From One Heath to One Sustainability: The Role of Contagious Mastitis Pathogens in Decreasing the Dairy Herd Sustainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herds and Sampling
2.2. Milk Quality Assay
2.3. Contagious Pathogen Assay
2.4. Welfare Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Herd Characteristics
3.2. Factors Affecting Milk Composition
3.3. Welfare
3.4. Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capper, J.L.; Cady, R.A. The effects of improved performance in the US dairy cattle industry on environmental impacts between 2007 and 2017. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buller, H.; Blokhuis, H.; Jensen, P.; Keeling, L. Towards Farm Animal Welfare and Sustainability. Animals 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froldi, F.; Lamastra, L.; Trevisan, M.; Mambretti, D.; Moschini, M. Environmental impacts of cow’s milk in Northern Italy: Effects of farming performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, T.; Mogensen, L.; Knudsen, M.T.; Hermansen, J.E. Effect of production system and farming strategy on greenhouse gas emissions from commercial dairy farms in a life cycle approach. Livest. Sci. 2011, 140, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinato, S.; Ferrero, F.; Rolando, G.; Comino, L.; Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G. A Living Lab approach for sustainable intensification of dairy production: A case study of an organic and a conventional farm in northern Italy. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 149, 126904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, J.L. The impact of controlling diseases of significant global importance on greenhouse gas emissions from livestock production. One Health Outlook 2023, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A. Measures and metrics of sustainable diets with a focus on milk, yogurt, and dairy products. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, L.B.; Flysjö, A.; Tholstrup, T. Greenhouse gas emissions of realistic dietary choices in Denmark: The carbon footprint and nutritional value of dairy products. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 58, 20687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, F.; Soler, L.G.; Touazi, D.; Darmon, N. High nutritional quality is not associated with low greenhouse gas emissions in self-selected diets of French adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgren, J.; Hiron, M.; Glimskar, A.