Genome-Wide Identification of Novel miRNAs and Infection-Related Proteins in Leishmania major via Comparative Analysis of the Protozoa, Vectors, and Mammalian Hosts
Abstract
1. Introduction
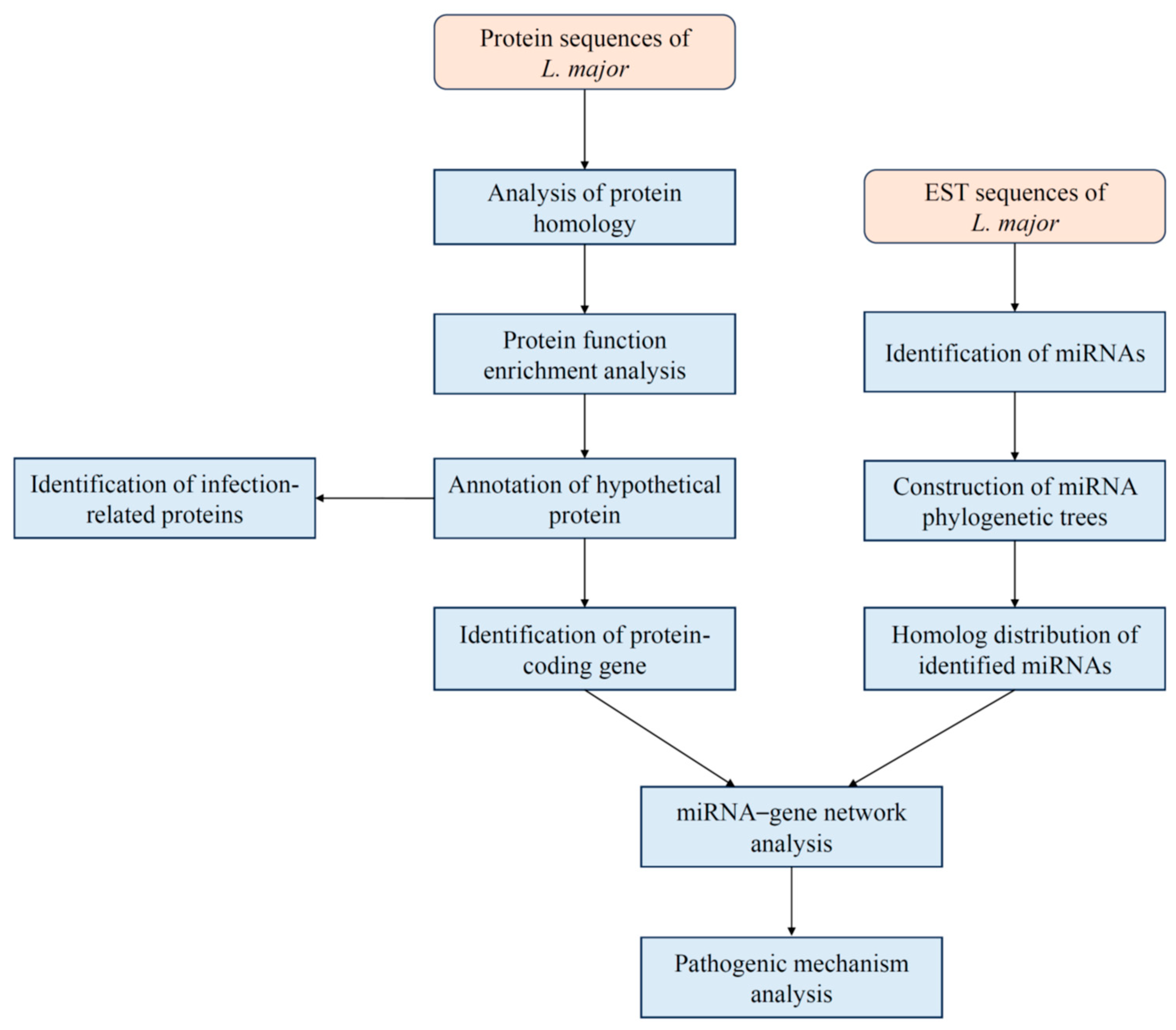
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome and Proteome Retrieval
2.2. Protein Homology Analysis
2.3. Protein Function Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Hypothetical Protein Annotation
2.5. Infection-Related Protein Identification
2.6. Identification of Novel miRNA
- (1)
- Maximum of 2 mismatches allowed;
- (2)
- Prediction of the minimum free energy frequency (FMFE) of matching sequence fragments using RNAfold (version 2.3) [19], with a cutoff FMFE ≤ 0.05;
- (3)
- Prediction of hairpin-like secondary structures using RNAfold (version 2.3);
- (4)
- Significant negative values of minimum folding free energy (MFE) and MFE index (MFEI) for secondary structures, calculated using:
2.7. Construction of miRNA Phylogenetic Tree
2.8. Distribution of Identified miRNAs
2.9. Construction of miRNA-Gene Interaction Network
3. Results
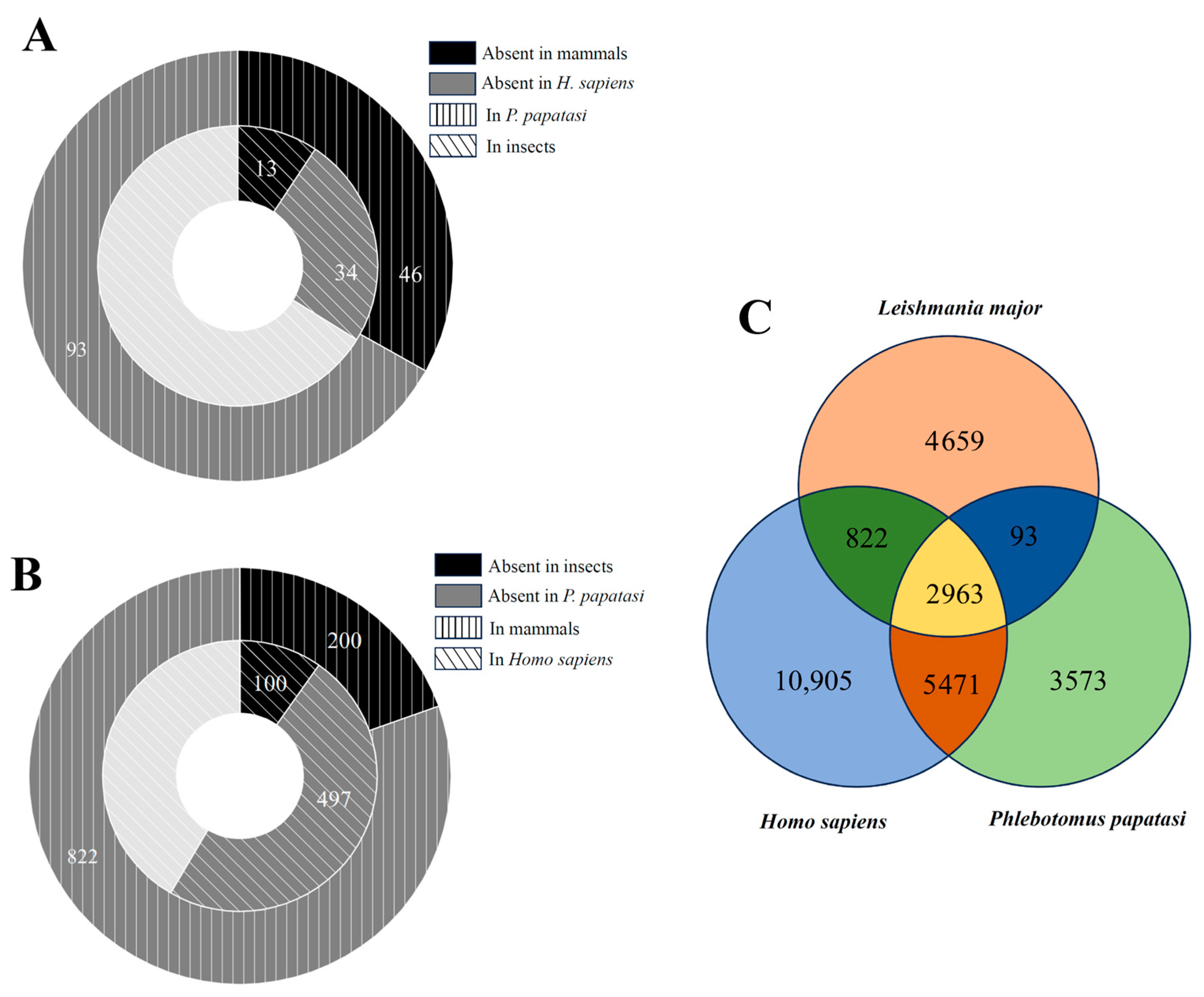
3.1. Protein Homolog Among L. major, Insects, and Mammals
3.2. Protein Distribution Among L. major, P. papatasi, and Humans
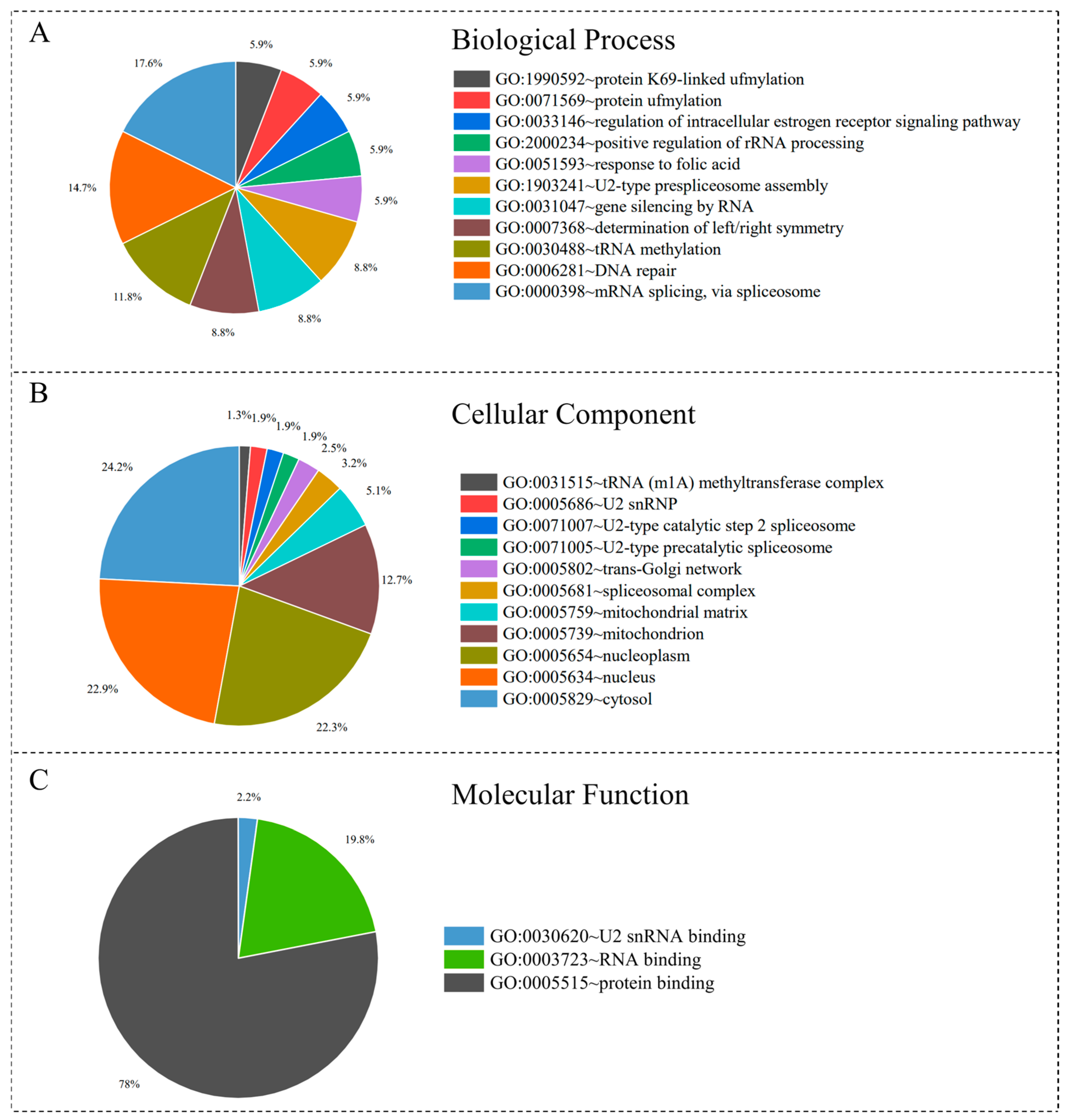
3.3. Function Enrichment Analysis of Homologous Proteins
3.4. Annotation of Hypothetical Proteins
3.5. Infection-Related Protein Analysis
3.6. Novel miRNA Analysis
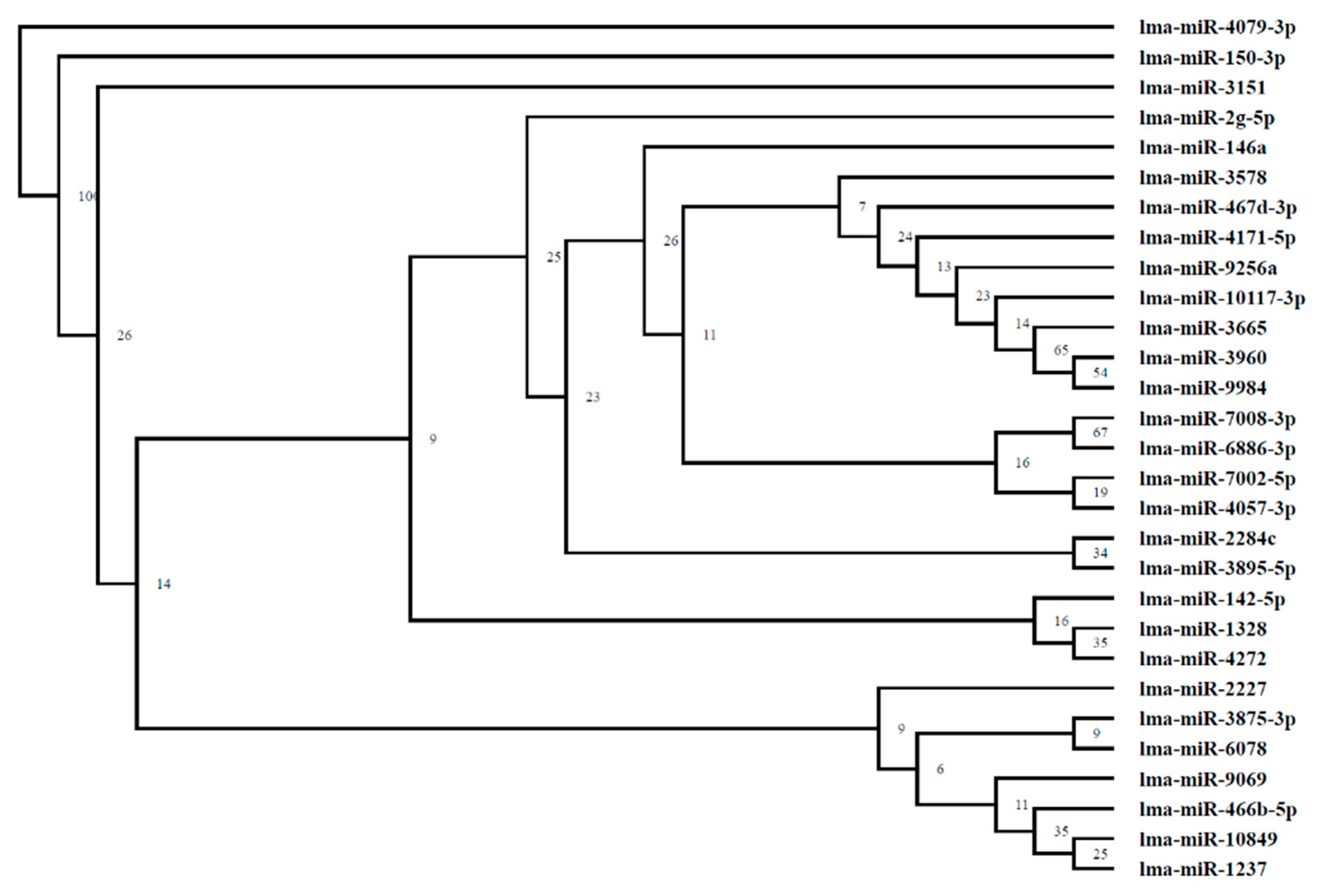
3.7. Analysis of miRNA Phylogenetic Tree
3.8. Distribution of Identified miRNAs in Mammals
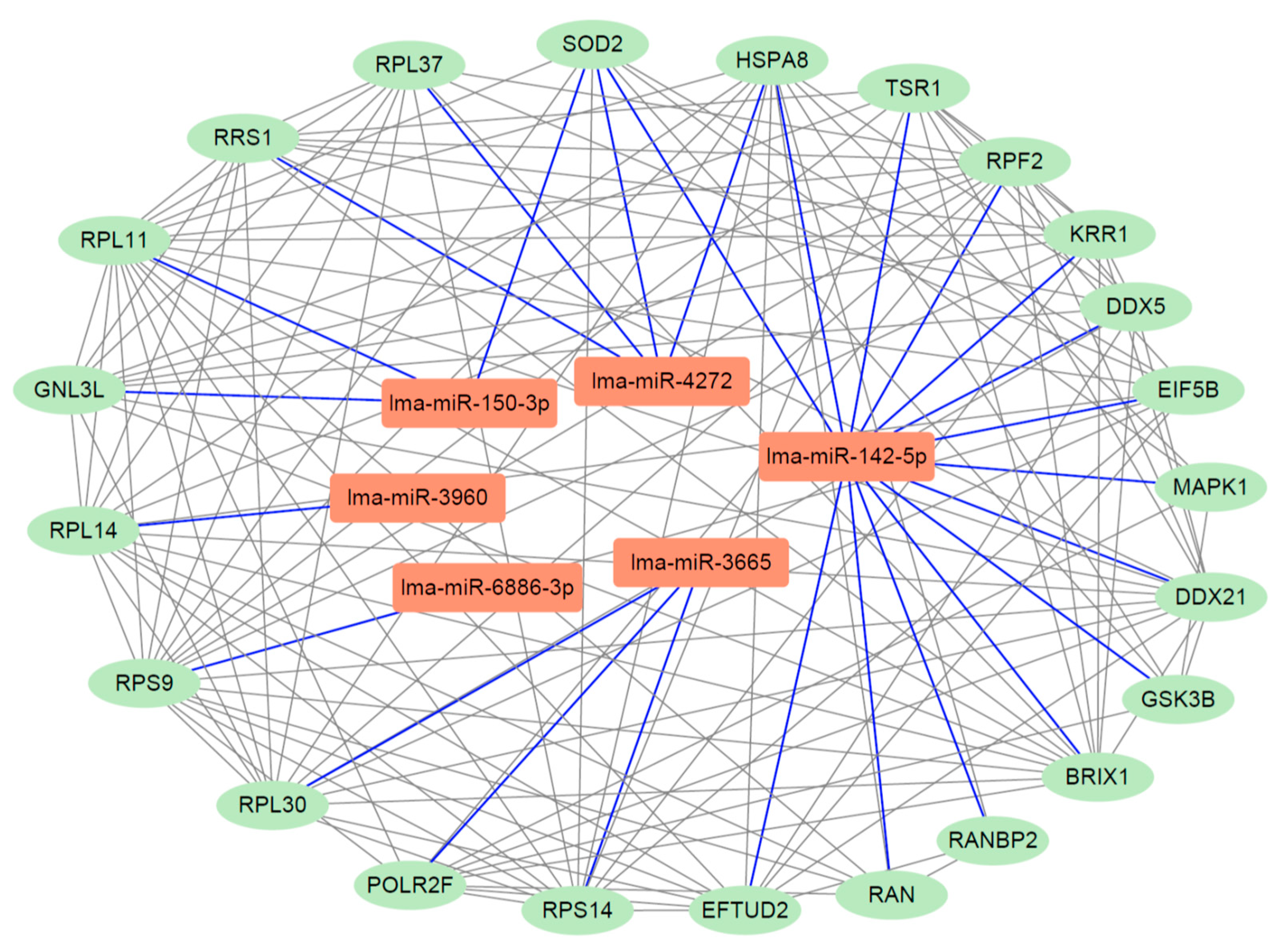
3.9. Analysis of miRNA-Gene Interaction Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcghee, S.; Angus, N.; Finnegan, A.; Lewis-Pierre, L.; Ortega, J. Assessment and treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the emergency department. Emerg. Nurse 2023, 28, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piyasiri, S.B.; Dewasurendra, R.; Samaranayake, N.; Karunaweera, N. Diagnostic Tools for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania donovani: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, P.M.; Matlashewski, G.; Mohan, S.; Le Rutte, E.; Mondal, D.; Khamesipour, A.; Malvolti, S. Vaccine value profile for