Unveiling Antibiotic Resistance, Clonal Diversity, and Biofilm Formation in E. coli Isolated from Healthy Swine in Portugal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection and Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Escherichia coli
2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance Gene and Virulence Genotyping of E. coli
2.5. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis
2.6. Biofilm Formation
3. Results
3.1. E.coli Isolation
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Profile of E. coli Isolates
3.3. Molecular Characterization and Whole Sequence Genome
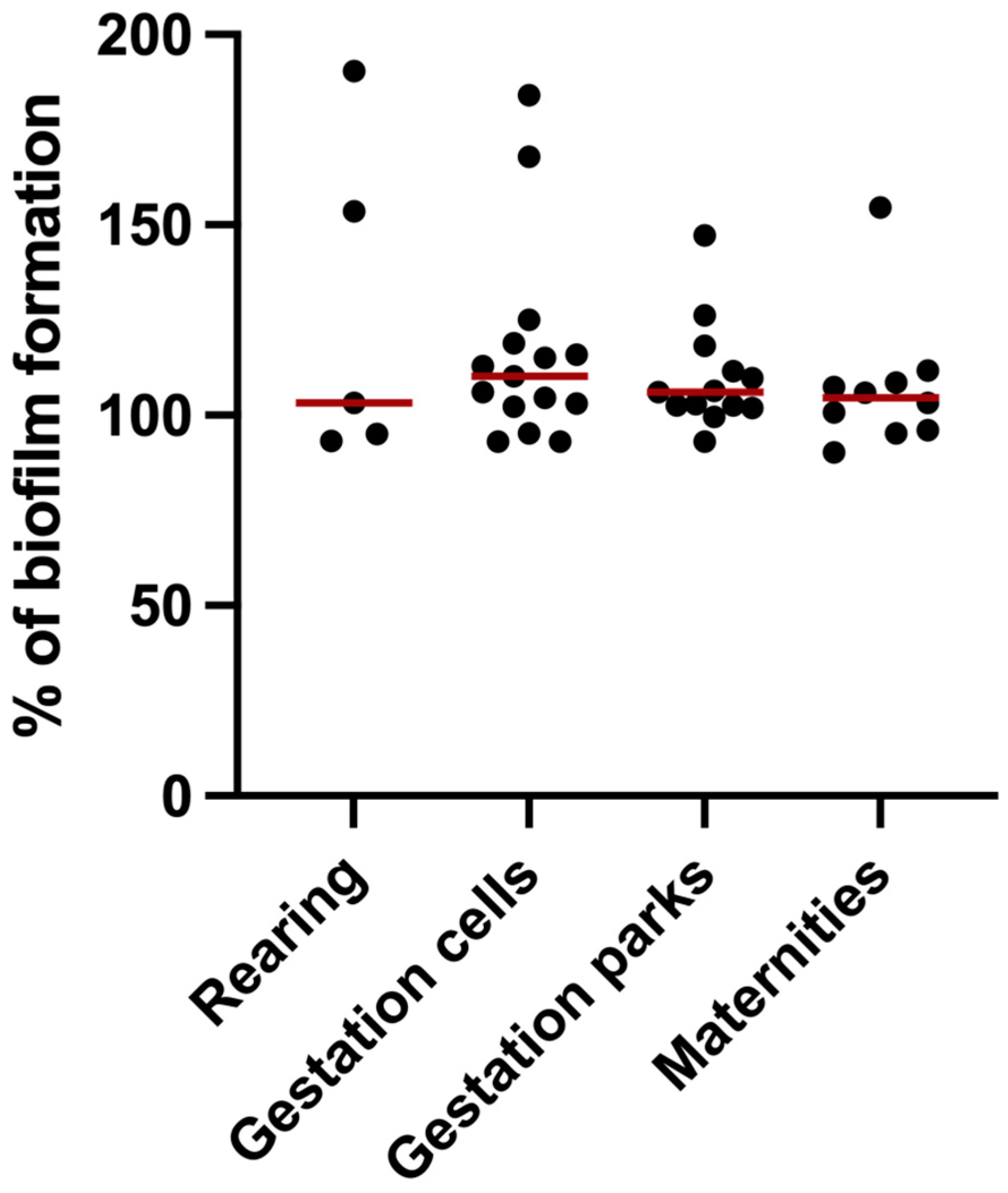
3.4. Biofilm Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdalla, S.E.; Abia, A.L.K.; Amoako, D.G.; Perrett, K.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. From Farm-to-Fork: E. coli from an Intensive Pig Production System in South Africa Shows High Resistance to Critically Important Antibiotics for Human and Animal Use. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathijs, E. Exploring Future Patterns of Meat Consumption. Meat Sci. 2015, 109, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, N.; García, S. Animals as Sources of Food-Borne Pathogens: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Igrejas, G.; Valentão, P.; Falco, V.; Poeta, P. Antimicrobial Resistance and Clonal Lineages of Escherichia coli from Food-Producing Animals. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.L.; Huamán, D.C.; Cueva, C.R.; Gonzales, C.D.; León, Y.I.; Espejo, T.S.; Monge, G.M.; Alcántara, R.R.; Hernández, L.M. Genomic Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying the Mcr-1 Gene Recovered from Pigs in Lima-Peru. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 99, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michele, P. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlock; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2023; pp. 2023–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Aarestrup, F.M. Veterinary Drug Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria of Animal Origin. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 96, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.d.L.E.; Caniça, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Escherichia coli as Commensal and Pathogenic Bacteria among Food-Producing Animals: Health Implications of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Production. Animals 2020, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. The Role of Epidemic Resistance Plasmids and International High-Risk Clones in the Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 565–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lagarde, M.; Vanier, G.; Arsenault, J.; Fairbrother, J.M. High Risk Clone: A Proposal of Criteria Adapted to the One Health Context with Application to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the Pig Population. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, C.M.; Zhao, C.; DebRoy, C.; Torcolini, J.; Zhao, S.; White, D.G.; Wagner, D.D.; McDermott, P.F.; Walker, R.D.; Meng, J. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli O157 Isolated from Humans, Cattle, Swine, and Food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, L.; Garenaux, A.; Harel, J.; Boulianne, M.; Nadeau, E.; Dozois, C.M. Escherichia coli from Animal Reservoirs as a Potential Source of Human Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. Coli. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Dai, X.; Zhang, L. Occurrence and Genomic Characterization of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli ST29 Strains from Swine with Abundant Virulence Genes. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 148, 104483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Niestępski, S. The Prevalence and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant and Virulent Escherichia coli Strains in the Municipal Wastewater System and Their Environmental Fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallau, N.; Wibawan, I.; Lukman, D.; Sudarwanto, M. Detection of Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) Escherichia coli and Tet Gene Prevalence at a Pig Farm in Kupang, Indonesia. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2018, 5, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Van Der Putten, B.C.L.; Fuchs, T.M.; Vinh, T.N.; Bootsma, M.; Oldenkamp, R.; La Ragione, R.; Matamoros, S.; Hoa, N.T.; Berens, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Reveals Host-Specific Genomic Traits in Escherichia coli. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, D.; Hesp, A.; van der Goot, J.; Joosten, P.; Sarrazin, S.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Dewulf, J.; Mevius, D.J.; On Behalf Of The Effort Consortium. Antimicrobial Resistance Prevalence in Commensal Escherichia coli from Broilers, Fattening Turkeys, Fattening Pigs and Veal Calves in European Countries and Association with Antimicrobial Usage at Country Level. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burow, E.; Rostalski, A.; Harlizius, J.; Gangl, A.; Simoneit, C.; Grobbel, M.; Kollas, C.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Käsbohrer, A. Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli from Pigs from Birth to Slaughter and Its Association with Antibiotic Treatment. Prev. Veter. Med. 2019, 165, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasmäe, B.; Häkkinen, L.; Kaart, T.; Kalmus, P. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus Spp. Isolated from Estonian Cattle and Swine from 2010 to 2015. Acta Vet. Scand. 2019, 61, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, P.; Bosco, C.; Bonilauri, P.; Luppi, A.; Fontana, M.C.; Fiorentini, L.; Rugna, G. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Factors Assessment in Escherichia coli Isolated from Swine in Italy from 2017 to 2021. Pathogens 2023, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleva, M.D.; Ilieva, Y.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Dimitrova, L.; Kim, T.C.; Tsvetkova, I.; Georgiev, Y.; Orozova, P.; Nedev, K.; Najdenski, H. Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Pig Farms and Surroundings in Bulgaria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuwan, W.; Intongead, S.; Saengsawang, P.; Romyasamit, C.; Narinthorn, R.; Nissapatorn, V.; Pereira, M.D.L.; Paul, A.K.; Wongtawan, T.; Boripun, R. Occurrence of Multidrug Resistance Associated with Extended-Spectrum Β-lactamase and the Biofilm Forming Ability of Escherichia coli in Environmental Swine Husbandry. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 103, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismarra, A.; Villa, Z.; Bonilauri, P.; Bacci, C. ESβL Escherichia coli Isolated in Pig’s Chain: Genetic Analysis Associated to the Phenotype and Biofilm Synthesis Evaluation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, A.A.P.; Srinivas, K.; Lyngdoh, V.; Momin, A.G.; Lapang, N.; Priya, G.B.; Ghatak, S.; Sanjukta, R.K.; Sen, A.; Das, S. Biofilm-Forming Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A One Health Challenge in Northeast India. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.-H.; Seo, K.; Lee, W.-K. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Genes, and Phylogenetic Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Patients and Swine Suffering from Diarrhea. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 13.1, 2023. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Carvalho, I.; Cunha, R.; Martins, C.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Safia Chenouf, N.; Pimenta, P.; Pereira, A.R.; Ramos, S.; Sadi, M.; Martins, Â.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Diversity of Clones among Faecal ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy and Sick Dogs Living in Portugal. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and Simple Determination of the Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Correia, E.; Pereira, J.E.; González-Machado, C.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus Aureus from Pets, Live-Stock, and Wild Animals: Relationship with Clonal Lineages and Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.M.; Acuff, G.; Bergeron, G.; Bourassa, M.W.; Gill, J.; Graham, D.W.; Kahn, L.H.; Morley, P.S.; Salois, M.J.; Simjee, S.; et al. Critically Important Antibiotics: Criteria and Approaches for Measuring and Reducing Their Use in Food Animal Agriculture. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1441, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haulisah, N.A.; Hassan, L.; Bejo, S.K.; Jajere, S.M.; Ahmad, N.I. High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in Isolates From Diseased Livestock. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 652351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefioye, O.J.; Weinreich, J.; Rödiger, S.; Schierack, P.; Olowe, O.A. Phylogenetic Characterization and Multilocus Sequence Typing of Extended-Spectrum Beta Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Food-Producing Animals, Beef, and Humans in Southwest Nigeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storey, N.; Cawthraw, S.; Turner, O.; Rambaldi, M.; Lemma, F.; Horton, R.; Randall, L.; Duggett, N.A.; Abuoun, M.; Martelli, F.; et al. Use of Genomics to Explore AMR Persistence in an Outdoor Pig Farm with Low Antimicrobial Usage. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawangpa, A.; Lertwatcharasarakul, P.; Boonsoongnern, A.; Ratanavanichrojn, N.; Sanguankiat, A.; Pinniam, N.; Jala, S.; Laopiem, S.; Tulayakul, P. Multidrug Resistance Problems Targeting Piglets and Environmental Health by Escherichia coli in Intensive Swine Farms. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.J.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Zingali, T.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.E.; Chapman, T.A.; Djordjevic, S.P. Porcine Commensal Escherichia coli: A Reservoir for Class 1 Integrons Associated with IS26. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; An, J.U.; Guk, J.H.; Song, H.; Yi, S.; Kim, W.H.; Cho, S. Prevalence, Characteristics and Clonal Distribution of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase- and AmpC β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Following the Swine Production Stages, and Potential Risks to Humans. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 710747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, C.; Nordmann, P.; Pittet, O.; Poirel, L. Does an Antibiotic Stewardship Applied in a Pig Farm Lead to Low Esbl Prevalence? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, T.; Reid, C.J.; Chapman, T.A.; Gaio, D.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.E.; Djordjevic, S.P. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis of Porcine Faecal Commensal Escherichia coli Carrying Class 1 Integrons from Sows and Their Offspring. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Feng, C.; Duan, Y.; Wang, P.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Ecological Risk under the Dual Threat of Heavy Metals and Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli in Swine-Farming Wastewater in Shandong Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajhar, S.; Brownlie, J.; Barlow, R. Characterization of biofilm-forming capacity and resistance to sanitizers of a range of E. coli O26 pathotypes from clinical cases and cattle in Australia. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Fredrick Wabwire, T.; Tumwine, G.; Waiswa, P. Antimicrobial Usage by Small-Scale Commercial Poultry Farmers in Mid-Western District of Masindi Uganda: Patterns, Public Health Implications, and Antimicrobial Resistance of E. Coli. Veter. Med. Int. 2023, 2023, 6644271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| E. coli Isolate | Farm Compartment | Antimicrobial Resistance | Phylogroup | Integrons | Virulence Factors | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype | Genotype | |||||
| AS1 | Rearing | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | sul3-cmlA-aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-ampC-ant (2)-aac(6)-Ib-sul2-blaIMP | A | int1-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS2 | Gestation cells | AMP-TOB-CIP-SXT-C-TE | parC | A | int1-int2 | fimA |
| AS4 | Maternities | IMI-AMP-AK-CN-S-TOB-CAZ-SXT-C-TE | ant(2)-sul2 | A | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA-aer |
| AS5 | Gestation parks | IMI-ATM-CN-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-tetM-ampC- ant(2)-aac(6)-Ib-sul2-blaIMP-strB | B1 | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA cnf1-aer |
| AS6 | Rearing | AMP-TOB-CIP-SXT-TE | sul3-parC-qnrS-ampC-aac(6)-Ib | D | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp-cnf1 |
| AS7 | Gestation parks | IMI-S-TOB-SXT-TE | aadA1-ampC-sul2-strB | B1 | int1-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS8 | Maternities | AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-ampC | A | int1-Rvint1 | cnf1 |
| AS9 | Gestation cells | AMP-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | cmlA-aadA1-tetM-ampC-tetB-int2 | A | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS10 | Gestation cells | AMP-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-ampC-tetB-aac(3)-IV | A | int1-Rvint1 | fimA-papC-bfp-cnf1 |
