Hepatitis C Virus and Molecular Mimicry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HCV and Immune Evasion
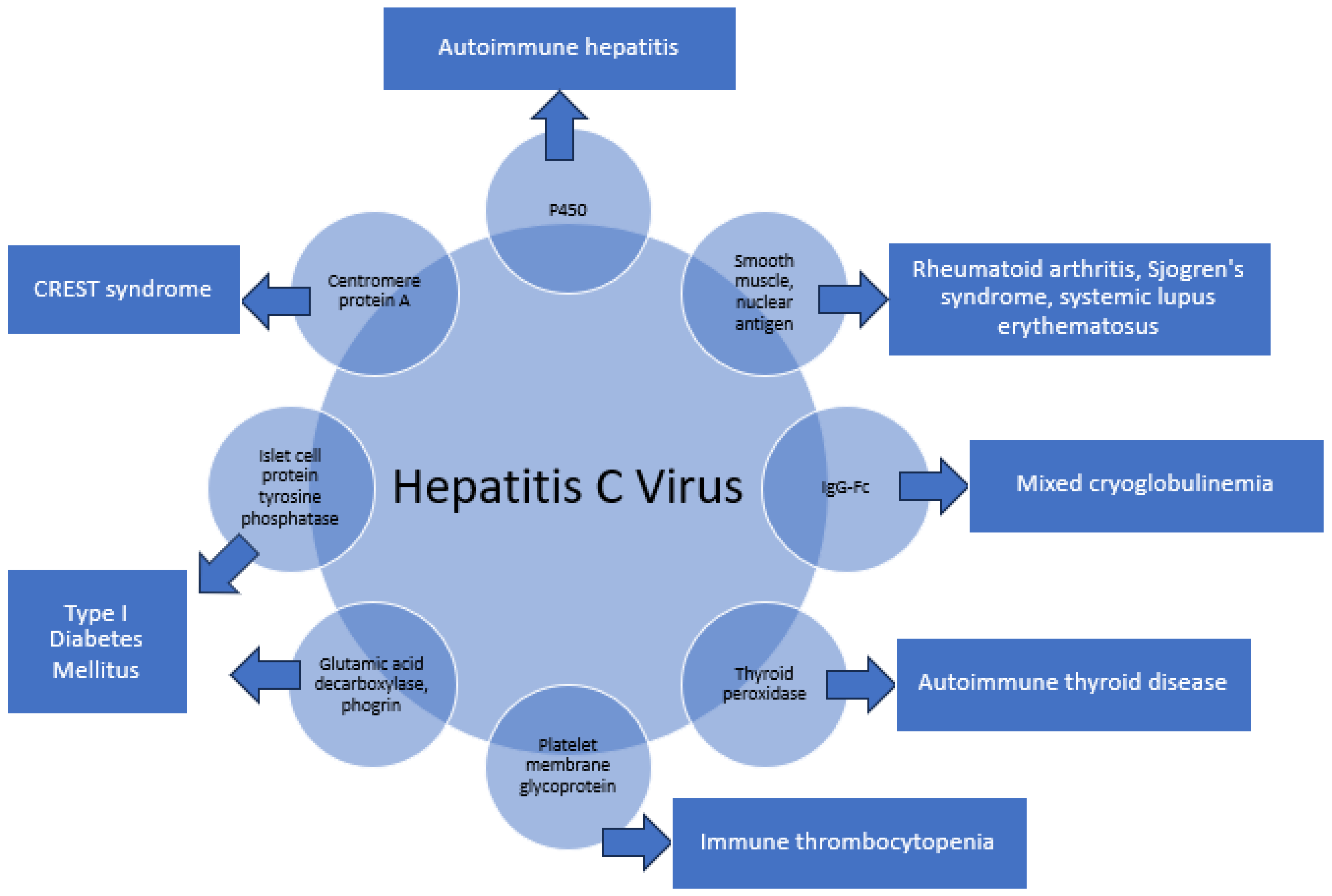
3. HCV and Autoimmune Disease
3.1. Specific Examples of Molecular Mimicry
3.1.1. P450-CYP2D6, CYP2A6, and CYP2A7 8–17 in Autoimmune Hepatitis
3.1.2. Human Nuclear and Smooth Muscle Antigens in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Sjogren’s Syndrome, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
3.1.3. IgG-Fc in Mixed Cryoglobulinemia
3.1.4. Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Peptides in Hashimoto’s and Grave’s Disease
3.1.5. Platelet Membrane Glycoprotein IIIa (GPIIIa49–66) in Immune Thrombocytopenia
3.1.6. Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 65-Kilodalton Isoform (GAD65), Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Islet Cell Antigen-2, and Phogrin in Type I Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
3.1.7. Centromere Protein-A (CENP-A) in CREST Syndrome
4. Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents
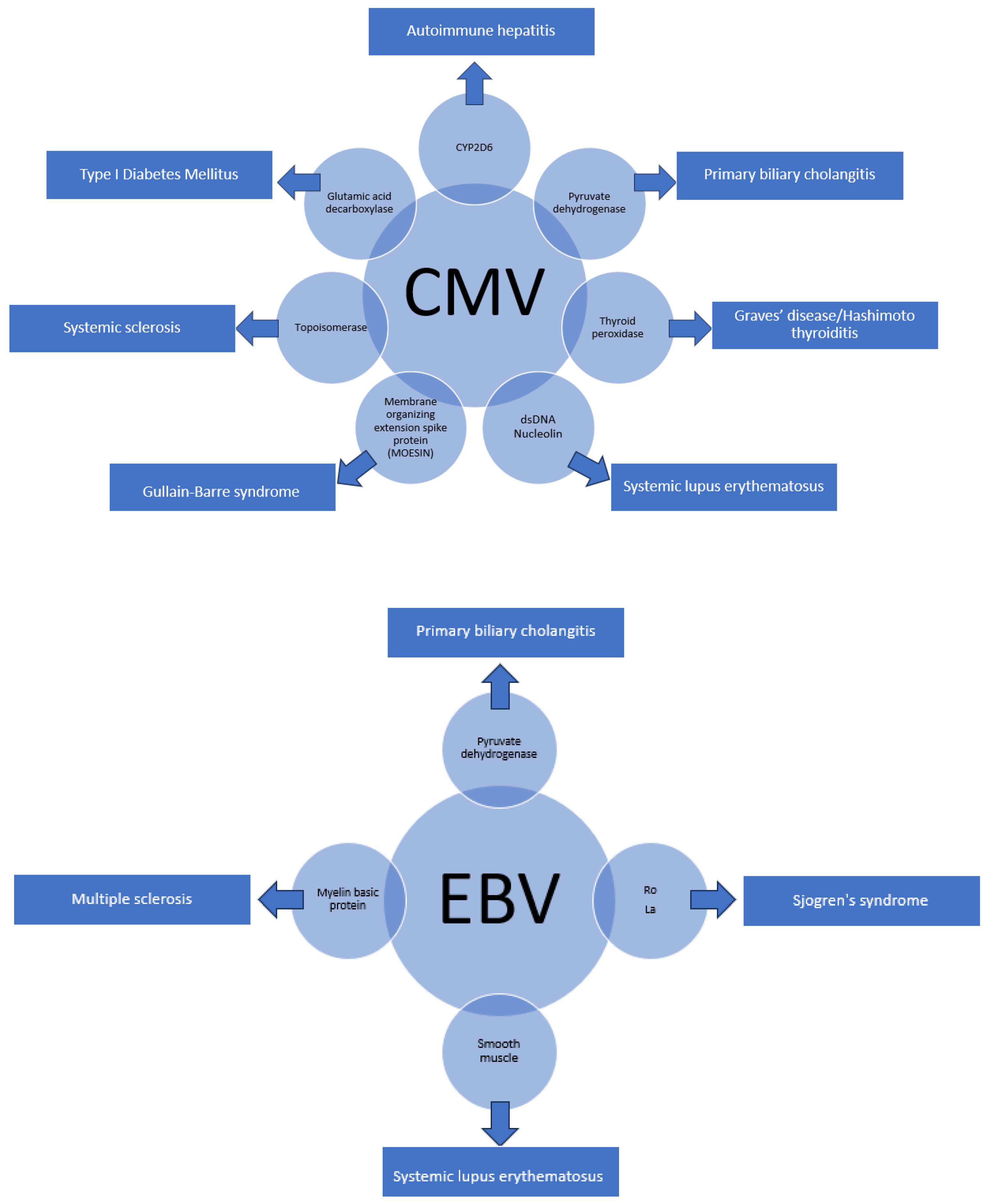
5. Other Viruses with Molecular Homology and Associated Autoimmune Conditions
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodnow, C.C. Balancing immunity and tolerance: Deleting and tuning lymphocyte repertoires. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderlugt, C.J.; Miller, S.D. Epitope spreading. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1996, 8, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.M.; Black, M.M. Epitope spreading: Protection from pathogens, but propagation of autoimmunity? Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.R.; Shi, S.T.; Lai, M.M. Hepatitis C virus and interferon resistance. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.R.; Shi, S.T.; Romano, P.R.; Barber, G.N.; Lai, M.M.C. Inhibition of the Interferon—Inducible Protein Kinase PKR by HCV E2 Protein. Science 1999, 285, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, M.J., Jr.; Korth, M.J.; Tang, N.M.; Tan, S.L.; Hopkins, D.A.; Dever, T.E.; Polyak, S.J.; Gretch, D.R.; Katze, M.G. Evidence that hepatitis C virus resistance to interferon is mediated through repression of the PKR protein kinase by the nonstructural 5A protein. Virology 1997, 230, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, S.J.; Paschal, D.M.; McArdle, S.; Gale, M.J., Jr.; Moradpour, D.; Gretch, D.R. Characterization of the effects of hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein expression in human cell lines and on interferon-sensitive virus replication. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-W.; Rocheleau, L.; Larke, B.; Chui, L.; Lee, B.; Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Omlin, T.; Pelchat, M.; Brown, E.G. Immunoglobulin mimicry by Hepatitis C Virus envelope protein E2. Virology 2005, 332, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacoub, P.; Renou, C.; Rosenthal, E.; Cohen, P.; Loury, I.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Yamamoto, A.M.; Camproux, A.C.; Hausfater, P.; Musset, L.; et al. Extrahepatic manifestations associated with hepatitis C virus infection. A prospective multicenter study of 321 patients. The GERMIVIC. Groupe d’Etude et de Recherche en Medecine Interne et Maladies Infectieuses sur le Virus de l’Hepatite C. Medicine 2000, 79, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkar, N.; Choudhuri, K.; Ma, Y.; Mahmoud, A.