Abstract
Records of Sarcocystis spp. diversity in rodents are relatively extensive; however, the increasing application of molecular approaches indicates that our current knowledge of these parasites remains incomplete. In the present study, morphological, genetic and phylogenetic data are provided on Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp. from the common vole (Microtus arvalis). Using light microscopy, the observed sarcocysts had a relatively thin (<1 μm) and smooth cyst wall. Via transmission electron microscopy, the sarcocyst wall thickness ranged from 0.7 to 1 μm, and the parasitophorous vacuolar membrane exhibited small knob-like blebs and was slightly wavy, type 1a. Based on 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1 and rpoB loci, S. arvalis n. sp. showed the highest similarity with Sarcocystis myodes from the bank vole (Clethronomys glareolus). According to the phylogenetic placement, S. arvalis n. sp. is the most closely related to Sarcocystis spp. with a rodent–mammal lifecycle. Morphologically, S. arvalis n. sp. forms sarcocysts that share a lot of similarities with those of S. myodes, Sarcocystis ratti and Sarcocystis cernae and molecular analysis is necessary for accurate species identification. Based on the abundance of the hosts and the proportion of voles in their diet, the most likely definitive hosts of S. arvalis n. sp. are red foxes, stone martens, least weasels, and domestic cats.
Keywords:
cox1; electron microscopy; Microtus arvalis; molecular analysis; phylogeny; rpoB; rRNA; Sarcocystis arvalis; Sarcocystis; voles 1. Introduction
As one of the most widespread and abundant small mammals in Europe, the common vole (Microtus arvalis) inhabits territory from northern Spain to central Russia and elevations up to 2600 m [1]. The grassland is the main habitat of the species, but it is also found in various semi-natural and agricultural ecosystems, including meadows, field margins, wildflower strips, and alfalfa fields [2]. During population peaks, the common vole invades crop fields [1].
Multi-annual cyclic or non-cyclic fluctuations of the densities, which occasionally exceed 1000 individuals/ha, can yield population outbreaks every 2–5 years [1,3,4]. Field margins can act as key refuges and dispersal corridors, sustaining vole populations and facilitating the recolonization of cultivated areas [2]. Therefore, the common vole is considered a dominant vertebrate pest in European farmlands, causing severe damage to cereals, alfalfa, and other crops [1].
The common vole is widespread in Lithuania, especially in agricultural landscapes. Countrywide studies found the vole in 75% of orchards and 80% of control habitats. It comprised about 30% of trapped small mammals and maintained stable proportions across years and seasons [5]. However, long-term monitoring shows a sharp decline, from 44% of trapped small mammals in the 1970s and 1980s to approximately 10% by 2021 [6], which is linked to land-use changes after the 1990s, such as pasture abandonment and intensification, as well as shifts in the landscape.
The common vole is a key host and reservoir of multiple zoonotic pathogens, with prevalence tied to its cyclic dynamics. In northwestern Spain, tularemia outbreaks caused by Francisella tularensis have consistently coincided with vole irruptions [7]. Voles carry a high prevalence of Bartonella species (e.g., B. grahamii, B. rochalimae, and B. taylorii), often in mixed infections linked to flea infestation [8]. Coinfections with F. tularensis are frequent at outbreak densities. Additionally, voles contribute to the circulation of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. and other vector-borne agents in Central Europe, with prevalence peaking during surges in vole density [9]. Thus, the irruptive dynamics of the common vole directly shape zoonotic risk. Studies conducted in Lithuania have determined that the common vole can harbour various pathogens, including Babesia spp., Echinococcus spp., Sarcocystis spp., and tick-borne encephalitis virus, among others [10,11,12].
Sarcocystis is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that use two hosts to complete their life cycle. The definitive host is usually a carnivore and rarely experiences a negative impact on their health. Sarcocystis spp. mature and develop in the intestines of the host, until parasites re-emerge into the environment after host defecates [13,14]. Intermediate hosts are infected after the consumption of water or food contaminated with sporocysts. Sarcocystis infections in intermediate hosts are usually either subclinical or cause only mild symptoms [13]. However, some Sarcocystis spp. can cause severe ailments, such as weakness, fever, weight loss, and internal bleeding that lasts until the parasite settles and forms sarcocysts in various muscles or even CNS; in rare cases, the infection can be lethal to the intermediate host [13,14,15].
There are approximately 50 valid Sarcocystis spp. that utilize rodents as intermediate hosts. Despite the high number of reported parasite species, as well as the diversity and abundance of intermediate host species, the number of comprehensive studies on the prevalence and species richness of Sarcocystis spp. in rodents remains relatively scarce. Most previous investigations relied on morphological methods, which are time-consuming, require specialized expertise, and pose challenges for species identification, particularly when hosts are infected with Sarcocystis spp. that form microscopic rather than macroscopic sarcocysts [13,16]. Furthermore, the reported prevalence of Sarcocystis spp. in rodents is often below 10%, thus requiring more effort to conduct the studies [10,17,18,19]. Although Sarcocystis spp. that use rodents do not appear to threaten human health directly, infected animals may exhibit altered behaviour that enhances their vulnerability to predation [20,21].
