Abstract
Streptococcus pyogenes is responsible for 20–30% of pharyngitis in children and 5–15% in adults. The ineffective treatment of group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections can result in postinfectious sequelae. This study aims to evaluate the frequency of GAS pharyngitis and assess the management of patients with pharyngitis and antibiotic use. We conducted a multicenter, retrospective analysis of medical records from nine primary care centers in Poland. The study enrolled 1949 medical records of patients (children 67.4%, adults 32.6%). An infection of Streptococcus pyogenes, based on a rapid strep test, was diagnosed in 830 patients (42.6%). In the comprehensive study group of 1949 patients, 1054 (54.1%) were given antibiotics. Notably, 224 patients had a negative rapid strep test result but still received antibiotic treatment, underscoring the complexity of treatment decisions. The most commonly used antibiotics were oral penicillin V in 431 cases (41%) and amoxicillin in 219 cases (20.8%). We observed no significant difference between positive rapid strep test results and patients’ sociodemographic data and comorbidities. The prevalence of GAS was 42.6% in the analyzed records of patients with pharyngitis, and 54.1% were prescribed antibiotics. Antibiotics were overprescribed for sore throats. Strategies are needed to promote rational antibiotic use.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS, group A Streptococcus) can be carried asymptomatically in the nasopharynx and on the skin. However, it can also cause a wide range of clinical manifestations ranging from mild localized infections to life-threatening invasive infections [1]. Non-invasive GAS diseases include pharyngitis, tonsillitis, cellulitis, impetigo, and scarlet fever. Life-threatening invasive GAS disease can present, among others, as necrotizing fasciitis and toxic shock syndrome, which are associated with high morbidity and mortality. The 2022/23 winter season saw a rise in the incidence rates of both invasive and non-invasive S. pyogenes infections, a trend that many countries have reported [2,3,4]. The probable cause of the higher morbidity was the increased population’s susceptibility to infections due to COVID-19 pandemic restrictions. Moreover, the increased incidence of iGAS coincided with the weeks with the highest influenza virus and RSV circulation, which cause damage to the respiratory epithelium, which could also facilitate bacterial colonization, adherence, and translocation through the epithelial barrier, promoting the way for bacterial infection [4]. According to current data from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), countries in the EU/EEA are reporting iGAS cases at the levels of pre-pandemic seasons [5]. This underscores the urgent need for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
In temperate climates, GAS pharyngitis occurs most frequently in the winter and early spring [6]. It is estimated that group A Streptococcus is responsible for 20–30% of sore throats in children and 5–15% of sore throats in adults, and over 616 million cases of GAS pharyngitis occur annually worldwide [7,8]. The ineffective treatment of GAS infections can result in postinfectious sequelae like acute rheumatic fever and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. There are approximately 470.000 new cases of acute rheumatic fever and 233.000 attributable deaths yearly, disproportionately affecting populations from developing countries [9].
We can use a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) and throat cultures to diagnose GAS infection in primary care. RADT, with its quick results (within minutes) and high specificity but moderate sensitivity, is a valuable tool in our diagnostic process. However, we must exercise caution and confirm negative results with a throat culture in children and adolescents, ensuring a thorough and comprehensive diagnosis. Throat culture stands as the gold standard for diagnosing GAS pharyngitis, a proof of its reliability and accuracy in primary care settings. If RADT yields a negative result in children or adolescents with symptoms, it is important to follow up with a throat culture. Despite the longer wait time of about 24 to 48 h, this comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnosis.
Sore throat is one of the most common reasons for visiting a primary care doctor. This is a non-specific symptom that both bacterial and viral infections can cause. Appropriate tests, including rapid antigen tests, can help determine proper treatment and limit the use of antibiotics for viral infections.
