiene hypothesis proposes that a lack of exposure to microorganisms, mainly pathogens, during childhood may lead to an imbalanced immune response and increase the risk of developing inflammatory diseases such as allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases [12]. In recent years, certain helminth species have been linked to the hygiene hypothesis, indicating a negative correlation between the prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases and some helminth infections. However, it is important to note that other helminths can exacerbate and even trigger inflammatory conditions [13]. In addition, it is also known that several pathogens may influence or even cause the development of cancer, such as human papillomavirus, which is linked to cervical cancer; Helicobacter pylori, associated with gastric cancer; and Hepatitis B and C viruses, which are related to liver cancer; protozoa, and less common helminth parasites have also been associated with the development of some neoplasia [14].
Helminths are a group of parasites that include nematodes (roundworms), trematodes (flukes), and cestodes (tapeworms) [15]. These organisms establish chronic infections and modulate the host’s immune system through their derived products [16]. Despite their diversity in sizes or life cycles, most immune responses triggered by helminth infections typically involve type 2 immunity, characterized by the production of cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13. This response also recruits several innate and adaptive immune cells, including eosinophils, basophils, mast cells, dendritic cells (DCs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells, T regulatory cells (Tregs), type 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2), alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs), and Th2 cells [17].
Although helminthiasis is recognized as a public health problem, many researchers employ various models to understand how helminths evade and modulate the immune response, and to develop therapies for inflammatory diseases. Experimental studies have consistently demonstrated a close association between helminth infections and favorable changes in the progression of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including inflammation-associated cancers such as CRC [18].
How do helminth infections influence cancer outcomes? The existing literature presents two different perspectives. Experimental studies in CRC models show that helminths may accelerate disease progression and lead to worse outcomes, while others indicate that helminths could help reduce tumor burden [19]. The mechanisms behind these effects are currently under intensive research and vary according to the type of cancer and the type of helminth involved in the study. To avoid confusing generalizations, this review focuses on the pro-tumorigenic and anti-tumorigenic effects of helminths and their derivatives, specifically in CRC (Table 1). We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how helminths affect the macroscopic, histopathological, immunological, and molecular aspects of CRC by reviewing the existing literature. The keywords “colorectal cancer”, “parasites”, “helminths”, “helminth infection”, and “helminth-derived products” were searched in the selected databases: PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Science Direct. The inclusion criteria specifically targeted studies that explored the relationship between CRC and helminths, while excluding works that examined other types of cancers and those that did not involve helminthic parasites, such as protozoa (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Effects of helminths and their products on different models of CRC.
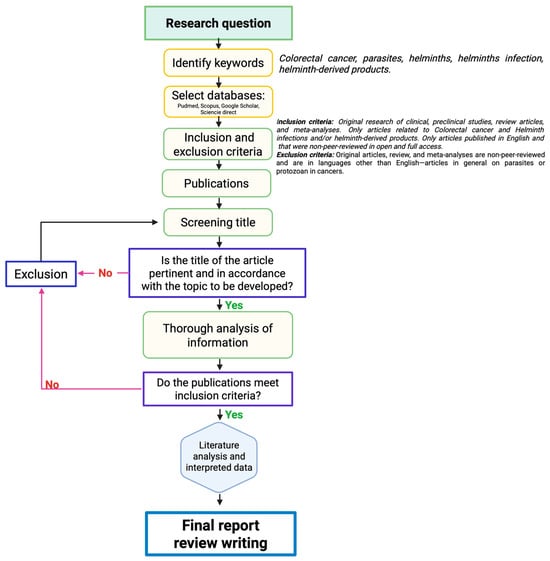
Figure 1.
Methodological approach of the selection/exclusion of the reviewed literature. Black arrows indicate the consecutive steps for selecting publication, until the final report and review writing. The arrows in pink indicate the criteria that lead to the exclusion of works non included in the final report. Purple frames indicates critical steps for deciding to selection or exclusion works.
2. The Impact of Helminth Infections on Colorectal Cancer
Helminthiases are among the most prevalent infections worldwide, affecting nearly 24% of the global population [42]. The widespread presence of helminth infections allows them to coexist with other chronic diseases, including cancer. A recent systematic review analyzed studies conducted in 26 countries and found that approximately 20.79% of patients with CRC were infected with helminthic parasites, with Schistosoma species being the most common culprits [43]. This suggests that a significant number of CRC patients may be susceptible to developing helminth infections. Therefore, it is essential to understand the impact of helminths on the development of CRC to prevent worse outcomes and to explore any potential beneficial effects they may have.
There are several general mechanisms by which helminth infections and their products may impact CRC development either positively or negatively: (1) indirect bypass affecting the host’s immune responses, (2) direct carcinogenic or anti-carcinogenic effect, (3) acute or chronic histo-mechanical damage, (4) altering the homeostasis of the microbiome, and (5) antigenic cross reactivity given a molecular mimicry.
The first section examines the negative and positive effects of helminth infections on the development of CRC. The second section, entirely experimental, discusses the impact of helminth-derived products at different stages of CRC onset in preclinical assays or in in vitro models, focusing on the mode of action involved in this disease. Notably, the primary mechanisms discussed involve modulating the host’s immune response, likely due to the characteristics of the in vivo models used in the reviewed literature (Table 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
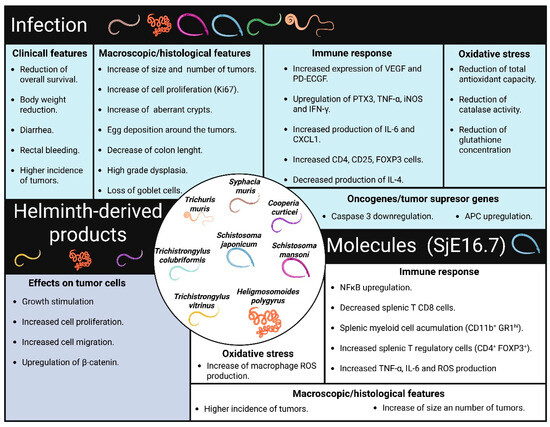
Figure 2.
Physiological changes associated with the protumor effects of helminths. Specific helminth infections contribute to tissue damage and adverse clinical outcomes in CRC. These infections trigger physiological changes in their hosts, including alterations in immune response and antioxidant mechanisms. The protein SjE16.7, which is derived from S. japonicum, has similar effects on the development of CRC. Additionally, helminth-derived products can directly affect tumor cells, promoting tumor growth.
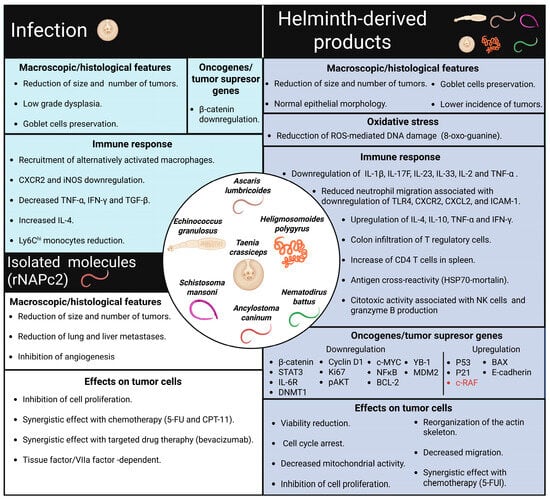
Figure 3.
Physiological changes are associated with the antitumor effects of helminths. Infection with T. crassiceps improves CRC outcomes by inducing an anti-inflammatory immune response in the host. Similarly, several helminth-derived products have been shown to reduce the incidence of colon tumors. Additionally, these products exhibit synergistic effects when combined with chemotherapy, directly influencing tumor cells by regulating oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Furthermore, the rNAPc2 recombinant protein, obtained from Ancylostoma caninum, has been found to reduce tumor growth and metastasis in different mouse models.
2.1. Pro-Tumorigenic Effects of Helminthic Infections in CRC
Few helminth parasites have been identified as direct causes of cancer development. In its monographs on identifying carcinogenic hazards to humans, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies infections with the helminths Opisthorchis viverrini and Schistosoma haematobium as Group 1 agents, which are proven to promote bile duct cancer. Additionally, infection with Schistosoma japonicum is classified as a group 2B agent, indicating that it is possibly carcinogenic to humans, mainly causing liver cancer, and has been associated with the development of CRC [14]. In this section, we discuss several findings suggesting that the potential unfavorable effect of helminth infections on cancer development may be more related to their immunological or bypass effects (Figure 2).
Patients with CRC who also show a Schistosoma sp. infection exhibit reduced overall survival rates [25,43]. This outcome may be related to egg deposition around the tumors, as reported in different cases of S. japonicum infection [21,26]. This phenomenon leads to an upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived endothelial growth factor (PD-ECGF) expression [22]. Notably, the increased expression of VEGF has been associated with the pro-angiogenic effects that promote tumor progression, migration, and metastasis [23].
