Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Clonorchis sinensis: An In Silico Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Collection
2.2. Alignment and Haplotype Network
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Gene Flow, Diversity and Neutrality Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Haplotype Analyses
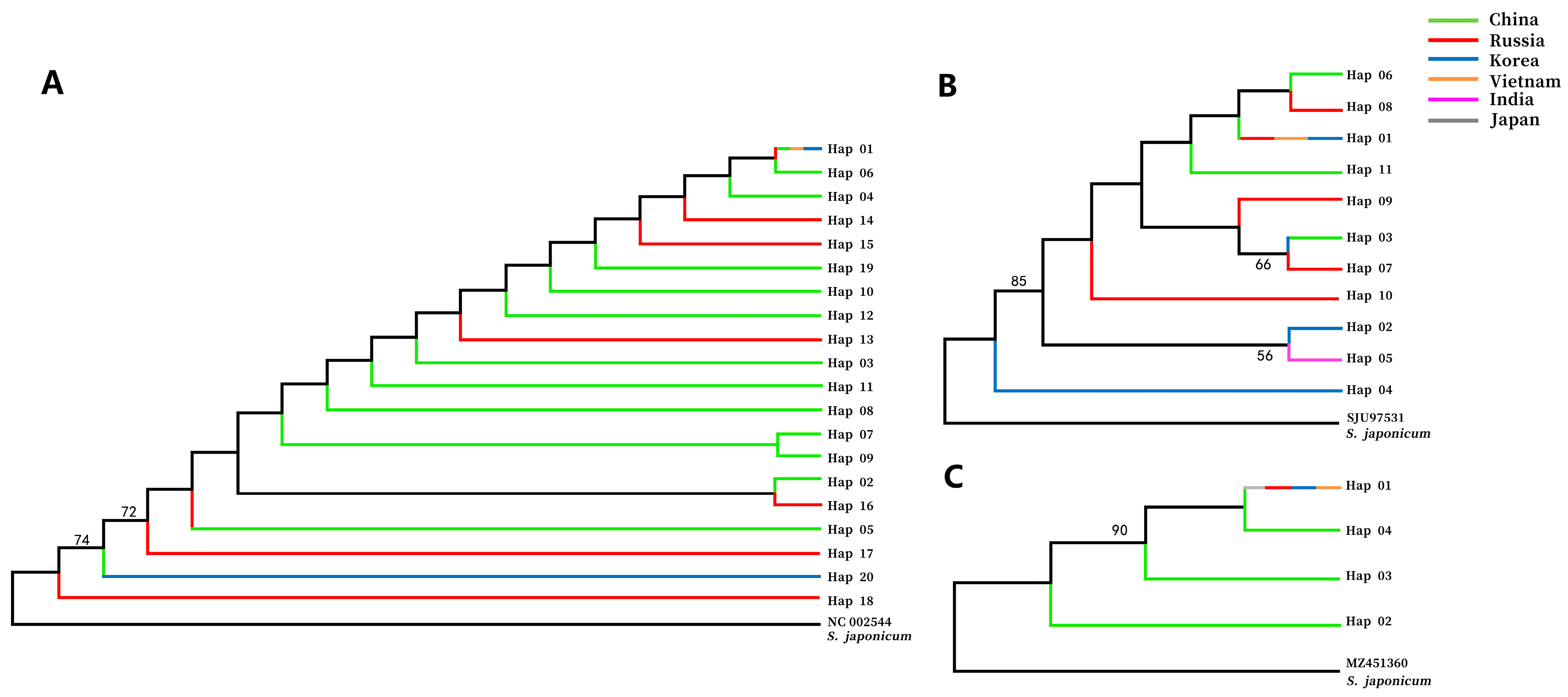
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.3. Gene Flow, Diversity and Neutrality Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, M.B.; Zhou, X.N. Clonorchis sinensis. Trends. Parasitol. 2021, 37, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.R.; Flohr, R.B. Fish- and shellfish–borne trematode infections in Canada. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. 1997, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, B.; Abruzzi, A. Food-borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 263–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asare, K.K.; Boampong, J.N.; Ameyaw, E.O.; Thomford, A.K.; Afoakwah, R.; Kwakye-Nuako, G.; Thomford, K.P.; Quashie, N.B. Microscopic identification of possible Clonorchis/Opisthorchis infection in two Ghanaian women with undiagnosed abdominal discomfort: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunyakti Kilinc, S.; Celik, F.; Kesik, H.K.; Simsek, S. In silico analysis of the biodiversity and conservation status of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (CO1) gene of Taenia multiceps. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, R.A.S.; Wedage, W.M.M.; Muthukumarana, L.S.; De Silva, B.G.D.N.K. Genetic diversity, phylogenetic and phylogeographic analysis of Anopheles culicifacies species complex using ITS2 and COI sequences. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumidae, A.; Ardpairin, J.; Pansri, S.; Homkaew, C.; Nichitcharoen, M.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. Genetic diversity and population structure of Physella acuta (Gastropoda: Physidae) in Thailand using mitochondrial gene markers: COI and 16S rDNA. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.H.; Li, Z.X.; Feng, G.N. Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Meretrix (Mollusca: Veneridae) based on mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Zool. Res. 2009, 30, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelomina, G.N.; Tatonova, Y.V.; Hung, N.M.; Ngo, H.D. Genetic diversity of the Chinese liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis from Russia and Vietnam. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodovnik, D.A.; Tatonova, Y.V.; Burkovskaya, P.V. The geographical vector in distribution of genetic diversity for Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panijpan, B.; Kowasupat, C.; Laosinchai, P.; Ruenwongsa, P.; Phongdara, A.; Senapin, S.; Wanna, W.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Kühne, J.; Fasquel, F. Southeast Asian mouth-brooding Betta fighting fish (Teleostei: Perciformes) species and their phylogenetic relationships based on mitochondrial COI and nuclear ITS1 DNA sequences and analyses. Meta Gene 2014, 2, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paskewitz, S.M.; Wesson, D.M.; Collins, F.H. The internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA in five members of the Anopheles gambiae species complex. Insect Mol. Biol. 1993, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.U.; Huh, S. Variation of nuclear and mitochondrial DNAs in Korean and Chinese isolates of Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2004, 42, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könnecke, M.; Akeroyd, F.A.; Bernstein, H.J.; Brewster, A.S.; Campbell, S.I.; Clausen, B.; Cottrell, S.; Hoffmann, J.U.; Jemian, P.R.; Männicke, D.; et al. The NeXus data format. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Santolamazza, F.; Cacciò, S.M.; La Rosa, G.; Antolová, D.; Auer, H.; Bagrade, G.; Bandelj, P.; Basso, W.; Beck, R.; et al. Mitochondrial genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of Echinococcus multilocularis in Europe. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Khalid, A.; Ali, R.M.A.; Saqib, M.; Qamar, W.; Li, L.; Ahmad, B.; Fu, B.Q.; Yan, H.B.; Jia, W.Z. Genetic variation and population structure of Fasciola hepatica: An in silico analysis. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 2155–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegren, H.; Galtier, N. Determinants of genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Pau, J.; Gómez, A.; Serra, M. Founder effects drive the genetic structure of passively dispersed aquatic invertebrates. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhan, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; et al. Spatial patterns and conservation of genetic and phylogenetic diversity of wildlife in China. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Wu, L.; Cai, H.; Mu, L.; Yu, J.F.; Fu, S.Y.; Si, X.Y. Genetic diversity analysis of Dermacentor nuttalli within Inner Mongolia, China. Parasite. Vector. 2021, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatonova, Y.V.; Chelomina, G.N.; Besprosvannykh, V.V. Genetic diversity of nuclear ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 rDNA sequence in Clonorchis sinensis Cobbold, 1875 (Trematoda: Opisthorchidae) from the Russian Far East. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.M.; Yong, T.S. Geographical variation of the liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis, from Korea and China based on the karyotypes, zymodeme and DNA sequences. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. 2001, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Long, X.C.; Lei, J.H.; Li, Y.L. Comparison of ancient and modern Clonorchis sinensis based on ITS1 and ITS2 sequences. Acta Trop. 2007, 101, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Liang, P.; Wang, X.; Mao, Q.; Men, J.; Chen, W.; Deng, C.; Zhou, C.; et al. Low divergence of Clonorchis sinensis in China based on multilocus analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, B.; Tang, Q.; Chen, R.; Han, S. Molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of nuclear rDNA sequences of Clonorchis sinensis isolates from human fecal samples in Heilongjiang province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.A.S.; Bowen, B.W. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. J. Hered. 1998, 89, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, J.E.N. Corals in space and time; the biogeography and evolution of the Scleractinia. Q. Rev. Biol. 1996, 71, 285. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, R.S. Evolutionary consequences of restricted gene flow among natural populations of the copepod Tigriopus californicus. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1986, 39, 526–535. [Google Scholar]
