Miamiensis avidus, a Novel Scuticociliate Pathogen Isolated and Identified from Cultured Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Large Yellow Croakers and Locality
2.2. Sample Collection and Inspection
2.3. Ciliate Isolation and Cultivation
2.4. Experimental Infection
2.5. Molecular Biological Examination
2.6. Histological Examination
2.7. Preparation of Specimen for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Indirect Immunofluorescence
2.9. Molecular Identification
3. Results
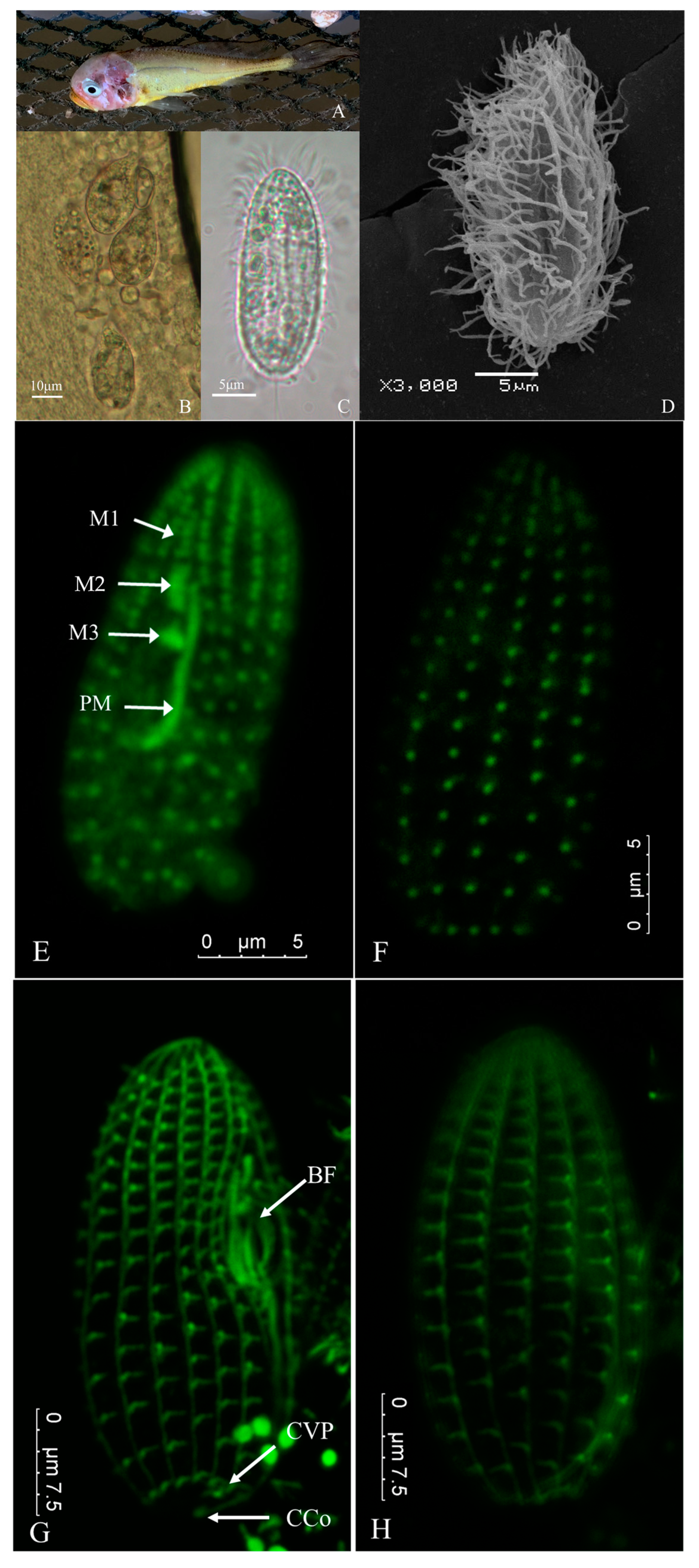
3.1. Clinical Symptoms of Natural Infection
3.2. Morphological Observation of Parasite
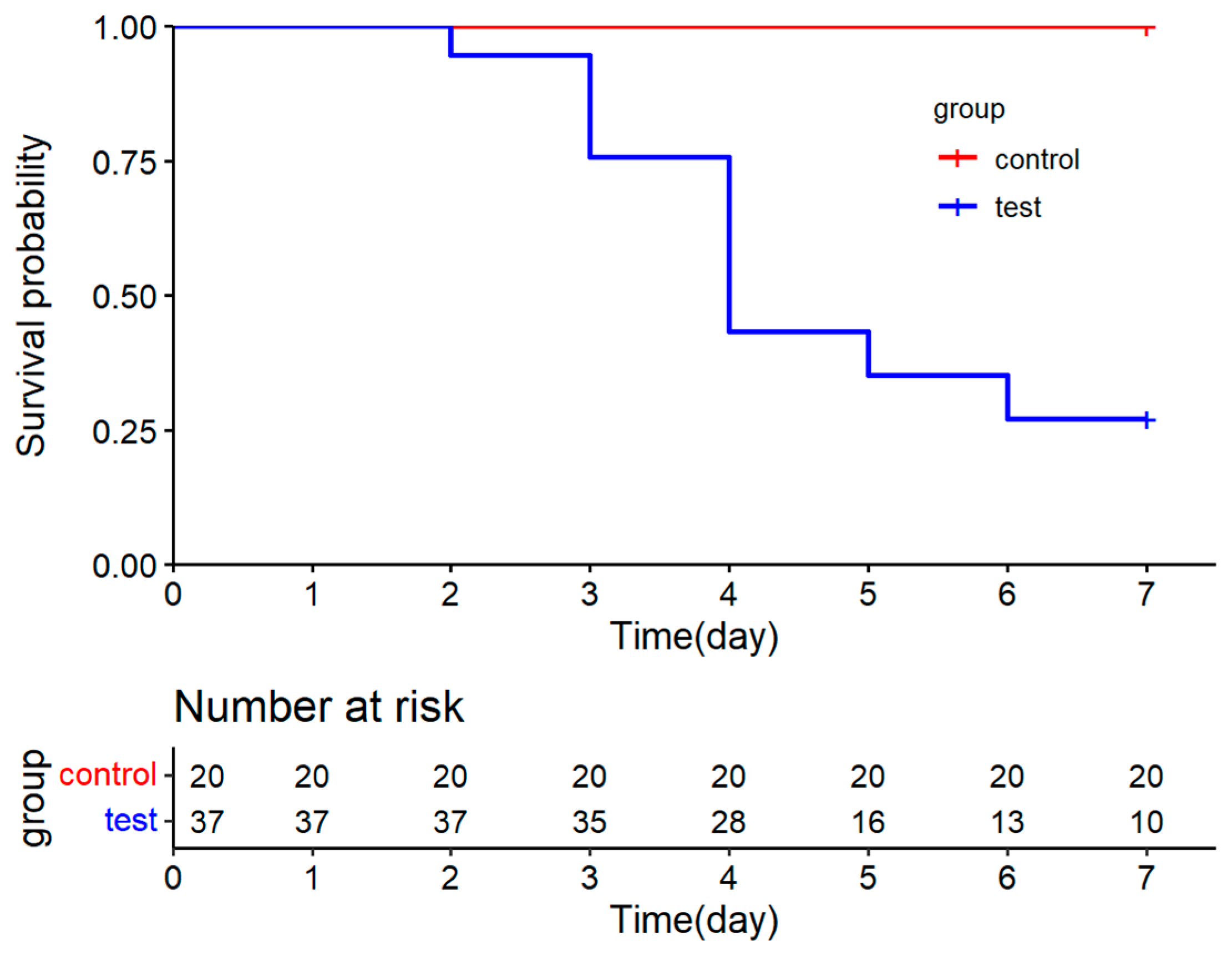
3.3. Experimental Infection
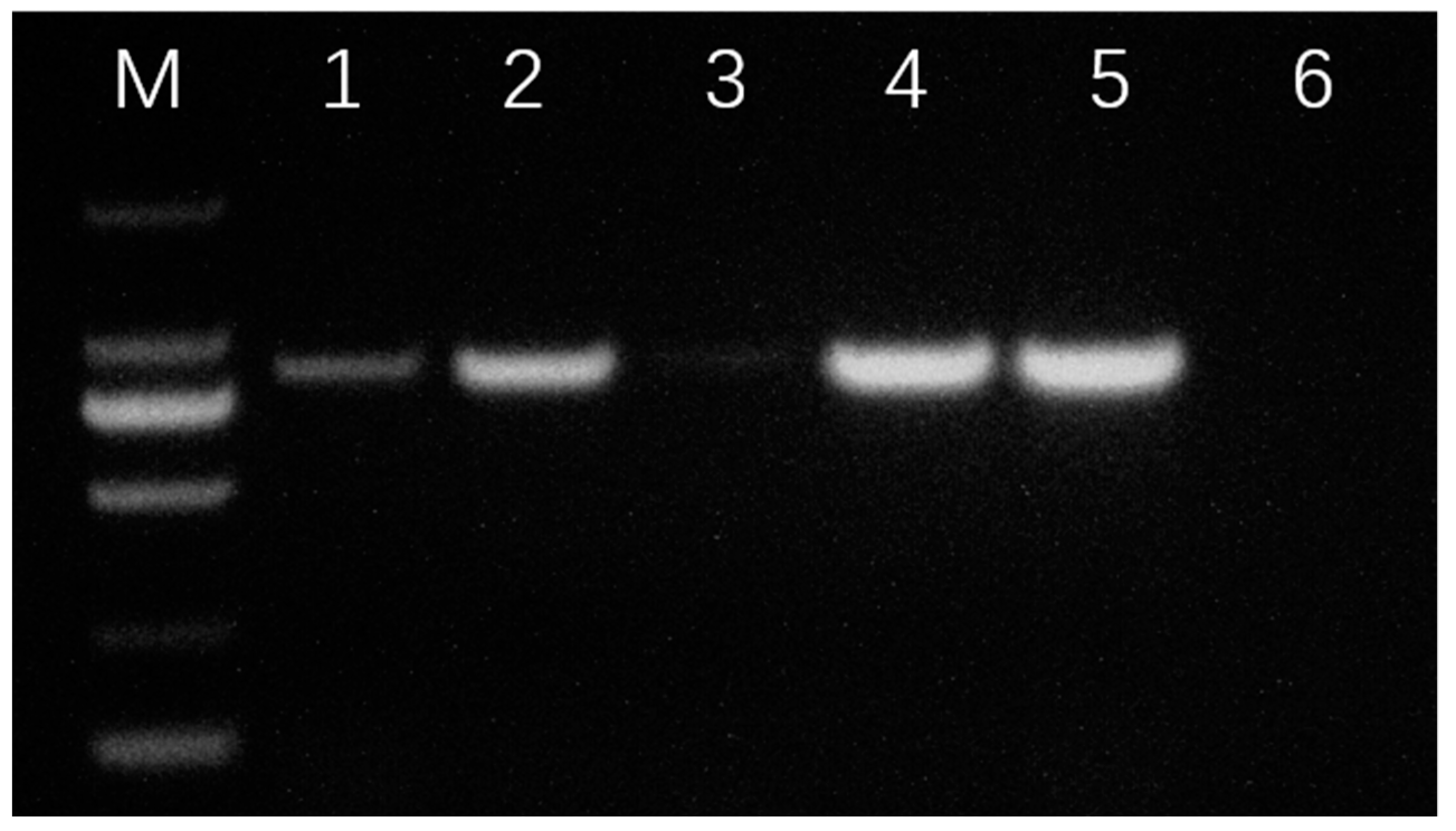
3.4. Parasitic Infection of Organ Examination Based on PCR
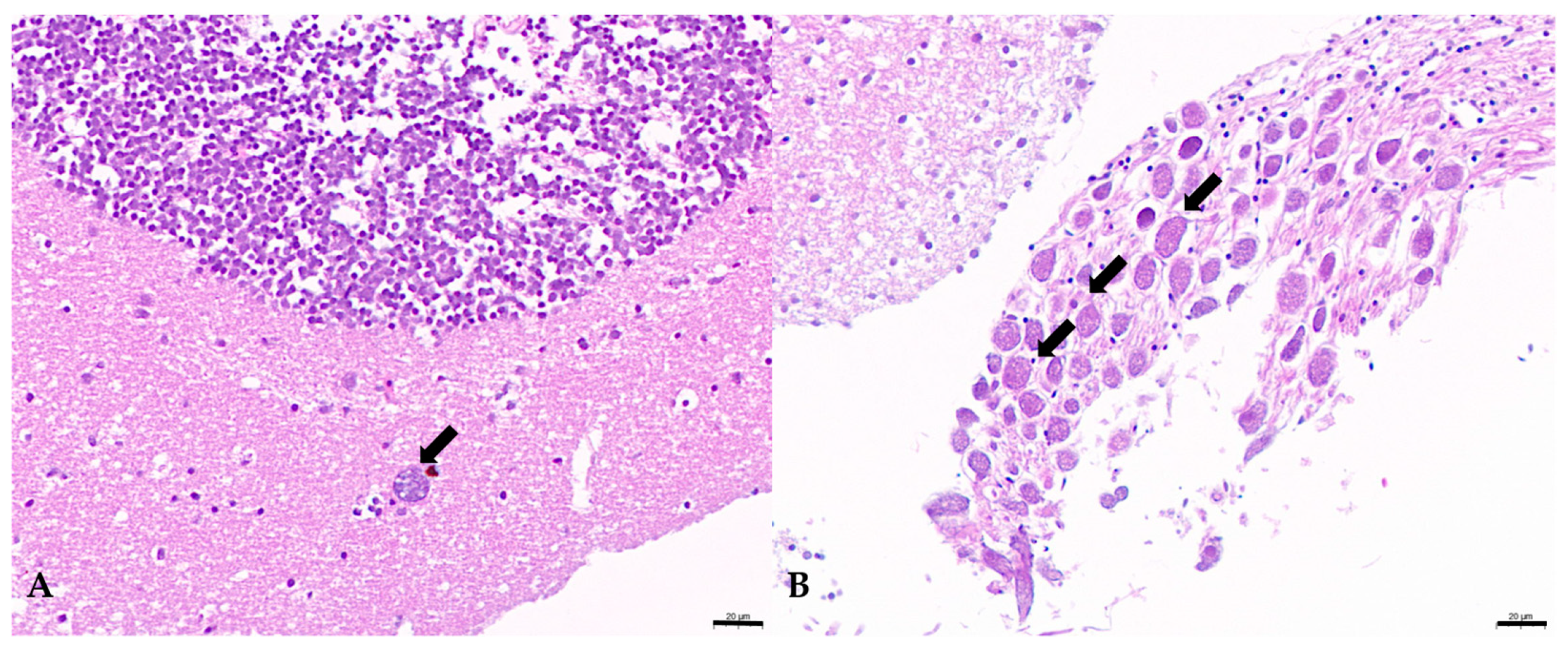
3.5. Histological Examination
3.6. Indirect Immunofluorescence
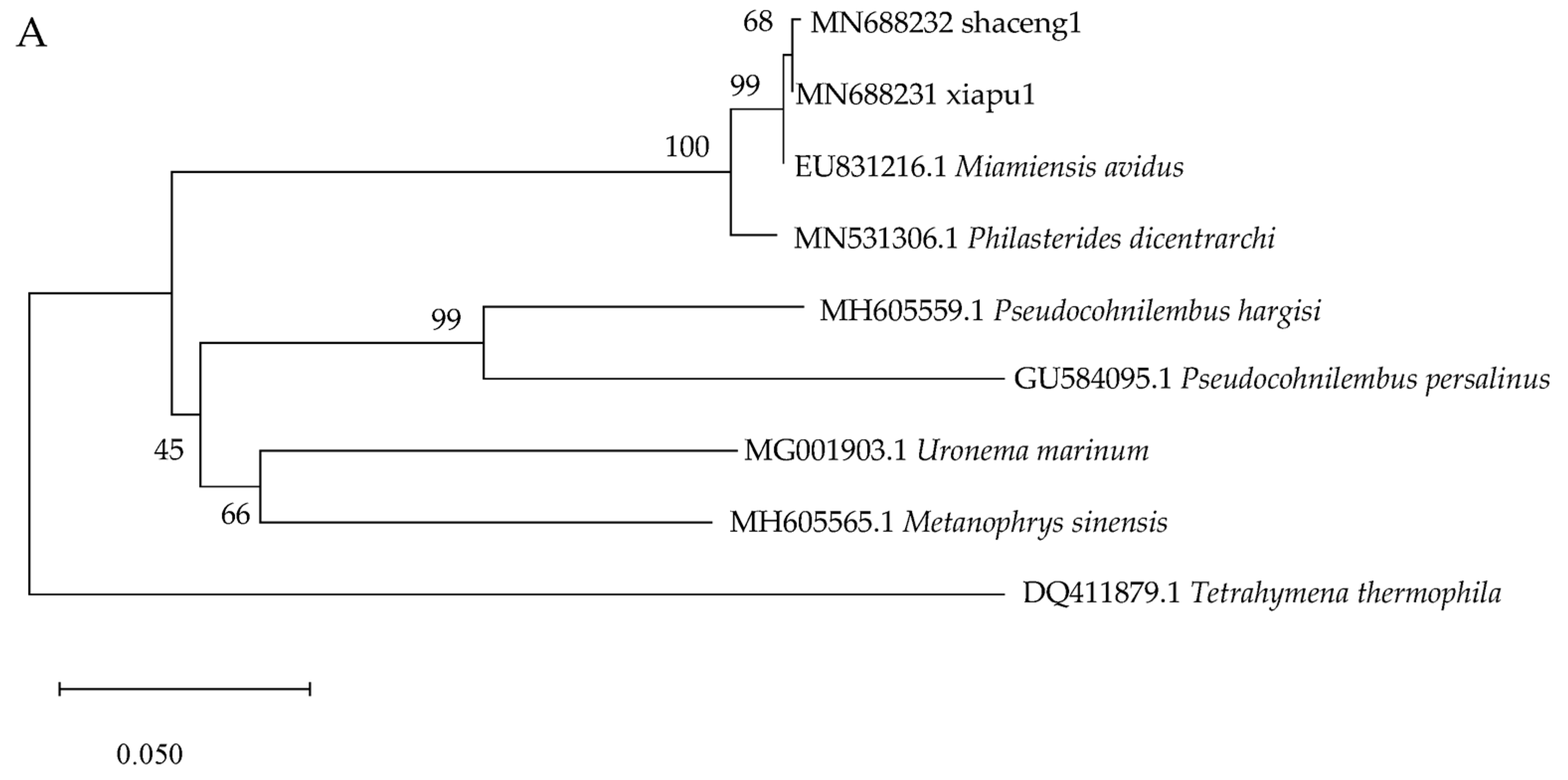
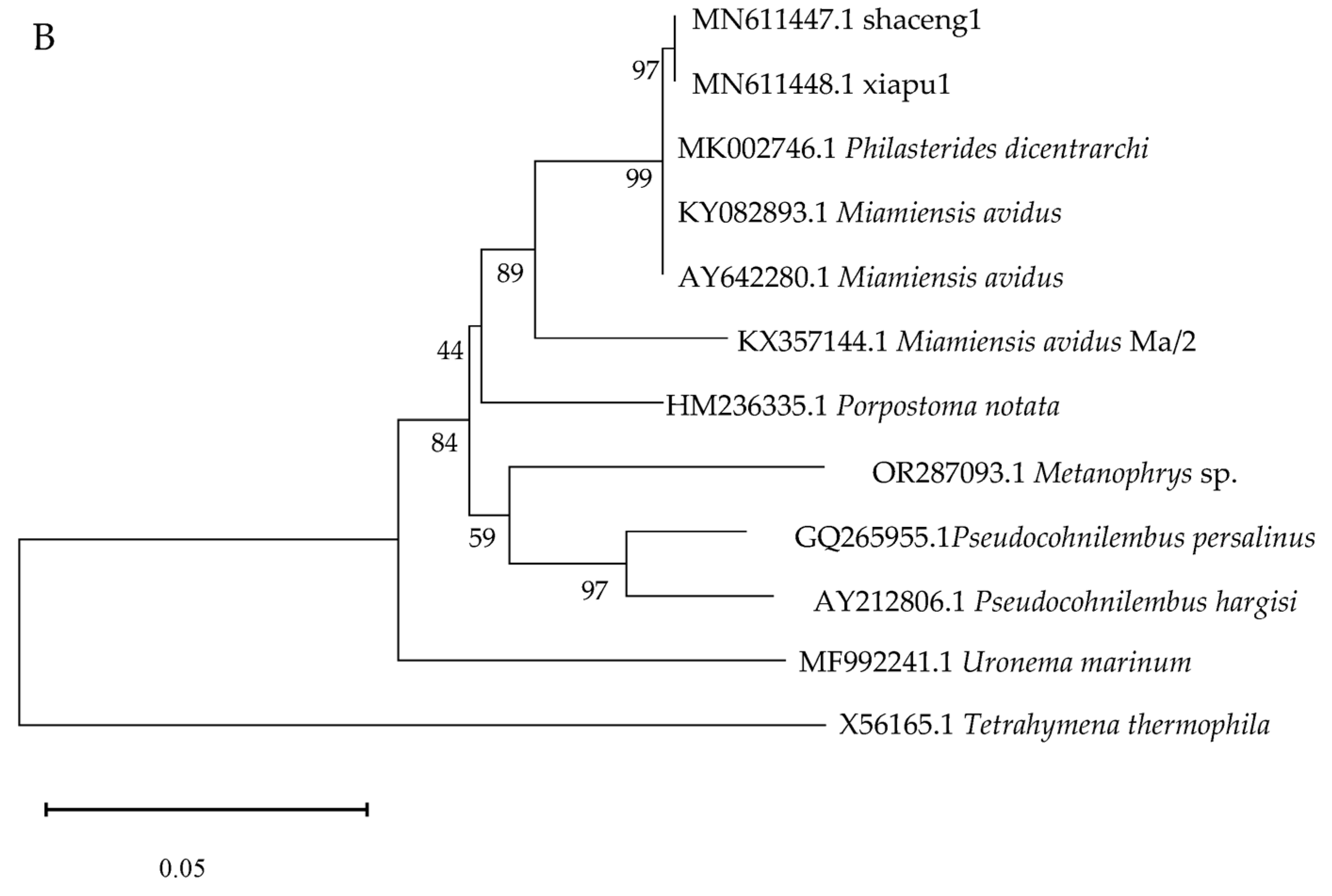
3.7. Molecular Identification
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bureau of Fisheries of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center & China Society of Fisheries. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook 2023; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, S.; Ke, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Pu, F.; Zhao, J.; Bai, H.; Peng, W.; Xu, P. Constructing a High-Density Genetic Linkage Map for Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and Mapping Resistance Trait Against Ciliate Parasite Cryptocaryon irritans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Diagnosis