Chronic inflammation is a critical factor that contributes to the development of CRC [11]. In this context, helminth infections can trigger inflammatory responses that may promote tumor growth in CRC. For example, infection with Schistosoma mansoni in mice has been shown to cause several pathological changes, including distortion of colonic crypts, glandular and mucosal dysplasia, nuclear hyperchromasia, and serration of the surface epithelium [44]. S. mansoni-infected mice also exhibited elevated serum levels of pentraxin 3 (PTX3) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), concurrently with local upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and TNF-α in the colon [44]. While there is no direct evidence that these molecules are responsible for the pathological changes associated with S. mansoni infection, studies have indicated that elevated levels of PTX3 are linked to decreased overall survival in post-surgery CRC patients [24]. Additionally, high levels of TNF-α correlated with more advanced tumor stages in CRC patients [45], while the overexpression of iNOS is known to promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis [46].
In intestinal living helminths, other mechanisms may influence CRC outcomes. In a study using the alkylating agent azoxymethane (AOM) and the polysaccharide dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) model, mice infected with Heligmosomoides polygyrus, one day after AOM treatment, exhibited accelerated weight loss and a higher incidence of colonic tumors. In contrast, mice infected at week 8 after the initiation of AOM/DSS induction did not exhibit significant differences in weight, and tumor incidence [47]. These findings suggest that H. polygyrus infection may promote colorectal tumorigenesis only at early stages of the disease, when this parasite induces mechanical harm upon attachment to the intestinal wall (see below).
Accordingly, H. polygyrus worsened the acute UC model induced by DSS, causing significant weight loss and a higher disease activity index compared with their uninfected counterparts. Moreover, histological analysis revealed more substantial changes in the colon, including shortening, loss of structural integrity, depletion of goblet cells, and increased recruitment of inflammatory cells [47]. Molecularly, the mechanism increasing UC by H. polygyrus involves the downregulation of IL-4 production and increased levels of IL-6 and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1). Interestingly, blocking IL-6 and CXCL1 reduced the severity of UC in infected mice. In contrast, the small intestine of infected mice treated with DSS did not show any pathological changes. Additionally, lower levels of IL-6 and CXCL1 were observed in the ileums of infected mice with DSS-induced colitis compared to their uninfected counterparts [47]. These findings are consistent with studies demonstrating a critical role of IL-6 in the AOM/DSS model, where IL-6 knock-out mice showed reduced tumor formation [20]. Additionally, CXCL1 expression correlated with decreased overall survival in CRC patients [48]. Notably, H. polygyrus larvae encyst, molt, and emerge as adult worms in the small intestine, indicating that this worm triggers a local immunosuppressive response. These findings suggest that helminth niches play a crucial role in shaping the effects of helminthiasis on CRC outcomes (discussed below).
Another case that highlights how intestinal helminths can affect CRC outcomes is the infection with Trichuris muris. This parasite establishes itself in the large intestine and caecum of the host, where it induces inflammatory conditions characterized by the production of cytokines, such as IL-6, TNF-α, and interferon gamma (IFN-γ), which generate, after chronic infection, pathological changes like those observed in the AOM model of CRC. Thus, on day 80 post-infection, T. muris was found to promote colon hyperplasia, the development of aberrant crypts, pre-adenomas, and an influx of inflammatory cells into the colonic lamina propria [49]. When these chronically infected animals were exposed to AOM, they developed increased levels of neoplasia scores within the colon. These results suggest the need to investigate the immune response in the colon during infection with T. muris to elucidate a potential mechanism that favors CRC.
Approximately 25% of CRC patients have a family history of the disease. Familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (FAP) is characterized by germline mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene, which result in an almost 100% risk of developing CRC [28]. Interestingly, there are studies on how helminth infections impact this condition. Thus, studies involving the APCmin/+ mouse model, the loss of APC heterozygosity induced by environmental factors, such as pathogen infections, can accelerate tumor formation in the gastrointestinal tract [50]. APCmin/+ mice infected with T. muris for 18 and 42 days exhibited tumor formation in the large intestine. This tumor development was prevented when CD4+, CD25+, FOXP3+ Tregs were depleted, indicating that T. muris infection influences CRC through immunosuppression mediated by Tregs [49]. These findings suggest that in patients with a family history of FAP, T. muris infection may trigger or enhance colonic tumor growth through Treg-mediated immunosuppression.
As previously mentioned, the niches where helminths reside may influence the effects of helminthiasis on CRC outcomes. To explore this further, an experiment was conducted using the APCmin/+ mouse model to compare the effects of two different types of helminths, the small intestine-dwelling H. polygyrus and the colon-dwelling T. muris, on CRC outcomes. Unlike T. muris infection, H. polygyrus infection did not promote tumor formation in the small intestine [49]. Interestingly, the results showed that these parasites did not promote tumor formation in their regular habitats. Still, they did favor tumor development in gastrointestinal areas that were distant from their usual niches. These findings align with previous studies indicating that H. polygyrus does not lead to tumor formation in the small intestine, its primary habitat, but does promote tumor formation in the colon. Additionally, lower levels of IL-6 and CXCL1 were observed in the ileum of H. polygyrus-infected mice treated with DSS, compared with the levels found in the colon of only infected mice [47]. These findings suggest that intestinal living helminths can trigger opposing immune responses in both their primary habitats and in distant areas. This opposing activity may either promote or inhibit CRC tumor progression, depending on the characteristics of the specific microenvironment.
Another exclusive intestinal helminth infection is that caused by Syphacia muris. A previous infection with this nematode resulted in downregulation of caspase 3 and APC, and the upregulation of COX2, promoting epithelial cell proliferation and increasing aberrant crypt formation in a CRC model induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH). Antioxidant assays revealed a reduced total antioxidant capacity in the host, which was associated with lower catalase activity and glutathione levels. These changes were linked to colonic tissue damage and an increased number of colonic tumors [51]. Oxidative stress and inflammation are closely interconnected and can exacerbate each other. During chronic inflammation, the production of ROS increases due to the recruitment of phagocytes, such as neutrophils [27]. These ROS can cause DNA damage through oxidation, leading to the accumulation of driver mutations. The most common ROS-induced mutation is the G-C transversion, which occurs due to the oxidation of guanine, resulting in the formation of 8-oxo guanine [52]. In response to oxidative stress, several antioxidant mechanisms are activated. This includes the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, thioredoxins, and glutathione peroxidase [27], which appear to be downregulated by S. muris infection [51]. Thus, these findings suggest that certain intestinal helminth infections may disrupt the balance between oxidative stress and antioxidants, ultimately leading to colon tissue damage and favoring the development of CRC.
At least four different helminth infections, caused by Schistosoma species, T. muris, S. muris, and H. polygyrus, have been linked to the initiation or exacerbation of colorectal tumors (Figure 2). Additionally, several physiological changes have been observed that are associated with the tumor-promoting effects of these helminth infections. These changes include the upregulation of angiogenic factors, disruption of antioxidant mechanisms, and the promotion of chronic inflammation (Figure 2). However, further research is needed to clarify the mechanisms by which helminth infections contribute to gastrointestinal tract dysfunction and the development of CRC.
2.2. Anti-Tumorigenic Effects of Helminthic Infections
The gut microbiota is an ecosystem made up of bacteria, fungi, viruses, Archaea, and parasites that interact with IECs to maintain homeostasis. This ecosystem plays a crucial role in the fermentation of non-digestible carbohydrates, nutrient absorption, vitamin synthesis, and modulation of host immunity. When the function or composition of the microbiota is disrupted, this condition is referred to as dysbiosis, which is associated with several diseases, including CRC [53].
In CRC patients, dysbiosis is characterized by an increase in pathogenic bacteria, including Fusobacterium nucleatum, Veillonella, Prevotella, and Streptococcus. These bacteria promote tumor initiation and progression through several mechanisms, such as genotoxin-mediated mutagenesis, modulation of oncogenic cell signaling pathways, alteration of chemotherapeutic metabolism, and induction of inflammation [54].