leishmaniasis. Vaccine 2023, 41, S153–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivens, A.C.; Peacock, C.S.; Worthey, E.A.; Murphy, L.; Aggarwal, G.; Berriman, M.; Sisk, E.; Rajandream, M.A.; Adlem, E.; Aert, R. The genome of the kinetoplastid parasite, Leishmania major. Science 2005, 309, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, E.; González-De La Fuente, S.; Solana, J.C.; Rastrojo, A.; Carrasco-Ramiro, F.; Requena, J.M.; Aguado, B. Gene annotation and transcriptome delineation on a de novo genome assembly for the reference Leishmania major Friedlin strain. Genes 2021, 12, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Tsui, K.W.S. Investigating function roles of hypothetical proteins encoded by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaj, R.; Mathimaran, A.; Prabhu, D.; Ramachandran, B.; Jeyaraman, J.; Muthupandian, S.; Asmelash, T. In silico approaches for the identification of potential allergens among hypothetical proteins from Alternaria alternata and its functional annotation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsarkar, P.; Ingale, P.; Singh, S. Systems studies uncover miR-146a as a target in leishmania major infection model. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12516–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Bappy, M.N.I.; Islam, M.S. Identification of conserved miRNAs and their targets in Jatropha curcas: An in silico approach. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2023, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.; Yao, D. Genome-Wide Screening for Pathogenic Proteins and microRNAs Associated with Parasite-Host Interactions in Trypanosoma brucei. Insects 2022, 13, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, A.; Smirlis, D. Leishmania protein kinases: Important regulators of the parasite life cycle and molecular targets for treating leishmaniasis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium The Uniprot. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. A tight link between orthologs and bidirectional best hits in bacterial and archaeal genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.L.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W.Z. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitherer, S.; Clos, J.