Fatal Paraclostridium sordellii Infection: Post-Mortem Assessment and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
- Autopsy findings
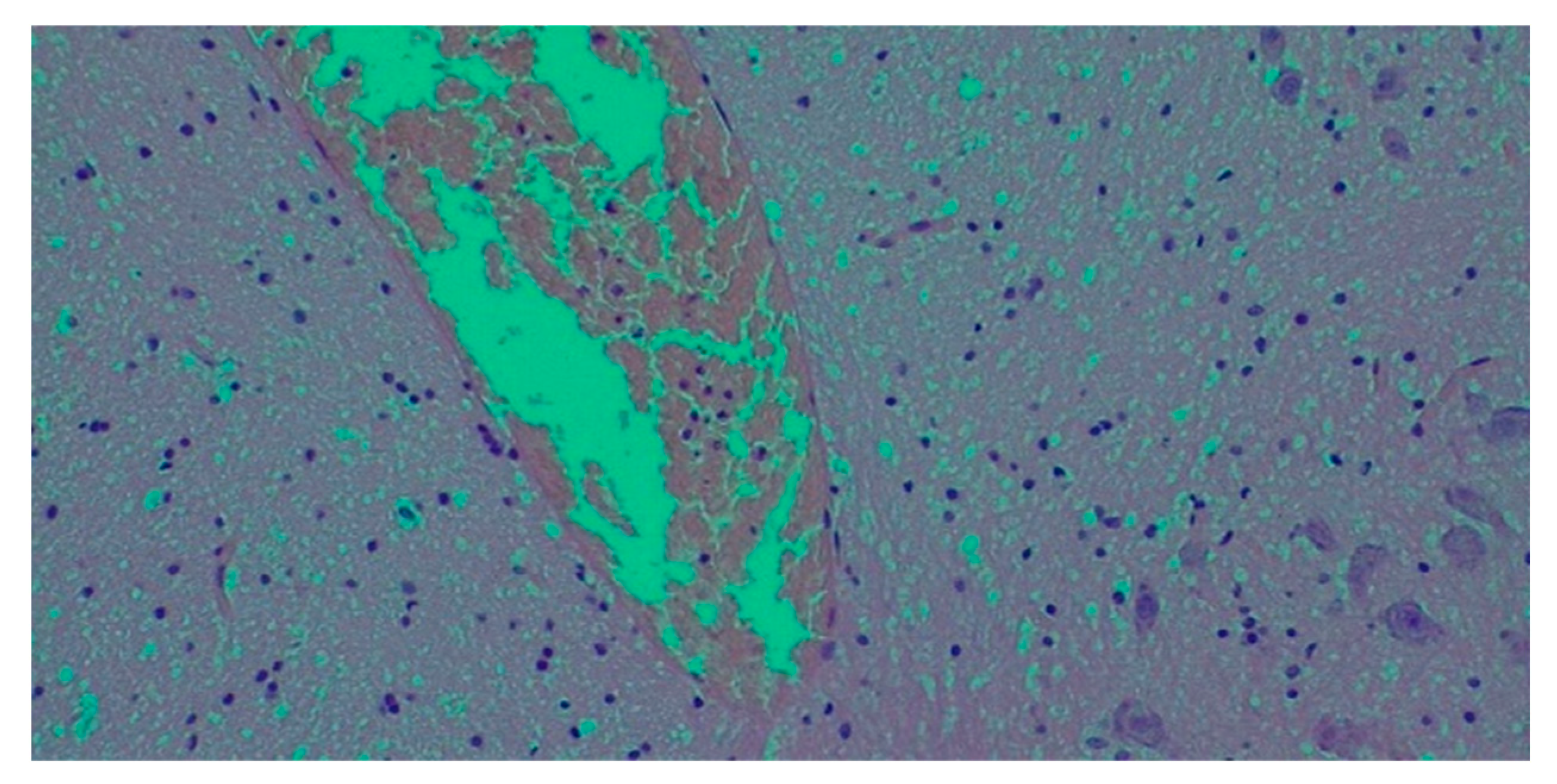
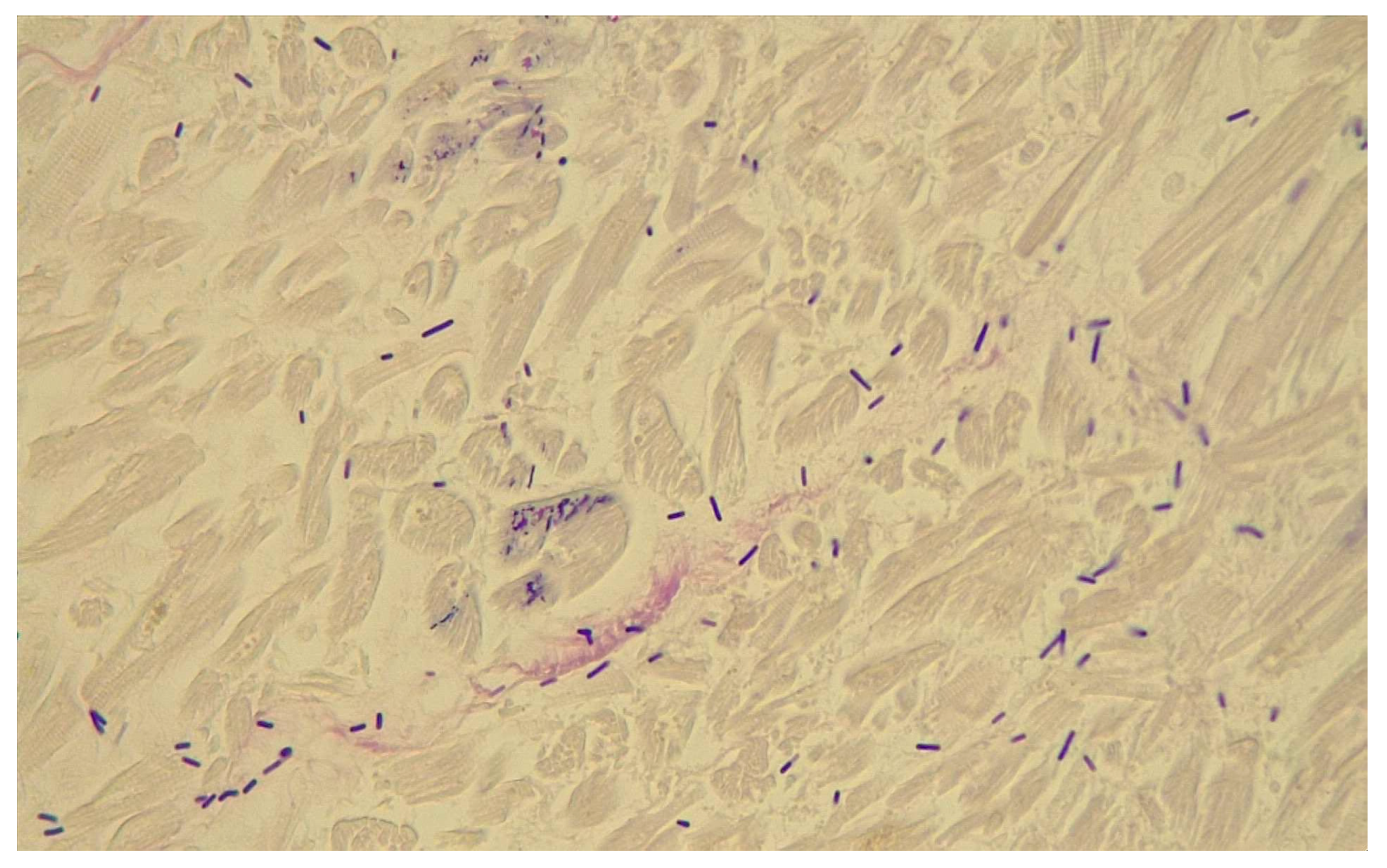
- Histological findings
3. Results
- Post-mortem microbiological investigations
- Toxicological findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasi Jyothsna, T.S.; Tushar, L.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V. Paraclostridium benzoelyticum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment and reclassification of Clostridium bifermentans as Paraclostridium bifermentans comb. nov. Proposal of a new genus Paeniclostridium gen. nov. to accommodate Clostridium sordellii and Clostridium ghonii. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1268–1274, Erratum in Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, S.; McQuay, S.; Rudra, B.; Gupta, R.S. Robust demarcation of the family Peptostreptococcaceae and its main genera based on phylogenomic studies and taxon-specific molecular markers. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mory, F.; Lozniewski, A.; Guirlet, M.N.; Guidat, D.; Bresler, L.; Weber, M.; Boissel, P. Severe sepsis Caused by Clostridium sordellii Following Liver Biopsy in a Liver Transplant Recipient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 1, 1522–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunniffe, J.G. Clostridium sordellii bacteraemia. J. Infect. 1996, 3, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, A.; Yee, L. The clinical spectrum of Clostridium sordellii bacteraemia: Two case reports and a review of the literature. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, S.; Zhang, K. Positive Clostridium difficile Stool Assay in a Patient with Fatal C. sordellii Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1284–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matten, J.; Buechner, V.; Schwarz, R. A Rare Case of Clostridium sordellii Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Patient. Infection 2009, 37, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.; Goslin, B. Clostridium sordellii Surgical Site Infection after Breast Mass Excision: Case Report. Surg. Infect. 2013, 14, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnecaze, A.K.; Stephens, S.E.E.; Miller, P.J. Non-lethal Clostridium sordellii bacteraemia in an immunocompromised patient with pleomorphic sarcoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016215240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varley, C.D.; Rogers, L.M.; Dixon, B.R.; Bernard, S.C.; Lacy, D.B.; Sulpizio, E.; Aronoff, D.M.; Townes, J.M. Persistent bacteremia and psoas abscess caused by a lethal toxin-deficient Paeniclostridium sordellii. Anaerobe 2022, 75, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Bhatnagar, J.; Guarner, J.; Reagan, S.; Hacker, J.K.; Van Meter, S.H.; Poukens, V.; Whiteman, D.B.; Iton, A.; Cheung, M.; et al. Fatal Toxic Shock Syndrome Associated with Clostridium sordellii after Medical Abortion. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, J.A.; Soper, D.E.; Lovell, G.; Todd, J.K. Maternal deaths associated with Clostridium sordellii infection. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitti, A.; Mastrantonio, P.; Spigaglia, P.; Urru, G.; Spano, A.I.; Moretti, G.; Cherchi, G.B. A fatal postpartum Clostridium sordellii associated toxic shock syndrome. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 50, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosolik, R.C.; Savage, B.A.; Vaccarello, L. Clostridium sordellii Toxic Shock Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 4, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rørbye, C.; Petersen, I.S.; Nilas, L. Postpartum Clostridium sordellii infection associated with fatal toxic shock syndrome. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2000, 79, 1134–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinave, C.; Le Templier, G.; Blouin, D.; Léveillé, F.; Deland, É. Toxic Shock Syndrome Due to Clostridium sordellii: A Dramatic Postpartum and Postabortion Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanton Jr, B.L.; Hanna, M.M.; Hafez-Khayyata, S.; Robinson-Dunn, B. Fatal Postpartum Infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2020, 28, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, J.N.; Hardy-Fairbanks, A.J. Clostridium sordelli Toxic Shock After Endometrial Ablation: Review of Gynecologic Cases. J. Gynecol. Surg. 2018, 34, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkbuli, A.; Diaz, B.; Ehrhardt, J.D.; Hai, S.; Kaufman, S.; McKenney, M.; Boneva, D. Survival from Clostridium toxic shock syndrome: Case report and review of the literature. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 50, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browdie, D.A.; Davis, J.H.; Koplewitz, M.J.; Corday, L.; Leadbetter, A.W. Clostridium Sordelli Infection. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1975, 15, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwood, K.; Evans, G.A.; Govender, S.T.; Woods, D.E. Clostridium sordellii infection and toxin neutralization. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1990, 9, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gredlein, C.M.; Silverman, M.L.; Downey, M.S. Polymicrobial Septic Arthritis Due to Clostridium Species: Case Report and Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, P.; Sautereau, J.; Le Coustumier, A.; Mory, F.; Bouchier, C.; Popoff, M.R. Foot Infection by Clostridium sordellii: Case Report and Review of 15 Cases in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, J.C.; Rapkin, R.H. Clostridia infection in the newborn. Pediatrics 1976, 58, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormley, D. Neonatal anaerobic (clostridial) cellulitis and omphalitis. Arch Dermatol. 1977, 113, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosloske, A.M.; Bartow, S.A. Debridement of periumbilical necrotizing fasciitis: Importance of excision of the umbilical vessels and urachal remnant. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1991, 26, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkiewicz, T.V.; Goodman, D.; Burke, B.; Lyerly, D.M.; Goswitz, J.; Ferrieri, P. Neonatal Clostridium sordellii toxic omphalitis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1993, 12, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rellinger, E.J.; Craig, B.T.; Craig-Owens, L.D.; Pacheco, M.C.; Chung, D.H.; Danko, M.E. Clostridium sordellii necrotizing omphalitis: A case report and literature review. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brett, M.M.; Hood, J.; Brazier, J.S.; Duerden, B.I.; Hahné, S.J. Soft tissue infections caused by spore-forming bacteria in injecting drug users in the United Kingdom. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinis, A.; Voultsos, M.; Grivas, P.; Dikeakos, P.; Liarmakopoulos, E.; Paschalidis, N.; Rizos, S. Vacuum-assisted therapy accelerates wound healing in necrotizing soft tissue infections: Our experience in two intravenous drug abuse patients. Infez. Med. 2013, 21, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.; Henry, R.; Strickland, M.; Wang, D.; Matsushima, K. Rapidly fatal necrotizing soft tissue infection due to Clostridium sordellii in an injection drug user. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 44, 480.e1–480.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangsberg, D.R.; Rosen, J.I.; Aragón, T.; Campbell, A.; Weir, L.; Perdreau-Remington, F. Clostridial Myonecrosis Cluster Among Injection Drug Users. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, N.M.; Harruff, R.C. Necrotizing Fasciitis: Manifestations, Microbiology and Connection with Black Tar Heroin. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldape, M.J.; Bryant, A.E.; Stevens, D.L. Clostridium sordellii Infection: Epidemiology, Clinical Findings, and Current Perspectives on Diagnosis and Treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Singleton, J.; Lyras, D. The Sialidase NanS Enhances Non-TcsL Mediated Cytotoxicity of Clostridium sordellii. Toxins 2016, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoppani, A.; Sordelli, D.O.; Méndez, B.S. Remembering a microbiologist: Alfredo Sordelli (1891–1967). Int. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, I.C.; Scott, J.P. Bacillus Sordellii, a Cause of Malignant Edema in Man. J. Infect. Dis. 1927, 41, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, C.A.O.; Silva, R.O.S.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Navarro, M.A.; Uzal, F.A. Gas gangrene in mammals: A review. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2020, 32, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzal, F.A.; Navarro, M.A.; Asin, J.; Henderson, E.E. Clostridial Diseases of Horses: A Review. Vaccines 2022, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gornatti-Churria, C.D.; Crispo, M.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Uzal, F.A. Gangrenous dermatitis in chickens and turkeys. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2018, 30, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, E.; Winikoff, B.; Charles, D.; Agnew, K.; Prentice, J.L.; Limbago, B.M.; Platais, I.; Louie, K.; Jones, H.E.; Shannon, C. Vaginal and Rectal Clostridium sordellii and Clostridium perfringens Presence Among Women in the United States. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 127, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, Y.; Fujisawa, T. Analysis of Clostridium cluster XI bacteria in human feces. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2019, 38, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidor, C.; Awad, M.; Lyras, D. Antibiotic resistance, virulence factors and genetics of Clostridium sordellii. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jank, T.; Aktories, K. Structure and mode of action of clostridial glucosylating toxins: The ABCD model. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, G.A.; Schué, V.; Monteil, H. Cloning and characterization of the cytotoxin L-encoding gene of Clostridium sordellii: Homology with clostridium difficile cytotoxin B. Gene 1995, 161, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirigi Reddy, A.R.; Girinathan, B.P.; Zapotocny, R.; Govind, R. Identification and Characterization of Clostridium sordellii Toxin Gene Regulator. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 4246–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geny, B.; Khun, H.; Fitting, C.; Zarantonelli, L.; Mazuet, C.; Cayet, N.; Szatanik, M.; Prevost, M.C.; Cavaillon, J.M.; Huerre, M.; et al. Clostridium sordellii Lethal Toxin Kills Mice by Inducing a Major Increase in Lung Vascular Permeability. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronoff, D.M. Clostridium novyi, sordellii, and tetani: Mechanisms of disease. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoff, M.R. Clostridium difficile and Clostridium sordellii toxins, proinflammatory versus anti-inflammatory response. Toxicon 2018, 149, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.E.; Stevens, D.L. Clostridial Myonecrosis: New Insights in Pathogenesis and Management. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2010, 12, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.G.; Pérez-Cárceles, M.D.; Osuna, E.; Legaz, I. Impact of the Human Microbiome in Forensic Sciences: A Systematic Review. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01451-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Schmoldt, A.; Andresen-Streichert, H.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. Revisited: Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of more than 1100 drugs and other xenobiotics. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thys, J.P.; Ectors, P.; Noel, P. Non-traumatic clostridial myositis: An unusual feature of brain death. Postgrad. Med. J. 1980, 56, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.; Leedom, J.M. Infective endocarditis due to Clostridium sordellii. Am. J. Med. 1987, 83, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.F.; Ireland, K. Fatal acute spontaneous endometritis resulting from Clostridium sordelli. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 91, 104–106, Erratum in Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 92, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchman, A.L.; Ponsillo, M.; Nagami, P.H. Empyema caused by Clostridium sordellii, a rare form of pleuropulmonary disease. J. Infect. 1991, 22, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spera, R.V.; Kaplan, M.H.; Allen, S.L. Clostridium sordellii Bacteremia: Case Report and Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borer, A.; Gilad, J.; Sikuler, E.; Riesenberg, K.; Schlaeffer, F.; Buskila, D. Fatal Clostridium sordellii ischio-rectal abscess with septicaemia complicating ultrasound-guided transrectal prostate biopsy. J. Infect. 1999, 38, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, F.; Aliaga, L.; Miranda, C.; de la Rosa, M. Clostridium sordelii corneal ulcer. Infection 2001, 29, 107–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: Unexplained deaths following knee surgery—Minnesota, 2001. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2001, 50, 1080. [Google Scholar]
- Lorea, P.; Baeten, Y.; Chahidi, N.; Franck, D.; Moermans, J.P. A severe complication of muscle transfer: Clostridial myonecrosis. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthet. 2004, 49, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, J.M.; Singh-Parikshak, R.; Sugar, A.; Johnson, M.W. Clostridium sordellii Endophthalmitis After Suture Removal from a Corneal Transplant. Cornea 2004, 23, 522–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebe, E.; Guilbert, E.; Jacot, F.; Shannon, C.; Winikoff, B. A Fatal Case of Clostridium sordellii Septic Shock Syndrome Associated with Medical Abortion. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 104 Pt 2, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.L.; Bhatnagar, J.; Reagan, S.; Zane, S.B.; D'Angeli, M.A.; Fischer, M.; Killgore, G.; Kwan-Gett, T.S.; Blossom, D.B.; Shieh, W.J.; et al. Toxic shock associated with Clostridium sordellii and Clostridium perfringens after medical and spontaneous abortion. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 192, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroulis, C.N.; Gerogianni, I.; Kouritas, V.K.; Karestsi, E.; Klapsa, D.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Petinaki, E. Direct detection of Clostridium sordellii in pleural fluid of a patient with pneumonic empyema by a broad-range 16S rRNA PCR. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 39, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.S.; Bhatnagar, J.; Cohen, A.L.; Hacker, J.K.; Zane, S.B.; Reagan, S.; Fischer, M.; Shieh, W.J.; Guarner, J.; Ahmad, S.; et al. Undiagnosed cases of fatal Clostridium-associated toxic shock in Californian women of childbearing age. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 353, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valour, F.; Boisset, S.; Lebras, L.; Martha, B.; Boibieux, A.; Perpoint, T.; Chidiac, C.; Ferry, T.; Peyramond, D. Clostridium sordellii Brain Abscess Diagnosed by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3443–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meites, E.; Zane, S.; Gould, C. Fata l Clostridium sordellii Infections after Medical Abortions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1382–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, R.; Verma, N.; Bahadur, T.; Chaudhary, P.