It is not hard to think that gastrointestinal-living helminths may modulate the microbiome in such tissue. Several reports indicate specific alterations in the microbiota in humans and murine models. Different species of all helminth classes have been associated with changes in the gut microbiome [55], but the impact of such alterations on an individual’s health is incompletely understood. Mechanistically, helminths may modify the microbiome by altering the metabolism of their hosts, impacting epithelial junctions, or even directly eliminating bacterial populations susceptible to the antimicrobial activities of their ES products through the induction of antimicrobial peptides and mucus production from the hosts [56]. Currently, there is no direct evidence linking changes in the microbiota caused by helminths to the development of CRC. However, it has been suggested that the eradication of helminths from human populations may be associated with an increase in dysbiosis and IBD [53]. Additionally, some studies indicate that certain helminth infections may protect their hosts from intestinal inflammation by altering the microbiome. Studies in mice infected with T. muris or H. polygyrus led to a reduction in the pathogenic bacterium Bacteroides vulgatus and an increase in the population of beneficial Clostridium species, thereby preventing intestinal inflammation [57]. Furthermore, male S. mansoni worm infections were found to protect mice from chemically induced colitis. In contrast, infection with both male and female worms exacerbated symptoms. Differences were observed in the microbiota of mice infected with male worms compared to those infected with both sexes, where male S. mansoni infection inhibited the growth of colitogenic bacteria. Notably, the protective effects of male S. mansoni worms were lost with the administration of antibiotics, suggesting a central role of bacterial microbiota [58]. Interestingly, these microbiome alterations do not affect the expulsion of the helminth Hymenolepis diminuta from the intestine [59]. Similarly to S. mansoni, eliminating gut microbiota by using antibiotics or in germ-free mice inhibits the protective effect of H. diminuta on ulcerative colitis [60], indicating that helminth-induced alterations in the microbiota are critically involved in the helminth control of intestinal inflammatory diseases. However, whether helminth-derived products induce such microbiome modulation is unknown, nor whether extraintestinal helminth infections may impact the colon microbiome and therefore CRC outcomes. Overall, these findings indicate that certain helminths may promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, which help reduce chronic inflammation in the intestine, a well-known risk factor for the development of CRC. However, further research is needed to understand better the relationship between helminths, microbiota, and CRC.
Taenia crassiceps is a cestode parasite that, in its adult stage, lives in the intestine of canids. Its larval stage (metacestode) can live in the muscle, brain, and peritoneal cavity of rodents. Intraperitoneal infection with the larval stage of T. crassiceps is characterized by the induction of a dual immune response. In the early acute stages, T. crassiceps infection triggers a temporary Th1-type immune response marked by high levels of IL-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ, nitric oxide, and IgG2a antibodies. However, in the chronic stages of infection (6 weeks or more), this Th1 response is replaced by a strong Th2-type immune response, which features elevated levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, the presence of AAMs, and high levels of IgG1 and IgE [61].
In the AOM/DSS CRC model, mice pre-infected six weeks earlier with T. crassiceps developed a lower incidence of colon tumors and reduced severity of CRC. Remarkably, 20% of the infected mice were tumor-free, exhibiting low-grade dysplasia and normal goblet cell counts. The remaining 80% of the infected mice had significantly fewer and smaller tumors than non-infected mice. Furthermore, the mice infected with T. crassiceps showed reduced levels of β-catenin in the colon [62], a marker for the advancement of CRC. Indeed, approximately 60–80% of CRC patients experience abnormal activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Elevated levels of nuclear β-catenin expression in CRC patients are associated with decreased overall survival rates, as the activation of β-catenin triggers the transcription of target genes that promote tumor cell proliferation [32]. Interestingly, similar results were reported in other solid tumor models, where mice infected with Trichinella spiralis for 35 days displayed a reduced size of liver tumors [63].
Unlike protumor helminth infections that promote tumor growth and trigger an inflammatory response in the intestine, mice pre-infected with T. crassiceps showed a reduced inflammatory infiltrate in the colonic lamina propria. This was associated with the low levels of the chemokines C-X-C chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) and C-C chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2), resulting in decreased recruitment of neutrophils and Ly6Chi monocytes. In contrast, anti-inflammatory cell populations, such as AAMs, were detected in the colon tissue. Additionally, levels of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, and the expression of iNOS, were reduced, while the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 increased significantly [62]. To further assess whether T. crassiceps infection decreases intestinal inflammation, infected mice were induced to develop acute colitis through DSS treatment. T. crassiceps infection effectively reduced clinical symptoms, including weight loss and disease activity index. Moreover, the infected mice maintained their colon size and preserved colonic epithelial structure. These beneficial effects were linked to the recruitment of AAMs to the colonic lamina propria. Furthermore, transferring AAMs isolated from T. crassiceps-infected mice improved symptoms of DSS-induced colitis in naïve receptor mice [64].
This section summarizes the connection between the immune response triggered by helminth infections and their significant impact on the development of CRC, particularly in the early stages of the disease. The reviewed literature suggests that particular helminth species promote a local inflammatory response or a localized injury that actively supports protumor activity, thereby facilitating the initiation of CRC (Figure 2). In stark contrast, other helminth infections, such as T. crassiceps, elicit strong global anti-inflammatory responses linked to antitumor effects that may unfueled the formation of colorectal tumors (Figure 3).
Based on these observations, we hypothesized that a delicate balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses in the host influences the effects of helminth infections on tumorigenesis in the early stages of sporadic CRC. In this context, helminth infections that stimulate an inflammatory response in the intestine may lead to tissue damage and the formation of tumors in the colon. Conversely, an anti-inflammatory response could help modulate intestinal inflammation, reducing tissue damage and preventing tumorigenesis in the colon.
The precise mechanisms by which helminth infections trigger inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses are still being elucidated. Intestinal helminths attach themselves to the epithelium through specialized structures, such as the scolex, which results in tissue damage [15]. This tissue injury promotes the release of alarmins, such as IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), from IECs. These alarmins activate ILC2, which activate the Th2 immune response and promote tissue repair. The impact of alarmins varies based on the parasite species, cellular source, and the immune microenvironment. Evidence suggests that alarmins are important for both host protection and tissue pathology [65]. Therefore, it is essential to understand how the stimulation of alarmins by helminths affects outcomes in CRC.
3. The Impact of Helminth-Derived Products on Colorectal Cancer
While certain helminth infections may have beneficial effects on CRC, using whole live parasites as helminth therapy is impractical and could pose a health risk to patients, as several studies have indicated. Although helminthiasis is generally not fatal, it can lead to several health issues, including anemia, malnutrition, stunted growth, internal organ blockage, and organ damage. Additionally, it can cause immune-related problems such as chronic inflammation, fibrosis, granuloma formation, and immunosuppression, depending on where the parasite is located [66]. Despite the risks associated with using whole helminths as therapy, six clinical trials have been conducted to date to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treating IBD with Trichuris suis eggs (TSO) (NCT01433471, NCT03565939, NCT01576471, NCT01434693, NCT01279577, NCT03079700). The current role of TSO as a treatment for IBD remains uncertain. Some clinical trials have indicated a reduction in disease severity among patients without serious adverse effects. However, meta-analysis studies suggest that no statistically significant results have been observed. Additionally, the small size of the study cohorts makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions [67].
To avoid the potentially serious adverse effects of whole and long-term helminth therapy, recent studies have focused on analyzing helminth-derived products as an alternative. Helminths excrete and secrete several products, including metabolites, glycans, lipids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, glycolipids, proteins, and glycoproteins. Helminth-derived products primarily interact with the host immune system in two principal ways: either by inducing a protective immune response or by evading the host immune response. Currently, these effects are studied as potential immunomodulatory and biotherapeutic drugs for chronic inflammatory diseases, including inflammation-associated cancers [68]. In this section, we reviewed the effects of helminth-derived products in CRC progression in in vitro and pre-clinical assays.
Anti-Tumorigenic Effects
In 1970, Berton Zbar and his colleagues demonstrated that immunization with the attenuated Bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) could stimulate the immune cells to target cancer cells. Today, BCG is an approved treatment for bladder cancer [69]. In this context, recent research has utilized pathogen-derived products as biotherapeutics to treat various diseases. Here, we reviewed evidence showing that helminth-derived products can enhance the immune response against CRC cells and potentially alter the tumor microenvironment to inhibit cancer cell proliferation.
In a heterotopic syngeneic mouse model of CRC, researchers transplanted the CRC cell line CT26 (5 × 105 cells) into the backs of BALB/c mice, and five days later, they administered three injections of hydatid cyst fluid (HCF) from Echinococcus granulosus or the 78 KDa fraction of HCF every two weeks. These treatments resulted in a significant reduction in the mean tumor area. Furthermore, while serum levels of IL-2 decreased, the levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ increased. Notably, high levels of IgG were observed one week after the last injection. In contrast, untreated mice showed a higher mean tumor area with low levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ [70].
Immunizing mice with HCF before tumor induction using the heterotopic syngenic model of CRC (CT26 colorectal cells) reduces tumor incidence by 40%. Moreover, administration of HCF at 4-, 7-, and 10-day post-tumor induction increases mouse survival by 40%. Additionally, anti-HCF antibodies generated in rabbits can target CT26 CRC cells. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that these anti-HCF antibodies also recognize the heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), found in E. granulosus, which shares 60% homology with mortalin. This protein binds to P53 and inhibits its antiproliferative activity [34].
Given that antibodies against E. granulosus cross-react with mortalin, it is essential to conduct further experiments to determine whether these antibodies contribute to the antitumor effects triggered by HCF and how these antibodies may cross both cell and nuclear membranes to bind to their putative target.
Helminth-derived products are significant sources of parasite antigens recognized by the host immune system. The presentation of these antigens leads to the production of antibodies against helminth products [16]. Interestingly, cancer cells and helminths share similar mucin-type O-glycan compositions, including α-N-acetylgalactosamine-O-serine/threonine, sialyl-Tn, or Thomsen–Friedenreich antigens. Consequently, antibodies against helminth products can cross-react with cancer cells [35].