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Muratori, L.; Bianchi, F.; Williams, R.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Cytochrome P4502D6193–212: A new immunodominant epitope and target of virus/self cross-reactivity in liver kidney microsomal autoantibody type 1-positive liver disease. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanos, D.; Choudhuri, K.; Vergani, D. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune liver disease: Virtuous intentions, malign consequences. Liver 2001, 21, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, M.P.; Johnson, E.F.; Griffin, K.J.; Tan, E.M.; Sullivan, K.F. Major antigen of liver kidney microsomal autoantibodies in idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis is cytochrome P450db1. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanos, D.; Lenzi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Ma, Y.; Muratori, L.; Williams, R.; Bianchi, F.; Vergani, D. Generation of liver/kidney microsomal-1 antibody in HCV infection the role of molecular mimicry. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32 (Suppl. S2), 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammer, A.R.; van der Burg, S.H.; Grabscheid, B.; Hunziker, I.P.; Kwappenberg, K.M.; Reichen, J.; Melief, C.J.; Cerny, A. Molecular Mimicry of Human Cytochrome P450 by Hepatitis C Virus at the Level of Cytotoxic T Cell Recognition. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutti, S.; Vidali, M.; Mombello, C.; Sartori, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Albano, E. Breaking self-tolerance toward cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) in chronic hepatitis C: Possible role for molecular mimicry. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, F.D.; Peakman, M.; Yun, M.; Sallie, R.; Smith, H.; Davies, E.T.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Primary and secondary liver/kidney microsomal autoantibody response following infection with hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, S.; Cainelli, F.; Renzini, C.; Concia, E. Autoimmune hepatitis type 2 induced by HCV and persisting after viral clearance. Lancet 1997, 350, 1298–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, F.; Cataleta, M.; Valentini, P.; Muratori, P.; Giostra, F.; Francesconi, R.; Muratori, L.; Lenzi, M.; Bianchi, G.; Zauli, D.; et al. Serum autoantibodies in chronic hepatitis C: Comparison with autoimmune hepatitis and impact on the disease profile. Hepatology 1997, 26, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorio, G.V.; Pensati, P.; Iorio, R.; Vegnente, A.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoantibody prevalence in children with liver disease due to chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Hu, W.; Shen, H.; Chen, J. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102437–102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.W.; Elbourne, K. Hepatitis C virus infection and autoimmunity. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 26, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Simmonds, P.; Mellor, J.; Ben Yahia, M.; Andre, C.; Voisin, M.-C.; Intrator, L.; Zafrani, E.-S.; Duval, J.; et al. Extrahepatic Immunologic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C and Hepatitis C Virus Serotypes. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995, 122, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorio, G.V.; Choudhuri, K.; Ma, Y.; Pensati, P.; Iorio, R.; Grant, P.; Garson, J.