Antiviral Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts Vitex negundo and Macaranga tanarius Against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.2. Virus and Cells
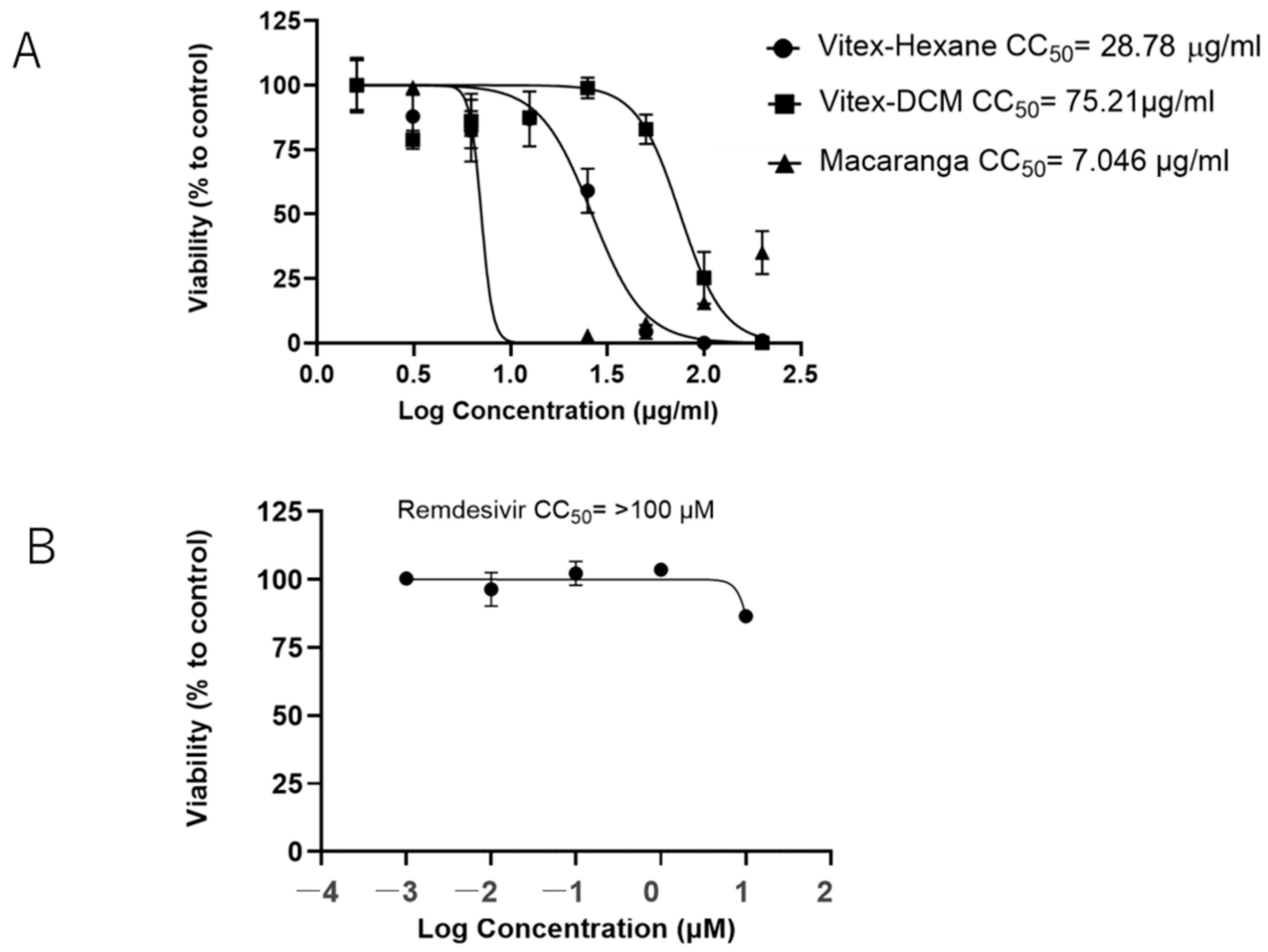
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Evaluation of the Antiviral Activity Against SARS-CoV-2
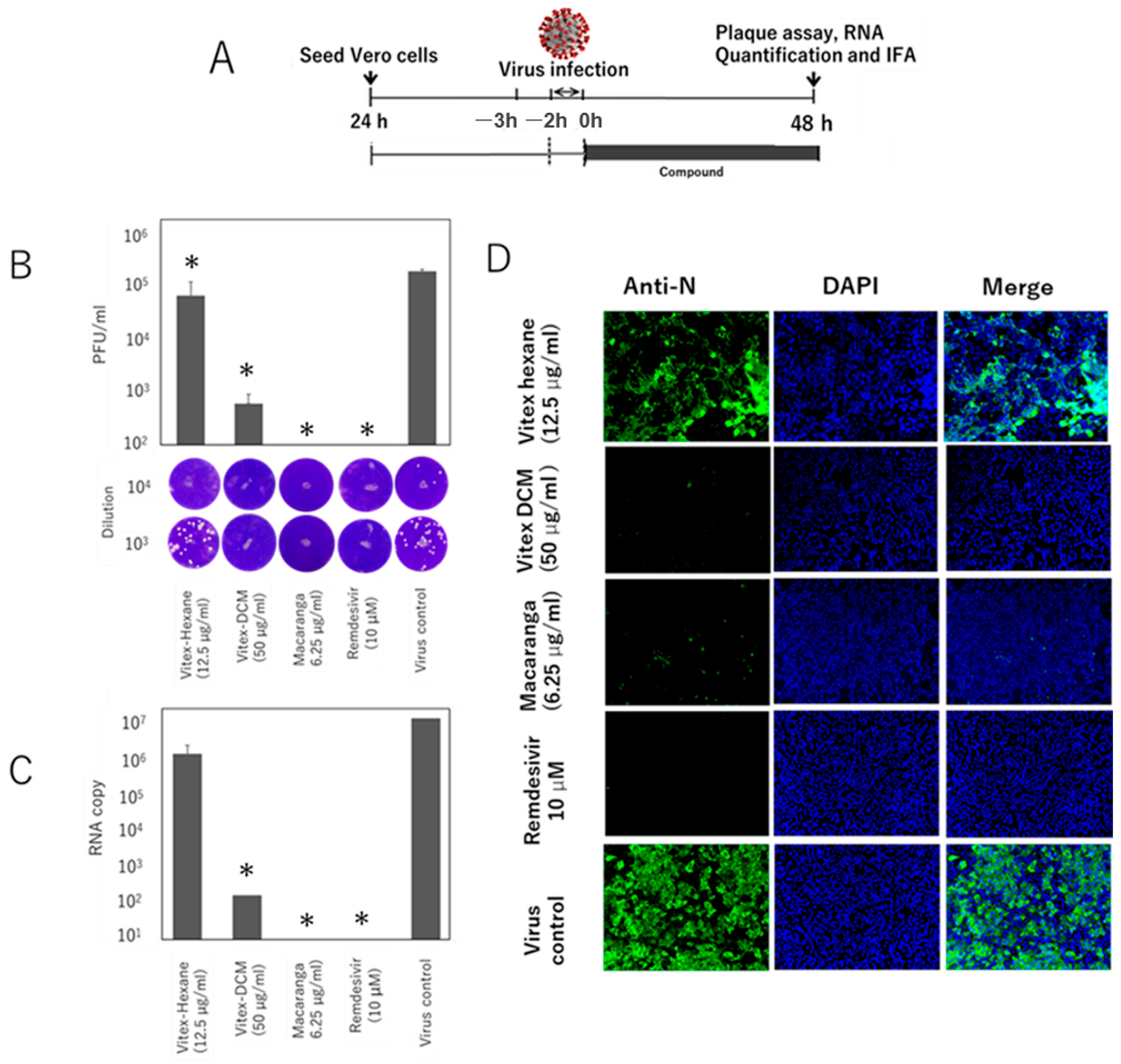
2.5. Time-of-Addition Assay
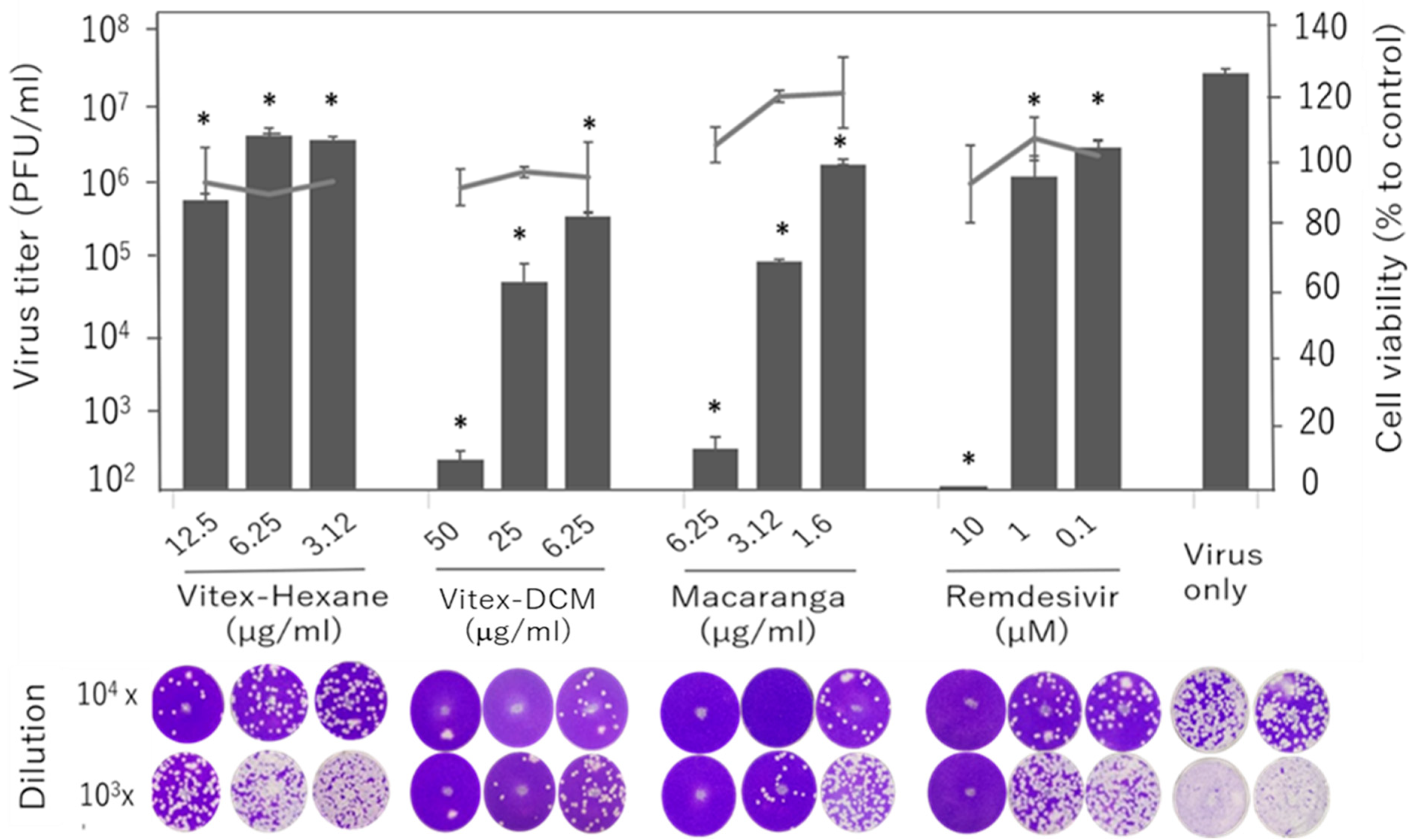
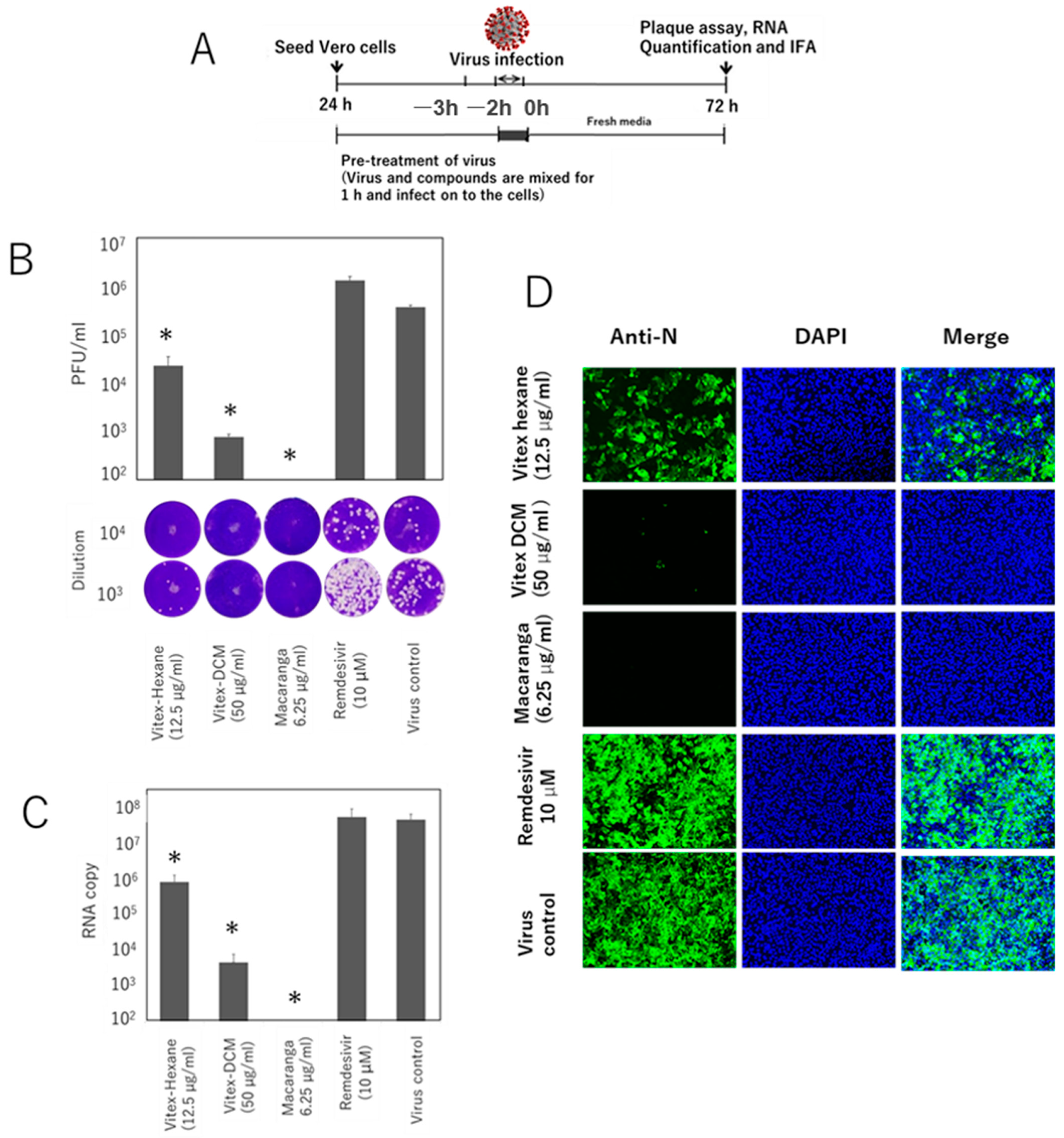
2.6. Virus Titration and Quantification of Antiviral Activity by Plaque Assay
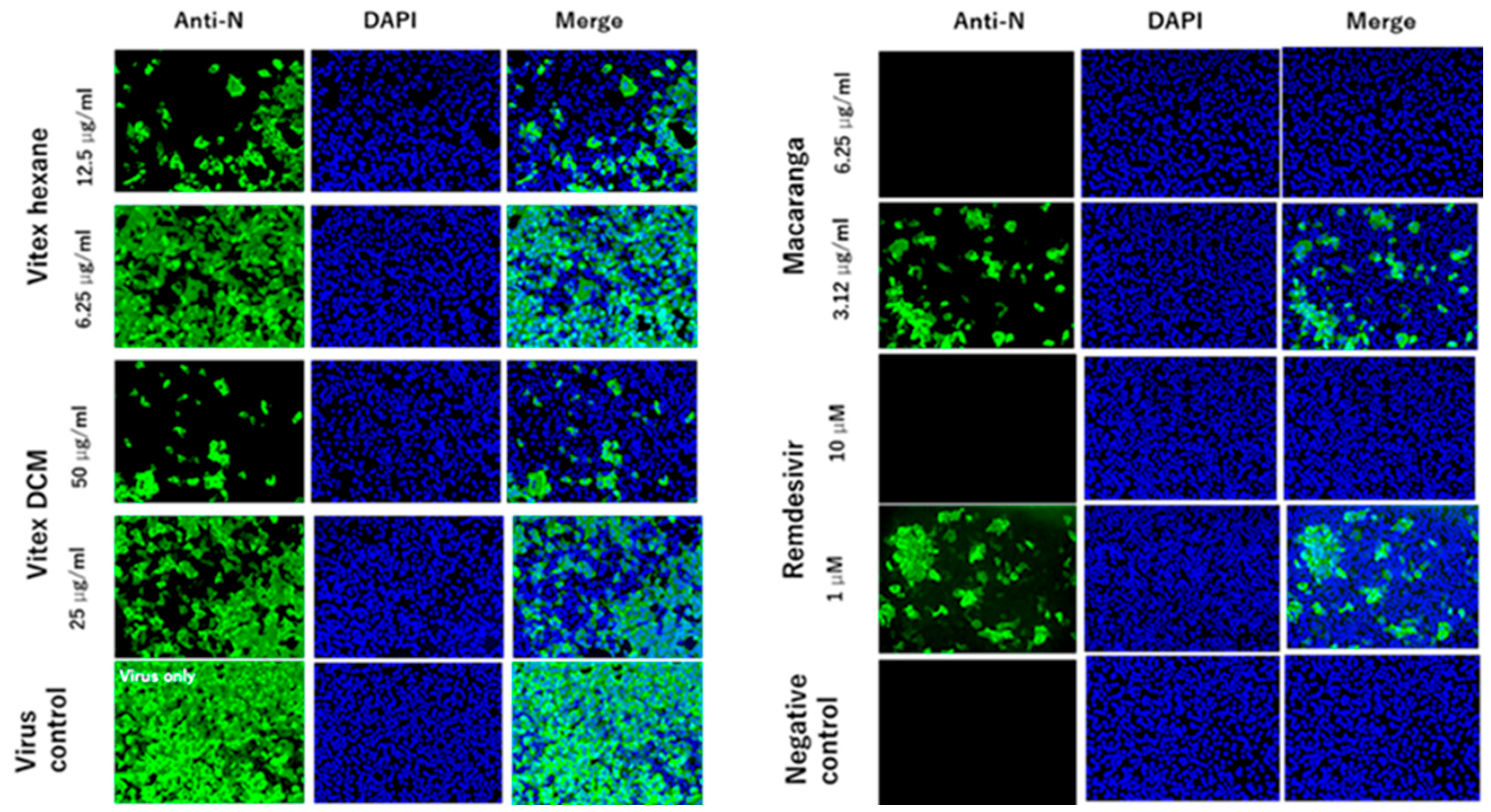
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.8. Quantification of Antiviral Activity by Quantitative Real Time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR)
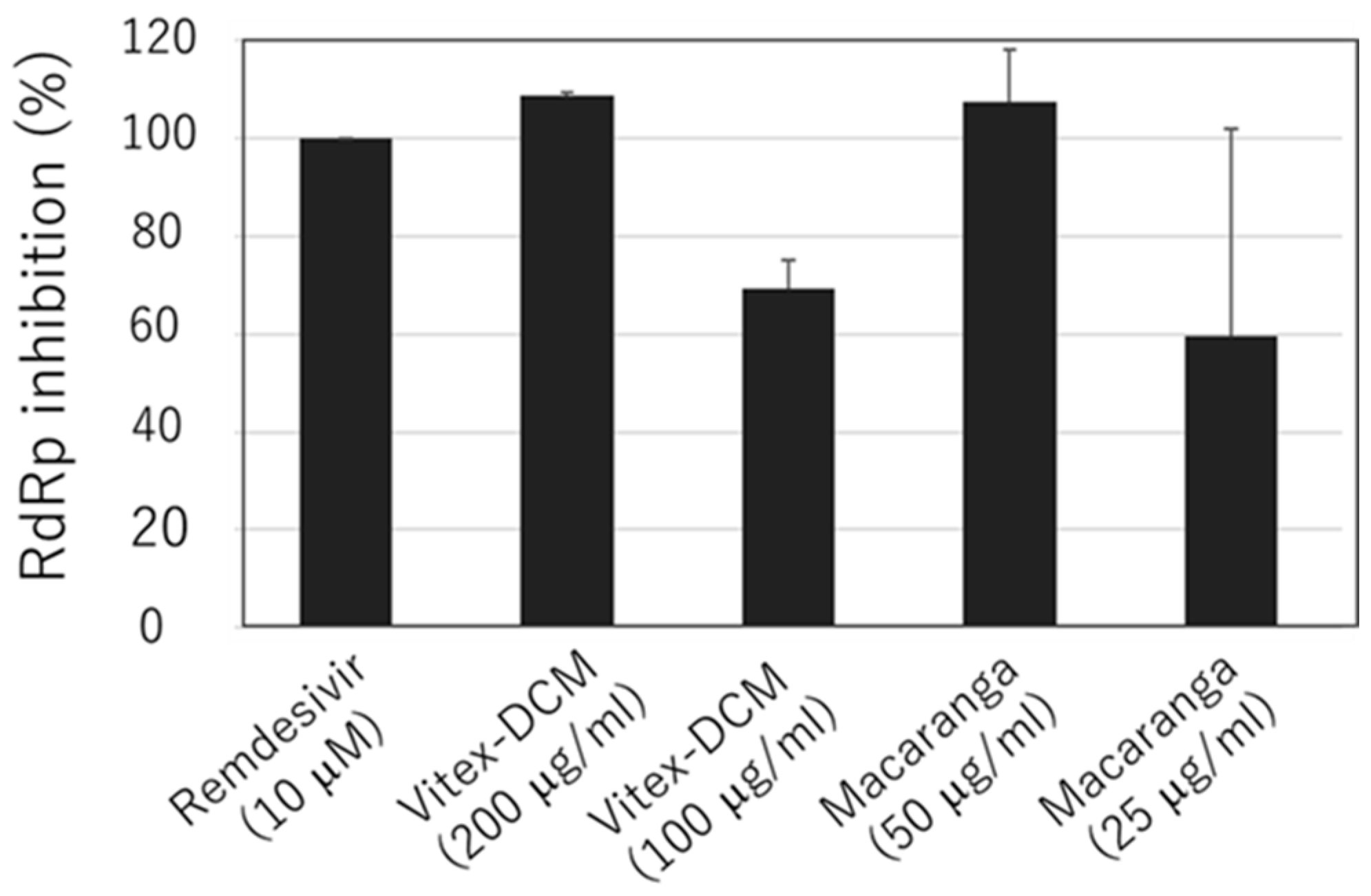
2.9. Inhibition Activity of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp)
2.10. Evaluation of the Synergistic Effect of Vitex-DCM and Macaranga with Remdesivir
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Vitex-Hexane, Vitex-DCM, and Macaranga Extracts Inhibit Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan Strain at Non-Toxic Concentrations
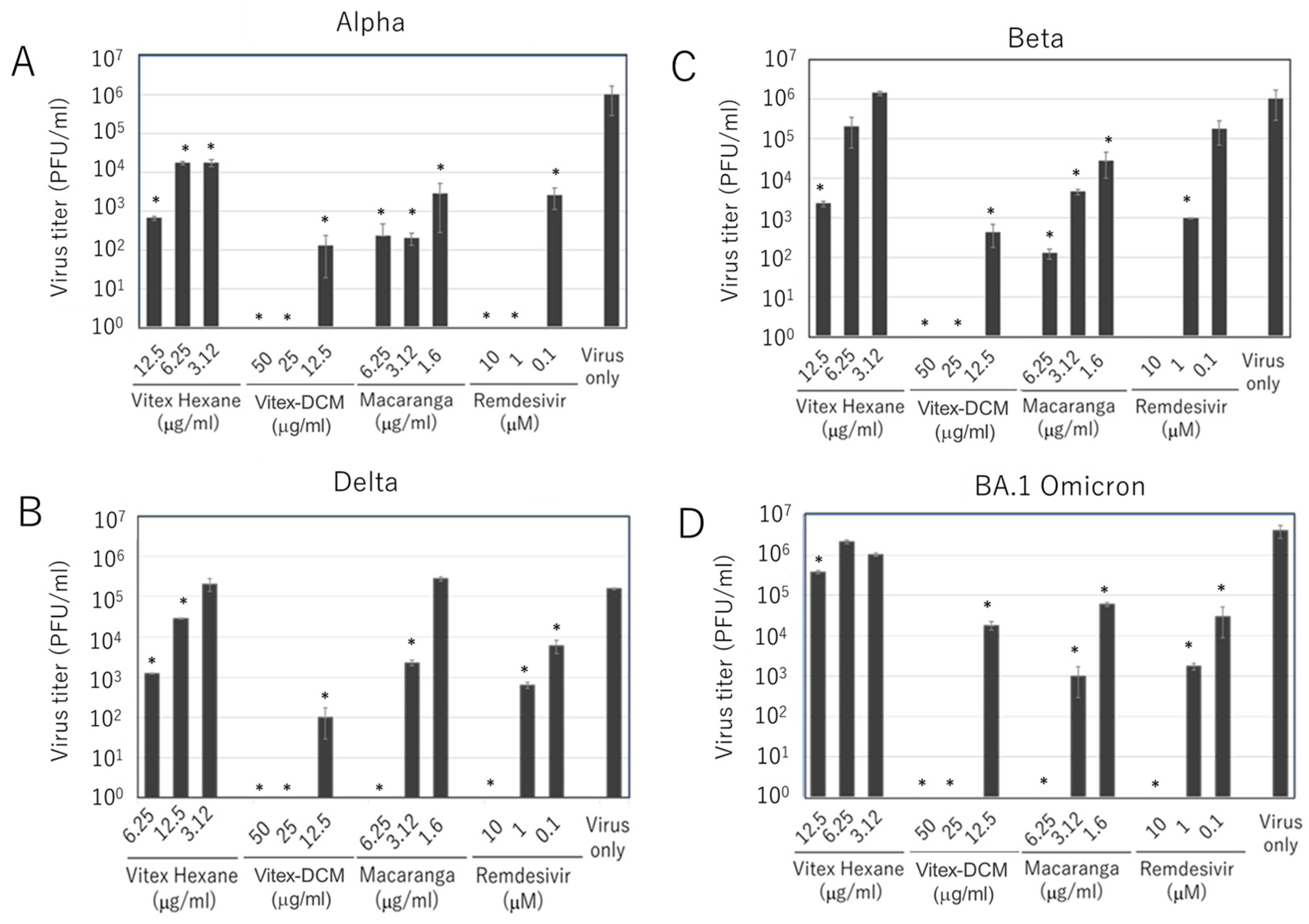
3.2. Inhibitory Effects of Vitex-Hexane, Vitex-DCM, and Macaranga Extracts Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.3. Pre- and Post-Entry Inhibitory Effects of the Extracts
3.4. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Activity of Vitex-DCM and Macaranga
3.5. Synergistic Effect of Vitex-DCM and Macaranga with Remdesivir
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouchier, R.A.; Kuiken, T.; Schutten, M.; van Amerongen, G.; van Doornum, G.J.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Peiris, M.; Lim, W.; Stöhr, K.; Osterhaus, A.D. Aetiology: Koch’s postulates fulfilled for SARS virus. Nature 2003, 423, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Stratton, C.W.; Tang, Y.W. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The mystery and the miracle. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, S.; Khalid, S.; Parveen, S.; Abbass, K.; Song, H.; Achim, M.V. COVID-19 outbreak: Impact on global economy. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1009393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Kuan, C.C. Vaccination to reduce severe COVID-19 and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacco, M.E.; Acuti Martellucci, C.; Baccolini, V.; De Vito, C.; Renzi, E.; Villari, P.; Manzoli, L. COVID-19 vaccines reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and hospitalization: Meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1023507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, M.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Hu, D.; Zheng, L.; Wang, D.W. Neuraminidase inhibitor treatment is associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 8, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L. The research progress of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors from 2020 to 2022. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 257, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinghorn, A.D.; Pan, L.; Fletcher, J.N.; Chai, H. The relevance of higher plants in lead compound discovery programs. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, B.B.; Tiwari, V.K. Natural products: An evolving role in future drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4769–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Kapralov, M.; Ashton, M. Plant-derived compounds as potential leads for new drug development targeting COVID-19. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 1522–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.R.; Antunes, B.S.; do Nascimento, G.O.; Kawall, J.C.S.; Oliveira, J.V.B.; Silva, K.G.D.S.; Costa, M.A.T.; Oliveira, C.R. Antiviral activity of medicinal plant-derived products against SARS-CoV-2. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, K.; Shi, S.; Tian, J.; Zhang, J. Efficacy and safety of herbal medicine (Lianhuaqingwen) for treating COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wu, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, X. Lianhua Qingwen Capsules Reduced the Rate of Severity in Patients with COVID-19: A System Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 9617429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Guan, W.J.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Q.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, Z.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Lianhuaqingwen capsules, a repurposed Chinese herb, in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeke, C.A.; Woldeyohanins, A.E.; Kifle, Z.D. Herbal medicine use for the management of COVID-19: A review article. Metabol. Open 2021, 12, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, D.; Prieto-Garcia, J.M.; Boylan, F.; Estrada, O.; Fonseca-Bazzo, Y.M.; Jamal, C.M.; Magalhães, P.O.; Pereira, E.O.; Tomczyk, M.; Heinrich, M. COVID-19: Is There Evidence for the Use of Herbal Medicines as Adjuvant Symptomatic Therapy? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 581840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maramba-Lazarte, C.C.; Cerrado, J.P.; Purificacion, J. Symptomatic treatment of mild COVID-19 with Vitex negundo (NIRPROMP formulation): A randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Basic App. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, O88–O109. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, M.K.; Shukla, R.; Sharma, N.K.; Manhas, A.; Srivastava, K.; Kumar, N.; Singh, P.K. Evaluation of ethnopharmacologically selected Vitex negundo L. for In vitro antimalarial activity and secondary metabolite profiling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 275, 114076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, B.S.; Mehra, R.; Navgeet; Kumar, S. Vitex negundo and its medicinal value. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Khadke, S.K.; Yamano, A.; Woo, J.T.; Lee, J. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of prenylated flavanones from Macaranga tanarius. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 153033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Ye, S.R.; Chen, Y.W. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of the Fruit of Macaranga tanarius, the Plant Origin of Taiwanese Green Propolis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, R.G.; Regidor, P.J.S.; Ruamero, E.C., Jr.; Allanigue, E.J.V.; Salinas, M.V. A network pharmacology and molecular docking approach in the exploratory investigation of the biological mechanisms of lagundi (Vitex negundo L.) compounds against COVID-19. Genom. Inform. 2023, 21, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayona, R.; Creencia, E. Discovery of a “Cocktail” of Potential SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors through Virtual Screening of Known Chemical Components of Vitex negundo L. (“Lagundi”). Med. Chem. 2022, 18, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raekiansyah, M.; Mori, M.; Nonaka, K.; Agoh, M.; Shiomi, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Morita, K. Identification of novel antiviral of fungus-derived brefeldin A against dengue viruses. Trop. Med. Health 2017, 45, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwe Tun, M.M.; Luvai, E.; New, K.M.; Toume, K.; Mizukami, S.; Hirayama, K.; Komatsu, K.; Morita, K. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of various PET-bottled Japanese green teas and tea compounds in vitro. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirato, K.; Nao, N.; Katano, H.; Takayama, I.; Saito, S.; Kato, F.; Katoh, H.; Sakata, M.; Nakatsu, Y.; Mori, Y.; et al. Development of Genetic Diagnostic Methods for Detection for Novel Coronavirus 2019(nCoV-2019) in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect Dis. 2020, 73, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanqui, A.B.; de Morais, D.R.; da Silva, C.M.; Santos, J.M.; Gomes, S.T.; Visentainer, J.V.; Eberlin, M.N.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; Matsushita, M. Subcritical extraction of flaxseed oil with n-propane: Composition and purity. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmir, J.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Sharif, K.M.; Mohamed, A.; Sahena, F.; Jahurul, M.H.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensor, L.L.; Menezes, F.S.; Leitão, G.G.; Reis, A.S.; dos Santos, T.C.; Coube, C.S.; Leitão, S.G. Screening of Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Phytother. Res. 2021, 15, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Ukaegbu, C.I. Extraction of phenolic compounds: A review. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaughule, R.S.; Barve, R.S. Role of herbal medicines in the treatment of infectious diseases. Vegetos 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutombo, P.N.; Kasilo, O.M.J.; James, P.B.; Wardle, J.; Kunle, O.; Katerere, D.; Wambebe, C.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Rahmatullah, M.; Nikiema, J.B.; et al. Experiences and challenges of African traditional medicine: Lessons from COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Glob. Health 2023, 8, e010813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, E. Reflections on the ‘discovery’ of the antimalarial qinghao. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Fidock, D.A.; Polyak, S.J.; Wagoner, J.; Towler, M.J.; Weathers, P.J. Artemisia annua L. extracts inhibit the in vitro replication of SARS-CoV-2 and two of its variants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, A.; Akbar Samad, A.B.; Vaqar, S. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570580/ (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.C.; Chew, K.W.; Deo, R.; Flynn, J.P.; Regan, J.; Crain, C.R.; Moser, C.; Hughes, M.D.; Ritz, J.; Ribeiro, R.M.; et al. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations during Bamlanivimab therapy in a phase II randomized clinical trial. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iketani, S.; Mohri, H.; Culbertson, B.; Hong, S.J.; Duan, Y.; Luck, M.I.; Annavajhala, M.K.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Uhlemann, A.C.; et al. Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir. Nature 2023, 613, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Lee, H.W.; Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Gribble, J.; George, A.S.; Hughes, T.M.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; et al. Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo0718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.J.; Choudhary, M.C.; Deo, R.; Yousuf, F.; Gomez, A.N.; Edelstein, G.E.; Boucau, J.; Glover, O.T.; Barry, M.; Gilbert, R.F.; et al. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2435431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarasu, K.; Patil, P.; Kaushik, M.; Chowdhury, D.; Joshi, R.K.; Hegde, H.V.; Kakade, M.B.; Hoti, S.L.; Cherian, S.; Parashar, D. In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Potential Medicinal Plant Extracts Against Dengue and Chikungunya Viruses. Front. Cell. Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 866452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Ikeda, K.; Ejima, D.; Naito, T.; Koyama, A.H. Antiviral and virucidal activities of natural products. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juszkiewicz, M.; Walczak, M.; Woźniakowski, G.; Szczotka-Bochniarz, A. Virucidal Activity of Plant Extracts against African Swine Fever Virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.K. Plant-Derived Bioactives: Production, Properties and Therapeutic Applications; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–619. [Google Scholar]
- Bekheit, M.S.; Panda, S.S.; Girgis, A.S. Potential RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors as prospective drug candidates for SARS-CoV-2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 252, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, K.; Musall, K.; Oo, A.; Cao, D.; Liang, B.; Hassandarvish, P.; Lan, S.; Slack, R.L.; Kirby, K.A.; Bassit, L.; et al. Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyr, Z.A.; Cheng, Y.S.; Lo, D.C.; Zheng, W. Drug combination therapy for emerging viral diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidari, A.; Sabbatini, S.; Schiaroli, E.; Bastianelli, S.; Pierucci, S.; Busti, C.; Comez, L.; Libera, V.; Macchiarulo, A.; Paciaroni, A.; et al. The Combination of Molnupiravir with Nirmatrelvir or GC376 Has a Synergic Role in the Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidari, A.; Sabbatini, S.; Schiaroli, E.; Bastianelli, S.; Pierucci, S.; Busti, C.; Saraca, L.M.; Capogrossi, L.; Pasticci, M.B.; Francisci, D. Synergistic Activity of Remdesivir-Nirmatrelvir Combination on a SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro Model and a Case Report. Viruses 2023, 15, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrynla, X.H.; Wehri, E.; Van Dis, E.; Biering, S.B.; Yamashiro, L.H.; Zhu, C.; Stroumza, J.; Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Graham, T.G.W.; Wang, X.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral synergy between remdesivir and approved drugs in human lung cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chera, A.; Tanca, A. Remdesivir: The first FDA-approved anti-COVID-19 Treatment for Young Children. Discoveries 2022, 10, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalkwijk, H.H.; Shewakramani, N.R.; Das, K.