Helminths influence the host’s immune system through their derived products [16]. In this context, experiments conducted using the DMH CRC mouse model demonstrated that a double dose of autoclaved T. spiralis antigens (ATSA, 70 mg/kg) or autoclaved S. mansoni antigens (ASMA, 5 μg/kg) administered during the 12th week post-cancer induction, resulted in increased overall survival rates of 60% and 80% by the 20th week of the study, respectively [71]. Concomitantly, groups of mice treated with ASMA or ATSA displayed lower IL-17 levels in serum compared with cancer control mice. Moreover, these treatments also increased the serum concentration of IL-10, CD4 T cells in the spleen, and favored the recruitment of Tregs into the colon. While ASMA-treated mice showed a reduction in colon tumor size, the number of neoplastic lesions, and the average lesion size per mouse, the ATSA-treated group showed an increased average lesion size compared to the untreated control group [71]. Thus, ATSA and ASMA treatments increase serum IL-10 levels and recruit FOXP3+ Tregs to the colon, having opposite effects on CRC outcomes. This suggests that helminth-derived products not only affect CRC progression through immunomodulation but also involve other mechanisms, including direct effects on tumor cells (discussed below).
Other helminth-derived molecules have also been tested against CRC. The larval phase of T. crassiceps is known by the release of excreted/secreted (ES) factors that alter the response of innate immune cells of mice and humans [61]. These molecules are mainly glycoproteins >50 kDa. Using the AOM/DSS model of CRC, a relatively early (before the third DSS cycle, when colon tumors initiate their growth) 200 μg administration of T. crassiceps excreted/secreted products (TcES) three times a week, starting on day 26 after induction and continuing until day 65, resulted in the inhibition of colonic tumor formation in 45% of treated mice. In the remaining 55% of cases, the developed tumors were smaller than those in untreated mice. Furthermore, mice receiving TcES exhibited normal colon epithelium morphology and maintained normal goblet cell counts [38].
The underlying mechanism of this inhibition involves a reduction in STAT3 phosphorylation through the downregulation of the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R). The inhibition of the IL-6-STAT3 signaling pathway was confirmed by a reduction in the transcription of STAT3 target genes, including DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) and Cyclin D1 [38]. Cyclin D1 is a proto-oncogene that plays a crucial role in the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase during cell cycle progression, thereby favoring tumor cell proliferation [39]. DNMT1 is closely associated with the activation of β-catenin and its transcriptional activity [72]. Notably, the nuclear translocation of β-catenin was reduced in TcES-treated mice [38].
Like T. crassiceps infection, treating CRC with TcES also reduces intestinal inflammation. CRC mice treated with TcES exhibited decreased colon tissue levels of pro-oncogenic cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-17F, IL-23, and IL-33. Additionally, a reduction in CXCR2 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) was associated with decreased tumor neutrophil infiltration [38]. In recent years, the protumor effects of neutrophils have been described, including the increased production of ROS [73,74]. Interestingly, lower levels of 8-oxo guanidine were found in TcES-treated mice compared to untreated ones [38]. Together, these data suggest that the reduction in neutrophil infiltration is associated with decreased ROS-mediated DNA damage. Another interesting and related finding was that TcES-treated mice also displayed a reduced activation of NFκB signaling. Consequently, the expression of target genes such as TNF-α and the anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) was downregulated [38]. Therefore, TcES downregulates inflammation-related signaling pathways involved in CRC development.
These findings demonstrate that the immunomodulatory properties of helminth-derived products can be harnessed as a prophylactic strategy to reduce intestinal inflammation and prevent tumor formation effectively. Furthermore, pursuing new treatment strategies, particularly combining chemotherapy with immunotherapy, is essential to improve patient outcomes [75]. In this context, mice with AOM/DSS-induced CRC at advanced stages (after the third DSS cycle) were treated with TcES (200 μg) in combination with 30 mg/kg of the chemotherapeutic agent 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU). Remarkably, mice receiving the combinatory treatment (TcES+5-FU) exhibited a 70% reduction in tumor load. In contrast, the individual treatments with 5-FU or TcES alone resulted in tumor reduction of only 15% and 40%, respectively [76].
The effective antitumor effect of combined treatment (TcES+5-FU) was associated with increased infiltration of cytotoxic cells, such as natural killer cells (NK), which promote tumor cell apoptosis by releasing granzyme B. In addition, this combined treatment also reduced the expression of murine double minute 2 (MDM2), a P53 repressor, leading to the upregulation of P53 and P21, suggesting that combined treatment leads to cell cycle arrest of tumor cells [76]. This effect may provide an opportunity for the recruited immune cells to exert their cytolytic function. Therefore, such evidence suggests that ES helminth products can be promising biotherapeutic adjuvants for chemotherapy.
The regulation of proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes observed in the treatment of ES helminth products raises the question of whether there is direct interaction between helminth ES products and CRC tumor cells. Our next section will address this question.
4. The Impact of Helminth-Derived Products on Colorectal Cancer, Beyond the Immune System
The revised reports above have primarily focused on the impact of helminths on CRC through modulation of the immune system. However, since intestinal helminths reside in the gastrointestinal tract, they come into direct contact with epithelial and tumor cells. This raises the question: what effects does this interaction have? To understand this, it is necessary to consider the two main models that explain the cellular origin of CRC. The first is the bottom-up model, which is associated with hereditary or familial history factors and suggests that CRC originates from stem cells at the bottom of intestinal crypts. The second is the top-down model, linked to sporadic cases of CRC, which posits that the cancer arises from stem-like cells at the top of the crypts [40]. Recent studies indicate that inflammatory CRC may originate from well-differentiated cells, such as Paneth cells [77]. However, this hypothesis is still under investigation.
Several effects of helminths on the gut epithelium have been documented. These effects include increased epithelial permeability, degradation of mucus, and mechanical damage, all of which promote alarmin production. Additionally, it has been hypothesized that helminths influence stem cell differentiation towards specific lineages, which helps maintain epithelial integrity while enhancing the persistence of the worm. In response, host epithelial cells can activate various signaling pathways to defend against these infections. These protective mechanisms include mucus production, cellular proliferation, and activation of the immune response [78]. This section examines the potential impact of the interaction between helminth-derived products and tumor cells on outcomes in CRC.
4.1. Pro-Tumorigenic Effects of Helminth-Derived Products
Few studies have reported direct pro-tumorigenic effects of helminth-derived molecules on CRC tumor cells. For example, exposure of the HT29-D4 human CRC cell line to 1 μg/mL of conditioned medium from Trichostrongylus colubriformis increased cell proliferation. Treating this conditioned medium with heat, acid hydrolysis, or precipitation using trichloroacetic acid reduced the cell proliferation of HT29-D4. This suggests that T. colubriformis secreted proteins may enhance the proliferation of colorectal tumor cells [79]. Similarly, stimulating HT29-D4 cells with 0.1 μg/mL of conditioned medium of Trichostrongylus vitrinus and 1–5 μg/mL of conditioned medium from Cooperia curticei also led to increased cell proliferation [30].
Cell migration is a key step in cancer invasion and metastasis, reflecting the pathological grades of malignancy associated with cancer cells [6]. Studies using the mouse CRC cell line CT26 revealed that exposure to 10 μg of H. polygyrus antigens or 10 μg of H. polygyrus excreted/secreted products (HES) increased cell migration and β-catenin expression. Interestingly, the effects of these antigens on human CRC cells contrast with those observed in CT26 cells (discussed below) [29]. Although this evidence suggests that helminth-derived products may promote cell migration and proliferation in CRC cells, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This highlights the need for further research to understand the underlying mechanisms.
4.2. Anti-Tumorigenic Effects of Helminth-Derived Products
The direct antitumor effects of helminth-derived products on CRC cell lines have been studied in several helminth species and in greater depth. Initial reports indicate that ES products from Nematodirus battus inhibited the proliferation of HT29-D4 cells [30]. Also, the Ascaris lumbricoides ES products (ALES) inhibited HCT116 cell proliferation [37]. However, the direct antiproliferative mechanisms of N. battus and A. lumbricoides products remain unclear.
Further investigations have explored the mechanisms behind the direct antitumor effects of helminth-derived products in several CRC cell lines. Research using the mouse CT26 cell line indicated that cells treated with egg antigens from S. mansoni showed no significant effects. However, treatment with 10 μg of HES decreased viable cell counts, reduced DNA synthesis, and mitochondrial activity. Conversely, treatment with 10 μg of antigens from H. polygyrus reduced viable cell numbers but did not affect DNA synthesis or mitochondrial function. Both treatments increased the expression of the proteins P53 and P21, suggesting that these proteins might contribute to the antiproliferative effects of H. polygyrus antigens. As previously mentioned, these treatments also induced cell migration in the CT26 cell line [29].
