Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection Inhibits Host Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the PERK Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells Culture and Plasmids
2.2. Bacterial Infection
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.5. Calcium Imaging
2.6. Apoptosis Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
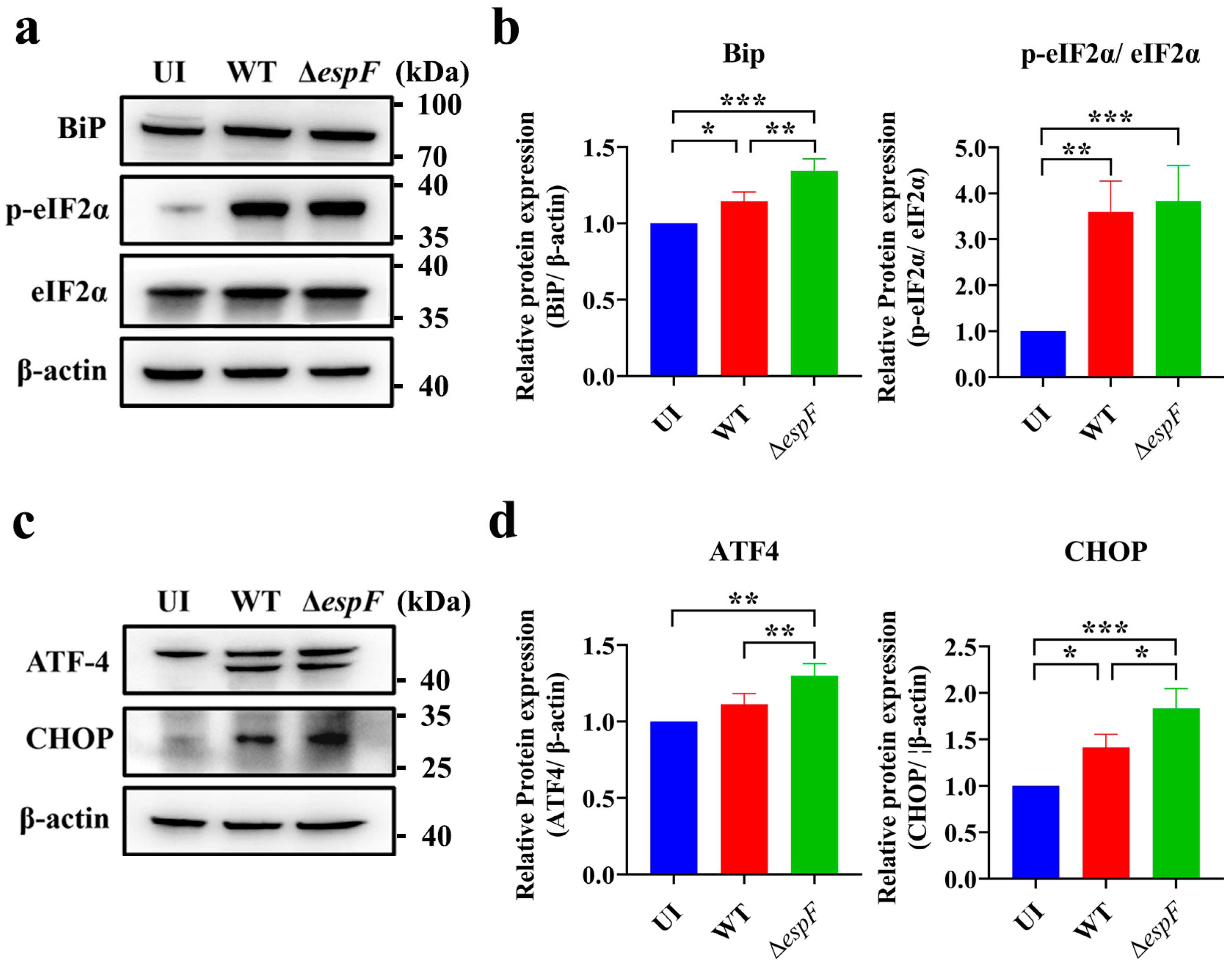
3.1. espF-Deletion O157:H7 Strain Infection Enhances ER Stress in Caco-2 Cells
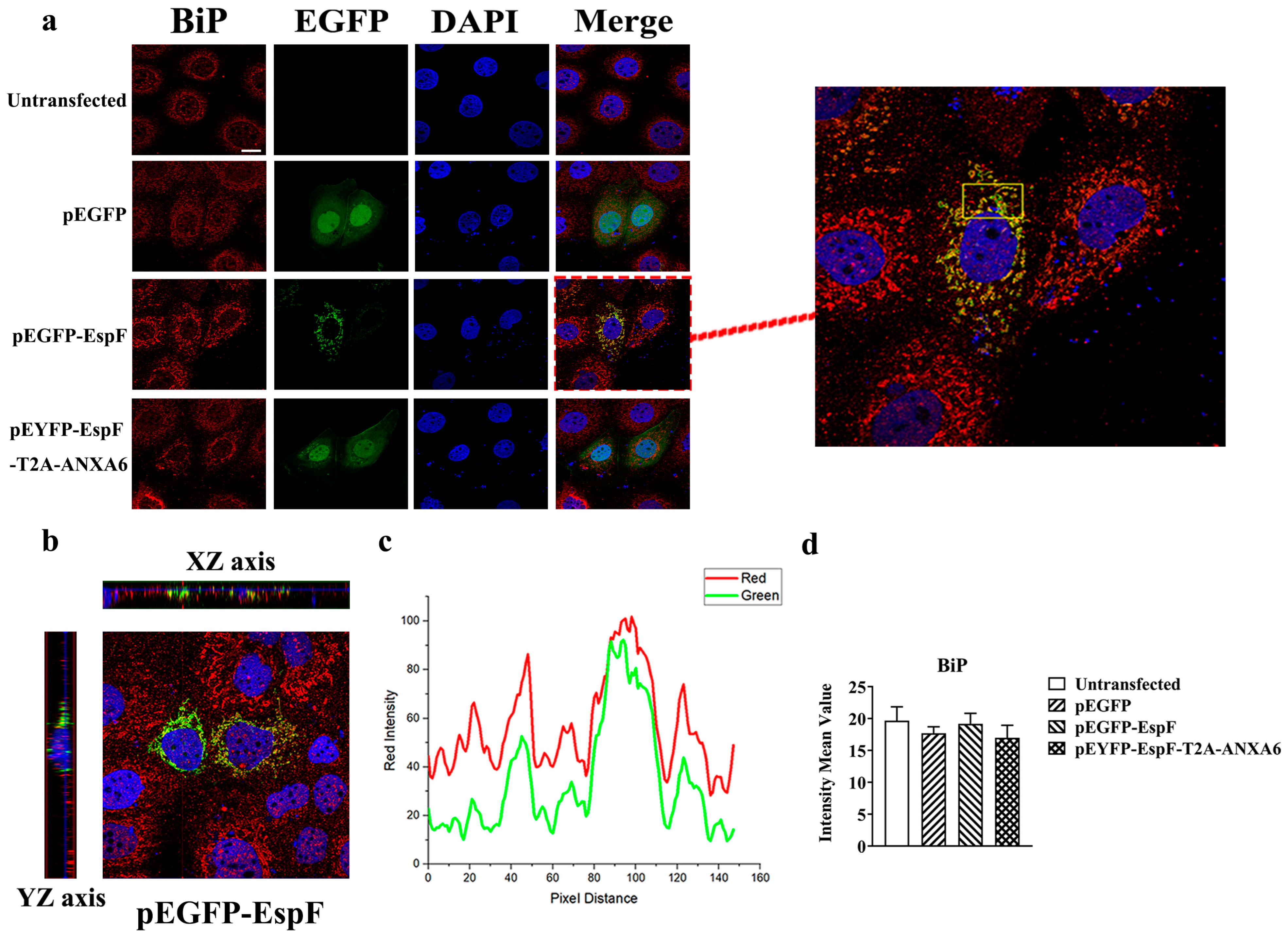
3.2. EspF Protein Co-Localizes with BiP in Caco-2 Cells
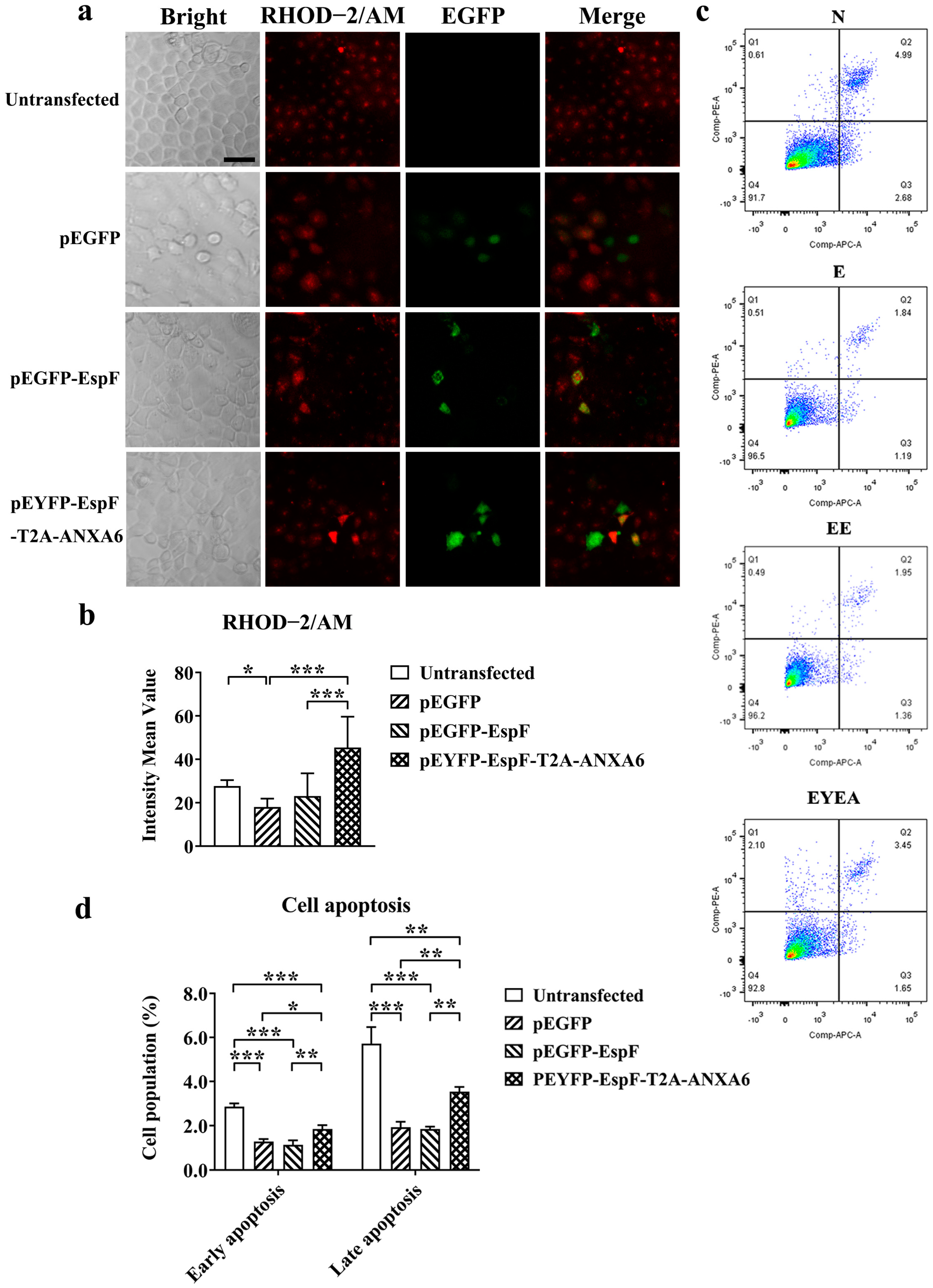
3.3. EspF–ANXA6 Interaction Inhibits ER Stress Through the PERK Pathway
3.4. EspF–ANXA6 Interaction Stimulates Calcium Release and Promotes Cell Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EHEC | Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| ANXA6 | Annexin A6 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| PERK | PKR-like ER kinase |
| Ca2+ | Calcium |
| A/E | Attachment and effacement |
| Stxs | Shiga toxins |
| ESPs | E. coli-secreted proteins |
| LEE | Locus of Enterocyte Effacement |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
| ΔespF | espF-deletion strain |
References
- Riley, L.W.; Remis, R.S.; Helgerson, S.D.; McGee, H.B.; Wells, J.G.; Davis, B.R.; Hebert, R.J.; Olcott, E.S.; Johnson, L.M.; Hargrett, N.T.; et al. Hemorrhagic Colitis Associated with a Rare Escherichia coli Serotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States--Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M. Pathogenic Functions and Diagnostic Utility of Cytokines/Chemokines in EHEC-HUS. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, K.; Wier, E.M.; Lei, Y.; Hodgson, A.; Xu, D.; Xia, X.; Zheng, D.; Ding, H.; Sears, C.L.; et al. Bacterial Genotoxin Accelerates Transient Infection–Driven Murine Colon Tumorigenesis. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Zaidi, S.; Alouffi, A.S.; Hassan, I.; Imran, A.; Khan, R.A. Computational Proteome-Wide Study for the Prediction of Escherichia coli Protein Targeting in Host Cell Organelles and Their Implication in Development of Colon Cancer. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7254–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Villamil, J.I.; Tapia, D.; Torres, A.G. Optimization of Multivalent Gold Nanoparticle Vaccines Eliciting Humoral and Cellular Immunity in an In Vivo Model of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Colonization. mSphere 2022, 7, e0093421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, H.; Kang, C.