Rabies Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Free-Ranging Invasive Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
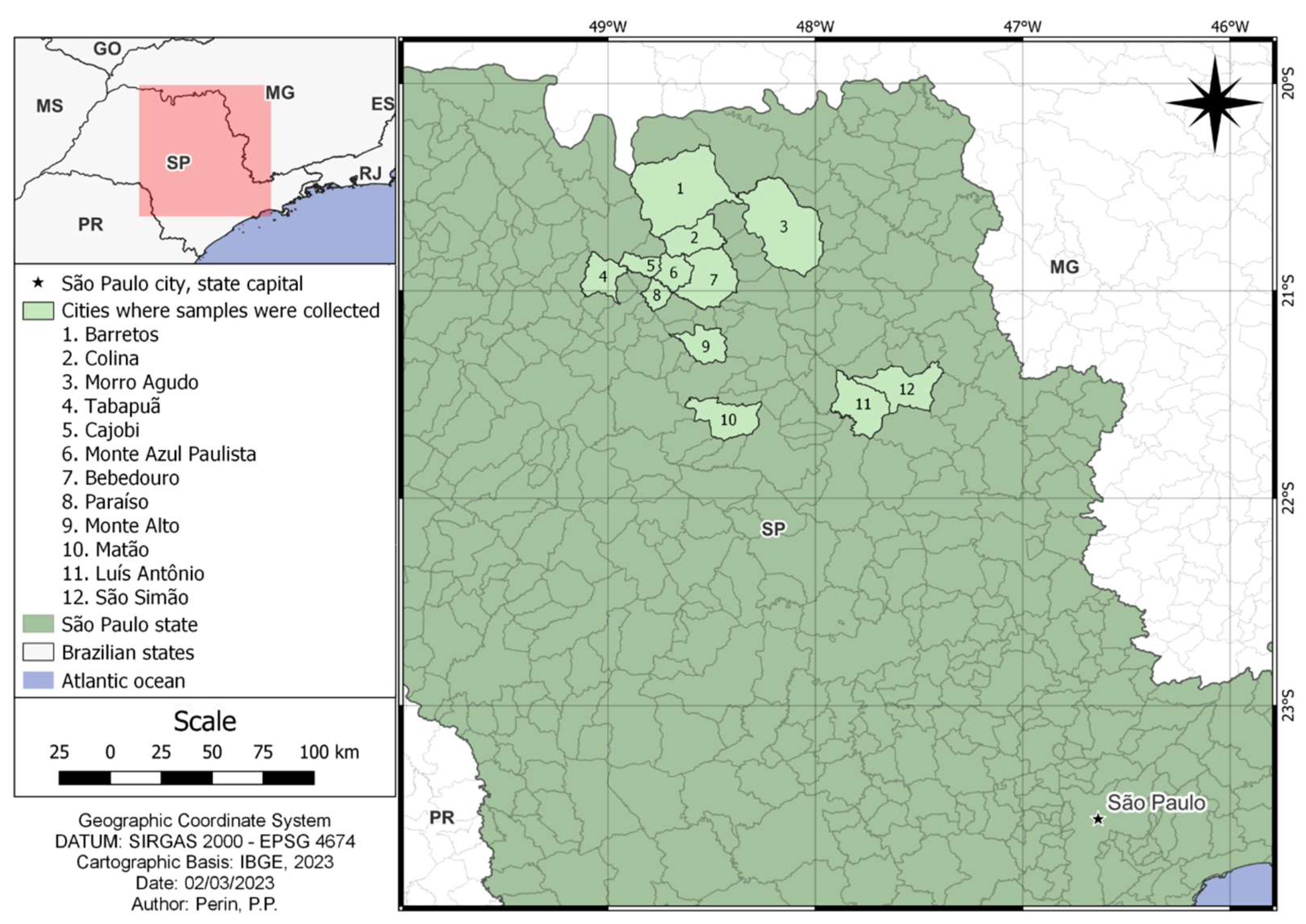
2.1. Study Area and Sample Acquisition
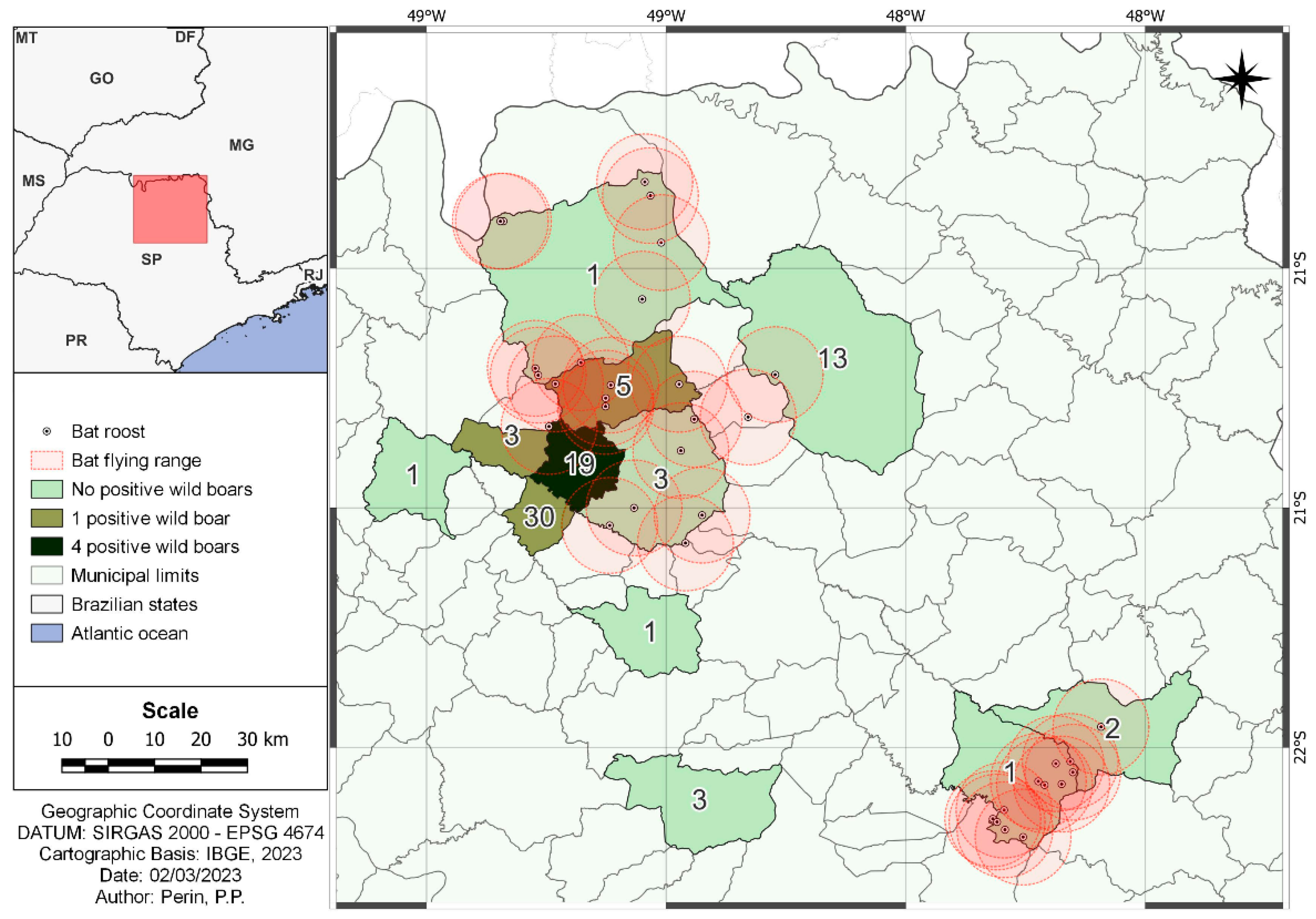
2.2. Bat Roost Identification
2.3. Histopathology
2.4. Direct Fluorescent Antibody Test
2.5. Viral Isolation
2.6. Detection of RABV Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Mustapha, A.I.; Bamidele, F.O.; Abubakar, A.T.; Ibrahim, A.; Oyewo, M.; Abdulrahim, I.; Yakub, J.M.; Olanrewaju, I.A.; Elelu, N.; Gibson, A.; et al. Perception of canine rabies among pupils under 15 years in Kwara State, North Central Nigeria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, M.A.; Ledesma, L.A.; Moura, W.C.; Lemos, E.R.S. From dogs to bats: Concerns regarding vampire bat-borne rabies in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, Twelfth Edition 2023. Chapter 3.1.18. Rabies (Infection with Rabies Virus and Other Lyssaviruses). Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Montebello, L.; Manrique Rocha, S.; Sciancalepore, S.; Hamrick, P.N.; Uieda, W.; Câmara, V.M.; Luiz, R.R.; Belotto, A. Fifty Years of the National Rabies Control Program in Brazil under the One Health Perspective. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, K.; Coudeville, L.; Lembo, T.; Sambo, M.; Kieffer, A.; Attlan, M.; Barrat, J.; Blanton, J.D.; Briggs, D.J.; Cleaveland, S.; et al. Estimating the global burden of endemic canine rabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.P.; Chand, R.; Huettmann, F.; Ghimire, T.R. Rabies Elimination: Is It Feasible without Considering Wildlife? J. Trop. Med. 2022, 2022, 5942693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plano de Monitoramento e Controle de Javalis (Sus scrofa). Available online: https://repositorio.icmbio.gov.br/bitstream/cecav/1499/1/Plano_de_Monitoramento_Javali_2019.pdf (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Galetti, M.; Pedrosa, F.; Keuroghlian, A.; Sazima, I. Liquid lunch–vampire bats feed on invasive feral pigs and other ungulates. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.; Batista, C.B.; Bender, D.; dos Reis, N.R.; Bazilio, S. Report on Desmodus rotundus (Chiroptera, Phyllostomidae) feeding on Sus scrofa (Artiodactyla, Suidae) blood. Bol. Soc. Bras. Mastozool. 