On the other hand, experiments using the human cell line HCT116 demonstrated that HES reduced cell viability and DNA synthesis without impacting mitochondrial activity. The antigens from H. polygyrus did not affect the HCT116 cells. However, like the CT26 cells, both treatments induced the upregulation of P53 and P21 in HCT116 cells. Unlike CT26 cells, exposure to H. polygyrus antigens and HES decreased cell migration and β-catenin expression in HCT116 cells [29].
These observations highlight the differences in the anti-tumorigenic activity of antigens among helminth species and the variations between total and ES antigens. Such differences may result in varying impacts on CRC cells. It is important to consider that helminth-derived products might induce species-specific responses, exhibiting a range of effects on CRC cells depending on their origin.
Recent studies, like those conducted using H. polygyrus, have demonstrated the direct impact of HCF from E. granulosus on both mice and human CRC cells. Exposure of the cell lines C26 with 20 μM of HCF and HCT116 with 30 μM of HCF caused cell cycle arrests in the G0 phase and reduced the number of cells in the M phase. Additionally, the treated cells showed increased apoptosis rates, marked by the upregulation of the proapoptotic protein BCL-2-associated X protein (BAX) and downregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 [33].
TcES also directly affected human CRC cell lines alone and in combination with the chemotherapeutic agent 5-FU. In one study, exposure of the human CRC cell line RKO to 12.5 μg/mL of TcES for 72 h reduced cell numbers, although it did not affect cell viability. Furthermore, TcES induced changes in cell morphology and promoted the formation of colonospheres by reorganizing the actin cytoskeleton. Like those results observed in the AOM/DSS mouse model, TcES decreased NFκB activation in RKO cells stimulated with 0.5 mg/mL of LPS for 20 min. Notably, the inhibition of c-RAF reversed the downregulation of NFκB, suggesting that TcES may operate through the c-RAF signaling pathway [38]. Interestingly, similar effects of TcES on NFκB and c-RAF were previously observed in mouse DCs [36], and seems a possible common pathway activated by other helminth glycoconjugates, as documented in S. mansoni [80], and more recently in E. granulosus products [81], in all cases, inhibiting DC-mediated inflammatory responses.
The combined therapy using 50 μg of TcES and 10 μM of 5-FU reduced the proliferation and migration of the HCT116 and RKO cell lines. The treatment upregulated P53 and P21 proteins and decreased Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1), a proto-oncogenic protein [76]. These findings suggest that TcES may activate tumor suppressor proteins and inhibit the activation of proto-oncogenic proteins. However, further research is necessary to understand the antitumor mechanisms of TcES.
In summary, the findings reviewed suggest that several factors influence the antitumoral effects of helminth-derived products and could involve a range of mechanisms (Figure 3). This may be due to the high complexity of their composition (several molecular compounds have been identified, including fatty acids, amino alcohols, indoles, sterols, glycosides, and sphingolipids). For this reason, it is essential to characterize and identify the components of helminth-derived products to facilitate the study of their interactions with CRC cells. Understanding these interactions may enable the identification of potential biotherapeutic molecules from helminths that improve CRC outcomes. Currently, several works describe the composition of some helminth-derived products or total antigens, including those of E. granulosus [82], T. spiralis [83], A. lumbricoides [37], T. crassiceps [84,85], among others. However, only two studies have focused on examining the effects of isolated/purified molecules from helminth-derived products on the development of CRC. These reports will be discussed in the following section.
5. The Impact of Isolated Molecules from Helminths in Colorectal Cancer Modulation
5.1. Pro-Tumorigenic Effects
Some researchers have focused on isolating specific molecules that preserve the primary biological function of whole helminth-derived products to better understand and identify them, and to reduce exposure to inactive molecules from helminths.
The molecule SjE16.7 has been identified as an EF-hand calcium-binding protein released from the eggs of S. japonicum and synthesized using yeast and Escherichia coli recombination systems. In the AOM/DSS CRC model, mice treated with 100 µg of SjE16.7 twice a week throughout the experiment showed no significant changes in body weight or colon length. However, by the 14th week after the experiment began, the mice treated with SjE16.7 exhibited a tumor incidence rate of 90 to 100%, compared to only 50 to 70% in the control cancer groups. Additionally, the colon tumors in SjE16.7-treated mice were larger than those in control mice [86].
This effect correlated with the accumulation of myeloid cells (CD11b+), Tregs, and a reduction in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The myeloid subset was primarily composed of Gr1hi cells, a well-established marker of neutrophils [86]. These findings indicate that SjE16.7 promotes an inflammatory response associated with the progression of CRC. The immunomodulatory effects of SjE16.7 were investigated in bone marrow-derived macrophages and the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line. Treatment with 1 µM of SjE16.7 led to increased production of ROS, activation of NFκB, and secretion of the cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α [86]. SjE16.7 is recognized by the mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and the human CRC cell lines Caco-2 and SW480 through the receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE). Knocking down RAGE in RAW 264.7 macrophages reduced ROS production, NFκB activation, and cytokine secretion induced by SjE16.7 [86].
As previously mentioned, ROS contributes to tissue damage and the development of colorectal tumors. In this regard, the immunomodulatory effects observed in macrophages could be proposed as a potential protumor mechanism of SjE16.7. Conversely, the increased FOXP3+ Tregs and the decreased CD4+ and CD8+ T cells indicate an immunosuppressive microenvironment mediated by SjE16.7, which may facilitate tumor progression. Given the contrasting immunomodulatory effects of SjE16.7, it is essential to investigate the patterns of cell infiltration in the colon induced by this molecule. Additionally, the recognition of SjE16.7 by CRC cell lines suggests that SjE16.7 may have a direct protumor effect.
5.2. Anti-Tumorigenic Effects
Another helminth-identified molecule, but with contrasting effects, is the recombinant nematode anticoagulant protein c2 (rNAPc2), which is a protein isolated initially from Ancylostoma caninum and expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris [31]. rNAPc2 specifically inhibits the tissue factor (TF)/factor VIIa complex, which is associated with angiogenesis and metastasis [87].
The antitumor effects of rNAPc2 have been proven in several CRC mouse models. In the APCmin/+ model, mice treated daily with 100 µg/kg of rNAPc2 until they reached 16 weeks of age showed reduced numbers of tumors in both the small intestine and colon compared to control mice. Additionally, histological analysis indicated a decrease in total tumor area and a lower percentage of adenocarcinomas in rNAPc2-treated mice [88].
The combination of rNAPc2 with chemotherapeutic drugs or specific antibodies has been shown to inhibit tumor formation. In a model involving human HCT116 xenograft transplantation into nude mice, those treated with rNAPc2, 5-FU, or bevacizumab (an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody) exhibited tumor volume reduction compared to untreated mice. However, mice receiving the combined therapy rNAPc2 and 5-FU or rNAPc2 and bevacizumab demonstrated a remarkable tumor volume reduction, even greater than that observed in the individual treatments. Additionally, mice treated with these combined therapies showed reduced angiogenesis and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation [88].
The anti-metastatic effects of rNAPc2 have been demonstrated in several CRC mouse models. In a study where pulmonary metastasis was induced by injecting CT26 cells into the tail vein, mice treated with increasing doses of rNAPc2, ranging from 10 to 1000 µg/kg, exhibited reduced lung weight and a lower number of surface metastases compared to untreated controls. Additionally, in a liver metastasis model where human HCT116 cells were administered via the portal vein to nude mice, those treated with rNAPc2 or the chemotherapeutic irinotecan (CPT-11) showed a decrease in tumor areas in the liver. Notably, the anti-metastatic effect was enhanced when rNAPc2 and CPT-11 were given together [88].
As mentioned above, rNAPc2 inhibits the TF complex, which is associated with angiogenesis and metastasis. For these reasons, authors have proposed that rNAPc2 antitumor effects may be linked to the surface expression of TF on tumor cells. Experiments using HCT116 cells with TF knockdown showed that these cells have slower growth in nude mice xenografts compared to HCT116 parental cells. Interestingly, tumors induced by HCT116 TF knockdown cells are resistant to the antitumor effects of rNAPc2 compared to HCT116 parental cells.
In summary, the reviewed literature indicates that helminths can have both negative and positive effects on the initiation and progression of CRC (Table 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3). Currently, research has mainly focused on harnessing the antitumor properties of helminths. However, studies involving helminth-derived products as a potential treatment for CRC are still limited to basic science research and preclinical trials, predominantly conducted using animal models and in in vitro cultures of human colorectal tumor cells. While these models provide valuable insights, they capture only a small fraction of the complex mechanisms involved in CRC development. Nevertheless, advancements in technology have led to the development of new models, such as genetically engineered mouse models, which enable more comprehensive research [41]. It is crucial to underscore the mechanisms of action shared by different helminths and their products on CRC modulation. These mechanisms, include the downregulation of inflammatory responses (consistent inhibition of TNFα and IL-17), blockade of STAT3 phosphorylation (activation of phosphatases?), and induction of proapoptotic proteins, along with reactivation of P53 that modulates cell proliferation, as depicted in Figure 4, appear to be genetic background independent, as at least BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice can benefit from these treatments.
