Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stool Sample Collection, 16s rRNA Sequencing, and Determination of GI-Colonizing Isolates
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Invasive and GI-Colonizing S. epidermidis Isolates
2.3. Comprehensive Genome Analysis
2.4. Whole-Genome Comparison of Colonizing Versus Infection Isolates
2.5. Phylogenetic Tree Construction, Tree Parsing, and Comparative Analyses
3. Results
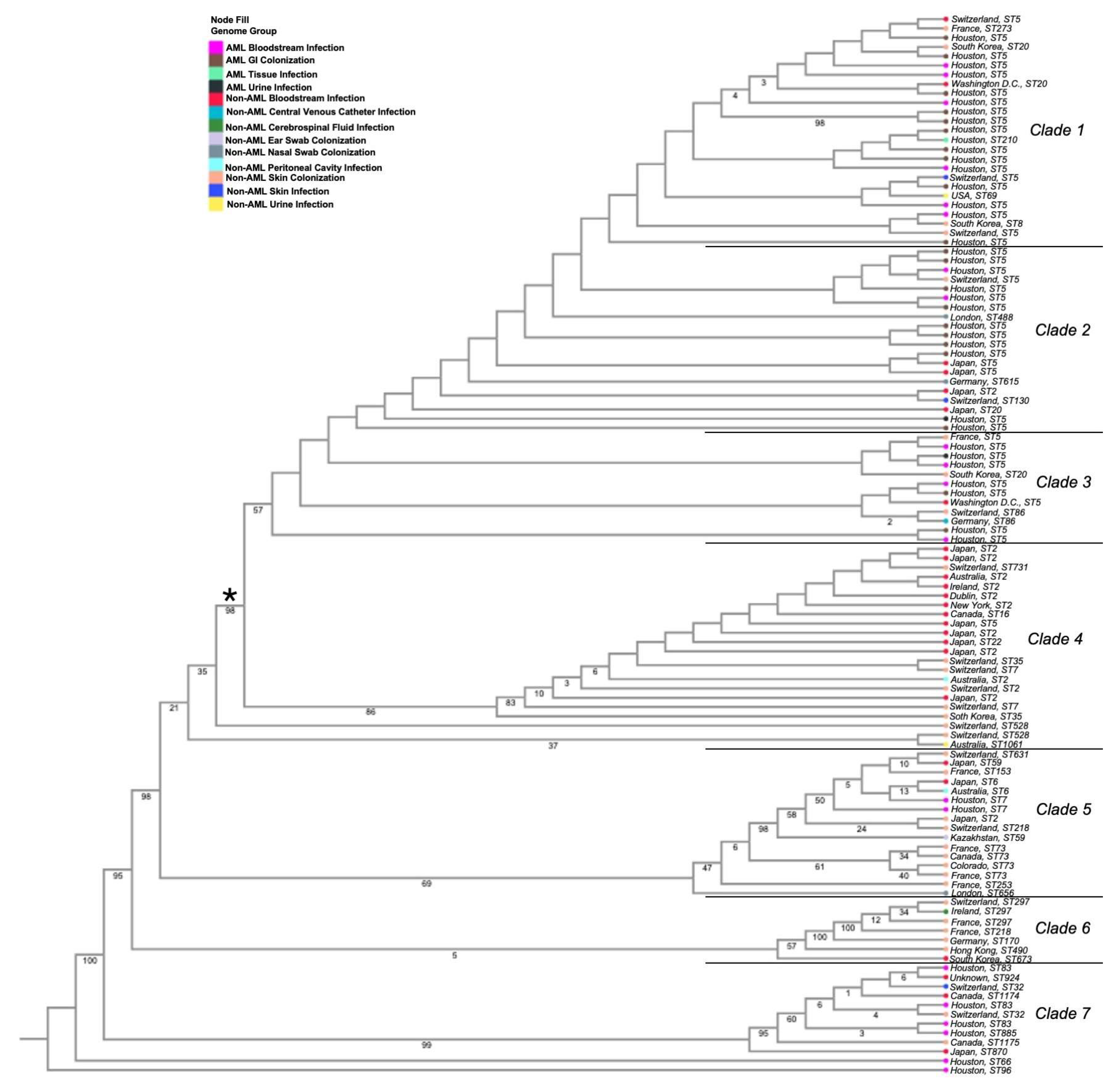
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses of Isolates
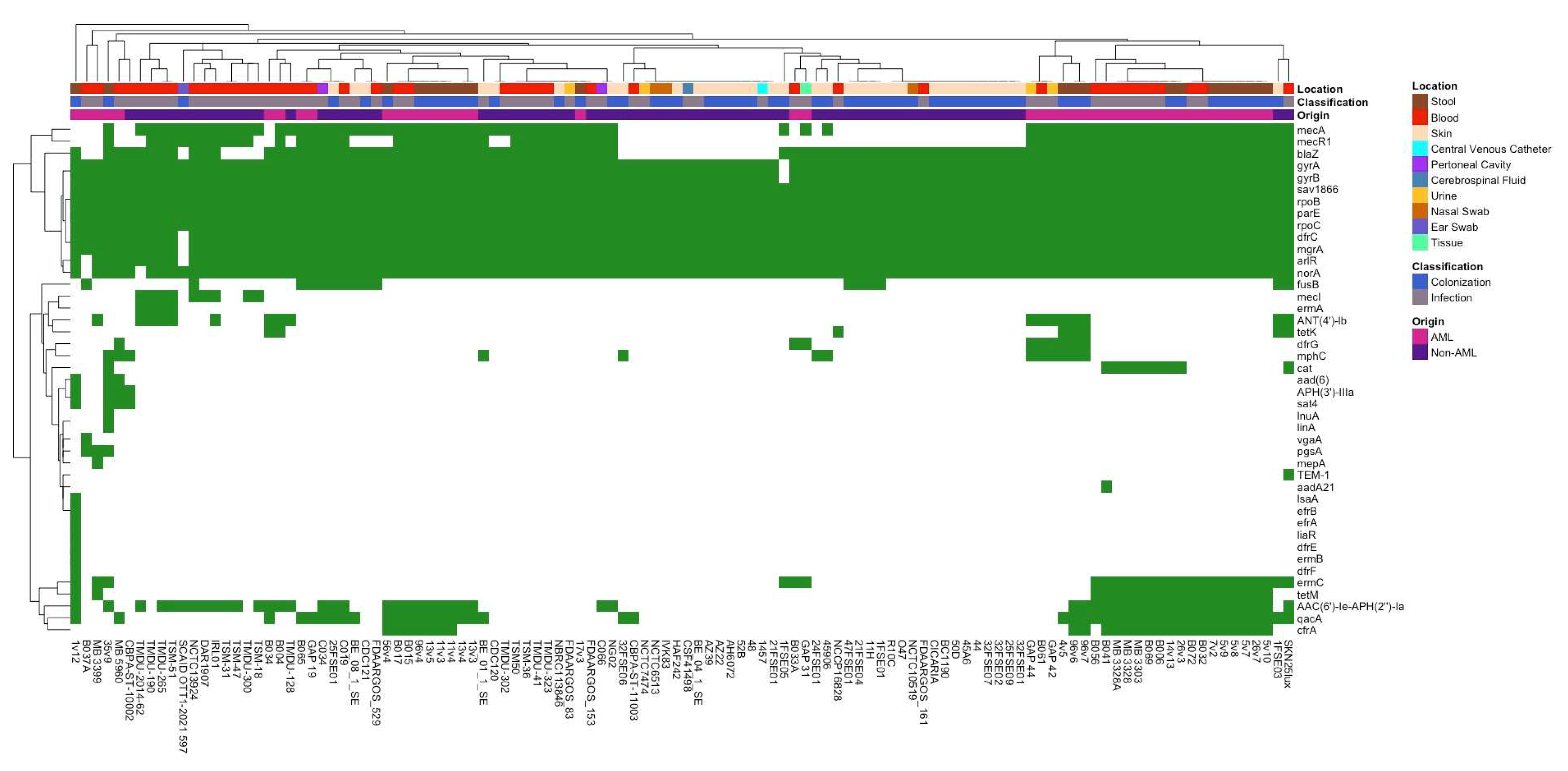
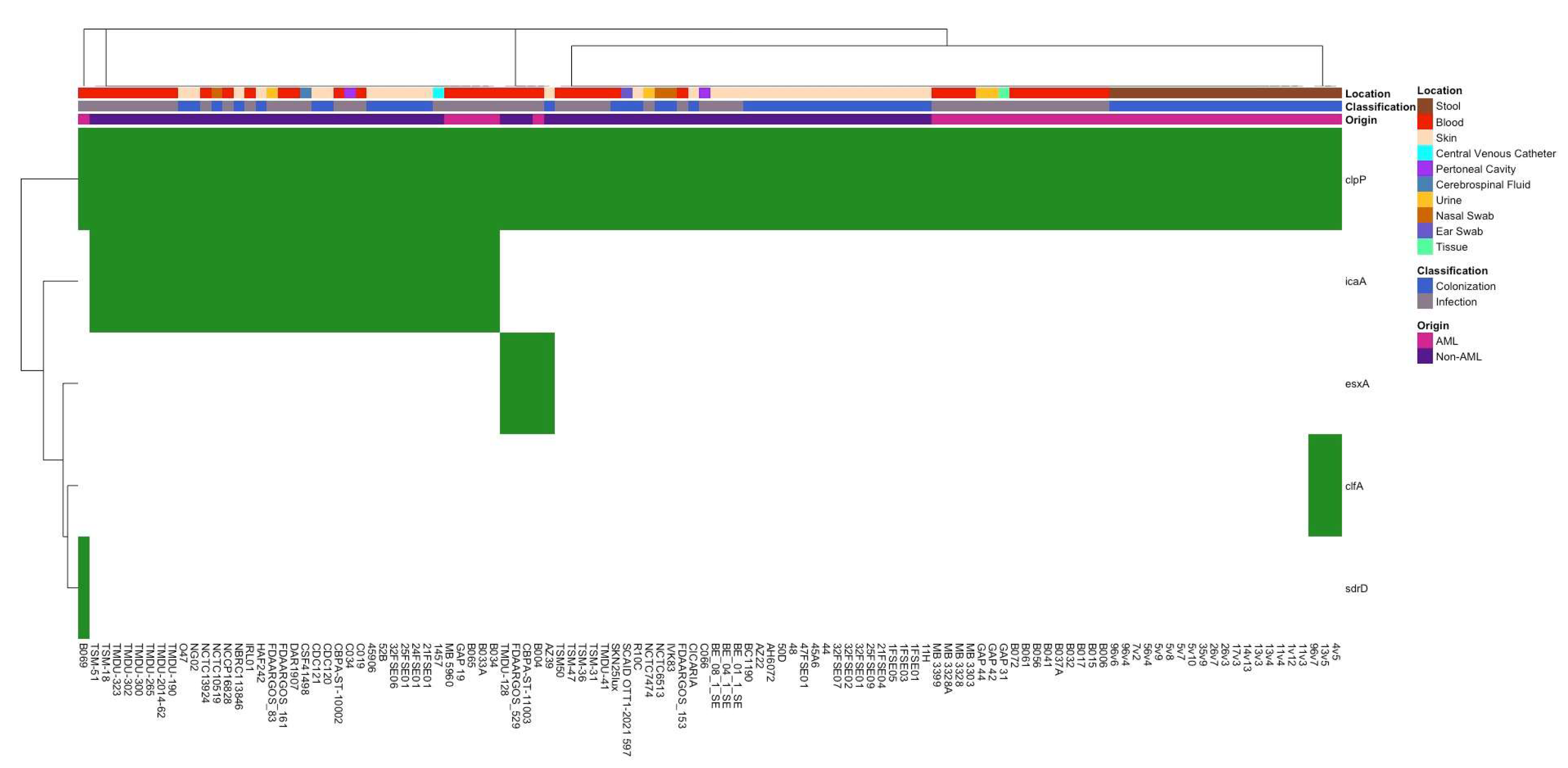
3.2. Differences in Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors Between Isolate Groups
3.3. Whole-Genome Comparison of Infection vs. Colonization Isolates
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gustinetti, G.; Mikulska, M. Bloodstream infections in neutropenic cancer patients: A practical update. Virulence 2016, 7, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, A.; Guddati, A.K. Infections in Hospitalized Cancer Patients. World J. Oncol. 2021, 12, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, S.; Godnaik, C. Incidence and management of infections in patients with acute leukemia following chemotherapy in general wards. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Kim, J.; Franklin, S.; Chang, C.-C.; Jenq, R.R.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Shelburne, S.A.; Galloway-Peña, J. Contribution of the Oral and Gastrointestinal Microbiomes to Bloodstream Infections in Leukemia Patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00415-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montassier, E.; Gastinne, T.; Vangay, P.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Bruley des Varannes, S.; Massart, S.; Moreau, P.; Potel, G.; De La Cochetière, M.F.; Batard, E.; et al. Chemotherapy-driven dysbiosis in the intestinal microbiome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francino, M.P. Antibiotics and the Human Gut Microbiome: Dysbioses and Accumulation of Resistances. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freifeld, A.G.; Bow, E.J.; Sepkowitz, K.A.; Boeckh, M.J.; Ito, J.I.; Mullen, C.A.; Raad, I.I.; Rolston, K.V.; Young, J.-A.H.; Wingard, J.R.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway-Peña, J.R.; Jenq, R.R.; Shelburne, S.A. Can Consideration of the Microbiome Improve Antimicrobial Utilization and Treatment Outcomes in the Oncology Patient? Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3263–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, Q.; Li, W.; Guo, W.; Stojadinovic, A.; Mannion, C.; Man, Y.; Chen, T. Antibiotics for cancer treatment: A double-edged sword. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5135–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taur, Y.; Xavier, J.B.; Lipuma, L.; Ubeda, C.; Goldberg, J.; Gobourne, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Dubin, K.A.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; et al. Intestinal Domination and the Risk of Bacteremia in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffie, C.G.; Jarchum, I.; Equinda, M.; Lipuma, L.; Gobourne, A.; Viale, A.; Ubeda, C.; Xavier, J.; Pamer, E.G. Profound Alterations of Intestinal Microbiota following a Single Dose of Clindamycin Results in Sustained Susceptibility to Clostridium difficile-Induced Colitis. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway-Peña, J.; Brumlow, C.; Shelburne, S. Impact of the Microbiota on Bacterial Infections during Cancer Treatment. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, F.B.; Andermann, T.M.; Tkachenko, E.; Senchyna, F.; Banaei, N.; Bhatt, A.S. Precision identification of diverse bloodstream pathogens in the gut microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.H.; Khatib, L.A.; Fitzgerald, A.S.; Graham-Wooten, J.; Ittner, C.A.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Chuang, Y.; Glaser, L.J.; Meyer, N.J.; Bushman, F.D.; et al. Tracking gut microbiome and bloodstream infection in critically ill adults. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, S.; Aitken, S.L.; Shi, Y.; Sahasrabhojane, P.V.; Robinson, S.; Peterson, C.B.; Daver, N.; Ajami, N.A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Shelburne, S.A.; et al. Oral and Stool Microbiome Coalescence and Its Association with Antibiotic Exposure in Acute Leukemia Patients. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 848580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Weisel, D.; Gao, F.; Uy, G.L.; Cashen, A.F.; Jacoby, M.A.; Wartman, L.D.; Ghobadi, A.; Pusic, I.; Romee, R.; et al. Patterns of infectious complications in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes patients treated with 10-day decitabine regimen. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.; Harris, L.G.; Morgenstern, M.; Mageiros, L.; Hitchings, M.D.; Méric, G.; Pascoe, B.; Sheppard, S.K.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F. Comparative Genomics Study of Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates from Orthopedic-Device-Related Infections Correlated with Patient Outcome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3089–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus epidermidis—Skin friend or foe? PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.A.; Kjerfve, C.; Choi, M.; Liu, W.; Churion, K.; Thomas, S.; Rohde, H.; Shelburne, S.; Skare, J.T.; Hook, M.