Infection-Associated Flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
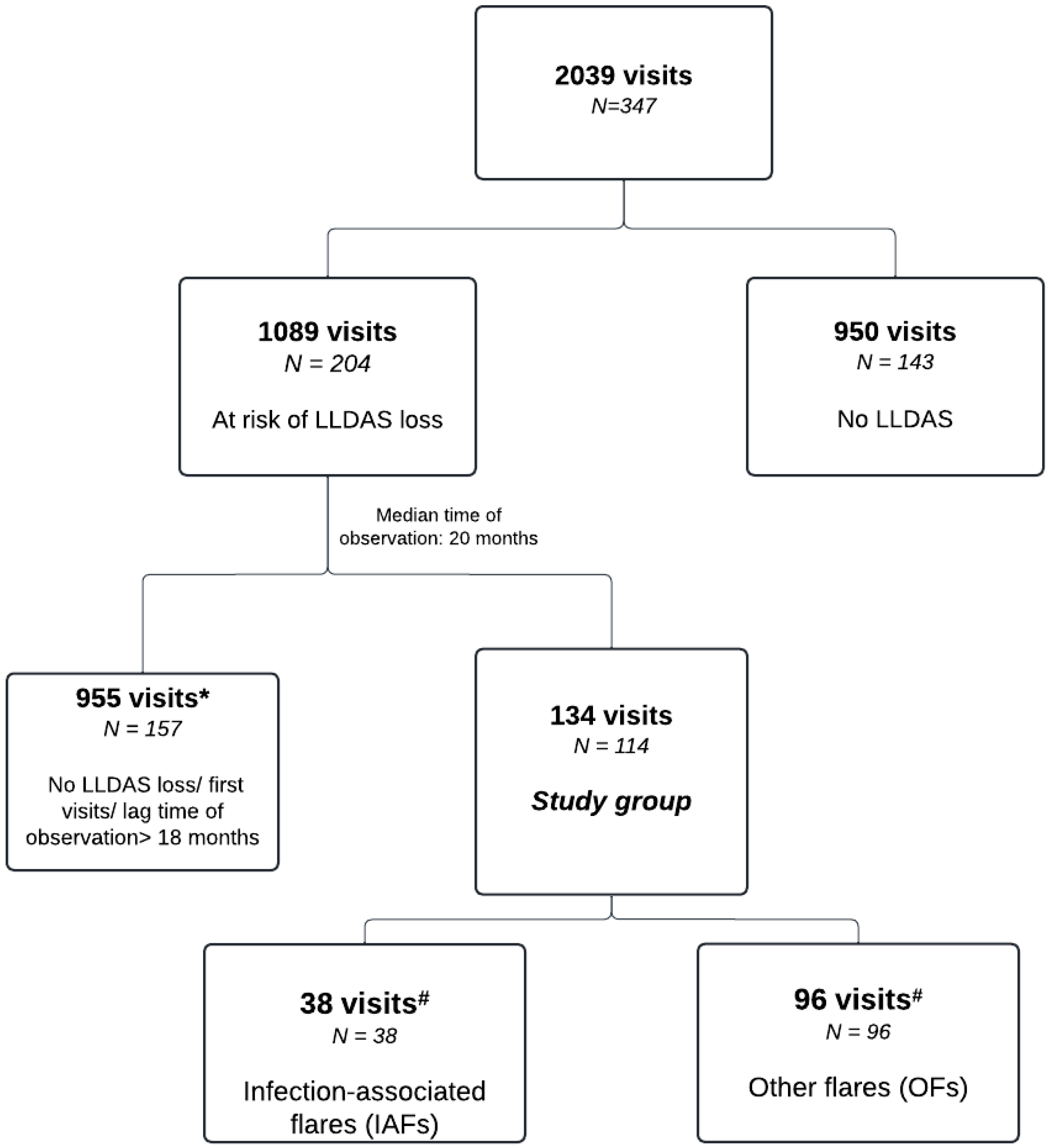
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Visit Selection
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and General Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Pre-Flare Disease Status
3.3. Flare Profiles by Groups
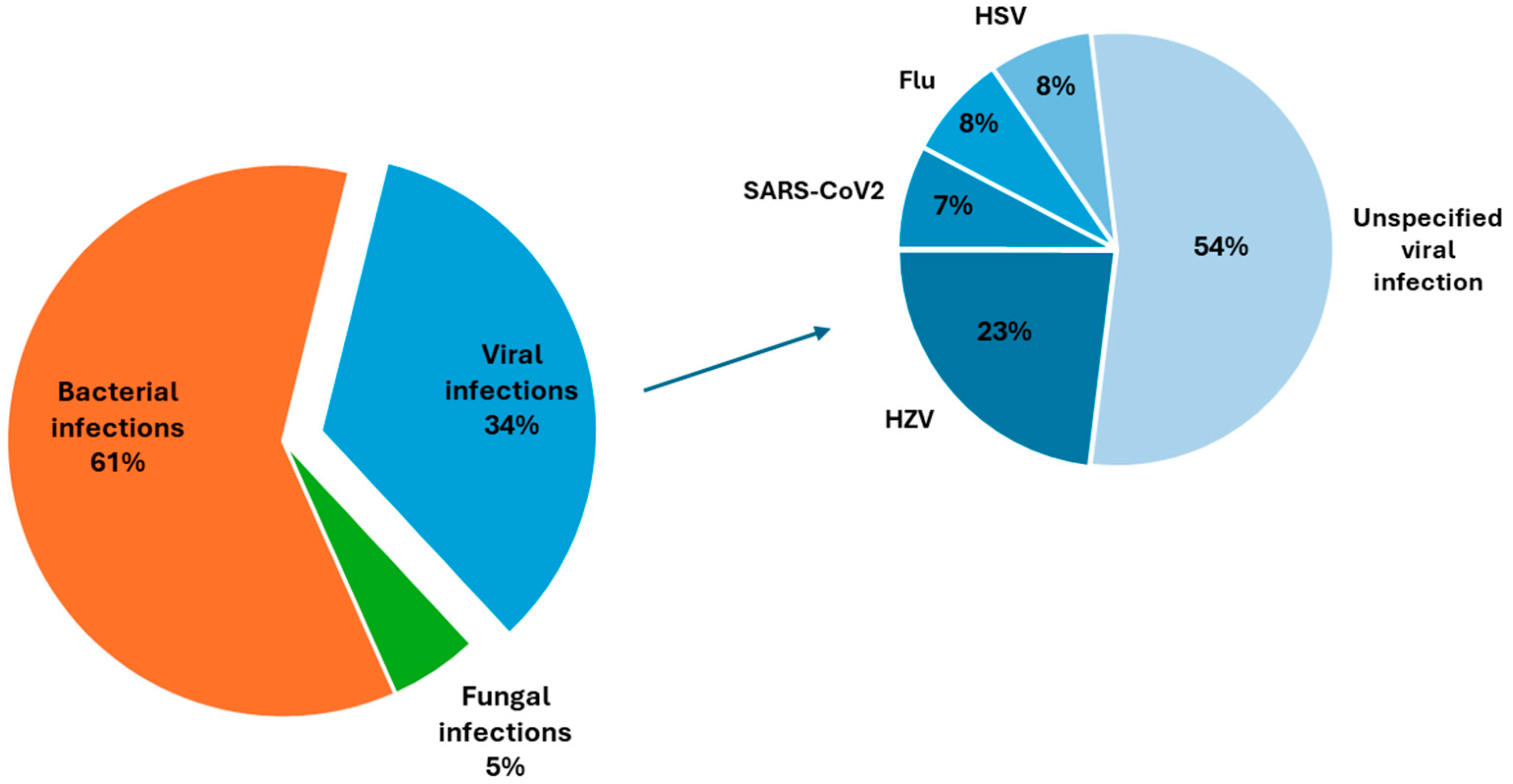
3.3.1. Characteristics of Infection-Associated Flares
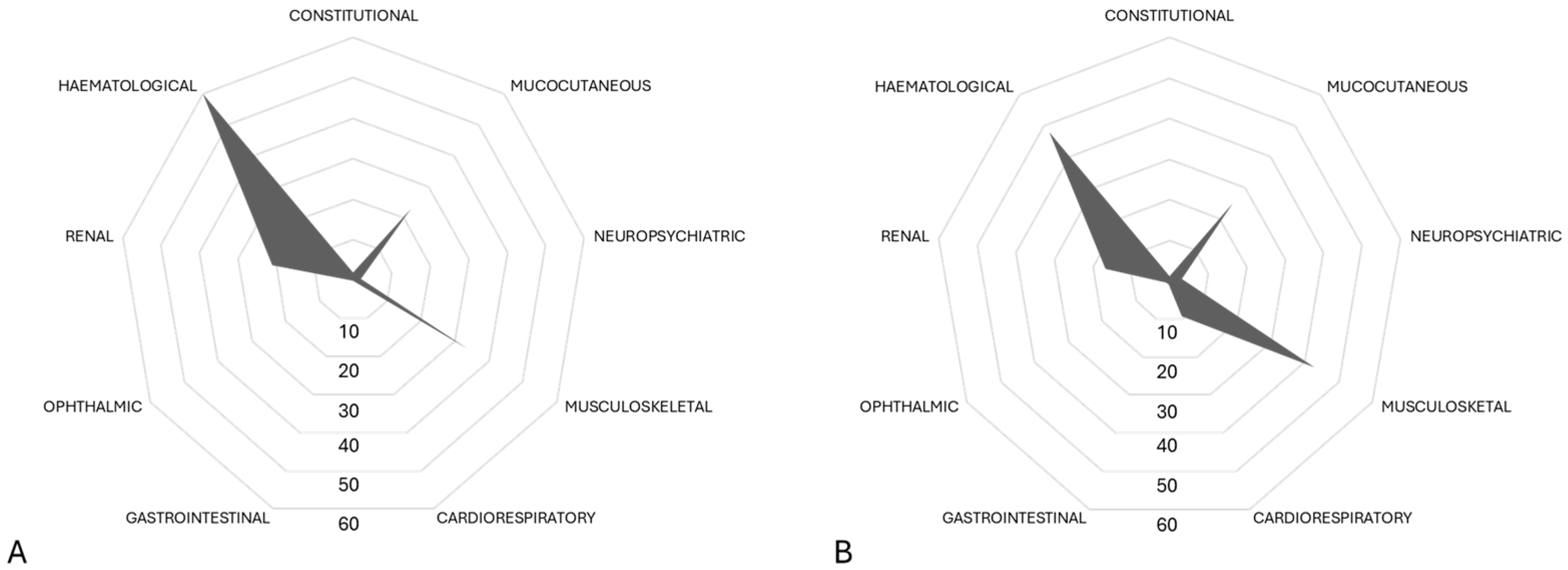
3.3.2. Clinical and Laboratory Features
3.3.3. Flare Severity
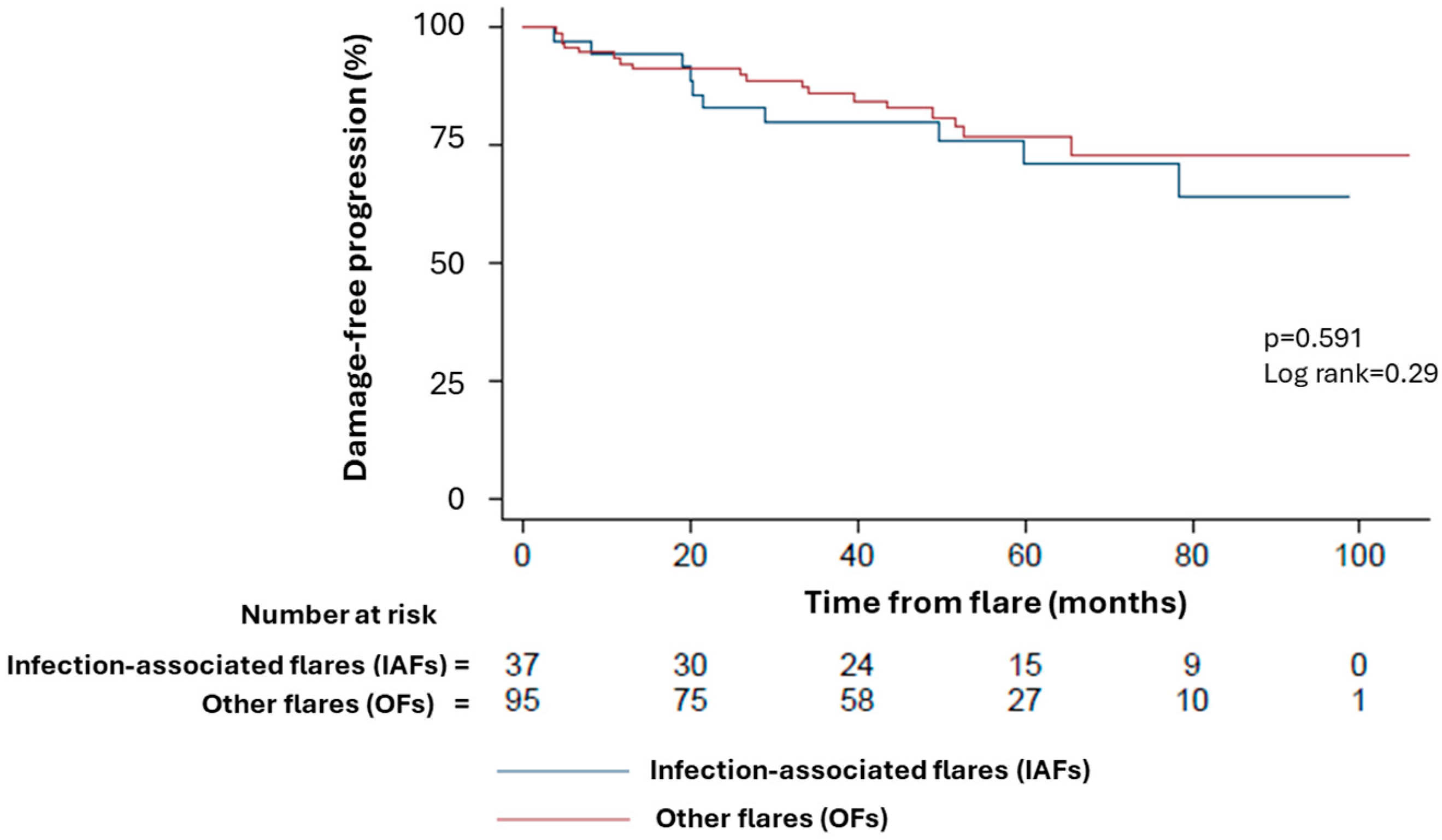
3.4. Long-Term Disease Course
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, C.H.; Sammaritano, L.R. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Tektonidou, M.G. Long-term outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus: Trends over time and major contributors. Rheumatology 2020, 59 (Suppl. S5), v29–v38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; Chan, T.M. B Cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis-Role in Pathogenesis and Effect of Immunosuppressive Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Gatto, M.; Sjowall, C. B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: Targets of new therapies and surveillance tools. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 952304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Gallo, L.M.; Oke, V.; Lundstrom, E.; Elvin, K.; Ling Wu, Y.; Eketjall, S.; Zickert, A.; Gustafsson, J.T.; Jonsen, A.; Leonard, D.; et al. Four Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Subgroups, Defined by Autoantibodies Status, Differ Regarding HLA-DRB1 Genotype Associations and Immunological and Clinical Manifestations. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 4, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Tassi, E.; Noviello, M.; Mazzi, B.A.; Moroni, L.; Citterio, L.; Zagato, L.; Tombetti, E.; Doglio, M.; Baldissera, E.M.; et al. Histone-Specific CD4(+) T Cell Plasticity in Active and Quiescent Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ren, J.; Dai, C.; Kannapell, C.C.; Wang, H.; Gaskin, F.; Fu, S.M. Nature of T cell epitopes in lupus antigens and HLA-DR determines autoantibody initiation and diversification. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, C.; Cardelli, C.; Zen, M.; Moroni, L.; Piga, M.; Ceccarelli, F.; Fasano, S.; De Marchi, G.; Coladonato, L.; Emmi, G.; et al. Anifrolumab in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Real-World, Multicenter Study. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 51, jrheum.2024-0053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Saccon, F.; Andreoli, L.; Bartoloni, E.; Benvenuti, F.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Bozzolo, E.; Brunetta, E.; Canti, V.; Cardinaletti, P.; et al. Durable renal response and safety with add-on belimumab in patients with lupus nephritis in real-life setting (BeRLiSS-LN). Results from a large, nationwide, multicentric cohort. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 124, 102729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, S.A.; Shamsasenjan, K.; Ahmadi, M.; Abbasi, B. CAR Treg: A new approach in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Lu, L. CAR-T cell therapy: New hope for systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2581–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. Trial of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scofield, L.; Reinlib, L.; Alarcon, G.S.; Cooper, G.S. Employment and disability issues in systemic lupus erythematosus: A review. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, M.; Arnaud, L. The Main Challenges in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Where Do We Stand? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Piraquive, V.; Nieto-Aristizabal, I.; Canas, C.A.; Tobon, G.J. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: Causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Acevedo-Vasquez, E.; Alarcon, G.S.; Pastor-Asurza, C.A.; Alfaro-Lozano, J.L.; Cucho-Venegas, J.M.; Segami, M.I.; Wojdyla, D.; Soriano, E.R.; Drenkard, C.; et al. The number of flares patients experience impacts on damage accrual in systemic lupus erythematosus: Data from a multiethnic Latin American cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, T.; Sutcliffe, N.; Mach, J.; Klaghofer, R.; Isenberg, D.A. Analysis of the relationship between disease activity and damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus--a 5-yr prospective study. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baragetti, A.; Ramirez, G.A.; Magnoni, M.; Garlaschelli, K.; Grigore, L.; Berteotti, M.; Scotti, I.; Bozzolo, E.; Berti, A.; Camici, P.G.; et al. Disease trends over time and CD4+CCR5+ T-cells expansion predict carotid atherosclerosis development in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerosa, M.; Beretta, L.; Ramirez, G.A.; Bozzolo, E.; Cornalba, M.; Bellocchi, C.; Argolini, L.M.; Moroni, L.; Farina, N.; Segatto, G.; et al. Long-Term Clinical Outcome in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Followed for More Than 20 Years: The Milan Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Consortium (SMiLE) Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, M.; Saccon, F.; Gatto, M.; Montesso, G.; Larosa, M.; Benvenuti, F.; Iaccarino, L.; Doria, A. Prevalence and predictors of flare after immunosuppressant discontinuation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in remission. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Bertsias, G.; Doria, A.; Isenberg, D.; Morand, E.; Petri, M.A.; Pons-Estel, B.A.; Rahman, A.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Voskuyl, A.; et al. 2021 DORIS definition of remission in SLE: Final recommendations from an international task force. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklyn, K.; Lau, C.S.; Navarra, S.V.; Louthrenoo, W.; Lateef, A.; Hamijoyo, L.; Wahono, C.S.; Chen, S.L.; Jin, O.; Morton, S.; et al. Definition and initial validation of a Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golder, V.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Huq, M.; Nim, H.T.; Louthrenoo, W.; Luo, S.F.; Wu, Y.-J.J.; Lateef, A.; Sockalingam, S.; Navarra, S.V.; et al. Lupus low disease activity state as a treatment endpoint for systemic lupus erythematosus: A prospective validation study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e95–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Canti, V.; Moiola, L.; Magnoni, M.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Coletto, L.A.; Dagna, L.; Manfredi, A.A.; Bozzolo, E.P. Performance of SLE responder index and lupus low disease activity state in real life: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, A.; Piga, M.; Cauli, A.; Mathieu, A. Predictors of flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Preventive therapeutic intervention based on serial anti-dsDNA antibodies assessment. Analysis of a monocentric cohort and literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.N.; Saraiva, L.; Jesus, D.; Doria, A.; da Silva, J.P.; Ines, L.S. Predictors of flare in SLE patients fulfilling lupus low disease activity state: A cohort study of 292 patients with 36-month follow-up. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 3627–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Perry, A.; Zimmerman, N.M.; Bryant, G. Predictors of flare-related inpatient or emergency department stay in systemic lupus erythematosus: A real-world analysis of Medicaid claims in the United States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2024, 30, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sumichika, Y.; Saito, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Temmoku, J.; Fujita, Y.; Matsuoka, N.; Asano, T.; Migita, K. Clinical features of flare in Japanese patients with new-onset SLE and risk factors for SLE flare in daily clinical practice: A single-center cohort study. Immunol. Med. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, F.; Chambers, S.; Rahman, A.; Isenberg, D.A. Serious infections in British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Hospitalisations and mortality. Lupus 2009, 18, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Zarza, J.E.; Alvarez-Hernandez, E.; Casasola-Vargas, J.C.; Estrada-Castro, E.; Burgos-Vargas, R. Prevalence of community-acquired and nosocomial infections in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2010, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, Y.B.; Kim, K.J.; Park, K.S.; Park, Y.J. Influenza infection as a trigger for systemic lupus erythematosus flares resulting in hospitalization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Olivares, N.; Ruiz-Arruza, I.; Martinez-Berriotxoa, A.; Egurbide, M.V.; Aguirre, C. Predictors of major infections in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Echavarri, C.; Capdevila, O.; Espinosa, G.; Suarez, S.; Marin-Ballve, A.; Gonzalez-Leon, R.; Rodriguez-Carballeira, M.; Fonseca-Aizpuru, E.; Pinilla, B.; Pallares, L.; et al. Infections in newly diagnosed Spanish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Data from the RELES cohort. Lupus 2018, 27, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, T.; Fujimori, D.; Yamamoto, Y. Systemic lupus erythematosus and immunodeficiency. Immunol. Med. 2019, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Nicholson, L.; Pooley, N.; Langham, S.; Embleton, N.; Marjenberg, Z.; Barut, V.; Desta, B.; Wang, X.; Langham, J.; et al. The risk of infections in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, F.P.B.; Najm, A.; Alunno, A.; Schoones, J.W.; Landewe, R.B.M.; Machado, P.M.; Navarro-Compan, V. Risk and prognosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: A systematic literature review to inform EULAR recommendations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danza, A.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G. Infection risk in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Susceptibility factors and preventive strategies. Lupus 2013, 22, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, B.; Virelli, G.; Pedrollo, E.; Caprioli, M.; Riva, M.; Renna, D.; Tonutti, A.; Luciano, N.; Ceribelli, A.; Gremese, E.; et al. High risk of misclassification of acute Parvovirus B19 infection into a systemic rheumatic disease. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2024, 8, rkae105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, F.; Collazos, J.; Mendoza, F.; De La Viuda, J.M.; Cazallas, J.; Urkijo, J.C.; Flores, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated with acute parvovirus B19 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, E.F.; Michaud, K.; Katz, R.; Wolfe, F. Increased incidence of herpes zoster among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2013, 22, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draborg, A.