| AS11 | Maternities | IMI-ATM-AMP-S-TOB-CIP-SXT-C-TE | sul3-cmlA-parC-blaTEM-tetB | D | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA-cnf1 |
| AS12 | Gestation parks | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-ampC-tetB-blaIMP | A | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp-cnf1 |
| AS13 | Gestation parks | AMP-TOB-CIP-SXT-TE | sul3-parC-aadA1-ant(2)-ampC | A | int1-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS14 | Gestation parks | AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | cmlA-blaTEM-ant(2)- | A | int2-Rvint1 | - |
| AS15 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-AK-S-TOB-CIP-SXT-TE | aac(6)-Ib-parC-aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-ampC-sul2-blaIMP | A | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS16 | Gestation cells | AMP-TOB-CIP-SXT-C-TE | sul3-cmlA-parC-tetM-ampC | A | int1-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS18 | Nulliparous | IMI-AMP-S-TOB-TE | aadA1-blaTEM-tetB-ampC-aac(6)-Ib-blaIMP-strB | A | int2 | bfp |
| AS19 | Rearing | IMI-AMP-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | sul3-cmlA-aadA1-tetB-ampC-sul2-strB-aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | int1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS20 | Gestation parks | AMP-TOB-SXT-C-TE | sul3-cmlA-ampC-sul2-aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | int1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS21 | Maternities | IMI-AMP-CN-TOB-CIP-SXT-C-TE | sul3-parC-blaTEM-ampC-aac(6)-Ib-blaIMP-aac(3)-IV | A | int1 | fimA |
| AS22 | Gestation cells | IMI-AUG-AMP-AK-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-aadA1-blaTEM-tetB-ampC-sul2-blaIMP-aac(3)-IV | A | int1-Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS23 | Maternities | IMI-AUG-AMP-CN-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-tetA-blaTEM-ampC | D | int1-int2-Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS24 | Maternities | AMP-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-tetA-blaTEM-tetB-aac(3)-IV | A | - | fimA |
| AS25 | Gestation parks | AMP-TOB-SXT-C-TE | cmlA-blaTEM-ampC-tetB-aac(6)-Ib-aac(3)-IV | A | int1-Rvint1 | fima-bfp |
| AS26 | Gestation cells | IMI-AUG-AMP-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | sul3-ampC | A | Rvint1 | fima-bfp |
| AS27 | Gestation cells | IMI-AUG-AMP-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | sul3-ampC | A | Rvint1 | fima-bfp |
| AS28 | Gestation parks | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-NA-CIP-SXT-TE | parC-tetA-blaTEM-tetB-ampC-sul2-blaIMP-strB | A | Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS29 | Gestation parks | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-NA-CIP-SXT-TE | aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-tetB-ampC-aac(6)-Ib-sul2 | A | int2 | fimA |
| AS30 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-cmlA-aadA1-tetB-blaTEM-ampC-aac(6)-Ib | A | rvint2-int2-Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS32 | Gestation parks | IMI-AUG-AMP-AK-CN-S-TOB-CTX-CAZ-CIP-SXT-TE | aac(6)-Ib-parC-aadA1-tetB-blaTEM-ampC-strB | A | rvint2-int2-Rvint1 | papG-III |
| AS35 | Maternities | IMI-AMP-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-ampC-aac(3)-IV | A | - | fimA |
| AS36 | Rearing | IMI-AMP-AK-CN-TOB-SXT-C-TE | teta-ant(2)-blaTEM-ampC-sul2 aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | - | fimA |