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, N. Clostridium sordellii as a Cause of Constrictive Pericarditis with Pyopericardium and Tamponade. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3700–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walk, S.T.; Jain, R.; Trivedi, I.; Grossman, S.; Newton, D.W.; Thelen, T.; Hao, Y.; Songer, J.G.; Carter, G.P.; Lyras, D.; et al. Non-toxigenic Clostridium sordellii: Clinical and microbiological features of a case of cholangitis-associated bacteremia. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetta, M.; Williamson, A.; Duong, S. Clostridium Sordellii as an Uncommon Cause of Fatal Toxic Shock Syndrome in a Postpartum 33-Year-Old Asian Woman, and the Need for Antepartum Screening for This Clostridia Species in the General Female Population. Lab. Med. 2016, 47, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.F.; Dieudonne, B.E. Clostridium sordelli causing malignant edema in a trauma patient: A case report and review of literature. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 30, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, R.; Bahadur, T.; Sagar, T.; Agrawal, S.K.; Arif, N.; Choudhary, S.K.; Verma, N. Infective Endocarditis Caused by C. sordellii: The First Case Report from India. J. Lab. Physicians 2021, 13, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, V.R.; Cabanilla, M.G. Under the Skin: A Case Series of Clostridium sordellii Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections in Patients Who Inject Drugs. Cureus 2023, 15, e43870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, L.; Kelly, B.; Soehl, J.; Wagar, M.; Rhoades, J.; Cowley, E.S.; Pryde, P.G.; Cutler, A.; Eschenbach, D. Peripartum Uterine Clostridial Myonecrosis: A Report of Two Fatal Cases. WMJ 2024, 123, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurth, L.; Johnston, W.; Black, K.; Doucet, J.; Weaver, J. Mortality in a Clostridium sordellii Case Series. J. Surg. Res. 2024, 304, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biospecimen | Microbes | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | Citrobacter freundii | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Brain | Klebsiella ornithinolytica | Rare colonies |
| Liver | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Spleen | Staphylococcus epidermidis | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Lactobacillus spp. | ||
| Right kidney | Enterococcus gallinarum | Rare colonies * Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Escherichia coli * | ||
| Bacterioides fragilis * | ||
| Left kidney | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Lung: right anterior upper lobe | Veillonella parvula | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Lung: right anterior medial lobe | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Lung: right anterior lower lobe | Negative | |
| Lung: left anterior upper lobe | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Discrete number of colonies * Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Veillonella parvula | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis * | ||
| Lung: left anterior lower lobe | Enteroccoccus faecalis | Obtained after broth enrichment |
| Blood 1st sample | Staphyloccoccus epidermidis | § obtained from anaerobic culture |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis | ||
| Escherichia coli | ||
| Paraclostridium sordellii § | ||
| Blood 2nd sample | Staphylococcus epidermidis | § obtained from anaerobic culture |
| Staphylococcus hominis | ||
