The Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Retrospective Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Comparison of Seasonal Peaks
2.2. Microbiology Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Positive Rates
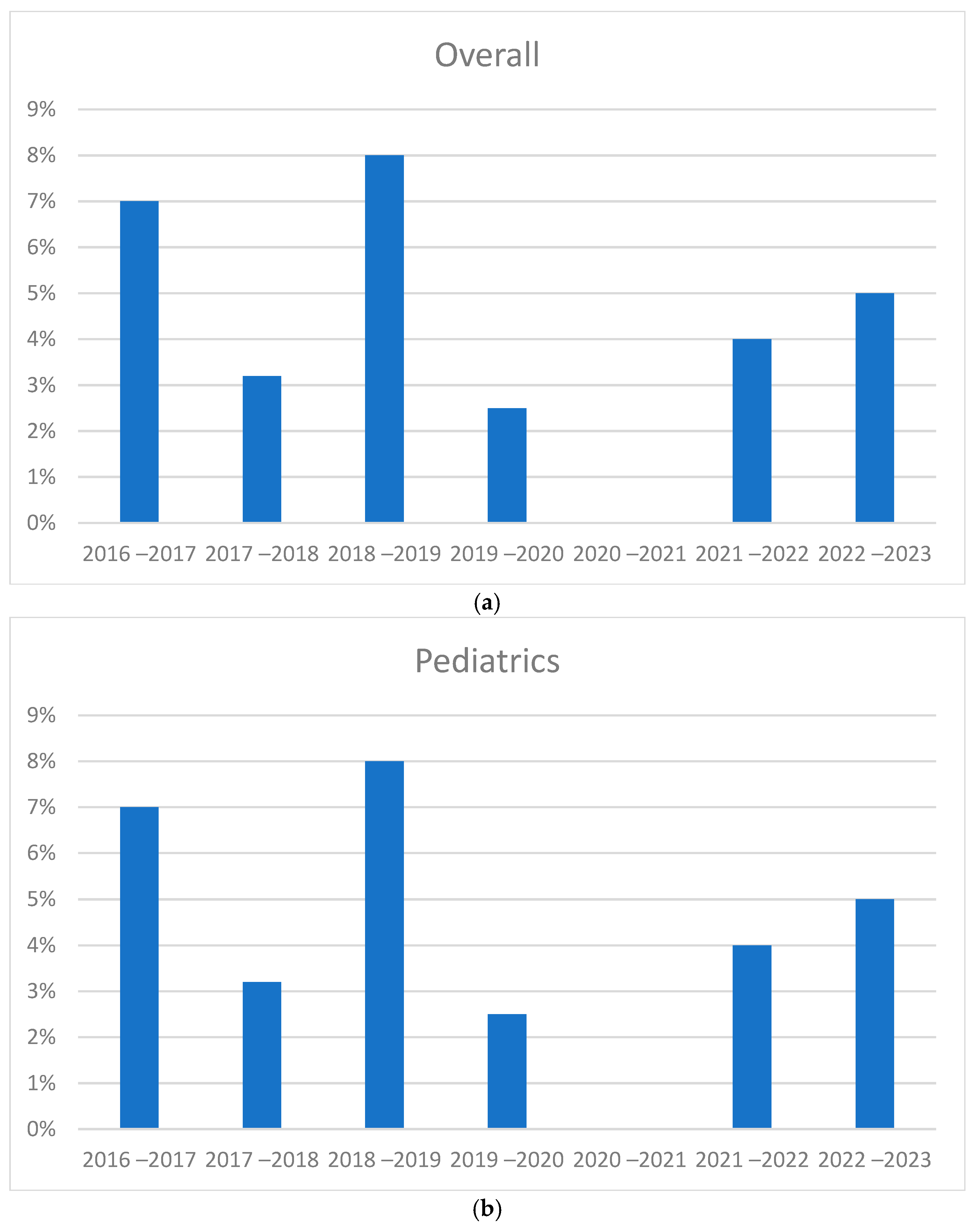
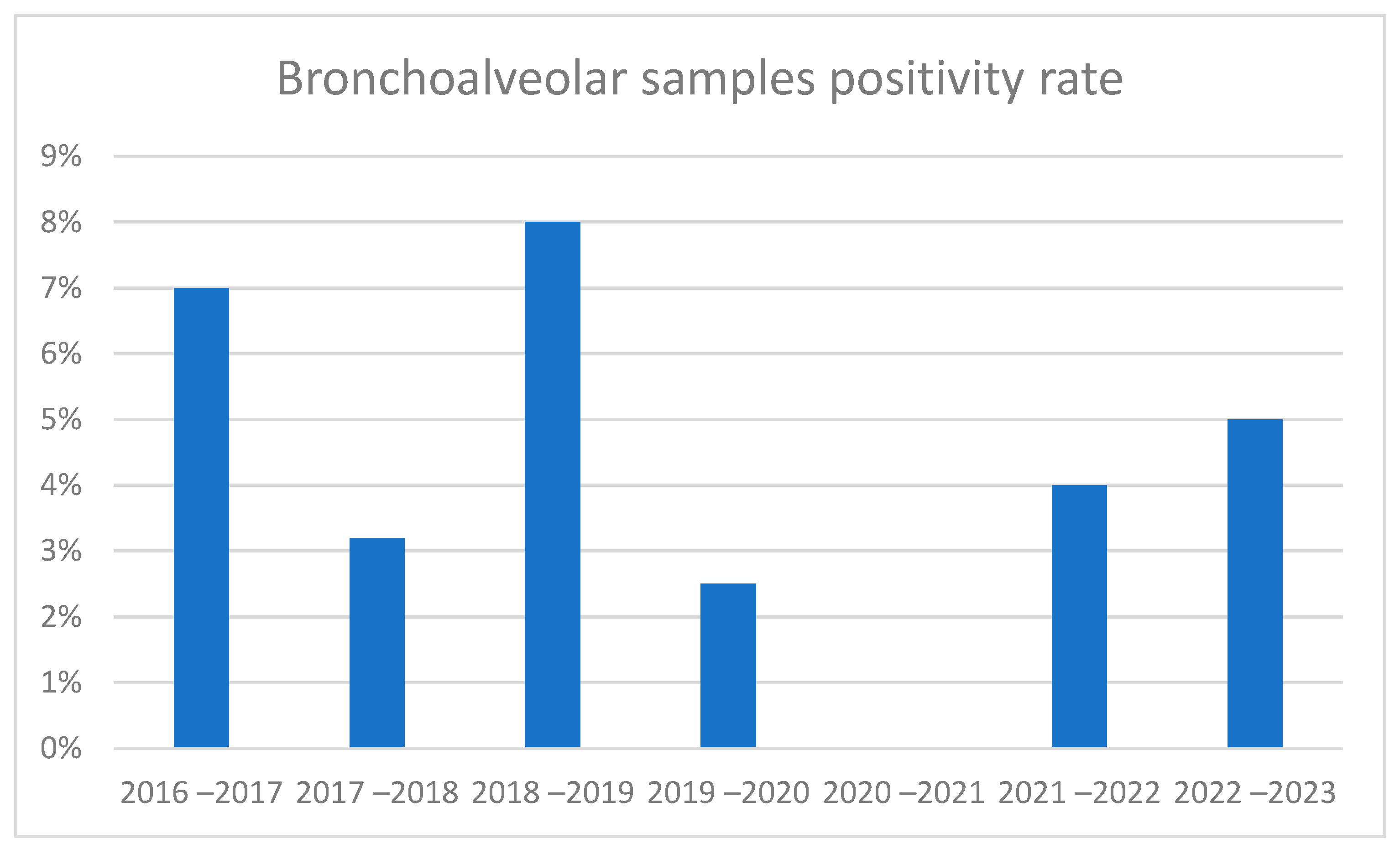
3.2. Trend in Cases During 2016–2023
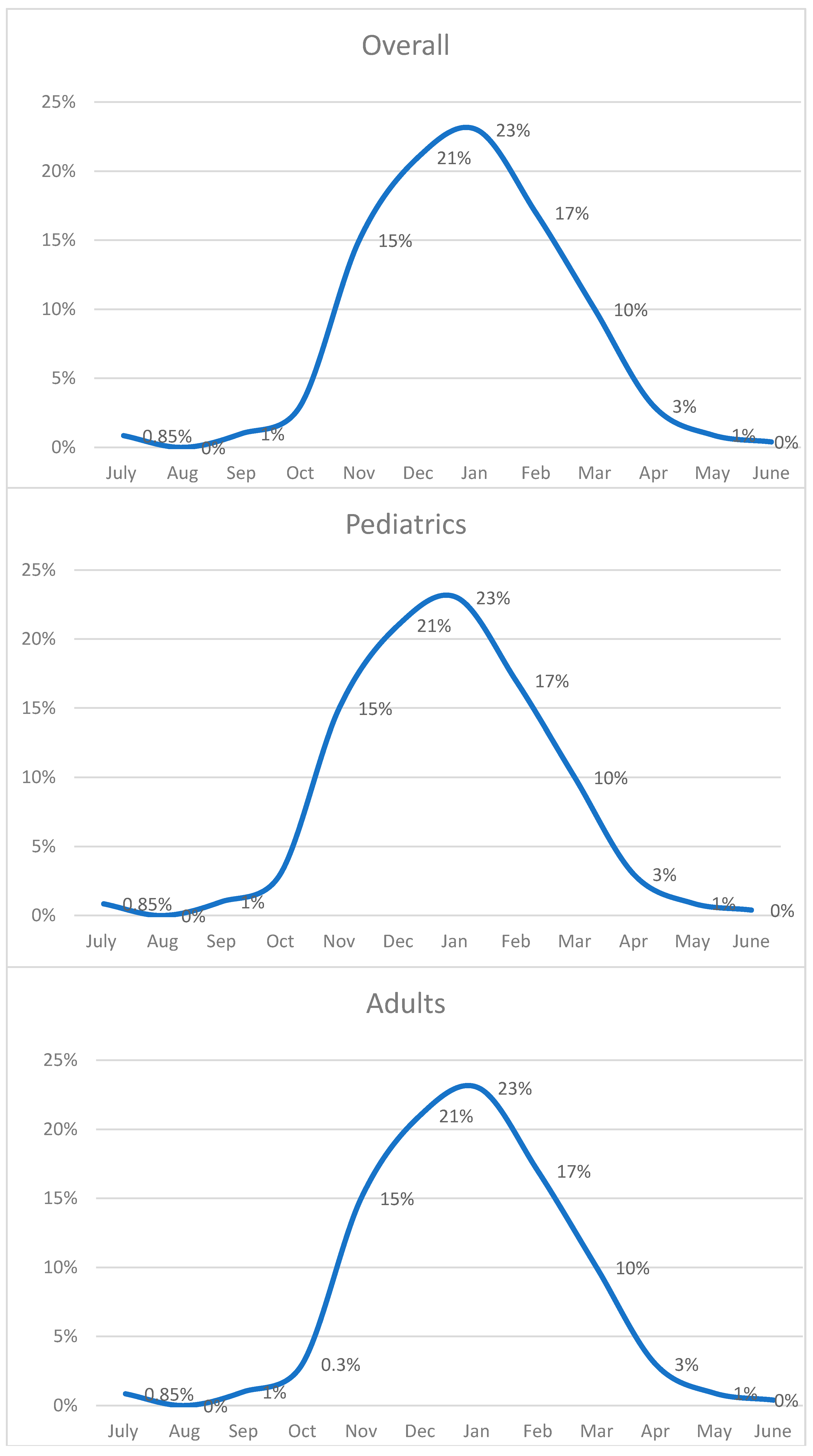
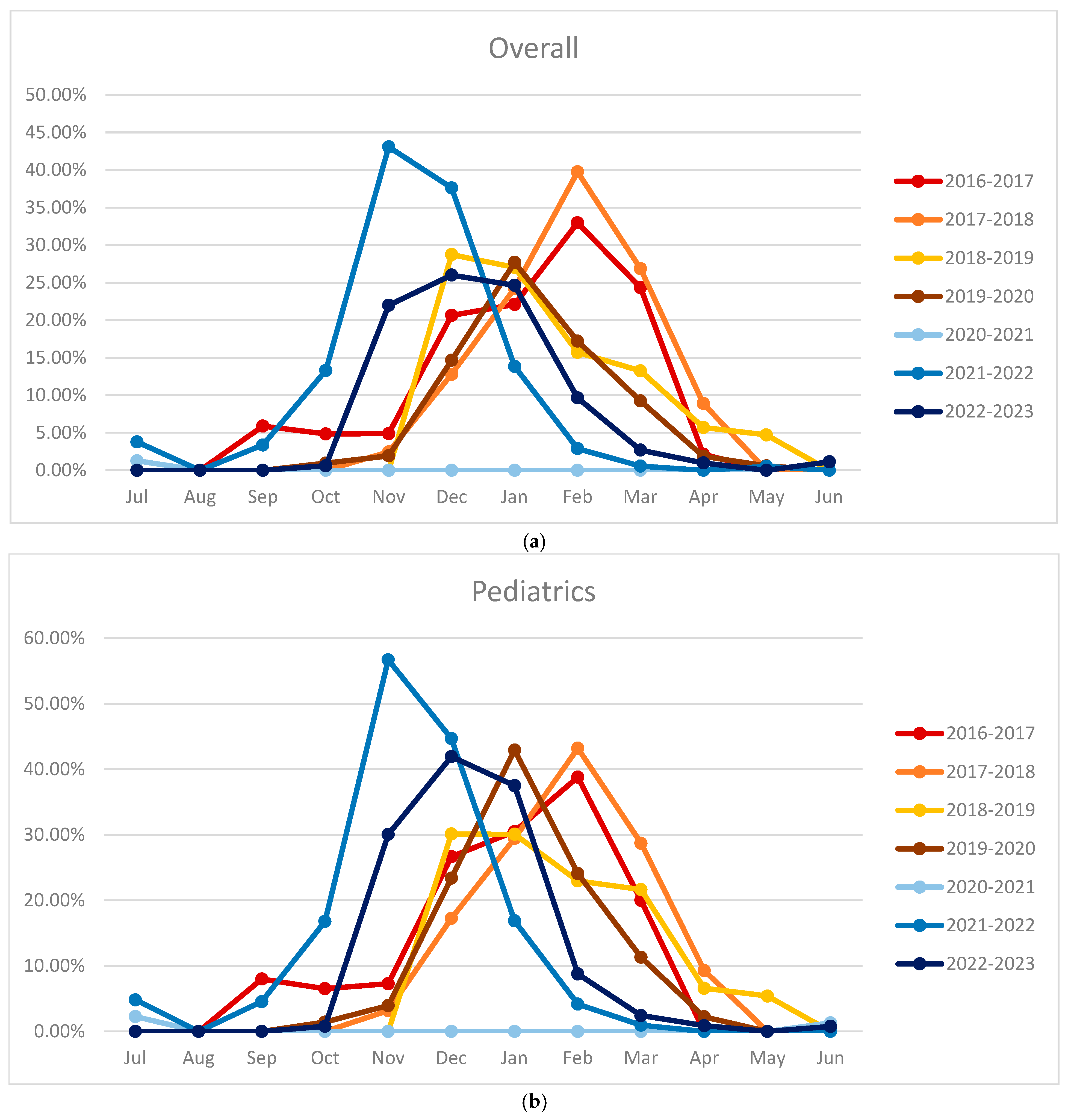
3.3. Monthly Positive Rates and Seasonal Trends
3.4. Comparison of Seasonal Peaks Results
4. Discussion
Effect of Infection Control Measures Applied During SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on RSV
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; A Madhi, S.; Omer, S.B.; Simões, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Disease Burden Estimates of Acute Lower Respiratory Infections Due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Children Younger than 5 Years in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Htar, M.T.T.; Yerramalla, M.S.; Moïsi, J.C.; Swerdlow, D.L. The Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, J.; Hussain, A.; Patel, K.; Hernandez, T.; Ray, S. Respiratory Syncytial Virus: A Comprehensive Review of Transmission, Pathophysiology, and Manifestation. Cureus 2023, 15, e36342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, N.; Omony, J.; Rinderknecht, S.; Kolberg, L.; Meyer-Bühn, M.; von Mutius, E.; Hübner, J.; von Both, U. Old foes following news ways?