Common voles serve as intermediate hosts for various Sarcocystis spp. that utilize three distinct groups of definitive hosts. Among them, some species, such as Sarcocystis putorii [13] and presumably Sarcocystis myodes [18,22], rely on mammals as their definitive hosts, whereas Sarcocystis cernae [20], Sarcocystis glareoli and Sarcocystis microti [17,21] use raptors as their definitive hosts. Additionally, common voles can get infected with Sarcocystis clethrionomyelaphis [23,24], a species that uses snakes as their definitive hosts. In the present paper, a new species of Sarcocystis found in the muscles of Lithuanian common voles is described based on microscopic analysis and DNA investigations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material and Morphological Characterization of Sarcocysts
During the preceding investigation (2020–2023), rodents from Lithuanian orchards were screened for Sarcocystis spp. by molecular analysis [18]. The presence of Sarcocystis spp. was assessed by pooling muscle samples, performing muscle digestion with pepsin, and subsequent molecular analysis. For molecular characterization, nested PCRs targeting partial 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (cox1) sequences were performed, followed by sequencing. As a result, four genetically distinct species were established, S. myodes, Sarcocystis cf. strixi, Sarcocystis sp. Rod1, and Sarcocystis sp. Rod2. In the present study, efforts were made to isolate and characterize the Sarcocystis sp. Rod1, both morphologically and molecularly, to provide a comprehensive description of the novel species. In the previous work [18], the DNA of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 was identified in two pooled samples of voles, one consisting of the common voles and another of the tundra voles (Alexandromys oeconomus). All skeletal muscle tissues from the Sarcocystis sp. Rod1-positive sample groups of common voles (n = 10) and tundra voles (n = 2) were included in the present analysis. Samples were collected in 2020, common voles from Užpaliai (55°38′9.6″ N, 25°34′55.2″ E) and tundra voles from Aukštikalniai (56°04′33.6″ N, 24°23′42″ E), Lithuania.
Muscle samples were examined under light microscope in freshly squashed muscle preparations [25]. Sarcocysts were extracted from muscles with the aid of needles. An effort was made to characterize the morphology of sarcocysts, including their shape and size, the bradyzoites that emerged from the cysts, and the structure of the cyst wall. The isolated sarcocysts were transferred to individual 1.5 mL tubes containing 70% ethanol until DNA extraction. The single sarcocyst was subjected to further examination by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), as previously described [26].
2.2. Molecular Characterization of Sarcocysts
The genomic DNA was extracted from two individual sarcocysts using the GeneJET Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania) according to the manufacturer’s tissue protocol. Two individual sarcocysts isolated were subjected to PCR amplification of seven genetic regions. These regions included four nuclear loci, 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 (ITS1 and ITS2), apicoplast RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB), and two mitochondrially encoded genes, cox1 and cytochrome b (cytb). Two sets of primers were utilized for 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA to obtain longer sequences for these genes. The primer sequences utilized for the amplification of specific DNA sequences are listed in Table 1. The PCR reactions were carried out with 2 × Taq Master Mix (Vazyme, Red Maple Hi-tech Industry Park, Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The PCR conditions were as follows: 3 min initial denaturation at 95 °C, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation for 15 s at 95 °C, annealing 15 s at 53–59 °C (determined by the primer pair used), elongation for 60 s at 72 °C, and final extension for 5 min at 72 °C. The evaluation of PCR fragments was conducted visually using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The purification of most of the amplified products was accomplished with the use of ExoI and FastAP (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania). In the case of the PCR product of the cox1 region, purification was achieved through the means of the GeneJET PCR Purification Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania). All samples were subjected to direct sequencing using the 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), using the same forward and reverse primers as those utilized for PCR for the most part. Two primers were designed specifically for the ITS2 gene region sequencing. All sequences generated in the present study are available in GenBank with accession numbers PX373535 (18S rRNA), PX373537-PX373538 (28S rRNA), PX409056 (ITS2), PX380122-PX380123 (cox1), PX380124 (rpoB).

Table 1.
Primers used in the present study to amplify various DNA regions of Sarcocystis sp.
2.3. Sequence Analysis
The sequences obtained were then compared with those of Sarcocystis spp. using the online Nucleotide BLAST programme (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 27 August 2025). For the phylogenetic analyses, the sequences were compared with homologous sequences of numerous Sarcocystis spp. Multiple sequence alignments were generated with the MUSCLE algorithm available in MEGA12 software, version 12.0.11 [32]. The determination of best fitting model and construction of the phylogenetic trees under the Bayesian inference was executed using TOPALi v2.5 software [33]. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted using following models: the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with gamma-distributed rate variation (HKY + G) was used to construct 28S rRNA phylogenetic tree, the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with gamma distribution and a proportion of invariant sites (HKY + G + I) was used for 18S rRNA and rpoB, and the Felsenstein 1981 model with gamma distribution (F81 + G) was set for cox1 phylogenetic tree. The final alignment of 18S rRNA sequences comprised 36 individual sequences and 1659 aligned nucleotide positions. For the phylogenetic analysis of 28S rRNA sequences, 32 sequences were selected, resulting in a final alignment of 1588 aligned nucleotide positions. The cox1 sequence alignment included 28 sequences and 927 aligned nucleotide positions. Finally, 21 sequences were used for the phylogenetic analysis of rpoB, yielding a final alignment of 672 aligned nucleotide positions.
3. Results
3.1. Host Data and Morphological Description of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1
The pooled samples of common voles included four males and six females, as well as individuals of various ages, with a total of three adult specimens in the pool. The weight of common voles ranged from 13.5 g to 47.0 g, with an average weight of 24.1 g. The average body length (from head to the tail) was 90.2 mm, with the shortest vole measuring 72.9 mm and the longest 112.9 mm. In contrast, both tundra voles were adults: a male weighing 34.4 g and measuring 101.2 mm in length, and a female weighing 43.8 g and measuring 112.0 mm in length. Sarcocysts of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 were found in one out of ten muscle samples of the common vole. The positive sample was collected from the largest specimen in the group, which weighed 47.0 g and measured 112.9 mm in length. This individual was an adult breeding male, captured within a currant orchard during the autumn season. A necropsy revealed a markedly enlarged spleen. By contrast, sarcocysts were not found in the skeletal muscles of two tundra voles.