The drug of choice for treating GAS pharyngitis is oral penicillin V or amoxicillin for ten days [7]. However, the existing Polish guidelines underline that the low dosage of amoxicillin used to treat bacterial pharyngitis might generate S. pneumoniae resistance [10]. Despite that, amoxicillin accounts for a significant percentage of prescribed antibiotics for treating GAS pharyngitis in Poland. In patients with a penicillin allergy, macrolides, clindamycin, and first-generation cephalosporins can be used; however, first-generation cephalosporin should not be used in patients with immediate-type hypersensitivity to penicillin [7]. All isolates of group A strep bacteria are susceptible to penicillin or cephalosporins. Nevertheless, some strains of S. pyogenes have developed resistance to other antibiotics. S. pyogenes resistance to macrolides and clindamycin is well known and varies geographically and temporally [7]. Appropriate antibiotic selection is crucial to the treatment optimization of infections and reduces the risk of drug resistance. This study aims to evaluate the frequency of GAS pharyngitis and determine sociodemographic and clinical indicators associated with GAS infection. Furthermore, this analysis aims to assess the management of patients with pharyngitis and antibiotic use. The gravity of the issue is underscored by the fact that inappropriate antibiotic use can lead to treatment failure and the development of drug-resistant strains, making our work in this area of the utmost importance.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted a multicenter, retrospective analysis of medical records to evaluate the frequency of GAS pharyngitis, sociodemographic and clinical indicators associated with GAS infection, and managing patients with pharyngitis in nine primary care centers in Poland. The study included data from two seasons: December 2022–March 2023 and December 2023–March 2024. The inclusion criterion was to analyze at least 75 records of pediatric and adult patients with pharyngitis in each medical center. We analyzed the results of rapid antigen tests for GAS, antibiotic use, types of antibiotics, sociodemographic data, comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, chronic respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and acquired or congenital immunodeficiency), and vaccination status (influenza and COVID-19).
Statistical Analysis
For all groups, the number of cases (N), the mean (X), median (M), range (min-max), lower and upper quartile (25q–75q), and standard deviation (SD) of the parameters were calculated. The median (interquartile range [IQR]) was used for the description of non-normally distributed data. Qualitative variables were presented as absolute values and percentages (%). The normality assumption was assessed by carrying out the Shapiro–Wilk test for the groups of data. Levene’s test was carried out to assess the homogeneity of variance assumption. For qualitative parameters, the frequency of the traits or characteristics in groups was analyzed using the χ2df test with the appropriate number of degrees of freedom, df (df = (m − 1) × (n − 1), where m—number of rows, n—number of columns). The verification of the hypothesis of equality of means groups of heterogeneous variance was performed by the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test. p ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using EPIINFO Ver. 7.2.3.1. and Statistica Ver. 13.3.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Analyzed Data
The study enrolled 1949 medical records of patients (Figure 1). Children’s (up to 18 years of age) medical records constituted 67.4% of analyzed data, and adults’ 32.6%.
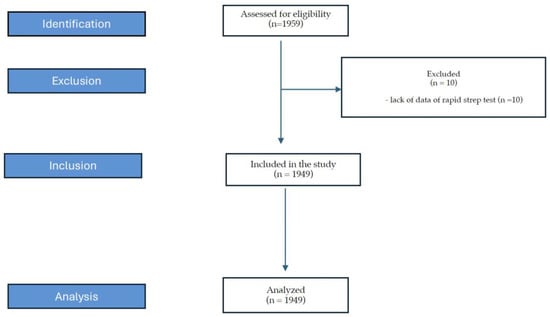
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the analyzed records.
The most significant percentage of patients were from cities with a population over 500,000 (45.2%) and rural areas (25%). The remaining patients came from towns with a population of less than 500,000. In total, 56% were female and 44% male, and their age ranged from 0 to 83 years (Table 1, Figure 2).

Table 1.
Age of participants.
