Cardiac Device-Related Infective Endocarditis Caused by Salmonella Infantis—Case Report and Review of Clinical and Epidemiologic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
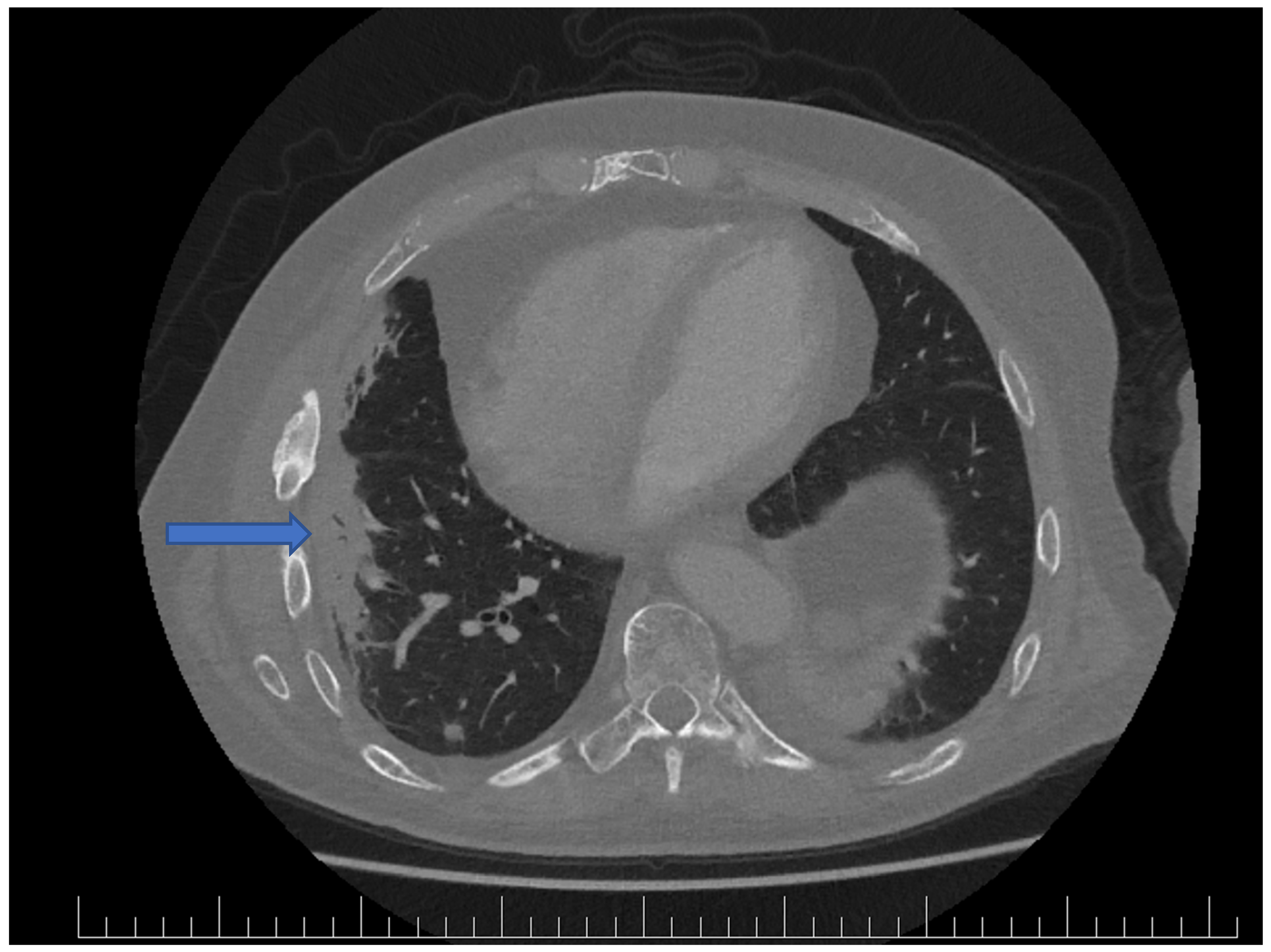
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Consideration
4.2. Diagnosis and Management of CDRIE
4.3. Microbiological Perspective
4.4. Epidemiology of S. Infantis
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattock, J.; Chattaway, M.A.; Hartman, H.; Dallman, T.J.; Smith, A.M.; Keddy, K.; Petrovska, L.; Manners, E.J.; Duze, S.T.; Smouse, S.; et al. A One Health Perspective on Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis, an Emerging Human Multidrug-Resistant Pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2016. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e05077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Notification 2024.5172 Salmonella enterica ser. Infantis in Frozen Chicken Inner Fillets Produced in Slovakia, from Chickens Slaughtered in Ukraine; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2024; Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/screen/notification/696000 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- European Commission. Salmonella Infantis in Frozen Chicken Breasts from Poland, via Slovakia; 2024.8171. 2024. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/screen/notification/723181 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of the Slovak Republic. Report on Zoonoses, Alimentary and Water-Borne Infections in the Slovak Republic for 2023; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of the Slovak Republic: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2025; ISBN 978-80-89738-45-8. Available online: https://www.mpsr.sk/download.php?fID=25606 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Alvarez, D.M.; Barrón-Montenegro, R.; Conejeros, J.; Rivera, D.; Undurraga, E.A.; Moreno-Switt, A.I. A Review of the Global Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica Serovar Infantis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 403, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Davis Weaver, N.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Gershberg Hayoon, A.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamadh, M.S.; Alanazi, R.B.; Alhowaish, T.S.; Alhabeeb, A.Y.; Algarni, S.T.; Wadaan, O.M.; Suliman, I.; Al-Ghamdi, M.G. Refractory Salmonella Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction and Aortic Pseudoaneurysm in a Patient with Double Prosthetic Valves: A Case Report. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, K.; Fife, A.; Murgatroyd, F.; Gall, N. Pacemaker Endocarditis: An Important Clinical Entity: Figure 1. BMJ Case Rep. 2009, 2009, bcr0220091608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, F.; Anguita, M.; Ruiz, M.; Castillo, J.C.; Delgado, M.; Mesa, D.; Romo, E.; Pan, M.; Suárez De Lezo, J. Clinical Features and Changes in Epidemiology of Infective Endocarditis on Pacemaker Devices over a 27-Year Period (1987–2013). Europace 2016, 18, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, D.; Lacroix, D.; Savoye, C.; Goullard, L.; Grandmougin, D.; Hennequin, J.L.; Kacet, S.; Lekieffre, J. Systemic Infection Related to Endocarditis on Pacemaker Leads: Clinical Presentation and Management. Circulation 1997, 95, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blusztein, D.; Strathmore, N. Salmonella Enteritidis Pacemaker Endocarditis without Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M.; Monney, P.; Frank, M.; Tzimas, G.; Tozzi, P.; Kirsch, M.