Sarcocysts detected in muscle tissues of the common vole measured approximately 1254 × 218 μm (range: 1058–624 × 112–281 μm; n = 3). The tips of the sarcocysts were not visible or had been cut off, however the cysts were relatively wide and large, so they were most likely cigar- or ribbon-shaped (Figure 1a). All sarcocysts had smooth cyst walls with no visible protrusions (Figure 1b). Sarcocysts had clearly visible septa, containing numerous bradyzoites. Upon extraction from sarcocysts for the purpose of measurement, the bradyzoites exhibited a thin and disintegrating appearance. A single intact bradyzoite was observed measuring 12.6 × 3.0 μm (Figure 1c).
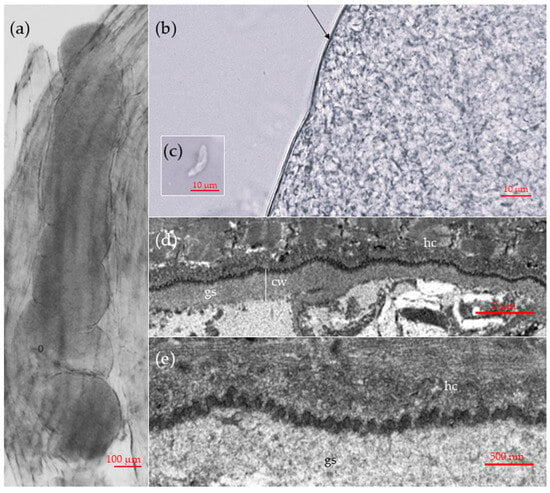
Figure 1.
Morphological features of sarcocysts of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1, designated in this study as Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp., isolated from the skeletal muscles of the common vole (Microtus arvalis) in Lithuania. (a–c) Light microscopy micrographs. Fresh muscle-squashed preparations. (a) Sarcocyst in the host muscle tissue. (b) Enlarged view of a cyst wall. Note a thin and apparently smooth cyst wall (arrow). (c) The intact bradyzoite. (d,e) TEM micrographs. (d) A fragment of cyst wall showing a slight waviness of the parasitophorous vacuolar membrane (e) Enlarged view on bleb-like structures on the sarcocyst wall; note muscular host cell (hc), cyst wall (cw) and ground substance (gs).
The TEM analysis of a single sarcocyst revealed that the cyst wall had a thickness ranging from 0.7 to 1 μm (Figure 1d). The parasitophorous vacuolar membrane exhibited small knob-like blebs and was slightly wavy (Figure 1d). The ground substance layer measured 0.6–0.9 μm in thickness. The sarcocyst wall corresponds to type 1a of the Dubey et al. [13] classification. While the composition of the cyst wall could be clearly delineated, the internal structures of the cyst exhibited substantial decay. Therefore, no internal structures or bradyzoites were visible.
3.2. Molecular Characterization and Phylogeny of Sarcocysts Isolated from the Common Vole
One sarcocyst was successfully characterized at four genetic loci, 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS2 and cox1, whereas the second excised sarcocyst was characterized at 28S rRNA, cox1 and rpoB. Amplification of ITS1 and cytB was not successful. Both isolates obtained from two individual sarcocysts showed 100% identity in 28S rRNA and cox1, indicating that they belong to the same species. Furthermore, in the current work, 1053 bp cox1 sequences shared 100% identity with 619 bp sequences of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 (OQ558008-OQ558009) (Table 2). Our 1545 bp 28S rRNA sequences demonstrated OQ557458 100% identity with the 735 bp sequence of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 from the common vole (OQ557458) and displayed 99.7% similarity with 735 bp sequence of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 from the tundra vole (OQ557457), differing by two SNPs (single-nucleotide polymorphisms). Thus, the parasite isolated in this work genetically matched that isolated from pooled and digested samples of voles and designated as Sarcocystis sp. Rod1. The partial ITS2 sequence obtained did not show any significant similarity to other sequences of Sarcocystis spp. Based on other genetic loci, the sequences generated in the present study showed the highest similarity to those of S. myodes originally described in the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) [22] and subsequently detected in several other rodent species. Specifically, genetic differences were at least 0.2% in cox1, 0.5% in 18S rRNA, 0.7% in rpoB, and at least 1.1% in 28S rRNA.

Table 2.
Molecular characteristics of Sarcocystis parasite isolated from sarcocysts of the common vole.
Furthermore, the sequences obtained in the present study demonstrated a high degree of similarity in 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and cox1 when compared with those of S. ratti and Sarcocystis meriones. Therefore, an analysis of sequence variation was conducted across all four closely related Sarcocystis spp., S. arvalis n. sp. (syn. Sarcocystis sp. Rod1) described in this study, S. myodes, S. ratti, and S. meriones at four loci (18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1, rpoB) to assess patterns of polymorphism and divergence (Figure 2). The number of variable sites differed among the genes and species, with a total of 78 variable sites detected across analyzed species. Among these, a total of 69 SNPs were observed to be fixed across the analyzed species, indicating that these sites differentiate consistently. Indel positions were treated as additional characters and included in the count of variable sites, with two indels identified. A comparative analysis between S. arvalis n. sp. and S. myodes revealed 38 SNPs, of which 31 were fixed. These fixed SNPs were distributed as follows: 7 in the 18S rRNA, 17 in the 28S rRNA, 5 in the rpoB, and the remaining 2 in the cox1. Notably, the 28S rRNA locus was the most informative for distinguishing S. arvalis n. sp. from S. myodes in this dataset.
