Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered MPV
2.2. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LCMSMS) Quantitation of Serum MPV Concentrations and Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.3. Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography Conditions
2.4. Pharmacokinetics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assay Performance
3.2. Safety and Tolerability of Oral Molnupiravir
3.3. Pharmacokinetics of Oral MPV and NHC in Cats with FIP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPV | molnupiravir |
| NHC | N4-hydroxycytidine |
| Cmax | peak serum concentration |
References
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottier, P.J.; Nakamura, K.; Schellen, P.; Volders, H.; Haijema, B.J. Acquisition of macrophage tropism during the pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis is determined by mutations in the feline coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14122–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and safety of the nucleoside analog GS-441524 for treatment of cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.S.; Coggins, S.; Barker, E.N.; Gunn-Moore, D.; Jeevaratnam, K.; Norris, J.M.; Hughes, D.; Stacey, E.; MacFarlane, L.; O’Brien, C.; et al. Retrospective study and outcome of 307 cats with feline infectious peritonitis treated with legally sourced veterinary compounded preparations of remdesivir and GS-441524 (2020–2022). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X231194460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Wittenburg, L.; Yan, V.C.; Theil, J.H.; Castillo, D.; Reagan, K.L.; Williams, S.; Pham, C.-D.; Li, C.; Muller, F.L. An optimized bioassay for screening combined anticoronaviral compounds for efficacy against feline infectious peritonitis virus with pharmacokinetic analyses of GS-441524, remdesivir, and molnupiravir in cats. Viruses 2022, 14, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sase, O. Molnupiravir treatment of 18 cats with feline infectious peritonitis: A case series. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1876–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; Jacque, N.; Novicoff, W.; Li, E.; Negash, R.; Evans, S.J. Unlicensed molnupiravir is an effective rescue treatment following failure of unlicensed GS-441524-like therapy for cats with suspected feline infectious peritonitis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan, K.L.; Brostoff, T.; Pires, J.; Rose, A.; Castillo, D.; Murphy, B.G. Open label clinical trial of orally administered molnupiravir as a first-line treatment for naturally occurring effusive feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, A.; Penchala, S.D.; Else, L.; Hale, C.; FitzGerald, R.; Walker, L.; Lyons, R.; Fletcher, T.; Khoo, S. The development and validation of a novel LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of Molnupiravir and its metabolite ß-d-N4-hydroxycytidine in human plasma and saliva. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, B.M.; Strizki, J.; Miller, R.R.; Kumar, S.; Brown, M.; Johnson, M.G.; Cheng, M.; De Anda, C.; Rizk, M.L.; Stone, J.A. Molnupiravir: Mechanism of action, clinical, and translational science. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, W.P.; Holman, W.; Bush, J.A.; Almazedi, F.; Malik, H.; Eraut, N.C.; Morin, M.J.; Szewczyk, L.J.; Painter, G.R. Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e02428-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, S.D.; Testa, B. The Biochemistry of Drug Metabolism–An Introduction: Part 7. Intra-Individual Factors Affecting Drug Metabolism. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1477–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Duncan, K.E.; Wickremasingha, P.K.; Zhao, T.; Liberti, M.V.; Lemoine, L.; Decaesteker, T.; Rottey, S.; Maas, B.M.; Gillespie, G. Assessment of pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability following twice-daily administration of molnupiravir for 10 days in healthy participants. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.; Coggins, S.; Korman, R.; King, J.; Malik, R. Treatment of feline infectious peritonitis in cats with molnupiravir: Clinical observations and outcomes for 54 cases. Aust. Vet. J. 2025, 103, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggins, S.; Govendir, M.; Norris, J.; Malik, R.; Hall, E.; Thompson, M.; Kimble, B. Pharmacokinetics of GS-441524 following intravenous remdesivir in six cats and results of therapeutic drug monitoring during treatment of feline infectious peritonitis: 22 cases (2021–2024). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2025, 66, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