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis ST2 strains associated with bloodstream infections contain a unique mobile genetic element encoding a plasmin inhibitor. mBio 2024, 15, e01907-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.M.; Strasheim, W.; Lowe, M.; Ueckermann, V.; Kock, M.M. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus epidermidis Implicated in Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections at an Academic Hospital in Pretoria, South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, F. Molecular Characteristics of Biofilm-Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates Causing Urinary Tract Infections. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 13, e61704. Available online: https://brieflands.com/articles/archcid-61704#abstract (accessed on 14 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- He, W.-P.; Gu, F.-F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.-X.; Xiao, S.-Z.; Zeng, Q.; Ni, Y.-X.; Han, L.-Z. Molecular characteristics and risk factor analysis of Staphylococcus aureus colonization put insight into CC1 colonization in three nursing homes in Shanghai. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altayb, H.N.; Elbadawi, H.S.; Baothman, O.; Kazmi, I.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Hosawi, S.; Chaieb, K. Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Sampedro, G.R.; Otto, M.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. The psmα locus regulates production of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin during infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3350–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway-Peña, J.R.; Shi, Y.; Peterson, C.B.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Brumlow, C.E.; Daver, N.G.; Alfayez, M.; Boddu, P.C.; Khan, M.A.W.; et al. Gut Microbiome Signatures Are Predictive of Infectious Risk Following Induction Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (EN)—QIAamp DNA Stool Handbook—June 2012—QIAGEN. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/resources/resourcedetail?id=e5f66d36-1f1c-4e89-828e-257088bdad53&lang=en (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Galloway-Peña, J.R.; Smith, D.P.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Wadsworth, W.D.; Fellman, B.M.; Ajami, N.J.; Shpall, E.J.; Daver, N.; Guindani, M.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Characterization of oral and gut microbiome temporal variability in hospitalized cancer patients. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway-Peña, J.; Smith, D.P.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Ajami, N.J.; Wadsworth, W.D.; Daver, N.G.; Chemaly, R.F.; Marsh, L.; Ghantoji, S.S.; Pemmaraju, N.; et al. The Role of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Infectious Complications During Induction Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer 2016, 122, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynildsrud, O.; Bohlin, J.; Scheffer, L.; Eldholm, V. Rapid scoring of genes in microbial pan-genome-wide association studies with Scoary. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrashedy, A.; Nayel, M.; Salama, A.; Zaghawa, A.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Hasan, M.E. Phylogenetic Analysis and Comparative Genomics of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis Strains in Egypt. J. Mol. Evol. 2024, 92, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabi, R.; Momtaz, H. Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance properties of the Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from hospital infections in Ahvaz, Iran. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, F.; Vourli, S.; Karavasilis, V.; Strommenger, B.; Dafopoulou, K.; Tsakris, A.; Werner, G.; Pournaras, S. Dissemination of linezolid-dependent, linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates belonging to CC5 in German hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiselle, J.; Meyer, P.; Lavigne, T.; Kaurin, J.; Merdji, H.; Schenck, M.; Studer, A.; Janssen-Langenstein, R.; Helms, J.; Hoellinger, B.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis bloodstream infections are a cause of septic shock in intensive care unit patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 135, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duygu Mert, A.M. Evaluation of Risk Factors and Causative Pathogens in Bloodstream Infections in Cancer Patients. Available online: https://gulhanemedj.org/articles/evaluation-of-risk-factors-and-causative-pathogens-in-bloodstream-infections-in-cancer-patients/doi/gulhane.galenos.2020.1320?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- VanAken, S.M.; Newton, D.; VanEpps, J.S. Improved diagnostic prediction of the pathogenicity of bloodstream isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briaud, P.; Zapf, R.L.; Mayher, A.D.; McReynolds, A.K.G.; Frey, A.; Sudnick, E.G.; Wiemels, R.E.; Keogh, R.A.; Shaw, L.N.; Bose, J.L.; et al. The Small RNA Teg41 Is a Pleiotropic Regulator of Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0023622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté Brescó, M.; Harris, L.G.; Thompson, K.; Stanic, B.; Morgenstern, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F. Pathogenic Mechanisms and Host Interactions in Staphylococcus epidermidis Device-Related Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Rahman, H.; Qasim, M.; Nawab, J.