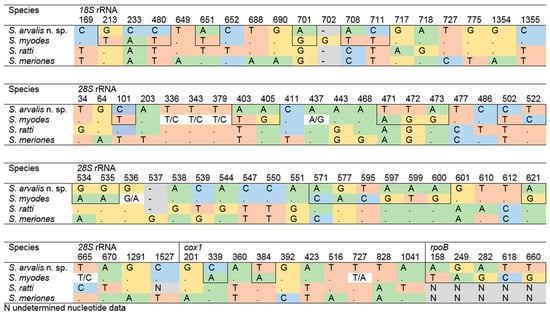
Figure 2.
The distribution of variable sites across the four loci for S. arvalis n. sp., S. myodes, S. ratti, and S. meriones. The positions of fixed single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between S. arvalis n. sp. and S. myodes are indicated by outlining.
Phylogenetic trees were built using four molecular loci, 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1 and rpoB (Figure 3). Phylograms constructed with 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1 sequences consistently placed S. arvalis n. sp. alongside S. myodes, S. ratti and S. meriones (Figure 3a–c). A sister clade was formed by Sarcocystis cymruensis and Sarcocystis muris (Figure 3a,c). Notably, these clusters were clearly distinct from Sarcocystis species that use birds and snakes as their definitive hosts. Phylogenetic analyses based on 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA and cox1 genes placed S. ratti in a well-supported cluster with S. meriones, as indicated by a high bootstrap value (Figure 3a–c). Based on rpoB, S. arvalis n. sp. clustered with S. myodes (Figure 3d) and formed a sister clade to S. cymruensis. The absence of rpoB sequences in other closely related species of S. arvalis n. sp. does not affect the overall phylogenetic patterns observed. These findings show that S. arvalis n. sp. is closely related to Sarcocystis spp. which may utilize predatory mammals as their definitive hosts.
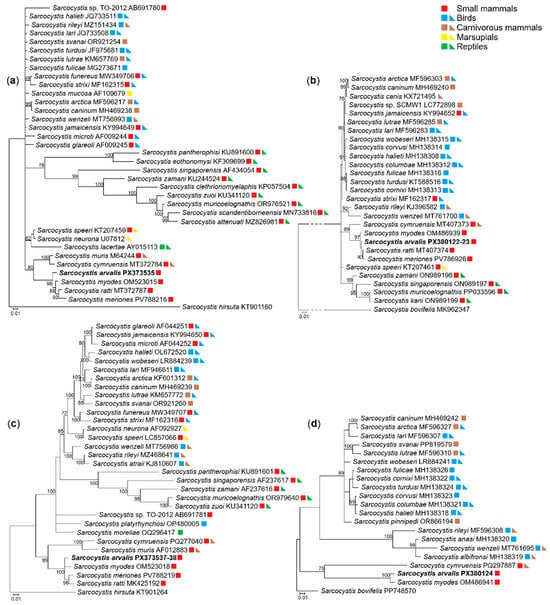
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic trees depicting the placement of Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp. among other Sarcocystis spp. The trees were constructed based on (a) 18S rRNA sequences, (b) cox1 sequences, (c) 28S rRNA sequences and (d) rpoB sequences. Phylograms were constructed using Bayesian methods and scaled according to the branch length. Sarcocystis hirsuta sequence was used as an outgroup for trees (a,c), while Sarcocystis bovifelis sequence was used as an outgroup for trees (b,d). Posterior probability support values higher than 70% are indicated next to branches. Coloured squares and triangles indicate the identified or presumed intermediate and definitive hosts of Sarcocystis spp., respectively.
3.3. Description of Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp.
Six species of Sarcocystis are reported to utilize common voles as an intermediate host (Table 3). Two of these species—S. putorii [13,20,34] and S. clethrionomyelaphis [23,24] produce macroscopic sarcocysts, that differ significantly from those found in this study. The remaining four species—S. microti, S. glareoli [35,36], S. myodes [22] and S. cernae [20] produce microscopic thin-walled sarcocysts in their intermediate hosts. However, S. glareoli and S. microti, form sarcocysts exclusively in the brains of their hosts. Additionally, S. cernae, S. glareoli and S. microti rely on raptors, specifically the European kestrel (Falco tinnunculus) [20] or buzzards of genus Buteo [17,21] as their definitive hosts. Meanwhile, molecular and phylogenetic analysis suggests that S. arvalis n. sp. is closely related to S. myodes, S. ratti, and S. meriones which may use mammals as their definitive hosts [22,25,37].

Table 3.
Sarcocystis species reported to use common vole (Microtus arvalis) as intermediate host.
A reliable distinction between sarcocysts of S. arvalis n. sp. and those of other morphologically similar species cannot be made by microscopy alone. The assessment of the morphology and dimensions of the sarcocysts and bradyzoites was hindered by the low number and poor condition of the observed cysts. The tips of the sarcocysts were not observed in any of the three isolated sarcocysts. During light microscopy, the bradyzoites seemed to be disintegrating. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that the interior of the cyst began to deteriorate immediately after the ground substance, making ultrastructural analysis of bradyzoites impossible to conduct. Molecular analyses revealed a close relationship between S. arvalis n. sp. and S. myodes; however, differences in 28S rRNA, as well as in 18S rRNA and rpoB sequences, support their recognition as distinct species.
- Taxonomic summary of Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp.
- Type intermediate host common vole (Microtus arvalis)
- Other intermediate hosts presumably Alexandromys (Microtus) oeconomus.
- Definitive host Unknown, based on phylogeny, predatory mammals are the most likely candidates.
- Locality Užpaliai (Utena district), Lithuania.
