Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients with Chronic Furunculosis and Osteomyelitis from Northwestern Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Identification of Microorganisms
2.3. Isolation of Chromosomal DNA
2.4. Real-Time PCR
- Taq DNA polymerase: 0.1 U/µL;
- MgCl2: 4 mM;
- dNTPs: 0.5 mM;
- 2 x reaction buffer with SYBR Green.
- ➢ DNA: 1 µL;
- ➢ Starter F: 2 µL;
- ➢ R starter: 2 µL;
- ➢ Sterile water: 2.5 µL;
- ➢ Master Mix: 7.5 µL.
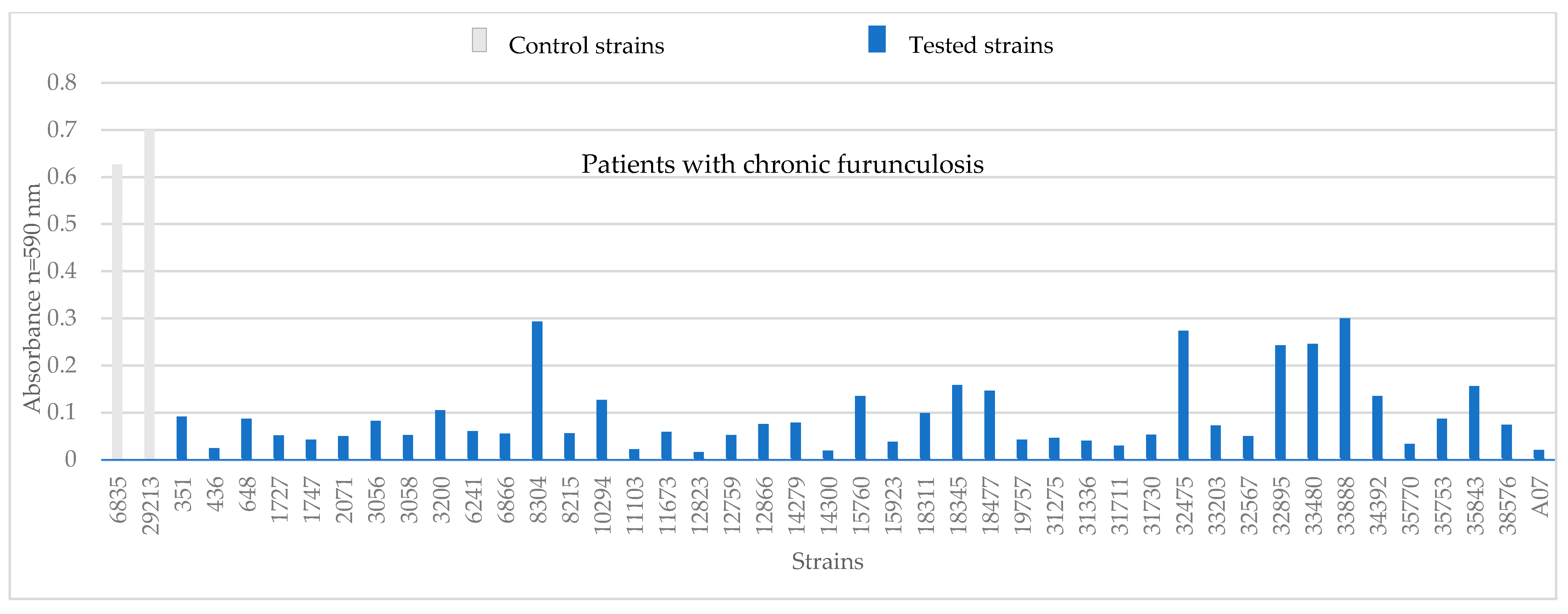
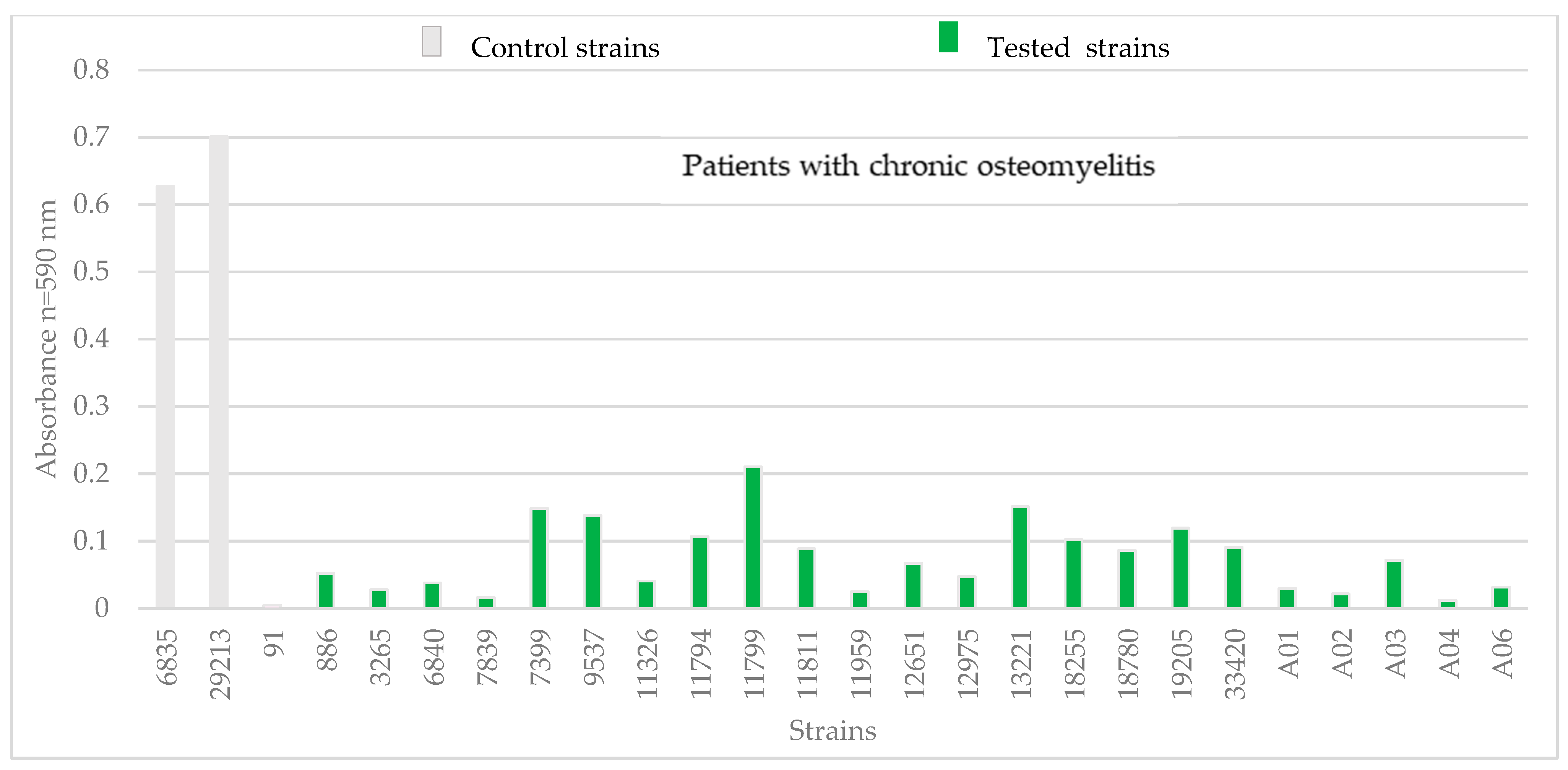
2.5. Biofilm Formation Ability of S. aureus Strains
2.6. Determination of S. aureus Sensitivity to Antibiotics
2.7. Statistical Analysis of the Results
3. Results
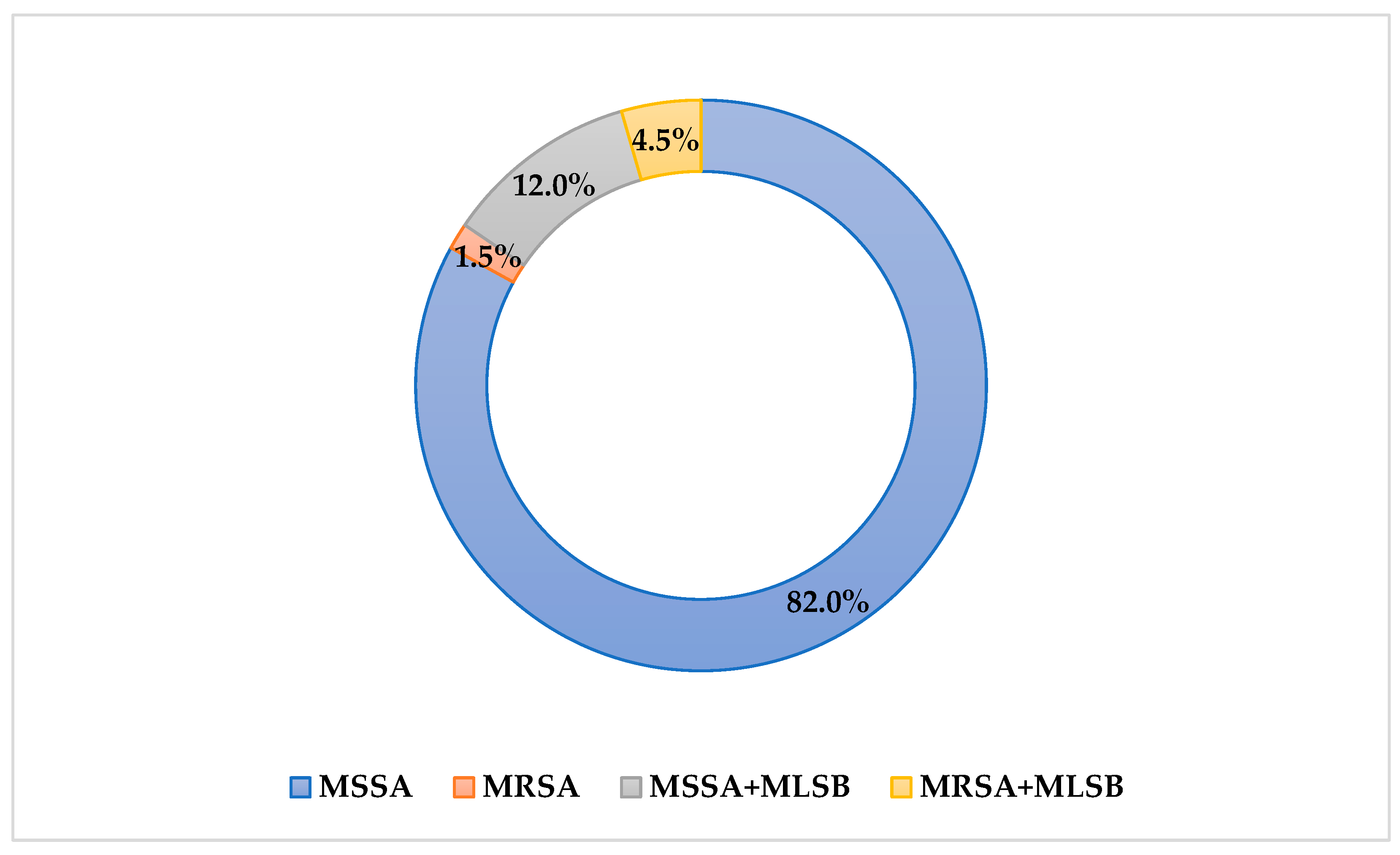
3.1. Phenotypic Assessments
3.2. Genotypic Assessments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Genes Strain Number | clfa | clfb | spa | cna | eap | hlgA | HlgB | hlg | Hld | bap | bbp | ebpS | Efb | fnbA | fnbB | Pvl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control strains | ||||||||||||||||
| 29213 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6538 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| strains from patients with chronic osteomyelitis | ||||||||||||||||
| 91 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 886 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3265 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6840 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 7839 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 7399 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 9537 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11326 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11794 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11799 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11811 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11959 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12651 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12975 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 13221 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 18255 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 18780 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 19205 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 33420 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 40034 | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 40675 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 41203 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 43846 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 43901 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| strains from patients with chronic furunculosis | ||||||||||||||||
| 351 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 436 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 648 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1727 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1747 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2071 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3056 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3058 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3200 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6241 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6866 