2016, 77, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Teider-Junior, P.I.; Felipetto, L.G.; Kmetiuk, L.B.; Machado, F.P.; Chaves, L.B.; dos Santos Cunha Neto, R.; Corona, T.F.; Martins, C.M.; Bach, R.W.; de Barros Filho, I.R.; et al. Exposure of wild boar (Sus scrofa) to the common vampire bat and lack of immune protection to rabies virus in brazilian hunters. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.P.; Jayson, E.A. Wild pig rabies-A case study from Pathippara, Malappuram, Kerala. IJRMS 2020, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Serological surveillance for rabies and canine distemper in wild boar in Heilongjiang province, China. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2023, 69, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Biomas. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/informacoes-ambientais/vegetacao/15842-biomas.html (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Clima. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/informacoes-ambientais/climatologia/15817-clima.html (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia (INMET). Clima. Available online: https://portal.inmet.gov.br (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Produção Agropecuária São Paulo. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/explica/producao-agropecuaria/sp (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Dean, D.J.; Abelseth, M.K.; Athanasiu, P. The fluorescence antibody test. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies; Meslin, F.X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, W.A.; Casey, G.A. Virus isolation in neuroblastoma cell culture. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies; Meslin, F.X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Castilho, J.G.; Iamamoto, K.; de Oliveira Lima, J.Y.; Scheffer, K.C.; Junior, P.C.; de Oliveira, R.D.N.; Macedo, C.I.; Achkar, S.M.; Carrieri, M.L.; Kotait, I. Padronização e aplicação da técnica de isolamento do vírus da raiva em células de neuroblastoma de camundongo (N2A). BEPA 2007, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.S.; Yager, P.A.; Baer, G.M. A rapid fluorescentfocus inhibition test (RFFIT) for determining rabies virus-neutralizing antibodies. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies; Meslin, F.X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, L.B.; Mazutti, A.L.C.; Capolare, G.M.M.; Scheffer, K.C.; Silva, A.C.R. Rabies virus neutralizing antibodies: Comparison of two evaluation tests in cell culture. In Proceedings of the XVII Reunião Internacional de Raiva nas Américas (RITA), Belém, Brazil, 23–28 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Caporale, G.M.M.; da Silva, A.D.C.R.; Peixoto, Z.M.P.; Chaves, L.B.; Carrieri, M.L.; Vassão, R.C. First production of fluorescent anti-ribonucleoproteins conjugate for diagnostic of rabies in Brazil. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2009, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Fooks, A.R.; Abela-Ridder, B. (Eds.) Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–289. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhwa, A.; Wilkins, K.; Gao, J.; Condori Condori, R.E.; Gigante, C.M.; Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Ellison, J.A.; Greenberg, L.; Velasco-Villa, A.; et al. A pan-lyssavirus Taqman real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of highly variable rabies virus and other lyssaviruses. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, C.M.; Dettinger, L.; Powell, J.W.; Seiders, M.; Condori Condori, R.E.; Griesser, R.; Okogi, K.; Carlos, M.; Pesko, K.; Breckenridge, M.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of the LN34 pan-lyssavirus real-time RT-PCR assay for post-mortem rabies diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornazari, F.; Scheffer, K.C.; dos Ramos Silva, S.; da Silva, K.R.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Teixeira, C.R.; Rolim, L.S.; Langoni, H. Seroprevalence to Rabies Virus in Wildlife in Brazil. J. Wildl. Dis. 2022, 58, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.M.A.; Demoner, L.; Cruvinel, T.M.; Kataoka, A.P.; Martorelli, L.; Machado, G.P.; Megid, J. Rabies Virus Exposure of Brazilian Free-ranging Wildlife from Municipalities without Clinical Cases in Humans or in Terrestrial Wildlife. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.; De Luco, D.F. Wild boars (Sus scrofa L.) in Uruguay: Scavengers or predators? Mammalia 2003, 67, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballari, S.A.; Barrios-García, M.N. A review of wild boar Sus scrofa diet and factors affecting food selection in native and introduced ranges. Mammal. Rev. 2014, 44, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A. A review of non-bite transmission of rabies virus infection. Br. Vet. J. 1979, 135, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.; García-Serrano, A.; Couto, S.; Ortuño, V.M.; García-González, R. Diet of wild boar Sus scrofa L. and crop damage in an intensive agroecosystem. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2006, 52, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotta-Neto, F.; Peres, P.H.; Piovezan, U.; Passos, F.C.; Duarte, J.M. Hunting practices of feral pigs (Sus scrofa) and predation by vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus) as a potential route of rabies in the Brazilian Pantanal. Austral Ecol. 2021, 46, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.F.D.; Martorelli, L.F.A.; Sodré, M.M.; Kataoka, A.P.A.G.; Rosa, A.R.D.; Oliveira, M.L.D.; Amatuzzi, E. Rabies diagnosis and serology in bats from the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. 2011, 44, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Muylaert, R.L.; Stevens, R.D.; Ribeiro, M.C. Threshold effect of habitat loss on bat richness in cerrado-forest landscapes. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1854–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, S.; Donnelly, C.A.; Nouvellet, P.; Woodroffe, R. Rabies virus-neutralising antibodies in healthy, unvaccinated individuals: What do they mean for rabies epidemiology? PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliquet, F.; Müller, T.; Mutinelli, F.; Geronutti, S.; Brochier, B.; Selhorst, T.; Schereffer, J.L.; Krafft, N.; Burow, J.; Schameitat, A.; et al. Standardisation and establishment of a rabies ELISA test in European laboratories for assessing the efficacy of oral fox vaccination campaigns. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2986–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Brisbin, I.L. Wild Pigs: Biology, Damage, Control Techinques and Management; Report Number SRNL-RP-2009-00869; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2009; p. 975099.