| AS37 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-aadA1-tetB--blaTEM-ampC-blaIMP aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | A | int2 | fimA-bfp |
| AS38 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-AK-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-ampC-aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | A | int2-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS39 | Gestation parks | IMI-AMP-AK-CN-S-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-ant(2)-tetB-blaTEM-ampC-aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | D | int2 | fimA |
| AS40 | Fattening | AMP-AK-TOB-C-TE | - | B1 | Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS41 | Fattening | AMP-TOB-SXT-C-TE | cmlA-tetM-blaTEM-ampC-aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | Rvint1 | fimA |
| AS43 | Gestation parks | AUG-AMP-AK-TOB-SXT-TE | sul3-cmlA-blaTEM-ampC-aac(6)-Ib-sul2 aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| AS44 | Maternities | AUG-AMP-AK-TOB-SXT-TE | tetB-ampC-sul2 aac(3)-II | B1 | rvint2 | fimA-bfp |
| AS45 | Gestation cells | AMP-S-SXT-TE | aadA1-tetA-blaTEM-ampC-aac(6)-Ib-sul2 aac(3)-II-aac(3)-IV | B1 | rvint2-Rvint1 | fimA-bfp |
| E. coli Isolate | Farm Compartment | Antimicrobial Resistance | Phylogroup | Integrons | Virulence Factors | MLST Type | O-Serotype | Plasmid Replicon | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype | Genotype | β-Lactamase Genes | Chromosomal Mutations | ||||||||
| AS3 | Maternities | IMI-AMP-AK-CN-S-TOB-NA-CIP-SXT-C-TE | aph(6)-Id; aph (3″)-Ib; sul2; tet(A); dfrA14; evgA; H-NS; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; AcrE; TolC; emrB; emrR; mdtG; mdtH; msbA; marA; aadA; aadA2; dfrA12; sul2; cpxA; mdtA; mdtB; sul3 | blaTEM-1A | ampC-promoter | B1 | int1-int2 | Cib; cnf1; csgA; cvaC; etsC; etsC; fimH; fyuA; gad; hlyA; hlyE; hlyF; hra; iroN; irp2; iss; iucC; iutA; IpfA; mchF; nipl; ompT;papAF1651A; papC; sitA; terC; traJ; traT; tsh; yehC; yehD | ST5229 | H10 | IncFIA; IncFIB |
| AS17 | Rearing | AMP-AK-S-TOB-CIP-SXT-TE | aadA2;dfrA12; tet(M); tet(A); cmlA1; floR; evgA; H-NS; PmrF; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; AcrE; marA; sul2; mdtH; cpxA; emrR; emrB; TolC; msbA; sul3; dfrA1 | blaTEM-234; blaTEM-230; blaTEM-217; blaTEM-207; blaTEM-198; blaTEM-176; blaTEM-104; blaTEM-70; blaTEM-30; blaTEM-1B | - | B1 | int1 | csgA; fimH; gad; hlyE; IpfA; nIpl; fimH; gad; hlyE; IpfA; terC; yehA; yehB; yehc; yehD | ST5757 | H51 | InFIB |
| AS31 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-CN-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | aadA1;tet(A); evgA; emrK; emrY; QnrS1; dfrA12; aadA2; sul3; kdpE; H-NS; PmrF; YojI; Escherichia coli acrA; acrB; mdtP; mdtO; mdtN; eptA; msbA; acrD; emrR; emrA; emrB; bacA; TolC; cpxA; mdtH; mdtH; AcrE; AcrF; marA; mdtE; gadX | blaTEM-1A; blaLAP- | gyrA; gyrB; parC; parE; pmrA;pmrB; folP; 23S | A | - | cea; csgA; fimH; gad; hlyE; IpfA; nIpl; terC; traJ; traT; yehA; yehB; yehC; yehD | ST10 | H43 | IncFII; lncY |
| AS33 | Maternities | IMI-AMP-AK-CN-S-TOB-CIP-SXT-TE | aadA1; aph(6)-Id; aph (3″)-Ib; sul2; sul3; tet(A); dfrA1; PmrF; H-NS; evgA; TolC; AcrE; msbA; emrB; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; marA; mdtG; cpxA; dfrA12; aadA2; aadA; sul3; QnrS1 | blaTEM-1B | gyrA; gyrB; parC; parE; pmrA;pmrB; folP; 23S; 16rrsB; 16S-rrsC; 16S-rrsH; гpoB | A | int2 | Cib; csgA; fimH; gad; hlyE; iss; IpfA; nIpl; ompT; terC; yehA; yehC; yehD | ST1147 | O162/H7 | ColpEC648; IncFIB; IncFIC(FIl); Incl1-lAlpha) |
