A Comprehensive Multi-Omics Study of Serum Alterations in Red Deer Infected by the Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Proteomics Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Preparation and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.2.2. Data Processing
2.2.3. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2.4. Validation of Proteomics Data
2.3. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Preparation and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.3.2. Data Processing
2.3.3. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Integration of Proteomics and Metabolomics Data
3. Results
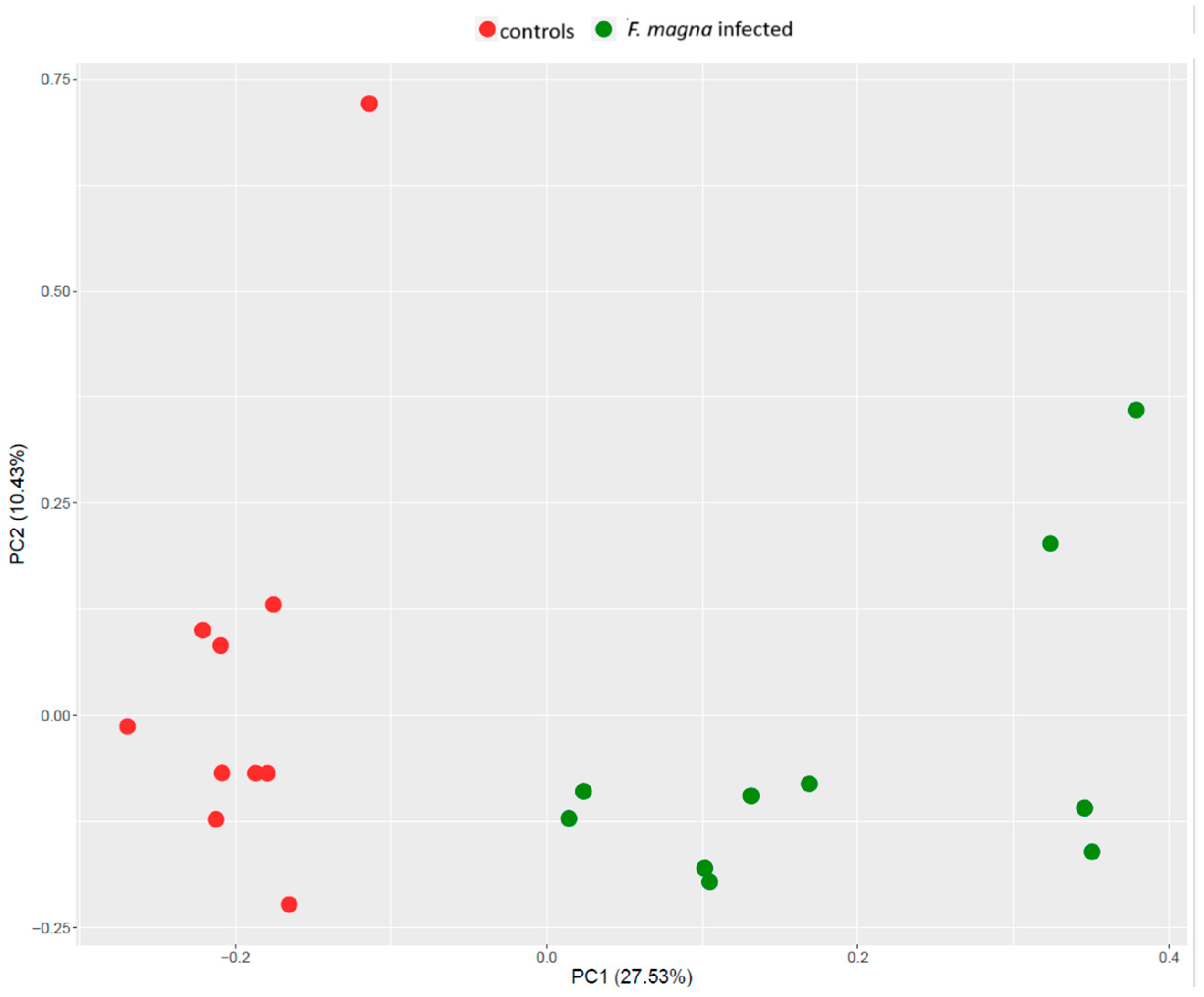
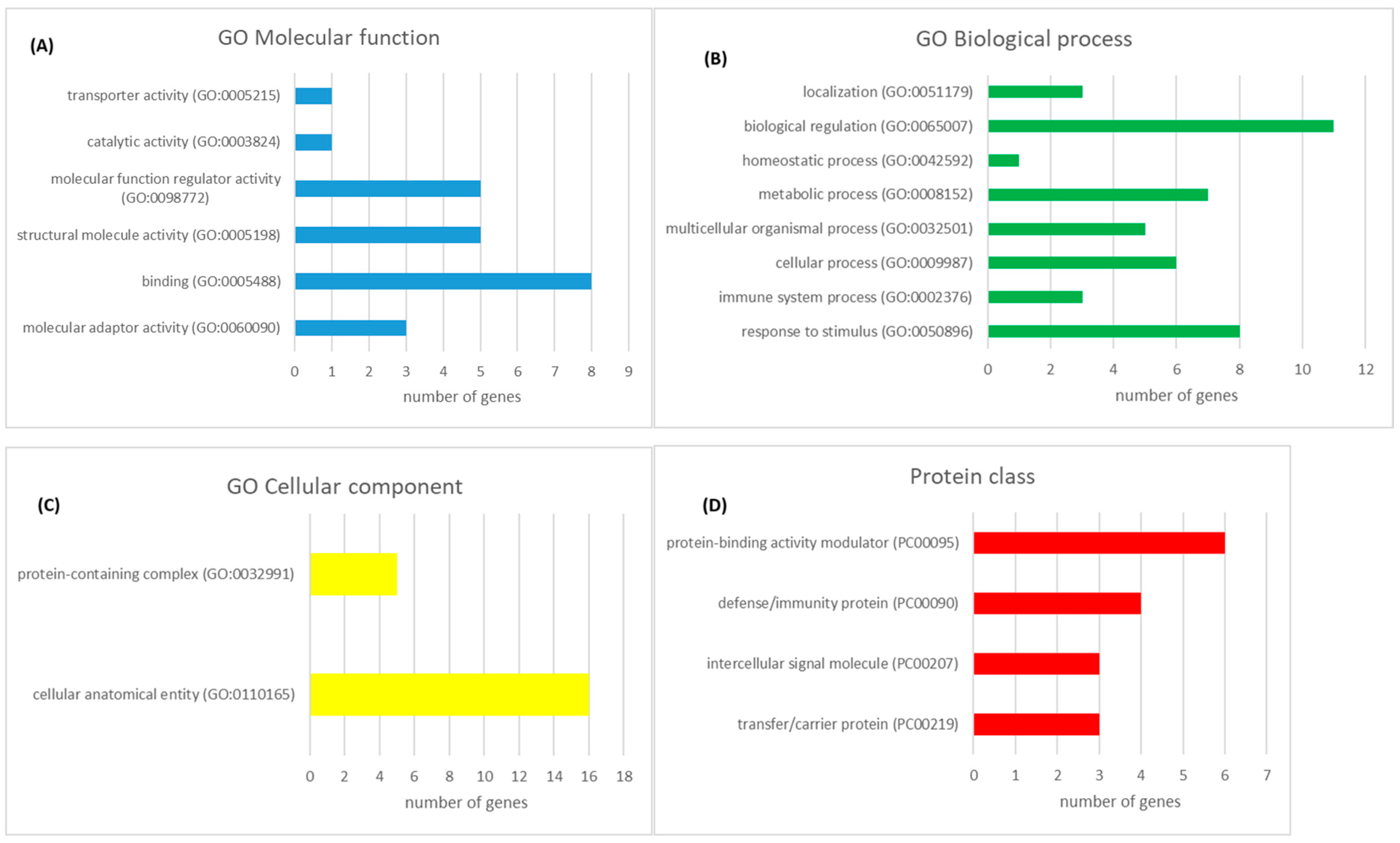
3.1. Proteomics Analysis
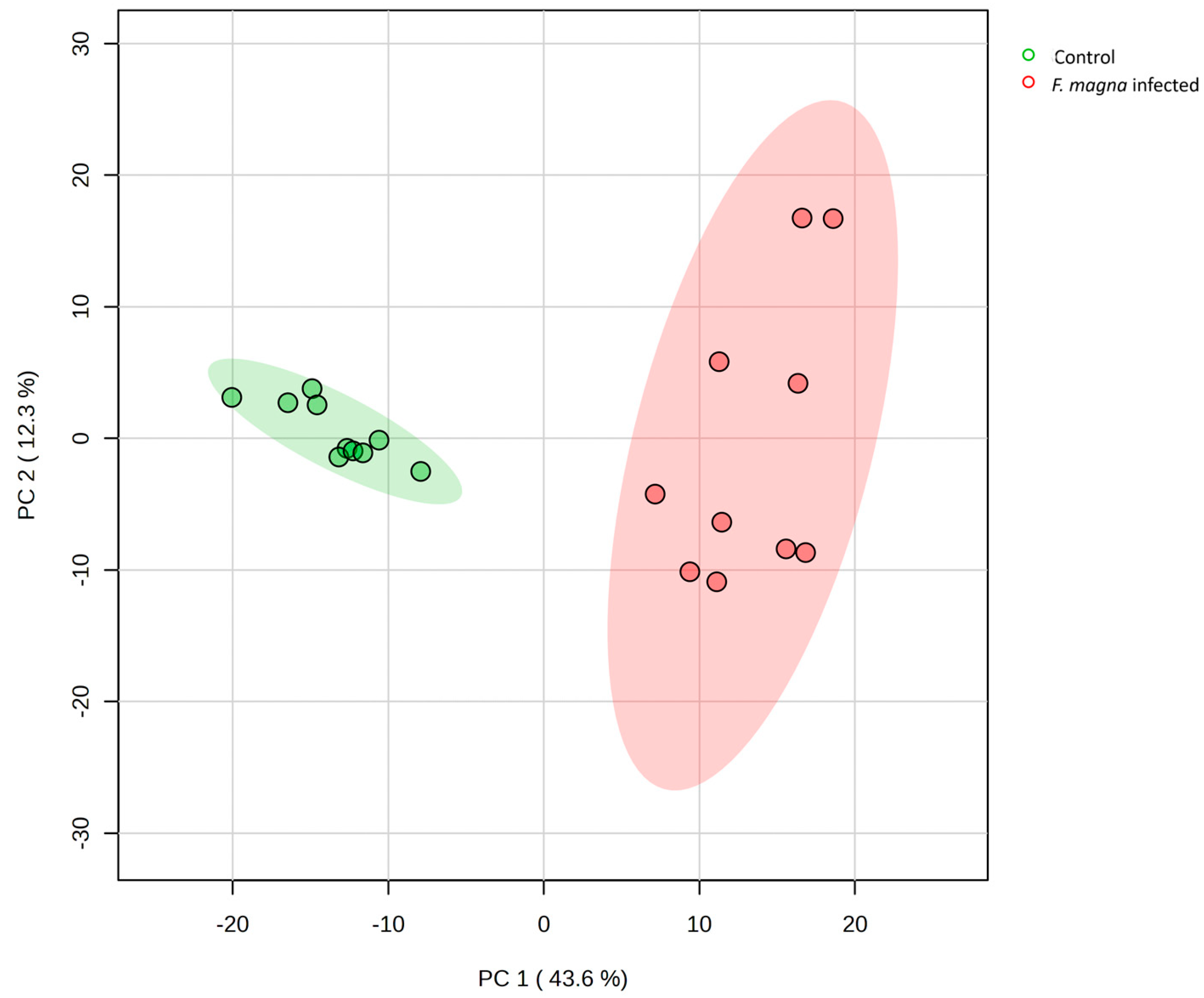
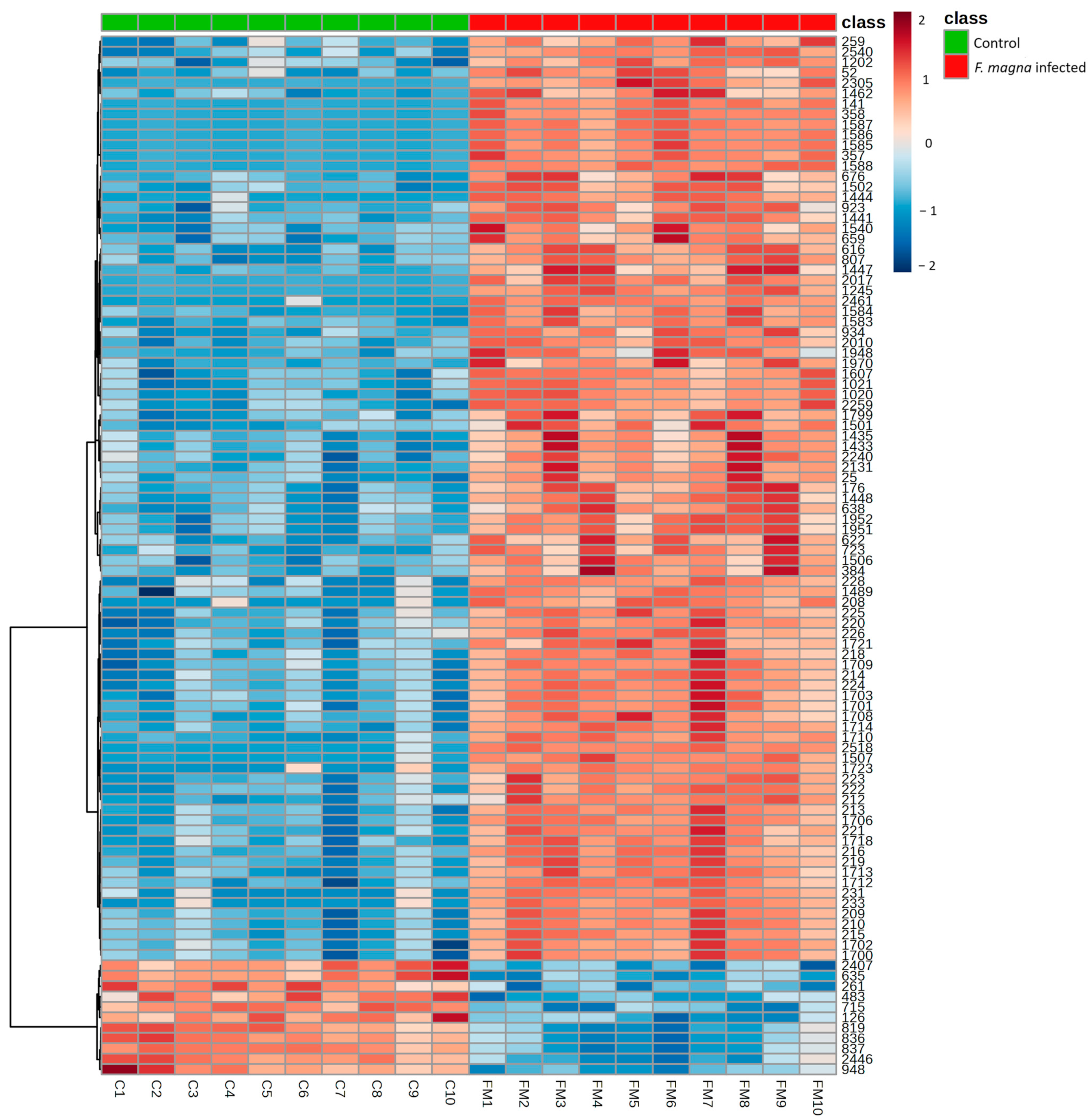
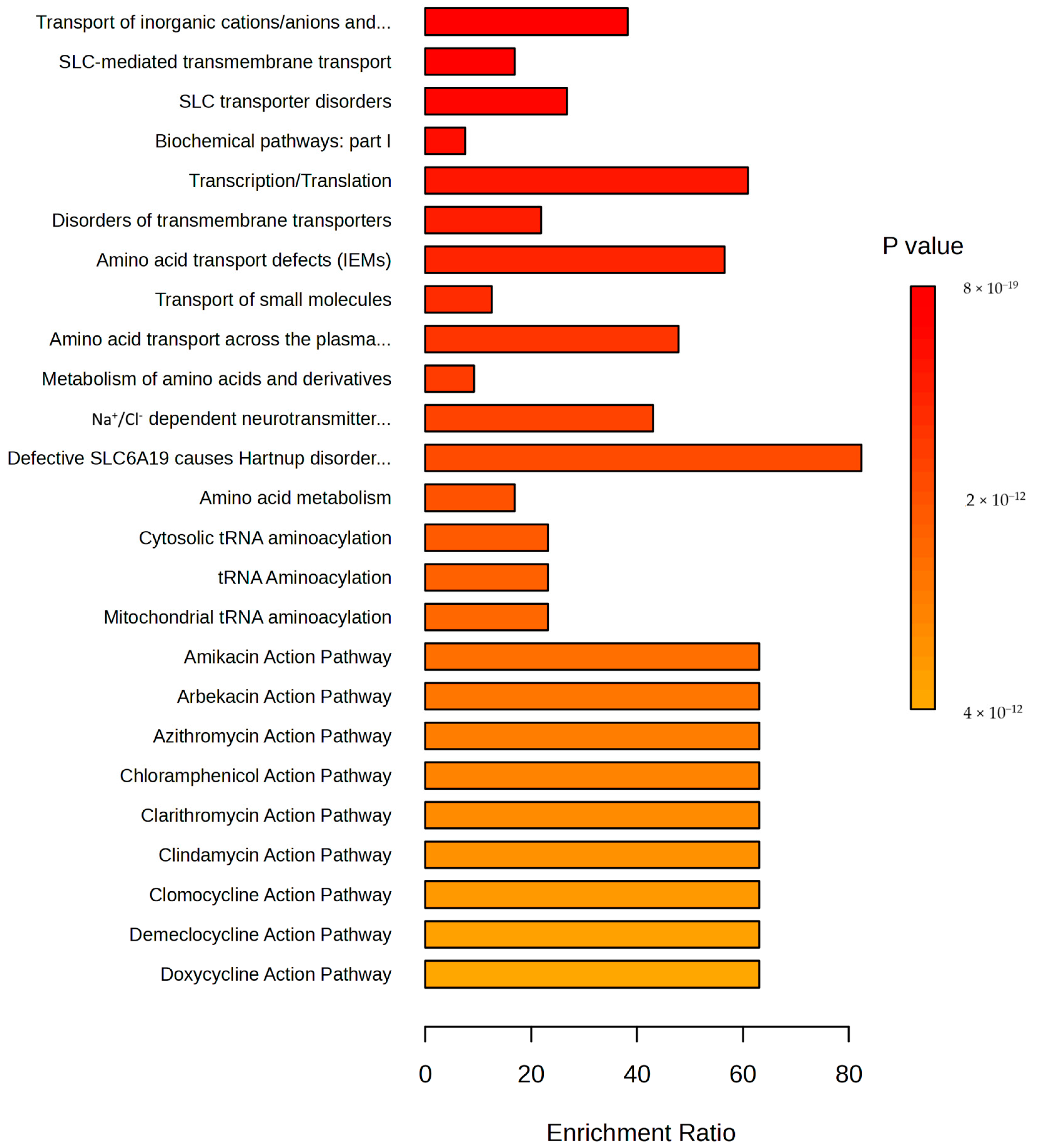
3.2. Metabolomics Analysis
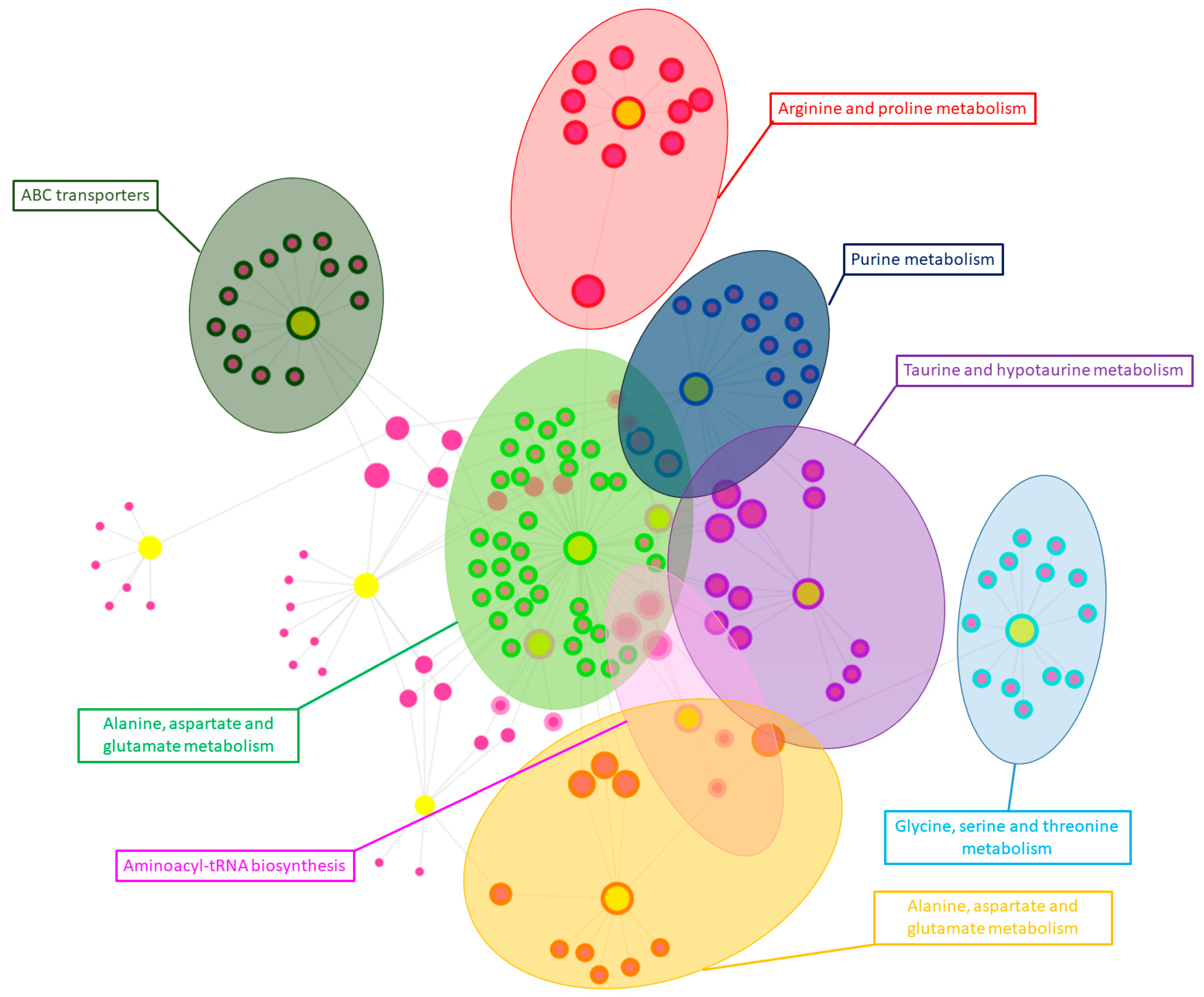
3.3. Integration of Proteomics and Metabolomics Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Proteomics
4.2. Metabolomics
4.3. Integration of Proteomics and Metabolomics Data
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife—Threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, H.; Dobson, A. Detecting disease and parasite threats to endangered species and ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheele, B.C.; Legge, S.; Blanchard, W.; Garnett, S.; Geyle, H.; Gillespie, G.; Harrison, P.; Lindenmayer, D.; Lintermans, M.; Robinson, N. Continental-scale assessment reveals inadequate monitoring for threatened vertebrates in a megadiverse country. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 235, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, D.M.; Carver, S.; Jones, M.E.; Krkošek, M.; Skerratt, L.F. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife: A critical perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Králová-Hromadová, I.; Juhásová, Ľ.; Bazsalovicsová, E. The Giant Liver Fluke, Fascioloides magna: Past, Present and Future Research; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Pybus, M.J. Liver Flukes. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Mammals; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 121–149. [Google Scholar]
- Foreyt, W.J. Experimental Fascioloides magna infections of mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus hemionus). J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreyt, W.J. Susceptibility of Bighorn Sheep (Ovis canadensis) to Experimentally-Induced Fascioloides magna Infections. J. Wildl. Dis. 1996, 32, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, C.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Califf, L.L.; Xu, T.; Hernandez, H.J.; Stadecker, M.J.; Yates, J.R.; Williams, D.L. Proteomic analysis of Schistosoma mansoni egg secretions. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 155, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Menon, R.; Donnelly, S.