Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp): A Marker for Detection of Human Coronavirus Families
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Analysis and Construction of the Pangenome of Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta Coronaviruses
2.2. Conformation of Tertiary Structures of Nsp Proteins
2.3. Evolutionary Relationships of Nsp Proteins in Coronavirus Families
3. Results
3.1. Annotation of the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta Coronaviruses Genomes
3.2. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
3.3. Identification of Nsp Domaizns in the Coronavirus Genome
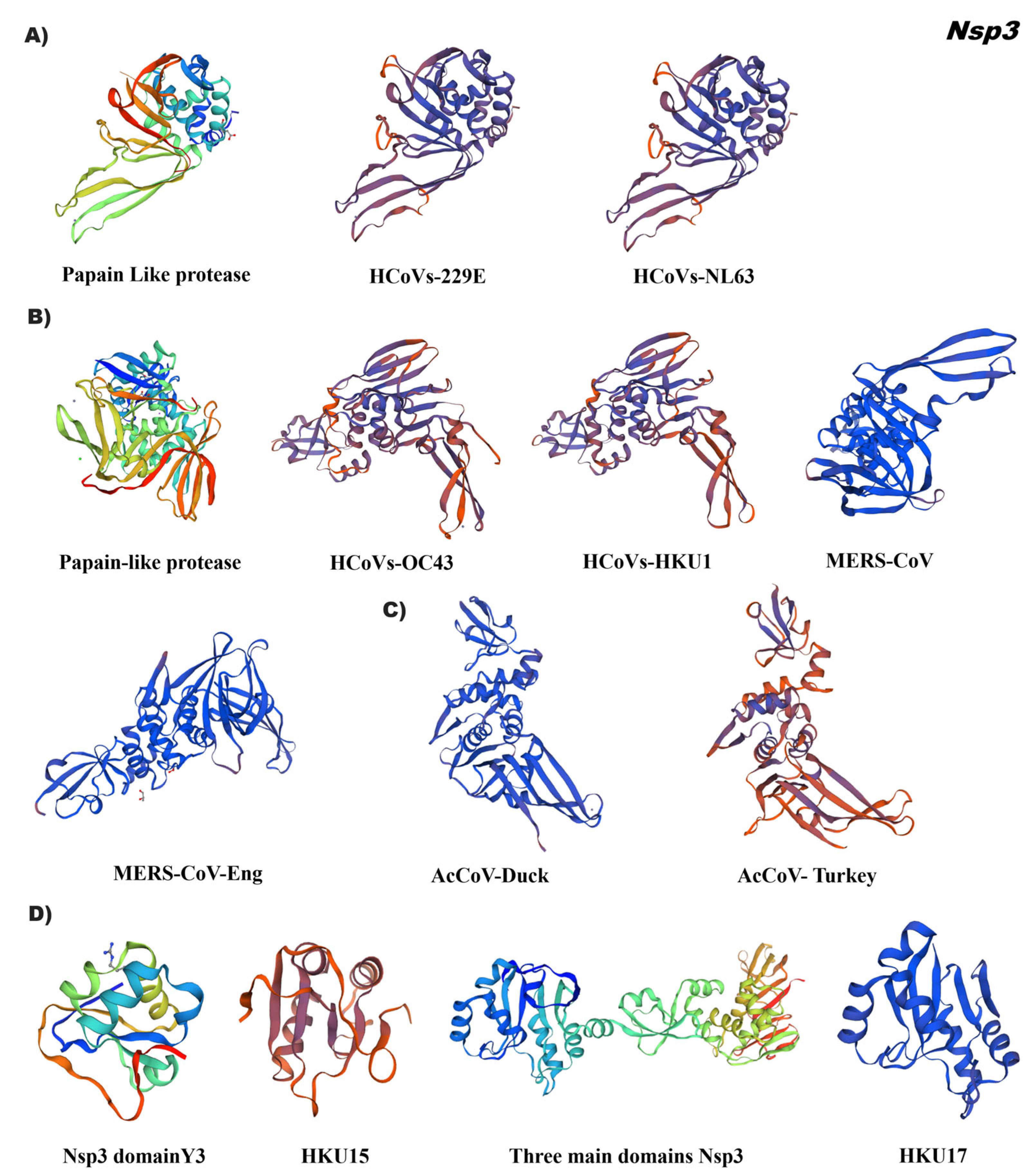
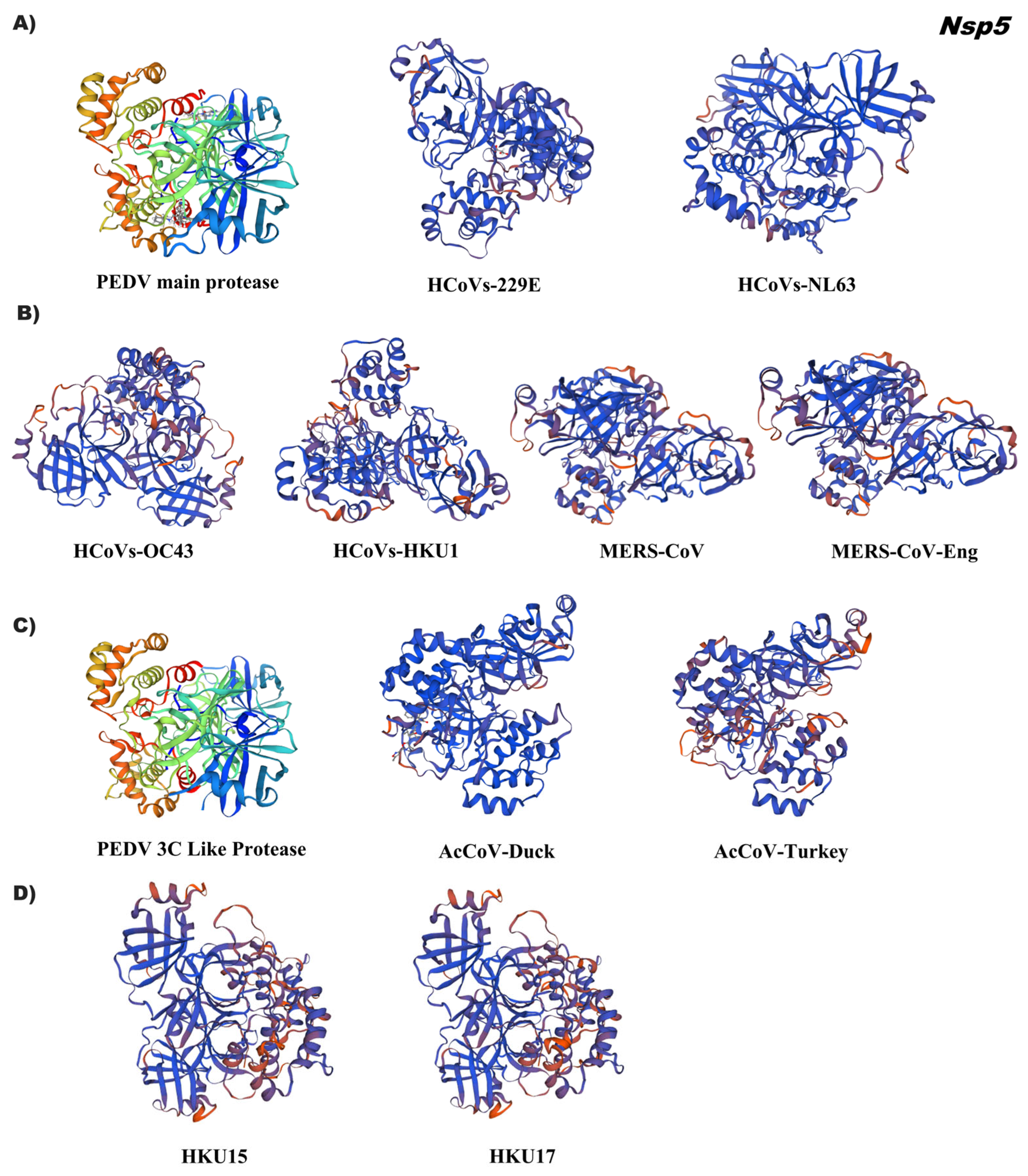
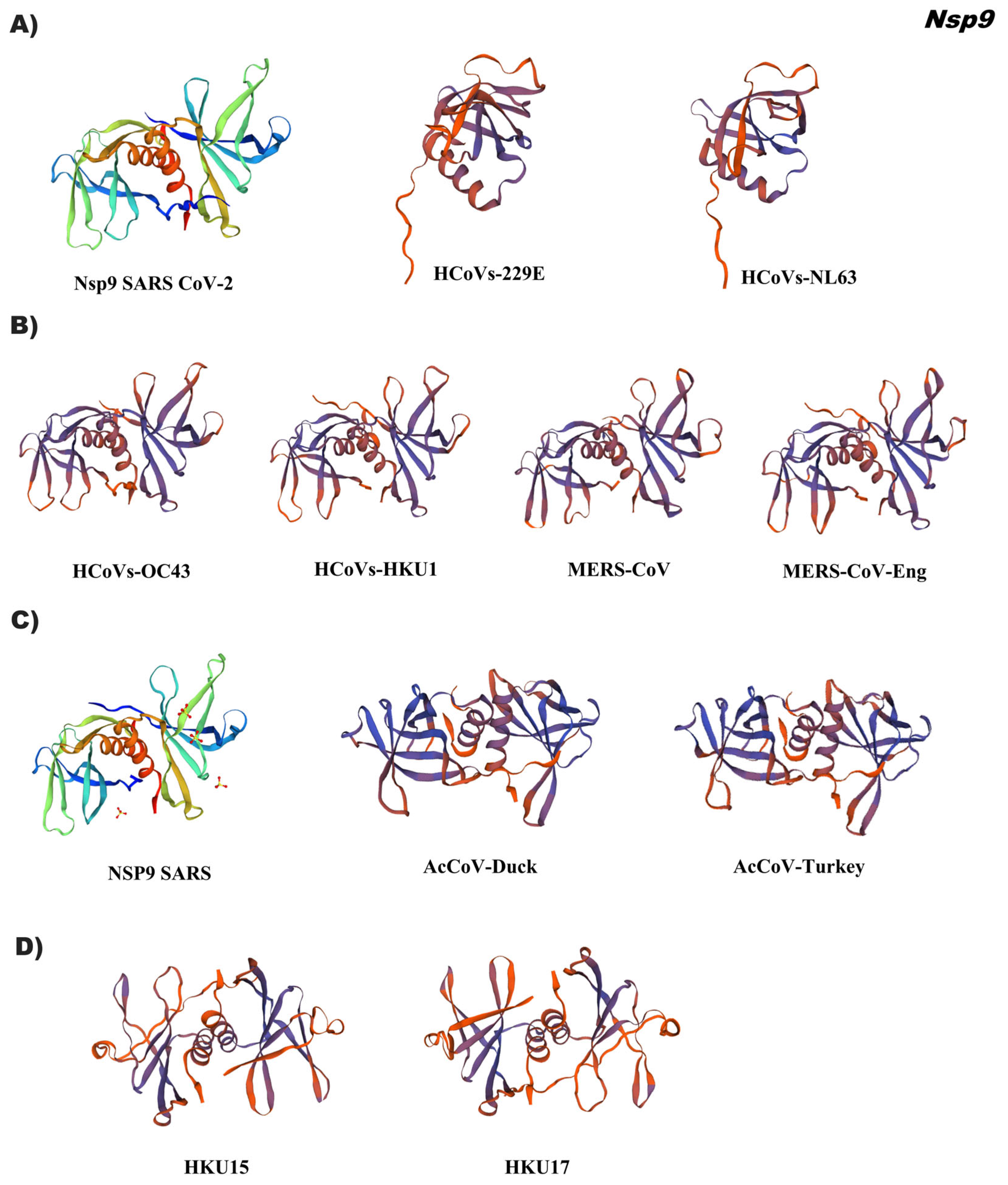
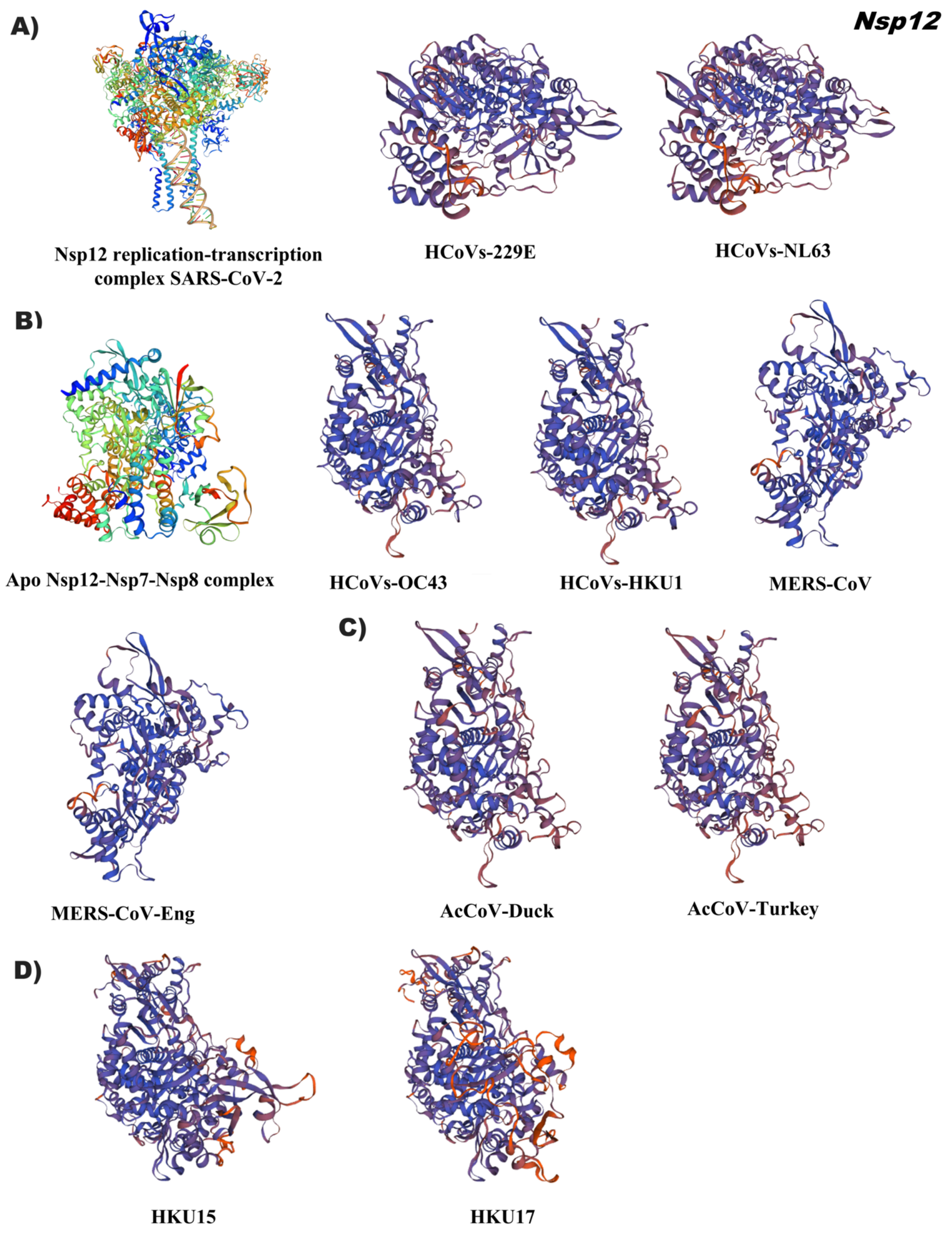
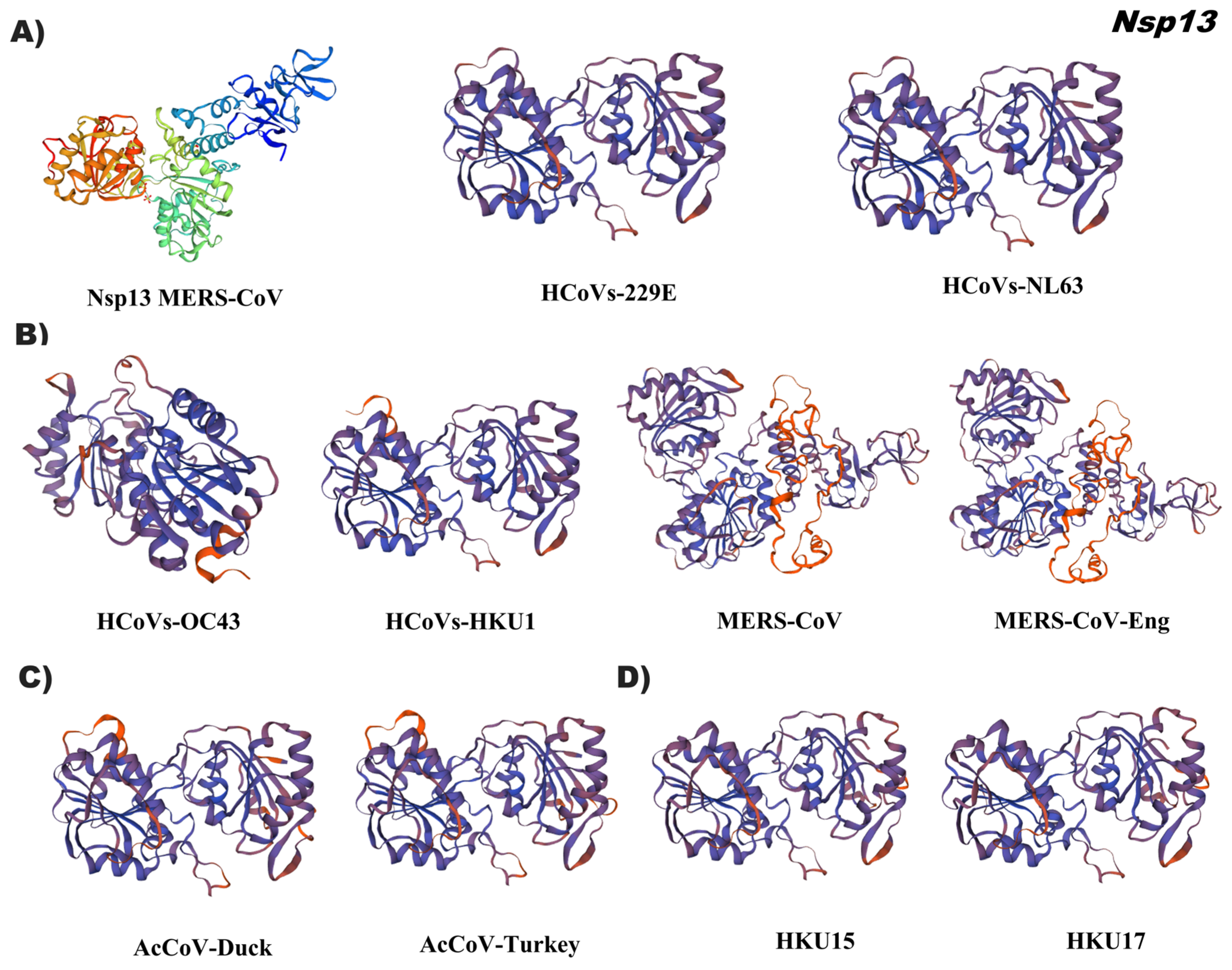
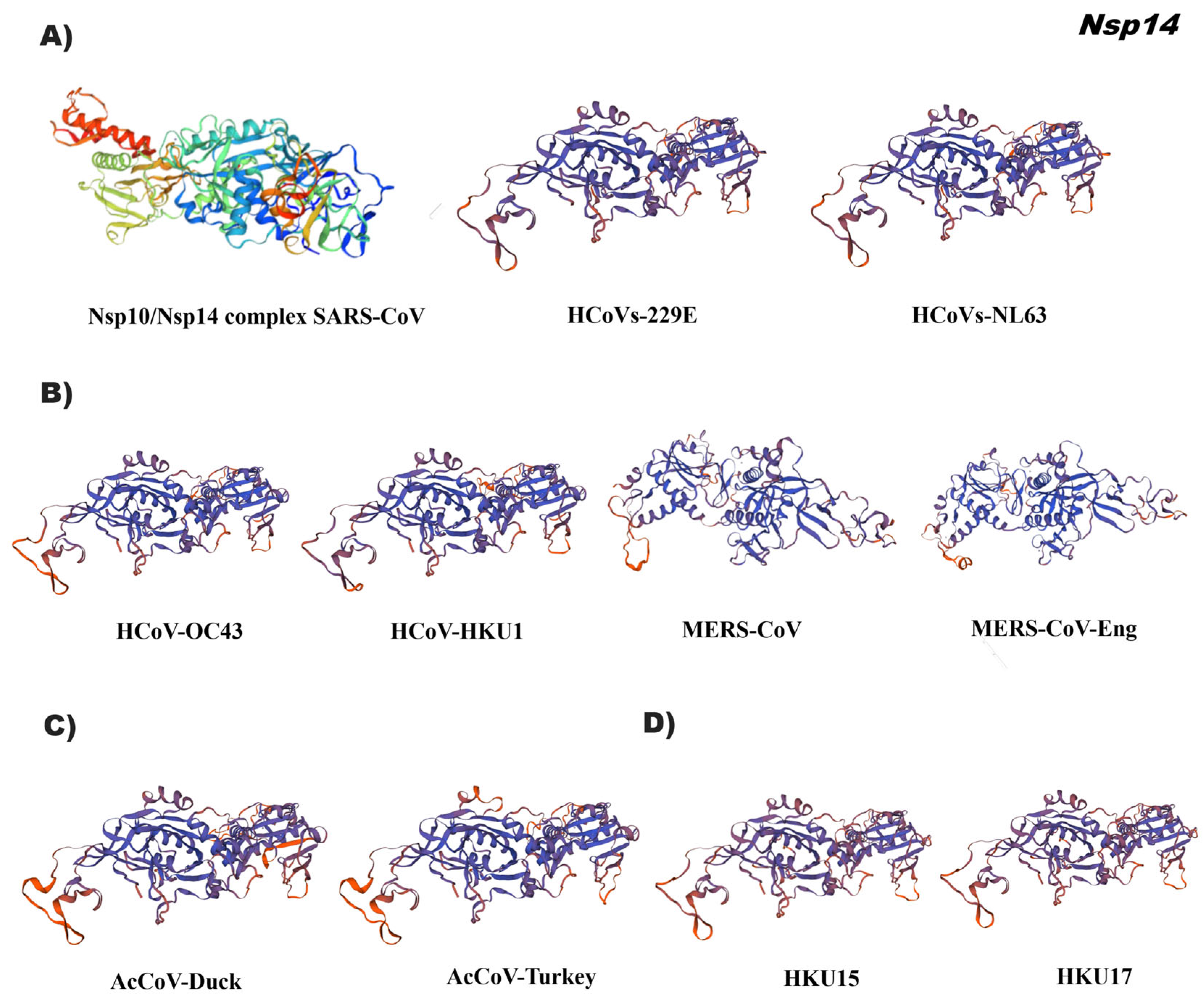
3.4. In Silico Tertiary Structures of Nsp from Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta Coronaviruses
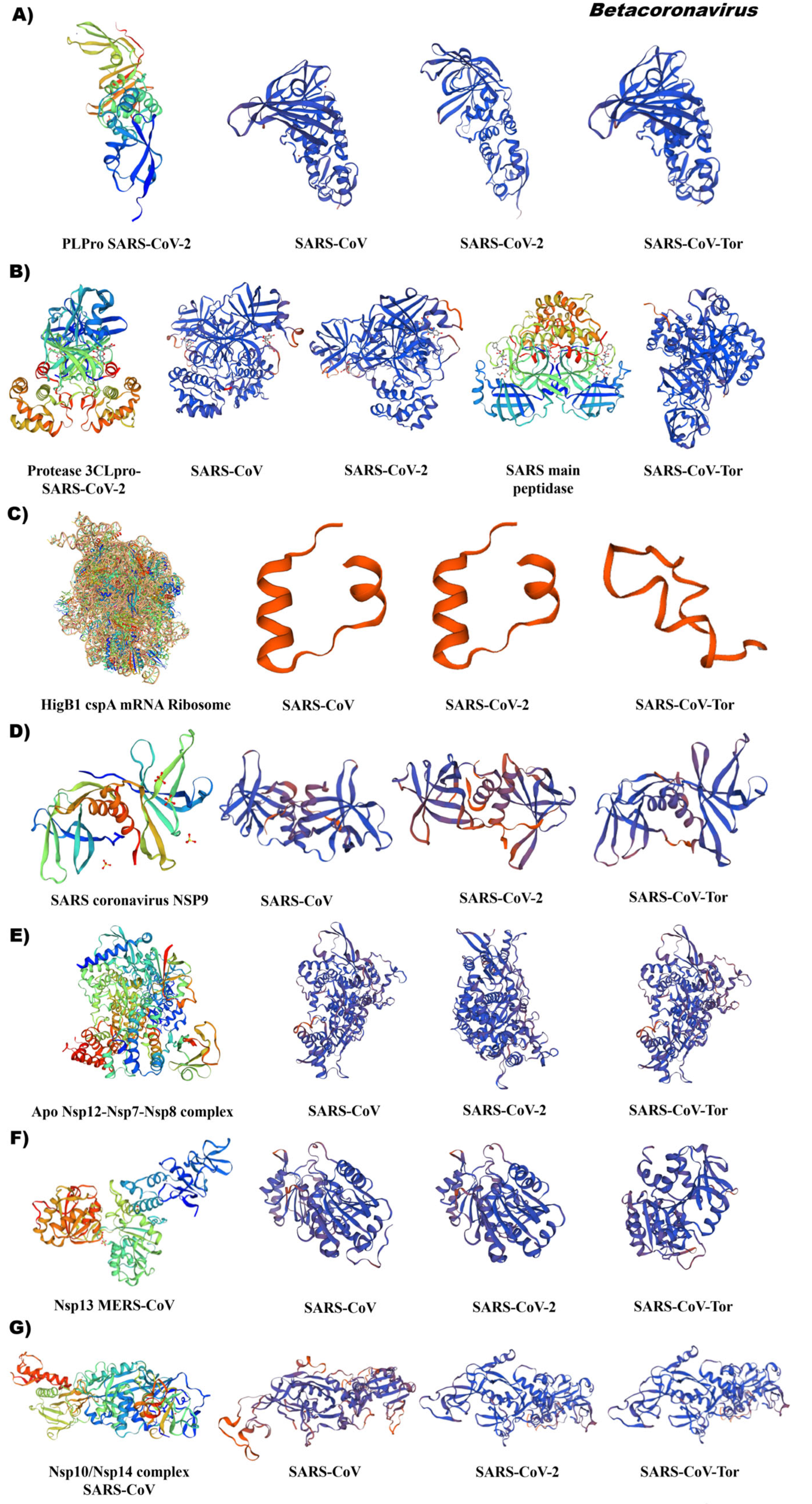
3.5. Comparative Analysis of the Tertiary Structural Conformation of Nsp in SARS-CoV
3.6. Evolutionary Relationships of Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp) of Different Coronavirus Genus
4. Discussion
4.1. Functional Annotation and Identification of Non-Structural Protein (Nsp) Domains in the Coronavirus Genome
4.2. Specific Domains of Nsp Can Be Used as Coronavirus Identification Markers
4.3. Changes in 3D-Structure of Nsp Suggest Adaptation of Coronaviruses during Their Viral Infection Mechanism
4.4. Possible Drug Binding Sites of Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp) in Coronaviruses
4.5. Evolutionary Relationships of Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp) of Different Coronavirus Genus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polatoğlu, I.; Oncu-Oner, T.; Dalman, I.; Ozdogan, S. COVID-19 in early 2023: Structure, replication mechanism, variants of SARS-CoV-2, diagnostic tests, and vaccine & drug development studies. MedComm 2023, 4, e228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abavisani, M.; Rahimian, K.; Mahdavi, B.; Tokhanbigli, S.; Mollapour Siasakht, M.; Farhadi, A.; Mansoor, K.; Mohammadamin, M.; Meshkat, Z. Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins: A global analysis. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gralinski, L.E.; Menachery, V.D. Return of the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe. 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaim, M.A.; El Naggar, R.F.; Clayton, E.; Munir, M. Structural and functional insights into non-structural proteins of coronaviruses. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkin, A.P.; Cottingham, R.W.; Henry, C.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stevens, R.L.; Maslov, S.; Dehal, P.; Ware, D.; Perez, F.; Canon, S.; et al. Kbase: The United States Department of Energy Systems Biology Knowledgebase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Schwede, T. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitszas, F.; Derbychire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Fan, C. Structural and biochemical characterization of SADS-CoV papain-like protease 2. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1228–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, K.S.; Ali, Y.M.; Yesilkaya, H.; Kohler, T.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Andrew, P.W.; Schwaeble, W.J.; Lynch, N.J. The pneumococcal surface proteins PspA and PspC sequester host C4-binding protein to inactivate complement C4b on the bacterial surface. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00742-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rut, W.; Lv, Z.; Zmudzinski, M.; Patchett, S.; Nayak, D.; Snipas, S.J.; Oualid, F.E.; Huang, T.T.; Bekes, M.; Drag, M.; et al. Activity profiling and crystal structures of inhibitor-bound SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease: A framework for anti-COVID-19 drug design. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Palm, G.J.; Mesters, J.R.; Siddell, S.G.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hilgenfeld, R. Structure of coronavirus main proteinase reveals combination of a chymotrypsin fold with an extra alpha-helical domain. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Zhang, S.; Zou, P.; Chen, J.; Kang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, C.; Jin, C.; Xia, B. Without its N-finger, the main protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus can form a novel dimer through its C-terminal domain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4227–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.; Kumari, S.; Pandey, B.; Mistry, H.; Bihani, S.C.; Das, A.; Prashar, V.; Gupta, G.D.; Panicker, L.; Kumar, M. Structural insights into SARS-CoV-2 proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Ward, A.B. Structure of the SARS-CoV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Prasad, B.V.; Selvarajan, R. RNA dependent RNA polymerases: Insights from structure, function and evolution. Viruses 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yan, L.; Ren, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Ming, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lou, Z.; et al. Delicate structural coordination of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Nsp13 upon ATP hydrolysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 6538–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferron, F.; Subissi, L.; Morais, A.T.S.D.; Le, N.T.T.; Sevajol, M.; Gluais, L.; Decroly, E.; Vonrhein, C.; Bricogne, G.; Canard, B.; et al. Structural and molecular basis of mismatch correction and ribavirin excision from coronavirus RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E162–E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barretto, N.; Jukneliene, D.; Ratia, K.; Chen, Z.; Mesecar, A.D.; Baker, S.C. The papain-like protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus has deubiquitinating activity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15189–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yang, H.; Shen, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, C.; Jin, Y.; Bartlam, M.; Rao, Z. Production of authentic SARS-CoV M(pro) with enhanced activity: Application as a novel tag-cleavage endopeptidase for protein overproduction. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Zhong, Q.; Gao, G.F. Overview of SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded proteins. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Ramirez, S.I.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Makino, S. Coronavirus non-structural protein 1: Common and distinct functions in the regulation of host and viral gene expression. Virus Res. 2015, 202, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoms, M.; Buschauer, R.; Ameismeier, M.; Koepke, L.; Denk, T.; Hirschenberger, M.; Kratzat, H.; Hayn, M.; Mackens, T.; Cheng, J.; et al. Structural basis for translational shutdown and immune evasion by the Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa Ribero, M.; Jouvenet, N.; Dreux, M.; Nisole, S. Interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the type I interferon response. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Lin, C.H.; Norris, S.L.; Wei, D.; Hu, Z.; Ji, S. Routes of transmission of influenza A H1N1, SARS CoV, and norovirus in air cabin: Comparative analyses. Indoor Air. 2018, 28, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, S.; Benvenuto, D.; Bianchi, M.; Giovanetti, M.; Pascarella, S.; Ciccozzi, M. COVID-2019: The role of the nsp2 and nsp3 in its pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, I.; Snijder, E.J.; Dimitrova, M.; Guillemot, J.C.; Lécine, P.; Canard, B. The SARS-Coronavirus PLnc domain of nsp3 as a replication/transcription scaffolding protein. Virus Res. 2008, 133, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, M.M.; Akhlaghpour, M.; Neuman, B.W.; Buchmeier, M.J. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural proteins 3, 4, and 6 induces double-membrane vesicles. Mbio 2013, 4, e00524-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijder, E.J.; Bredenbeek, P.J.; Dobbe, J.C.; Thiel, V.; Ziebuhr, J.; Poon, L.L.; Guan, Y.; Rozanov, M.; Spaan, W.J.M.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARS-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 331, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krichel, B.; Falke, S.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Redecke, L.; Uetrecht, C. Processing of the SARS-CoV pp1a/ab nsp7–10 region. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillen, H.S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nature 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Snijder, E.J. The PRRSV replicase: Exploring the multifunctionality of an intriguing set of nonstructural proteins. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Yan, L.; Ming, Z.; Jia, Z.; Lou, Z.; Rao, Z. Structural and biochemical characterization of endoribonuclease Nsp15 encoded by Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00893-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miknis, Z.J.; Donaldson, E.F.; Umland, T.C.; Rimmer, R.A.; Baric, R.S.; Schultz, L.W. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nsp9 dimerization is essential for efficient viral growth. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littler, D.R.; Gully, B.S.; Colson, R.N.; Rossjohn, J. Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 9, Nsp 9. IScience 2020, 23, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Malone, B.; Llewellyn, E.; Grasso, M.; Shelton, P.M.M.; Olinares, P.D.B.; Maruthi, K.; Eng, E.T.; Valandaslar, H.; Chait, B.T.; et al. Structural basis for helicase-polymerase coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex. Cell 2020, 182, 1560.e13–1573.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Banach, M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Sarkar, K.; Sil, P.C.; Nabavi, S.M. Should we try SARS-CoV-2 helicase inhibitors for COVID-19 therapy? Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harcourt, B.H.; Jukneliene, D.; Kanjanahaluethai, A.; Bechill, J.; Severson, K.M.; Smith, C.M.; Rota, P.A.; Baker, S.C. Identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replicase products and characterization of papain-like protease activity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13600–13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhammad, Y.M.O.; Kashipathy, M.M.; Roy, A.; Gagné, J.P.; McDonald, P.; Gao, P.; Nonfoux, L.; Battaile, K.P.; Johnson, D.K.; Holmstrom, E.D.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 conserved macrodomain is a monoADP-ribosylhydrolase. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01969-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, K.; Bonfiglio, J.J.; Mikoč, A.; Matic, I.; Ahel, I. Specificity of reversible ADP-ribosylation and regulation of cellular processes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, P.S. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 66, 193–292. [Google Scholar]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, W.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Ma, J.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, D.; Ziebuhr, J.; et al. Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e324. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.S.; Johnson, M.A.; Herrmann, T.; Geralt, M.; Wuthrich, K. Novel-barrel fold in the nuclear magnetic resonance structure of the replicase nonstructural protein 1 from the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathelet, M.G.; Orr, M.; Frieman, M.B.; Baric, R.S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus evades antiviral signaling: Role of NSP1 and rational design of an attenuated strain. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11620–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wei, Z.; Song, J. Dissection study on the severe acute respiratory syndrome 3C-like protease reveals the critical role of the extra domain in dimerization of the enzyme: Defining the extra domain as a new target for design of highly specific protease inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24765–24773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlam, M.; Xu, Y.; Rao, Z. Structural proteomics of the SARS coronavirus: A model response to emerging infectious diseases. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2007, 8, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holshue, M.L.; DeBolt, C.; Lindquist, S.; Lofy, K.H.; Wiesman, J.; Bruce, H.; Spitters, C.; Ericson, K.; Wilkerson, S.; Tural, A.; et al. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the united states. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.O.; Marchand, B.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W.; Snijder, E.J.; Weiss, S.; Eoff, R.L.; Singh, K.; Sarafianos, S.G. Mechanism of nucleic acid unwinding by SARS-CoV helicase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Ge, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of an extended SARS-CoV-2 replication and transcription complex reveals an intermediate state in Cap synthesis. Cell 2021, 184, 184.e10–193.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.K.; Blanco, M.R.; Bruce, E.A.; Honson, D.D.; Chen, L.M.; Chow, A.; Bhat, P.; Ollikainen, N.; Quinodoz, S.A.; Loney, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 disrupts splicing, translation, and protein trafficking to suppress host defenses. Cell 2020, 183, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Deng, F.; Shi, K.; Ye, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.; Peng, G. Dimerization of coronavirus nsp9 with diverse modes enhances its nucleic acid binding affinity. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 1028–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Plante, J.A.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Ge, X.Y.; Donaldson, E.F.; et al. A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.A.; Jones, S.J.; Astell, C.R.; Holt, R.A.; Brooks-Wilson, A.; Butterfield, Y.S.; Khattra, J.; Asano, J.K.; Baber, S.A.; Chan, S.Y.; et al. The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science 2003, 300, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minskaia, E.; Hertzig, T.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C.; Canard, B.; Ziebuhr, J. Discovery of an RNA virus 3′-5′exoribonuclease that is critically involved in coronavirus RNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5108–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, B.; Wang, M.; Jing, H.; Xu, H.; Jiang, X.; Yan, M.; Liang, W.; Zheng, H.; Wan, K.; Liu, Q.; et al. Molecular evolution analysis and geographic investigation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in palm civets at an animal market and on farms. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11892–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.W.; Wong, B.H.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, S.Y.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-D.; Chi, W.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Ferral, L.; Hung, C.-F.; Wu, T.-C. Coronavirus vaccine development: From SARS and MERS to COVID-19. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, S.J.; Gilardi, K.; Menachery, V.D.; Goldstein, T.; Ssebide, B.; Mbabazi, R.; Navarette, I.; Liang, E.; Wells, H.; Hicks, A.; et al. Further evidence for bats as the evolutionary source of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Mbio 2017, 8, e00373-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.L.; Firth, C.; Street, C.; Henriquez, J.A.; Petrosov, A.; Tashmukhamedova, A.; Hutchinson, S.K.; Eghilm, M.; Osinubi, M.O.V.; Niezgoda, M.; et al. Identification of a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in a leaf-nosed bat in Nigeria. MBio 2010, 1, e00208-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, E.I.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Farraj, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Al-Saeed, M.S.; Hashem, A.M.; Madani, T.A. Evidence for camel-to-human transmission of MERS coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Family/Function | Protein Coding Gene * | Genome |
|---|---|---|
| Hemagglutinin-esterase glycoprotein | gp02 | HCoVs-229E HCoVs-NL63 HCoVs-HKU1 MERS-CoV MERS-CoV-Eng SARS-CoV SARS-CoV-2 SARS-CoV-Tor2 AcCoV- Turkey Porcine coronavirus HKU15 |
| Spike protein | gp03 | HCoVs-OC43 HCoVs-HKU1 AcCoV-Duck Porcine coronavirus HKU15 Sparrow coronavirus HKU17 |
| Spike surface glycoprotein | gp04 | HCoVs-OC43 |
| gp06 | HCoVs-NL63 | |
| Porcine coronavirus HKU15 | ||
| Sparrow coronavirus HKU17 | ||
| gp07 | HCoVs-229E HCoVs-HKU1 | |
| gp11 | AcCoV-Duck | |
| AcCoV- Turkey | ||
| Nucleocapsid phosphoprotein | gp08 | HCoVs-OC43 HCoVs-HKU1 |
| Envelope protein | gp03 | Porcine coronavirus HKU15 Sparrow coronavirus HKU17 |
| gp05 | HCoVs-229E HCoVs-NL63 HCoVs-HKU1 | |
| gp06 | AcCoV-Duck AcCoV- Turkey | |
| Membrane protein | gp04 | HCoVs-NL63 Porcine coronavirus HKU15 |
| Sparrow coronavirus HKU17 | ||
| gp06 | Human coronavirus 229E Human coronavirus HKU1 | |
| gp07 | HCoVs-OC43 AcCoV-Duck AcCoV- Turkey |
| Protein Family Domain (CDD) | Alphacoronavirus (AVA26872.1) * | Betacoronavirus (YP_009724389.1) * | Gammacoronavirus (YP_009825006.1) * | Deltacoronavirus (AWV67106.1) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shared domains | ||||
| Non-structural protein 2 (Nsp2) and related proteins | cd21514: similar alphaCoV_Nsp2_HCoV-229E | cd21516: betaCoV_Nsp2_SARS-like | cl40697: cv_gamma-delta_Nsp2_IBV-like Superfamily | cd21512: cv_gamma-delta_Nsp2_IBV-like |
| Non-structural protein 4 transmembrane domain (Nsp4) | cd21473: cv_Nsp4_TM | cd21473: cv_Nsp4_TM | cd21473: cv_Nsp4_TM | cd21473: cv_Nsp4_TM |
| Coronavirus non-structural protein 4 C-terminal (Nsp4) | pfam16348: Corona_NSP4_C | pfam16348: Corona_NSP4_C | cl24800: Corona_NSP4_C Superfamily | cl24800: Corona_NSP4_C Superfamily |
| Non-structural protein 5 (Nsp5), major protease (Mpro) | cd21665: alphaCoV_Nsp5_Mpro | cd21666: betaCoV_Nsp5_Mpro | cd21667: gammaCoV_Nsp5_Mpro | cd21668: deltaCoV_Nsp5_Mpro |
| Non-structural protein 6 (Nsp6) | cd21558: alphaCoV-Nsp6 | cd21560: betaCoV-Nsp6 | cd21559: gammaCoV-Nsp6 | cd21561: deltaCoV-Nsp6 |