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Alsharif, K.F.; Alzahrani, F.M. Staphylococcus epidermidis Pathogenesis: Interplay of icaADBC Operon and MSCRAMMs in Biofilm Formation of Isolates from Pediatric Bacteremia in Peshawar, Pakistan. Medicina 2022, 58, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.J.; Shalon, N.; Wardenburg, K.; DeVeaux, A.; Wallace, M.A.; Hall-Moore, C.; Ndao, I.M.; Sullivan, J.E.; Radmacher, P.; Escobedo, M.; et al. Gut pathogen colonization precedes bloodstream infection in the neonatal intensive care unit. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadg5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Walsh, C.J.; Sayavedra, L.; Diaz-Calvo, T.; Thapa, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Mayer, M.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Narbad, A. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Fecal Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates Suggests Plasticity to Adapt to Different Human Body Sites. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Annotation | Infectious (Present) | Non-Infectious (Present) | Infectious (Not Present) | Non-Infectious (Not Present) | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xerC_2 | Tyrosine recombinase XerC | 13 | 2 | 43 | 53 | 8.012 | 0.00414 |
| group_1639 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_4686 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_4687 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_4688 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_9012 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_9046 | Hypothetical protein | 12 | 2 | 44 | 53 | 7.227 | 0.00809 |
| group_14970 | IS6 family transposase IS431mec | 22 | 6 | 34 | 49 | 5.284 | 0.00085 |
| mecA_2 | PBP2a family beta-lactam-resistant peptidoglycan transpeptidase MecA | 43 | 25 | 13 | 30 | 3.969 | 0.00090 |
| group_2675 | Signal peptidase IB | 34 | 16 | 22 | 39 | 3.767 | 0.00113 |
| group_4522 | Hypothetical protein | 43 | 27 | 13 | 28 | 3.430 | 0.00318 |
| ugpQ | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase, cytoplasmic | 43 | 27 | 13 | 28 | 3.430 | 0.00318 |
| group_697 | 2-succinylbenzoate--CoA ligase | 11 | 25 | 45 | 30 | 0.293 | 0.00458 |
| group_2478 | Hypothetical protein | 7 | 19 | 49 | 36 | 0.271 | 0.00731 |