—Pandemic-related changes in the epidemiology of viral respiratory tract infections. Infection 2023, 52, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Guzman, E.; Simons, L.M.; Dean, T.J.; Agnes, F.; Pawlowski, A.; Alisoltanidehkordi, A.; Nam, H.H.; Ison, M.G.; Ozer, E.A.; Lorenzo-Redondo, R.; et al. Deviations in RSV Epidemiological Patterns and Population Structures in the United States Following the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shbaklo, N.; Lupia, T.; De Rosa, F.G.; Corcione, S. Infection Control in the Era of COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lupia, T.; Corcione, S.; Shbaklo, N.; Boglione, L.; Torresan, S.; Pinna, S.M.; Rizzello, B.; Bosio, R.; Fornari, V.; Brusa, M.T.; et al. Real-Life Experience of Molnupiravir in Hospitalized Patients Who Developed SARS-CoV-2-Infection: Preliminary Results from CORACLE Registry. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boglione, L.; Corcione, S.; Shbaklo, N.; Lupia, T.; Scabini, S.; Pinna, S.M.; Borrè, S.; De Rosa, F.G. Predictors of mortality in patients with COVID-19 infection in different health-care settings: A retrospective analysis from a CORACLE study group. Infect. Dis. Health 2022, 28, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Olsen, S.J.; Winn, A.K.; Budd, A.P.; Prill, M.M.; Steel, J.; Midgley, C.M.; Kniss, K.; Burns, E.; Rowe, T.; Foust, A.; et al. Changes in influenza and other respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic-United States, 2020–2021. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 21, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Terliesner, N.; Unterwalder, N.; Edelmann, A.; Corman, V.; Knaust, A.; Rosenfeld, L.; Gratopp, A.; Ringe, H.; Martin, L.; von Bernuth, H.; et al. Viral infections in hospitalized children in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic: Association with non-pharmaceutical interventions. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 935483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, U.; Lehfeld, A.-S.; Tolksdorf, K.; Cai, W.; Reiche, J.; Biere, B.; Dürrwald, R.; Buda, S. Respiratory infections in children and adolescents in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Health Monit. 2023, 8, 20–38. [Google Scholar]
- Billard, M.; van de Ven, P.M.; Baraldi, B.; Kragten-Tabatabaie, L.; Bont, L.J.; Wildenbeest, J.G. International changes in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) epidemiology during the COVID-19 pandemic: Association with school closures. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Mattia, G.; Nenna, R.; Mancino, E.; Rizzo, V.; Pierangeli, A.; Villani, A.; Midulla, F. During the COVID-19 pandemic where has respiratory syncytial virus gone? Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3106–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Summeren, J.; Meijer, A.; Aspelund, G.; Casalegno, J.S.; Erna, G.; Hoang, U.; Paget, J. Low levels of respiratory syncytial virus activity in Europe during the 2020/21 season: What can we expect in the coming summer and autumn/winter? Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, J.-S.; Sikazwe, C.; Xie, R.; Deng, Y.-M.; Sullivan, S.G.; Michie, A.; Levy, A.; Cutmore, E.; Blyth, C.C.; Britton, P.N.; et al. Off-Season RSV Epidemics in Australia after Easing of COVID-19 Restrictions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Armistead, I.; Messacar, K.; Alden, N.B.; Schmoll, E.; Austin, E.; Dominguez, S.R. Shifting Epidemiology and Severity of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Pediatr. 2023, 177, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bourdeau, M.; Vadlamudi, N.K.; Bastien, N.; Embree, J.; Halperin, S.A.; Jadavji, T.; Langley, J.M.; Lebel, M.H.; Le Saux, N.; Moore, D.; et al. Canadian Immunization Monitoring Program Active (IMPACT) Investigators. Pediatric RSV-Associated Hospitalizations Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2336863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McNab, S.; Do, L.A.H.; Clifford, V.; Crawford, N.W.; Daley, A.; Mulholland, K.; Cheng, D.; South, M.; Waller, G.; Barr, I.; et al. Changing Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Australia—Delayed Re—Emergence in Victoria Compared to Western Australia/New South Wales (WA/NSW) After Prolonged Lock-Down for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 2365–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodjat, P.; Christensen, P.A.; Subedi, S.; Bernard, D.W.; Olsen, R.J.; Long, S.W. The