and Treatment of a Ciliate Endoparasific in the Large YellowCroaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). J. Fish. Res. 2011, 33, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fang, M.; Ye, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, D.L. Genome-wide association analysis on host resistance against the rotten body disease in a naturally infected population of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2021, 548, 737615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Jiang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Lin, N. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of a Scuticociliate in Large Yellow Croakers. Fujian J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2023, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Xie, X.; Yin, F. Isolation, characterization and virulence of Metanophrys sp. (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in China. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.J.; Nigrelli, R.F.; Ruggieri, G.D. Studies on the morphology of Uronema marinum Dujardin (Ciliatea: Uronematidae) with a description of the histopathology of the infection in marine fishes. J. Fish Dis. 1980, 3, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiño, B.; Lamas, J.; Pata, M.P.; Arranz, J.A.; Sanmartín, M.L.; Leiro, J. Intraspecific Variability in Several Isolates of Philas-terides dicentrarchi (syn. Miamiensis avidus), a Scuticociliate Parasite of Farmed Turbot. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-J.; Kitamura, S.-I.; Song, J.-Y.; Joung, I.-Y.; Oh, M.-J. Complete small subunit rRNA gene sequence of the scuticociliate Miamiensis avidus pathogenic to olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 64, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Cho, J.B.; Lee, E.H.; Kwon, S.R.; Kim, S.K.; Nam, Y.K.; Kim, K.H. Pseudocohnilembus persalinus is an Additional Species Causing Scuticociliatosis in Olive Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 62, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.; Costa, A.; Barandela, T.; Saraiva, A.; Rodrigues, P. Scuticociliate infection and pathology in cultured turbot Scophthalmus maximus from the north of Portugal. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 74, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, G. First isolation of Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) associated with skin ulcers from reared pharaoh cuttlefish Sepia pharaonis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 122, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Xu, K.D. Pathogenic Protozoa in Mariculture; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M.S. Scuticociliatosis and Its Recent Prophylactic Measures in Aquaculture with Special Reference to South Korea Taxonomy, Diversity and Diagnosis of Scuticociliatosis: Part I Control Strategies of Scuticociliatosis: Part II. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2010, 29, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retallack, H.; Okihiro, M.S.; Britton, E.; Sommeran, S.V.; DeRisi, J.L. Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Reveals Mi-amiensis Avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) in the 2017 Epizootic of Leopard Sharks (Triakis Semifasciata) in San Francisco Bay, California, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregui, L.; Serrano, S.; Guinea, A. Microtubular Elements of the Marine Antarctic Ciliate Euplotes focardii (Ciliophora, Hypotrichia). Arch. Protistenkd. 1994, 144, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, J.; Tian, M.; Pan, X.; Warren, A.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, D.; Miao, W. Genome of the Facultative Scuticociliatosis Pathogen Pseudocohnilembus persalinus Provides Insight into its Virulence through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlin, L.; Elwood, H.J.; Stickel, S.; Sogin, M.L. The Characterization of Enzymatically Amplified Eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-Coding Regions. Gene 1988, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-J.; Im, E.-Y.; Strüder-Kypke, M.C.; Kitamura, S.-I.; Woo, P.T.K. Small subunit ribosomal RNA and mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene sequences of 21 strains of the parasitic scuticociliate Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatia). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 108, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.C.; Moewus, L. Miamiensis avidus ng, n. sp., a Marine Faculative Parasite in the Ciliate Order Hymenostomatida. J. Protozool. 1964, 11, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramá, A.; Iglesias, R.; Álvarez, M.; Leiro, J.; Aja, C.; Sanmartin, M. Philasterides dicentrarchi (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida): Experimental infection and possible routes of entry in farmed turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 2003, 217, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-J.; Kitamura, S.