Abstract
(1) Background: Methylobacterium radiotolerans (M. radiotolerans) is a fastidious, aerobic, Gram-negative bacillus primarily found in environmental sources such as soil and sewage, with rare clinical isolation. Its identification remains challenging due to poor growth with conventional culture methods. (2) Case presentation: A 42-year-old male patient with early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ETP-ALL) presented with M. radiotolerans bacteremia during hospitalization. The organism was successfully isolated from peripheral blood using the Myco/F Lytic culture vial (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Lincoln, MT, USA). Comparative analysis demonstrated markedly superior growth of M. radiotolerans in Myco/F Lytic culture vials compared with Plus Aerobic/F Lytic and Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F culture vials (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Lincoln, MT, USA). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing, performed with the epsilometer test (E-test) and Bauer–Kirby disk diffusion (BK) method, guided the selection of an appropriate therapeutic regimen. The patient’s infection was ultimately controlled following targeted antimicrobial therapy. (3) Conclusions: M. radiotolerans demonstrates a distinct growth preference for the Myco/F Lytic culture medium. This observation highlights the importance of considering alternative culture media in cases of rare or fastidious bacterial infections that cannot be reliably detected using conventional Plus Aerobic/F Lytic or Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F culture vials, which are typically employed for clinical isolation of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
1. Introduction
M. radiotolerans is an aerobic, slow-growing, Gram-negative bacillus that forms characteristic pink-pigmented colonies [1]. This bacterium is predominantly isolated from environmental sources such as leaf surfaces, soil, and sewage [2,3]. Although generally considered to have low pathogenicity, it acts as an opportunistic pathogen in immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with underlying conditions such as leukemia, end-stage renal disease, or organ transplantation [4,5]. Of note, indwelling intravascular devices represent a major risk factor for bloodstream infections, and most of the previously reported clinical cases have been catheter-related [5,6]. Furthermore, as a pseudomonad, M. radiotolerans is capable of forming surface-associated capsules and demonstrates tolerance to chlorine-based disinfectants and elevated temperatures [7]. These traits facilitate its persistence in healthcare environments, where it has been detected in hospital tap water [3], creating opportunities for nosocomial transmission.
Notably, due to its fastidious nature, M. radiotolerans is hardly detectable under conventional culture conditions, which may partly explain the limited number of documented clinical infections [4,8,9,10]. Here, we report a confirmed case of M. radiotolerans bloodstream infection identified via the BACTEC™ Myco/F Lytic Culture Vial (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Lincoln, MT, USA), describe its morphological features during culture, and present its antimicrobial susceptibility profile.
2. Case Description
On 2 July 2024, a 42-year-old male with ETP-ALL was admitted with a 10-day history of sore throat, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, and intermittent fever. On admission, vital signs were stable, and physical examination revealed a 2 × 2 cm ulcerated, crusted wound on the right ankle. Peripheral blood smear revealed numerous round or oval blasts, characterized by large nuclei with finely granular chromatin, well-defined nuclear membranes, occasional nuclear indentations or clefts, and one to two prominent nucleoli. The cytoplasm was minimal, exhibiting a pale blue hue (Figure 1A). Bone marrow smear demonstrated markedly hypercellular proliferation, predominantly composed of pro-lymphoblasts. The blasts exhibited large nuclei with finely dispersed chromatin, thickened nuclear membranes, occasional nuclear indentations and clefts, and prominent nucleoli, typically single. The cytoplasm ranged from scant to moderate in volume, with a gray-blue appearance, occasionally containing small vacuoles (Figure 1B). Specific laboratory tests are presented in Table 1.
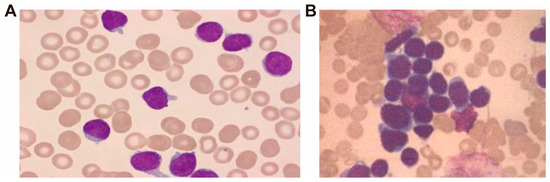
Figure 1.