| AS34 | Gestation cells | IMI-AMP-AK-S-TOB-NA-CIP-SXT-C-TE | aadA2; aadA1; cmIA1; qnrB19; sul3; tet(A); dfrA12; H-NS; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; emrR; emrB; mdtG; mdtH; evgA; bac; cpxA; mdtA; YojI; mdtN; gadX; mdtF; mdtE; marA; TolC; eptA; SAT-2 | blaTEM-1B | gyrA; gyrB; parC; parE; pmrA;pmrB; folP; 23S; 16S-rrsB; 16S-rrsC; 16S-rrsH; гpoB; ampC-promoter | A | - | astA; csgA; fimH; gad; hlyE; nIpl; terC; traJ; traT; yehA; yehB; yehC; yehD | ST48 | O101/H9 | IncFIA(HI1); IncFIB(K); IncFIl; IncX1 |
| AS42 | Gestation parks | AUG-AMP-AK-TOB-SXT-TE | aadA2; aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; qnrS1; sul3; tet(A); dfrA12; H-NS; evgA; mdtE; msbA; AcrE; emrB; emrR; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; mdtG; mdtH; marA; cpxA; TolC; sul2 | blaTEM-1B; blaLAP-2 | gyrA; gyrB; parC; parE; pmrB; folP; 23S; ampC; 16S-rrsB; 16S-rrsC; 16S-rrsH; гpoB; ampC-promoter | B1 | Rvint1 | astA; csgA; fimH; fyuA; hlyE; irp2; kpsE;kpsMIll_K98; nIpl; terC; traJ; traT; tsh; yehA; yehB; yehC;yehD | ST101 | O13/O129/H11 | Col (MG828); IncFIB(K); IncFIB(pLF82); IncFIl; IncX1; p0111 |
| AS46 | Gestation cells | AMP-AK-S-TOB-SXT-C-TE | aadA1; aph(3’)-la; CmIA1; flor; tet(M); tet(A); mdtN; YojI; PmrF; acrB; Escherichia coli acrA; cpxA; acrD; emrA; emrB; mdtH; mdtG; bacA; TolC; H-NS; marA; msbA; dfrA12; aadA2; evgS; evgA; gadX; mdtF; mdtE; AcrE; AcrF; emrY; sul3 | blaTEM-1B | gyrA; parC; parE; pmrA; pmrB; folP; 23S; 16S-rrsB; 16S-rrsC; 16S-rrsH; гpoB; ampC-promoter | B1 | Rvint1 | anr; csgA; fdeC; fimH; gad; hlyE; iss; IpfA; nIpl; terC; traJ; traT; yehA; yehB; yehC; yehD | ST10 | H2/H35/O128 | InFIB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.d.L.E.; Azevedo, M.; Cordeiro, R.; Pereira, J.E.; Valentão, P.; Falco, V.; Igrejas, G.; Caniça, M.; et al. Unveiling Antibiotic Resistance, Clonal Diversity, and Biofilm Formation in E. coli Isolated from Healthy Swine in Portugal. Pathogens 2024, 13, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040305
Silva A, Silva V, Dapkevicius MdLE, Azevedo M, Cordeiro R, Pereira JE, Valentão P, Falco V, Igrejas G, Caniça M, et al. Unveiling Antibiotic Resistance, Clonal Diversity, and Biofilm Formation in E. coli Isolated from Healthy Swine in Portugal. Pathogens. 2024; 13(4):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040305
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Adriana, Vanessa Silva, Maria de Lurdes Enes Dapkevicius, Mónica Azevedo, Rui Cordeiro, José Eduardo Pereira, Patrícia Valentão, Virgílio Falco, Gilberto Igrejas, Manuela Caniça, and et al. 2024. "Unveiling Antibiotic Resistance, Clonal Diversity, and Biofilm Formation in E. coli Isolated from Healthy Swine in Portugal" Pathogens 13, no. 4: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040305
APA StyleSilva, A., Silva, V., Dapkevicius, M. d. L. E., Azevedo, M., Cordeiro, R., Pereira, J. E., Valentão, P., Falco, V., Igrejas, G., Caniça, M., & Poeta, P. (2024). Unveiling Antibiotic Resistance, Clonal Diversity, and Biofilm Formation in E. coli Isolated from Healthy Swine in Portugal. Pathogens, 13(4), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040305