- Wada, M.Y.; Rocha, S.M.; Maia-Elkhoury, A.N.S. Situação da raiva no Brasil, 2000 a 2009. Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde 2011, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.A.; Valderrama, W.; Recuenco, S.; Uieda, W.; Suzán, G.; Avila-Flores, R.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Almeida, M.; de Andrade, F.A.G.; Molina-Flores, B.; et al. Defining new pathways to manage the ongoing emergence of bat Rabies in Latin America. Viruses 2020, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Pasteur. Vacinação—Dados Estatísticos. Available online: https://www.saude.sp.gov.br/instituto-pasteur/paginas-internas/vacinacao/dados-estatisticos (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Gilbert, A.T.; Chipman, R.B. Rabies control in wild carnivores. In Rabies: Scientific Basis of the Disease and Its Management, 4th ed.; Fooks, A.R., Jackson, A.C., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 605–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Raiva. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-de-a-a-z/r/raiva (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Vengušt, G.; Hostnik, P.; Cerovšek, M.; Cilenšek, P.; Malovrh, T. Presence of antibodies against rabies in wild boars. Acta Vet. Hun. 2011, 59, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalu, M.A.; Wasniewski, M.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Servat, A.; Daraban Bocaneti, F.; Tanase, O.I.; Velescu, E.; Cliquet, F. Detection of rabies antibodies in wild boars in north-east Romania by a rabies ELISA test. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Yang, D.K.; Wang, J.Y.; An, D.J. The presence of rabies virus-neutralizing antibody in wild boars (Sus scrofa), a non-target bait vaccine animal in Korea. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, C.R.D.M.; Silva, M.L.C.R.; Gomes, A.A.D.B.; Garcia, A.I.E.; Ito, F.H.; Brandão, P.E.; Riet-Correa, F. Paralytic rabies in swine. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistema Eletrônico de Informações ao Cidadão (e-SIC). 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.br/abin/pt-br/acesso-a-informacao/servico-de-informacao-ao-cidadao (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Thompson, R.A. Parasite zoonoses and wildlife: One health, spillover and human activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, D.M.R.; de Barros, L.D.; Nino, B.D.S.L.; de Souza Pollo, A.; dos Santos Silva, A.C.; Perles, L.; André, M.G.; Machado, R.Z.; Garcia, J.L.; Lux Hoppe, E.G. Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from the State of São Paulo, Brazil: Serology, molecular characterization, and hunter’s perception on toxoplasmosis. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 23, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glud, H.A.; George, S.; Skovgaard, K.; Larsen, L.E. Zoonotic and reverse zoonotic transmission of viruses between humans and pigs. Apmis 2021, 129, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.O.S.; Costa Filho, R.B.; Pessoa, L.C.D.; Pires, P.S.; Salvarani, F.M.; Soares Filho, P.M.; Assis, R.A.; Lobato, F.C.F. Surto de raiva em suínos em Miracema, Tocantins, Brasil. Ciênc. Vet. Trop. 2008, 11, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- da Rosa Venancio, F.; dos Santos Alberti, T.; Zamboni, R.; Scheid, H.V.; Brunner, C.B.; Sallis, E.S.V.; Raffi, M.B. Raiva paralítica em suíno no Rio Grande do Sul. RCA 2020, 30, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Nociti, D.L.P.; Caramori Júnior, J.G.; Matta, G.C.A.; Aguiar, D.M. Raiva em suíno no estado de Mato Grosso-relato de infecção conjunta com bovino da mesma propriedade. AIB 2021, 76, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kureishi, A.; Xu, L.Z.; Wu, H.; Stiver, H.G. Rabies in China: Recommendations for control. Bull. World Health Organ. 1992, 70, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, H.F.L.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Nguyen, K.A.T.; de Jong, M.D.; Taylor, W.R.J.; Le, T.V.; Nguyen, H.H.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Farrar, J.; Horby, P.; et al. Furious rabies after an atypical exposure. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, L.E.; Umoh, J.U.; Dzikwi, A.A. Assessment of risk of possible exposure to rabies among processors and consumers of dog meat in Zaria and Kafanchan, Kaduna state, Nigeria. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2014, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, A.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, D.V.; Ngo, G.C.; Pham, T.Q.; Inoue, S.; Nishizono, A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, A.K.T. Rabies-infected dogs at slaughterhouses: A potential risk of rabies transmission via dog trading and butchering activities in Vietnam. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secretaria de Agricultura e Abastecimento do Estado de São Paulo (SAA-SP). Legislação: Resolução SAA—41, de 28/05/2021. Available online: https://www.defesa.agricultura.sp.gov.br/legislacoes/resolucao-saa-41-de-28-05-2021,1493.html (accessed on 29 February 2024).