reemergence of seasonal respiratory viruses in Houston, Texas, after relaxing COVID-19 restrictions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00430-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xu, M.; Lu, L.; Ma, A.; Cao, L.; Su, L.; Dong, N.; Jia, R.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J. The changing pattern of common respiratory and enteric viruses among outpatient children in Shanghai, China: Two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4696–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicherz, F.; Xu, R.Y.; Abu-Raya, B.; Majdoubi, A.; Michalski, C.; Golding, L.; Stojic, A.; Vineta, M.; Granoski, M.; Cieslak, Z.; et al. Waning Immunity Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Raya, B.; Paramo, M.V.; Reicherz, F.; Lavoie, P.M. Why Has the Epidemiology of RSV Changed during the COVID-19 Pandemic? eClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hartog, G.; van Kasteren, P.B.; Schepp, R.M.; Teirlinck, A.C.; van der Klis, F.R.; van Binnendijk, R.S. Decline of RSV-specific antibodies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Reeves, R.M.; Wang, X.; Bassat, Q.; Brooks, W.A.; Cohen, C.; Moore, D.P.; Nunes, M.; Rath, B.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global patterns in monthly activity of influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus, and metapneumovirus: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1031–e1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

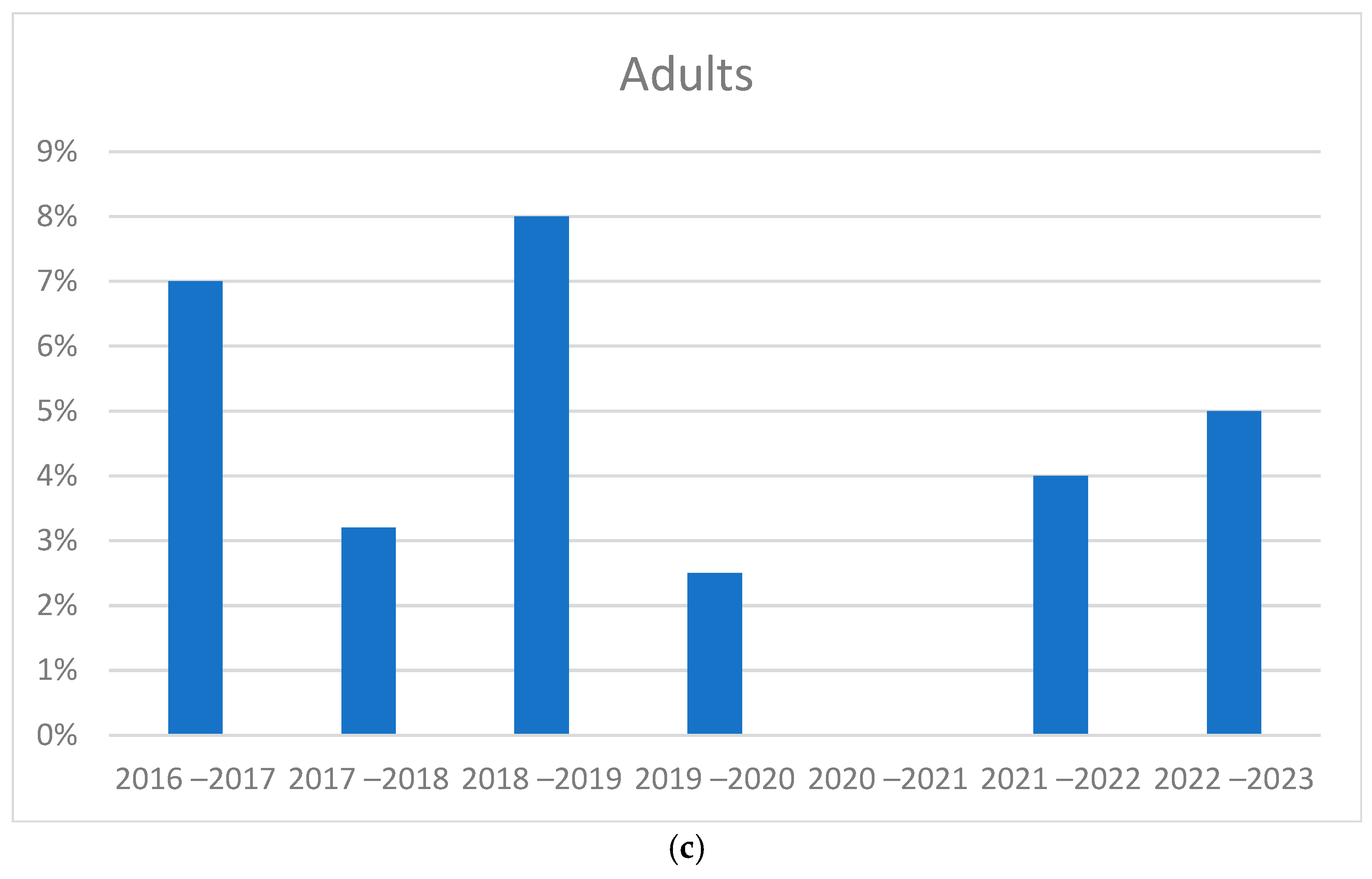

| Variable | Negative N = 12,477 (88.5%) | Positive N = 1608 (11.5) | Total N = 14,085 (100) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 5589 (44.7) | 737 (45.8) | 6326 (44) | 0.627 |
| Male | 7014 (56.2) | 879 (54.6) | 7893 (56) | 0.395 |
| Ward | ||||
| Adult | 4927 (39.4) | 270 (16.7) | 5197 (36) | <0.001 |
| Undefined | 216 (1.7) | 15 (0.93) | 231 (1.6) | 0.019 |
| Pediatric | 7460 (59.7) | 1331 (82.7) | 8791 (62.4) | <0.001 |
| Material type | ||||
| A. Bronchoalveolar sample | 1739 (13.9) | 74 (4.6) | 1813 (12.8) | <0.001 |
| Biopsy/excision | 3 (0.02) | 3 (0.02) | - | |
| Respiratory biopsy | 10 (0.08) | 10 (0.07) | - | |
| Broncho aspirate | 275 (2.2) | 30 (1.8) | 305 (2.16) | 0.389 |
| Bronchoalveolar lavage | 1450 (11.6) | 44 (2.7) | 1494 (10.6) | <0.001 |
| B. Swabs | 10,738 (86) | 1534 (95.3) | 12,272 (87) | 0.006 |
| Pharyngeal | 2341(18.7) | 267 (16.6) | 2608 (18.5) | 0.079 |
| Nasopharyngeal | 2027 (16.2) | 461 (28.6) | 2488 (17.6) | <0.001 |
| Nasal swab/aspirate | 6370 (51) | 806 (50) | 7176 (50.9) | 0.688 |
| Positive tests per specimen group | ||||
| Swab | 10,738 (87.5) | 1534 (12.5) | 12,272 (100) | 0.006 |
| Broncoalveolar | 1739 (96) | 74 (4) | 1813 (100) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Negative N = 4927 (94) | Positive N = 270 (5.1) | Total N = 5197 (100) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 2116 (43) | 115 (42) | 2231 (43) | 0.908 |