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Westergaard, M.; Mortensen, S.; Larsen, J.L.; Houen, G.; Duus, K. Reduced response to Epstein-Barr virus antigens by T-cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus Sci. Med. 2014, 1, e000015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, A.; Colombo, E.; Dai, H.; Agarwal, R.; Mark, K.A.; Banki, K.; Poiesz, B.J.; Phillips, P.E.; Hoch, S.O.; Reveille, J.D.; et al. Antibody reactivity to the HRES-1 endogenous retroviral element identifies a subset of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and overlap syndromes. Correlation with antinuclear antibodies and HLA class II alleles. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draborg, A.H.; Sandhu, N.; Larsen, N.; Lisander Larsen, J.; Jacobsen, S.; Houen, G. Impaired Cytokine Responses to Epstein-Barr Virus Antigens in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 6473204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monneaux, F.; Muller, S. Epitope spreading in systemic lupus erythematosus: Identification of triggering peptide sequences. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Quan, T.; Nolasco, H.; Park, S.H.; Hong, M.S.; Crouch, J.; Pamer, E.G.; Howe, J.G.; Craft, J. Defective control of latent Epstein-Barr virus infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Alves, C.E.C.; Pontes, G.S. Epstein-Barr virus: The mastermind of immune chaos. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1297994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smatti, M.K.; Cyprian, F.S.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al Thani, A.A.; Almishal, R.O.; Yassine, H.M. Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses 2019, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, V.; Rondaan, C.; Heijstek, M.W.; Agmon-Levin, N.; van Assen, S.; Bijl, M.; Breedveld, F.C.; D’Amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; et al. 2019 update of EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Andersen, J.; Aringer, M.; Arnaud, L.; Bae, S.C.; Boletis, J.; Bruce, I.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Ministry of Health. Piano Nazionale Prevenzione Vaccinale 2017–2019. National Vaccine Prevention Plan 2017–2019. 2017. Available online: http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2571_allegato.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Touma, Z.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B. Vaccination and auto-immune rheumatic diseases: Lessons learnt from the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus vaccination campaign. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urowitz, M.B.; Anton, A.; Ibanez, D.; Gladman, D.D. Autoantibody response to adjuvant and nonadjuvant H1N1 vaccination in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattui, S.E.; Liew, J.W.; Kennedy, K.; Sirotich, E.; Putman, M.; Moni, T.T.; Akpabio, A.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Berenbaum, F.; Bulina, I.; et al. Early experience of COVID-19 vaccination in adults with systemic rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Vaccine Survey. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, V.; Eviatar, T.; Zisman, D.; Peleg, H.; Paran, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Zisapel, M.; Elalouf, O.; Kaufman, I.; Meidan, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: A multicentre study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerosa, M.; Schioppo, T.; Argolini, L.M.; Sciascia, S.; Ramirez, G.A.; Moroni, G.; Sinico, R.A.; Bonelli, G.; Alberici, F.; Mescia, F.; et al. The Impact of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Batani, V.; Moroni, L.; De Luca, G.; Pizzetti, G.; Sala, S.; Peretto, G.; Campochiaro, C.; Della-Torre, E.; Bozzolo, E.P.; et