Cytomorphological features of peripheral blood (A) and bone marrow (B) smear, Wright-Giemsa stain, ×400.

Table 1.
Specific laboratory tests during hospitalization.
For ongoing management, a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) was placed on 5 July. On hospital day 6, following initiation of chemotherapy, the patient developed a fever (38.6 °C). Peripheral blood cultures were obtained using BACTEC™ Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F and Plus Aerobic/F Lytic Culture Vials, but no organisms were isolated. The fever resolved transiently with meropenem and loxoprofen. However, on 11 July, the patient experienced recurrent fever (38.3 °C). Repeated blood cultures using the same culture vials remained negative. The patient still had recurrent fever despite empirical treatment with vancomycin and loxoprofen. Multiple subsequent cultures over the following days yielded no growth after 7 days of incubation.
On 21 July 2024, the patient developed a high-grade fever (40.4 °C) accompanied by a marked elevation in PCT (33 ng/mL). Empiric antimicrobial therapy was escalated to include vancomycin, imipenem, and caspofungin, alongside antipyretics including intravenous lysergic acid, indomethacin suppositories, and oral loxoprofen. Concurrently, peripheral blood was inoculated into Plus Aerobic/F Lytic, Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F, and Myco/F Lytic culture vials. Only the Myco/F Lytic vial flagged positive at 75 h; the other vials remained negative after 7 days.
Gram staining of the positive culture revealed rod-shaped and occasionally bifurcated Gram-negative bacilli (Figure 2A). Subculture on blood agar and China blue agar plates (37 °C, 5% CO2) yielded sparse, small pink colonies on the blood agar plate after four days (Figure 2B). Identification via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) (ZHUHAI DL BIOTECH Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China) confirmed M. radiotolerans with >99.9% confidence, which was corroborated by 16S rRNA gene sequencing (GenBank accession: PV362230; performed by Beijing Ruibo Xingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).
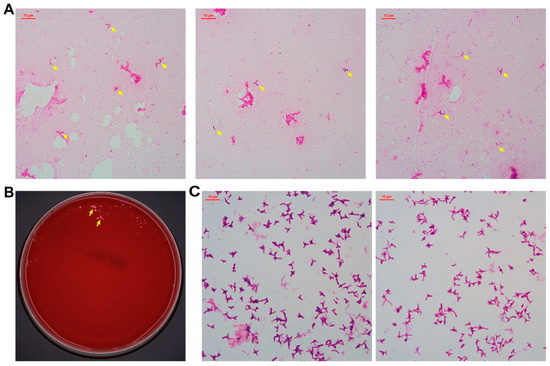
Figure 2.
Cell morphology and colony appearance of M. radiotolerans isolates. Gram staining after growing in Myco/F Lytic culture vials for 75 h, and these arrows point to M. radiotolerans (A). After 4 days on blood agar, and these arrows point to M. radiotolerans colonies (B). Gram staining after 5 days on blood agar (C).
Following laboratory identification of the pathogen, the PICC was removed, and antimicrobial therapy was adjusted to imipenem combined with levofloxacin based on experience from previous M. radiotolerans infection case reports [6]. The patient subsequently experienced defervescence and a gradual decline in PCT levels (Figure 3). The patient was discharged on 31 July 2024, with a one-week course of oral levofloxacin. At follow-up two weeks later, the patient remained afebrile and free of infectious symptoms.
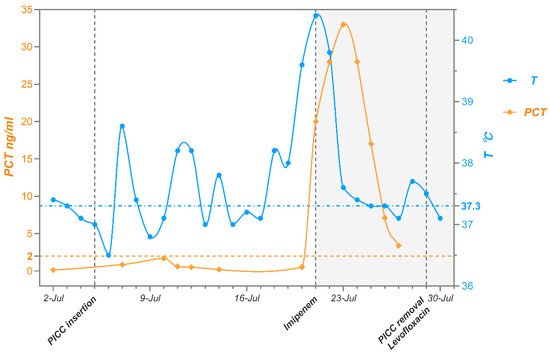
Figure 3.