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, X.; Yang, B. Genomic Island-Encoded Regulatory Proteins in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Virulence 2024, 15, 2313407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Wan, C. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Effector Protein EspF Interacts With Host Protein ANXA6 and Triggers Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK)-Dependent Tight Junction Dysregulation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 613061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, J.J.; Mallick, E.M.; Scanlon, K.M.; Turner, J.R.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Leong, J.M.; Snapper, S.B. Attaching-and-Effacing Pathogens Exploit Junction Regulatory Activities of N-WASP and SNX9 to Disrupt the Intestinal Barrier. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhu, M.-J. Suppressing Autophagy: A Strategy by Escherichia coli O157:H7 for Its Survival on Host Epithelial Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Yan, K.; Wan, C. Clever Cooperation: Interactions Between EspF and Host Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liu, Y.; Hodgson, A.; Xu, D.; Guo, W.; Yu, H.; She, W.; Zhou, C.; Lan, L.; Fu, K.; et al. EspF Is Crucial for Citrobacter Rodentium-Induced Tight Junction Disruption and Lethality in Immunocompromised Animals. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Herrmann, B.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A.C.; Engevik, K.A.; Ihekweazu, F.; Shi, Z.; Luck, B.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Esparza, M.; et al. Bifidobacterium dentium -Derived y-Glutamylcysteine Suppresses ER-Mediated Goblet Cell Stress and Reduces TNBS-Driven Colonic Inflammation. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1902717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; You, K.; Pichaud, M.; Haiser, H.J.; Graham, D.B.; Vlamakis, H.; Porter, J.A.; Xavier, R.J. Gut Bacterial Metabolites Modulate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senft, D.; Ronai, Z.A. UPR, Autophagy, and Mitochondria Crosstalk Underlies the ER Stress Response. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Hosokawa, N.; Kaufman, R.J.; Nagata, K.; Mori, K. A Time-Dependent Phase Shift in the Mammalian Unfolded Protein Response. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, R.J. Orchestrating the Unfolded Protein Response in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-A.; Song, C.-H. Insights Into the Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-S.; Chen, Y.; Fan, L.; Xi, Q.-L.; Wu, G.-H.; Li, X.-X.; Yuan, T.-L.; He, S.-Q.; Yu, Y.; Shao, M.