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Vegnente, A.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; et al. Mimicry between the hepatitis C virus polyprotein and antigenic targets of nuclear and smooth muscle antibodies in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 133, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, C. Mixed cryoglobulinemia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schamberg, N.J.; Lake-Bakaar, G.V. Hepatitis C Virus-related Mixed Cryoglobulinemia: Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and New Therapies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 3, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Re, V.; Sansonno, D.; Simula, M.P.; Caggiari, L.; Gasparotto, D.; Fabris, M.; Tucci, F.A.; Racanelli, V.; Talamini, R.; Campagnolo, M.; et al. HCV-NS3 and IgG-Fc crossreactive IgM in patients with type II mixed cryoglobulinemia and B-cell clonal proliferations. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, D.; Sadallah, S.; Trendelenburg, M.; Limal, N.; Sene, D.; Piette, J.C.; Schifferli, J.A.; Cacoub, P. Anti-C1q antibodies in hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 145, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comarmond, C.; Cacoub, P.; Saadoun, D. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C-associated cryoglobulinemia vasculitis at the era of direct-acting antivirals. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820942617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C.; Pampana, A.; Fallahi, P.; Nesti, C.; Pasquini, M.; Marchi, S.; Ferrannini, E. Thyroid disorders in chronic hepatitis C. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanos, D.; Lenzi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Ma, Y.; Aluigi, P.; Lari, F.; Muratori, L.; Williams, R.; Bianchi, F.; Vergani, D. Thyroid peroxidase is a molecular mimicry target of anti-hepatitis C virus humoral response. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32 (Suppl. S2), 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barut, S.; Gunal, O.; Erkorkmaz, U.; Yildiz, F. Thyroid dysfunction in Turkish patients with chronic hepatitis C receiving peginterferon plus ribavirin in the period of 2005–2010. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aster, R.H. Molecular mimicry and immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2009, 113, 3887–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chou, Y.; Tsai, S.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S. Hepatitis C virus infection-related Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kawasaki, E.; Imagawa, A.; Awata, T.; Ikegami, H.; Uchigata, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Shimada, A.; Nakanishi, K.; Makino, H.; et al. Type 1 diabetes and interferon therapy: A nationwide survey in Japan. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nakanishi, K.; Saitoh, S. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Associated with Interferon Therapy. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fabris, P.; Floreani, A.; Tositti, G.; Vergani, D.; De Lalla, F.; Betterle, C. Type 1 diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic hepatitis C before and after interferon therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zornitzki, T.; Malnick, S.; Lysyy, L.; Knobler, H. Interferon therapy in hepatitis C leading to chronic type 1 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerstad, S.S.; Grock, S.F.; Lee, H.J.; Hasham, A.; Sundaram, N.; Tomer, Y. Diabetes and Hepatitis C: A Two-Way Association. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanos, D.-P.; Rigopoulou, E.I. Viral/self-mimicry and immunological cross-reactivity as a trigger of hepatic C virus associated autoimmune diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, Y.; Azuma, N.; Onouchi, H.; Kunimatsu, M.; Tomita, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Sugimoto, K. Autoepitopes on autoantigen centromere protein-A (CENP-A) are restricted to the N-terminal region, which has no homology with histone H3. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, W.C.; Rothfield, N. Identification of a family of human centromere proteins using autoimmune sera from patients with scleroderma. Chromosoma 1985, 91, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Extrahepatic manifestations and autoantibodies in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 871401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Houglum, J.E. Interferon: Mechanisms of action and clinical value. Clin Pharm. 1983, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morihisa, Y.; Chung, H.; Towatari, S.; Yamashita, D.; Inokuma, T. Autoimmune hepatitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis after direct-acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus: A case report. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Wychowski, C.; Lin, C.; Feinstone, S.M.; Rice, C.M. Expression and identification of hepatitis C virus polyprotein cleavage products. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.E.; Feng, A.; Meng, W.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Mack, E.; Artandi, M.; Barman, L.; Bennett, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chang, I.; et al. New-onset IgG autoantibodies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Rojas, M.; Rodriguez, Y.; Zapata, E.; Ramirez-Santana, C.; Anaya, J.M. Persistent autoimmune activation and proinflammatory state in post-coronavirus disease 2019 syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Ramos, A.E.; Martin-Nares, E.; Hern’andez-Molina, G. New onset of autoimmune diseases following COVID-19 diagnosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, Y.; Rojas, M.; Beltr, S.; Polo, F.; Camacho-Domínguez, L.; Morales, S.D.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.M. Autoimmune and autoinflammatory conditions after COVID-19 vaccination. New case reports and updated literature review. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 132, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goh, L.; Kerkar, N. Hepatitis C Virus and Molecular Mimicry. Pathogens 2024, 13, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070527
Goh L, Kerkar N. Hepatitis C Virus and Molecular Mimicry. Pathogens. 2024; 13(7):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070527
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoh, Lynette, and Nanda Kerkar. 2024. "Hepatitis C Virus and Molecular Mimicry" Pathogens 13, no. 7: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070527
APA StyleGoh, L., & Kerkar, N. (2024). Hepatitis C Virus and Molecular Mimicry. Pathogens, 13(7), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070527




