Comparative Analysis of Concentration and Quantification Methods for Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Their Phage-Mediated Dissemination in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Comparison of ARG Concentration Methods in Treated Wastewater
2.3. Treated Wastewater and Biosolids DNA Extraction
2.4. Purification of Phage Particles
2.5. ARGs Quantification Methods
2.5.1. qPCR Quantification Settings and Reaction Conditions
2.5.2. ddPCR Quantification Settings and Reaction Conditions
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
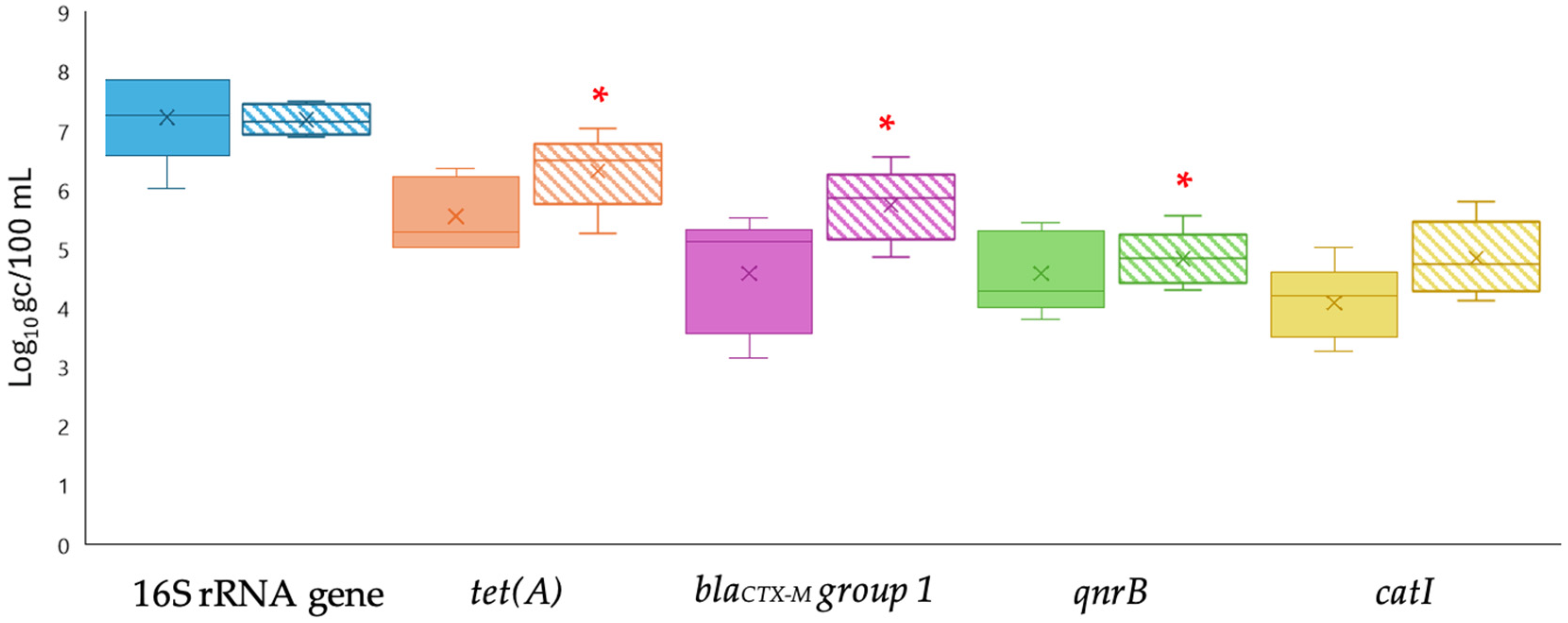
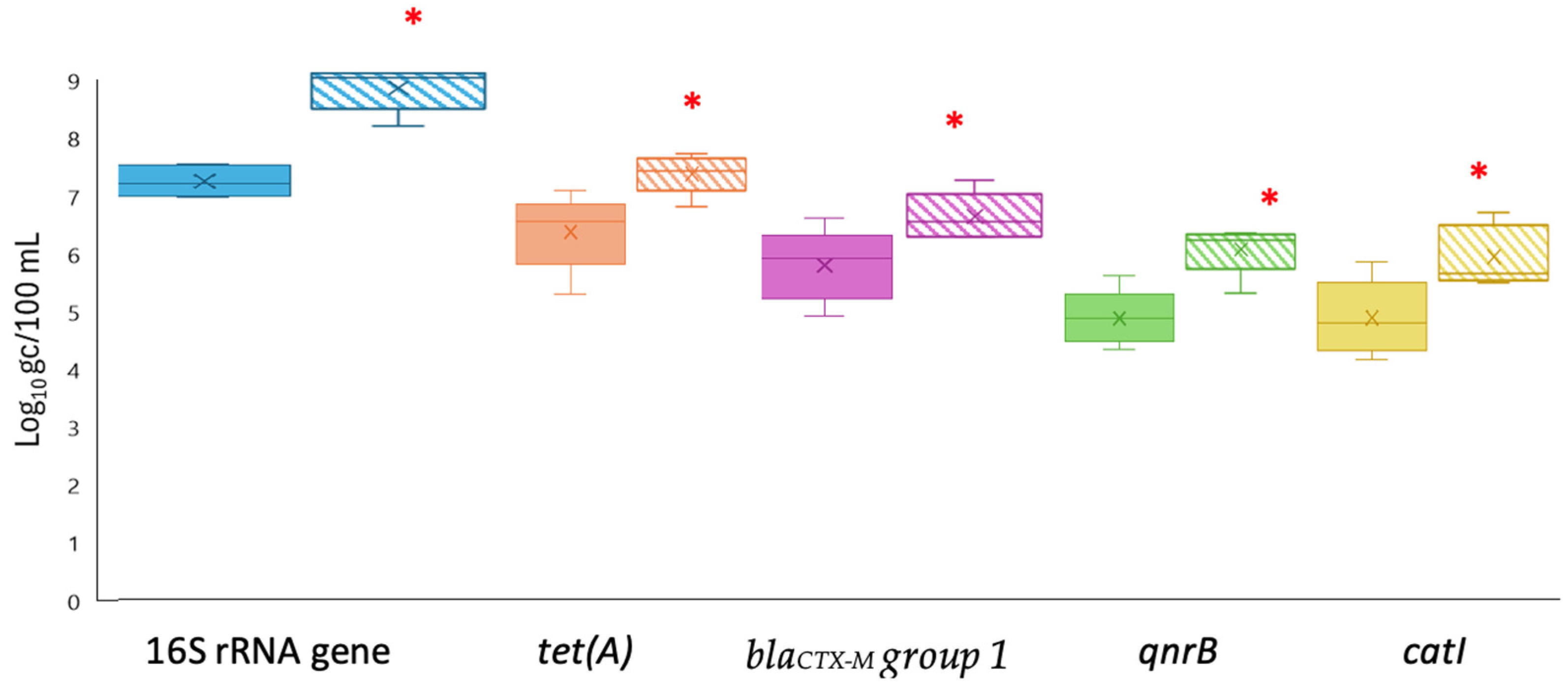
3.1. Comparison of ARG Concentration Methods in Treated Wastewater by qPCR
3.2. Comparison of qPCR and ddPCR Methods for ARG Quantification
3.3. Detection of ARGs in the Phage Fraction in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Shin, H.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.; Hur, H.-G. Resistome Study in Aquatic Environments. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drane, K.; Sheehan, M.; Whelan, A.; Ariel, E.; Kinobe, R. The Role of Wastewater Treatment Plants in Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance: Source, Measurement, Removal and Risk Assessment. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 May 2020 on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX%3A32020R0741 (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Lin, H.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Luo, Y. Enhanced sensitivity of extracellular antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) to environmental concentrations of antibiotic. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.; Bohm, K.; Dyet, K.; Weaver, L.; Pattis, I. Comparative analysis of qPCR and metagenomics for detecting antimicrobial resistance in wastewater: A case study. BMC Res. Notes 2025, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, K.; Keenum, I.; Calarco, J.; Davis, B.C.; Milligan, E.M.; Harwood, V.J.; Pruden, A. Standardizing Methods with QA/QC Standards for Investigating the Occurrence and Removal of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria/Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARB/ARGs) in Surface Water, Wastewater, and Recycled Water. Available online: https://www.waterrf.org/research/projects/standardizing-methods-qaqc-standards-investigating-occurrence-and-removal (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Ma, C.; Zhou, F.; Lu, D.; Xu, S.; Luo, J.; Gan, H.; Gao, D.; Yao, Z.; He, W.; Kurup, P.U.; et al. Quantification and cultivation of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) from various urban water environments: A comprehensive analysis of precondition methods and sample characteristics. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Greenwald, H.; Kennedy, L.C.; Kantor, R.S.; Jiang, R.; Pisarenko, A.; Chen, E.; Nelson, K.L. Microbial Water Quality through a Full-Scale Advanced Wastewater Treatment Demonstration Facility. ACS ES T Eng. 2022, 2, 2206–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Han, Z.; Su, D.; Luan, X.; Yu, L.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. Assessing impacts of municipal wastewater treatment plant upgrades on bacterial hazard contributions to the receiving urban river using SourceTracker. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.-H.; Luo, X.-Y.; Liu, D.-F.; Han, J.; Wang, H.-D.; Min, D.; Yu, H.-Q. Optimized Antibiotic Resistance Genes Monitoring Scenarios Promote Sustainability of Urban Water Cycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9636–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekalski, N.; Gascón Díez, E.; Bürgmann, H. Wastewater as a point source of antibiotic-resistance genes in the sediment of a freshwater lake. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Belkum, A.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Mallard, F.; Rochas, O.; Dunne, W.M. Innovative and rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Han, Q.; Yu, Q.; Wanyan, R.; Li, H. Bibliometric analysis of papers on antibiotic resistance genes in aquatic environments on a global scale from 2012 to 2022: Evidence from universality, development and harmfulness. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-Throughput Droplet Digital PCR System for Absolute Quantitation of DNA Copy Number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughesman, C.B.; Lu, X.J.D.; Liu, K.Y.P.; Zhu, Y.; Poh, C.F.; Haynes, C. A Robust Protocol for Using Multiplexed Droplet Digital PCR to Quantify Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Clinical Tissue Specimens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Laperriere, G.; Germain, H. Droplet Digital PCR versus qPCR for gene expression analysis with low abundant targets: From variable nonsense to publication quality data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, T.; Adell, A.D.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Spégel, P.; Turner, C.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Fuursted, K.; Lood, R. Biogeographical variation in antimicrobial resistance in rivers is influenced by agriculture and is spread through bacteriophages. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 4869–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, O.; Nichols, D.; Rocha-Melogno, L.; Bivins, A.; Berendes, D.; Soria, F.; Andrade, M.; Deshusses, M.A.; Bergin, M.; Brown, J. Antimicrobial resistance genes are enriched in aerosols near impacted urban surface waters in La Paz, Bolivia. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniesa, M.; García, A.; Miró, E.; Mirelis, B.; Prats, G.; Jofre, J.; Navarro, F. Bacteriophages and Diffusion of β-lactamase Genes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabban, A.D.; Hite, E.; Callaway, T.R. Evolution of Foodborne Pathogens via Temperate Bacteriophage-Mediated Gene Transfer. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.H.; Pourtois, J.D.; Haddock, N.L.; Furukawa, D.; Kelly, K.E.; Amanatullah, D.F.; Burgener, E.; Milla, C.; Banaei, N.; Bollyky, P.L. Prophages are infrequently associated with antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. mSphere 2025, 10, e00904-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enault, F.; Briet, A.; Bouteille, L.; Roux, S.; Sullivan, M.B.; Petit, M.-A. Phages rarely encode antibiotic resistance genes: A cautionary tale for virome analyses. ISME J. 2017, 11, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L. Implications of bacteriophages on the acquisition and spread of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, R. The role of bacteriophages in facilitating the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Jaque, M.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Muniesa, M. Transfer of antibiotic-resistance genes via phage-related mobile elements. Plasmid 2015, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzaka, T.; Tani, K.; Nasu, M. High-frequency phage-mediated gene transfer in freshwater environments determined at single-cell level. ISME J. 2010, 4, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jończyk, E.; Kłak, M.; Międzybrodzki, R.; Górski, A. The influence of external factors on bacteriophages—review. Folia Microbiol 2011, 56, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; et al. Role played by the environment in the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) through the food chain. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, M.U.; Nwobi, O.C.