| Paraclostridium sordellii § | ||
| Urine | Negative | |
| Rectal swab | Negative | |
| Nasopharyngeal swab SARS-CoV2 | Negative |
| Compound | Concentrations (ng/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Blood | Peripheral Blood | Urine | Vitreous Humor | Bile | |
| Cocaine | 3329 | 2197 | 2962 | 337 | 35,847 |
| Benzoylecgonine | 61 | 101 | 2120 | 125 | - |
| Methadone | 234 | 515 | 738 | 132 | 752 |
| Lorazepam | 12 | 11 | - | <LOQ * | 31 |
| Authors | N° of Cases * | Subject Age and Sex | Type of Case | Fatal Outcome? | Autopsy Performed? | How Was C.s. Diagnosed? | Toxin Presence Verified? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Browdie et al., 1975 [20] | 1 | 23 years M | Traumatic injury | yes | yes | Cultural from wound | no |
| Bogdan et al., 1976 [24] | 1 | 13 days F | Omphalitis | yes | yes | Cultural from blood and fluid from the site of infection | no |
| Gormley et al., 1977 [25] | 1 | 4 days F | Omphalitis | yes | yes | Cultural from fluid from the site of infection | no |
| Thys et al., 1980 [54] | 1 | 18 years M | Other | yes ** | yes | Isolated from muscle and blood sample | no |
| Barnes et al., 1987 [55] | 1 | 61 years M | Other | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples and pleural fluid | no |
| Hogan et al., 1989 [56] | 1 | 39 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from an exudate of myometrium acquired at autopsy | no |
| McGregor et al., 1989 [12] | 3 | 28 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from “clot” from vagina | no |
| 23 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | Cultural from cervical lesion | no | ||
| 23 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from intraoperative and autopsy samples | yes | ||
| Grimwood et al., 1990 [21] | 1 | 4 years F | Traumatic injury | no | -- | Cultural from necrotic tissue from the site of infection | yes |
| Kosloske et al., 1991 [26] | 1 | 9 days F | Omphalitis | no | -- | Cultural from exudate and tissues from site of infection | no |
| Buchman et al., 1991 [57] | 1 | 95 years F | Other | no *** | no | Cultural from pleural fluid | no |
| Spera J, et al., 1992 [58] | 1 | 37 years M | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | no |
| Adamkiewicz et al., 1993 [27] | 1 | 17 days F | Omphalitis | yes | yes | Cultural from peritoneal fluid and umbilical tissue | yes |
| Mory et al., 1995 [3] | 1 | 48 years F | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | yes | yes | Cultural from blood samples and liver tissue acquired at autopsy | yes |
| Bitti et al., 1996 [13] | 1 | 29 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | Cultural from blood | yes |
| Cunnife et al., 1996 [4] | 1 | 55 years M | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | yes | yes | Cultural from blood and stool samples | yes |
| Sosolik et al., 1996 [14] | 1 | 24 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from resected necrotic tissue | no |
| Borer et al., 1999 [59] | 1 | 73 years M | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | yes | yes | Cultural from blood samples | no |
| Gredlein et al., 2000 [22] | 1 | 37 years M | Traumatic injury | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | no |
| Rorbye et al., 2000 [15] | 1 | 40 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | Cultural from discharge from site of infection | no |
| Abdulla et al., 2000 [5] | 2 | 81 years F | Other | yes | yes | Cultural from blood samples | no |
| 12 years M | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | no | ||
| Cobo et al., 2001 [60] | 1 | 17 years F | Other | no | -- | Cultural from a corneal ulcer | no |
| CDC* 2001 [61] | 1 | 23 years M | Other | yes | yes | Cultural from blood | no |
| Bangsberg et al., 2002 [32] | 2 | 28 years F | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from surgical wound | no |
