Experimental Infection in Mice with Cryptosporidium Isolated from Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
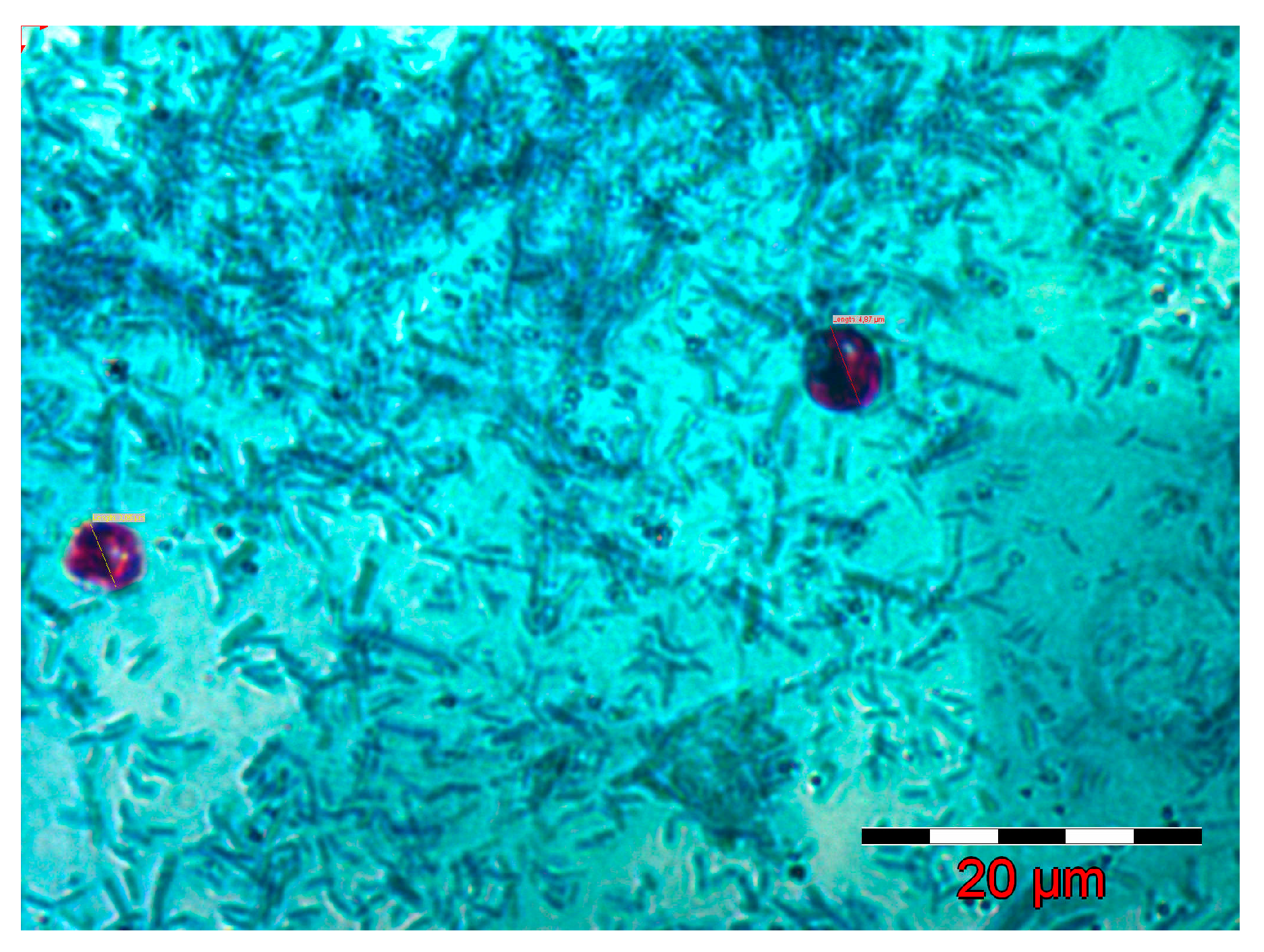
2.1. Inoculum
- Consecutive filtration through sieves with mesh sizes of 500 µm and 100 µm and five layers of gauze.
- Centrifugation at 1000 rpm followed by two successive washes with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
- Flotation of the sediment in Sheather’s sucrose solution.
- Recovery of oocysts using a pipette and washing in PBS.
- Addition of penicillin (100 IU/mL) and streptomycin (1 mg/mL) to the oocyst suspension.
- C. parvum containing 3350 oocysts/mL,
- C. ryanae containing 3650 oocysts/mL,
- C. canis containing 3100 oocysts/mL.