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Ezeonu, I.M. Mobile Tigecycline Resistance: An Emerging Health Catastrophe Requiring Urgent One Health Global Intervention. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 808744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, N.P.; Svanevik, C.S.; Ghavidel, F.Z.; Grevskott, D.H. First report of mobile tigecycline resistance gene tet(X4)-harbouring multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from wastewater in Norway. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, M.; Nucleo, E.; Spalla, M.; Zara, F.; Novazzi, F.; Marchetti, V.M.; Piazza, A.; Bitar, I.; De Cicco, M.; Paolucci, S.; et al. Occurrence of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamases, KPC-Type, and MCR-1.2-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from Wells, River Water, and Wastewater Treatment Plants in Oltrepò Pavese Area, Northern Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Dasí, D.; González, A.; Ferrús, M.A.; Castillo, M.Á. Occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes in agricultural irrigation waters from Valencia city (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer-Lluch, M.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Jebri, S.; Hmaied, F.; Muniesa, M.; Jofre, J. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacterial and bacteriophage fractions of Tunisian and Spanish wastewaters as markers to compare the antibiotic resistance patterns in each population. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenum, I.; Liguori, K.; Calarco, J.; Davis, B.C.; Milligan, E.; Harwood, V.J.; Pruden, A. A framework for standardized qPCR-targets and protocols for quantifying antibiotic resistance in surface water, recycled water and wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 4395–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Truchado, P.; Cordero-García, R.; Gil, M.I.; Soler, M.A.; Rancaño, A.; García, F.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Allende, A. Surveillance on ESBL-Escherichia coli and Indicator ARG in Wastewater and Reclaimed Water of Four Regions of Spain: Impact of Different Disinfection Treatments. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Randazzo, W.; Falcó, I.; Allende, A.; Sánchez, G. Comparing analytical methods to detect SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrañaga, O.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Quirós, P.; Gómez-Gómez, C.; Blanch, A.R.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Muniesa, M. Phage particles harboring antibiotic resistance genes in fresh-cut vegetables and agricultural soil. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Sung, K.; Nawaz, M.S. Detection of aacA-aphD, qacEδ1, marA, floR, and tetA genes from multidrug-resistant bacteria: Comparative analysis of real-time multiplex PCR assays using EvaGreen® and SYBR® Green I dyes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2011, 25, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallenne, C.; Da Costa, A.; Decré, D.; Favier, C.; Arlet, G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important β-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.B.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, E.-C.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. Prevalence of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Determinants over a 9-Year Period. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.H.; Huh, M.-D.; Kim, E.; Lee, H.-H.; Jeong, H.D. Characterization of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene by multiplex polymerase chain reaction in multidrug-resistant strains isolated from aquatic environments. Aquaculture 2003, 217, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fujimoto, C.; Haruki, Y.; Maeda, T.; Kokeguchi, S.; Petelin, M.; Arai, H.; Tanimoto, I.; Nishimura, F.; Takashiba, S. Quantitative real-time PCR using TaqMan and SYBR Green for Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, tetQ gene and total bacteria. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno Ferraro, G.; Bonomo, C.; Brandtner, D.; Mancini, P.; Veneri, C.; Briancesco, R.; Coccia, A.M.; Lucentini, L.; Suffredini, E.; Bongiorno, D.; et al. Characterisation of microbial communities and quantification of antibiotic resistance genes in Italian wastewater treatment plants using 16S rRNA sequencing and digital PCR. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2024, 933, 173217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaz, H.; Younas, S.; Abosalif, K.O.A.; Junaid, K.; Alzahrani, B.; Alsrhani, A.; Abdalla, A.E.; Ullah, M.I.; Qamar, M.U.; Hamam, S.S.M. Molecular analysis of blaSHV, blaTEM, and blaCTX-M in extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae recovered from fecal specimens of animals. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sghaier, S.; Abbassi, M.S.; Pascual, A.; Serrano, L.; Díaz-De-Alba, P.; Said, M.B.; Hassen, B.; Ibrahim, C.; Hassen, A.; López-Cerero, L. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from animal origin and wastewater in Tunisia: First detection of O25b-B23-CTX-M-27-ST131 Escherichia coli and CTX-M-15/OXA-204-producing Citrobacter freundii from wastewater. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgren, J.; Matussek, A.; Mattsson, A.; Svensson, L.; Lindgren, P.-E. Prevalence of norovirus and factors influencing virus concentrations during one year in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Muniesa, M. Persistence of naturally occurring antibiotic resistance genes in the bacteria and bacteriophage fractions of wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 95, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavé, L.; Brothier, E.; Abrouk, D.; Bouda, P.S.; Hien, E.; Nazaret, S. Efficiency and sensitivity of the digital droplet PCR for the quantification of antibiotic resistance genes in soils and organic residues. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10597–10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Rana, A.; Sung, W.; Munir, M. Competitiveness of Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) and Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction (ddPCR) Technologies, with a Particular Focus on Detection of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs). Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraka, V.; Andersson, T.; Makenga, G.; Francis, F.; Minja, D.T.R.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Tang, M.-H.E.; Fuursted, K.; Lood, R. Unveiling Rare Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance in Tanzanian Cholera Outbreak Waters. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, I.; Khalifa, L.; Gallois, N.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Klümper, U.; Youdkes, D.; Palmony, S.; Dagai, L.; Berendonk, T.U.; Merlin, C.; et al. Microbiome and Resistome Profiles along a Sewage-Effluent-Reservoir Trajectory Underline the Role of Natural Attenuation in Wastewater Stabilization Reservoirs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00170-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Petrin, S.; Fontaneto, D.; Losasso, C.; Eckert, E.M.; Tassistro, G.; Borello, A.; Ricci, A.; Wilson, W.H.; Pruzzo, C.; et al. ddPCR applied on archived Continuous Plankton Recorder samples reveals long-term occurrence of class 1 integrons and a sulphonamide resistance gene in marine plankton communities. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, W.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Drzymała, J.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S. Wastewater treatment plants as a reservoir of integrase and antibiotic resistance genes—An epidemiological threat to workers and environment. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-Guzmán, I.; Sánchez-Alberola, S.; Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Falcó, I.; Díaz-Reolid, A.; Puchades-Colera, P.; Ballesteros, S.; Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Coll, J.M.; Núñez, E.; et al. Longitudinal study on the multifactorial public health risks associated with sewage reclamation. npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, T.C.; Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Jerome, K.R. Tolerance of Droplet-Digital PCR vs Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Inhibitory Substances. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidstedt, M.; Rådström, P.; Hedman, J. PCR inhibition in qPCR, dPCR and MPS—Mechanisms and solutions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawaju, B.R.; Yan, G. Assessment of Common Factors Associated with Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Quantification of Paratrichodorus allius in Soil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, M.A.; Boehm, A.B.; Salit, M.; Spencer, S.K.; Wigginton, K.R.; Noble, R.T. The Environmental Microbiology Minimum Information (EMMI) Guidelines: qPCR and dPCR Quality and Reporting for Environmental Microbiology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10210–10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, D.; Peruzy, M.F.; Aponte, M.; Mancusi, A.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Capuano, F.; Murru, N. Comparison of droplet digital PCR vs real-time PCR for Yersinia enterocolitica detection in vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 354, 109321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, C.; Calderon, M.N.; Arias, M.M.; Leguizamon, J.E. Validation of Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction for Salmonella spp. Quantification. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H.; Kim, E.; Yang, S.-M.; Kim, D.-S.; Suh, S.-M.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, H.-Y. Comparison of Real-Time PCR and Droplet Digital PCR for the Quantitative Detection of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum. Foods 2022, 11, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Gai, Z.; Huo, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Xing, S.; Shi, G.; Shi, F.; et al. Comparison between digital PCR and real-time PCR in detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Quantitative PCR Assays for Quantitative Detection of Xanthomonas citri Subsp. citri. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, D.; Narvhus, J.; Skeie, S.B. Detection and quantification of Bacillus cereus group in milk by droplet digital PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 127, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer-Lluch, M.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Bacteriophage DNA Fraction of Environmental Samples. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Variatza, E.; Balcázar, J.L. Bacteriophages as a reservoir of extended-spectrum β -lactamase and fluoroquinolone resistance genes in the environment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O456–O459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz Barron, M.; Kneis, D.; Elena, A.X.; Bagra, K.; Berendonk, T.U.; Klümper, U. Quantification of the mobility potential of antibiotic resistance genes through multiplexed ddPCR linkage analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2023, 99, fiad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshini, J.; Raj, M.; Karunasagar, I. Prevalence of blaCTX-M-15 in Coliphages Isolated from Sewage. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, K.; Song, G.; Zhao, S.; Liu, R. Risk control of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) during sewage sludge treatment and disposal: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaia, C.M.; Rocha, J.; Scaccia, N.; Marano, R.; Radu, E.; Biancullo, F.; Cerqueira, F.; Fortunato, G.; Iakovides, I.C.; Zammit, I.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in wastewater treatment plants: Tackling the black box. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Effects of emerging pollutants on the occurrence and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.C.; Paul, J.H. Gene Transfer by Transduction in the Marine Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2780–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Wintersdorff, C.J.H.; Penders, J.; van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Wolffs, P.F.G. Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Microbial Ecosystems through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, B.J.; Partridge, S.R.; Sheppard, A.E. Impacts of mobile genetic elements on antimicrobial resistance genes in gram-negative pathogens: Current insights and genomic approaches. Microbiol. Res. 2026, 302, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Antibiotic Group | Target Gene | Oligonucleotide | Sequence | qPCR and ddPCR Conditions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline | tet(A) | FW | CCGCGCTTTGGGTCATT | 95 °C for 10 min; 40 cycles of (95 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 1 min) | [39] |
| R | TGGTCGCGTCCCAGTGA | ||||
| Probe | FAM-TCGGCGAGGATCG-BHQ1 | ||||
| β-lactam | blaCTX-M group 1 | FW | TTAGGAARTGTGCCGCTGYA | 50 °C for 2 min; 95 °C for 3 min; 40 cycles of (95 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min) | [40] |
| R | CGATATCGTTGGTGGTRCCAT | ||||
| Quinolones | qnrB | FW | GATCGTGAAAGCCAGAAAGG | 50 °C for 2 min; 95 °C for 3 min; 40 cycles of (95 °C for 5 s, 50 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min) | [41] |
| R | ATGAGCAACGATGCCTGGTA | ||||
| Chloramphenicol | catI | FW | GGTGATATGGGATAGTGTT | 50 °C for 2 min; 95 °C for 3 min; 40 cycles of (95 °C for 5 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min) | [42] |
| R | CCATCACATACTGCATGATG | ||||
| 16S rRNA gene | F1048 | GTGSTGCAYGGYTGTCGTCA | 50 °C for 2 min; 95 °C for 3 min; 35 cycles of (95 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min) | [43] | |
| R1194 | ACGTCRTCCMCACCTTCCTC | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falcó, I.; Allende, A.; Cutripi, F.; Aznar, R.; Sánchez, G.; Truchado, P. Comparative Analysis of Concentration and Quantification Methods for Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Their Phage-Mediated Dissemination in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101050
Falcó I, Allende A, Cutripi F, Aznar R, Sánchez G, Truchado P. Comparative Analysis of Concentration and Quantification Methods for Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Their Phage-Mediated Dissemination in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101050
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalcó, Irene, Ana Allende, Francesca Cutripi, Rosa Aznar, Gloria Sánchez, and Pilar Truchado. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Concentration and Quantification Methods for Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Their Phage-Mediated Dissemination in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101050
APA StyleFalcó, I., Allende, A., Cutripi, F., Aznar, R., Sánchez, G., & Truchado, P. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Concentration and Quantification Methods for Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Their Phage-Mediated Dissemination in Treated Wastewater and Biosolids. Pathogens, 14(10), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101050