| Male | 2811 (57) | 155 (57) | 2966 (57) | |
| Material type | ||||
| A. Bronchoalveolar sample | 1349 (27) | 38 (14) | 1387 (26) | <0.001 |
| Biopsy/excision | 3 (0.06) | 3 (0.05) | ||
| Respiratory biopsy | 9 (0.18) | 9 (0.17) | ||
| Broncho aspirate | 59 (1.19) | 1 (0.3) | 60 (1.15) | 0.219 |
| Bronchoalveolar lavage | 1278 (26) | 37 (13.7) | 1315 (25) | <0.001 |
| B. Swabs | 3487 (70) | 230 (85) | 3717 (71) | 0.044 |
| Pharyngeal | 1180 (24) | 69 (25) | 1249 (24) | 0.639 |
| Nasopharyngeal | 411 (8.3) | 26 (9.6) | 437 (8.4) | <0.001 |
| Nasal swab/aspirate | 1896 (38.4) | 135 (50) | 2031 (39) | 0.015 |
| Positive tests per specimen group | ||||
| Swab | 3487 (93) | 230 (6.19) | 3717 (100) | |
| Broncoalveolar | 1349 (97) | 38 (2.74) | 1387 (100) | |
| Variable | Negative N = 7460 | Positive N = 1330 | Total N = 8791 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 3385 (45) | 618 (46) | 4003 (45) | 0.653 |
| Male | 4075 (54) | 713 (53) | 4788 (54) | 0.709 |
| Material type | ||||
| A. Bronchoalveolar sample | 317 (4.2) | 34 (2.5) | 351 (3.9) | 0.004 |
| Broncho aspirate | 206 (2.7) | 27 (2) | 206 (2.3) | <0.001 |
| Bronchoalveolar lavage | 110 (1.4) | 7 (0.5) | 110 (1.2) | 0.005 |
| B. Swabs | 7114 (95) | 1295 (97) | 7114 (80) | 0.623 |
| Pharyngeal | 1126 (15) | 197 (14) | 1126 (12) | 0.819 |
| Nasopharyngeal | 1555 (20) | 430 (32) | 1555 (17) | <0.001 |
| Nasal swab/aspirate | 4433 (59) | 668 (50) | 4433 (50) | <0.001 |
| Positive tests per specimen group | ||||