Temperature and PCT trends during the patient’s hospitalization.
3. Additional Microbiological Studies
In this case, the isolation and identification of M. radiotolerans were pivotal for diagnosis and therapeutic decision-making. Notably, the organism was successfully detected only in the Myco/F Lytic culture vial, while multiple cultures using Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F and Plus Aerobic/F Lytic culture vials remained negative. This observation suggested that M. radiotolerans may have a growth preference for the Myco/F Lytic culture medium.
To evaluate this hypothesis, a controlled experiment was conducted. A standardized suspension of M. radiotolerans (10–50 CFU/mL) in sterile saline was inoculated (1 mL per vial) into Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F, Plus Aerobic/F Lytic, and Myco/F Lytic culture vials [11]. All vials were incubated in the BD BACTEC™ FX Blood Culture System (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Baltimore, MD, USA) for up to 14 days. Only the Myco/F Lytic culture vials flagged positive, with an average detection time of 71 h; the other vials remained negative. Subsequent subculture on Mueller-Hinton agar confirmed the presence of M. radiotolerans, supporting the feasibility of Myco/F Lytic culture vials for cultivating this fastidious organism.
Prior to strain identification, routine clinical cultures using blood agar and China blue agar incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 yielded limited growth, with only small colonies observed on the blood agar plate, consistent with previous reports [5]. Given the slow growth rate of M. radiotolerans, antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) using the VITEK 2 Automated System (bioMérieux, Craponne, France) was not feasible. Therefore, AST was conducted using standard methods for Gram-negative bacilli, including the E-test and BK methods.
Considering earlier studies reporting poor growth of M. radiotolerans on Mueller-Hinton (MH) and blood MH agar under standard conditions [5], we subcultured the isolate onto MH agar and incubated it at 30 °C. After three days, satisfactory growth was observed (Figure 4A). Following five days of incubation, clear zones of inhibition were noted around several antibiotic discs (Figure 4B–F). To rule out contamination, multiple colonies with varying morphology from the AST plates were randomly selected for MALDI-TOF MS identification, all confirming M. radiotolerans with high confidence (>99.9%). All agar media used in this study were produced by Thermo Fisher Scientific Biochemical Products (Beijing, China) Co., Ltd.
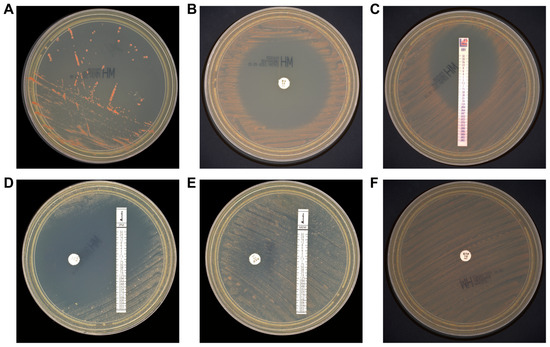
Figure 4.
Colony morphology and antibiotic susceptibility of M. radiotolerans isolates. Colonies appeared on Mueller-Hinton agar after 3 days (A). AST on Mueller-Hinton agar for 5 days. Minocycline (B), eravacycline (C), imipenem (D), meropenem (E), and ertapenem (F).
AST results are presented in Table 2. Neither EUCAST nor CLSI has established specific clinical breakpoints for M. radiotolerans [12]. Therefore, antimicrobial susceptibility interpretation was extrapolated from general susceptibility patterns. Consistent with previous reporting practices, and considering that M. radiotolerans is taxonomically classified within the Pseudomonas genus, we referred to the interpretive criteria established for standard antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa [8,9]. Nevertheless, owing to the prolonged incubation period required for M. radiotolerans isolates, a more conservative approach was applied when evaluating antibiotic susceptibility. In terms of carbapenems, the isolate exhibited susceptibility exclusively to imipenem, while showing resistance to meropenem and ertapenem. It also demonstrated susceptibility to tetracyclines, gentamicin, and levofloxacin, but was resistant to cephalosporins, vancomycin, and aztreonam, findings that are largely consistent with previous reports [3,8].