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 8304 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 8215 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10294 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11103 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11673 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12756 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12823 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12866 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 14279 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| 14300 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 15760 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 15923 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 18311 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 18345 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 18477 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 19757 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 31136 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 31275 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 31711 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 31730 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 32475 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| 32567 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 32895 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 33203 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 33480 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 33888 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 34392 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 35753 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 35770 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 35843 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 38576 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 45736 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
References
- Touaitia, R.; Mairi, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Basher, N.S.; Idres, T.; Touati, A. Staphylococcus aureus: A review of the pathogenesis and virulence mechanisms. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, A.E.; Giai, C.; Gómez, M.I. Staphylococcus aureus adaptation to the skin in health and persistent/recurrent infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, T.A.; Unakal, C.G. Staphylococcus aureus infection. In StatPearls. Internet; StatPearls Publishing: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, A.D.; Lo, C.K.L.; Komorowski, A.S.; Suresh, M.; Guo, K.; Garg, A.; Tandon, P.; Senecal, J.; Del Corpo, O.; Stefanova, I.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdová, D.; Ruml, T.; Viktorová, J. Mechanism of staphylococcal resistance to clinically relevant antibiotics. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 77, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/112642 (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control, U. CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019; Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasela, M.; Grzegorczyk, A.; Nowakowicz-Dębek, B.; Malm, A. The prevalence of virulence determinants and antibiotic resistance patterns in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a nursing home in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Xu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Pan, Q.