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M.; Schleicher, U.; Bogdan, C.; Soulat, D. Characterization of the protein tyrosine phosphatase LmPRL-1 secreted by Leishmania major via the exosome pathway. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00084-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalavi, K.; Jorjani, O.; Faghihi, M.A.; Mowla, S.J. Cytokine gene expression alterations in human macrophages infected by Leishmania major. Cell J. Yakhteh 2021, 22, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Catta-Preta, C.; Neish, R.; Sadlova, J.; Powell, B.; Alves-Ferreira, E.; Geoghegan, V.; Carnielli, J.; Newling, K.; Hughes, C. Systematic functional analysis of Leishmania protein kinases identifies regulators of differentiation or survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Lorenz, R. The ViennaRNA Web Services. RNA Bioinform. 2015, 1269, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.D.; Cui, S.D.; Huang, Y.X.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.T.; Bao, J.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.L.; et al. miRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Lopes, C.T.; Huck, G.; Dong, Y.; Sumer, O.; Bader, G.D. Cytoscape.js: A graph theory library for visualisation and analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wan, R.; Shi, Y. Molecular mechanisms of pre-mRNA splicing through structural biology of the spliceosome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, A.; Bruno, F.; Castelli, G.; Persico, G.; Buffi, G.; Ceccarelli, M.; Ligi, D.; Mannello, F.; Vitale, F.; Magnani, M. Transcriptional signatures in human macrophage-like cells infected by Leishmania infantum, Leishmania major and Leishmania tropica. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashatan, N.A.; Tavirani, M.R.; Zali, H.; Koushki, M.; Ahmadi, N. Prediction of Leishmania major key proteins via topological analysis of protein-protein interaction network. Galen Med. J. 2018, 7, e1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerns, S.J.; Agafonov, R.V.; Cho, Y.J.; Pontiggia, F.; Otten, R.; Pachov, D.V.; Kutter, S.; Phung, L.A.; Murphy, P.N.; Thai, V. The energy landscape of adenylate kinase during catalysis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Tang, P.W.; Welles, J.E.; Pan, W.; Javed, Z.; Elhaw, A.T.; Mythreye, K.; Kimball, S.R.; Hempel, N. HuR-dependent