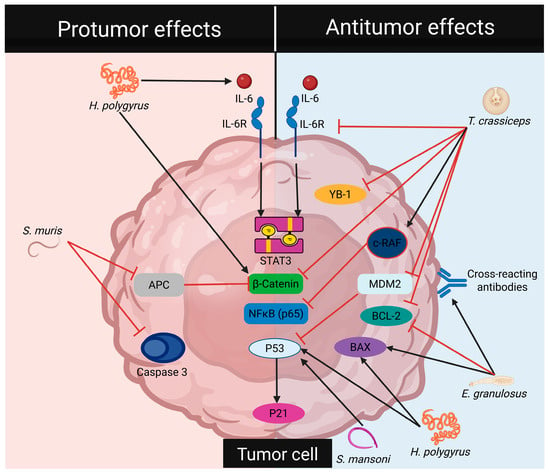
Figure 4.
Helminths regulate cell signaling pathways in tumor cells. Pro-tumorigenic effects of helminths involve the activation of transcription factors associated with cell proliferation and the inhibition of pro-apoptotic proteins. In contrast, anti-tumorigenic effects of helminths inhibit the activation of transcription factors related to cell proliferation, downregulate anti-apoptotic proteins, and upregulate pro-apoptotic proteins.
On the other hand, ongoing clinical trials are investigating the use of helminth-derived products for the treatment of several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and IBD. In these trials, the efficacy and safety of helminth-derived products have been demonstrated, with some yielding successful results [89]. For instance, a pilot Phase 2a clinical trial evaluated the protein P28 glutathione-S-transferase, which resulted in a reduced Crohn’s Disease Activity Index without severe adverse events, limited to local reactions at the injection site and mild gastrointestinal disorders [90].
Thus, it is not impossible to achieve this in a few years, once isolated or enriched helminth-derived products are molecularly better characterized and tested in CRC.
6. Concluding Remarks
In this review, we gathered evidence on how helminths influence outcomes in CRC. Helminths and their products can either promote or inhibit colonic tumor progression depending on various factors, such as the species of helminths, their primary site of localization, the origin of the colorectal tumor, and the stage of the disease. While several physiological changes have been observed in mice bearing CRC when infected with helminths or treated with helminth-derived products, the exact mechanisms impacting CRC outcomes are not yet fully understood. One of the most studied mechanisms is immune modulation. Evidence suggests that in inflammation-associated cancer models, the balance between immunosuppression and exacerbation of inflammation mediated by helminths is a key factor in tumor progression during the early stages of the disease. Specifically, helminths that exacerbate inflammation may promote tumor formation, while those that suppress immune responses may inhibit it. Conversely, in hereditary CRC models, immunosuppression induced by helminths could promote tumorigenesis. This highlights the importance of considering both the origin and stage of the tumor in evaluating the effects of helminths on CRC.
Given that helminth therapy using whole parasites is impractical and could compromise patient health, recent research has focused on helminth-derived products as a more viable therapeutic approach. The extraction of helminth-derived products has enabled the study of new mechanisms by which these organisms may impact CRC.
Like active helminth infections, the investigation of ES helminth products as immune modulators has been extensively studied. Antitumor effects of these products have been linked to both the stimulation and the suppression of immune responses. Evidence indicates that the immune stimulatory effects of helminth-derived products may occur through cross-reactivity between helminth and cancer antigens. Conversely, ES helminth products may downregulate key inflammatory transcription factors that favor CRC.
Recent studies have also demonstrated that, in addition to immunomodulatory mechanisms, helminth-derived products could interact directly with CRC cells. In this context, ES helminth products have shown the potential to either promote or inhibit cell proliferation and cell death. Tumor-promoting effects are associated with the activation of proto-oncogenes and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins, while antitumor effects are linked to the upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins (Figure 4).
One of the main challenges in utilizing ES helminth products as potential biotherapeutics lies in the complexity of their composition. As a complex mixture of biomolecules, studying their interaction with tumor cells can be difficult. Further characterization and identification of the components of ES helminth products will allow researchers to investigate their interaction with specific receptors in immune, tumor, and epithelial cells, aiding in the development of potential biotherapeutic agents. Nevertheless, we must consider potential adverse effects, such as immunosuppression or the induction of PDL-1 and PD-L2 expression, that may compromise the use of immunotherapy aimed at blocking immunologic checkpoints.
Research on helminth-derived products as a potential treatment for CRC is currently limited to basic science studies and preclinical trials conducted in animal models and in vitro cultures using human colorectal tumor cells. While these models provide valuable insights, they only capture a small fraction of the complex mechanisms involved in the development of CRC. It is important to note that accurately reproducing the development and progression of CRC is challenging due to the multifactorial nature of the disease. CRC is a heterogeneous condition, meaning there are numerous differences among patients’ tumors, and even variations in tumors from the same patient. Thus, there is no ideal in vitro or preclinical model for any human disease. However, numerous efforts are underway to develop preclinical models that closely resemble human diseases. Several models attempt to replicate human disease in colorectal cancer as closely as possible. The models described in this review are limited and involve chemical inducers, injecting syngeneic heterotopic tumor cells, single-gene mutations, and the induction of inflammation. They all have limitations in several aspects, such as the development of a limited number of mutations, restricted tumor heterogeneity, and poor metastasis development. However, these preclinical models have generated valuable information for understanding the development of CRC in humans, particularly in terms of the role of innate and adaptive immune response, chronic inflammation, and insights into the tumor microenvironment. There are more preclinical models of CRC. However, with the advent of genetically modified animals, it has become possible to develop models with up to four CRC-related mutations in the same animal, thereby generating a model that more closely resembles the classification of the four consensus molecular subtypes described in human CRC. Furthermore, organoids or tumor cells from patients have been grafted into immunodeficient mice to investigate more effective treatments for the patients, thereby providing precision medicine, which aims to develop therapeutic strategies tailored to the specific characteristics of tumors. However, these aforementioned models have not yet been addressed from the perspective of treatment with helminth-derived molecules. Thus, this is a point that researchers in this field should develop soon to solidify the potential beneficial effects of using helminth ES products. Finally, as mentioned before, the use of helminth infection is not an option, given the potential harmful for the patients; we propose instead the use of helminth-derived products, not to displace the conventional drugs in CRC (even when their efficacy is low) but the combination of such products with standard drugs to improve their efficacy and reduce the drug doses to decrease the severe side effects in patients. Understanding how these products impact CRC is vital for advancing translational research that can identify new therapeutic targets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Á.S.-B. and L.I.T.; investigation, C.Á.S.-B., M.T.O.-M. and M.G.M.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Á.S.-B., K.V.F.-M. and J.A.C.-P.; writing—review and editing, C.Á.S.-B. and L.I.T.; supervision, L.I.T. and M.R.-S.; funding acquisition, L.I.T. and M.R.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica-DGAPA-UNAM, grant number IV200425. Cuauhtémoc Ángel Sánchez-Barrera is a doctoral student of the Programa de Doctorado en Ciencias Biomédicas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), and a recipient of a CONACHYT fellowship CVU: 77080.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 5-FU | 5-Fluorouracil |
| AAMs | Alternatively activated macrophages |
| ALES | Ascaris lumbricoides ES products |
| AOM | Azoxymethane |
| APC | Adenomatous polyposis coli |
| ASMA | Autoclaved Schistosoma mansoni antigens |
| ATSA | Autoclaved Trichinella spiralis antigens |
| BAX | BCL-2-associated X protein |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette-Guerin |
| BCL-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| CCR2 | C-C chemokine receptor 2 |
| CMS | Consensus molecular subtypes |
| COX2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CPT-11 | Irinotecan |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| CXCL1 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 |
| CXCR2 | C-X-C chemokine receptor 2 |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| DMH | 1,2-dimethylhydrazine |
| DNMT1 | DNA methyltransferase 1 |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| ES | Excreted/secreted |
| FAP | Familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome |
| HCF | Hydatid cyst fluid |
| HES | Heligmosomoides polygyrus excreted/secreted products |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IECs | Intestinal epithelial cells |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| Ig E/G/G1/G2a | Immunoglobulin E/G/G1/G2a |
| IL-1β/2/4/5/6/9/10/13/17/17F/23/25/33 | Interleukin 1β/2/4/5/6/9/10/13/17/17F/23/25/33 |
| IL-6R | IL-6 receptor |
| ILC2 | Type 2 innate lymphocytes |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| MDM2 | Murine double minute 2 |
| MYC | Myelocytomatosis |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NK | Natural killer cells |
| PDECGF | Platelet-derived endothelial growth factor |
| PTX3 | Pentraxin 3 |
| RAGE | Receptors for advanced glycation end products |
| rNAPc2 | Recombinant nematode anticoagulant protein c2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TcES | Taenia crassiceps excreted/secreted products |
| TF | Tissue factor |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| Th 1/2/17 | T helper 1/2/17 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| Tregs | T regulatory cells |
| TSLP | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WNT | Wingless-related integration site |