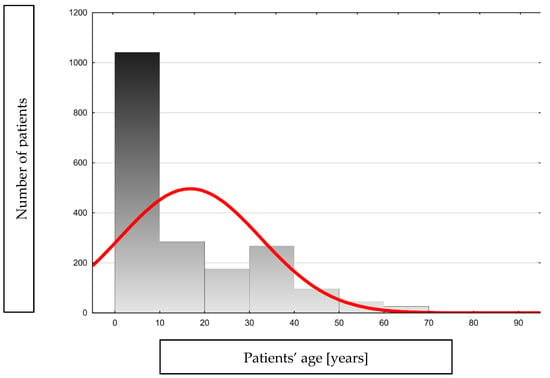
Figure 2.
Histogram showing the age distribution of the analyzed group.
3.1.1. Viral Infection Prophylaxis
In the study group, 128 (6.6%) patients underwent protective vaccination against the influenza virus and 556 (28.5%) patients against COVID-19.
3.1.2. Comorbidity
In the analyzed group of patients, 22 (1.1%) suffer from diabetes, 104 (5.3%) have chronic respiratory diseases, 21 (1.1%) suffer from cardiovascular diseases, and 79 (4.1%) are treated for hypertension. Additionally, 12 (0.6%) patients have been diagnosed with congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies.
3.2. Streptococcus Pyogenes’ Infection
An infection of Streptococcus pyogenes, based on rapid strep test (BIOSYNEX STREP A, Switzerland, France), was diagnosed in 830 patients (42.6%)—579 in children and 251 in adults. Median time from symptom onset to rapid strep test was 2 days (Table 2). In 312 patients’ medical records, there were no data of time from symptom onset to test.

Table 2.
Analysis of the time from symptom onset to rapid strep test.
3.3. Antibiotics Usage
In the comprehensive study group of 1949 patients, 1054 (54.1%) were given antibiotics, a thorough representation of the patient population. In total, 830 patients had positive strep test results. Notably, 224 patients had a negative rapid strep test result but still received antibiotic treatment, underscoring the complexity of treatment decisions. The most commonly used antibiotics were oral penicillin V in 431 cases (41%) and amoxicillin in 219 cases (20.8%). Table 3 presents the exact distribution of antibiotics used and Table 4 presents the analysis of distribution of antibiotics and rapid strep test results.

Table 3.
The distribution of antibiotics used for infections.

Table 4.
The analysis of distribution of antibiotics and rapid strep test results.
3.4. Statistical Analysis of Rapid Strep Test Results and Sociodemographic and Clinical Indicators
The statistical analysis showed no significant difference between positive rapid strep test results and patients’ age (p = 0.0577), sex (p = 0.809), vaccination status (influenza, p = 0.151; COVID-19, p = 0.436), and comorbidities (chronic respiratory diseases, p = 0.641; cardiovascular diseases, p = 0.676; hypertension, p = 0.281; and congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies, p = 0.948) (Table 5). Although we saw a relationship between negative rapid test results and diabetes, the difference between the groups did not meet the threshold for statistical significance (p = 0.0582) (Table 5).

Table 5.
Analysis of rapid strep test results and sociodemographic and clinical indicators.
4. Discussion
Our study attempted to evaluate the frequency of pharyngitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes in primary care and antibiotic usage. There has been a high increase in GAS infections in the past three years. In our study group, among 1949 patients who presented with pharyngitis, 42.6% of cases were caused by Streptococcus pyogenes infection, confirmed by a rapid strep test. In the post-COVID period, a significant increase in infections caused by group A streptococci was observed. The prevalence of GAS infections and their complications varies between poorly developed and well-developed countries, highlighting the importance of a unified approach. In underdeveloped countries, the high number of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) and the incidence of deaths are associated with RHD. Conversely, in well-developed countries, the high incidence of deaths due to invasive GAS infection necessitates a joint effort, especially in the post-pandemic COVID-19 era. Since the beginning of December 2022, an unusually high rise in cases of and deaths from GAS infections has been reported in many European countries [4]. In Denmark, patients ≥ 85 years had the highest iGAS incidence rates, peaking at 7.4 per 100,000 in the age group per month; however, the highest relative increase compared with pre-pandemic restrictions was detected among children younger than five years, which peaked at 3.2 per 100,000 in the age group in March 2023 [11]. Fatality rates were similar to previous years across all age groups: 30% among patients ≥ 85 years and less than 5% among children under 5 years [11].