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Ge, S.; Cao, M.; Su, D.; Li, Y. Proteomic profiling of the endogenous peptides of MRSA and MSSA. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, Z.Y.; Cui, S.Y.; Ma, Z.B.; Deng, H.; Kong, W.L.; Yang, L.W.; Lin, C.; Xiong, W.G.; Zeng, Z.L. Biofilm production ability, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus from various veterinary hospitals. Pathogens 2020, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, E.; Chung, H.; Lee, Y.W.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Risk factors of recurrent infection in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A competing risk analysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0012622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poolman, J.T.; Torres, V.J.; Missiakas, D.; Welten, S.P.M.; Fernandez, J.; DuMont, A.L.; O’Keeffe, A.; Konstantinov, S.R.; Morrow, B.; Burghout, P.; et al. A SpA+LukAB vaccine targeting Staphylococcus aureus evasion factors restricts infection in two minipig infection models. NPJ Vaccines 2025, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, E.; Farrokhi, E.; Zamanzad, B.; Shahini Shams Abadi, M.; Deris, F.; Soltani, A.; Gholipour, A. Prevalence and distribution of adhesins and the expression of fibronectin-binding protein (FnbA and FnbB) among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Shahrekord Hospitals. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, A.; Najar Peerayeh, S.; Bakhshi, B.; Mirzaee, M. The Microbial Surface Components Recognizing Adhesive Matrix Molecules (MSCRAMMs) Genes among Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from Hospitalized Children. Iran. J. Pathol. 2015, 10, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh, V.K.; Rivera, J.J.; Smeds, E.; Ko, Y.P.; Bowden, M.G.; Wann, E.R.; Gurusiddappa, S.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Höök, M. A structural model of the Staphylococcus aureus ClfA-fibrinogen interaction opens new avenues for the design of anti-staphylococcal therapeutics. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. The potential use of toxin antibodies as a strategy for controlling acute Staphylococcus aureus infections. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicca, M.R.; Oliveira Pinto, E.; Sousa Filho, W.P.; de Brum, G.F.; da Silva, T.C.; Vizzotto, B.S. Molecular investigation of a furunculosis outbreak at a penitentiary in southern Brazil. Infect. Dis. Health 2025, 30, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, M.S.; Mattappallil, A.; Finkel, D.; Parker, D. Clinical Impact of Staphylococcus aureus Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Qiu, X.S.; Jiang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Tang, L.M.; Shi, H.F. Microwaves increase the effectiveness of systemic antibiotic treatment in acute bone infection: Experimental study in a rat model. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, W.; Hunt, C.; Nehring, L.; Barnum, B.; Ashton, N.; Williams, D. Biofilm growth on simulated fracture fixation plates using a customized CDC biofilm reactor for a sheep model of biofilm-related infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinka, J.; Hachmeister, M.; Geraci, J.; Sordelli, D.; Hansen, U.; Niemann, S.; Oetermann, S.; Peters, G.; Löffler, B.; Tuchscherr, L. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from chronic osteomyelitis are characterized by high host cell invasion and intracellular adaptation, but still induce inflammation. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraveji, Z.; Tabatabaei, M.; Shirzad Aski, H.; Khoshbakht, R. Characterization of hemolysins of Staphylococcus strains isolated from human and bovine, southern Iran. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Galia, L.; Ligozzi, M.; Bertoncelli, A.; Mazzariol, A. Triplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Staphylococcus aureus, Panton-Valentine Leucocidin and Methicillin Resistance directly from clinical samples. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, P.; Li, J. Characterization of adhesin genes, staphylococcal nuclease, hemolysis, and biofilm formation among Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from different sources. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, P.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Pruss, A.; Wojciuk, B.; Giedrys-Kalemba, S.; Dołęgowska, B.; Zielińska-Bliźniewska, H.; Olszewski, J.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Kochan, E. Synergistic effect of fennel essential oil and hydrogen peroxide on bacterial biofilm. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M.; Junka, A.; Brożyna, M.; Migdał, P.; Kwiek, B.; Nowak, M.; Mączyńska, B.; Bartoszewicz, M. The in vitro ability of Klebsiella pneumoniae to form biofilm and the potential of various compounds to eradicate it from urinary catheters. Pathogens 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, R.; Kanematsu, H.; Ogawa, A.; Kogo, T.; Miura, H.; Kawai, R.; Hirai, N.; Kato, T.; Yoshitake, M.; Barry, D.M. Quantitative Analyses of biofilm by using crystal violet staining and optical reflection. Materials 2022, 15, 6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Su, P.W.; Moi, S.H.; Chuang, L.Y. Biofilm Formation in Acinetobacter baumannii: Genotype-phenotype correlation. Molecules 2019, 24, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechrid, A.; Pérez-Vázquez, M.; Smaoui, H.; Hariga, D.; Rodríguez-Baños, M.; Vindel, A.; Baquero, F.; Cantón, R.; del Campo, R. Molecular analysis of community-acquired methicillin-susceptible and resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from bacteraemic and osteomyelitis infections in children from Tunisia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.T.; Lyra, T.G.; Alves, N.N.; Caldas, R.M.; Barberino, M.G.; Nascimento-Carvalho, C.M. Methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus infection among children. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.J.; Benvenuti, M.A.; Mignemi, M.E.; Martus, J.; Wood, J.B.; Thomsen, I.P.; Schoenecker, J.G. Similar clinical severity and outcomes for methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus pediatric musculoskeletal infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Calle, C.; Morata, L.; Cobos-Trigueros, N.; Martinez, J.A.; Cardozo, C.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremic pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.Y.; Jiang, W.; Mojica, N.; Tseng, K.K.; McNeill, R.