Challenges and Achievements in the In Vitro Culture of Balantioides coli: Insights into the Excystation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Initial Processing of Samples
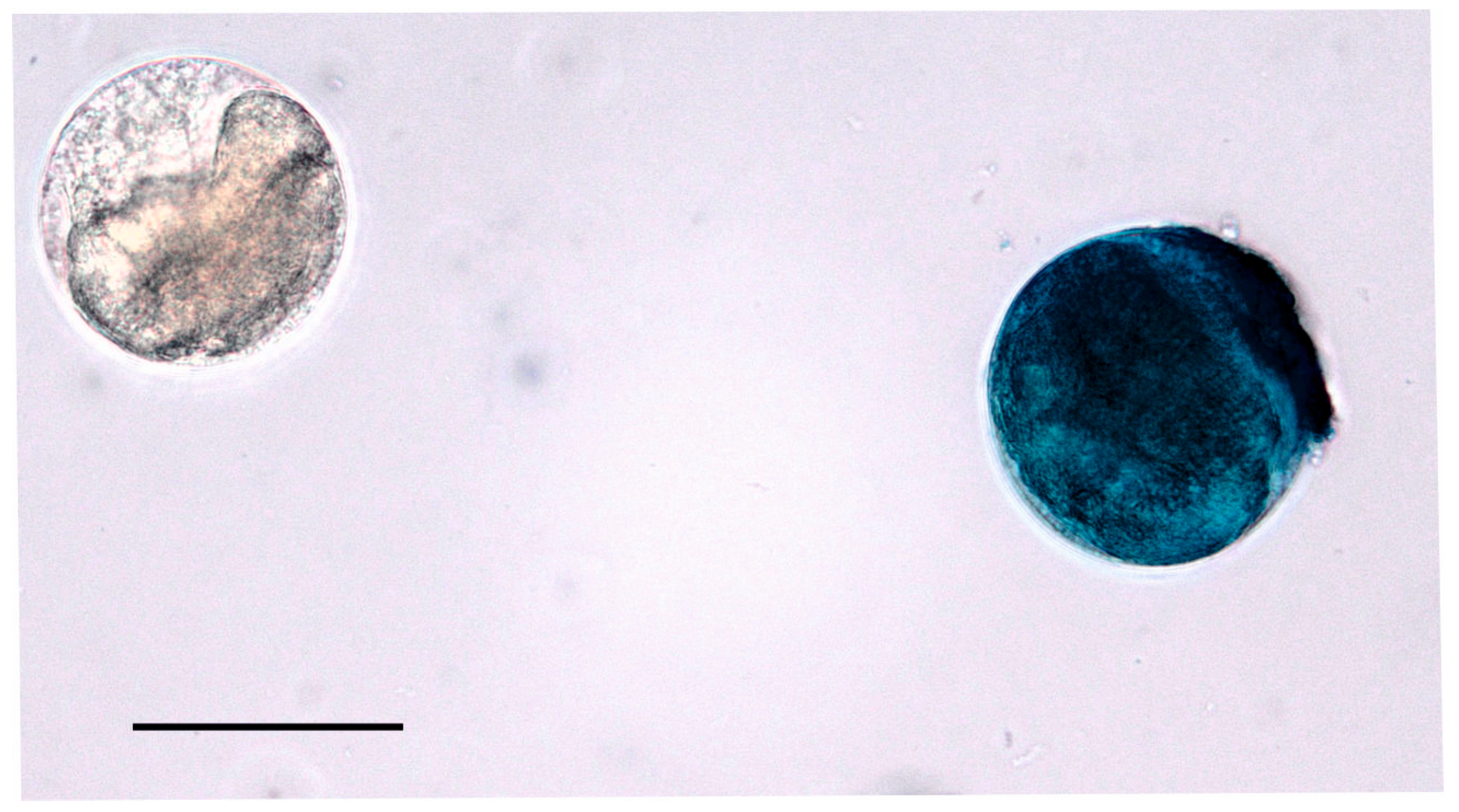
2.2. Cyst Quantification and Viability Assessment
2.3. Genetic Identification of the Isolates
2.4. Culture Media
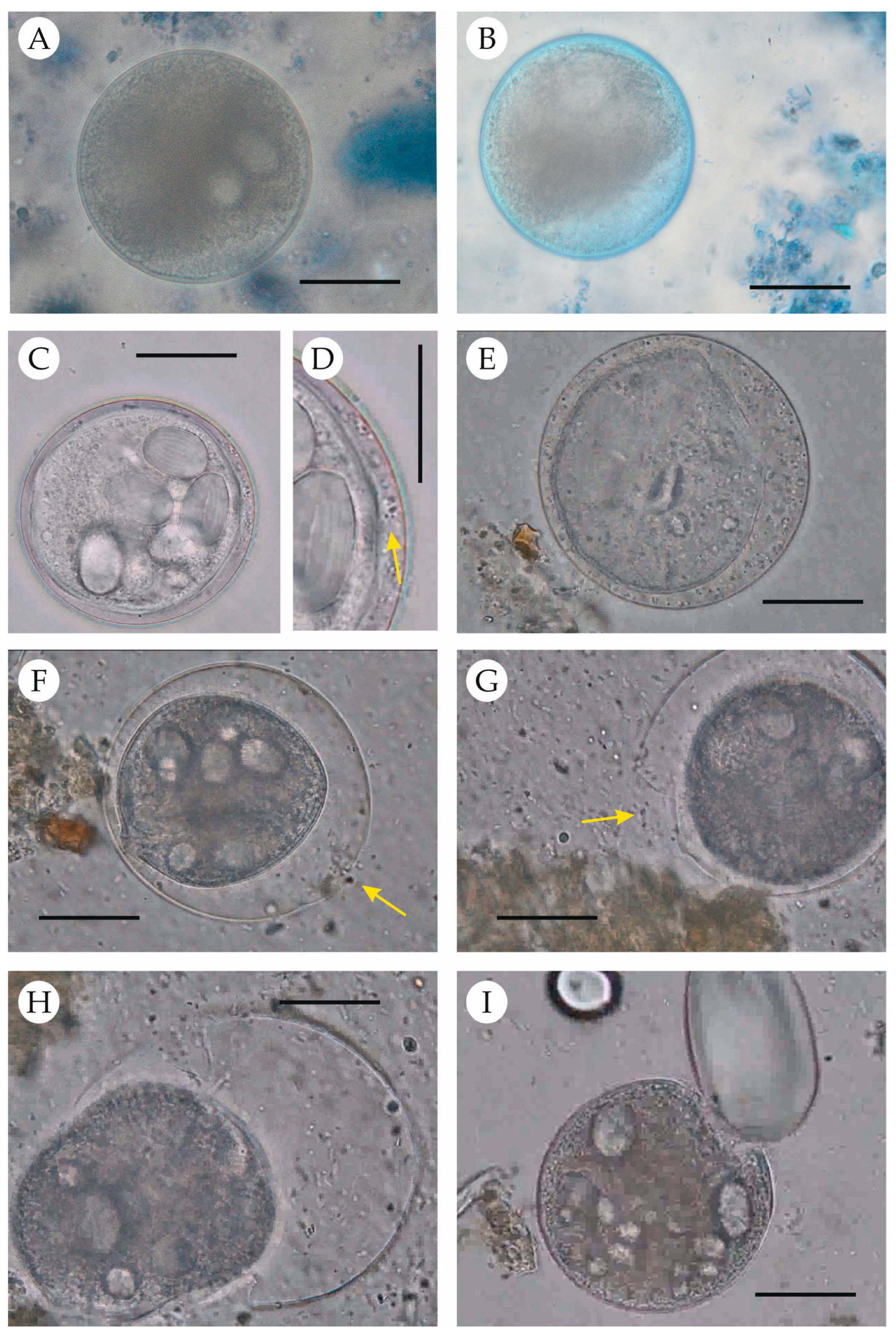
2.5. Excystation Procedure
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visvesvara, G.S.; Garcia, L.S. Culture of protozoan parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Hemphill, A. Drug target identification in protozoan parasites. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, L.S.; Harlow, D.R.; Cunnick, C.C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1978, 72, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillin, F.D.; Reiner, D.S.; McCaffery, J.M. Cell biology of Giardia lamblia. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 50, 679–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Haque, R.; Hackney, J.A.; Eichinger, D.J.; Singh, U. Identification of developmentally regulated genes in Entamoeba histolytica: Insights into mechanisms of stage conversion in a protozoan parasite. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1426–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, B.; Anderson, I.; Davies, R.; Alsmark, U.C.M.; Samuelson, J.; Amedeo, P.; Roncaglia, P.; Berriman, M.; Hirt, R.P.; Mann, B.J.; et al. The genome of the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nature 2005, 433, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, H.G.; McArthur, A.G.; Gillin, F.D.; Aley, S.B.; Adam, R.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Best, A.A.; Cande, W.Z.; Chen, F.; Cipriano, M.J.; et al. Genomic minimalism in the early diverging intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia. Science 2007, 317, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Jex, A.; Svärd, S.G. A chromosome-scale reference genome for Giardia intestinalis WB. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Gordo, F.; García-Rodríguez, J.J. Balantioides coli . Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.D. On Balantidium coli (Malmsten) and Balantidium suis (sp.nov.), with an account of their neouromotor apparatus. Univ. Calif. Publ. Zool. 1922, 20, 243–300. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkal, H.; Sangwan, A.K. Morphological differentiation between pig and buffalo parasitic ciliates to identify species. Haryana Vet. 2019, 58, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Do, D.T.; Duong, M.T.; Nguyen, N.M.; Nguyen, P.L.D.; Nguyen, H.N. Phylogenetics and pathogenicity of Balantioides coli isolates in Vietnamese weaned pigs. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rodríguez, J.J.; Köster, P.C.; Ponce-Gordo, F. Cyst detection and viability assesment of Balantioides coli in environmental samples: Current status and future needs. Food Waterborne Parasitol 2022, 26, e00143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization & Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Multicriteria-based ranking for risk management of food-borne parasites. In Microbiological Risk Assessment Series No. 23; FAO/World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2014; p. 302. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/112672 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Bouwknegt, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Graham, H.; Robertson, L.J.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; Euro-FBP workshop participants. Prioritisation of food-borne parasites in Europe, 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17–00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.J. Bacteria-free Entamoeba invadens. Nature 1953, 172, 1192–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, L.S. Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica. Science 1961, 134, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.A. Giardia lamblia: Isolation and axenic cultivation. Exp. Parasitol. 1976, 39, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, L.S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J. Parasit. 1957, 43, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackmann, T.J.; Sen, A.; Firkins, J.L. Culture techniques for ciliate protozoa from the rumen: Recent advances and persistent challenges. Anaerobe 2024, 87, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Meulia, T.; Firkins, J.L.; Yu, Z. Inhibition of the rumen ciliate Entodinium caudatum by antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barret, H.P.; Yarbrough, N. A method for the cultivation of Balantidium coli. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1921, 1, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.G.; Diamond, L.S. Methods for cultivation of luminal parasitic protists of clinical importance. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Barbosa, A.; Pereira Bastos, O.M.; Uchôa, C.M.A.; Pissinatti, A.; Filho, P.R.F.; Dib, L.V.; Azevedo, E.P.; de Siqueira, M.P.; Cardozo, M.L.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. Isolation and maintenance of Balantidium coli (Malmsteim, 1857) cultured from fecal samples of pigs and non-human primates. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 210, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Barbosa, A.; Lessa Cardozo, M.; Verdan Dib, L.; Monteiro Fonseca, A.B.; Anutes Uchôa, C.M.; Pereira Bastos, O.M.; Reis Amendoeira, M.R. Comparative study of three xenic media culture for cultivation of Balantidium coli strains. Brazil. J. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wang, T.; Zhao, L.; Sun, C. Modified DMEM xenic culture medium for propagation, isolation and maintenance of Balantioides coli. Acta Trop. 2021, 214, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho Class, C.S.; Lisboa Corrêa, L.; Batalha Knackfuss, F.; Reis Amendoeira, M.R.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; da Silva Barbosa, A. The phylogenetic characterization of Balantioides coli isolated in the Pavlova culture medium supplemented with coconut water and animal serum. Pathogens 2024, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailenger, J. Mechanisms of parasitical concentration in coprology and their practical consequences. J. Am. Med. Technol. 