Winter months are also associated with a burden of GAS pharyngitis in people of all ages, but especially in children. Sore throat is one of the most common clinical problems in general practice, and the majority of them are viral, so most patients do not benefit from antibiotics. Clinical guidelines recommend prescribing antibiotics for pharyngitis only when there is a high probability that the condition has been caused by GAS [7,12].
Our study revealed that penicillin V, the first-choice antibiotic, was used in 41.0% of cases, followed by amoxicillin at 20.8% and cefadroxil at 12.5%. The high percentage of prescribed amoxicillin reveals poor adherence to the Polish guidelines limiting the use of a low dosage of amoxicillin to treat GAS pharyngitis [10]. Other prescribed antibiotics were clarithromycin, azithromycin, cefuroxime axetil, amoxicillin- clavulanate, levofloxacin, cefaclor, cefixime, and clindamycin. Notably, no strains resistant to penicillin were observed in Poland, reinforcing its efficacy and reliability. Moreover, 224 patients had negative rapid strep test results, but still received antibiotic treatment. It seems that doctors prescribe antibiotics out of fear that the patient could eventually develop complications. However, they do not remember that overprescribing is associated with the growing antibiotic resistance and side effects, e.g., diarrhea. Some patients might also expect a prescription for an antibiotic even if the rapid strep test result is negative. Another study indicated that 23% (80/345) of participants had a positive throat swab for GAS, but 65% (225/345) of all participants were prescribed immediate and 12% (43/345) delayed antibiotics [13]. Moreover, the authors of the mentioned study showed results of a retrospective analysis of the Centor score for 337 patients, of whom 49% had a low (score ≤ 2) and 48% had a high Centor score (>2) [13]. For 50% of participants, prescribing was in line with National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) clinical guidelines, i.e., a Centor score of 3 or 4 [13]. The results of these studies indicated that antibiotics were overprescribed for sore throat, and this is worrying in light of global antimicrobial resistance.
The drug of choice, penicillin V, has proven highly effective when given at 500 mg twice daily for ten days. In patients with a penicillin allergy, macrolides, clindamycin, and first-generation cephalosporins can be used; however, first-generation cephalosporin should not be used in patients with immediate-type hypersensitivity to penicillin [7]. Group A strep bacteria with Streptococcus pyogenes are susceptible to penicillin or cephalosporins. Some studies have suggested greater efficacy with cephalosporins than penicillin, possibly because of their resistance to β-lactamase-producing organisms in the pharynx and due to their higher efficacy in killing ingested bacterial cells [14,15]. This means that cephalosporins are less likely to be affected by the enzymes produced by the bacteria that can degrade penicillin, making them more effective in some cases. However, cephalosporins are more expensive than penicillin, are associated with more significant side effects, and have a broader spectrum of activity.
Nevertheless, some strains of S. pyogenes have developed resistance to other antibiotics. Azithromycin, clarithromycin, and erythromycin are effective in treating GAS pharyngitis. Macrolide antibiotics are an essential alternative to penicillin, especially in treating infections in people with penicillin hypersensitivity. Azithromycin is efficacious in treating GAS pharyngitis when given for only 5 days (500 mg on the first day and then 250 mg for 4 days taken as a single dose), clarithromycin for ten days (250 mg twice daily), and erythromycin for ten days (500 mg twice daily). However, macrolide-resistant GAS has been reported in many countries. Recent data indicated that macrolide-resistant strains of S. pyogenes were detected in Bulgaria (23–40%), Greece (20.4%), Spain (8.7%), Hungary (10.5%), Russia (12.1–17.2%), the USA (16–23%), Brazil (14.3%), China (94.74%), Japan (34.9–60%), Australia (6%), and northwest Ethiopia (21.4%) [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Also clindamycin-resistant strains of S. pyogenes are well known and vary geographically and temporally [7,22].