| Swab | 7114 (84.6) | 1295 (15.4) | 8409 (100) | |
| Broncoalveolar | 317 (90.3) | 34 (9.6) | 351 (100) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solidoro, P.; Curtoni, A.; Costa, C.; De Rosa, F.G.; Bondi, A.; Sidoti, F.; Shbaklo, N.; Patrucco, F.; Favre, D.; Zanotto, E.; et al. The Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Retrospective Evaluation. Pathogens 2025, 14, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040375
Solidoro P, Curtoni A, Costa C, De Rosa FG, Bondi A, Sidoti F, Shbaklo N, Patrucco F, Favre D, Zanotto E, et al. The Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Retrospective Evaluation. Pathogens. 2025; 14(4):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040375
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolidoro, Paolo, Antonio Curtoni, Cristina Costa, Francesco Giuseppe De Rosa, Alessandro Bondi, Francesca Sidoti, Nour Shbaklo, Filippo Patrucco, Davide Favre, Elisa Zanotto, and et al. 2025. "The Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Retrospective Evaluation" Pathogens 14, no. 4: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040375
APA StyleSolidoro, P., Curtoni, A., Costa, C., De Rosa, F. G., Bondi, A., Sidoti, F., Shbaklo, N., Patrucco, F., Favre, D., Zanotto, E., Corcione, S., & Rinaldo, R. F. (2025). The Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Retrospective Evaluation. Pathogens, 14(4), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040375