al. Cardiac Safety of mRNA-Based Vaccines in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus-like Disorders with a History of Myocarditis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallard, M.; Adinolfi, A.; Belloli, L.; Casu, C.; Di Cicco, M.; Destefani, C.; Di Rosa, B.; Gentile, M.G.; Filippini, D.A.; Luisi, A.; et al. Active vaccination campaign to increase seasonal influenza vaccination coverage: A monocenter experience in a cohort of Italian patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Shen, X.; Zhou, A.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. A survey of systemic lupus erythematosus patients’ attitudes toward influenza and pneumococcal vaccination in Southwest China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1018899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira de Rezende, R.; Mattos, G.; de Mello Leal Augusto, R.; Machado Gayer, C.; Mendes Klumb, E. Predictors for seasonal influenza vaccination and reasons for inadequate vaccination coverage against a broad spectrum of vaccine-preventable diseases: A cross-sectional study among a Brazilian cohort of adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2019, 28, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Hellmann, D.; Hochberg, M. Validity and reliability of lupus activity measures in the routine clinic setting. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tani, C.; Vagelli, R.; Stagnaro, C.; Carli, L.; Mosca, M. Remission and low disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: An achievable goal even with fewer steroids? Real-life data from a monocentric cohort. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Shen, L.; Huq, M.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Golder, V.; Louthrenoo, W.; Chen, Y.H.; Hamijoyo, L.; Luo, S.F.; Wu, Y.J.; et al. Impact of low disease activity, remission, and complete remission on flares following tapering of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematous: A multinational cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e584–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, M.; Floris, A.; Cappellazzo, G.; Chessa, E.; Congia, M.; Mathieu, A.; Cauli, A. Failure to achieve lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) six months after diagnosis is associated with early damage accrual in Caucasian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felten, R.; Kawka, L.; Dubois, M.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Fuentes-Silva, Y.; Piga, M.; Arnaud, L. Tolerance of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: The international VACOLUP study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e613–e615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Asperti, C.; Cucca, V.; Yacoub, M.R. Challenges to Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in Patients with Immune-Mediated Diseases. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangfeld, A.; Schafer, M.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; Liew, J.W.; Ljung, L.; Mateus, E.F.; Richez, C.; Santos, M.J.; Schmajuk, G.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Gerosa, M.; Bellocchi, C.; Arroyo-Sánchez, D.; Asperti, C.; Argolini, L.M.; Gallina, G.; Cornalba, M.; Scotti, I.; Suardi, I.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Agents and Monoclonal Antibodies in Patients with SLE: A Case-Control Study. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Mikdashi, J. A Framework to Overcome Challenges in the Management of Infections in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Open Access Rheumatol. 