LINC1467 Activates the IPO8–p65 Axis to Restrict Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Virus Replication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Plasmids and Transfection
2.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Immunoprecipitation and Western Blotting
2.5. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
2.6. RNA Pull-Down Assay
2.7. Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.9. Mouse Model
2.10. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
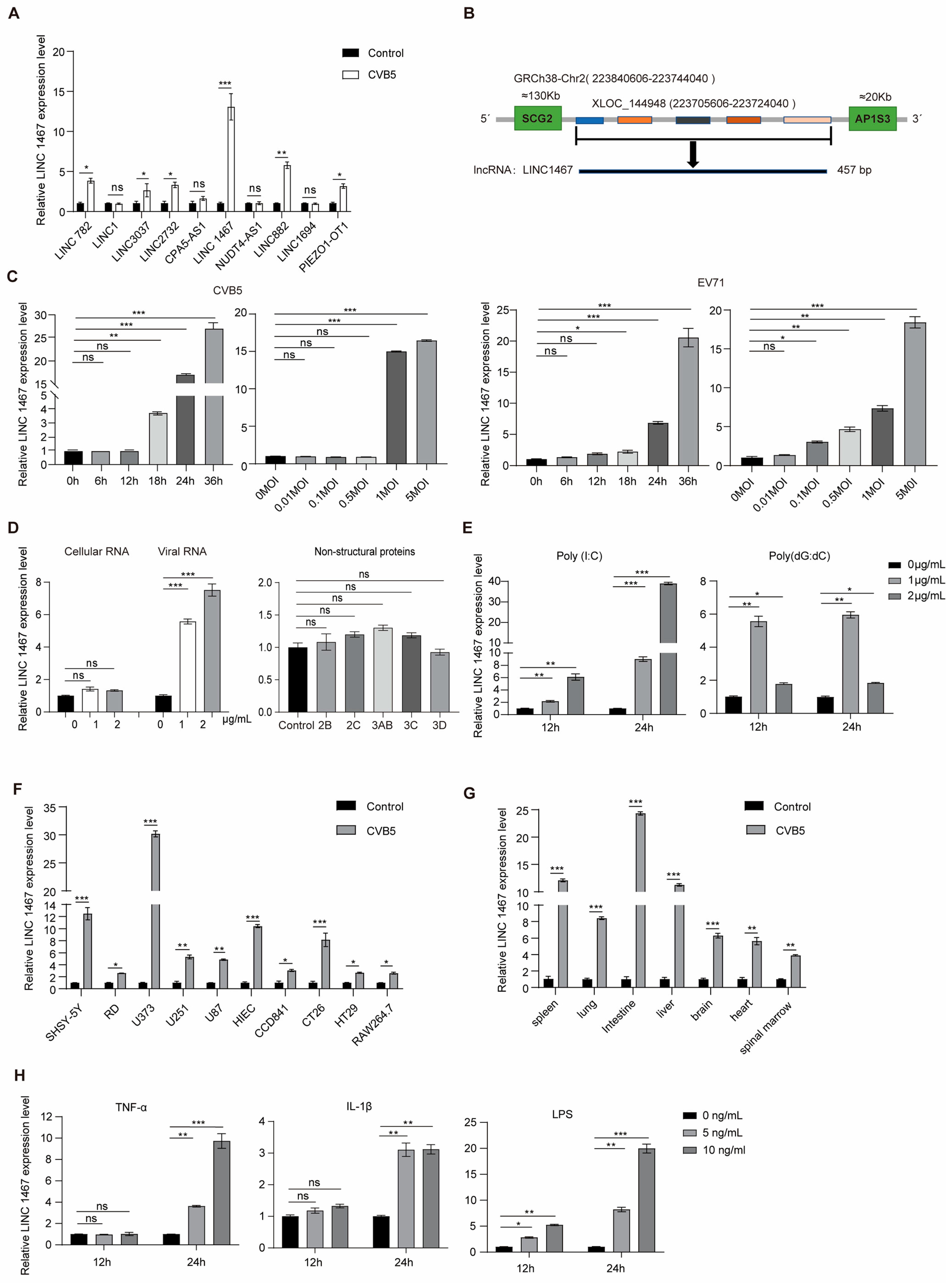
3.1. Characterization of LINC1467 in SH-SY5Y Cells
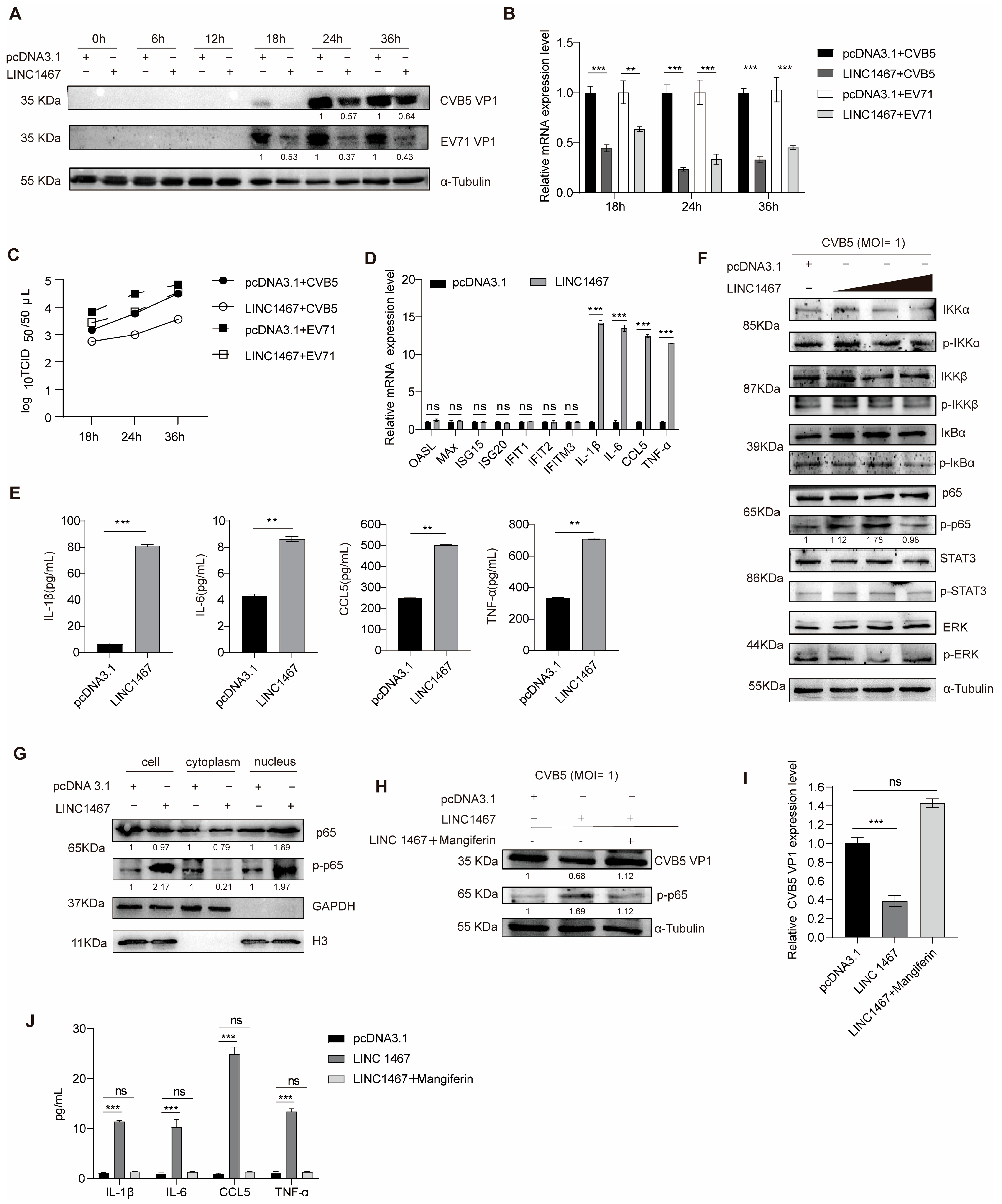
3.2. LINC1467 Suppresses HFMD Pathogen Replication by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway
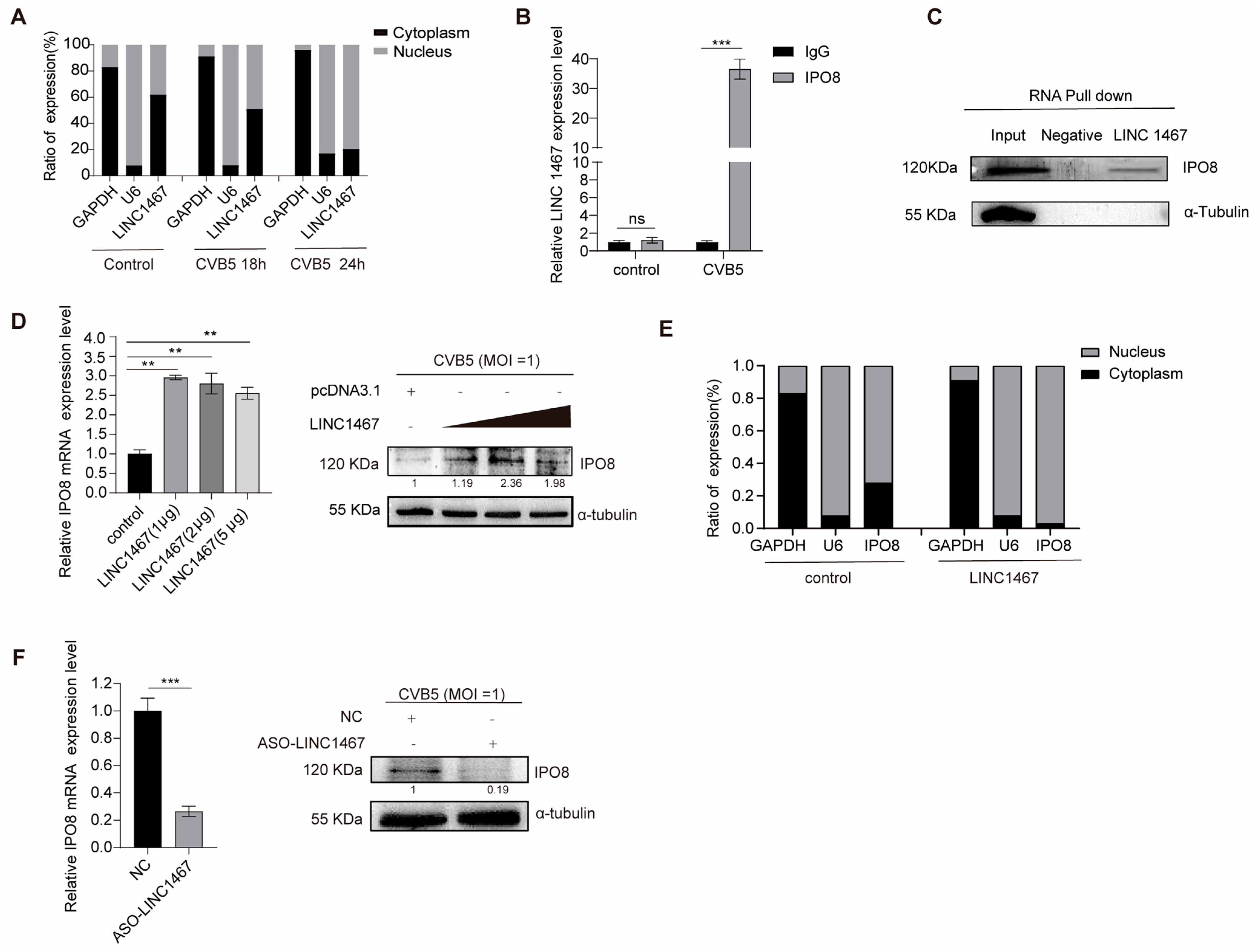
3.3. LINC1467 Specifically Interacts with the Host Protein IPO8
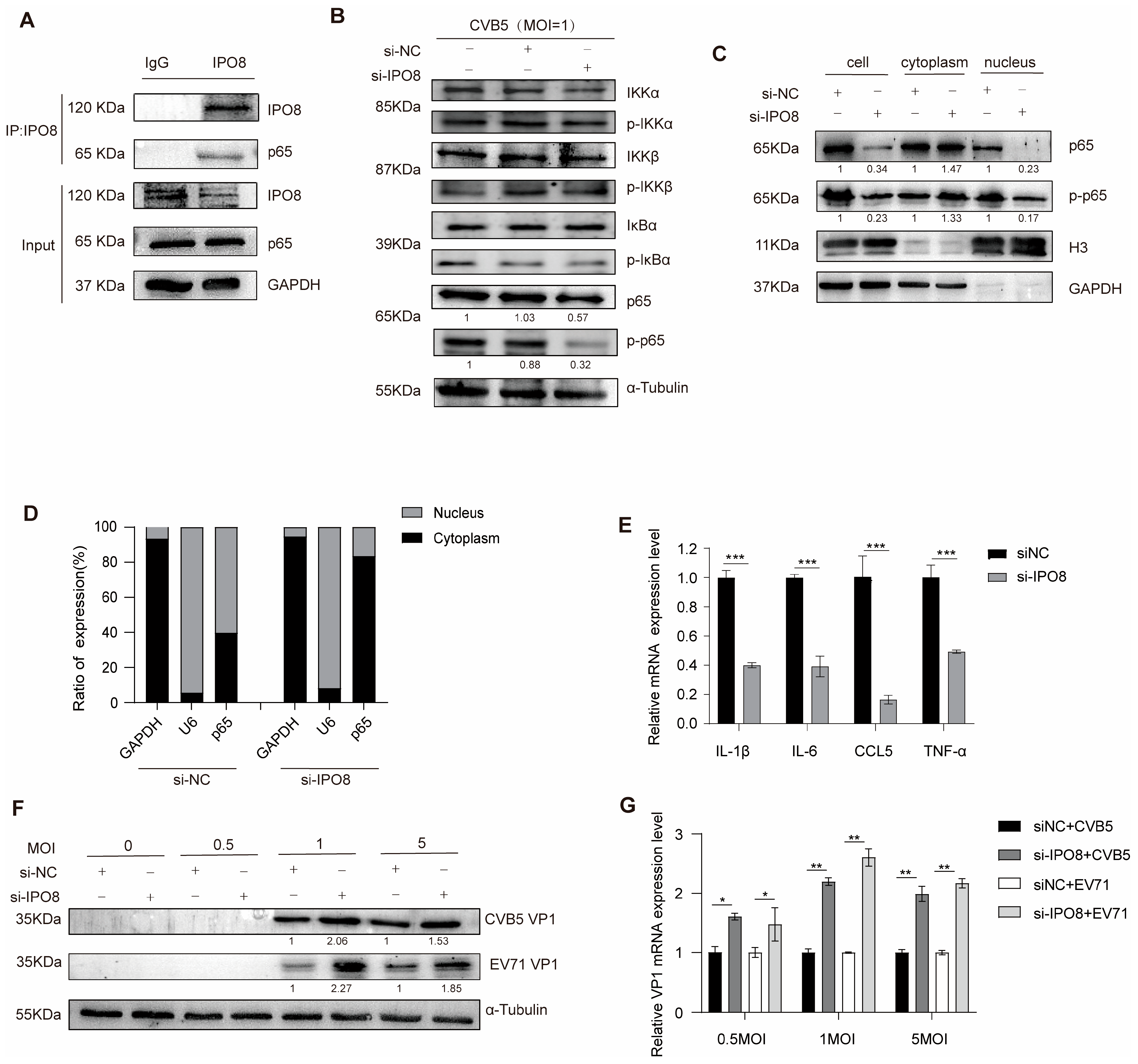
3.4. Functional Characterization of IPO8
3.5. LINC1467 Exerts Its Function in an IPO8-Dependent Manner
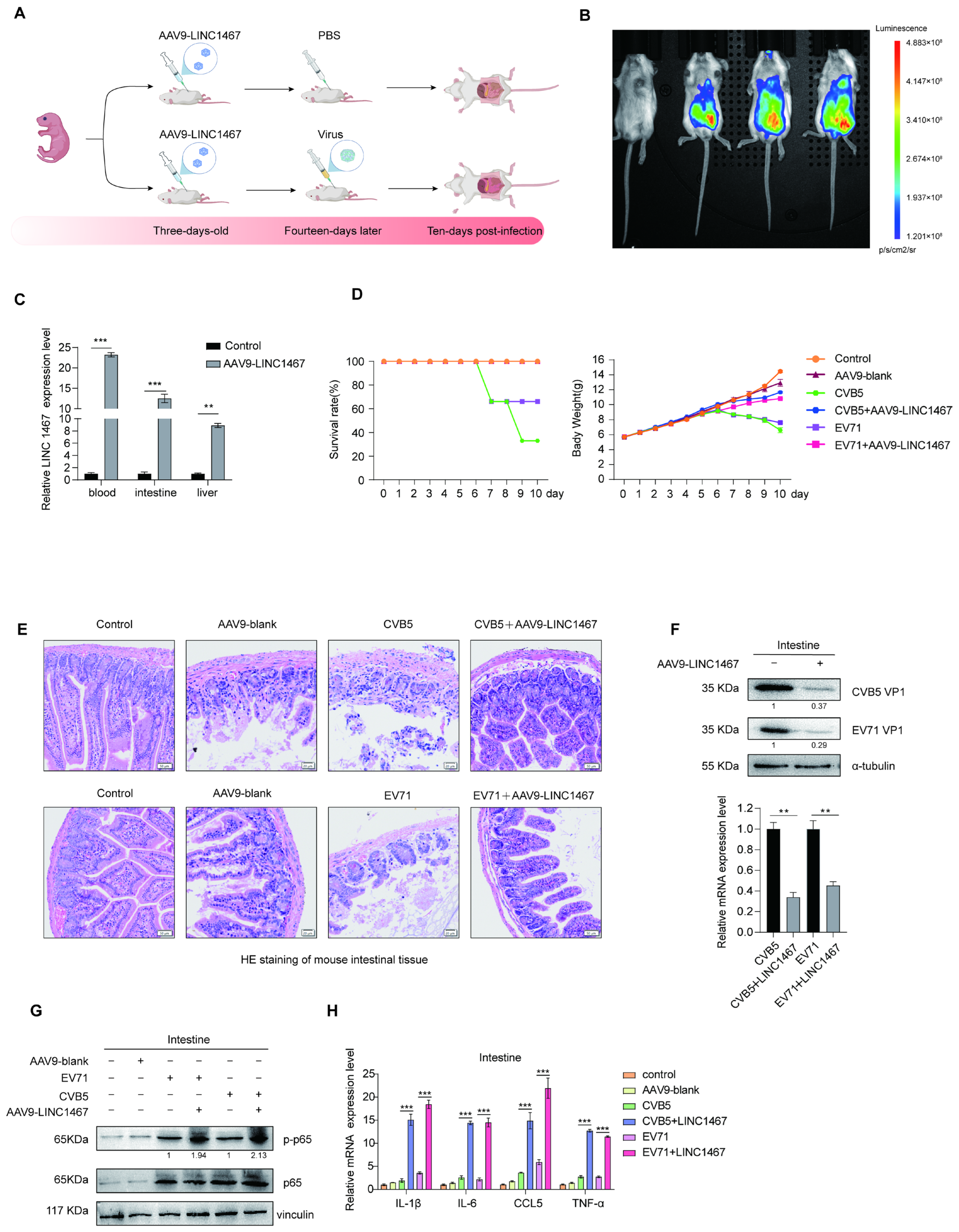
3.6. Validation of the Antiviral Role of LINC1467 in Vivo
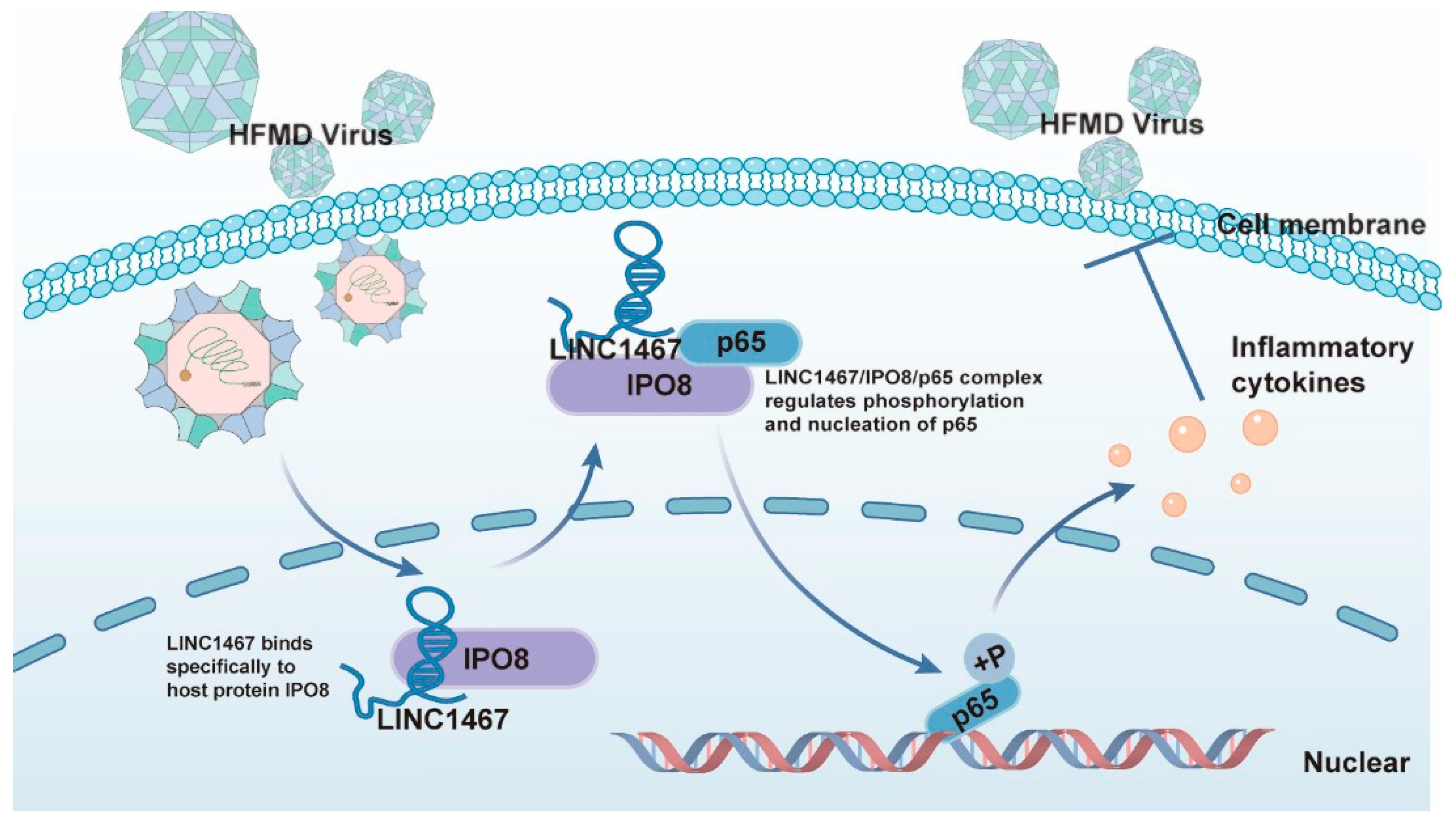
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, P.; Ji, W.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dai, B.; Han, S.; Chen, S.; Jin, Y.; Duan, G. Current status of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, G.; Carr, M.J.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanaoka, N.; Fujimoto, T. Enterovirus-Associated Hand-Foot and Mouth Disease and Neurological Complications in Japan and the Rest of the World. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Razzaque, M.A.; Sangtongdee, U.; Arpnikanondt, C.; Tassaneetrithep, B.; Arthan, D.; Paratthakonkun, C.; Soonthornworasiri, N. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Thailand: A Comprehensive Modelling of Epidemic Dynamics. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 6697522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yi, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreaks before and during availability of EV-A71 vaccine in China’s mainland: Analysis of outbreak surveillance data from 2011 to 2023. Lancet Reg. Health West Pac. 2025, 59, 101603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puenpa, J.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. The History of Enterovirus A71 Outbreaks and Molecular Epidemiology in the Asia-Pacific Region. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.S.; Du, J.; Sun, D.P.; Zhu, Q.R.; Chen, L.Y.; Ye, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.Q.; Cui, F.; Lu, Q.B. A review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology and clinical presentation of coxsackievirus A6 causing hand-foot-mouth disease in China and global implications. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggen, J.; Thibaut, H.J.; Strating, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. The life cycle of non-polio enteroviruses and how to target it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarroux, J.; Morillon, A.; Pinskaya, M. History, Discovery, and Classification of lncRNAs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1008, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vierbuchen, T.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Long non-coding RNAs in antiviral immunity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 111, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Awasthee, N.; Rai, V.; Chava, S.; Gunda, V.; Challagundla, K.B. Long non-coding RNAs and nuclear factor-κB crosstalk in cancer and other human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, L.N.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhao, D.Y.; Liu, F. LncRNA-AK149641 regulates the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α in P815 mast cells by targeting the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, P.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; et al. An NF-κB-responsive long noncoding RNA, PINT, regulates TNF-α gene transcription by scaffolding p65 and EZH2. Faseb. J. 2021, 35, e21667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Cao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Nie, X.; Ruan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ruan, G.; Zhu, Z.; Han, W.; Ding, C. The lncRNA PILA promotes NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis by stimulating the activity of the protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT1. Sci. Signal 2022, 15, eabm6265. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, S.; Sengar, S.; Shree, B.; Mohapatra, S.; Basu, A.; Sharma, V. An RBM10 and NF-κB interacting host lncRNA promotes JEV replication and neuronal cell death. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0118323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, N.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, H.; Guan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Duan, M. LINC01197 inhibits influenza A virus replication by serving as a PABPC1 decoy. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, W. Analysis of the long noncoding RNA profiles of RD and SH-SY5Y cells infected with coxsackievirus B5, using RNA sequencing. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Li, D.; Zhou, G.; Dang, D.; Chen, S.; Sun, T.; Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; et al. Characterization of Critical Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs and mRNAs in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells and Mouse Skeletal Muscle Infected by Enterovirus 71 Using RNA-Seq. Viruses 2018, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Tu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Sheng, J.; Han, S.; Yin, J.; Peng, B.; et al. The long non-coding RNA expression profile of Coxsackievirus A16 infected RD cells identified by RNA-seq. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Teng, P.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, W. Long noncoding RNA 1392 regulates MDA5 by interaction with ELAVL1 to inhibit coxsackievirus B5 infection. Virol. Sin 2023, 38, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Mahony, T.J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Ou, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. LINC2781 enhances antiviral immunity against coxsackievirus B5 infection by activating the JAK-STAT pathway and blocking G3BP2-mediated STAT1 degradation. mSphere 2025, 10, e0006225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, D.; Cong, S.; Du, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Feng, C.; Bao, G.; Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. Co-infection and enterovirus B: Post EV-A71 mass vaccination scenario in China. BMC Infect Dis. 2022, 22, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, L. Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease-Associated Enterovirus and the Development of Multivalent HFMD Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.T.; Aziz, F.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Arguelles, S. Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Shi, H.Y.; Lu, Y.Y.; Lin, J. Centella asiatica alleviates psoriasis through JAK/STAT3-mediated inflammation: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, M. Mangiferin for the Management of Liver Diseases: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudowska-Sawczuk, M.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) in Development and Treatment of COVID-19: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, H.; Su, F.; Li, D.; et al. A cytoplasmic NF-κB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IκB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M. The Crosstalk Between Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs and Nuclear Factor Kappa B in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 775250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Han, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 2014, 344, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Song, X.; Huang, L.; Xiao, J.; Jin, F.