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Ranganathan, S. An Integrated Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis of the Secretome of the Helminth Pathogen Fasciola hepatica: Proteins Associated with Invasion and Infection of the Mammalian Host*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotillo, J.; Pearson, M.; Becker, L.; Mulvenna, J.; Loukas, A. A quantitative proteomic analysis of the tegumental proteins from Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula reveals novel potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.A.; Wright, J.M.; de Castro-Borges, W.; Parker-Manuel, S.J.; Dowle, A.A.; Ashton, P.D.; Young, N.D.; Gasser, R.B.; Spithill, T.W. Exploring the Fasciola hepatica tegument proteome. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvenna, J.; Sripa, B.; Brindley, P.J.; Gorman, J.; Jones, M.K.; Colgrave, M.L.; Jones, A.; Nawaratna, S.; Laha, T.; Suttiprapa, S.; et al. The secreted and surface proteomes of the adult stage of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta-Astroz, Y.; Oliveira, F.S.d.; Nahum, L.A.; Oliveira, G. Helminth secretomes reflect different lifestyles and parasitized hosts. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotillo, J.; Toledo, R.; Mulvenna, J.; Loukas, A. Exploiting Helminth–Host Interactomes through Big Data. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantacessi, C.; Mulvenna, J.; Young, N.D.; Kasny, M.; Horak, P.; Aziz, A.; Hofmann, A.; Loukas, A.; Gasser, R.B. A deep exploration of the transcriptome and “excretory/secretory” proteome of adult Fascioloides magna. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2012, 11, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleš, J.; Lovrić, L.; Gelemanović, A.; Beer Ljubić, B.; Rubić, I.; Bujanić, M.; Konjević, D. Complementary liver and serum protein profile in wild boars infected by the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna using tandem mass tags quantitative approach. J. Proteom. 2021, 247, 104332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimonji, K.; Konjević, D.; Bujanić, M.; Rubić, I.; Farkaš, V.; Beletić, A.; Grbavac, L.; Kuleš, J. Liver Proteome Alterations in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) Infected by the Giant Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.; Dalton, J.P. Complementary transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal the cellular and molecular processes that drive growth and development of Fasciola hepatica in the host liver. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.K.; Hu, R.S.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Sheng, Z.A.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zheng, W.B.; Zhu, X.Q.; He, J.J. Global serum proteomic changes in water buffaloes infected with Fasciola gigantica. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchuk, P.; Yeshi, K.; Loukas, A. Metabolomics and lipidomics studies of parasitic helminths: Molecular diversity and identification levels achieved by using different characterisation tools. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokova, D.; Mayboroda, O.A. Twenty Years on: Metabolomics in Helminth Research. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, K.; Aronov, P.A.; Hammock, B.D. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Ko, E.; Mersha, T.B. A roadmap for multi-omics data integration using deep learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, I.; Verma, S.; Kumar, S.; Jere, A.; Anamika, K. Multi-omics Data Integration, Interpretation, and Its Application. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2020, 14, 1177932219899051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazeri, S.; Sargison, N.; Kelly, R.F.; Bronsvoort, B.M.D.; Handel, I. Evaluation of the Performance of Five Diagnostic Tests for Fasciola hepatica Infection in Naturally Infected Cattle Using a Bayesian No Gold Standard Approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatić, A.; Guillemin, N.; Kaab, H.; McKeegan, D.; O’Reilly, E.; Bain, M.; Kuleš, J.; Eckersall, P.D. Quantitative proteomics using tandem mass tags in relation to the acute phase protein response in chicken challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mushayahama, T.; Albou, L.-P.; Mi, H. PANTHER: Making genome-scale phylogenetics accessible to all. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milacic, M.; Beavers, D.; Conley, P.; Gong, C.; Gillespie, M.; Griss, J.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D672–D678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloaguen, Y.; Morton, F.; Daly, R.; Gurden, R.; Rogers, S.; Wandy, J.; Wilson, D.; Barrett, M.; Burgess, K. PiMP my metabolome: An integrated, web-based tool for LC-MS metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 4007–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; E MacDonald, P.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: Towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, J.D.; Zhou, G.; Lu, Y.; Kolic, J.; Ellis, C.; Johnson, J.D.; Macdonald, P.E.; Xia, J. Web-based multi-omics integration using the Analyst software suite. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 1467–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosvall, M.; Bergstrom, C.T. Maps of random walks on complex networks reveal community structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiklinski, K.; O’Neill, S.M.; Donnelly, S.; Dalton, J.P. A prospective view of animal and human Fasciolosis. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckersall, P.D.; Bell, R. Acute phase proteins: Biomarkers of infection and inflammation in veterinary medicine. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catley, A.; Kock, R.A.; Hart, M.G.; Hawkey, C.M. Haematology of clinically normal and sick captive reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 239–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R.J.; Oliver, R.E.; Saunders, B.W.; Poole, W.S. Changes in blood coagulation parameters of red deer (Cervus elaphus) experimentally infected with malignant catarrhal fever. N. Z. Vet. J. 1987, 35, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.P.; Reynolds, G.E.; Mackintosh, C.G.; Griffin, J.F. Evaluation of relationship between plasma fibrinogen concentration and tuberculin testing in red deer. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1991, 198, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.P.; Mackintosh, C.G.; Griffin, J.F.T. The haematology of acute bacterial infection in farmed red deer Cervus elaphus: Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Comp. Haematol. Int. 1994, 4, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, T.; Medjoubi-N, N.; Porquet, D. Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1482, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; Lim, Y.-P.; Siryaporn, E.; Moldawer, L.L.; Pribble, J.P.; Palardy, J.E.; Souza, S. Longitudinal studies of inter-alpha inhibitor proteins in severely septic patients: A potential clinical marker and mediator of severe sepsis*. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomopoulou, K.; Ricklin, D.; Ward, P.A.; Lambris, J.D. Interactions between coagulation and complement—Their role in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delafontaine, P.; Song, Y.-H.; Li, Y. Expression, Regulation, and Function of IGF-1, IGF-1R, and IGF-1 Binding Proteins in Blood Vessels. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saric, J.; Li, J.V.; Swann, J.R.; Utzinger, J.; Calvert, G.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dirnhofer, S.; Dallman, M.J.; Bictash, M.; Holmes, E. Integrated Cytokine and Metabolic Analysis of Pathological Responses to Parasite Exposure in Rodents. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saric, J.; Li, J.V.; Utzinger, J.; Wang, Y.; Keiser, J.; Dirnhofer, S.; Beckonert, O.; Sharabiani, M.T.A.; Fonville, J.M.; Nicholson, J.K.; et al. Systems parasitology: Effects of Fasciola hepatica on the neurochemical profile in the rat brain. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2010, 6, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, X.; Qiu, H.; Ma, X.; Lv, Q.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Chang, Q. Metabolomic and systematic biochemical analysis of sheep infected with Fasciola hepatica. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 313, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Cloarec, O.; Chollet, J.; Tanner, M.; Singer, B.H.; Utzinger, J. Metabonomic investigations in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni: An approach for biomarker identification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12676–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, M.; Young, S.P. Metabolomics—A novel window into inflammatory disease. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, w13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyńska, P.; Sobala, Ł.F.; Mikołajczyk, K.; Jodłowska, M.; Jaśkiewicz, E. Sialic Acids as Receptors for Pathogens. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewison, T.; Su, Y.; Disfany, F.M.; Liang, Y.; Knox, C.; Maciejewski, A.; Poelzer, J.; Huynh, J.; Zhou, Y.; Arndt, D.; et al. SMPDB 2.0: Big improvements to the Small Molecule Pathway Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D478–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Utzinger, J.; Xiao, S.