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; Keeling, L.J. Environmental Quality and Compliance with Animal Welfare Legislation at Swedish Cattle and Sheep Farms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülzari, S.; Ahmadi, B.V.; Stott, A.W. Impact of subclinical mastitis on greenhouse gas emissions intensity and profitability of dairy cows in Norway. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 150, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villettaz Robichaud, M.; Rushen, J.; de Passillé, A.M.; Vasseur, E.; Haley, D.; Pellerin, D. Associations between on-farm cow welfare indicators and productivity and profitability on Canadian dairies: II. On tiestall farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4352–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villettaz Robichaud, M.; Rushen, J.; de Passillé, A.M.; Vasseur, E.; Orsel, K.; Pellerin, D. Associations between on-farm animal welfare indicators and productivity and profitability on Canadian dairies: I. On freestall farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4341–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, S.E.; Mitloehner, F.M. Invited review: Contemporary environmental issues: A review of the dairy industry’s role in climate change and air quality and the potential of mitigation through improved production efficiency. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3407–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, M.A.; Shepley, E.; Cue, R.I.; Warner, D.; Dubuc, J.; Vasseur, E. The hidden cost of disease: I. Impact of the first incidence of mastitis on production and economic indicators of primiparous dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7932–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, J.L.; Williams, P. Investing in health to improve the sustainability of cattle production in the United Kingdom: A narrative review. Vet. J. 2023, 296–297, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, P.F.; van Middelaar, C.E.; de Boer, I.J.M.; Bokkers, E.A.M. The impact of foot lesions in dairy cows on greenhouse gas emissions of milk production. Agric. Syst. 2018, 167, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADAS. Study to Model the Impact of Controlling Endemic Cattle Diseases and Conditions on National Cattle Productivity, Agricultural Performance and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Final Report to Defra/AHVLA on Project FFG1016. (No. AC0120); DEFRA: Wolverhampton, UK, 2015; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Hospido, A.; Sonesson, U. The environmental impact of mastitis: A case study of dairy herds. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostert, P.F.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; de Boer, I.J.M.; van Middelaar, C.E. Estimating the impact of clinical mastitis in dairy cows on greenhouse gas emissions using a dynamic stochastic simulation model: A case study. Animal 2019, 13, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sora, V.M.; Panseri, S.; Nobile, M.; Di Cesare, F.; Meroni, G.; Chiesa, L.M.; Zecconi, A. Milk Quality and Safety in a One Health Perspective: Results of a Prevalence Study on Dairy Herds in Lombardy (Italy). Life 2022, 12, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A. Contagious mastitis control. FIL-IDF Bull. 2007, 416, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghen, F.; Sora, V.M.; Meroni, G.; Laterza, G.; Martino, P.A.; Soggiu, A.; Bonizzi, L.; Zecconi, A. Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from a Public Database from a One Health Perspective—Sample Origin and Geographical Distribution of Isolates. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghen, F.; Sora, V.M.; Meroni, G.; Laterza, G.; Martino, P.A.; Soggiu, A.; Bonizzi, L.; Zecconi, A. Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Staphyloccocus aureus Isolates from a Public Database in a One Health Perspective—Sample Characteristics and Isolates’ Sources. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, G.; Sora, V.M.; Martino, P.A.; Sbernini, A.; Laterza, G.; Zaghen, F.; Soggiu, A.; Zecconi, A. Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Streptococcus agalactiae Sequences from a Public Database in a One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crestani, C.; Forde, T.L.; Lycett, S.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Fasth, C.; Persson-Waller, K.; Zadoks, R.N. The fall and rise of group B Streptococcus in dairy cattle: Reintroduction due to human- to- cattle host jumps? Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, GPP3–GPP0060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Calvinho, L.F.; Fox, K.L. Staphylococcus aureus intramammary infections. IDF Bull. 2006, 408, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, M.E.; Haine, D.; Gillespie, B.; Oliver, S.P.; Messier, S.; Comeau, J.; Scholl, D.T. Bayesian estimation of the diagnostic accuracy of a multiplex real-time PCR assay and bacteriological culture for 4 common bovine intramammary pathogens. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6436–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW). Statement on the use of animal-based measures to assess the welfare of animals. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, G.; Lorenzi, V.; Mazza, F.; Clemente, G.A.; Iacomino, C.; Bertocchi, L.; Fusi, F. Best Farming Practices for the Welfare of Dairy Cows, Heifers and Calves. Animals 2021, 11, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baber, J.R.; Sawyer, J.E.; Wickersham, T.A. Estimation of human-edible protein conversion efficiency, net protein contribution, and enteric methane production from beef production in the United States. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2018, 2, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetroiu, R.; Cismileanu, A.E.; Cofas, E.; Petre, I.L.; Rodino, S.; Dragomir, V.; Marin, A.; Turek-Rahoveanu, P.A. Assessment of the Relations for Determining the Profitability of Dairy Farms, A Premise of Their Economic Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Dell’Orco, F.; Rizzi, N.; Vairani, D.; Cipolla, M.; Pozzi, P.; Zanini, L. Cross-sectional study on the prevalence of contagious pathogens in bulk tank milk and their effects on somatic cell counts and milk yield. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 19, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.; Fréchette, A.; Barkema, H.W.; Mussell, A.; Scholl, D.T. Invited review: Effect of udder health management practices on herd somatic cell count. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, I.; Kelton, D.F.; Barkema, H.W.; Keefe, G.P.; Roy, J.P.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; DeVries, T.J. Bacterial concentrations in bedding and their association with dairy cow hygiene and milk quality. Animal 2020, 14, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, M.; Flysjö, A.; Cederberg, C.; Swensson, C. Variation in carbon footprint of milk due to management differences between Swedish dairy farms. Animal 2011, 5, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, A.S.; Fox, L.K.; Hancock, D.D. Removal of Hair Surrounding the Teat and Associated Bacterial Counts on Teat Skin Surface, in Milk, and Intramammary Infections. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2003, 50, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Piccinini, R.; Fox, K.L. Epidemiologic study of intramammary infections with Staphylococcus aureus during a control program in nine commercial dairy herds. JAVMA 2003, 223, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mein, G.A. The Role of the Milking Machine in Mastitis Control. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Frosi, S.; Cipolla, M.; Gusmara, C. Effects of chronic mastitis and its treatment with ketoprofen on the milk ejection curve. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, E.F.S. Scientific opinion on welfare of dairy cows in relation to udder problems based on a risk assessment with special reference to the impact of housing, feeding, management and genetic selection. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Area of Interest | Number of Questions/ Observation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General information | 22 | |
| Biosecurity | 21 | |
| Lactating cows | 22 | Including animal-based measures (flank and udder cleanliness, skin lesions, lameness, teat score and cleanliness, and body condition score) and avoidance distance in the barn and at the feeding place. |
| Nonlactating cows | 22 | |
| Heifers | 23 | |
| Calves | 18 | |
| Milking | 20 | |
| Udder | 6 | Including data on antimicrobial use and the application of preventive measures to decrease AMR. |
| Housing | N | Mean of Lactating Cows (N) | Mean of Dry Cows (N) | Mean Total Cow (N) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | ||
| Deep litter | 77 (64.2%) | 40.3 | 5 | 113 | 7.8 | 0 | 33 | 48.1 | 8 | 140 |
| Cubicles | 43 (35.8%) | 111.3 | 12 | 460 | 21.9 | 2 | 125 | 133.2 | 14 | 585 |
| Total | 120 | 65.9 | 5 | 460 | 12.9 | 0 | 125 | 78.8 | 8 | 585 |
| Size | Cubicles | Deep Litter | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–30 | 2 (4.7%) a,1 | 19 (24.7%) b | 21 (17.5%) |
| 31–50 | 6 (14.0%) a | 31 (40.3%) b | 37 (30.8%) |
| 51–80 | 13 (30.2%) a | 17 (22.1%) a | 30 (25.0%) |
| >81 | 22 (51.2%) a | 10 (13.0%) b | 32 (26.7%) |
| Total | 43 (35.8%) | 77 (64.2%) | 120 (100%) |