-L.; et al. The Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Is Essential for Protecting against Colitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15327–15336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, S.; De Vos, M.; Olievier, K.; Peeters, H.; Elewaut, D.; Lambrecht, B.; Pouliot, P.; Laukens, D. Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Different Implication for Colonic and Ileal Disease? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretin, A.; Carrière, J.; Dalmasso, G.; Bergougnoux, A.; B’chir, W.; Maurin, A.-C.; Müller, S.; Seibold, F.; Barnich, N.; Bruhat, A.; et al. Activation of the EIF2AK4-EIF2A/eIF2α-ATF4 Pathway Triggers Autophagy Response to Crohn Disease-Associated Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli Infection. Autophagy 2016, 12, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, K.M.; Casanova, V.; Kemp, S.; Staines, K.A.; Satsangi, J.; Barlow, P.G.; Henderson, P.; Stevens, C. The Inflammatory Bowel Disease Drug Azathioprine Induces Autophagy via mTORC1 and the Unfolded Protein Response Sensor PERK. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Ju, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ma, W.; Wan, C. Screening for Host Proteins Interacting with Escherichia coli O157:H7 EspF Using Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Cherla, R.P.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga Toxin 1 Induces Apoptosis through the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response in Human Monocytic Cells. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, M.H.; Hartland, E.L.; McCaffrey, K. Effectors Targeting the Unfolded Protein Response during Intracellular Bacterial Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Muñoz, M.; Hamilton, S.L.; Kaetzel, M.A.; Hazarika, P.; Dedman, J.R. Modulation of Ca2+ Release Channel Activity from Sarcoplasmic Reticulum by Annexin VI (67-kDa Calcimedin). J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15894–15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-M.; Luo, L.-M.; Lin, P.; Pu, Q.; Wang, B.; Qin, S.; Wu, Q.; Yu, X.-J.; Wu, M. Annexin A2 Regulates Unfolded Protein Response via IRE1-XBP1 Axis in Macrophages during P. Aeruginosa Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, K.; Fu, M.; Liang, S.; Zhao, H.; Fu, C.; Yang, L.; Song, Z.; Sun, D.; Wan, C. EspF of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Enhances Apoptosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells: An Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation-Based Comparative Proteomic Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 900919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, M.C.; Larburu, N.; Durairaj, V.; Adams, C.J.; Ali, M.M.U. UPR Proteins IRE1 and PERK Switch BiP from Chaperone to ER Stress Sensor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.; Elmaghrabi, Y.A.; Köse, M.; Beevi, S.S.; Jose, J.; Meneses-Salas, E.; Blanco-Muñoz, P.; Conway, J.R.W.; Swarbrick, A.; Timpson, P.; et al. Annexin A6 Improves Anti-Migratory and Anti-Invasive Properties of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR Overexpressing Human Squamous Epithelial Cells. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2961–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patergnani, S.; Danese, A.; Bouhamida, E.; Aguiari, G.; Previati, M.; Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C. Various Aspects of Calcium Signaling in the Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Proliferation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preissler, S.; Rato, C.; Yan, Y.; Perera, L.A.; Czako, A.; Ron, D. Calcium Depletion Challenges Endoplasmic Reticulum Proteostasis by Destabilising BiP-Substrate Complexes. Elife 2020, 9, e62601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, T.; Hoque, M.; Conway, J.R.W.; Reverter, M.; Wahba, M.; Beevi, S.S.; Timpson, P.; Enrich, C.; Rentero, C. Annexin A6—A Multifunctional Scaffold in Cell Motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2017, 11, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.-H.; Jung, S.-M.; Shin, E.; Chung, G.T.; Seong, W.-K.; Cho, S.-H. Comparison of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157 and EHEC Non-O157 Isolates from Patients with Diarrhea in Korea. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 70, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, P.; Jeon, B.C.; Song, M.Y.; Kwak, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Inhibition of O-GlcNAcylation Protects from Shiga Toxin-mediated Cell Injury and Lethality in Host. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood, C. Therapeutic Uses of Bacterial Subunit Toxins. Toxins 2021, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Fang, Y.; Wang, K.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, P.; Gu, J.; et al. Shiga Toxins Induce Autophagic Cell Death in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway. Autophagy 2015, 11, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, L.A.; Kuss-Duerkop, S.K.; Keestra-Gounder, A.M. IRE1α-Driven Inflammation Promotes Clearance of Citrobacter Rodentium Infection. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0048121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsuki, H.; Ogura, K.; Moss, J.; Yahiro, K. Host Response to the Subtilase Cytotoxin Produced by Locus of Enterocyte Effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Keita, Å.V.; Saxena, A.; Reyes, J.L.; Mancini, N.L.; Al Rajabi, A.; Wang, A.; Baggio, C.H.; Dicay, M.; Van Dalen, R.; et al. ER-Stress Mobilization of Death-Associated Protein Kinase-1–Dependent Xenophagy Counteracts Mitochondria Stress–Induced Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3073–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elfiky, A.A. GRP78: A Cell’s Response to Stress. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Zhou, D.; Bai, F.; Li, J.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, G.; Jin, Y.; Wang, A. VceC Mediated IRE1 Pathway and Inhibited CHOP-Induced Apoptosis to Support Brucella Replication in Goat Trophoblast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.; Tsolis, R.M. Bacteria, the Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Unfolded Protein Response: Friends or Foes? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mommersteeg, M.C.; Simovic, I.; Yu, B.; van Nieuwenburg, S.A.V.; Bruno, I.M.J.; Doukas, M.; Kuipers, E.J.; Spaander, M.C.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; et al. Autophagy Mediates ER Stress and Inflammation in Helicobacter Pylori-Related Gastric Cancer. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2015238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinaud, L.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Phalipon, A. Host Cell Targeting by Enteropathogenic Bacteria T3SS Effectors. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlitz, A.; Karunakaran, K.; Herweg, J.-A.; Krohne, G.; Van De Linde, S.; Rieck, E.; Sauer, M.; Rudel, T. The Chlamydial Organism Simkania negevensis Forms ER Vacuole Contact Sites and Inhibits ER-Stress: Simkania Vacuole Formation and ER-Stress Inhibition. Cell Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1224–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, M.; Zihler Berner, A.; Chervet, N.; Chassard, C.; Lacroix, C. Comparison of the Caco-2, HT-29 and the Mucus-Secreting HT29-MTX Intestinal Cell Models to Investigate Salmonella Adhesion and Invasion. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 94, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefaniková, A.; Klačanová, K.; Pilchová, I.; Hatok, J.; Račay, P. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 Inhibitor SU9516 Increases Sensitivity of Colorectal Carcinoma Cells Caco-2 but Not HT29 to BH3 Mimetic ABT-737. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2017, 36, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Fachi, J.L.; Ma, K.; Ulezko Antonova, A.