2023, 15, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, J.; Barrera-Vargas, A.; Ortiz-Hernandez, R.; Alcocer-Varela, J.; Ponce-de-Leon, A.; Gomez-Martin, D. Microbiological and immunological profile of patients with severe lupus flares related to bloodstream infections: A retrospective cohort study. Lupus 2018, 27, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonana-Nacach, A.; Camargo-Coronel, A.; Yanez, P.; Sanchez, L.; Jimenez-Balderas, F.J.; Fraga, A. Infections in outpatients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A prospective study. Lupus 2001, 10, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandino, I.J.; Scolnik, M.; Bertiller, E.; Scaglioni, V.; Catoggio, L.J.; Soriano, E.R. Complement levels and risk of organ involvement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2017, 4, e000209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathian, A.; Breillat, P.; Dorgham, K.; Bastard, P.; Charre, C.; Lhote, R.; Quentric, P.; Moyon, Q.; Mariaggi, A.A.; Mouries-Martin, S.; et al. Lower disease activity but higher risk of severe COVID-19 and herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with pre-existing autoantibodies neutralising IFN-alpha. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chi, H.; Teng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H.; Su, Y.; Liu, H.; Ye, J.; Shi, H.; Hu, Q.; et al. Neutralizing anti-IFN-gamma IgG was increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and associated with susceptibility to infection. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Guthridge, J.M.; Chen, H.; Bourn, R.L.; Kamp, S.; Munroe, M.E.; Macwana, S.R.; Bean, K.; Sridharan, S.; Merrill, J.T.; et al. Immunologic findings precede rapid lupus flare after transient steroid therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Davis, H.; McCorkell, L.; Soares, L.; Wulf-Hanson, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID science, research and policy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2148–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, J.; Segura, B.T.; Wincup, C.; Rahman, A. Unmet Needs in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 55, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Kawata, A.K.; Fernandes, A.W.; Gajria, K.; Greth, W.; Hareendran, A.; Ethgen, D. Impaired health status and the effect of pain and fatigue on functioning in clinical trial patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, S.J.; Bastin, M.E.; Hamilton, I.F.; Hunt, D.; Ritchie, S.J.; Amft, E.N.; Thomson, S.; Belch, J.F.; Ralston, S.H.; Wardlaw, J.M. Fatigue and cognitive function in systemic lupus erythematosus: Associations with white matter microstructural damage. A diffusion tensor MRI study and meta-analysis. Lupus 2017, 26, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, L.; Mazzetti, M.; Ramirez, G.A.; Farina, N.; Bozzolo, E.P.; Guerrieri, S.; Moiola, L.; Filippi, M.; Di Mattei, V.; Dagna, L. Beyond Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Focus on Post-traumatic Stress Disorder and Alexithymia. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mertz, P.; Amoura, Z.; Voll, R.E.; Schwarting, A.; Maurier, F.; Blaison, G.; Bonnotte, B.; Poindron, V.; Fiehn, C.; et al. Patterns of fatigue and association with disease activity and clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piga, M.; Congia, M.; Gabba, A.; Figus, F.; Floris, A.; Mathieu, A.; Cauli, A. Musculoskeletal manifestations as determinants of quality of life impairment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floris, A.; Chessa, E.; Sebastiani, G.D.; Prevete, I.; Iannone, F.; Coladonato, L.; Govoni, M.