| YB-1 | Y-box binding protein 1 |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, A.; Rudzki, G.; Lewandowski, T.; Stryjkowska-Góra, A.; Rudzki, S. Risk Factors for the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748211056692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosenberg, E.; Kaur, A.; Babiker, H.M. A Review of Hereditary Colorectal Cancers; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Sun, M.; Ranganathan, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; et al. The Largest Chinese Cohort Study Indicates Homologous Recombination Pathway Gene Mutations as Another Major Genetic Risk Factor for Colorectal Cancer with Heterogeneous Clinical Phenotypes. Research 2023, 6, 0249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; De Reyniès, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The Consensus Molecular Subtypes of Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Su, T.; Xiao, T.; Xu, H.; Zhao, S. Colorectal Cancer Risk in Ulcerative Colitis: An Updated Population-Based Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2025, 84, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, I.; Bergsten, E.; Charpy, C.; Chamaillard, M.; Mestivier, D. Virulent Bacteria as Inflammatory and Immune Co-Factor in Colon Carcinogenesis: Evidence from Two Monozygotic Patients and Validation in CRC Patient and Healthy Cohorts. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 749750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Fung, T.T.; Wu, K.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Cao, Y.; Hu, F.B.; Ogino, S.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Association of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Colorectal Cancer Risk in Men and Women. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Greten, F.R. The Inflammatory Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Revs. Immunol. 2021, 21, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.G.; Lundsmith, E.T.; Hamilton, K.E. Inflammation and Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Color. Cancer Rep. 2017, 13, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiemsma, L.T.; Reynolds, L.A.; Turvey, S.E.; Finlay, B.B. The Hygiene Hypothesis: Current Perspectives and Future Therapies. Immunotargets Ther. 2015, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, N.; Weatherhead, J.; Sastry, K.J.; Hotez, P.J. The Hygiene Hypothesis and Its Inconvenient Truths about Helminth Infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC List of Classifications—IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/list-of-classifications (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Castro, G.A. Helminths: Structure, Classification, Growth, and Development. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers, M.W.; Rickard, M.D. Excretory–Secretory Products of Helminth Parasites: Effects on Host Immune Responses. Parasitology 1988, 96, S123–S166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, F.; Le Gros, G. Tissue-Specific Immunity in Helminth Infections. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwiernik, J.; Arłukowicz, T.; Zwiernik, B.; Matyskieła, T.; Gimeła-Dargiewicz, M.; Rakowska, A.; Januszko-Giergielewicz, B.; Rotkiewicz, E. Therapeutic Applicability of Helminths in Autoimmune Diseases—Literature Overview. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejas, B.E.; Martínez-Saucedo, D.; Terrazas, L.I. Parasites as Negative Regulators of Cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastille, E.; Frede, A.; McSorley, H.J.; Gräb, J.; Adamczyk, A.; Kollenda, S.; Hansen, W.; Epple, M.; Buer, J.; Maizels, R.M.; et al. Intestinal Helminth Infection Drives Carcinogenesis in Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, K.; Kato, T.; Okada, S.; Matsumoto, R.; Nishida, K.; Komuro, H.; Iida, M.; Tsujimoto, S.; Suganuma, T. Ascending Colon Cancer Associated with Deposited Ova of Schistosoma Japonicum in Non-Endemic Area. IDCases 2016, 6, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, B.V.A.; Bösmüller, H.; Schubert, T.; Bissinger, A.L. Sigmoid Colon Cancer Due to Schistosomiasis. Infection 2019, 47, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.L.; Wang, B.; Lu, Q.M.; Dong, L.R.; Cao, C.X.; Xu, S.L.; Shen, W.Y. Expression of Vascular Growth Factors in Intestinal Tissues in Colorectal Carcinoma Patients with Schistosomiasis Japonica. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2013, 25, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, N.A.; Keshk, W.A.; Shoheib, Z.S.; Ashour, D.S.; Shamloula, M.M. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and L-Fucose as Indispensable Participants in Schistosomiasis-Associated Colonic Dysplasia. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, Q.B.; He, W.B.; Wang, Z.Q. Clinicopathological Characteristics and Prognosis of Schistosomal Colorectal Cancer. Color. Dis. 2016, 18, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, K.; Wang, L.; Jing, H.; Pan, W.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Bu, D.; Cheng, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Comparison of Non-Schistosomal Colorectal Cancer and Schistosomal Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, E.I.; Harras, S.F.; Abdalla, A.G.; Mona, M.H. Syphacia Muris Infection in Rats Attenuates Colorectal Carcinogenesis through Oxidative Stress and Gene Expression Alterations. Implications for Modulatory Effects by Bryostatin-1. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, K.S.; Cliffe, L.J.; Bancroft, A.J.; Forman, S.P.; Thompson, S.; Booth, C.; Grencis, R.K. Chronic Trichuris Muris Infection Causes Neoplastic Change in the Intestine and Exacerbates Tumour Formation in APC Min/+ Mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, F.; Hoste, H.; Mallet, S.; Fournel, S.; Nano, J.L. Effects of the Excretory/Secretory Products of Six Nematode Species, Parasites of the Digestive Tract, on the Proliferation of HT29-D4 and HGT-1 Cell Lines. Epithelial Cell Biol. 1995, 4, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoste, H.; Nano, J.L.; Mallet, S.; Huby, F.; Fournel, S.; Rampal, P. Stimulation of HT29-D4 Cell Growth by Excretory/Secretory Products of the Parasite Nematode Trichostrongylus Colubriformis. Epithelial Cell Biol. 1995, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Du, X.; Tang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Hu, W.; Helmby, H.; Chen, G.; et al. Schistosoma Japonicum SjE16.7 Protein Promotes Tumor Development via the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 566061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Cabrera, S.; Callejas, B.E.; Ledesma-Soto, Y.; Coronel, J.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Gutiérrez-Cirlos, E.B.; Ávila-Moreno, F.; Rodríguez-Sosa, M.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Marquina-Castillo, B.; et al. Extraintestinal Helminth Infection Reduces the Development of Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Talib, N.N.; Nisha, M.; Ramasamy, R.; Pang, J.C. Preliminary Studies on the Effect of Excretory-Secretory (ES) Ascaris Lumbricoides Antigens on Colorectal Cell Line Viability. Trop. Biomed. 2024, 41, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamirad, S.; Daneshpour, S.; Mofid, M.R.; Andalib, A.; Eskandariyan, A.; Mousavi, S.; Yousofi Da-rani, H. Inhibition of Mouse Colon Cancer Growth Following Immunotherapy with a Fraction of Hydatid Cyst Fluid. Exp. Parasitol. 2023, 249, 108501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berriel, E.; Russo, S.; Monin, L.; Festari, M.F.; Berois, N.; Fernández, G.; Freire, T.; Osinaga, E. Anti-tumor Activity of Human Hydatid Cyst Fluid in a Murine Model of Colon Cancer. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 230176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motavallihaghi, S.; Tanzadehpanah, H.; Soleimani Asl, S.; Shojaeian, A.; Yousefimashouf, M.; Barati, N. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Hydatid Cyst Fluid on Colon Cancer Cell Line (C26). Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.A.; Prince, S.; Smith, K.A. Gastrointestinal Nematode-Derived Antigens Alter Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration through Regulation of Cell Cycle and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.M.; Ismail, C.A.; El-Azzouni, M.Z.; Ghazy, A.A.; Hadi, M.A. Immuno-Therapeutic Potential of Schistosoma Mansoni and Trichinella Spiralis Antigens in a Murine Model of Colon Cancer. Invest. New Drugs 2019, 37, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas, B.E.; Mendoza-Rodríguez, M.G.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; Reyes-Martínez, S.; Sánchez-Barrera, C.A.; Rodríguez-Sosa, M.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Martínez-Saucedo, D.; Chirino, Y.I.; León-Cabrera, S.A.; et al. Helminth-derived Molecules Inhibit Colitis-associated Colon Cancer Development through NF-κB and STAT3 Regulation. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Rodríguez, M.G.; Medina-Reyes, D.; Sánchez-Barrera, C.A.; Fernández-Muñoz, K.V.; Gar-cía-Castillo, V.; Ledesma-Torres, J.L.; González-González, M.I.; Reyes, J.L.; Pérez-Plascencia, C.; Rodríguez-Sosa, M.; et al. Helminth-Derived Molecules Improve 5-Fluorouracil Treatment on Experimental Colon Tumorigenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Aguilar, G.; Palencia, S.; Newton, E.; Abo, A. RNAPc2 Inhibits Colorectal Cancer in Mice through Tissue Factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections-World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Hataminejad, M.; Basirpour, B.; Baharlou, M.; Gholami Koohestan, M.; Ziaei Hezarjaribi, H.; Rahimi Esboei, B.; Gholami, S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Saberi, R. Global Prevalence and Correlation of Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025, 25, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), VEGF Receptors and Their Inhibitors for Antiangiogenic Tumor Therapy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L. Increased Serum Pentraxin-3 Level Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer after Curative Surgery, a Cohort Study. Medicine 2018, 97, e11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinggih; Limanu, F.; Labeda, I.; Lusikooy, R.E.; Mappincara; Faruk, M. The Relationship of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Levels in Plasma toward the Stage and Differentiation Degree in Colorectal Cancer. MCP 2021, 4, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochman, E.; Mahajna, J.; Shenzer, P.; Dahan, A.; Blatt, A.; Elyakim, R.; Reznick, A.Z. The Expression of INOS and Nitrotyrosine in Colitis and Colon Cancer in Humans. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and STAT3 Are Required for Survival of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Development of Colitis Associated Cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, D.; Jian, J.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X.; Yang, C. Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 1 Is Associated with Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, G.; Kasi, A. Familial Adenomatous Polyposis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Sui, H.; Fang, F.; Li, Q.; Li, B. The Application of ApcMin/+ Mouse Model in Colorectal Tumor Research. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, G.; Ahsan, H. Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in the Development of Cancer and Various Chronic Conditions. J. Carcinog. 2006, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.C.; Yu, J. Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Development and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; He, S.; Liao, B.; Wang, M.; Lin, H.; Hu, B.; Lan, X.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, M.; et al. Orally Administrated Hydrogel Harnessing Intratumoral Microbiome and Microbiota-Related Immune Responses for Potentiated Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Research 2024, 7, 0364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Pu, L.; Guo, A.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Du, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Helminth Reshapes Host Gut Microbiota and Immunoregulation by Deploying an Antimicrobial Program of Innate Immunity. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2496447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosschot, T.P.; Reynolds, L.A. The Impact of a Helminth-Modified Microbiome on Host Immunity. Mucosal. Immunol. 2018, 11, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, D.; Bowcutt, R.; Lee, S.C.; Tang, M.S.; Kurtz, Z.D.; Ding, Y.; Honda, K.; Gause, W.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Bonneau, R.A.; et al. Helminth Infection Promotes Colonization Resistance via Type 2 Immunity. Science 2016, 352, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, A.; Aviello, G.; Schwartz, C.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fallon, P.G. Schistosoma Mansoni Worm Infection Regulates the Intestinal Microbiota and Susceptibility to Colitis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00275-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shute, A.; Wang, A.; Jayme, T.S.; Strous, M.; McCoy, K.D.; Buret, A.G.; McKay, D.M. Worm Expulsion Is Independent of Alterations in Composition of the Colonic Bacteria That Occur during Experimental Hymenolepis Diminuta-Infection in Mice. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shute, A.; Callejas, B.E.; Li, S.H.; Wang, A.; Jayme, T.S.; Ohland, C.; Lewis, I.A.; Layden, B.T.; Buret, A.G.; McKay, D.M. Cooperation between Host Immunity and the Gut Bacteria Is Essential for Helminth-Evoked Suppression of Colitis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peón, A.N.; Espinoza-Jiménez, A.; Terrazas, L.I. Immunoregulation by Taenia Crassiceps and Its Antigens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 498583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matly, A.; Quinn, J.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Park, J.H.; Edwards, J. The Relationship between β-Catenin and Patient Survival in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 163, 103337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tang, B.; Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Excretory-Secretory Product of Trichinella Spiralis Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth by Regulating the Immune Response and Inducing Apoptosis. Acta Trop. 2022, 225, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledesma-Soto, Y.; Callejas, B.E.; Terrazas, C.A.; Reyes, J.L.; Espinoza-Jiménez, A.; González, M.I.; León-Cabrera, S.; Morales, R.; Olguín, J.E.; Saavedra, R.; et al. Extraintestinal Helminth Infection Limits Pathology and Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression during DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis: A Role for Alternatively Activated Macrophages and Prostaglandins. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 563425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Liu, S.; He, X. Critical and Diverse Role of Alarmin Cytokines in Parasitic Infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1418500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, F.J.; Chieffi, P.P.; Da Silva, L.C.; Bresson-Hadni, S.; Mantion, G.A.; Miguet, J.P.; Vuitton, D.A.; Ferreira, M.S.; Strauss, E. Helminthiasis. In Textbook of Hepatology: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1040–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, H.; Tang, D.W.T.; Wong, S.H.; Lal, D. Helminths in Alternative Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Intest. Res. 2024, 23, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magno, C.; Melloni, D.; Galì, A.; Mucciardi, G.; Nicocia, G.; Morandi, B.; Melioli, G.; Ferlazzo, G. The Anti-Tumor Activity of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin in Bladder Cancer Is Associated with an Increase in the Cir-culating Level of Interleukin-2. Immunol Lett 2002, 81, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeshi, K.; Ruscher, R.; Loukas, A.; Wangchuk, P. Immunomodulatory and Biological Properties of Helminth-Derived Small Molecules: Potential Applications in Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Front. Parasitol. 2022, 1, 984152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshpour, S.; Bahadoran, M.; Hejazi, S.H.; Eskandarian, A.A.; Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Darani, H.Y. Common Antigens between Hydatid Cyst and Cancers. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.P. The Regulation of Cyclin D1 Degradation: Roles in Cancer Development and the Potential for Therapeutic Invention. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Du, Z.; Ravasz, M.; Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Ewing, R.M. A Protein Interaction between β-Catenin and Dnmt1 Regulates Wnt Signaling and DNA Methylation in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishalian, I.; Bayuh, R.; Levy, L.; Zolotarov, L.; Michaeli, J.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils (TAN) Develop pro-Tumorigenic Properties during Tumor Progression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barrera, C.Á.; Olguín, J.E.; Terrazas, L.I. A Dual Role for Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. In The Innate Immune System in Health and Disease: From the Lab Bench Work to Its Clinical Implications; Morales-Montor, J., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 145–185. [Google Scholar]
- Olguin, J.E.; Mendoza-Rodriguez, M.G.; Sanchez-Barrera, C.A.; Terrazas, L.I. Is the Combination of Immunotherapy with Conventional Chemotherapy the Key to Increase the Efficacy of Colorectal Cancer Treatment? World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 15, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huels, D.J.; Sansom, O.J. Stem vs Non-Stem Cell Origin of Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, M.P.; Joosten, R.; Schmitt, M.; Välimäki, N.; Sacchetti, A.; Rajamäki, K.; Choi, J.; Procopio, P.; Silva, S.; van der Steen, B.; et al. Non-stem cell lineages as an alternative origin of intestinal tumorigenesis in the context of inflammation. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karo-Atar, D.; Gregorieff, A.; King, I.L. Dangerous Liaisons: How Helminths Manipulate the Intestinal Epithelium. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrazas, C.A.; Alcántara-Hernández, M.; Bonifaz, L.; Terrazas, L.I.; Satoskar, A.R. Helminth Excreted/Secreted Products Are Recognized by Multiple Receptors on DCs to Block the TLR Response and Bias Th2 Polarization in a CRAF Dependent Pathway. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundup, S.; Srivastava, L.; Norberg, T.; Watford, W.; Harn, D. A Neoglycoconjugate Containing the Human Milk Sugar LNFPIII Drives Anti-Inflammatory Activation of Antigen Presenting Cells in a CD14 Dependent Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Li, L.; Dong, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, X. Glycomolecules in Echinococcus Granulosus Cyst Fluid Inhibit TLR4-Mediated Inflammatory Responses via c-Raf. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Loukas, A.; McManus, D.P.; Mulvenna, J. Proteomic Characterisation of Echinococcus Granulosus Hydatid Cyst Fluid from Sheep, Cattle and Humans. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Bai, X. Extracellular Vesicles from Trichinella Spiralis: Proteomic Analysis and Protective Immunity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, L.; Díaz-Zaragoza, M.; Hernández, M.; Navarro, L.; Hernández-Ávila, R.; Encarnación-Guevara, S.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Landa, A. Differential Protein Expression of Taenia Crassiceps ORF Strain in the Murine Cysticercosis Model Using Resistant (C57BL/6) Mice. Pathogens 2023, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Zaragoza, M.; Jiménez, L.L.; Hernández, M.; Hernández-Ávila, R.; Navarro, L.; Ochoa-Sánchez, A.; Encarnación-Guevara, S.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Landa, A. Protein Expression Profile of Taenia crassiceps Cysticerci Related to Th1- and Th2-Type Responses in the Mouse Cysticercosis Model. Acta Trop. 2020, 212, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.Y.; Vlasuk, G.P. Recombinant Nematode Anticoagulant Protein C2 and Other Inhibitors Targeting Blood Coagulation Factor VIIa/Tissue Factor. J. Intern. Med. 2003, 254, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algaze, S.; Elliott, A.; Walker, P.; Battaglin, F.; Yang, Y.; Millstein, J.; Jayachandran, P.; Arai, H.; Soni, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Tissue Factor Expression in Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherlapati, M.H. Mouse Models in Colon Cancer, Inferences, and Implications. iScience 2023, 26, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, J.O.; Weinstock, J.V. Clinical Trials of Helminth Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases: Rationale and Findings. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).