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Z.; Kaufman, R.J.; Ciorba, M.A.; Deepak, P.; Colonna, M. The IRE1α/XBP1 Pathway Sustains Cytokine Responses of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e174198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, S.T.; Fazio, A.; Lipinski, S.; Jahn, M.T.; Aden, K.; Ito, G.; Wottawa, F.; Kuiper, J.W.P.; Coleman, O.I.; Tran, F.; et al. Activating Transcription Factor 6 Mediates Inflammatory Signals in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Upon Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1357–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Sterea, A.M.; El Hiani, Y. Lessons from the Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Transporters—A Cancer Connection. Cells 2020, 9, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; McGrath, B.; Cavener, D.R. PERK (EIF2AK3) Regulates Proinsulin Trafficking and Quality Control in the Secretory Pathway. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Yue, L.; You, F.; Tao, C. Panax notoginseng Saponins Alleviate Osteoporosis and Joint Destruction in Rabbits with Antigen-induced Arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Tian, M.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. The C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Transcription Factor Functions in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Microbial Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, N.; Gorman, A.M.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A. The eIF2α Kinases: Their Structures and Functions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3493–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Hua, Y.; Wan, C. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection Inhibits Host Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the PERK Pathway. Pathogens 2025, 14, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050440
Xu L, Liang S, Wang Y, Gao M, Zhang B, Zhao W, Hua Y, Wan C. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection Inhibits Host Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the PERK Pathway. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050440
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Litai, Song Liang, Yaoguo Wang, Min Gao, Bao Zhang, Wei Zhao, Ying Hua, and Chengsong Wan. 2025. "Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection Inhibits Host Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the PERK Pathway" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050440
APA StyleXu, L., Liang, S., Wang, Y., Gao, M., Zhang, B., Zhao, W., Hua, Y., & Wan, C. (2025). Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection Inhibits Host Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the PERK Pathway. Pathogens, 14(5), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050440