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Bauernschmitt, R.; Epprecht, J.; Guery, B.; et al. Evaluation of the 2023 Duke-ISCVID and 2023 Duke-ESC Clinical Criteria for the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in a Multicenter Cohort of Patients With Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.R.; Uslan, D.Z.; Khan, A.H.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Jenkins, S.M.; Baddour, L.M. Infective Endocarditis Complicating Permanent Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Infection. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Río, A.; Anguera, I.; Miró, J.M.; Mont, L.; Fowler, V.G.; Azqueta, M.; Mestres, C.A. Surgical Treatment of Pacemaker and Defibrillator Lead Endocarditis. Chest 2003, 124, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.G.; Durack, D.T.; Selton-Suty, C.; Athan, E.; Bayer, A.S.; Chamis, A.L.; Dahl, A.; DiBernardo, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Duval, X.; et al. The 2023 Duke-International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiati, C.; Pollice, P.; Lepera, M.E.; Favale, S. Pacemaker Lead Endocarditis Investigated with Intracardiac Echocardiography: Factors Modulating the Size of Vegetations and Larger Vegetation Embolic Risk during Lead Extraction. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Leprince, P.; Nataf, P.; Hausfater, P.; Dorent, R.; Wechsler, B.; Bors, V.; Pavie, A.; Piette, J.C.; Gandjbakhch, I. Pacemaker Infective Endocarditis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; De Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Aljahdali, N.; Zhao, S.; Tang, H.; Harbottle, H.; Hoffmann, M.; Frye, J.G.; Foley, S.L. Infection Biology of Salmonella enterica. EcoSal Plus 2024, 12, eesp-0001-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoff, M.Y.; Bockemühl, J.; Gheesling, L.L. Supplement 2002 (No. 46) to the Kauffmann–White Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; De Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2008–2010 (no. 48) to the White–Kauffmann–Le Minor Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.C.; Chen, J.C.; Watkins, L.K.F.; Campbell, D.; Folster, J.P.; Tate, H.; Wasilenko, J.; Van Tubbergen, C.; Friedman, C.R. CTX-M-65 Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase–Producing Salmonella enterica Serotype Infantis, United States1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, G.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Horizontal Transfer of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis Resistance and Virulence Plasmid pESI to the Gut Microbiota of Warm-Blooded Hosts. mBio 2016, 7, e01395-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Itagaki, M.; Shiroki, Y.; Yamada, M.; Tokoro, M.; Kojima, A.; Ishihara, K.; Esaki, H.; Tamura, Y.; Takahashi, T. Antimicrobial Resistance Types and Genes in Salmonella enterica Infantis Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken Meat and Broiler Chickens on Farms. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.H.; Paul, N.C.; Sischo, W.C.; Crespo, R.; Guard, J. Population Dynamics and Antimicrobial Resistance of the Most Prevalent Poultry-Associated Salmonella Serotypes. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Sánchez, K.; Tataje-Lavanda, L.; Villanueva-Pérez, D.; Bendezú, J.; Montalván, Á.; Zimic-Peralta, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Fernández-Díaz, M. Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Infantis Strain Isolated from Broiler Chicken in Peru. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00826-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Baquero, M.; Medina, J.; De Zutter, L. Occurrence, Genotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella Collected from the Broiler Production Chain Within an Integrated Poultry Company. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 299, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomazova, A.N.; Gordeeva, V.D.; Krylova, E.V.; Soltynskaya, I.V.; Davydova, E.E.; Ivanova, O.E.; Komarov, A.A. Mega-plasmid Found Worldwide Confers Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Infantis of Broiler Origin in Russia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 319, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Valinsky, L.; Weinberger, M.; Guy, S.; Jaffe, J.; Schorr, Y.I.; Raisfeld, A.; Agmon, V.; Nissan, I. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis, Israel. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, I.L.; Heuzenroeder, M.W. A comparison of Three Molecular Typing Methods for the Discrimination of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, E.; Wong, D.M.A.L.F.; Patrick, M.E.; Binsztein, N.; Cieslik, A.; Chalermchaikit, T.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Ellis, A.; Angulo, F.J.; Wegener, H.C.; et al. Web-based Surveillance and Global Salmonella Distribution, 2000–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chironna, M.; Tafuri, S.; Gallone, M.S.; Sallustio, A.; Martinelli, D.; Prato, R.; Germinario, C. Outbreak of Salmonella infantis Gastroenteritis Among People Who Had Eaten at a Hash House in Southern Italy. Public Health 2014, 128, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; Braun, P.G.; Fehlhaber, K.; Prager, R.; Pfeifer, Y.; Rabsch, W. Typing of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis Isolates from 51 Outbreaks in Germany Between 1974 and 2009 by a Novel Phage-Typing Scheme. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, H.C.; Hald, T.; Wong, D.L.F.; Madsen, M.; Korsgaard, H.; Bager, F.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Mølbak, K. Salmonella Control Programs in Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, H.C.; Baggesen, D.L. Investigation of an Outbreak of Human Salmonellosis Caused by Salmonella enterica ssp. Enterica Serovar Infantis by Use of Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 32, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Aabo, S.; Birk, T.; Mordhorst, H.; Bjarnadóttir, B.; Agersø, Y. Survival and Growth of Epidemically Successful and Nonsuccessful Salmonella enterica Clones after Freezing and Dehydration. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, E.; Tietze, E.; Helmuth, R.; Junker, E.; Prager, R.; Schroeter, A.; Rabsch, W.; Fruth, A.; Toboldt, A.; Malorny, B. Clonal Dissemination of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis in Germany. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, M.; Rotstein, D.S.; Reimschuessel, R.; Schwensohn, C.A.; Woody, D.H.; Davis, S.W.; Hunt, A.D.; Arends, K.D.; Achen, M.; Cui, J.; et al. Outbreak of Salmonella enterica Serotype Infantis Infection in Humans Linked to Dry Dog Food in the United States and Canada, 2012. JAVMA J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Ishihara, T.; Horikawa, K.; Oda, T. Features of Salmonella Serovars Among Food Handlers in Kyushu, Japan. New Microbiol. 2007, 30, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Basler, C.; Forshey, T.M.; Machesky, K.; Erdman, C.M.; Gomez, T.M.; Brinson, D.L.; Nguyen, T.-A.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bosch, S.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Multistate Outbreak of Human Salmonella Infections Linked to Live Poultry from a Mail-Order Hatchery in Ohio—February–October 2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 258. [Google Scholar]
- The Czech Agriculture and Food Inspection Authority (CAFIA). Warning for Consumers: Salmonella in Chilled Chicken Meat from Abroad; The Czech Agriculture and Food Inspection Authority (CAFIA): Brno, Czech Republic, 2024. Available online: https://www.szpi.gov.cz/en/article/2024-warning-for-consumers-salmonella-in-chilled-chicken-meat-from-abroad.aspx?utm (accessed on 15 March 2025).
| Susceptible | MIC (mg/L) | Cut-Off Susceptible | Cut-Off Resistant | Resistant | MIC (mg/L) | Cut-Off | Cut-Off Resistant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piperacilin-tazobactam | 2 | ≤8 | ≥32 | Ampicilin | >32 | ≤8 | >32 |
| Cefotaxime | 0.25 | ≤1 | ≥4 | Ampicilin-sulbactam | >16 | ≤8 | ≥32 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.5 | ≤4 | ≥16 | Cefuroxime | >32 | ≤8 | ≥32 |
| Cefepime | 0.25 | ≤2 | ≥16 | Gentamycin | >32 | ≤4 | ≥16 |
| Ertapenem | 0.03 | ≤4 | ≥16 | Tetracyclin | >32 | ≤4 | ≥16 |
| Meropenem | 0.12 | ≤4 | ≥16 | Ciprofloxacin | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≥2 |
| Trimetoprim-sulphametoxasole | 1 | ≤2 | ≥4 | ||||
| Colimycine | 0.05 | ≤2 | ≥4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doležalová, K.; Soják, L.; Grigláková, A.; Jurenka, J.; Sedlák, M.; Horniaková, L.; Kromka, P.; Szántová, M.; Sabaka, P. Cardiac Device-Related Infective Endocarditis Caused by Salmonella Infantis—Case Report and Review of Clinical and Epidemiologic Implications. Pathogens 2025, 14, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050474
Doležalová K, Soják L, Grigláková A, Jurenka J, Sedlák M, Horniaková L, Kromka P, Szántová M, Sabaka P. Cardiac Device-Related Infective Endocarditis Caused by Salmonella Infantis—Case Report and Review of Clinical and Epidemiologic Implications. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoležalová, Kristína, Lubomír Soják, Annamária Grigláková, Ján Jurenka, Martin Sedlák, Lucia Horniaková, Peter Kromka, Mária Szántová, and Peter Sabaka. 2025. "Cardiac Device-Related Infective Endocarditis Caused by Salmonella Infantis—Case Report and Review of Clinical and Epidemiologic Implications" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050474
APA StyleDoležalová, K., Soják, L., Grigláková, A., Jurenka, J., Sedlák, M., Horniaková, L., Kromka, P., Szántová, M., & Sabaka, P. (2025). Cardiac Device-Related Infective Endocarditis Caused by Salmonella Infantis—Case Report and Review of Clinical and Epidemiologic Implications. Pathogens, 14(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050474