1979, 41, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Gordo, F.; Fonseca-Salamanca, F.; Martínez-Díaz, R.A. Genetic heterogeneity in Internal Transcribed Spacer genes of Balantidium coli (Litostomatea, Ciliophora). Protist 2011, 162, 774–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Gordo, F.; Jimenez-Ruiz, E.; Martínez-Díaz, R.A. Tentative identification of the species of Balantidium from ostriches (Struthio camelus) as Balantidium coli-like by analysis of polymorphic DNA. Vet Parasitol. 2008, 157, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkenmann, A.J. Pathogenicity, cultivation, and reproduction of protozoon parasites. N. Y. Med. J. 1919, 59, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, A.P. The behaviour of Balantidium coli Maim. in cultures. Parasitology 1927, 19, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobell, C.; Laidlaw, P.P. On the cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and some other entozoic amoebae. Parasitology 1926, 18, 283–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, C.W. Balantidia from pigs and guinea-pigs: Their viability, cyst production and cultivation. Science 1927, 66, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.J. Studies on the Balantidium from the guinea-pig. J. Morphol. Physiol. 1927, 44, 417–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, R.W.; Coria, N.A. The Partial Purification of Balantidium coli from Swine. J. Parasitol. 1935, 21, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumaker, E. The cultivation of Balantidium coli. Amer. J. Hyg. 1931, 13, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosin, M.; von Brand, T. Studies on the respiratory metabolism of Balantidium coli. J. Infect. Dis. 1953, 93, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, R.M. Balantidium coli . In Microbiology of Waterborne Diseases: Microbiological Aspects and Risks, 2nd ed.; Percival, S.L., Yates, M.V., Williams, D.W., Chalmers, R.M., Gray, N.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, F.L.; Visvesvara, G.S. Amebae and ciliated protozoa as causal agents of waterborne zoonotic disease. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarey, G. Balantidiasis in South Persia. Br. Med. J. 1952, 1, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomajbíková, K.; Petrželková, K.J.; Profousová, I.; Petrášová, J.; Modrý, D. Discrepancies in the occurrence of Balantidium coli between wild and captive African great apes. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, E. A study of Balantidium coli Stein 1863, in relation to cytology and behavior in culture. J. Morphol. 1953, 93, 405–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.E.G. The cultivation of Balantidium coli throughout its viable temperature range. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1961, 55, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, V. Balantidium coli . In Parasitic Protozoa, 2nd. ed.; Kreier, J.P., Baker, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, E.L. Quantitative determination of the balanticidal activity of certain drugs and chemicals as a basis for treatment of infections with Balantidium coli. Philipp. J. Sci. sect. B Trop. Med. 1913, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Areán, V.M.; Koppisch, E. Balantidiasis: A review and report of cases. Am. J. Hyg. 1956, 32, 1089–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Lamy, L.; Lahmi, H. Determinisme de Ia zygose chez Balantidium coli en culture: Action de Ia temperature. C. R. Soc. Bioi. Paris. 1951, 14S, 994. [Google Scholar]
- Welfer, G.A.; Brady, R.A.; Natchlar, S.K.; Watson, Z.L.; Rundlet, E.J.; Alejo, J.L.; Singh, A.P.; Mishra, N.K.; Altman, R.B.; Blanchard, S.C. Impacts of ribosomal RNA sequence variation on gene expression and phenotype. Phil. Trnas. R. Soc. B 2025, 380, 20230379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etewa, S.E.; Abdel-Rahman, S.A.; Fathy, G.M.; Abo El-Maaty, D.A.; Sarhan, M.H. Parasitic contamination of commonly consumed fresh vegetables and fruits in some rural areas of Sharkyia Governorate, Egypt. Afro-Egypt. J. Infec. Endem. Dis. 2017, 7, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borazjani, R.N.; May, L.L.; Noble, J.A.; Avery, S.V.; Ahearn, D.G. Flow cytometry for determination of the efficacy of contact lens disinfecting solutions against Acanthamoeba spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, G.H. Studies on Paramecium. III. The effects of vital dyes on Paramecium caudatum. Biol. Bull. 1927, 52, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Zapién, A.G.; González-Robles, A.; Mora-Galindo, J. Congo Red effect on cyst viability and Cell Wall Structure of Encysting Entamoeba invadens. Arch. Med. Res. 1999, 30, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibañez-Escribano, A.; Esteban-Sánchez, L.; Fonseca-Berzal, C.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; García-Rodríguez, J.J. Challenges and Achievements in the In Vitro Culture of Balantioides coli: Insights into the Excystation Process. Pathogens 2025, 14, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080725
Ibañez-Escribano A, Esteban-Sánchez L, Fonseca-Berzal C, Ponce-Gordo F, García-Rodríguez JJ. Challenges and Achievements in the In Vitro Culture of Balantioides coli: Insights into the Excystation Process. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080725
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbañez-Escribano, Alexandra, Lorena Esteban-Sánchez, Cristina Fonseca-Berzal, Francisco Ponce-Gordo, and Juan José García-Rodríguez. 2025. "Challenges and Achievements in the In Vitro Culture of Balantioides coli: Insights into the Excystation Process" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080725
APA StyleIbañez-Escribano, A., Esteban-Sánchez, L., Fonseca-Berzal, C., Ponce-Gordo, F., & García-Rodríguez, J. J. (2025). Challenges and Achievements in the In Vitro Culture of Balantioides coli: Insights into the Excystation Process. Pathogens, 14(8), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080725