| 52 years M | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative sample of tissues from site of infection | no | ||
| Sinave et al., 2002 [16] | 1 | 26 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from endometrial biopsy | no |
| Lorea et al., 2004 [62] | 1 | 49 years M | Other | no | -- | Cultural from perioperative samples | no |
| Zink et al., 2004 [63] | 1 | 33 years M | Other | no | -- | Cultural from vitreous sample | no |
| Wiebe et al., 2004 [64] | 1 | 27 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from endometrial biopsy and perioperative samples | no |
| Fischer et al., 2005 [11] | 4 | 18 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | PCR assay from DNA extracted from uterine tissues fixed in formalin | yes |
| 21 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | PCR assay from DNA extracted from uterine tissues fixed in formalin | yes | ||
| 22 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | PCR assay from DNA extracted from uterine tissues fixed in formalin | yes | ||
| 34 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | PCR assay from DNA extracted from uterine tissues fixed in formalin | yes | ||
| Brett et al., 2005 [29] | 1 | unknown M | Drug related | yes | no | not specified | no |
| Aldape et al., 2006 [34] | 2 | 4 years M | Traumatic injury | yes | yes | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | no |
| 21 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | no | ||
| Elsayed et al., 2006 [6] | 1 | 61 years F | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | yes | yes | Cultural from blood samples | yes |
| Cohen et al., 2007 [65] | 2 | 25 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | no | -- | Cultural from blood and cervical samples | yes |
| 18 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Immunohistochemical and PCR assay on uterine tissue | yes | ||
| Matten et al., 2009 [7] | 1 | 59 years M | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples and from pleural and liver drainage | yes |
| Foroulis et al., 2009 [66] | 1 | 56 years M | Other | no | -- | PCR analysis from pleural fluid | yes |
| Ho et al., 2009 [67] | 2 | 32 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Immunohistochemical and PCR assay on fixed tissue | yes |
| 40 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Immunohistochemical and PCR assay on fixed tissue | yes | ||
| Valour et al., 2010 [68] | 1 | 31 years F | Traumatic injury | no | -- | PCR analysis on DNA from infected brain tissue | yes |
| Meites et al., 2010 [69] | 2 | 29 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | PCR assay from infected tissue | no |
| 21 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | PCR assay from infected tissue | no | ||
| Chaudhry et al., 2011 [70] | 1 | 8 months M | Other | no | -- | Cultural and PCR assay from intraoperative samples | yes |
| Walk et al., 2011 [71] | 1 | 81 years F | Other | no | -- | Cultures from blood samples and PCR assay on the cultured strains | yes |
| Smith et al., 2013 [8] | 1 | 37 years F | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | no | -- | Cultural from samples from site of infection | no |
| Marinis et al., 2013 [30] | 1 | 25 years F | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | no |
| Bouvet et al., 2015 [23] | 1 | 78 years M | Traumatic injury | not specified | no | Cultural from blood and PCR assay on subculture | yes |
| Guzzetta et al., 2016 [72] | 1 | 33 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | yes | Cultural from episiotomy site and blood samples | no |
| Rellinger et al., 2016 [28] | 1 | 8 days M | Omphalitis | yes | yes | Cultural from intraoperative samples of tissues from site of infection | no |
| Bonnecaze et al., 2016 [9] | 1 | 67 years F | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | no |