SOD2 protein synthesis is an early adaptation to anchorage-independence. Redox Biol. 2022, 53, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonam, S.R.; Ruff, M.; Muller, S. HSPA8/HSC70 in immune disorders: A molecular rheostat that adjusts chaperone-mediated autophagy substrates. Cells 2019, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization World Health. Leishmaniasis: Key Facts. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Taylor, S.S.; Kornev, A.P. Protein kinases: Evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somee, R.; Eslami, G.; Vakili, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase and aquaglyceroporin gene expression in treatment failure Leishmania major. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Anand, A.; Bhat, A.; Maras, J.S.; Goyal, N. Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis unravels MAPK1 regulated phosphoproteins in Leishmania donovani. J. Proteom. 2021, 240, 104189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Valapala, M. Regulation of autophagy by the glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Cao, X.; Sun, S.; Sun, B.; Gao, J. Inhibition of GSK3B phosphorylation improves glucose and lipid metabolism disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Pawar, S.A.; Mishra, N.; Pawar, H. Revisiting the Sequenced Sand Fly Phlebotomus Papatasi Proteome. Acta Parasitol. 2025, 70, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, S.; Daum, P.; Danzer, H.; Hauke, M.; Jäck, H.M.; Wittmann, J. Identification of miR-128 target mRNAs that are expressed in B cells using a modified dual luciferase vector. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Accession Number | Current Annotation | Our Annotated Protein | Gene | E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | XP_001686672.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Intraflagellar transport protein 122 | IFT122 | 2.27 × 10−149 |
| 2 | XP_888594.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 21B | TTC21B | 1.57 × 10−117 |
| 3 | XP_001684649.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 2 protein homolog | Bbs2 | 2.43 × 10−103 |
| 4 | XP_001686229.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | BCS1-like protein | BCS1L | 1.14 × 10−83 |