-I.; Song, J.-Y.; Oh, M.-J. Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) causes systemic infection of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and is a senior synonym of Philasterides dicentrarchi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 73, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, E.M.M.; Tange, N.; Shimada, A.; Morita, T. Experimental Scuticociliatosis in Japanese Flounder Infected with Miamiensis avidus: Pathological Study on the Possible Neural Routes of Invasion and Dissemination of the Scuticociliate inside the Fish Body. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, R.; Paramá, A.; Álvarez, M.; Leiro, J.; Sanmartín, M. Antiprotozoals effective in vitro against the scuticociliate fish pathogen Philasterides dicentrarchi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 49, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Baek, K.-W.; Kim, A.; Luan, N.T.; Lim, Y.; Roh, H.J.; Kim, N.; Kim, D.-H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Genome based quantification of Miamiensis avidus in multiple organs of infected olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by real-time PCR. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Chen, L.; Zeng, H. Chemotaxis of Miamiensis avidus to Tissue Homogenates of Four Mariculture Fishes. Fujian J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 43, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dragesco, A.; Dragesco, J.; Coste, F.; Gasc, C.; Romest, B.; Raymond, J.C.; Bouix, G. Philasterides dicentrarchi, n. sp., (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida), a Histophagous Opportunustic Parasite of Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnacus, 1758), a Reared Marine Fish. Eur. J. Protistol. 1995, 31, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.B.; Wilbert, N. Redefinition and Redescription of Some Marine Scuticociliates from China, with Report of a New Species, Metanophrys sinensis nov. spec. (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida). Zool. Anz. 2000, 239, 45–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, X.; Ma, H. Morphological Studies on Eight Marine Scuticocilates (protozoa, ciliophora) from China. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2011, 35, 929–939. [Google Scholar]
- Whang, I.; Kang, H.-S.; Lee, J. Identification of scuticociliates (Pseudocohnilembus persalinus, P. longisetus, Uronema marinum and Miamiensis avidus) based on the cox1 sequence. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felipe, A.P.; Lamas, J.; Sueiro, R.A.; Folgueira, I.; Leiro, J.M. New data on flatfish scuticociliatosis reveal that Miamiensis avidus and Philasterides dicentrarchi are different species. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1394–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunthorn, M.; Klier, J.; Bunge, J.; Stoeck, T. Comparing the Hyper–Variable V4 and V9 Regions of the Small Subunit rDNA for Assessment of Ciliate Environmental Diversity. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Katz, L.A.; Song, W. Insights into the phylogenetic and taxonomy of philasterid ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Scuticociliatia) based on analyses of multiple molecular markers. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 64, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strüder-Kypke, M.C.; Lynn, D.H. Comparative Analysis of the Mitochondrial Cytochromecoxidase Subunit I (COI) Gene in Ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) and Evaluation of its Suitability as a Biodiversity Marker. Syst. Biodivers. 2010, 8, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lu, B.; Fan, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X. Taxonomic Clarification of a Well-Known Pathogenic Scuticociliate, Miamiensis avidus Thompson & Moewus, 1964 (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatia). J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Paramá, A.; Álvarez, M.F.; Leiro, J.; Fernández, J.; Sanmartín, M.L. Philasterides dicentrarchi (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida) as the Causative Agent of Scuticociliatosis in Farmed Turbot Scophthalmus maximus in Galicia (NW Spain). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 46, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, R.; Paramá, A.; Álvarez, M.; Leiro, J.; Aja, C.; Sanmartin, M. In vitro growth requirements for the fish pathogen Philasterides dicentrarchi (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida). Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 111, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, E.M.M.; Naota, M.; Morita, T.; Tange, N.; Shimada, A. Pathological Study on the Scuticociliatosis Affecting Farmed Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagishi, N.; Yoshinaga, T.; Ogawa, K. Effect of hyposalinity on the infection and pathogenicity of Miamiensis avidus causing scuticociliatosis in olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 86, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, N.; Pan, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, B.; Gong, H.; Zeng, H. Miamiensis avidus, a Novel Scuticociliate Pathogen Isolated and Identified from Cultured Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Pathogens 2024, 13, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080618
Lin N, Pan Y, Zhan Z, Xu B, Gong H, Zeng H. Miamiensis avidus, a Novel Scuticociliate Pathogen Isolated and Identified from Cultured Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Pathogens. 2024; 13(8):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080618
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Nengfeng, Ying Pan, Zifeng Zhan, Binfu Xu, Hui Gong, and Hong Zeng. 2024. "Miamiensis avidus, a Novel Scuticociliate Pathogen Isolated and Identified from Cultured Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)" Pathogens 13, no. 8: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080618
APA StyleLin, N., Pan, Y., Zhan, Z., Xu, B., Gong, H., & Zeng, H. (2024). Miamiensis avidus, a Novel Scuticociliate Pathogen Isolated and Identified from Cultured Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Pathogens, 13(8), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080618