-H.; Xue, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Tanner, M.; Singer, B.H.; Holmes, E. System level metabolic effects of a Schistosoma japonicum infection in the Syrian hamster. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J. Forty years of helminth biochemistry. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J. Biochemistry of Parasitic Helminths; Red Globe Press London: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Vance, D.E. Thematic Review Series: Glycerolipids. Phosphatidylcholine and choline homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, W.R.; Gallowitsch Puerta, M.; Ochani, M.; Ochani, K.; Moskovic, D.; Lin, X.; Czura, C.J.; Miller, E.J.; Al-Abed, Y.; Tracey, K.J.; et al. Choline Suppresses Inflammatory Responses. Shock 2006, 25, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Tracey, K.J. Cholinergic control of inflammation. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.M. Fasciola gigantica: Purification and characterization of adenosine deaminase. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshad, V.; Guraya, S. Comparative histochemical observations on the excretory system of helminth parasites. Z. Parasitenkd. 1977, 52, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.r.; Kuhel, D.G.; Németh, Z.n.H.; Mabley, J.G.; Stachlewitz, R.F.; Virág, L.s.; Lohinai, Z.; Southan, G.J.; Salzman, A.L.; Szabó, C. Inosine Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokine Production by a Posttranscriptional Mechanism and Protects Against Endotoxin-Induced Shock1. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, W.; Ming, Z.; Dong, H.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Metabolic Changes Reveal the Development of Schistosomiasis in Mice. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizota, T.; Hishiki, T.; Shinoda, M.; Naito, Y.; Hirukawa, K.; Masugi, Y.; Itano, O.; Obara, H.; Kitago, M.; Yagi, H.; et al. The hypotaurine-taurine pathway as an antioxidative mechanism in patients with acute liver failure. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2022, 70, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Sütçü, R.; Cetin, E.S.; Aridogan, B.C.; Delibaş, N.; Demirci, M. Lipid peroxidation level and antioxidant enzyme activities in the blood of patients with acute and chronic fascioliasis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, L.; Siemieniuk, E.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidant potential of rat liver in experimental infection with Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 96, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, L.; Siemieniuk, E.; Skrzydlewska, E. Fasciola hepatica: Effects on the antioxidative properties and lipid peroxidation of rat serum. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, D.C.; Johnson, E.; Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: The power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Williams, A.R.; Abeer, M.M. Importance of ABC Transporters in the Survival of Parasitic Nematodes and the Prospect for the Development of Novel Control Strategies. Pathogens 2023, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, Z.; Konjević, D.; Severin, K. Monitoring and treatment of Fascioloides magna in semi-farm red deer husbandry in Croatia. Vet. Res. Commun. 2005, 29, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overend, D.; Bowen, F. Resistance of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole. Aust. Vet. J. 1995, 72, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, L.; Gaasenbeek, C.P.; Vellema, P.; Borgsteede, F.H. Resistance of Fasciola hepatica against triclabendazole in cattle and sheep in The netherlands. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 91, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, I.; Brennan, G.P.; Hanna, R.E.B.; Robinson, M.W.; Skuce, P.J. Drug resistance in liver flukes. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2020, 12, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, C.; Brennan, G.P.; Lanusse, C.E.; Alvarez, L.I.; Trudgett, A.; Hoey, E.; Fairweather, I. Inhibition of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism enhances ex vivo susceptibility of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole. Parasitology 2010, 137, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, C.; Brennan, G.P.; Lanusse, C.E.; Alvarez, L.I.; Trudgett, A.; Hoey, E.; Fairweather, I. Inhibition of triclabendazole metabolism in vitro by ketoconazole increases disruption to the tegument of a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, C.; Brennan, G.P.; Lanusse, C.E.; Alvarez, L.I.; Trudgett, A.; Hoey, E.; Fairweather, I. Potentiation of triclabendazole action in vivo against a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica following its co-administration with the metabolic inhibitor, ketoconazole. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epel, D.; Luckenbach, T.; Stevenson, C.N.; Macmanus-Spencer, L.A.; Hamdoun, A.; Smital, T. Efflux transporters: Newly appreciated roles in protection against pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3914–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Ansell, B.R.E.; Hall, R.S.; Gasser, R.B.; Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Scheerlinck, J.-P.Y. Transcriptional analysis identifies key genes involved in metabolism, fibrosis/tissue repair and the immune response against Fasciola hepatica in sheep liver. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Adinolfi, E. Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, A.; Sun, B.; Fu, Z.; Yu, D. Roles of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in immune regulation and immune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
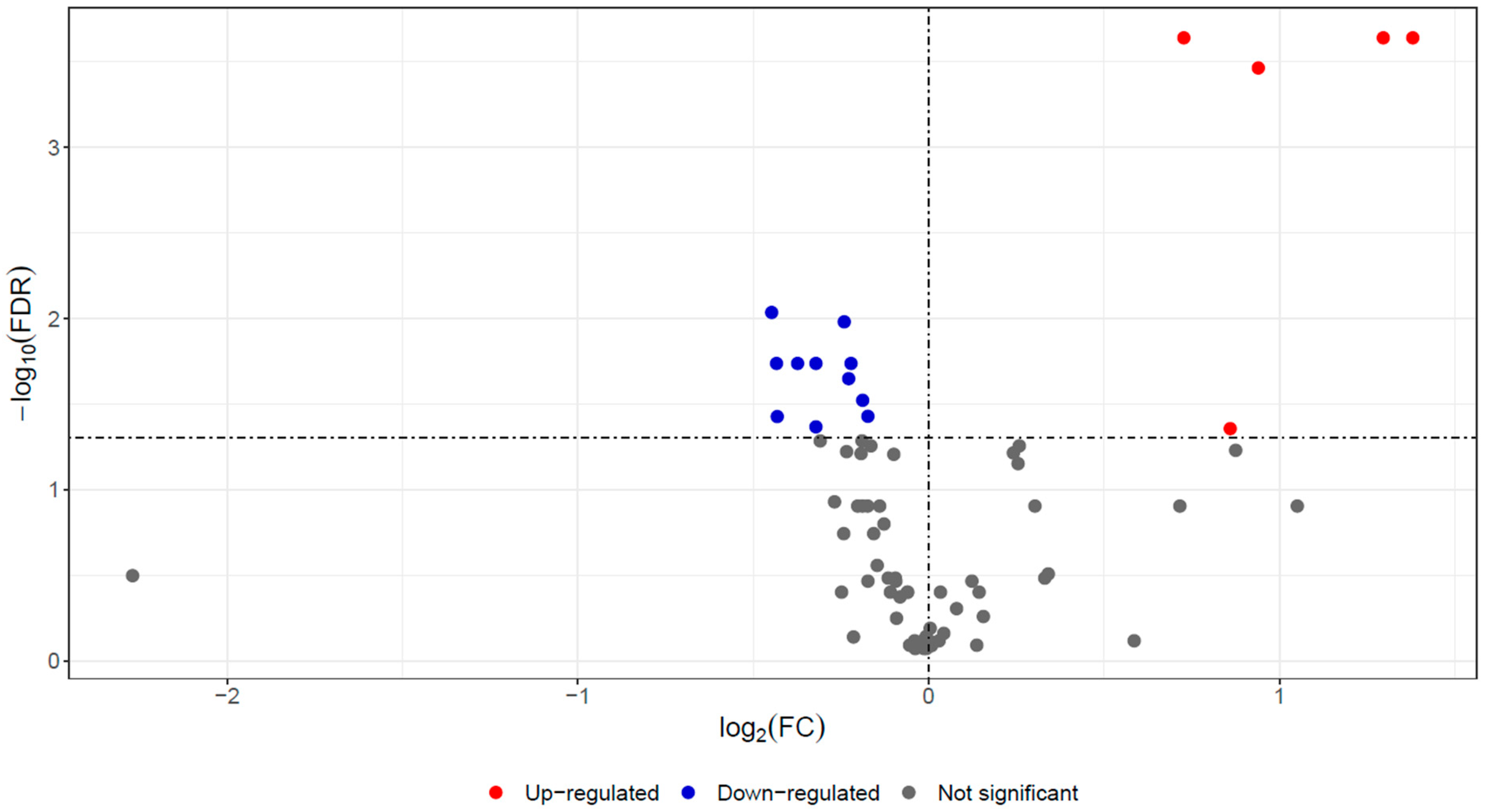



| Accession | Gene Name | Description | p Value | FDR | log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A212DAA2 | FGA | Fibrinogen alpha chain | 1 × 10−5 | 0.0002 | 1.380 |
| A0A212D7J2 | FGB | Fibrinogen beta chain | 1 × 10−5 | 0.0002 | 1.296 |