- Bermingham, E.; Avise, J.C. Molecular zoogeography of freshwater fishes in the southeastern United States. Genetics 1986, 113, 939–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. New thoughts on an old riddle: What determines genetic diversity within and between species? Genomics 2016, 108, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Rozas, J. Statistical properties of new neutrality tests against population growth. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, J.C.; Schneider, J.A.; Tanguay, D.A.; Choi, J.; Acharya, T.; Stanley, S.E.; Jiang, R.; Messer, C.J.; Chew, A.; Han, J.H.; et al. Haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in 313 human genes. Science 2001, 293, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamathevan, J.J.; Hasan, S.; Emes, R.D.; Amrine-Madsen, H.; Rajagopalan, D.; Topp, S.D.; Kumar, V.; Word, M.; Simmons, M.D.; Foord, S.M.; et al. The role of positive selection in determining the molecular cause of species differences in disease. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Kong, X.Y.; Yu, Z.N.; Kong, J.; Ma, S.; Chen, L.M. Genetic diversity and historical demography of Chinese shrimp Feneropenaeus chinensis in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea based on mitochondrial DNA analysis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Gasser, R.B.; Li, F.; Bao, M.; Huang, W.; Zou, F.; Zhao, G.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Genetic variability within and among Haemonchus contortus isolates from goats and sheep in China. Parasite Vector. 2013, 6, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, F.; Wassermann, M.; Banda, F.; Mbaya, H.; Aschenborn, J.; Aschenborn, O.; Koskei, P.; Umhang, G.; De La Rue, M.; Elmahdi, I.E.; et al. Genetic polymorphism and population structure of Echinococcus ortleppi. Parasitology 2017, 144, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.L.; Alcala, N.; Rosenberg, N.A. FSTruct: An F-based tool for measuring ancestry variation in inference of population structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2614–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the genetics of populations. In Variability Within and Among Natural Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]

| Indexes | COX1 (205 bp) | ITS1 (241 bp) | ITS2 (250 bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of sequences | 168 | 275 | 91 |
| No. of mutations | 56 | 83 | 14 |
| Parsimony informative sites | 15 | 2 | 0 |
| No. of haplotypes | 20 | 11 | 4 |
| Haplotype diversity (Hd) | 0.444 ± 0.049 | 0.1129 ± 0.026 | 0.065 ± 0.036 |
| Nucleotide diversity (π) | 0.00559 ± 0.00204 | 0.00768 ± 0.00410 | 0.00124 ± 0.00104 |
| Tajima’s D | −2.68924 *** | −2.79729 *** | −2.46024 ** |
| Fu’s Fs | −15.056 | −4.195 | −1.591 |
| FLD | −7.40921 ** | −9.53714 ** | −6.24115 ** |
| FLF | −6.42975 ** | −7.60466 ** | −5.57906 ** |
| Fst | 0.00994 | 0.03787 | 0.00000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Lan, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhang, A.; Qiu, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, C. Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Clonorchis sinensis: An In Silico Analysis. Pathogens 2024, 13, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110991
Zhang X, Lan Z, Wei W, Zhang A, Qiu H, Gao J, Wang C. Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Clonorchis sinensis: An In Silico Analysis. Pathogens. 2024; 13(11):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110991
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinhui, Zhuo Lan, Wei Wei, Aihui Zhang, Hongyu Qiu, Junfeng Gao, and Chunren Wang. 2024. "Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Clonorchis sinensis: An In Silico Analysis" Pathogens 13, no. 11: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110991
APA StyleZhang, X., Lan, Z., Wei, W., Zhang, A., Qiu, H., Gao, J., & Wang, C. (2024). Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Clonorchis sinensis: An In Silico Analysis. Pathogens, 13(11), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110991