- Type specimen Hapantotype an epoxy resin-embedded block (NRCP00005) containing the fixed sarcocyst used for species description is deposited in the State Scientific Research Institute Nature Research Centre, Vilnius, Lithuania.
- Sequences deposited in NCBI GenBank with accession numbers PX373535, PX373537-PX373538, PX380122-PX380124 and PX409056.
- Etymology The Latin name of the common vole, Microtus arvalis, was used for the species name.
- ZooBank registration The Life Science Identifier (LSID) of the article is urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:595E6C8F-05A3-4E37-BB57-0B1970C22D9F.
- The LSID for the new name Sarcocystis arvalis is urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:FD7D1C59-B3E5-415E-B938-F83AFA48E69D.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sarcocystis spp. in Common Voles Prevalence
A notable gap remains in the current understanding of the occurrence of Sarcocystis spp. in wild rodents. Among these hosts, the common vole is relatively well studied, with investigations carried out in several European countries, including the Czech Republic, Germany, France, Lithuania, and the Netherlands. Investigations examining the brain of these animals have produced contrasting results. No sarcocysts were detected in common voles collected in Germany [39,40] or Lithuania [19,35]. However, in France, 9.2% of brains tested positive for S. microti and 0.1% for S. glareoli [41]. In the Czech Republic, Sarcocystis infection was identified in 3.9% of common voles, with a higher rate (8.3%) recorded in individuals preyed upon by common buzzards (B. buteo) [21]. A later study in the same country reported a 5.0% prevalence of S. microti in common vole brains [17]. Investigations of muscle tissues yielded similarly variable results. In the Netherlands, S. cernae and S. putorii were detected in 9.3% and 2.2% of common voles, respectively, with the prevalence of S. cernae reaching 20.6% in animals caught by common kestrels (F. tinnunculus) [20]. In the Czech Republic, 2.9% of common voles were infected with S. putorii and S. cernae [17]. In Lithuania, prevalence of Sarcocystis spp. in muscles of common voles ranged from 4.0% to 20.4% depending on the study and location [10,16]. In summary, studies indicate a low to moderate occurrence of Sarcocystis spp. in common voles, with infection rates varying by organ examined (brain or muscle) and by geographic location.
4.2. Molecular Research of Sarcocystis spp. in Rodents from Lithuania
In recent years, considerable efforts have been made to clarify the prevalence and species richness of Sarcocystis parasites in wild rodents from Lithuania through molecular methods. A study conducted in 2024 successfully detected DNA of three species, Sarcocystis funereus, S. glareoli, and S. myodes in blood samples from bank voles and yellow-necked mice (Apodemus flavicollis) [42]. Of particular interest, S. funereus had only recently been described using the Tengmalm’s owl (Aegolius funereus) as a definitive host, while its natural intermediate host remained unknown [43,44]. These findings therefore provided the first evidence that bank voles presumably serve as intermediate hosts of this parasite. Similar results were obtained in 2023, when 91 pools of muscle samples, representing 679 small mammals of the genera Apodemus, Microtus, and Sorex, collected from orchards in Lithuania, were analyzed by molecular techniques. Although infection rates were higher in voles than in mice, the difference was not statistically significant. Sequencing of 28S rRNA and cox1 fragments revealed four distinct Sarcocystis taxa, S. myodes, Sarcocystis cf. strixi, and two previously undescribed species, tentatively named Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 and Sarcocystis sp. Rod2 [18]. These findings demonstrated the utility of DNA-based approaches for detecting and characterizing Sarcocystis spp. in small mammals, where microscopy is often unreliable due to low infection levels and limited amounts of tissue. The present work represents a continuation of the work initiated in 2023, with a focus on further characterizing the novel taxon Sarcocystis sp. Rod1. The sarcocysts examined here, however, appeared fractured and fragile, likely due to the age of the samples (collected in 2020). Most bradyzoites showed signs of degradation, which may explain the unsuccessful amplification of ITS1 and cytB. Nevertheless, sequencing of other genetic loci was successful and confirmed that the DNA obtained from isolated sarcocysts corresponded to Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 sequences identified previously.
4.3. Sarcocystis spp. Richness in Common Voles
Several Sarcocystis spp. are known or suspected to use the common vole as an intermediate host, including S. putorii, S. cernae, S. myodes, S. microti, S. glareoli, and S. clethrionomyelaphis. Among these, S. putorii and S. clethrionomyelaphis are characterized by the formation of macroscopic sarcocysts in their intermediate hosts. Notably, S. putorii is transmissible via carnivores of the family Mustelidae; however, this species has a distinct type 9b cyst wall, which does not correspond to the cyst wall morphology observed in the present study [34]. In contrast, S. clethrionomyelaphis uses snakes of the Elaphe, Zamenis and Pantherophis genera as its definitive hosts and features cyst wall type 9 [23,24]. Sarcocystis microti, S. glareoli, S. myodes and S. cernae form only microscopic sarcocysts, which feature type 1a cyst wall. However, S. microti and S. glareoli are only known to form sarcocysts in the CNS of their intermediate hosts [36]. Additionally, S. microti, S. glareoli [17,36] and S. cernae [20] utilizes raptors as their definitive hosts, whereas S. myodes potentially uses mammals as their definitive hosts [22]. Of the six Sarcocystis spp. reported from common voles, three (S. glareoli, S. microti, and S. myodes) have been genetically characterized [22,36]. Sequences of S. microti and S. glareoli markedly differ from those of S. arvalis n. sp., whereas S. myodes and S. arvalis n. sp. display a high degree of sequence similarity, suggesting a close evolutionary relationship (Figure 2). Nonetheless, subtle but consistent differences in 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA sequences, together with similarities to S. ratti and S. meriones, indicate that all four taxa represent closely related yet distinct entities (Table 2 and Figure 2). Comparable situations have been described previously. A comprehensive molecular study of Sarcocystis spp. with a rodent-snake life cycle revealed the so-called S. zuoi complex, comprising several distinct taxa (Sarcocystis sp., Sarcocystis kani, Sarcocystis attenuati, Sarcocystis scandentiborneensis, and Sarcocystis zuoi), some of which share identical cox1 sequences and can only be discriminated by 18S rRNA analysis [45]. Similarly, it is plausible that S. arvalis n. sp., S. myodes, S. ratti, and S. meriones likewise form a molecularly cryptic complex of Sarcocystis spp. with rodent-mammal life cycles, which can be reliably distinguished only through 28S rRNA and ITS1 analyses [22,25,37]. The high degree of morphological similarity among sarcocysts, together with overlapping intermediate host ranges, further complicates species identification. These findings therefore reinforce the necessity of utilizing molecular approaches for accurate identification of Sarcocystis spp. in common voles, and more broadly in other rodents.