| 5 | XP_001685262.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment protein 3 | ERGIC3 | 1.49 × 10−77 |
| 6 | XP_001686195.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Carnosine N-methyltransferase | CARNMT1 | 7.04 × 10−72 |
| 7 | XP_001682610.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Intraflagellar transport 80 | IFT80 | 2.75 × 10−68 |
| 8 | XP_003722084.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | WD repeat domain 34 | DYNC2I2 | 2.63 × 10−66 |
| 9 | XP_003722065.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Cilia and flagella associated protein 58 | CFAP58 | 5.87 × 10−61 |
| 10 | XP_001682381.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 27 | TTC27 | 1.01 × 10−58 |
| 11 | XP_001684329.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Zinc finger MYND domain-containing protein 10 | ZMYND10 | 3.96 × 10−56 |
| 12 | XP_001680824.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Basic immunoglobulin-like variable motif-containing protein | BIVM | 5.13 × 10−56 |
| 13 | XP_001683666.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | PWP1 homolog, endonuclein | PWP1 | 8.23 × 10−54 |
| 14 | XP_003722868.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | Hypoxia up-regulated protein 1 | HYOU1 | 9.27 × 10−53 |
| 15 | XP_001682917.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | tRNA (uracil(54)-C(5))-methyltransferase | TRMT2B | 6.68 × 10−52 |
| Group | Accession | Gene | Protein Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase | XP_001683373.1 | PRKAB2 | 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-2 |
| Kinase | XP_003722471.1 | PRKAG1 | 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-1 |
| Kinase | ABE47512.1 | ADK2 | Adenylate kinase 2 |
| Kinase | XP_001681879.1 | ADK7 | Adenylate kinase 7 |
| Kinase | XP_001682080.1 | ADK8 | Adenylate kinase 8 |
| Kinase | XP_001687191.1 | ADK9 | Adenylate kinase 9 |
| Kinase | XP_001686496.1 | BCKDK | Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001684075.1 | CERK | Ceramide kinase |