| Variable | Rabies % (p/n, CI) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 2.3% (1/43, 0.4–12.1%) |
| Female | 16.7% (6/36, 7.9–31.9%) |
| Age | |
| ≤6 months | 5.0% (1/20, CI = 0.9–23.6%) |
| >6 months | 10.2% (6/59, CI = 4.7–20.5%) |
| Mesoregion (cities) | |
| Araraquara (Matão) | 0% (0/3, CI = 0–56.1%) |
| São José do Rio Preto (Cajobi, Paraíso, Tabapuã) | 5.9% (2/34, CI = 1.6–19.1%) |
| Ribeirão Preto (Barretos, Bebedouro, Colina, Luís Antônio, Monte Alto, Monte Azul Paulista, Morro Agudo, São Simão) | 11.9% (5/42, CI = 5.2–25.0%) |
| Variable | Rabies % (p/n, CI) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 2.6% (1/38, 0.5–13.5%) |
| Female | 17.6% (6/34, 8.3–33.5%) |
| Age | |
| ≤6 months | 5.6% (1/18, CI = 1.0–25.7%) |
| >6 months | 11.1% (6/54, CI = 5.2–22.2%) |
| Mesoregion (cities) | |
| Araraquara (Matão) | 0% (0/2, CI = 0–65.7%) |
| São José do Rio Preto (Cajobi, Paraíso, Tabapuã) | 6.1% (2/33, CI = 1.7–19.6%) |
| Ribeirão Preto (Barretos, Bebedouro, Colina, Luís Antônio, Monte Alto, Monte Azul Paulista, Morro Agudo, São Simão) | 13.5% (5/37, CI = 5.9–28.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perin, P.P.; Turmina, T.; Arias-Pacheco, C.A.; Gomes, J.S.; Andrade, L.d.O.; Zolla, N.d.O.; Mendonça, T.O.; Oliveira, W.J.; Fahl, W.d.O.; Scheffer, K.C.; et al. Rabies Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Free-Ranging Invasive Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Brazil. Pathogens 2024, 13, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040303
Perin PP, Turmina T, Arias-Pacheco CA, Gomes JS, Andrade LdO, Zolla NdO, Mendonça TO, Oliveira WJ, Fahl WdO, Scheffer KC, et al. Rabies Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Free-Ranging Invasive Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Brazil. Pathogens. 2024; 13(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040303
Chicago/Turabian StylePerin, Patricia Parreira, Talita Turmina, Carmen Andrea Arias-Pacheco, Jonathan Silvestre Gomes, Lívia de Oliveira Andrade, Natália de Oliveira Zolla, Talita Oliveira Mendonça, Wilson Junior Oliveira, Willian de Oliveira Fahl, Karin Correa Scheffer, and et al. 2024. "Rabies Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Free-Ranging Invasive Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Brazil" Pathogens 13, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040303
APA StylePerin, P. P., Turmina, T., Arias-Pacheco, C. A., Gomes, J. S., Andrade, L. d. O., Zolla, N. d. O., Mendonça, T. O., Oliveira, W. J., Fahl, W. d. O., Scheffer, K. C., Cunha Neto, R. d. S., Chierato, M. E. R., Mori, E., Felicio, A. L. d. A., Haga, G. S. I., Guido, M. C., Barrochelo, L. H., Marcos, A. d. S., & Lux Hoppe, E. G. (2024). Rabies Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Free-Ranging Invasive Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Brazil. Pathogens, 13(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040303