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Y. Roles of long non-coding RNAs and emerging RNA-binding proteins in innate antiviral responses. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9407–9424. [Google Scholar]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Chi, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, G.F.; et al. NRAV, a long noncoding RNA, modulates antiviral responses through suppression of interferon-stimulated gene transcription. Cell Host Microbe. 2014, 16, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakielny, S.; Dreyfuss, G. Transport of proteins and RNAs in and out of the nucleus. Cell 1999, 99, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Importin 8 regulates the transport of mature microRNAs into the cell nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10270–10275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Duclaux-Loras, R.; Revenu, C.; Charbit-Henrion, F.; Begue, B.; Duroure, K.; Grimaud, L.; Guihot, A.L.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Zarhrate, M.; et al. Bi-allelic variants in IPO8 cause a connective tissue disorder associated with cardiovascular defects, skeletal abnormalities, and immune dysregulation. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2021, 108, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiao, Y.; He, J.; Wang, W.; Du, Y.; Yu, X. Importin 8 is involved in human periodontitis by the NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 711–716. [Google Scholar]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CVB5-VP1 | CCAGTGCCCACGAAATAAA | TTGCCTATGCTGATGAACGGT |
| EV71-VP1 | GCAGCGGAACCGACTACTTTG | GCCTGYCTAAGRCCTGCGAA |
| Human-LINC1467 | CTGCCCTTGACACCTCAAAGA | AACAGAGGCAAACAGTCTCCA |
| Mouse-LINC1467 | CGGTGCAGGAGAATCTGTCA | AACAGAGGCAAACAGTCTCCA |
| TNF-α | GCCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCTAC | GGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGAT |
| IL-1β | ACCTTCCAGGATGAGGACATGA | CTAATGGGAACGTCACACACCA |
| IL-6 | CACATGTTCTCTGGGAAATCG | TTGTATCTCTGGAAGTTTCAGAT |
| CCL5 | CGCTGTCATCCTCATTGCTA | CCATTTCTTCTGGGTT |
| OASL | TTGTGCCTGCCTACAGAGC | TTCAGCTTAGTTGGCCGATGT |
| MXA | TTCAGCACCTGATGGCCTATC | TGGATGATCAAAGGGATGTGG |
| ISG15 | CTCTGAGCATCCTGGTGAGGAA | AAGGTCAGCCAGAACAGGTCGT |
| ISG20 | TGACCTGAAGCACGACTTCC | CAGGCTGTTCTGGATGCTCT |
| IFIT1 | TCTCAGAGGAGCCTGGCTAAG | CCACACTGTATTTGGTGTCTAGG |
| IFIT2 | ACCTCTGGACTGGCAATAGC | GTCAGGATTCAGCCGAATGG |
| IFITM3 | CATCGTCATCCCAGTGCTGAT | ATGGAAGTTGGAGTACGTGGG |
| IPO8 | TGTTCAGCTCCTTCCTGATTC | CTTCTTACACTTCCACCATAC |
| GAPDH | GTATGACAACGAATTTGGCTACA | AGCACAGGGTACTTTATTGATGG |
| U6 | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| Name | Interaction Propensity | Z-Score | kDa |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2RTX5 TARS3 | 31.96 | 1.22 | 92 |
| A5YKK6 CNOT1 | 27.54 | 0.94 | 266 |
| B5MCY1 TDRD15 | 29.2 | 1.05 | 221 |
| B5ME19 EIF3CL | 29.78 | 1.08 | 105 |