| Kinase | XP_003722687.1 | DOLK | Dolichol kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001687055.1 | EEF2K | Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001684391.1 | IDNK | Gluconate kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001681095.1 | HUNK | Hormonally up-regulated neu tumor-associated kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001684669.1 | LRRK2 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 |
| Kinase | XP_001682126.1 | FCSK | L-fucose kinase |
| Kinase | QED45586.1 | MEK1 | MAPK/ERK kinase 1 |
| Kinase | XP_001685169.2 | MAP3K1 | Mitogen-activated proteinkinase 1 |
| Kinase | XP_003721529.1 | CMPK2 | Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase |
| Kinase | XP_001684788.1 | PI4KB | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta |
| Kinase | AAK28278.1 | PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 |
| Kinase | XP_001685063.1 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta type |
| Kinase | XP_001681082.1 | STK16 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 16 |
| Kinase | XP_001685938.1 | VPRBP | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VPRBP |
| Kinase | XP_001683073.1 | TK1 | Thymidine kinase, |
| Kinase | XP_001682584.1 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes |
| Tyrosine phosphatase | XP_001681298.1 | DUSP12 | Dual specificity protein phosphatase 12 |
| Tyrosine phosphatase | XP_001686824.1 | ACP3 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase ACP3 |
| Tyrosine phosphatase | XP_001683775.1 | PTPMT1 | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase mitochondrial 1 |
| LMA miRNA | miRNA Sequence | Length | EST Accession | Mismatch | MFE | Frequency of MFE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lma-miR-3151 | ACGGGTGGCGCAATGGGATCAG | 22 | AQ901763.1 | 2 | −43.0 | 3.3% |
| lma-miR-3665 | AGCAGGTGCGGGGCGGCG | 18 | BH018980.1 | 1 | −40.0 | 4.9% |
| lma-miR-3960 | GGCGGCGGCGGAGGCGGGGG | 20 | AQ849868.1 | 1 | −38.2 | 3.7% |
| lma-miR-9069 | CACGGTGCTGCTGTGGACACG | 21 | AQ902536.1 | 2 | −36.5 | 1.9% |
| lma-miR-3895-5p | ATTGAGTTGATTACGATGG | 19 | AQ848942.1 | 2 | −35.3 | 4.3% |
| lma-miR-146a | TGAGAACTGAATTCCATGGGTT | 22 | AQ848800.1 | 0 | −35.0 | 1.6% |
| lma-miR-150-3p | CTGGTACAGAGGATGGAAGGG | 21 | AQ901862.1 | 2 | −33.6 | 2.5% |
| lma-miR-1328 | GAGAGAGAAATGAGAACT | 18 | BH019430.1 | 1 | −31.6 | 2.2% |
| lma-miR-1237 | TCTTTCTGCTCCGTCCCCCAG | 21 | T93471.1 | 2 | −30.4 | 5.0% |