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Perl, T.M. National costs associated with methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus hospitalizations in the United States, 2010–2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu Lattar, S.M.; Tuchscherr, L.P.; Caccuri, R.L.; Centrón, D.; Becker, K.; Alonso, C.A.; Barberis, C.; Miranda, G.; Buzzola, F.R.; von Eiff, C.; et al. Capsule expression and genotypic differences among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with chronic or acute osteomyelitis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.R. Evolution of Staphylococcus aureus during human colonization and infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Marini, B.; Stroffolini, G.; Geremia, N.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Campanile, F.; Bartoletti, M.; Alloisio, G.; Di Risio, L.; Viglietti, G.; et al. The virulence toolkit of Staphylococcus aureus: A comprehensive review of toxin diversity, molecular mechanisms, and clinical implications. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2025, 44, 1797–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/surveillance-antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2019 (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- Saderi, H.; Emadi, B.; Owlia, P. Phenotypic and genotypic study of macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin B (MLSB) resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in Tehran, Iran. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, BR48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, L.; Machado, V.; Cuello, D.; Aguerrebere, P.; Seija, V.; Braga, V.; Varela, G. Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance phenotypes and their associated genotypes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a tertiary level public hospital of Uruguay. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2020, 52, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, K.; Qrei, W.; Abdeen, Z. Screening of genes encoding adhesion factors and biofilm production in methicillin resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Palestinian patients. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Bataille, J.F.; Drancourt, M.; Curvale, G.; Argenson, J.N.; Groulier, P.; Raoult, D. Ambulatory treatment of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus-infected orthopedic implants with high-dose oral co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Pasquet, A.; Legout, L.; Beltrand, E.; Dubreuil, L.; Migaud, H.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Senneville, E. Efficacy and tolerance of rifampicin–linezolid compared with rifampicin–cotrimoxazole combinations in prolonged oral therapy for bone and joint infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, W.; Schmid, T.; D’este, M.; Guillaume, O.; Foster, A.; Decosterd, L.; Richards, R.G.; Eglin, D.; Zeiter, S.; Moriarty, T.F. A Hyaluronic acid hydrogel loaded with gentamicin and vancomycin successfully eradicates chronic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus orthopedic infection in a sheep model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01840-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, N.; Ryan, E.J.; Widaa, A.; Sexton, G.; Fennell, J.; O’Rourke, S.; Cahill, K.C.; Kearney, C.J.; O’Brien, F.J.; Kerrigan, S.W. Staphylococcal osteomyelitis: Disease progression, treatment challenges, and future directions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00084-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, H.; Rudkin, J.K.; Black, N.S.; Gallagher, L.; O’Neill, E.; O’Gara, J.P. Methicillin resistance and the biofilm phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnsholt, T. The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS 2013, 121, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Ueda, M.; Kanzaki, H.; Tada, J.; Arata, J. Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from impetigo and furuncle: Role of fibrinogen and fibrin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1997, 16, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paharik, A.E.; Horswill, A.R. The Staphylococcal biofilm: Adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol. Spect. 2016, 4, 529–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Berends, E.T.M.; Chan, R.; Schwab, E.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K.; Torres, V.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms release leukocidins to elicit extracellular trap formation and evade neutrophil-mediated killing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7416–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and its regulation mechanism. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomehzadeh, N.; Emrani, S.S. Assessment of biofilm formation, antibiotic resistance patterns, and the prevalence of adhesion-related genes in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Heliyon 2024, 11, e41537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, F.; Zhao, J.; Lou, N.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Li, Y. Molecular characteristics and virulence gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus causing bloodstream infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, F.S.; Saintive, S.; Carvalho Ferreira, D.; Rocha Silva, A.B.; Guimarães, L.C.; Braga, B.S.; Dios Abad, E.; Ribeiro, M.; Netto Dos Santos, K.R. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from infected skin lesions present several virulence genes and are associated with the CC30 in Brazilian children with atopic dermatitis. Virulence 2021, 12, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strommenger, B.; Braulke, C.; Heuck, D.; Schmidt, C.; Pasemann, B.; Nübel, U.; Witte, W. spa typing of Staphylococcus aureus as a frontline tool in epidemiological typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giormezis, N.; Doudoulakakis, A.; Tsilipounidaki, K.; Militsopoulou, M.; Kalogeras, G.; Stamouli, V.; Kolonitsiou, F.; Petinaki, E.; Lebessi, E.; Spiliopoulou, I. Emergence of a mupirocin-resistant, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus clone associated with skin and soft tissue infections in Greece. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Von Eiff, C.; Sinha, B.; Joost, I.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. eap gene as novel target for specific identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.M.; Bowden, M.G.; Brown, E.L.; Laabei, M.; Massey, R.C. Staphylococcus aureus extracellular adherence protein triggers tnfα release, promoting attachment to endothelial cells via protein A. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillaspy, A.F.; Patti, J.M.; Smeltzer, M.S. Transcriptional regulation of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen adhesin gene, cna. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, C.; Solano, C.; Valle, J.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Bap, a Staphylococcus aureus surface protein involved in biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bride, L.L.; Pereira, M.F.; Barbosa, M.C.; Silva, N.C.; Klein, N.M.; Nascimento, T.C.; Schuenck, R.P. Differences in resistance profiles and virulence genes among methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus of different lineages at a public tertiary hospital. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20190095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiuk, H.; Kopron, K.; Grumann, D.; Goerke, C.; Kolata, J.; Jursa-Kulesza, J.; Giedrys-Kalemba, S.; Bröker, B.M.; Holtfreter, S. Association of recurrent furunculosis with panton-valentine leukocidin and the genetic background of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.D.; Kausar, H.; Smith, S.; Lazar, P.G.; Kroll-Desrosiers, A.R.; Hollins, C., 3rd; Barton, B.A.; Ward, D.V.; Ellison, R.T., 3rd. Epidemiological and clinical features of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin positive Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boan, P.; Tan, H.L.; Pearson, J.; Coombs, G.; Heath, C.H.; Robinson, J.O. Epidemiological, clinical, outcome and antibiotic susceptibility differences between PVL positive and PVL negative Staphylococcus aureus infections in Western Australia: A case control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmantar, T.; Chaieb, K.; Makni, H.; Miladi, H.; Ben Abdallah, F.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Detection by PCR of adhesins genes and slime production in clinical Staphylococcus aureus. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristan, A.; Benito, Y.; Montserret, R.; Boisset, S.; Dusserre, E.; Penin, F.; Ruggiero, F.; Etienne, J.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Lina, G.; et al. The signal peptide of Staphylococcus aureus panton valentine leukocidin LukS component mediates increased adhesion to heparan sulfates. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, M.; Hermans, K.; Devriese, L.A.; Maes, D.; Haesebrouck, F. Screening of genes encoding adhesion factors and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from poultry. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodén Wästfelt, M.K.; Flock, J.I. Incidence of the highly conserved fib gene and expression of the fibrinogen-binding (Fib) protein among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2347–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence 5′-3′ | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| hlgA-F | CTGATTACTATCCAAGAAATTCGATTG | |
| hlgA-R | CTTTCCAGCCTACTTTTTTATCAGT | [22] |
| hlgB-F | GTGCACTTACTGACAATAGTGC | |
| hlgB-R | GTTGATGAGTAGCTACCTTCAGT | [22] |
| hld-F | AAGAATTTTTATCTTAATTAAGGAAGGAGTG | |
| hld-R | TTAGTGAATTTGTTCACTGTGTCGA | [22] |
| hlg-F | GTCAYAGAGTCCATAATGCATTTAA | |
| hlg-R | CACCAAATGTATAGCCTAAAGTG | [22] |
| spa-F | CAGATAACAAATTAGCTGATAAAAACAT | |
| spa-R | CTAAGGCTAATGATAATCCACCAAATAC | [21] |
| clfa-F | ATTGGCGTGGCTTCAGTGCT | |
| clfa-R | CGTTTCTTCCGTAGTTGCATTTG | [21] |
| clfb-F | GCTGCAAAAATGCAAGATCA | |
| clfb-R | TTGCCGCCATAAATGTGTTA | [21] |
| cna-F | AAAGCGTTGCCTAGTGGAGA | |
| cna-R | AGTGCCTTCCCAAACCTTTT | [21] |