| O00411 POLRMT | 28.42 | 1 | 138 |
| O14647 CHD2 | 29.65 | 1.08 | 211 |
| O14746 TERT | 29.06 | 1.04 | 126 |
| O14776 TCERG1 | 47.87 | 2.21 | 123 |
| O14787 TNPO2 | 38.15 | 1.6 | 101 |
| O14980 XPO1 | 29.24 | 1.05 | 123 |
| O15037 KHNYN | 26.76 | 0.9 | 74 |
| O15042 U2SURP | 38.02 | 1.6 | 118 |
| O15381 NVL | 34.23 | 1.36 | 95 |
| O15397 IPO8 | 37.06 | 1.54 | 120 |
| O15455 TLR3 | 31.82 | 1.21 | 103 |
| O43143 DHX15 | 27.89 | 0.97 | 90 |
| O43290 SART1 | 50.26 | 2.36 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Luo, Y.; Chen, W. LINC1467 Activates the IPO8–p65 Axis to Restrict Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Virus Replication. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101071
Zhang X, Li J, Ding L, Zhang J, Yang F, Luo Y, Chen W. LINC1467 Activates the IPO8–p65 Axis to Restrict Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Virus Replication. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101071
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaokui, Jinwei Li, Li Ding, Jihong Zhang, Fan Yang, Yonghan Luo, and Wei Chen. 2025. "LINC1467 Activates the IPO8–p65 Axis to Restrict Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Virus Replication" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101071
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, J., Ding, L., Zhang, J., Yang, F., Luo, Y., & Chen, W. (2025). LINC1467 Activates the IPO8–p65 Axis to Restrict Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Virus Replication. Pathogens, 14(10), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101071