| arsB_2 | Arsenical pump membrane protein | 28 | 44 | 28 | 11 | 0.250 | 0.00135 |
| group_1377 | Hypothetical protein | 7 | 20 | 49 | 35 | 0.250 | 0.00405 |
| spsB_3 | Signal peptidase IB | 20 | 38 | 36 | 17 | 0.249 | 0.00059 |
| yhfS | Putative acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase YhfS | 29 | 46 | 27 | 9 | 0.210 | 0.00049 |
| group_1486 | Putative protein YxeI | 6 | 20 | 50 | 35 | 0.210 | 0.00165 |
| group_5702 | Hypothetical protein | 5 | 18 | 51 | 37 | 0.202 | 0.00227 |
| group_15014 | IS200/IS605 family transposase ISSep3 | 3 | 13 | 53 | 42 | 0.183 | 0.00701 |
| group_2646 | Ribulose-5-phosphate reductase 2 | 2 | 11 | 54 | 44 | 0.148 | 0.00809 |
| group_3670 | DNA-invertase hin | 2 | 11 | 54 | 44 | 0.148 | 0.00809 |
| group_3678 | Putative protein | 2 | 11 | 54 | 44 | 0.148 | 0.00809 |
| group_5714 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 11 | 54 | 44 | 0.148 | 0.00809 |
| group_5814 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 11 | 54 | 44 | 0.148 | 0.00809 |
| group_3608 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 13 | 54 | 42 | 0.120 | 0.00208 |
| group_5695 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 13 | 54 | 42 | 0.120 | 0.00208 |
| group_2806 | Hypothetical protein | 3 | 18 | 53 | 37 | 0.116 | 0.00022 |
| group_5693 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 14 | 54 | 41 | 0.108 | 0.00102 |
| group_5697 | Hypothetical protein | 2 | 14 | 54 | 41 | 0.108 | 0.00102 |
| Gene | SCOARY Annotation | Phyre Annotation (Confidence) | InterproScan Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| xerC_2 | Tyrosine recombinase XerC | Tyrosine recombinase xerA (100) | Phage Integrase |
| group_1639 | Hypothetical Protein | DNA Binding Protein (100) | No Prediction |
| group_4686 | Hypothetical Protein | Hydrolase Inhibitor (52.9) | No Prediction |
| group_4687 | Hypothetical Protein | Repression Modulator (99.7) | Unknown Function |
| group_4688 | Hypothetical Protein | Arsenic Responsive Repressor (78.2) | No Prediction |
| group_9012 | Hypothetical Protein | Viral Protein (98.9) | No Prediction |
| group_9046 | Hypothetical Protein | Structural Protein (97.0) | No Prediction |
| group_14970 | IS6 family transposase IS431mec | Mutator family transposase (98.4) | IS6 Family Transposase |
| mecA_2 | PBP2a family beta-lactam-resistant peptidoglycan transpeptidase MecA | Penicillin-binding protein 2A (100) | Beta-Lactamase |
| group_2675 | Signal peptidase IB | Hydrolase (100) | Signal Peptidase |
| group_4522 | Hypothetical Protein | Thioesterase/thiol ester dehydrase-isomerase (100) | Hydratase/Beta-methylmalyl-CoA Dehydratase |
