Rhipicephalus microplus and Its Impact on Anaplasma marginale Multistrain Infections in Contrasting Epidemiological Contexts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
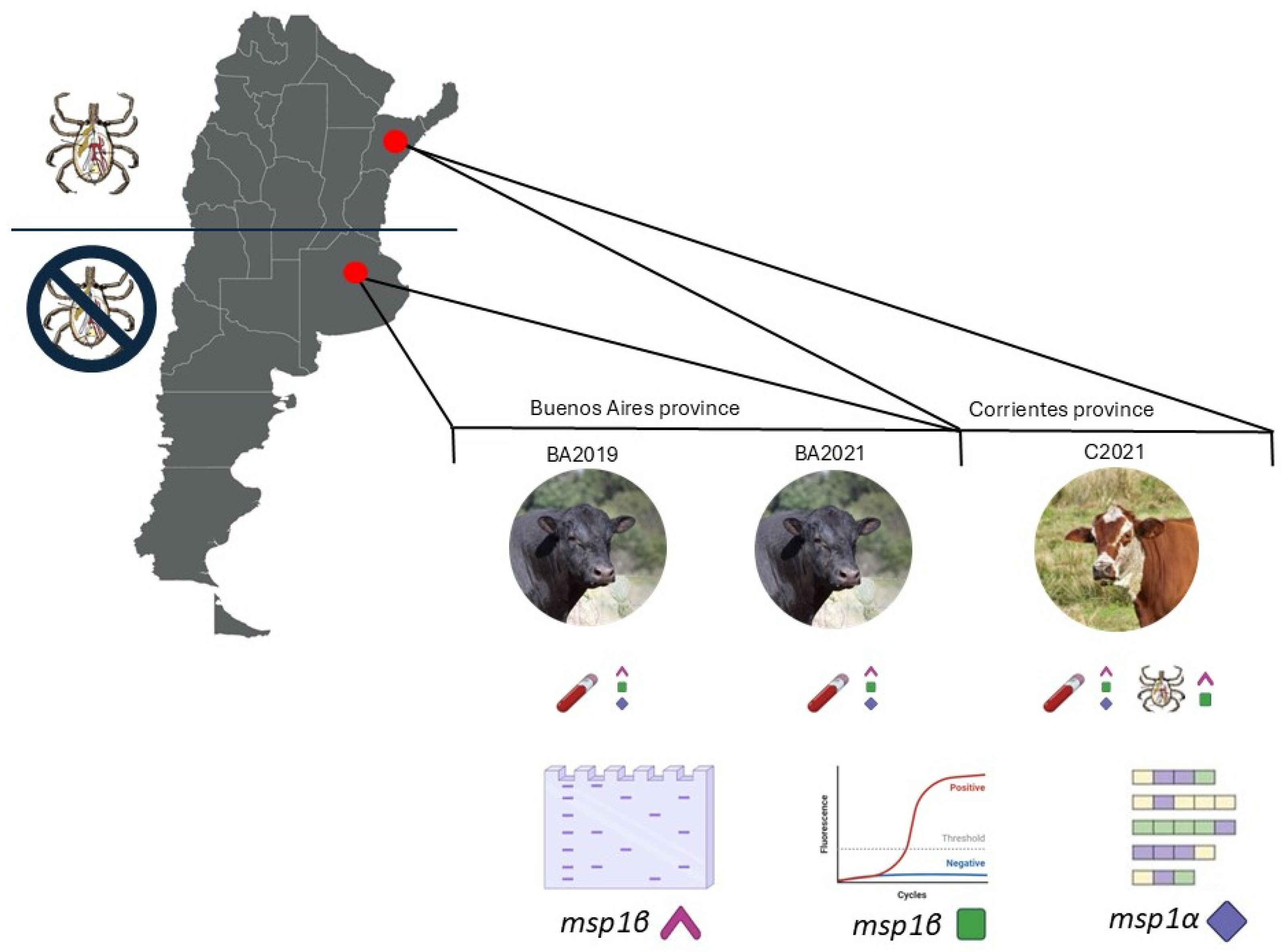
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Pathogen Detection
2.3. Molecular Quantification
2.4. Molecular Characterization
3. Results
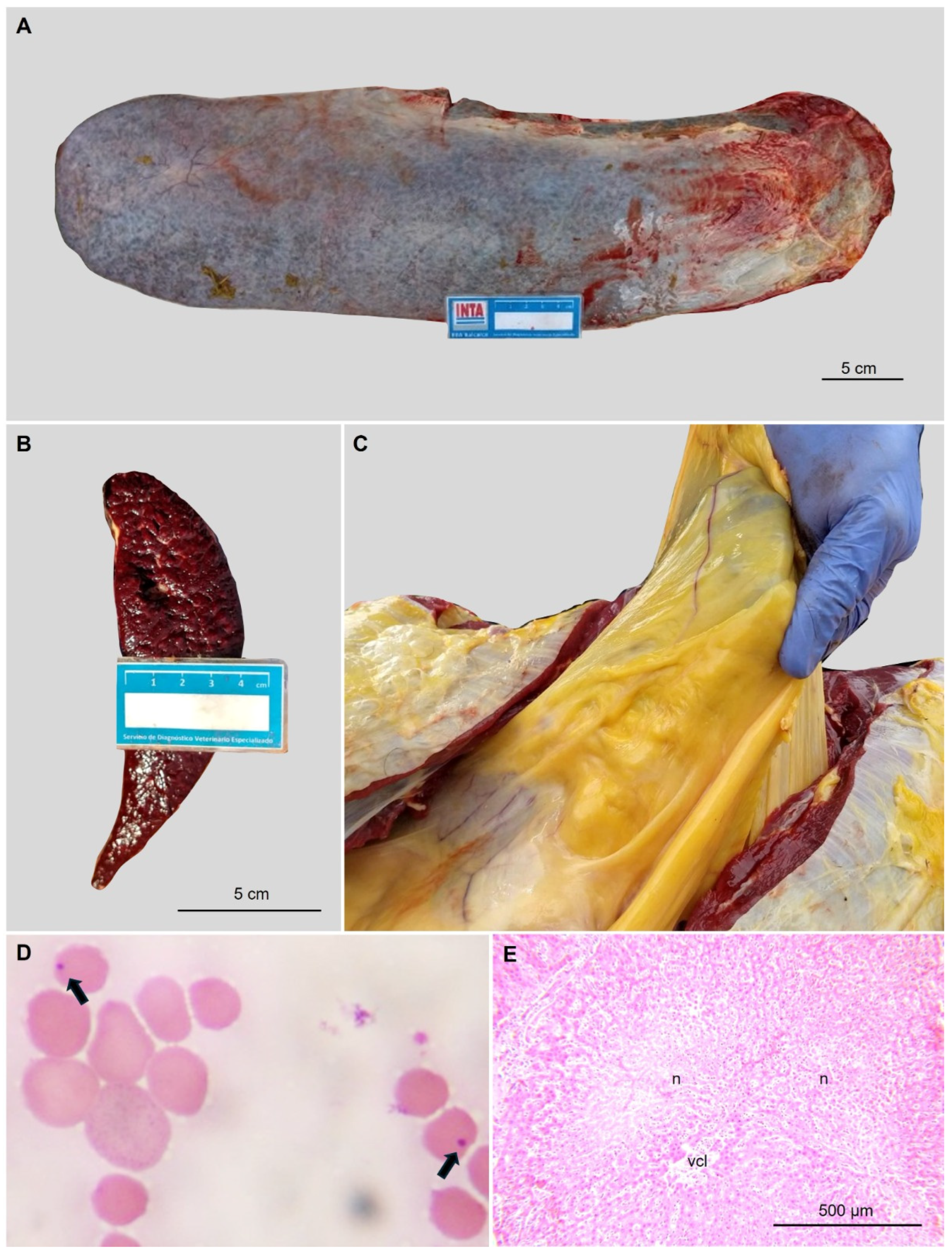
3.1. Pathogen Detection and Molecular Quantification
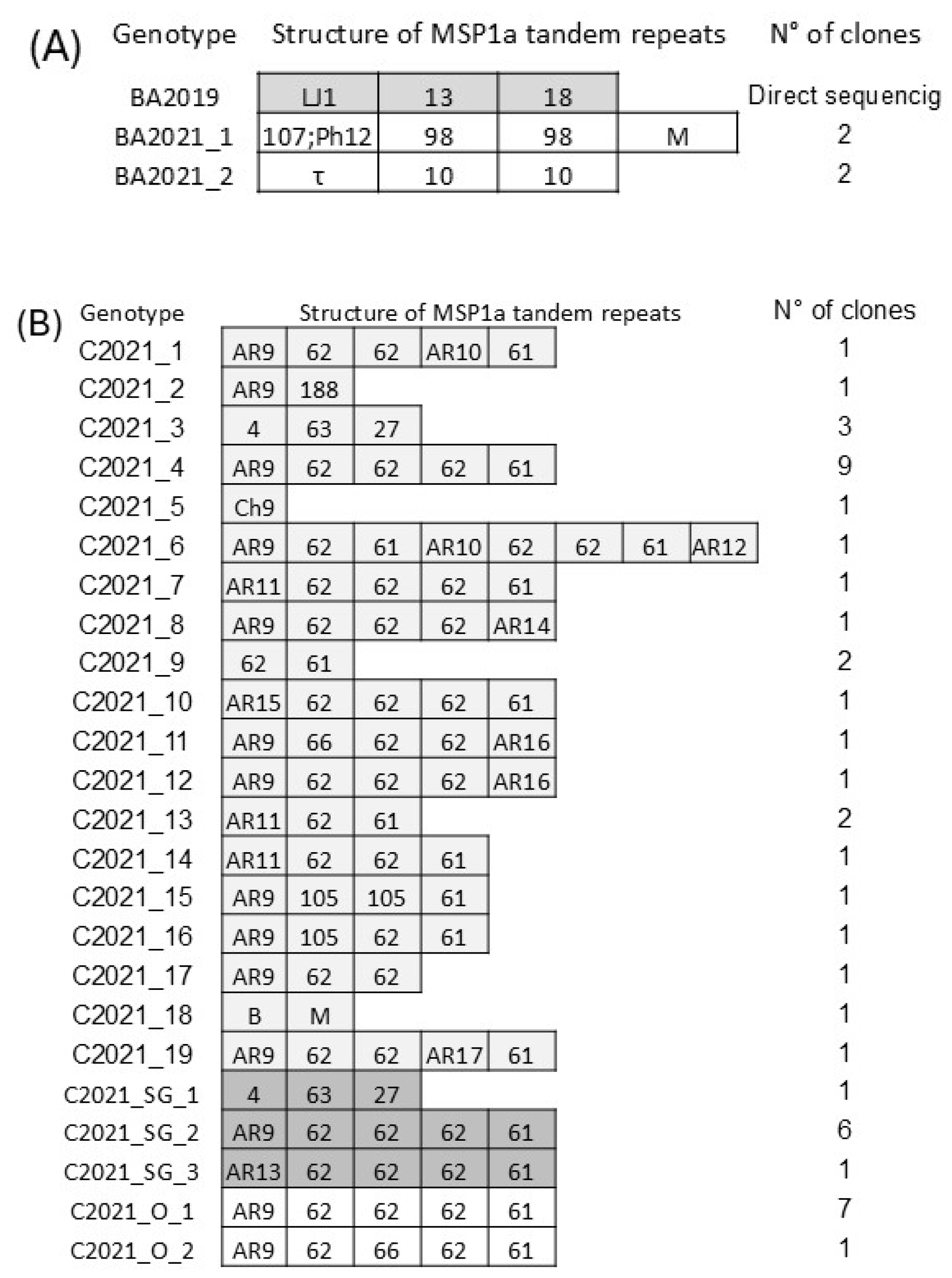
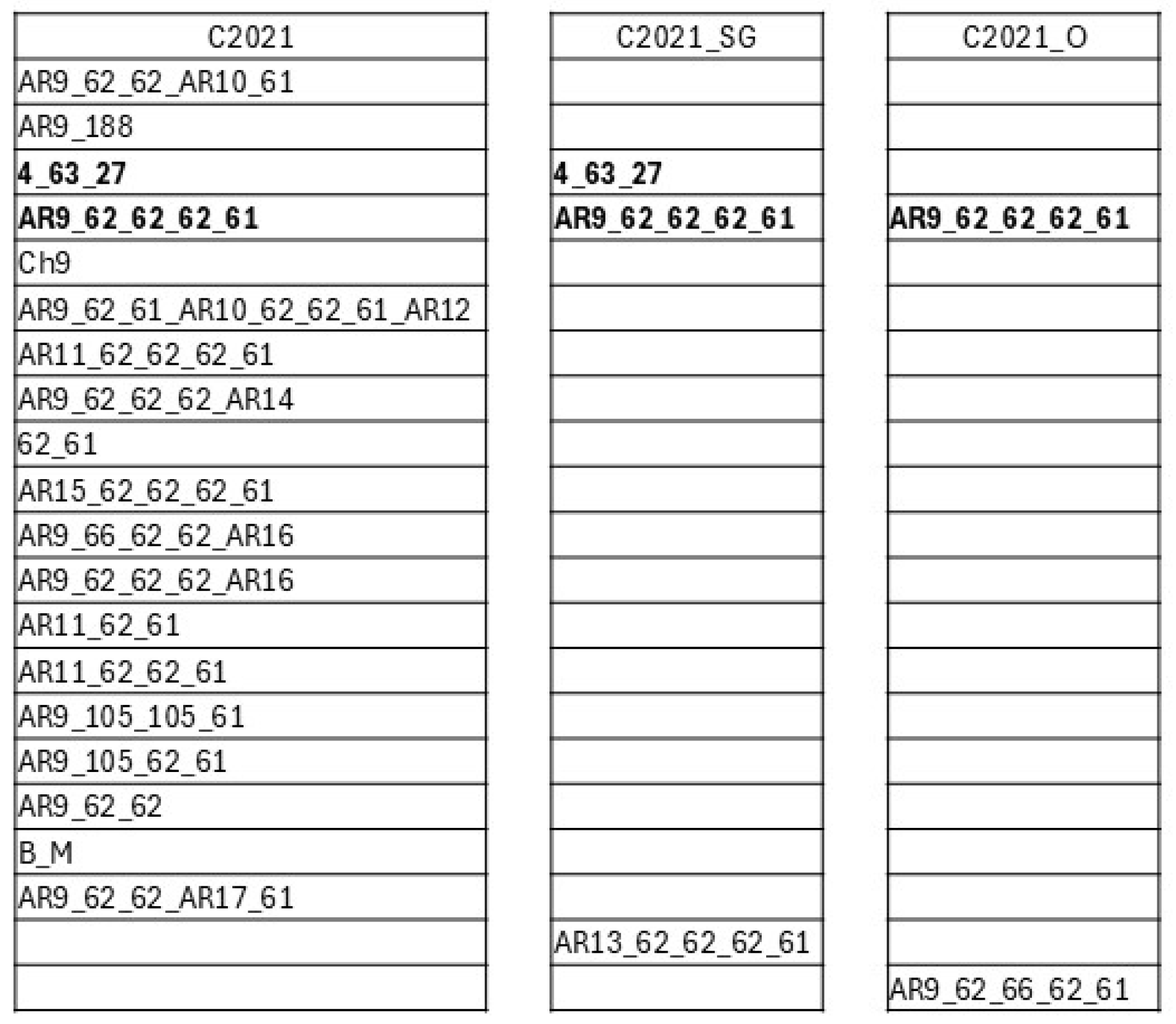
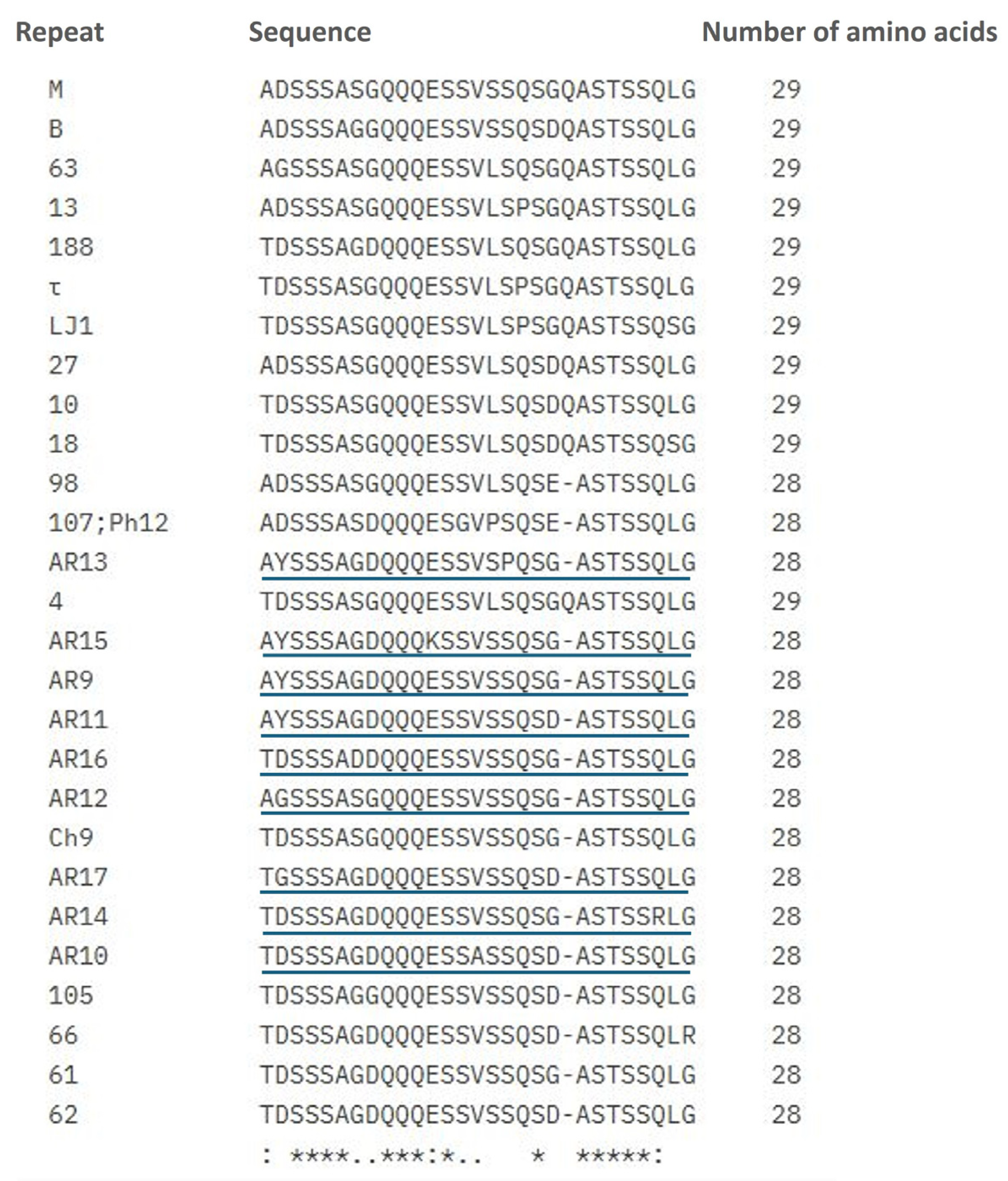
3.2. Strain Genotyping Through the Variable Region of the msp1a Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aubry, P.; Geale, D.W. A review of Bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemi, E.C.; Tomassone, L.; Farber, M.D. Tick-borne Rickettsiales: Molecular tools for the study of an emergent group of pathogens. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 119, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Földvári, G.; Elek, V.; Naranjo, V.; Farkas, R.; de la Fuente, J. Molecular identification of Anaplasma marginale and rickettsial endosymbionts in blood-sucking flies (Diptera: Tabanidae, Muscidae) and hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 154, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Parveen, A.; Ashraf, S.; Hussain, M.; Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S.; Shaikh, R.S.; Iqbal, F. First Report Regarding the Simultaneous Molecular Detection of Anaplasma marginale and Theileria annulata in Equine Blood Samples Collected from Southern Punjab in Pakistan. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemi, E.C.; Imbert, M.; de la Fournière, S.; Orozco, M.M.; Martinez, J.P.; Rosas, A.C.; Montenegro, V.N.; Farber, M.D. Closing the gaps to understand the tick transmission of Anaplasma marginale among giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) in Argentina. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocan, K.M.; De La Fuente, J.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. The genus Anaplasma: New challenges after reclassification. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruybal, P.; Moretta, R.; Perez, A.; Petrigh, R.; Zimmer, P.; Alcaraz, E.; Echaide, I.; de Echaide, S.T.; Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; et al. Genetic diversity of Anaplasma marginale in Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumalsamy, N.; Sharma, R.; Subramanian, M.; Nagarajan, S.A. Hard Ticks as Vectors: The Emerging Threat of Tick-Borne Diseases in India. Pathogens 2024, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, S.; Morel, N.; Masagué, M.F.O. Epidemiología y Control de la Garrapata Común del Bovino Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) Microplus en Argentina; Catholic University of Córdoba: Cordoba, Argentina, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, G.D.; Lucas, M.; Ortiz, H.G.; Gonçalves, L.d.S.; Blodorn, E.; Domingues, W.B.; Nunes, L.S.; Saravia, A.; Parodi, P.; Riet-Correa, F.; et al. Molecular of Anaplasma marginale Theiler (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae) in horseflies (Diptera: Tabanidae) in Uruguay. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, J.; Garcia-Garcia, J.C.; Blouin, E.F.; Kocan, K.M. Differential adhesion of major surface proteins 1a and 1b of the ehrlichial cattle pathogen Anaplasma marginale to bovine erythrocytes and tick cells. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koku, R.; Herndon, D.R.; Avillan, J.; Morrison, J.; Futse, J.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Brayton, K.A.; Noh, S.M. Both Coinfection and Superinfection Drive Complex Anaplasma marginale Strain Structure in a Natural Transmission Setting. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0016621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.A.; Tsoungui Obama HC, J.; Kamanga, G.; Kayanula, L.; Adil Mahmoud Yousif, N. The many definitions of multiplicity of infection. Front. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, 961593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primo, M.E.; Sarli, M.; Thompson, C.S.; Torioni, S.M.; Echaide, I.E. Sensitivity of Anaplasma marginale genotypes to oxytetracycline assessed by analyzing the msp1α gene in experimentally infected cattle. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fournière, S.; Guillemi, E.C.; Paoletta, M.S.; Pérez, A.; Obregón, D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Sarmiento, N.F.; Farber, M.D. Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, S.; Venzal, J.; González Acuña, D.; Martins, T.M.; Guglielmone, A.A. Ticks of the Southern Cone of America: Diagnosis, Distribution, and Hosts with Taxonomy, Ecology and Sanitary Importance; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, K.; Goddard, J.; Varela-Stokes, A. Examination of the internal morphology of the ixodid tick, Amblyomma maculatum Koch, (Acari: Ixodidae); a “how to” pictorial dissection guide. Midsouth Entomol. 2009, 2, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, T.G.; Dietrich, G.; Brandt, K.; Dolan, M.C.; Piesman, J.; Gilmore, R.D. Saliva, salivary gland, and hemolymph collection from Ixodes scapularis ticks. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 60, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgiç, H.B.; Karagenç, T.; Simuunza, M.; Shiels, B.; Tait, A.; Eren, H.; Weir, W. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Theileria annulata, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale in cattle. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roellig, D.M.; Gomez-Puerta, L.A.; Mead, D.G.; Pinto, J.; Ancca-Juarez, J.; Calderon, M.; Bern, C.; Gilman, R.H.; Cama, V.A. Hemi-nested PCR and RFLP methodologies for identifying blood meals of the Chagas disease vector, Triatoma infestans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’oliveira, C.; van der Weide, M.; Jacquiet, P.; Jongejan, F. Detection of Theileria annulata by the PCR in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from cattle in Mauritania. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1997, 21, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carelli, G.; Decaro, N.; Lorusso, A.; Elia, G.; Lorusso, E.; Mari, V.; Ceci, L.; Buonavoglia, C. Detection and quantification of Anaplasma marginale DNA in blood samples of cattle by real-time PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Fuente, J.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Kocan, K.M. Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of North American isolates of Anaplasma marginale (Rickettsiaceae: Ehrlichieae). Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 97, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, H.N.; Brayton, K.A.; Gebremedhin, A.H. RepeatAnalyzer: A tool for analysing and managing short-sequence repeat data. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hove, P.; Chaisi, M.E.; Brayton, K.A.; Ganesan, H.; Catanese, H.N.; Mtshali, M.S.; Mutshembele, A.M.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Collins, N.E. Co-infections with multiple genotypes of Anaplasma marginale in cattle indicate pathogen diversity. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquerra, E.V.; Herndon, D.R.; Mendoza, F.A.; Mosqueda, J.; Palmer, G.H. Anaplasma marginale superinfection attributable to pathogen strains with distinct genomic backgrounds. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5286–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maitre, A.; Wu-Chuang, A.; Aželytė, J.; Palinauskas, V.; Mateos-Hernández, L.; Obregon, D.; Hodžić, A.; Moro, C.V.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Paoli, J.-C.; et al. Vector microbiota manipulation by host antibodies: The forgotten strategy to develop transmission-blocking vaccines. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Clinical Condition | msp1β End-Point PCR | msp1β Real-Time PCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| BA2019 | symptomatic | Positive | 7 × 106 |
| BA2021 | asymptomatic | Positive | 8 × 102 |
| C2021 | symptomatic | positive | 1 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez, A.E.; Guillemi, E.C.; Sarmiento, N.F.; Cantón, G.J.; Farber, M.D. Rhipicephalus microplus and Its Impact on Anaplasma marginale Multistrain Infections in Contrasting Epidemiological Contexts. Pathogens 2025, 14, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020160
Pérez AE, Guillemi EC, Sarmiento NF, Cantón GJ, Farber MD. Rhipicephalus microplus and Its Impact on Anaplasma marginale Multistrain Infections in Contrasting Epidemiological Contexts. Pathogens. 2025; 14(2):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020160
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez, Agustina E., Eliana C. Guillemi, Nestor F. Sarmiento, Germán J. Cantón, and Marisa D. Farber. 2025. "Rhipicephalus microplus and Its Impact on Anaplasma marginale Multistrain Infections in Contrasting Epidemiological Contexts" Pathogens 14, no. 2: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020160
APA StylePérez, A. E., Guillemi, E. C., Sarmiento, N. F., Cantón, G. J., & Farber, M. D. (2025). Rhipicephalus microplus and Its Impact on Anaplasma marginale Multistrain Infections in Contrasting Epidemiological Contexts. Pathogens, 14(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020160