| A0A212D8V0 | FGG | Fibrinogen gamma chain | 2 × 10−5 | 0.0003 | 0.940 |
| A0A212D4K0 | Histone H4 | 1 × 10−2 | 0.0440 | 0.860 | |
| A0A212CNC6 | ORM1 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein | 1 × 10−5 | 0.0002 | 0.727 |
| A0A212D5P0 | ALB | Albumin | 8 × 10−3 | 0.0373 | −0.173 |
| A0A212CG89 | C8A | Complement C8 alpha chain | 6 × 10−3 | 0.0301 | −0.188 |
| A0A212C922 | ITIH1 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 | 1 × 10−2 | 0.0519 | −0.190 |
| A0A212CDE1 | LOC506828 | Uncharacterized protein (BLAST: Pregnancy zone protein) | 3 × 10−3 | 0.0183 | −0.221 |
| A0A212CQC9 | CFH | Complement factor H | 4 × 10−3 | 0.0225 | −0.228 |
| A0A212CC12 | ITIH2 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 2 | 1 × 10−3 | 0.0105 | −0.241 |
| A0A212CIM7 | HRG | Histidine-rich glycoprotein | 1 × 10−2 | 0.0519 | −0.309 |
| A0A212CMY9 | IGHM | Ig-like domain-containing protein | 1 × 10−2 | 0.0430 | −0.321 |
| A0A212CIC4 | FETUB | Fetuin-B | 3 × 10−3 | 0.0183 | −0.321 |
| A0A212DHP9 | APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | 2 × 10−3 | 0.0183 | −0.374 |
| A0A212CI17 | CD5L | CD5 molecule like | 8 × 10−3 | 0.0374 | −0.432 |
| A0A212CQ10 | CFH | Complement factor H | 3 × 10−3 | 0.0183 | −0.434 |
| A0A212D5R7 | JCHAIN | Joining chain of multimeric IgA and IgM | 7 × 10−4 | 0.0092 | −0.447 |
| Peak ID | Name | Mass | RT | p Value | FDR | log2(FC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1447 | Methylmalonic acid | 117.0196 | 700.59 | 4 × 10−8 | 1.25 × 10−6 | 4.87 |
| 72 | Isonicotinic acid | 124.0394 | 436.77 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.004722 | 4.03 |
| 42 | 4-Methoxybenzyl propanoate | 258.1101 | 646.48 | 6 × 10−7 | 8.05 × 10−6 | 3.71 |
| 1551 | L-Aspartate | 132.0305 | 690.35 | 2 × 10−5 | 9.79 × 10−5 | 3.67 |
| 1497 | Inosine | 267.074 | 554.37 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.004966 | 3.43 |
| 1441 | Malate | 133.0145 | 734.56 | 2 × 10−10 | 1.92 × 10−8 | 3.38 |
| 1855 | Glycerol 3-phosphate | 171.0068 | 646.54 | 6 × 10−7 | 8.49 × 10−6 | 3.35 |
| 298 | Imidazole-4-acetate | 127.0502 | 584.57 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.004722 | 3.25 |
| 6 | Inosine | 269.0881 | 555.54 | 1 × 10−3 | 0.004086 | 3.18 |
| 95 | 2-Hydroxyadenine | 152.0568 | 634.21 | 8 × 10−8 | 2.15 × 10−6 | 3.08 |
| 364 | Pantothenic acid | 220.1179 | 463.76 | 2 × 10−7 | 4.23 × 10−6 | 2.76 |
| 1844 | Pantothenic acid | 218.1038 | 463.33 | 2 × 10−7 | 4.55 × 10−6 | 2.74 |
| 20 | Choline | 104.107 | 1037.39 | 3 × 10−7 | 5.93 × 10−6 | 2.47 |
| 1433 | Pseudouridine | 243.0627 | 522 | 3 × 10−8 | 8.99 × 10−7 | 2.39 |
| 1948 | Citraconic acid | 129.0197 | 700.79 | 5 × 10−8 | 1.52 × 10−6 | 2.32 |
| 199 | Taurine | 126.022 | 729.49 | 4 × 10−7 | 7.08 × 10−6 | 2.26 |
| 2256 | Cytidine | 242.0789 | 597.61 | 6 × 10−3 | 0.012562 | 2.15 |
| 1671 | Ureidopropionic acid | 131.0465 | 709.18 | 1 × 10−3 | 0.003059 | 2.15 |
| 1486 | Taurine | 124.0076 | 730 | 2 × 10−7 | 4.20 × 10−6 | 2.06 |