| Non-structural protein 8 (Nsp8) | cd21830: alphaCoV_Nsp8 | pfam08717: nsp8 | cd21832: gammaCoV_Nsp8 | cd21833: deltaCoV_Nsp8 |
| Non-structural protein 10 (Nsp10) | cd21901: alpha_betaCoV_Nsp10 | cd21901: alpha_betaCoV_Nsp10 | cd21902: gammaCoV_Nsp10 | cd21903: deltaCoV_Nsp10 |
| RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of coronaviruses | cd21588: alfaCoV_RdRp | cd21591: SARS-CoV-like_RdRp | cd21587: gammaCoV_RdRp | cd21590: deltaCoV_RdRp |
| Helicase domain of non-structural protein 13 (Nsp13) | cd21723: alphaCoV_Nsp13-helicase | cd21722: betaCoV_Nsp13-helicase | cd21720: gammaCoV_Nsp13-helicase | cd21721: deltaCoV_Nsp13-helicase |
| Stem domain of Nsp13 helicase and related proteins | cd21689: stalk_CoV_Nsp13-like | cd21689: stalk_CoV_Nsp13-like | cd21689: stalk_CoV_Nsp13-like | cd21689: stalk_CoV_Nsp13-like |
| Cys/His-rich zinc-binding domain (CH/ZBD) helicase Nsp13 of the coronavirus SARS and related proteins | cd21401: ZBD_cv_Nsp13-like | cd21401: ZBD_cv_Nsp13-like | cd21401: ZBD_cv_Nsp13-like | cd21401: ZBD_cv_Nsp13-like |
| Non-structural protein 14 (Nsp14) | cd21660: alphaCoV_Nsp14 | cd21659: betaCoV_Nsp14 | cd21658: gammaCoV_Nsp14 | cd21657: deltaCoV_Nsp14 |
| N-terminal domain of Non-structural protein 15 (Nsp15) and related proteins | cd21171: NTD_alpha_betaCoV_Nsp15-like | cd21171: NTD_alpha_betaCoV_Nsp15-like | cd22650: NTD_gammaCoV_Nsp15-like | cd21172: NTD_deltaCoV_Nsp15-like |
| Papain-like protease (PLpro) | cd21731: alphaCoV_PLPro | cd21732: betaCoV_PLPro | cd21733: gammaCoV_PLPro | cd21734: deltaCoV_PLPro |
| specific domains | ||||
| Non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1) | cd21875: PEDV-like_alphaCoV_Nsp1 | cd21796: SARS-CoV-like_Nsp1_N | nd | nd |
| C-terminal domain Nsp1 of coronavirus and betacoronaviruses SARS-related in lineage B | nd | cd22662: SARS-CoV-like_Nsp1_C | nd | nd |
| Coronavirus replicase Nsp2, C-terminal | pfam19212: CoV_NSP2_C | nd | nd | nd |
| Coronavirus 2′-O-methyltransferase | nd | pfam06460: CoV_Methyltr_2 | nd | nd |
| Pneumococcal surface protein PspC, LPXTG-anchored form | nd | nd | cl41463: PspC_subgroup_2 Superfamily | nd |
| Domain X (or Mac1 domain) of viral non-structural protein 3 and related macrodomains | cd21557: Macro_X_Nsp3-like | nd | cd21557: Macro_X_Nsp3-like | cd21557: Macro_X_Nsp3-like |
| C-terminal non-structural protein 3 (Nsp3) including E, Y transmembrane domains | cd21712: TM_Y_alphaCoV_Nsp3_C | cd21717: TM_Y_SARS-CoV-like_Nsp3_C | cd21710: TM_Y_gammaCoV_Nsp3_C | cd21711: TM_Y_deltaCoV_Nsp3_C |
| Nucleic acid-binding domain of the Nsp3 coronavirus and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-related betacoronaviruses in the B lineage | nd | cd21822: SARS-CoV-like_Nsp3_NAB | nd | nd |
| Betacoronavirus-specific marker of SARS-related coronavirus Nsp3 and B-lineage betacoronavirus | nd | cd21814: SARS-CoV-like_Nsp3_betaSM | nd | nd |
| SARS C-terminal (SUD) single domain of Nsp3 of SARS coronavirus and related betacoronaviruses in the B lineage | nd | cd21525: SUD_C_SARS-CoV_Nsp3 | nd | nd |