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Assays Performed
2.4. Ethical Approval
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, U.; Zahedi, A.; Paparini, A. Cryptosporidium in Humans and Animals—A One Health Approach to Prophylaxis. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.; Hunter, P.R.; Chalmers, R.M.; Tyler, K.M. Cryptosporidium Pathogenicity and Virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzipori, S.; Angus, K.W.; Campbell, I.; Gray, E.W. Cryptosporidium: Evidence for a Single-Species Genus. Infect. Immun. 1980, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J. Cryptosporidiosis and Cryptosporidium species in animals and humans: A thirty colour rainbow? Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.; Zahedi, A.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans. Animals 2021, 11, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Shams, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, S.; Ali, A. Evaluation of Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Cryptosporidium Infection in Rural Population of District Buner, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, A.V.; Tyrrell, P.; Wennogle, S.; Chandrashekar, R.; Lappin, M.R. Experimental Infection of Cats with Cryptosporidium felis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyzzer, E.E. Cryptosporidium parvum (sp. nov.), a coccidium found in the small intestine of the common mouse. Arch. Protistenkd. 1912, 26, 394–412. [Google Scholar]
- Spano, F.; Putignani, L.; Crisanti, A.; Sallicandro, P.; Morgan, U.M.; LeBlancq, S.M.; Tchack, L.; Tzipori, S.; Widmer, G. Multilocus Genotypic Analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum Isolates from Different Hosts and Geographical Origins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3255–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzipori, S. Cryptosporidiosis in Animals and Humans. Microbiol. Rev. 1983, 47, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dărăbuș, G. Criptosporidioza—Cercetări Privind Etiologia, Epidemiologia, Patogenia, Diagnosticul și Tratamentul în Infecțiile Naturale și Experimentale. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitatea de Științe Agricole și Medicină Veterinară a Banatului, Timișoara, Romania, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fayer, R.; Trout, J.M.; Xiao, L.; Morgan, U.M.; Lai, A.A.; Dubey, J.P. Cryptosporidium canis n. sp. from Domestic Dogs. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, U.M.; Xiao, L.; Monis, P.; Fall, A.; Irwin, P.J.; Fayer, R.; Denholm, K.M.; Limor, J.; Lal, A.A.; Thompson, R.C. Cryptosporidium spp. in Domestic Dogs: The ‘Dog’ Genotype. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2202–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza-Diaz, S.; Amar, C.; Iversen, A.M.; Stanley, P.J.; McLauchlin, J. Unusual Cryptosporidium Species Recovered from Human Feces: First Description of Cryptosporidium felis and Cryptosporidium ‘Dog Type’ from Patients in England. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dărăbuș, G.; Olariu, R. The Homologous and Interspecies Transmission of Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium meleagridis. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2003, 6, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, R.; Jian, F.; Zhang, S.; Ning, C.; Zhang, L. A Canine Model of Experimental Infection with Cryptosporidium canis. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 195, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlaam, A.; Sannella, A.R.; Ferrari, N.; Temesgen, T.T.; Rinaldi, L.; Normanno, G.; Cacciò, S.M.; Robertson, L.J.; Giangaspero, A. Ready-to-eat salads and berry fruits purchased in Italy contaminated by Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Entamoeba histolytica. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 370, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Nair, L.V.; Ghosal, A.; Sardar, S.K.; Dutta, S.; Ganguly, S. Genetic characterization reveals evidence for an association between water contamination and zoonotic transmission of a Cryptosporidium sp. from dairy cattle in West Bengal, India. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 17, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayer, R.; Santín, M.; Trout, J.M. Cryptosporidium ryanae n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in cattle (Bos taurus). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ježková, J.; Prediger, J.; Holubová, N.; Sak, B.; Konečný, R.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Rost, M.; McEvoy, J.; Kváč, M. Cryptosporidium ratti n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) and genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. in brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) in the Czech Republic. Parasitology 2021, 148, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ryan, U.M. Molecular Epidemiology. In Cryptosporidium and Cryptosporidiosis; Fayer, R., Xiao, L., Eds.; CRC Press and IWA Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 119–171. [Google Scholar]