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Mosca, M.; Tani, C.; et al. Glucocorticoid tapering and associated outcome in patients with newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus: The real-world GULP prospective observational study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathian, A.; Arnaud, L.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G. Is it safe to withdraw low-dose glucocorticoids in SLE patients in remission? Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselios, K.; Gladman, D.D.; Su, J.; Urowitz, M.B. Gradual Glucocorticosteroid Withdrawal Is Safe in Clinically Quiescent Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, T.; Takita, M.; Senoo, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Lower trust in national government links to no history of vaccination. Lancet 2020, 395, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, N.; Tharwat, S.; Shereef, R.R.E.; Elsaman, A.M.; Khalil, N.M.; Fathi, H.M.; Salem, M.N.; El-Saadany, H.M.; Samy, N.; El-Bahnasawy, A.S.; et al. Rheumatology university faculty opinion on coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) vaccines: The vaXurvey study from Egypt. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Argolini, L.M.; Bellocchi, C.; Moroni, L.; Della-Torre, E.; Farina, N.; Caporali, R.F.; Beretta, L.; Gerosa, M.; Bozzolo, E.P.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus throughout one year. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 231, 108845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Patients (n = 114) | OFs (n = 96) | IAFs (n = 38) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Women: n (%) | 100 (88) | 85 (88) | 33 (87) |
| Age at disease onset (years): median (IQR) | 28 (20–36) | 29 (20–37) | 26 (20–37) |
| Age at time of flare (years): median (IQR) | 44 (35–52) | 44 (35–52) | 32 (34–54) |
| Follow-up duration at time of flare (months): median (IQR) | 30 (13–62) | 34 (15–71) | 22(12–43) |
| General clinical characteristics (history): n (%) | |||
| Musculoskeletal involvement | 93 (80) | 78 (81) | 30 (79) |
| Mucocutaneous involvement | 82 (81) | 70 (72) | 26 (68) |
| Renal involvement | 47 (40) | 38 (39) | 17 (44) |
| NPSLE | 28 (24) | 22 (22) | 10 (26) |
| Cardiopulmonary involvement | 14 (12) | 9 (9) | 6 (15) |
| Haematological manifestations | 94 (82) | 78 (81) | 30 (79) |
| Constitutional symptoms | 46 (40) | 38 (39) | 17 (45) |
| Gastrointestinal manifestations | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
| Anti-phospholipid syndrome | 11 (10) | 9 (9) | 6 (16) |
| Serology (history): n (%) | |||
| Anti-dsDNA | 85 (74) | 71 (74) | 30 (79) |
| Anti-Sm | 30 (26) | 24 (25) | 10 (26) |
| Low complement (C3 and/or C4) | 31 (27) | 27 (28) | 11 (29) |
| Antiphospholipid antibodies | |||
| 35 (30) | 29 (30) | 13 (34) |
| 18 (16) | 18 (18) | 7 (18) |
| 23 (20) | 20 (1) | 8 (21) |
| All Flares (n = 134) | OFs (n = 96) | IAFs (n = 38) | Viral IAFs (n = 13) | Bacterial IAFs (n = 23) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease activity measures: median (IQR) | |||||
| SLEDAI-2K | 2(0–4) | 2 (0–4) | 2 (2–4) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (2–4) |
| PGA | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) |
| Patient-reported NRS | 7 (6–8) | 8 (7–8) | 8 (7–9) | 7 (7–8) | 8 (7–9) |
| Serology: n (%) | |||||
| Anti-dsDNA | 87 (65) | 56 (58) | 18 (47) | 5 (38) | 10 (43) |
| Low complement (C3 and/or C4) | 71 (52) | 43 (44) | 16 (42) | 4 (31) | 13 (57) |
| Treatment status: n (%) | |||||
| Hydroxychloroquine | 120 (90) | 88 (92) | 32 (84) | 11 (85) | 19 (83) |
| Immunosuppressants | |||||
| MTX | 12 (9) | 7 (7) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) |