| Gray et al., 2018 [73] | 1 | 61 years M | Traumatic injury | not specified | -- | Cultural from wound site | no |
| Mattson et al., 2018 [18] | 1 | 45 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative sample from site of infection | no |
| Elkubuli et al., 2018 [19] | 1 | 31 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | no | -- | Immunohistochemical and PCR assay on intraoperative samples | no |
| Boyanton et al., 2019 [17] | 1 | 29 years F | Gynecological/obstetrician | yes | no | Cultural from ascites samples | no |
| Silva et al., 2020 [31] | 1 | 37 years F | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | no |
| Chaudhry et al., 2021 [74] | 1 | 28 years F | Other | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes |
| Varley et al., 2022 [10] | 1 | 63 years M | Immunosuppressed/oncological patient | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | yes |
| Milano et al., 2023 [75] | 4 | 34 years M | Lupus/drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes |
| 41 years M | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 42 years M | Morbid obesity/drug related | yes | yes | Cultural from abdominal wall tissue | yes | ||
| 47 years M | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| Jacques et al., 2024 [76] | 2 | 30 years F | 42 weeks gestation | yes | yes | Uterine and placental cultures | yes |
| Cultural from blood samples | no | ||||||
| Adolescence F | Medication abortion | yes | yes | Endometrial culture | yes | ||
| Kurth et al., 2024 [77] | 15 | 30 | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes |
| 69 | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 33 | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 68 | / | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 58 | / | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 76 | / | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 50 | / | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 53 | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 64 | / | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | yes | ||
| 42 | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 54 | / | no | -- | Cultural from blood samples | yes | ||
| 60 | Drug related | no | -- | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 47 | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 57 | Drug related | yes | no | Cultural from intraoperative samples from site of infection | yes | ||
| 80 | / | yes | no | Cultural from blood samples | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Focardi, M.; Faccioli, S.; Defraia, B.; Grifoni, R.; Bianchi, I.; Vaiano, F.; Novelli, L.; Ciccone, N.; Capasso, E.; Malentacchi, F.; et al. Fatal Paraclostridium sordellii Infection: Post-Mortem Assessment and Review of the Literature. Pathogens 2025, 14, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070703
Focardi M, Faccioli S, Defraia B, Grifoni R, Bianchi I, Vaiano F, Novelli L, Ciccone N, Capasso E, Malentacchi F, et al. Fatal Paraclostridium sordellii Infection: Post-Mortem Assessment and Review of the Literature. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070703
Chicago/Turabian StyleFocardi, Martina, Simone Faccioli, Beatrice Defraia, Rossella Grifoni, Ilenia Bianchi, Fabio Vaiano, Luca Novelli, Nunziata Ciccone, Emanuele Capasso, Francesca Malentacchi, and et al. 2025. "Fatal Paraclostridium sordellii Infection: Post-Mortem Assessment and Review of the Literature" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070703
APA StyleFocardi, M., Faccioli, S., Defraia, B., Grifoni, R., Bianchi, I., Vaiano, F., Novelli, L., Ciccone, N., Capasso, E., Malentacchi, F., Pinchi, V., & Rossolini, G. M. (2025). Fatal Paraclostridium sordellii Infection: Post-Mortem Assessment and Review of the Literature. Pathogens, 14(7), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070703