It is crucial to initiate penicillin treatment within nine days of the onset of symptoms of GAS pharyngitis, as it has been proven to be effective in preventing rheumatic fever. The absence of documented resistance of GAS to penicillin further underscores the importance of early treatment, highlighting its role in eradicating the organism from the pharynx. Treatment failures in GAS pharyngitis are a significant concern in preventing rheumatic fever.
Our analysis showed no significant difference between positive rapid strep test results and patients’ sociodemographic data and comorbidities. Although we saw a relationship between negative rapid test results and diabetes, the difference between the groups did not meet the threshold for statistical significance. Given the small number of patients with diabetes, this observation is also at a very high risk of uncontrolled confounding. Moreover, some studies indicated for an increased risk of the GAS disease in patients with diabetes [23,24,25], and efforts to develop a vaccine and enhanced treatment regimens for iGAS might improve prognoses for patients with diabetes.
Limitations: Our study may not be representative for the whole population. Due to a limited sample size, results might differ in other regions. We did not analyze detailed clinical history,, e.g., allergy to antibiotics. Moreover, rapid strep tests have some limitations: they are not as accurate as molecular tests and have a higher rate of false negatives. We did not compare differences in management between adults and children. Furthermore, the doctors did not perform cultures and we had no information about the susceptibility pattern of Streptococcus pyogenes (especially the percentage of isolates resistant to macrolides).
5. Conclusions
The prevalence of GAS was 42.6% in the analyzed records of patients with pharyngitis, and 54.1% of all patients were prescribed antibiotics. Antibiotics were overprescribed for pharyngitis. Strategies are needed to promote rational antibiotic use. A system offering easy access to the monitoring of regional resistance patterns, their dynamics, and the spread of resistant strains is needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.B. (Martyna Biała), P.L., B.K. and M.B. (Mateusz Babicki); methodology: M.B. (Martyna Biała) and P.L.; formal analysis, M.B. (Martyna Biała), P.L. and M.B. (Mateusz Babicki); investigation: M.B. (Mateusz Babicki), W.M., S.J., D.G., A.Ż., K.K., P.G., J.L., A.M., D.K. and A.W.; data curation: M.B. (Martyna Biała), P.L., M.B. (Mateusz Babicki), B.K. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation: M.B. (Martyna Biała), P.L. and B.K.; writing—review and editing, M.B. (Mateusz Babicki) and K.K.; visualization: M.B. (Martyna Biała) and P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Wroclaw Medical University Ethics Committee (KB-565/2023N).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kanwal, S.; Vaitla, P. Streptococcus Pyogenes. In StatPearls [Internet]; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guy, R.; Henderson, K.L.; Coelho, J.; Hughes, H.; Mason, E.L.; Gerver, S.M.; Demirjian, A.; Watson, C.; Sharp, A.; Brown, C.S.; et al. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infection notifications, England, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gier, B.; Marchal, N.; de Beer-Schuurman, I.; Te Wierik, M.; Hooiveld, M.; de Melker, H.E.; van Sorge, N.M.; Members of the GAS Study Group; Members of the ISIS-AR Study Group. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) infections (iGAS) in young children in The Netherlands, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe). Increase in Invasive Group A Streptococcal Infections among Children in Europe, Including Fatalities 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news/item/12-12-2022-increase-in-invasive-group-a-streptococcal-infections-among-children-in-europe--including-fatalities (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Communicable Diseases Threat. Week 12, 17–23 March 2024. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/communicable-disease-threats-report-week-12-2024.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Shulman, S.T.; Bisno, A.L.; Clegg, H.W.; Gerber, M.A.; Kaplan, E.L.; Lee, G.; Martin, J.M.; Van Beneden, C. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Guidance for Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/group-a-strep/hcp/clinical-guidance/strep-throat.