Table 2.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing results for M. radiotolerans.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
M. radiotolerans is an opportunistic environmental bacterium, with only a few clinical cases reported to date [9,13]. This may be attributed to its low pathogenicity or the challenges associated with its isolation and identification in clinical settings. Table 3 presents the clinical features of M. radiotolerans infections documented in the literature to date. These infections typically occur in immunocompromised individuals with severe underlying conditions. Patients often exhibit pronounced symptoms and limited response to commonly used empirical antibiotics [8]. Delayed or missed diagnosis in such cases can lead to severe consequences [9], underscoring the critical importance of accurate and timely identification.

Table 3.
Clinical features of M. radiotolerans infections are described.
Among these infected patients, leukemia is the most common underlying condition. Similar to the patient in this case, leukemia patients experience severe disruption of the survival space for normal hematopoietic stem cells due to their bone marrow being occupied by malignantly proliferating leukemia cells. This leads to a sharp decline in the number of key immune cells such as neutrophils and lymphocytes. Furthermore, leukemic cells themselves exhibit functional abnormalities, rendering them incapable of mounting effective immune responses [16]. Simultaneously, they secrete multiple immunosuppressive factors (such as TGF-β and IL-10), creating an inhibitory microenvironment that further weakens the function of remaining normal immune cells [17]. Moreover, treatments like chemotherapy or radiotherapy, while eliminating cancer cells, also inflict further damage on the already compromised immune system, resulting in persistent and severe immune deficiency, such as treatment-related neutropenia [18]. This creates an opportunity for pathogens with low pathogenicity like M. radiotolerans to thrive.
This article reports for the first time that M. radiotolerans bacteremia can be effectively detected using Myco/F Lytic blood culture vials, ensuring timely smear microscopy and subculture of positive samples. Final identification was achieved through MALDI-TOF MS or 16S rRNA sequencing. This approach offers a practical workflow for clinical microbiology laboratories, contributes to strain database enrichment, and supports the refinement of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for bloodstream infections. In cases of suspected septic shock with persistently negative results from standard Plus Aerobic/F Lytic and Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F culture vials, Myco/F Lytic culture vials may enhance the detection of this fastidious organism, thereby guiding targeted antimicrobial therapy and potentially improving outcomes in rare bacterial infections.
This study has several limitations. First, the mechanism underlying the improved recovery of M. radiotolerans using Myco/F Lytic culture vials, compared with Plus Aerobic/F Lytic and Lytic/10 Anaerobic/F culture vials, remains unclear. One possible explanation is that M. radiotolerans may be better adapted to low-nutrient environments, whereas nutrient-rich media could suppress its growth [6]. As a fastidious bacterium with a preference for carbon–carbon bond–containing compounds [19], previous reports have shown that it grows well on Sabouraud agar but poorly on chocolate and blood agar [5,8], suggesting that medium composition may directly influence its proliferation. Alternatively, specific components within the Myco/F Lytic vials may promote its growth. Further studies are required to clarify these possibilities and to establish optimal culture conditions that will enhance the isolation and identification of this organism. Second, in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed an unusual carbapenem resistance pattern: M. radiotolerans was highly susceptible to imipenem but exhibited complete resistance to meropenem and ertapenem. The molecular mechanisms underlying this discrepancy remain unknown and warrant further investigation.