4.4. Suspected Definitive Host of Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp.
Being one of the key small mammalian prey species in European ecosystems, the common vole is heavily predated on by both mammalian carnivores and avian raptors. Among the mammalian predators, the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) is particularly important: studies from Poland and Belarus show that foxes rely heavily on Microtus voles during peak vole years, sometimes displaying clear specialization [46,47]. Mustelids, especially the least weasel (Mustela nivalis) and stoat (M. erminea), are highly specialized hunters and exert strong pressure on vole populations [48]. Badgers (Meles meles), stone marten (Martes foina), and European pine marten (M. martes) also prey on voles, though they show more varied diets [49]. Domestic cats (Felis catus) may also contribute locally to predation of these rodents [48].
In northern Europe, main predators of common voles are small mustelids, particularly least weasel and stoat, which are highly dependent on voles and unable to switch effectively to alternative prey. In contrast, generalist predators such as red fox and several avian raptors, such as the common buzzard (B. buteo), European kestrel, short-eared owl (Asio flammeus), long-eared owl (Asio otus), and Tengmalm’s owl (A. funereus), can switch to alternative prey when vole densities decline [50]. The combined pressure from generalist predators (like foxes and martens) and specialist predators (like weasels and owls) helps explain vole population fluctuations, with mustelids and owls acting as strong regulators in open landscapes, while foxes dominate predation in mixed habitats [46,48,49].
Other mammalian carnivores whose diet includes Microtus voles, specifically the common vole, include the European polecat (Mustela putorius), the American mink (Neovison vison), the golden jackal (Canis aureus), the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides), and the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) [51,52,53,54,55,56]. The raccoon (Procyon lotor) also might be included in this list [57]. However, the European polecat, the raccoon, and the golden jackal are very scarce in Lithuania [58]. The contribution of common voles to the diet of the Eurasian otter, the raccoon dog, the gray wolf (Canis lupus), and the lynx (Lynx lynx) is not significant [59]. Although many carnivores occasionally feed on common voles, the phylogenetic placement of Sarcocystis arvalis n. sp. strongly suggests that its definitive hosts are predatory mammals. Considering both the abundance of common voles and their importance in the diet of various carnivores, the most likely definitive hosts are wild carnivores such as red foxes, stone martens, and least weasels, as well as domestic cats.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P.; methodology, V.S., E.R.-L., D.L.B. and P.P.; software, P.P. and D.L.B.; validation, P.P., L.B. and D.B.; formal analysis, V.S., E.R.-L. and D.L.B.; investigation, V.S., E.R.-L. and D.L.B.; resources, P.P., D.B., L.B.; data curation, V.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L.B., E.R.-L., L.B. and P.P.; writing—review and editing, D.L.B., E.R.-L., L.B., P.P., V.S. and D.B.; visualization, P.P. and D.L.B.; supervision, P.P., L.B. and D.B.; project administration, D.B.; funding acquisition, P.P. and D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania (grant number S-MIP-23-4).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with Lithuanian legislation (the Republic of Lithuania Law on the Welfare and Protection of Animals No. XI-2271, “Requirements for the Housing, Care and Use of Animals for Scientific and Educational Purposes”, approved by Order No B1-866, 31 October 2012 of the Director of the State Food and Veterinary Service (Paragraph 4 of Article 16) and European legislation (Directive 2010/63/EU) on the protection of animals. The study was approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of the State Scientific Research Institute Nature Research Centre (protocol No GGT-8, 24 March 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS2, cox1 and rpoB sequences of Sarcocystis arvalis are available via the NCBI GenBank database under accession numbers PX373535, PX373537-PX373538, PX380122-PX380124, PX409056.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jacob, J.; Manson, P.; Barfknecht, R.; Fredricks, T. Common vole (Microtus arvalis) ecology and management: Implications for risk assessment of plant protection products. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pastor, R.; Luque-Larena, J.J.; Lambin, X.; Mougeot, F. “Living on the edge”: The role of field margins for common vole (Microtus arvalis) populations in recently colonised Mediterranean farmland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ 2016, 231, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briner, T.; Favre, N.; Nentwig, W.; Airoldi, J.-P. Population dynamics of Microtus arvalis in a weed strip. Mammal. Biol. 2007, 72, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, B.F.; Jacob, J.; Petri, A.; Esther, A. Topography and soil properties contribute to regional outbreak risk variability of common voles (Microtus arvalis). Wildl. Res. 2011, 38, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirkė, V.; Balčiauskas, L.; Balčiauskienė, L. Common vole as a focal small mammal species in orchards of the northern zone. Diversity 2021, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balčiauskas, L.; Balčiauskienė, L. Small mammal diversity changes in a Baltic country, 1975–2021: A review. Life 2022, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Larena, J.J.; Mougeot, F.; Roig, D.V.; Lambin, X.; Rodríguez-Pastor, R.; Rodríguez-Valín, E.; Anda, P.; Escudero, R. Tularemia outbreaks and common vole (Microtus arvalis) irruptive population dynamics in northwestern Spain, 1997–2014. Vector. Borne. Zoonotic. Dis. 2015, 15, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pastor, R.; Escudero, R.; Lambin, X.; Vidal, M.D.; Gil, H.; Jado, I.; Rodríguez-Vargas, M.; Luque-Larena, J.J.; Mougeot, F. Zoonotic pathogens in fluctuating common vole (Microtus arvalis) populations: Occurrence and dynamics. Parasitology 2019, 146, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balážová, A.; Nosková, E.; Široký, P.; Durrant, C.; Baláž, V. Diversity and dynamics of zoonotic pathogens within a local community of small mammals. Biologia 2021, 76, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grikienienė, J. Investigations into endoparasites of small mammals in the environs of lake Drūkšiai. Acta. Zool. Litu. 2005, 15, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrūnaitė, L.; Kitrytė, N.; Križanauskienė, A. Blood parasites (Babesia, Hepatozoon and Trypanosoma) of rodents, Lithuania: Part I. Molecular and traditional microscopy approach. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkute, E.; Pautienius, A.; Grigas, J.; Sidorenko, M.; Radzijevskaja, J.; Paulauskas, A.; Stankevicius, A. The prevalence of Tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild rodents captured in Tick-borne encephalitis foci in highly endemic Lithuania. Viruses 2024, 16, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Sarcocystosis of Animals and Humans; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4987-1015-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Neosporosis, toxoplasmosis, and sarcocystosis in ruminants: An update. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, B.M. Zoonotic sarcocystis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grikienienė, J.; Mažeikytė, R. Investigation of sarcosporidians (Sarcocystis) of small mammals in Kamasta landscape reserve and its surroundings. Acta. Zool. Litu. 2000, 10, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, M.; Vo, P.; Votýpka, J.; Weidinger, K. Heteroxenous coccidia (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) in the populations of their final and intermediate hosts: European buzzard and small mammals. Acta. Protozool. 2004, 43, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Prakas, P.; Stirkė, V.; Šneideris, D.; Rakauskaitė, P.; Butkauskas, D.; Balčiauskas, L. Protozoan parasites of Sarcocystis spp. in rodents from commercial orchards. Animals 2023, 13, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Jasiulionis, M.; Šukytė, T.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Stirkė, V.; Balčiauskas, L.; Butkauskas, D. First observations of buzzards (Buteo) as definitive hosts of Sarcocystis parasites forming cysts in the brain tissues of rodents in Lithuania. Biology 2024, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, I.; Dijkstra, C. Sarcocystis cernae: A parasite increasing the risk of predation of its intermediate host, Microtus arvalis. Oecologia 1987, 74, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voříšek, P.; Votýpka, J.; Zvára, K.; Svobodová, M. Heteroxenous coccidia increase the predation risk of parasitized rodents. Parasitology 1998, 117, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Jasiulionis, M.; Balčiauskas, L.; Prakas, P.; Stirkė, V.; Butkauskas, D. Morphological and molecular description of Sarcocystis myodes n. sp. from the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) in Lithuania. Biology 2022, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuschka, F.-R. Sarcocystis clethrionomyelaphis n. sp. from snakes of the genus Elaphe and different voles of the family Arvicolidae. J. Parasitol. 1986, 72, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-J.; Liu, T.-T.; Liu, Q.; Esch, G.W.; Chen, J.-Q. Sarcocystis clethrionomyelaphis Matuschka, 1986 (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) infecting the large oriental vole Eothenomys miletus (Thomas) (Cricetidae: Microtinae) and its phylogenetic relationships with other species of Sarcocystis Lankester, 1882. Syst. Parasitol. 2015, 91, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Kirillova, V.; Gavarāne, I.; Grāvele, E.; Butkauskas, D.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Kirjušina, M. Morphological and molecular description of Sarcocystis ratti n. sp. from the black rat (Rattus rattus) in Latvia. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Rehbein, S.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Butkauskas, D.; Prakas, P. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Sarcocystis capracanis, Sarcocystis cornagliai and Sarcocystis rossii n. sp. infecting the alpine ibex (Capra ibex). Parasit. Vectors. 2025, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryan, F.A.M.; Prakas, P.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Šneideris, D.; Abd-Al-Aal, Z.; Alhoot, A.A.A.; El-Kabbany, A.I.; Tahrani, L.M.A.; El-Azazy, O.M.E. Sarcocystis cymruensis in the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) from an urban district in Kuwait: Detailed morphologic and molecular characterization. Acta. Parasitol. 2025, 70, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutkienė, L.; Prakas, P.; Sruoga, A.; Butkauskas, D. The mallard duck (Anas platyrhynchos) as intermediate host for Sarcocystis wobeseri sp. nov. from the barnacle goose (Branta leucopsis). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Molecular characterisation of Sarcocystis rileyi from a common eider (Somateria mollissima) in Norway. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Phylogenetic relationships among Sarcocystis species in cervids, cattle and sheep inferred from the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J. Infection of the asian gray shrew Crocidura attenuata (Insectivora: Soricidae) with Sarcocystis attenuati n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) in China. Parasit. Vectors. 2022, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular evolutionary genetic analysis version 12 for adaptive and green computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Wright, F.; Rowe, G.; Marshall, D.F.; Husmeier, D.; McGuire, G. TOPALi: Software for automatic identification of recombinant sequences within DNA multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1806–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, W.; Laarman, J.J. Current Concepts on the Biology, Evolution and Taxonomy of Tissue Cyst-Forming Eimeriid Coccidia. In Advances in Parasitology; Lumsden, W.H.R., Muller, R., Baker, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; Volume 20, pp. 293–468. [Google Scholar]