| 363 | 3-Deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-2-nonulosonic acid | 310.1132 | 647.3 | 5 × 10−5 | 0.000255 | 1.94 |
| 1561 | N-Acetylneuraminic acid | 308.0994 | 628.17 | 2 × 10−5 | 0.000128 | 1.93 |
| 1683 | N-Acetylglutamic acid | 188.0569 | 654.1 | 1 × 10−4 | 0.000591 | 1.60 |
| 50 | L-Glutamate | 148.0604 | 674.5 | 2 × 10−6 | 1.74 × 10−5 | 1.54 |
| 83 | 3-Dehydroxycarnitine | 146.1176 | 616.16 | 3 × 10−5 | 0.000162 | 1.49 |
| 1573 | Galactonic acid | 195.0514 | 655.33 | 1 × 10−5 | 9.32 × 10−5 | 1.38 |
| 1458 | L-Glutamate | 146.0462 | 674.96 | 2 × 10−6 | 1.75 × 10−5 | 1.38 |
| 1576 | L-Alanine | 88.0406 | 688.94 | 5 × 10−5 | 0.000248 | 1.04 |
| 682 | Citramalic acid | 190.0709 | 653.62 | 1 × 10−3 | 0.002955 | 0.90 |
| 2455 | Malonate | 103.0039 | 727.57 | 5 × 10−4 | 0.001558 | 0.82 |
| 5 | Betaine | 118.0862 | 557.5 | 4 × 10−5 | 0.000196 | 0.78 |
| 43 | 3-Methylhistidine | 170.0924 | 610.68 | 3 × 10−5 | 0.000158 | 0.73 |
| 1687 | Pterolactam | 114.0563 | 618.23 | 8 × 10−5 | 0.000381 | 0.71 |
| 24 | L-Proline | 116.0706 | 618.02 | 1 × 10−5 | 9.31 × 10−5 | 0.69 |
| 1814 | 3-Methylhistidine | 168.0782 | 611.63 | 1 × 10−6 | 1.12 × 10−5 | 0.67 |
| 282 | L-Serine | 106.0499 | 730.75 | 1 × 10−2 | 0.02085 | 0.54 |
| 1657 | L-Phenylalanine | 164.0721 | 515.76 | 2 × 10−4 | 0.000915 | 0.50 |
| 195 | L-Methionine | 150.0584 | 573.73 | 4 × 10−3 | 0.008503 | 0.49 |
| 57 | L-Citrulline | 176.1029 | 719.55 | 2 × 10−2 | 0.032129 | 0.48 |
| 1599 | L-Leucine | 130.0876 | 550.18 | 7 × 10−4 | 0.002242 | 0.46 |
| 1964 | L-Valine | 116.072 | 555.79 | 2 × 10−4 | 0.000882 | 0.39 |
| 1565 | L-Leucine | 130.0876 | 540.2 | 7 × 10−3 | 0.014649 | 0.36 |
| 55 | L-Isoleucine | 132.1019 | 540.6 | 5 × 10−3 | 0.010758 | 0.33 |
| 70 | D-Alloisoleucine | 132.1019 | 560.86 | 1 × 10−2 | 0.021533 | 0.32 |
| 2459 | L-Kynurenine | 207.0779 | 548.26 | 9 × 10−3 | 0.018014 | -0.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuleš, J.; Bujanić, M.; Rubić, I.; Šimonji, K.; Konjević, D. A Comprehensive Multi-Omics Study of Serum Alterations in Red Deer Infected by the Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna. Pathogens 2024, 13, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110922
Kuleš J, Bujanić M, Rubić I, Šimonji K, Konjević D. A Comprehensive Multi-Omics Study of Serum Alterations in Red Deer Infected by the Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna. Pathogens. 2024; 13(11):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110922
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuleš, Josipa, Miljenko Bujanić, Ivana Rubić, Karol Šimonji, and Dean Konjević. 2024. "A Comprehensive Multi-Omics Study of Serum Alterations in Red Deer Infected by the Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna" Pathogens 13, no. 11: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110922
APA StyleKuleš, J., Bujanić, M., Rubić, I., Šimonji, K., & Konjević, D. (2024). A Comprehensive Multi-Omics Study of Serum Alterations in Red Deer Infected by the Liver Fluke Fascioloides magna. Pathogens, 13(11), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13110922