| lma-miR-9984 | CGCCGCGGCGGCGGCGGC | 18 | AQ848798.1 | 0 | −30.3 | 3.2% |
| lma-miR-7002-5p | TTGGCTTCGGGGAGTACGTGG | 21 | AL160967.1 | 2 | −30.3 | 0.7% |
| lma-miR-10117-3p | GCGGACCATTCAAGATCATC | 20 | AL354177.1 | 2 | −29.0 | 4.2% |
| lma-miR-2284c | AAAAAGTTCGTTTTGGTTTT | 20 | AQ846415.1 | 1 | −28.1 | 4.8% |
| lma-miR-4272 | CATTCAACTAGTGATTGT | 18 | AQ853128.1 | 2 | −27.9 | 3.3% |
| lma-miR-3875-3p | TATTTGCGCTAGATAGCGC | 19 | BH020336.1 | 2 | −27.1 | 3.6% |
| lma-miR-2227 | TGGCAGTGTTGAAAGACGTC | 20 | BH885692.1 | 2 | −26.7 | 2.7% |
| lma-miR-142-5p | CCCATAAAGTAGAAAGCACT | 20 | BH018364.1 | 2 | −26.7 | 4.1% |
| lma-miR-9256a | TGATCTGGCCACTCAGTGTG | 20 | BH885819.1 | 2 | −26.2 | 0.6% |
| lma-miR-466b-5p | TATGTGTGTGTGTATGTCCATG | 22 | AA680932.1 | 1 | −25.7 | 1.4% |
| lma-miR-6886-3p | TGCCCTTCTCTCCTCCTGCCT | 21 | AQ847748.1 | 2 | −21.3 | 3.3% |
| lma-miR-3578 | GAATCCACCACGAACAACTTC | 21 | AQ850014.1 | 1 | −20.8 | 1.0% |
| lma-miR-7008-3p | TGTGCTTCTTGCCTCTTCTCAG | 22 | AL160615.1 | 2 | −19.1 | 0.7% |
| lma-miR-2g-5p | CTCTCCCAATTGTTGTCATGTG | 22 | AL160715.1 | 2 | −17.9 | 0.8% |
| lma-miR-10849 | ACTGTGAGCGCAGAATCTCCT | 21 | AQ845711.1 | 1 | −17.4 | 0.6% |
| lma-miR-6078 | CCGCCTGAGCTAGCTGTGG | 19 | AQ843843.1 | 2 | −17.3 | 2.0% |
| lma-miR-4171-5p | TGACTCTCTTAAGGAAGCCA | 20 | BH885526.1 | 1 | −16.7 | 3.9% |
| lma-miR-4079-3p | TAGCTCTAGCTGATGTAGCA | 20 | AQ844078.1 | 2 | −16.4 | 0.4% |
| lma-miR-4057-3p | TTTGCTACGGCCACCAAGATCT | 22 | AQ849400.1 | 2 | −16.2 | 1.5% |
| lma-miR-467d-3p | ATATACATACACACACCTACAC | 22 | AA728206.1 | 2 | −15.4 | 2.2% |
| LMA miRNA | Mammal | Non-Mammal | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa | mmu | efu | bta | ptr | oan | eca | cja | oni | bma | pte | cin | hpo | cbr | |
| lma-miR-3151 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-3665 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-3960 | YES | YES | ||||||||||||
| lma-miR-9069 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-3895-5p | ||||||||||||||
| lma-miR-150-3p | YES | YES | ||||||||||||
| lma-miR-1328 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-1237 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-9984 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-7002-5p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-10117-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-2284c | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-4272 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-3875-3p | ||||||||||||||