- Grikienienė, J.; Mažeikytė, R.; Balčiauskas, L. The first data on brain parasites of the genus Frenkelia (Protista: Coccidia) in some small rodent species in Lithuania. Acta. Zool. Litu. 2003, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugridge, N.B.; Morrison, D.A.; Johnson, A.M.; Luton, K.; Dubey, J.P.; Votýpka, J.; Tenter, A.M. Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Frenkelia: A review of its history and new knowledge gained from comparison of large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene sequences. Int. J. Parasitol 1999, 29, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryan, F.A.M.; El-Azazy, O.M.E.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Šneideris, D.; Tahrani, L.M.A.; Butkauskas, D.; Prakas, P. Morphological and molecular description of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp. from the libyan jird (Meriones libycus) in Kuwait. Animals 2025, 15, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Švažas, S.; Bea, A.; Šneideris, D.; Villanúa, D.; Butkauskas, D.; Prakas, P. Molecular confirmation of raptors from Spain as definitive hosts of numerous Sarcocystis species. Animals 2025, 15, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krücken, J.; Blümke, J.; Maaz, D.; Demeler, J.; Ramünke, S.; Antolová, D.; Schaper, R.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. Small rodents as paratenic or intermediate hosts of carnivore parasites in Berlin, Germany. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waindok, P.; Özbakış-Beceriklisoy, G.; Janecek-Erfurth, E.; Springer, A.; Pfeffer, M.; Leschnik, M.; Strube, C. Parasites in brains of wild rodents (Arvicolinae and Murinae) in the city of Leipzig, Germany. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites. Wildl. 2019, 10, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet-Calvet, E.; Kia, E.B.; Giraudoux, P.; Quéré, J.P.; Delattre, P.; Ashford, R.W. Frenkelia parasites in a small mammal community. Dynamics of infection and effect on the host. Parasite 2004, 11, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prakas, P.; Gudiškis, N.; Kitrytė, N.; Bagdonaitė, D.L.; Baltrūnaitė, L. Detection of three Sarcocystis species (Apicomplexa) in blood samples of the bank vole and yellow-necked mouse from Lithuania. Life 2024, 14, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máca, O.; Kouba, M.; Korpimäki, E.; González-Solís, D. Molecular identification of Sarcocystis sp. (Apicomplexa, Sarcocystidae) in offspring of tengmalm’s owls, Aegolius funereus (Aves, Strigidae). Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 804096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máca, O.; Kouba, M.; Langrová, I.; Panská, L.; Korpimäki, E.; González-Solís, D. The tengmalm’s owl Aegolius funereus (Aves, Strigidae) as the definitive host of Sarcocystis funereus sp. nov. (Apicomplexa). Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1356549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, T.; Raisch, L.; Richter, S.; Wirth, M.; Birenbaum, D.; Ginting, S.; Khoprasert, Y.; Mackenstedt, U.; Wassermann, M. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic characterization of Sarcocystis kani sp. nov. and other novel, closely related Sarcocystis spp. infecting small mammals and colubrid snakes in Asia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites. Wildl. 2023, 22, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidawa, D.; Kowalczyk, R. The effects of sex, age, season and habitat on diet of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in Northeastern Poland. Acta. Theriol. 2011, 56, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorovich, V.E.; Sidorovich, A.A.; Izotova, I.V. Variations in the diet and population density of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in the mixed woodlands of Northern Belarus. Mammal. Biol. 2006, 71, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, G.; Giraudoux, P.; Delattre, P. Numerical and dietary responses of a predator community in a temperate zone of Europe. Ecography 2009, 32, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Heltai, M. Feeding habits of sympatric Mustelids in an agricultural area of Hungary. Acta. Zool. Hung. 2011, 57, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Hanski, I.; KorpimÄki, E. Microtine rodent dynamics in Northern Europe: Parameterized models for the predator-prey interaction. Ecology 1995, 76, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecha, A.W.; Antczak, M. Diet of the european polecat Mustela putorius in an agricultural area in Poland. Folia. Zool. Brno 2013, 62, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.J.; Bogdziewicz, M.; Czyż, M.J. Diet of the american mink Neovison vison in an agricultural landscape in Western Poland. Folia. Zool. Brno 2013, 62, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, P.N.A.M.J.G.; Lelieveld, G.; De Knegt, H.J. Diet composition of the golden jackal Canis aureus in South-East Europe—A review. Mamm. Rev. 2021, 51, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrūnaitė, L. Diet composition of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes L.), pine marten (Martes Martes L.) and raccoon dog (Nyctereutes Procyonoides Gray) in clay plain landscape, Lithuania. Acta. Zool. Litu. 2002, 12, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Molnár, T. Diet of otters in three different habitats in Hungary. Folia. Zool. Brno. 2003, 52, 378–388. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrūnaitė, L. Seasonal diet of the otter (Lutra lutra L.) in natural river ecosystems of South-Eastern Lithuania. Acta. Zool. Litu. 2006, 16, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stope, M.B. The raccoon (Procyon lotor) as a neozoon in Europe. Animals 2023, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balčiauskas, L.; Pilāts, V.; Timm, U. Mammal fauna changes in Baltic countries during last three decades. Diversity 2025, 17, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prūsaitė, J. Fauna of Lithuania. Mammals; Mokslas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1988. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).