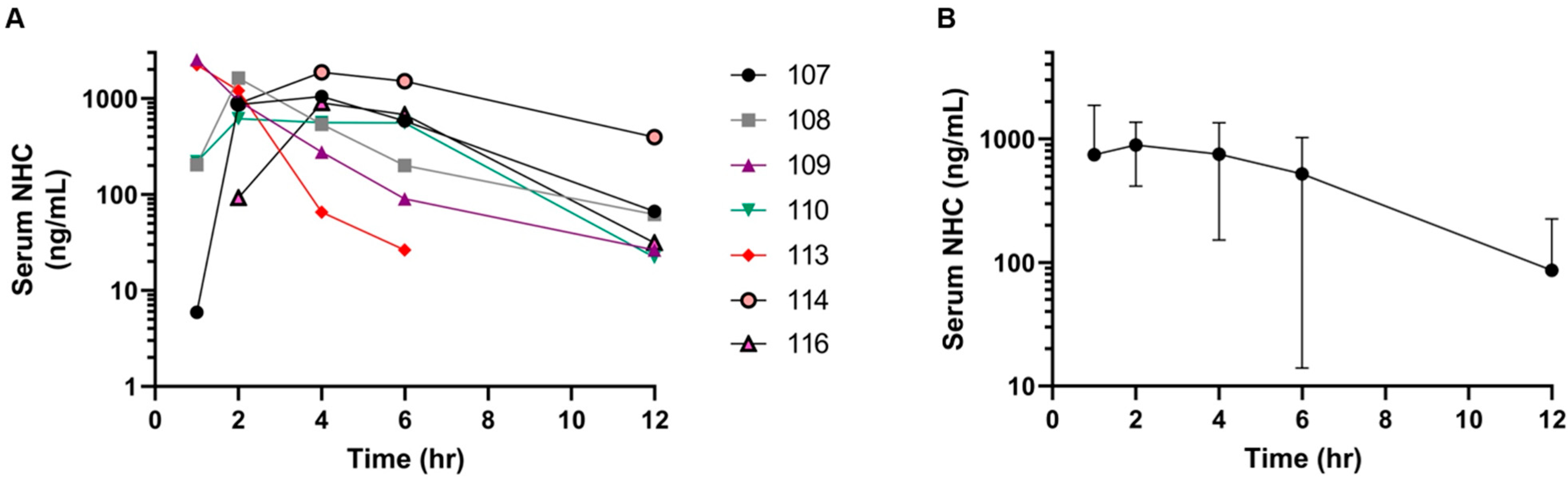
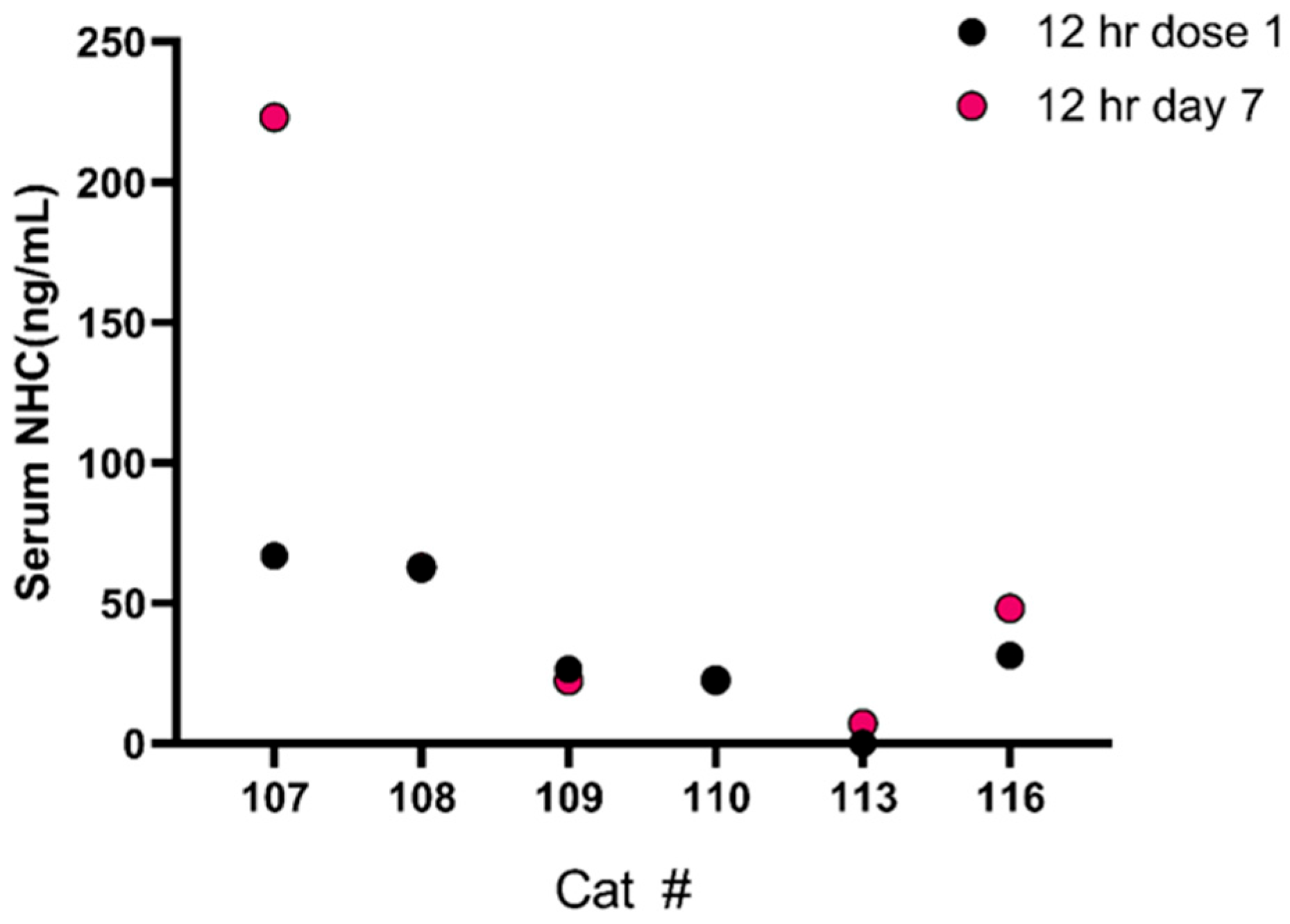
| Number | Age (Years) | Sex | Breed | FIP Form | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 107 | 0.34 | MN | DSH | effusive | dead (day 10) |
| 108 | 3.01 | MN | DSH | effusive | in remission |
| 109 | 1.06 | MN | DSH | effusive | in remission |
| 110 | 1.45 | FS | Maine Coon | ocular | in remission |
| 113 | 0.43 | MN | DSH | non-effusive | in remission |
| 114 | 1.08 | MN | DSH | effusive | in remission |
| 116 | 2.00 | FS | Bengal | effusive | in remission |
| MPV | NHC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Median (Range) | Mean ± SD | Median (Range) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 37 ± 5 † | 39 (232) | 1551 ± 720 | 1630 (1913) |
| Tmax (h) | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 1 (3) | 2.6 ± 1.4 | 2 (3) |
| AUC0-T (h·ng/mL) | 222 ± 237 | 127 (653) | 5919 ± 2874 | 4749 (8100) |
| AUC0-Inf (h·ng/mL) | 6296 ± 3573 | 4957 (10,040) | ||
| Kel (1/h) | 0.344 ± 0.152 ‡ | 0.35 (0.76) | ||
| T1/2 (h) | 1.6 ± 1.1 ‡ | 1.9 (2.7) | ||
| Vz/F (L) | 24.4 ± 11.3 | 23.5 (30.6) | ||
| Cl/F (L/h) | 9.2 ± 3.9 | 10.4 (9.8) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Černá, P.; Wittenburg, L.; Hawley, J.; Willis, M.; Siegenthaler, B.; Lappin, M.R. Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070666
Černá P, Wittenburg L, Hawley J, Willis M, Siegenthaler B, Lappin MR. Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070666
Chicago/Turabian StyleČerná, Petra, Luke Wittenburg, Jennifer Hawley, McKenna Willis, Britta Siegenthaler, and Michael R. Lappin. 2025. "Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070666
APA StyleČerná, P., Wittenburg, L., Hawley, J., Willis, M., Siegenthaler, B., & Lappin, M. R. (2025). Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens, 14(7), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070666