| ugpQ | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase, cytoplasmic | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (100) | No Prediction |
| group_697 | 2-succinylbenzoate--CoA ligase | Ligase (100) | No Prediction |
| group_2478 | Hypothetical Protein | RAS and A-Factor Converting Enzyme (99.8) | No Prediction |
| arsB_2 | Arsenical pump membrane protein | Transport Protein (99.7) | Arsenical pump membrane protein |
| group_1377 | Hypothetical Protein | Hydrolase (100) | Exonuclease |
| spsB_3 | Signal peptidase IB | Hydrolase (100) | Signal Peptidase |
| yhfS | Putative acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase YhfS | Beta-ketothiolase (100) | Thiolase-like superfamily |
| group_1486 | Putative protein YxeI | Hydrolase (100) | Peptidase C59 Family Enzyme |
| group_5702 | Hypothetical Protein | Lyase (14.4) | No Prediction |
| group_15014 | IS200/IS605 family transposase ISSep3 | ISHP608 Transposase (100) | No Prediction |
| group_2646 | Ribulose-5-phosphate reductase 2 | Oxidoreductase (100) | No Prediction |
| group_3670 | DNA-invertase hin | Hydrolase (100) | Site-specific recombinase resolvase |
| group_3678 | Putative protein | Unknown Protein (100) | CSA family |
| group_5714 | Hypothetical Protein | Putative regulator of transfer genes (99.8) | No Prediction |
| group_5814 | Hypothetical Protein | Myeloproxidase inhibitor SPIN (66.6) | No Prediction |
| group_3608 | Hypothetical Protein | Signaling Protein (78.4) | No Prediction |
| group_5695 | Hypothetical Protein | Prohormone (59.2) | No Prediction |
| group_2806 | Hypothetical Protein | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member | No Prediction |
| group_5693 | Hypothetical Protein | Viral Protein (8.7) | No Prediction |
| group_5697 | Hypothetical Protein | Acetyltransferase (98.3) | No Prediction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McMahon, S.; Franklin, S.; Batool, M.; Sadasivan, N.; Fatima, S.; Galloway-Peña, J. Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates. Pathogens 2025, 14, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070627
McMahon S, Franklin S, Batool M, Sadasivan N, Fatima S, Galloway-Peña J. Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070627
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcMahon, Stephanie, Samantha Franklin, Maliha Batool, Nitya Sadasivan, Safa Fatima, and Jessica Galloway-Peña. 2025. "Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070627
APA StyleMcMahon, S., Franklin, S., Batool, M., Sadasivan, N., Fatima, S., & Galloway-Peña, J. (2025). Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates. Pathogens, 14(7), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070627