| AZA | 24 (18) | 18 (18) | 7 (18) | 2 (15) | 5 (22) |
| MMF | 44 (32) | 38 (39) | 7 (18) | 2 (15) | 5 (22) |
| CyA | 4(3) | 3 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) |
| Belimumab | 21 (15) | 16 (16) | 3 (8) | 1 (8) | 2 (9) |
| Treatment changes: n (%) | |||||
| Corticosteroid tapering | 21 (16) | 10 (10) | 11 (29) * | 4 (31) | 6 (26) |
| Corticosteroid discontinuation | 13 (10) | 9 (9) | 4 (10) | 2 (5) | 2 (9) |
| Immunosuppressant discontinuation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| All Flares (n = 134) | OFs (n = 96) | IAFs (n = 38) | Viral IAFs (n = 13) | Bacterial IAFs (n = 23) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease activity measures: median (IQR) | |||||
| SLEDAI-2K | 5 (4–6) | 5 (4–6) | 5 (3–6) | 3 (0–6) | 6 (4–6) |
| Delta SLEDAI-2K | 2 (0–4) | 2 (0–4) | 2 (0–5) | 1 (0–4) | 4 (2–5) |
| Total BILAG score | 1 (1–2) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) |
| PGA | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (1–1) |
| Patient-reported NRS | 7 (6–8) | 7 (6–8) | 7 (5–8) | 6 (4–7) | 7 (5–8) |
| Serology: n(%) | |||||
| Anti-dsDNA | 87 (65) | 64 (67) | 23 (61) | 5 (38) * | 16 (74) |
| Low complement (C3 and/or C4) | 71 (53) | 53 (55) | 18 (47) | 3 (23) | 12 (57) |
| Other laboratory features: median (IQR) | |||||
| Hb (g/dL) | 12.8 (12–14) | 1.8 (11.8–14) | 12.6 (11.6–13.7) | 13 (11–13) | 12.5 (12–14) |
| Platelets × 103/microlitre | 227 (182–269) | 239(189–277) | 210 (169–262) | 177 (162–236) * | 215 (177–262) |
| WBCs/microlitre | 5000 (3600–6675) | 5375 (3875–6825) | 4510 (3100–5547) | 4630 (2880–6720) | 4400 (3100–5050) |
| Neutrophils (%) | 61 (53–67) | 61 (55–66) | 60 (47–68) | 62 (49–71) | 59 (42–66) |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 26 (53–67) | 26 (19–32) | 27 (19–40) | 25 (18–35) | 29 (20–41) |
| Monocytes (%) | 9 (7–12) | 9 (7–12) | 10 (8–12) | 9 (8–11) | 11 (9–12) |
| Eosinophils (%) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 3 (1–4) |
| Basophils (%) | 1 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–1) |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.8 (0.6–0.9) | 0.8 (0.6–0.9) | 0.8 (0.6–1) | 0.8 (0.8–1.1) | 0.7 (0.7–1) |
| AST (U/L) | 22 (17–26) | 21 (17–25) | 23 (17–27) | 19 (13–28) | 24 (20–29) |
| ALT (U/L) | 17 (13–23) | 17 (13–22) | 19 (14–29) | 19 (15–31) | 20 (14–28) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramirez, G.A.; Calabrese, C.; Secci, M.; Moroni, L.; Gallina, G.D.; Benanti, G.; Bozzolo, E.P.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Dagna, L. Infection-Associated Flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pathogens 2024, 13, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110934
Ramirez GA, Calabrese C, Secci M, Moroni L, Gallina GD, Benanti G, Bozzolo EP, Matucci-Cerinic M, Dagna L. Infection-Associated Flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pathogens. 2024; 13(11):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110934
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamirez, Giuseppe A., Chiara Calabrese, Marta Secci, Luca Moroni, Gabriele D. Gallina, Giovanni Benanti, Enrica P. Bozzolo, Marco Matucci-Cerinic, and Lorenzo Dagna. 2024. "Infection-Associated Flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Pathogens 13, no. 11: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110934
APA StyleRamirez, G. A., Calabrese, C., Secci, M., Moroni, L., Gallina, G. D., Benanti, G., Bozzolo, E. P., Matucci-Cerinic, M., & Dagna, L. (2024). Infection-Associated Flares in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pathogens, 13(11), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110934