Unexplained fever is a thorny problem frequently encountered in clinical practice. This case emphasized the significance of sample collection and submission methods for the detection rate of fastidious bacteria. The successful detection via Myco/F Lytic culture vials underscores their potential utility in improving early diagnosis of this rare organism and may provide a valuable approach for cases with negative standard culture results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.X. and L.L.; methodology, L.L.; validation, J.X. and L.L.; formal analysis, J.X. and L.L.; data curation, J.X.; writing—original draft preparation, J.X.; writing—review and editing, X.Q. and Y.X.; visualization, J.X.; supervision, X.Q.; project administration, X.Q. and Y.X.; funding acquisition, Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding, grant number 2022-PUMCH-B-074.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (I-5PJ0129 2025-01-10).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the subject involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| M. radiotolerans | Methylobacterium radiotolerans |
| ETP-ALL | Early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| E-test | Epsilometer test |
| BK | Bauer-Kirby disk diffusion |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PICC | Peripherally inserted central catheter |
| MALDI-TOF MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| AST | Antibiotic susceptibility testing |
| MH | Mueller-Hinton |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
References
- Holt, J.G.; Krieg, N.R.; Sneath, P.H.A.; Staley, J.T.; Williams, S.T. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.I.S.; Brandao, E.; Santos, E.; Batista, M.V.A.; Estevam, C.S.; Alexandre, M.R.; Fernandes, M.F. Pendimethalin biodegradation by soil strains of Burkholderia sp. and Methylobacterium radiotolerans. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20210924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhata, K.; Kato, Y.; Goto, K.; Hara, M.; Yoshida, S.; Fukuyama, M. Isolation and identification of species from the tap water in hospitals in Japan and their antibiotic susceptibility. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 50, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cal, M.; Cazzavillan, S.; Cruz, D.; Nalesso, F.; Brendolan, A.; Rassu, M.; Ronco, C. Methylobacterium radiotolerans bacteremia in hemodialysis patients. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2009, 26, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tarrand, J.J.; Han, X.Y. Microbiological and clinical features of four cases of catheter-related infection by Methylobacterium radiotolerans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaneko, M.; Tominaga, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Shikata, H. Hemodialysis vascular access infection caused by Methylobacterium radiotolerans: The first confirmed case in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaleva, J.; Degener, J.E.; van der Mei, H.C. Methylobacterium and its role in health care-associated infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordovana, M.; Deni, A.; Kostrzewa, M.; Abdalla, M.; Ambretti, S. First report of Methylobacterium radiotolerans bacteraemia identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 30, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Qi, X.; Ma, B.; Xu, P.; Yuan, Y. First case of infective endocarditis caused by Methylobacterium radiotolerans. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Desai, A.; Desai, K. A Case Report of Methylobacterium radiotolerans Bacteremia and Brain Abscesses. Infect. Microbes Dis. 2021, 3, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, O.; Ormanoglu, G.; Koroglu, M.; Aydemir, Y. Comparison of time-to-detection of Mindray TDR and BacT/ALERT(R)3D blood culture systems using simulated blood cultures. Acta Clin. Belg. 2024, 79, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Photolo, M.M.; Mavumengwana, V.; Sitole, L.; Tlou, M.G. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of a Bacterial Endophyte, Methylobacterium radiotolerans MAMP 4754, Isolated from Combretum erythrophyllum Seeds. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 9483670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Cheng, A.; Liu, W.-L.; Tan, C.-K.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chung, K.-P.; Lee, M.-R.; Hsueh, P.-R. Infections caused by unusual Methylobacterium species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3329–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rit, K.; Chakraborty, B.; Mukherjee, T.; Chakrabarty, P.S.; Consultant, C.; Jo, D. A Case Report of Methylobacterium Radiotolerans Bacteremia in a Haemodialysis Patient Successfully Treated by Combination Therapy of Levofloxacin and Meropenem. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Dai, M.; Li, Q.; Liu, N.; Lin, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Jin, H.; et al. Early T-Cell Precursor Leukemia Has a Higher Risk of Induction-Related Infection among T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adult. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8867760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forconi, F.; Moss, P. Perturbation of the normal immune system in patients with CLL. Blood 2015, 126, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Borg, C.; Bachelot, T.; Sebban, C.; Philip, I.; Clapisson, G.; Le Cesne, A.; Biron, P.; Chauvin, F.; Blay, J.Y.; et al. Baseline and early lymphopenia predict for the risk of febrile neutropenia after chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patt, T.E.; Cole, G.C.; Hanson, R.S. Methylobacterium, a New Genus of Facultatively Methylotrophic Bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1976, 26, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).