| eap-F | AGTCATTGATTACAACAA | |
| eap-R | CTTATTAAATGTTAAGCTTG | [21] |
| bap-F bap-R | GAGCCAAGACAAAGGTGAAG GTAGCCATAGCACGGAACAT | [24] |
| fnba–F fnba–R | TCCGCCGAACAACATACC TCAAGCACAAGGACCAAT | [24] |
| fnbb–F fnbb–R | TCTGCGTTATGAGGATTT ACAGTAGAGGAAAGTGG | [24] |
| fib–F fib–R | AGATGCGAGCGAAGGGTA TAAACGAAACTAAGTTGACTGC | [24] |
| ebps–F ebps–R | GGTGAACCTGAACCGTAG CTGGCAAGGCGAATAACT | [24] |
| bbp–F bbp–R | CTTAGCAGTTCAACAGGGTG TTGGCTTTATTGTGATGGTC | [24] |
| pvl–F pvl-R | AAATGCTGGACAAAACTTCTTGG TTTGCAGCGTTTTGTTTTCG | [23] |
| Stages | spa, eap, clfb | cna, clfa | hlgA, hlgB, hld, hlg | Pvl | bbp, epbs, fib | fnbpa, fnbpb | Bap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial denaturation | 95 °C/ 5 min | 95 °C/ 5 min | 94 °C/ 7 min | 94 °C/ 5 min | 95 °C/ 5 min | 95 °C/ 5 min | 95 °C/ 5 min |
| Denaturation | 95 °C/ 5 min | 95 °C/ 5 min | 94 °C/ 1 min | 95 °C/ 15 s | 95 °C/ 40 s | 95 °C/ 40 s | 95 °C/ 40 s |
| Annealing | 50 °C/ 1 min | 55 °C/ 1 min | 58 °C/ 1 min | 60 °C/ 30 s | 56 °C/ 50 s | 54 °C/ 50 s. | 58 °C/ 50 s |
| Elongation | 72 °C/ 1 min | 72 °C/ 1 min | 72 °C/ 1 min | 60 °C/ 30 s | 65 °C/ 5 s | 65 °C/ 5 s. | 65 °C/ 5 s |
| Final elongation | 72 °C/ 10 min | 72 °C/ 10 min | 72 °C/ 7 min | 72 °C/ 3 min | 72 °C/ 50 s | 72 °C/ 50 s. | 72 °C/ 50 s |
| End of the process | 72 °C/ 12 min | 72 °C/ 12 min | 72 °C/ 7 min | 72 °C/ 10 min | 72 °C/ 10 min | 72 °C/ 10 min | 72 °C/ 10 min |
| Gene Name | Osteomyelitis | Furunculosis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSCRAMM | Clfa | 100 | 100 |
| Clfb | 100 | 100 | |
| spA | 100 | 100 | |
| Can | 95.8 | 100 | |
| Eap | 100 | 100 | |
| Bap | 100 | 100 | |
| Bbp | 100 | 97.7 | |
| ebpS | 100 | 100 | |
| fnbA | 100 | 100 | |
| fnbB | 100 | 97.7 | |
| Fib | 100 | 100 | |
| Cytotoxin | hlgA | 95.8 | 100 |
| HlgB | 95.8 | 100 | |
| Hlg | 95.8 | 100 | |
| Hld | 100 | 100 | |
| Pvl | 100 | 97.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wcisłek, A.; Jursa-Kulesza, J.; Masiuk, H.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Hukowska-Szematowicz, B.; Prowans, P.; Ziętek, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients with Chronic Furunculosis and Osteomyelitis from Northwestern Poland. Pathogens 2025, 14, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090923
Wcisłek A, Jursa-Kulesza J, Masiuk H, Grygorcewicz B, Hukowska-Szematowicz B, Prowans P, Ziętek P, Kosik-Bogacka D. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients with Chronic Furunculosis and Osteomyelitis from Northwestern Poland. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090923
Chicago/Turabian StyleWcisłek, Aleksandra, Joanna Jursa-Kulesza, Helena Masiuk, Bartłomiej Grygorcewicz, Beata Hukowska-Szematowicz, Piotr Prowans, Paweł Ziętek, and Danuta Kosik-Bogacka. 2025. "Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients with Chronic Furunculosis and Osteomyelitis from Northwestern Poland" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090923
APA StyleWcisłek, A., Jursa-Kulesza, J., Masiuk, H., Grygorcewicz, B., Hukowska-Szematowicz, B., Prowans, P., Ziętek, P., & Kosik-Bogacka, D. (2025). Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients with Chronic Furunculosis and Osteomyelitis from Northwestern Poland. Pathogens, 14(9), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090923