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-hcp/strep-throat.html (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.D.S.; Koziatek, C.A.; Rajnik, M. Acute Rheumatic Fever. [Updated 2 August 2023]. In StatPearls [Internet]; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK594238/ (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Hryniewicz, W.; Albrecht, P.; Radzikowski, A. Rekomendacje Postepowania w Pozaszoitalnych Zakażeniach Układu Oddechowego 2016. Available online: https://antybiotyki.edu.pl/rekomendacje/rekomendacje-diagnostyki-i-terapii-zakazen/ (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Johannesen, T.B.; Munkstrup, C.; Edslev, S.M.; Baig, S.; Nielsen, S.; Funk, T.; Kristensen, D.K.; Jacobsen, L.H.; Ravn, S.F.; Bindslev, N.; et al. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infections and emergence of novel, rapidly expanding sub-lineage of the virulent Streptococcus pyogenes M1 clone, Denmark, 2023. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HSE. HSE Expert Advisory Committee: Antibiotic Prescribing, Pharyngitis/Sore Throat/Tonsillitis. 2021. Available online: https://www.hse.ie/eng/services/list/2/gp/antibiotic-prescribing/conditions-and-treatments/upper-respiratory/pharyngitis-sore-throat-tonsillitis/ (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- de Paor, M.; Boland, F.; Fahey, T.; Smith, S.; MacDonncha, E.; Vellinga, A. Management of sore throat (with focus on GAS) in young adults. Clin. Infect. Pract. 2024, 23, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.R.; Pichichero, M.E. Meta-analysis of cephalosporins versus penicillin for treatment of group A streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Rohde, M. Reduced ability of penicillin to eradicate ingested group A streptococci from epithelial cells: Clinical and pathogenetic implications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhtarova, A.; Gergova, R.; Mitov, I. Distribution of macrolide resistance mechanisms in Bulgarian clinical isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes during the years of 2013–2016. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arêas, G.P.; Schuab, R.B.; Neves, F.P.; Barros, R.R. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, emm type distribution and genetic diversity of Streptococcus pyogenes recovered in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M.; Ábrók, M.; Lázár, A.; Burián, K. Beta-Haemolytic Group A, C and G Streptococcal Infections in Southern Hungary: A 10-Year Population-Based Retrospective Survey (2008–2017) and a Review of the Literature. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2020, 13, 4739–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meletis, G.; Soulopoulos Ketikidis, A.L.; Floropoulou, N.; Tychala, A.; Kagkalou, G.; Vasilaki, O.; Mantzana, P.; Skoura, L.; Protonotariou, E. Antimicrobial resistance rates of Streptococcus pyogenes in a Greek tertiary care hospital: 6-year data and literature review. New Microbiol. 2023, 46, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, T.A.J.; Story, C.; Green, E.; Williamson, K.M.; Newton, P.; Jenkins, F.; Varadhan, H.; van Hal, S. Insights gained from sequencing Australian non-invasive and invasive Streptococcus pyogenes isolates. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Rivers, J.; Mathis, S.; Li, Z.; Velusamy, S.; Nanduri, S.A.; Van Beneden, C.A.; Snippes-Vagnone, P.; McGee, L.; Chochua, S.; et al. Genomic Surveillance of Streptococcus pyogenes Strains Causing Invasive Disease, United States, 2016–2017. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergova, R.; Boyanov, V.; Muhtarova, A.; Alexandrova, A. A Review of the Impact of Streptococcal Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance on Human Health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, G.; Hao, Y.; Pondo, T.; Miller, L.; Petit, S.; Thomas, A.; Lindegren, M.L.; Farley, M.M.; Dumyati, G.; Como-Sabetti, K.; et al. The Impact of Obesity and Diabetes on the Risk of Disease and Death due to Invasive Group A Streptococcus Infections in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, M.; Wang’ondu, R.; Cooney, L.M., Jr. Group A Streptococcal Bacteremia following Streptococcal Pharyngitis in an Older Patient with Diabetes: A Case Report. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E. Severe Group A Streptococcal Infections. 2016 Feb 10. In Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]; Ferretti, J.J., Stevens, D.L., Fischetti, V.A., Eds.; University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK333425/ (accessed on 30 July 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).