| lma-miR-2227 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-142-5p | YES | YES | YES | |||||||||||
| lma-miR-9256a | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-466b-5p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-6886-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-3578 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-7008-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-2g-5p | YES | YES | ||||||||||||
| lma-miR-10849 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-6078 | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-4171-5p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-4079-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-4057-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-467d-3p | YES | |||||||||||||
| lma-miR-146a | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Qian, J.; Yan, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z. Genome-Wide Identification of Novel miRNAs and Infection-Related Proteins in Leishmania major via Comparative Analysis of the Protozoa, Vectors, and Mammalian Hosts. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101068
Liu T, Qian J, Yan Y, Zeng X, Yang Z. Genome-Wide Identification of Novel miRNAs and Infection-Related Proteins in Leishmania major via Comparative Analysis of the Protozoa, Vectors, and Mammalian Hosts. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101068
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tianyi, Jinyang Qian, Yicheng Yan, Xi Zeng, and Zhiyuan Yang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of Novel miRNAs and Infection-Related Proteins in Leishmania major via Comparative Analysis of the Protozoa, Vectors, and Mammalian Hosts" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101068
APA StyleLiu, T., Qian, J., Yan, Y., Zeng, X., & Yang, Z. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of Novel miRNAs and Infection-Related Proteins in Leishmania major via Comparative Analysis of the Protozoa, Vectors, and Mammalian Hosts. Pathogens, 14(10), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101068