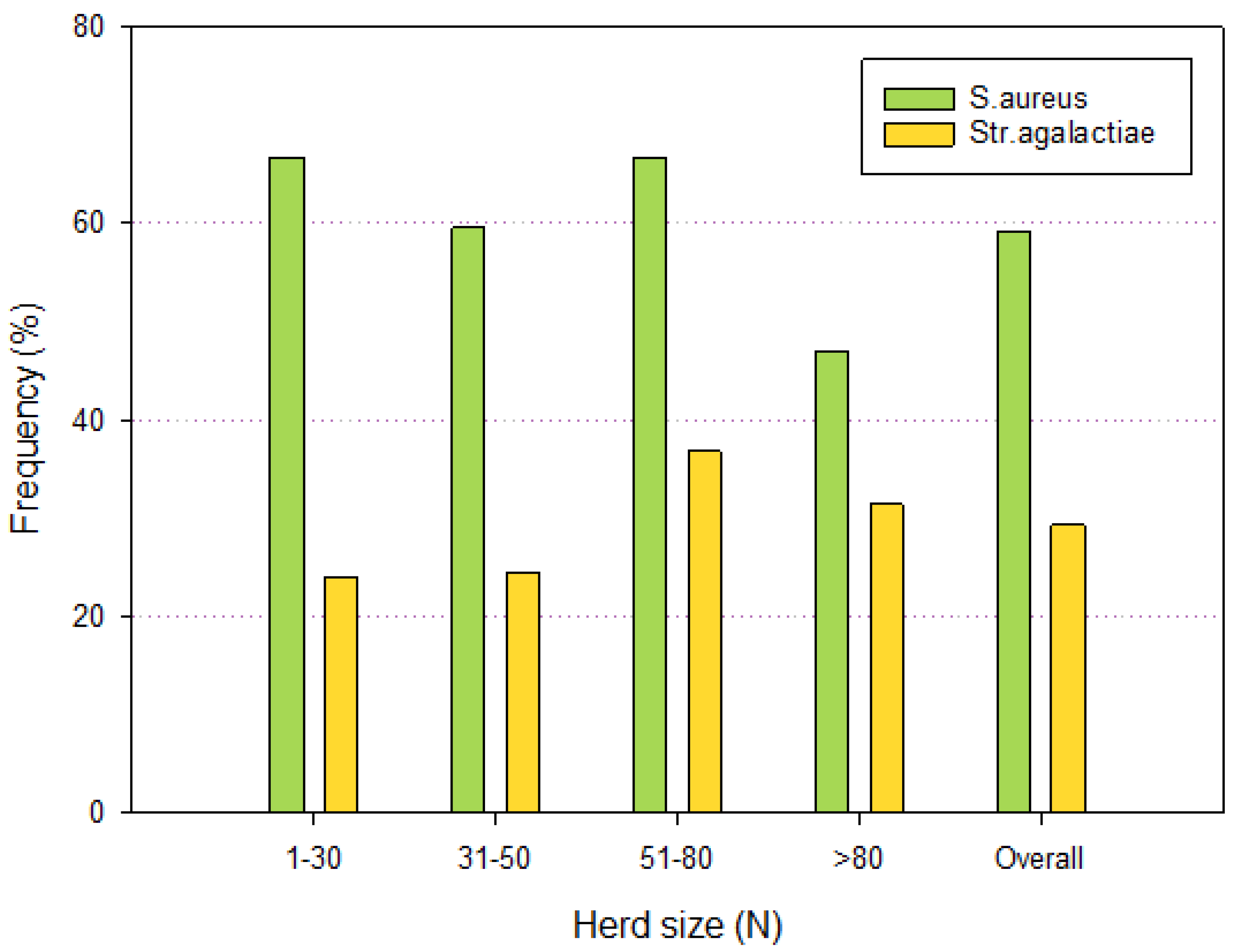
| Housing | N | S. aureus | S. agalactiae | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (%) | Lower 95% Limit | Upper 95% Limit | Frequency (%) | Lower 95% Limit | Upper 95% Limit | ||
| Deep litter | 77 | 64.93 | 57.40 | 72.47 | 33.77 | 26.30 | 41.23 |
| Cubicles | 43 | 48.83 | 38.27 | 59.40 | 20.93 | 12.33 | 29.53 |
| Total | 120 | 59.16 | 52.95 | 65.38 | 29.16 | 23.41 | 34.92 |
| Parameter | Factors | R2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Housing | Herd Size | Positivity to S. aureus | Housing × Size | Housing × Positivity to S. aureus | Herd Size × Positivity to S. aureus | ||
| Fat (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0391 | <0.0001 | 0.0180 | 0.0064 | 59.9% |
| Proteins (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0503 | <0.0001 | 0.0119 | 0.0042 | 61.2% |
| Lactose (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0520 | <0.0001 | 0.0158 | 0.0077 | 60.0% |
| NFDM 1 (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0530 | <0.0001 | 0.0146 | 0.0078 | 60.3% |
| Milk delivered (ton) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0541 | <0.0001 | 0.0155 | 0.0109 | 59.8% |
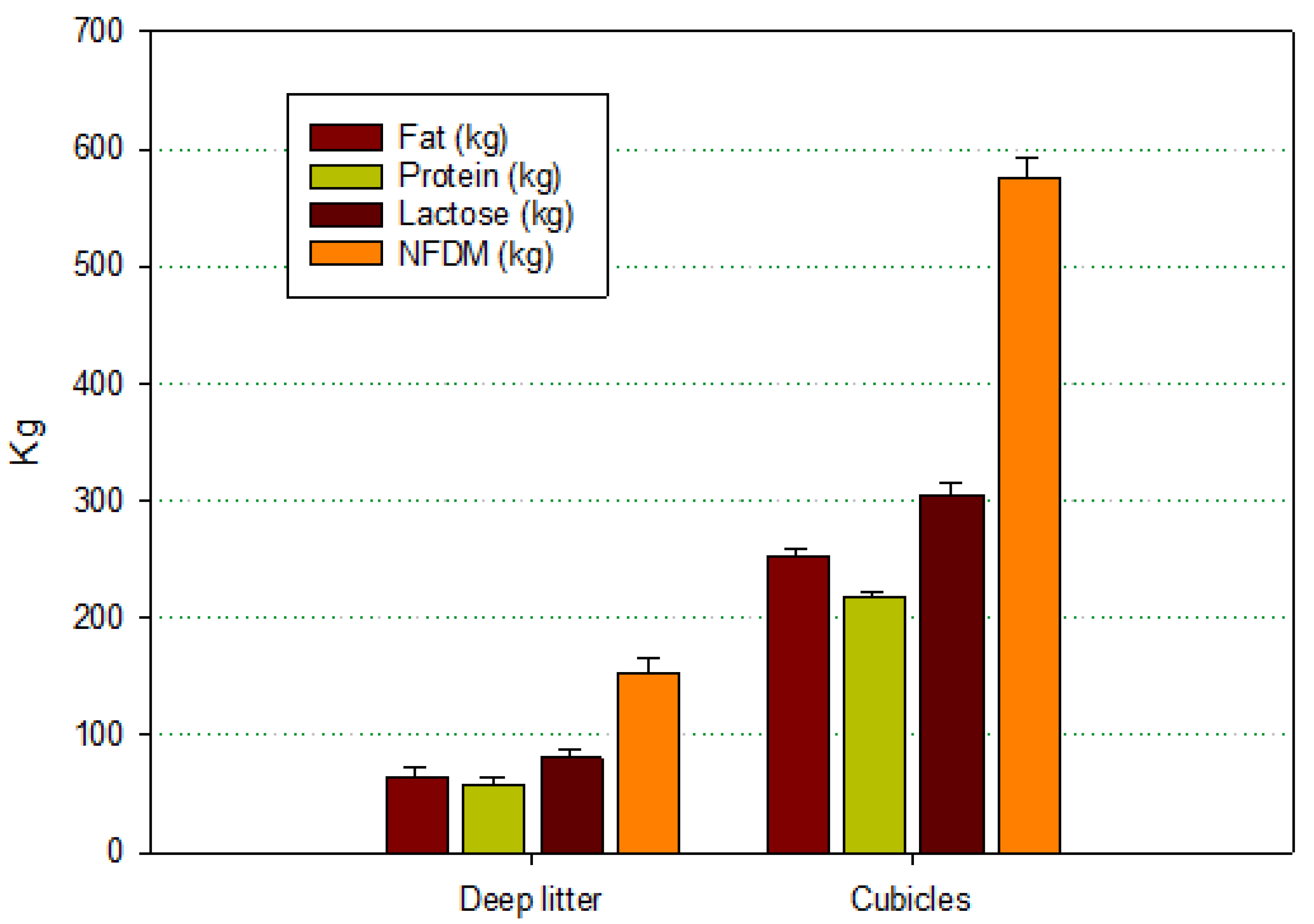
| Housing | Status | Fat | Protein | Lactose | NFDM 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep litter | S. aureus | 61.76 ± 40.82 a,2 | 54.26 ± 35.94 a | 76.18 ± 49.82 a | 144.12 ± 94.23 a |
| Negative | 70.36 ± 42.72 a | 62.17 ± 36.21 a | 86.81 ± 49.28 a | 164.27 ± 93.91 a | |
| Cubicles | S. aureus | 196.19 ± 190.69 a | 168.75 ± 157.73 a | 236.21 ± 224.86 a | 445.79 ± 421.82 a |
| Negative | 235.55 ± 180.42 b | 200.31 ± 150.20 b | 279.76 ± 214.21 b | 528.88 ± 402.52 b |
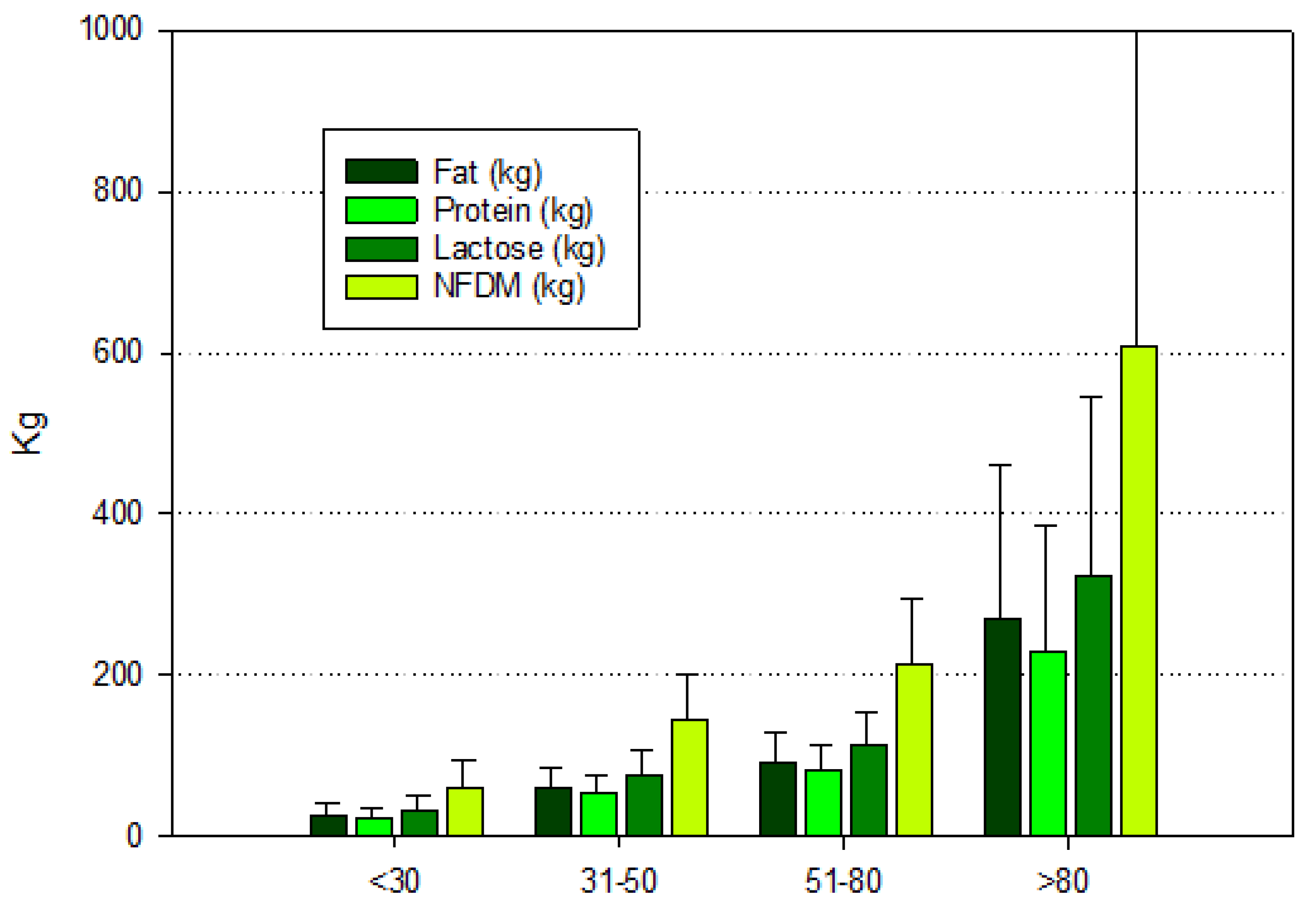
| Size | Status | Fat | Protein | Lactose | NFDM 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–30 | S. aureus | 26.51 ± 12.31 a,2 | 22.67 ± 11.04 a | 32.03 ± 15.04 a | 60.61 ± 28.66 a |
| Negative | 27.25 ± 14.50 b | 24.32 ± 13.30 b | 35.41 ± 19.00 b | 66.02 ± 35.43 b | |
| 31–50 | S. aureus | 57.22 ± 21.37 a | 50.06 ± 18.68 a | 70.07 ± 25.83 a | 132.64 ± 48.78 a |
| Negative | 69.72 ± 25.40 a | 62.21 ± 22.67 a | 87.06 ± 31.48 a | 164.45 ± 59.20 a | |
| 51–80 | S. aureus | 86.11 ± 35.16 a | 76.02 ± 31.05 a | 106.44 ± 41.30 a | 201.15 ± 78.66 a |
| Negative | 106.17 ± 33.26 a | 93.00 ± 29.39 a | 127.54 ± 36.66 a | 242.63 ± 71.43 a | |