- CerTest BIOTEC SL. CERTEST Crypto: One Step Test to Detect Cryptosporidium in Card Format. Available online: https://www.certest.es/products/crypto-giardia-3/ (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Dan, Ș.; Radu, S.; Șeicaru, A.; Cristescu, P. Data Regarding Natural and Experimental Infestation with Cryptosporidium in Birds and Laboratory Animals. In Proceedings of the Seminar: Progress in Therapy and Control of Parasitic Zoonoses, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 1987; Volume 13, pp. 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Blagburn, B.L.; Ernest, J.A. Experimental Cryptosporidium parvum Infections in Chickens. J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, P.J.; Tham, V.L.; Saram, W.G.; Paull, K.L.; McDermott, S. Cryptosporidium Infections in Birds and Mammals and Attempted Cross-Transmission Studies. Vet. Parasitol. 1987, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, R.J.; Robertson, I.D.; Irwin, P.J.; Mencke, N.; Thompson, R.C. Canine Gastrointestinal Parasitic Zoonoses in India. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Coco, V.F.; Córdoba, M.A.; Sidoti, A.; Santín, M.; Drut, R.; Basualdo, J.A. Experimental Infection with Cryptosporidium parvum IIaA21G1R1 Subtype in Immunosuppressed Mice. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, N.M.; Zalat, R.S.; Khaled, E.; Elmansory, B.M. Evaluation of the Therapeutic Efficacy of Some Essential Oils in Experimentally Immunosuppressed Mice Infected with Cryptosporidium parvum. J. Parasit. Dis. 2023, 47, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, D.; Angus, K.W.; Snodgrass, D.R.; Tzipori, S. Experimental Cryptosporidiosis in Laboratory Mice. Infect. Immun. 1982, 38, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshay, E.V.N.; Nassef, N.E.; El Shafei, O.K.; Saleh, M.M.; Kora, M.A.; Shalaan, F.H. Therapeutic Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitor (Omeprazole) on Cryptosporidium parvum in Immunosuppressed Experimental Mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2023, 47, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjola, S.; Lindberg, L.A. Experimental Cryptosporidiosis in Mice, Calves, and Chickens. Acta Vet. Scand. 1986, 27, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Day p.i. | Examination Method | GROUP I Infected with C. parvum Infected/Total Mice | GROUP II Infected with C. ryanae INFECTED/Total Mice | GROUP III Infected with C. canis Infected/Total Mice | Mother Mice Infected/Total Mice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Direct examination | 9/9− | 10/10− | 11/11− | 3/3− * |
| 4 | Direct examination | 8/9±; 1/9+ | 10/10± | 11/11± | 3/3− * |
| 7 | Direct examination | 7/9±; 2/9− | 6/10±; 4/10− | 5/11±; 6/11− | ND |
| 10 | Direct examination | 2/9±; 7/9− | 3/10±; 7/10− | 1/11±; 10/11− | ND |
| 14 | Quick Crypto Test | 9/9+ | 10/10+ | 11/11+ | ND |
| 17 | Quick Crypto Test | 9/9+ | 10/10+ | 11/11+ | 3/3+ |
| 23 | Quick Crypto Test | 9/9+ | 10/10+ | 11/11+ | 3/3+ |
| 31 | Quick Crypto Test | 9/9+ | 10/10+ | 11/11+ | 3/3+ |
| 40 | Quick Crypto Test | 9/9+ | 10/10+ | 11/11+ | 3/3+ |
| No Mice | Group I | Group II | Group III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | |
| 1 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 0 |
| 2 | 7 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 14 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 5 | 0 |
| 7 | 7 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| 8 | 9 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 0 | |||
| 11 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Group I | Group II | Group III | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | Day 4 p.i. | Day 7 p.i. | Day 10 p.i. | |
| Mean | 8.111111 | 5 | 0.666667 | 6.2 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 6.636364 | 2 | 0.545455 |
| Standard Error | 0.857069 | 1.178511 | 0.471405 | 0.742369 | 0.936305 | 0.628932 | 0.560401 | 0.750757 | 0.545455 |
| Median | 8 | 5 | 0 | 7 | 2.5 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Mode | 8 | 9 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.571208 | 3.535534 | 1.414214 | 2.347576 | 2.960856 | 1.988858 | 1.858641 | 2.48998 | 1.809068 |
| Sample Variance | 6.611111 | 12.5 | 2 | 5.511111 | 8.766667 | 3.955556 | 3.454545 | 6.2 | 3.272727 |
| Kurtosis | 3.521119 | −1.35543 | 4 | −0.64606 | −1.24007 | −0.2244 | −0.18943 | −1.63892 | 11 |
| Skewness | 1.544483 | −0.34911 | 2.12132 | −0.74974 | 0.442401 | 1.245704 | −0.49083 | 0.617529 | 3.316625 |
| Range | 9 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Minimum | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Maximum | 14 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| Sum | 73 | 45 | 6 | 62 | 29 | 12 | 73 | 22 | 6 |
| Count | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| Confidence Level (95.0%) | 1.976406 | 2.717652 | 1.087061 | 1.679354 | 2.118069 | 1.422743 | 1.248652 | 1.672791 | 1.215348 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dărăbuș, R.G.; Ilie, M.S.; Dărăbuș, G.; Morariu, S.; Dărăbuș, D.M.; Mederle, N.; Imre, M.; Sîrbu, I.O.; Olariu, T.R. Experimental Infection in Mice with Cryptosporidium Isolated from Humans. Pathogens 2025, 14, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090843
Dărăbuș RG, Ilie MS, Dărăbuș G, Morariu S, Dărăbuș DM, Mederle N, Imre M, Sîrbu IO, Olariu TR. Experimental Infection in Mice with Cryptosporidium Isolated from Humans. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090843
Chicago/Turabian StyleDărăbuș, Rodica Georgiana, Marius Stelian Ilie, Gheorghe Dărăbuș, Sorin Morariu, Diana Maria Dărăbuș, Narcisa Mederle, Mirela Imre, Ioan Ovidiu Sîrbu, and Tudor Rareș Olariu. 2025. "Experimental Infection in Mice with Cryptosporidium Isolated from Humans" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090843
APA StyleDărăbuș, R. G., Ilie, M. S., Dărăbuș, G., Morariu, S., Dărăbuș, D. M., Mederle, N., Imre, M., Sîrbu, I. O., & Olariu, T. R. (2025). Experimental Infection in Mice with Cryptosporidium Isolated from Humans. Pathogens, 14(9), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090843