| Papain-like protease (PLPro) found in non-structural protein 3 (Nsp3) | cl40457: CoV_PLPro Superfamily | nd | nd | nd |
| First ubiquitin-like domain (Ubl) located at the N-terminus of SARS-CoV coronavirus Nsp3 and related proteins | nd | nd | cl28922: Ubl1_cv_Nsp3_N-like Superfamily | nd |
| Single-stranded poly(A) binding domain of Nsp3 | cl13138: SUD m Superfamily | |||
| Non-structural protein 7 (Nsp7) | cd21826: alphaCoV_Nsp7 | cd21827: betaCoV_Nsp7 | nd | cd21829: deltaCoV_Nsp7 |
| Non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) | cd21897: alphaCoV_Nsp9 | nd | cd21899: gammaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21900: deltaCoV_Nsp9 |
| mRNA cap-1 methyltransferase from Nsp13 | cl20156: NSP13 Superfamily | nd | cl20156: NSP13 Superfamily | cl20156: NSP13 Superfamily |
| Domain 1B of NSP13 helicase and related proteins of the SARS coronavirus | cd21409: 1B_cv_Nsp13-like | nd | nd | cd21409: 1B_cv_Nsp13-like |
| Nidoviral uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU) domain of non-structural protein 15 (Nsp15) and related proteins | cd21161: NendoU_cv_Nsp15-like | cd21161: NendoU_cv_Nsp15-like | nd | cd21161: NendoU_cv_Nsp15-like |
| Middle domain of Non-structural Protein 15 (Nsp15) and related proteins | cd21167: M_alpha_beta_cv_Nsp15-like | nd | cd21168: M_gcv_Nsp15-like | cd21169: M_dcv_Nsp15-like |
| Macrodomain superfamily | nd | cl00019: Macro_SF Superfamily | nd | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Rosas-García, N.M.; Ayil-Gutiérrez, B.A.; Bello-López, J.M.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, F.A.; Anguebes-Franseschi, F.; Damas-Damas, S.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, Y.d.J. Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp): A Marker for Detection of Human Coronavirus Families. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091185
Tamayo-Ordóñez MC, Rosas-García NM, Ayil-Gutiérrez BA, Bello-López JM, Tamayo-Ordóñez FA, Anguebes-Franseschi F, Damas-Damas S, Tamayo-Ordóñez YdJ. Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp): A Marker for Detection of Human Coronavirus Families. Pathogens. 2023; 12(9):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091185
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamayo-Ordóñez, María Concepción, Ninfa María Rosas-García, Benjamín Abraham Ayil-Gutiérrez, Juan Manuel Bello-López, Francisco Alberto Tamayo-Ordóñez, Francisco Anguebes-Franseschi, Siprian Damas-Damas, and Yahaira de Jesús Tamayo-Ordóñez. 2023. "Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp): A Marker for Detection of Human Coronavirus Families" Pathogens 12, no. 9: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091185
APA StyleTamayo-Ordóñez, M. C., Rosas-García, N. M., Ayil-Gutiérrez, B. A., Bello-López, J. M., Tamayo-Ordóñez, F. A., Anguebes-Franseschi, F., Damas-Damas, S., & Tamayo-Ordóñez, Y. d. J. (2023). Non-Structural Proteins (Nsp): A Marker for Detection of Human Coronavirus Families. Pathogens, 12(9), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091185