| >81 | S. aureus | 257.05 ± 198.01 a | 221.20 ± 161.66 a | 310.03 ± 231.72 a | 585.19 ± 433.73 a |
| Negative | 281.38 ± 181.53 b | 238.35 ± 150.84 b | 333.49 ± 216.10 b | 630.33 ± 405.39 b |
| Housing 1 | S. aureus 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Litter | Cubicles | Positive | Negative | |
| Mean | 20.140 | 23.920 | 20.625 | 227.543 |
| Standard deviation | 55.84 | 42.16 | 45.40 | 55.51 |
| Risk Factors | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inferior Limit | Superior Limit | |||
| Bucket milking vs. parlor milking | 9.16 | 1.43 | 58.61 | 0.019 |
| Absence of forestripping milk observation and disposal vs. presence | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.91 | 0.043 |
| Absence or unproper post-milking teat disinfection vs. proper disinfection | 54.83 | 3.11 | 966.85 | 0.006 |
| Post-milking teat disinfection with a non-authorized product vs. proper disinfection | 11.98 | 1.32 | 108.40 | 0.027 |
| Frequent use of oxytocin vs. no use | 10.45 | 1.38 | 78.95 | 0.023 |
| Animal purchase vs. no purchase | 18.20 | 2.98 | 110.92 | 0.002 |
| Absence of monthly individual milk analysis vs. presence | 12.46 | 2.70 | 57.42 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaghen, F.; Sora, V.M.; Zanirato, G.; Zecconi, A. From One Heath to One Sustainability: The Role of Contagious Mastitis Pathogens in Decreasing the Dairy Herd Sustainability. Pathogens 2024, 13, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100914
Zaghen F, Sora VM, Zanirato G, Zecconi A. From One Heath to One Sustainability: The Role of Contagious Mastitis Pathogens in Decreasing the Dairy Herd Sustainability. Pathogens. 2024; 13(10):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100914
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaghen, Francesca, Valerio M. Sora, Giampaolo Zanirato, and Alfonso Zecconi. 2024. "From One Heath to One Sustainability: The Role of Contagious Mastitis Pathogens in Decreasing the Dairy Herd Sustainability" Pathogens 13, no. 10: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100914
APA StyleZaghen, F., Sora, V. M., Zanirato, G., & Zecconi, A. (2024). From One Heath to One Sustainability: The Role of Contagious Mastitis Pathogens in Decreasing the Dairy Herd Sustainability. Pathogens, 13(10), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100914