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. Combination of ganciclovir and trifluridine prevents drug-resistance emergence in HSV-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 68, e0011024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raekiansyah, M.; Ngwe Tun, M.M.; Ang, A.; Lee, A.; Macalino, S.J.; Billones, J.; Takamatsu, Y.; Urano, T.; Murao, L.A.E.; Quiming, N.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts Vitex negundo and Macaranga tanarius Against SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens 2025, 14, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080820
Raekiansyah M, Ngwe Tun MM, Ang A, Lee A, Macalino SJ, Billones J, Takamatsu Y, Urano T, Murao LAE, Quiming N, et al. Antiviral Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts Vitex negundo and Macaranga tanarius Against SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080820
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaekiansyah, Muhareva, Mya Myat Ngwe Tun, Alexandra Ang, Alexandra Lee, Stephani Joy Macalino, Junie Billones, Yuki Takamatsu, Takeshi Urano, Lyre Anni E. Murao, Noel Quiming, and et al. 2025. "Antiviral Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts Vitex negundo and Macaranga tanarius Against SARS-CoV-2" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080820
APA StyleRaekiansyah, M., Ngwe Tun, M. M., Ang, A., Lee, A., Macalino, S. J., Billones, J., Takamatsu, Y., Urano, T., Murao, L. A. E., Quiming, N., Morita, K., & Carrillo, M. C. (2025). Antiviral Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts Vitex negundo and Macaranga tanarius Against SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens, 14(8), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080820




