Plasma Blood Levels of Tafenoquine following a Single Oral Dosage in BALBc Mice with Acute Babesia microti Infection That Resulted in Rapid Clearance of Microscopically Detectable Parasitemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
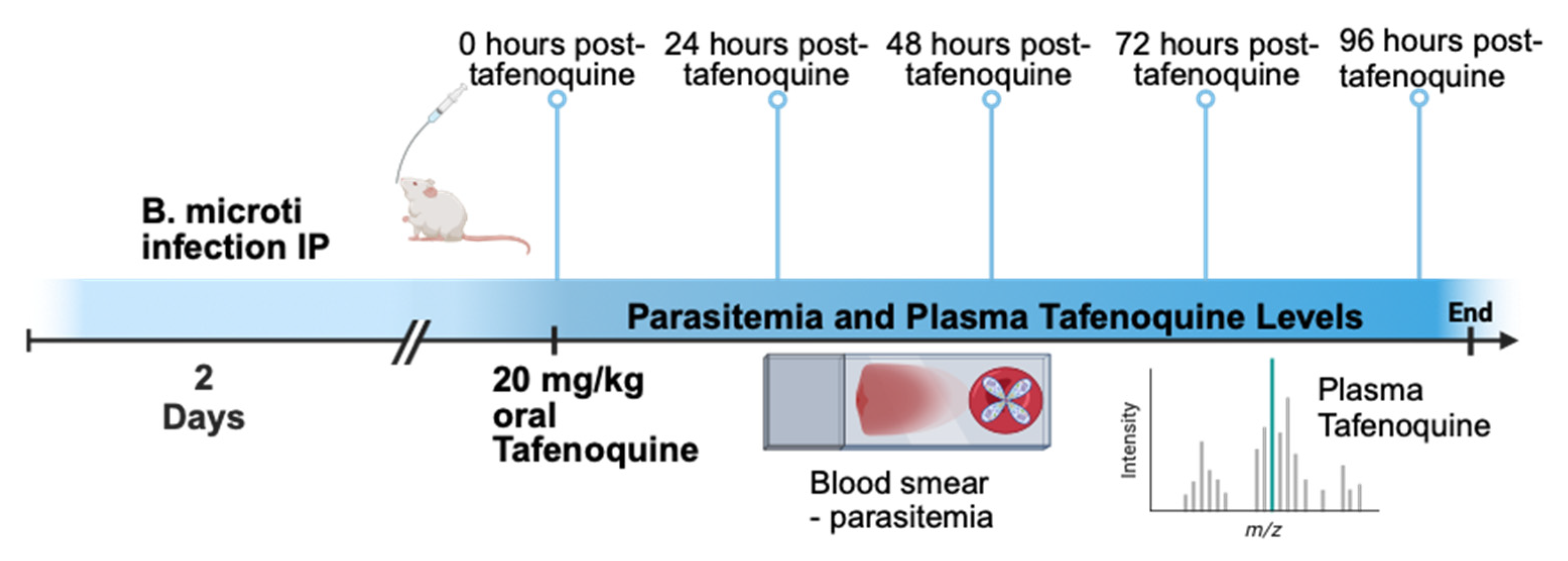
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Infection and Parasitemia
2.2. Tafenoquine Treatment
2.3. Blood Collection
2.4. Plasma Tafenoquine Levels
2.5. Microscopic Analysis of Parasitemia
2.6. Statistical Analysis
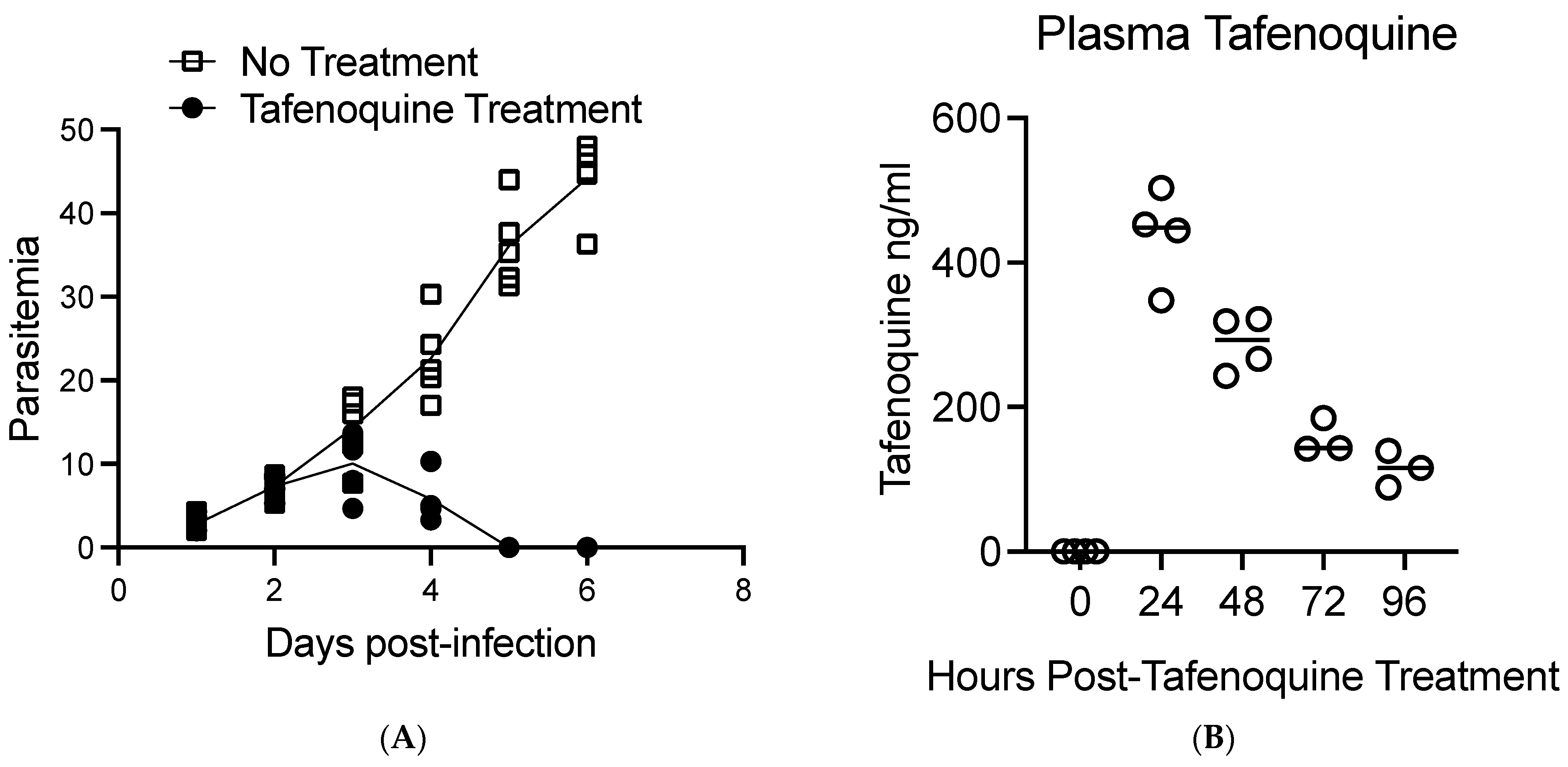
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Important Areas for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubernot, D.M.; Nakhasi, H.L.; Mied, P.A.; Asher, D.M.; Epstein, J.S.; Kumar, S. Transfusion-transmitted babesiosis in the United States: Summary of a workshop. Transfusion 2009, 49, 2759–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; O’Bryan, J.; Krause, P.J. The global emergence of human babesiosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.M.; Corrin, T.; Wilhelm, B.; Uhland, C.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Waddell, L.A. Zoonotic babesia: A scoping review of the global evidence. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Sajid, M.S.; Pascoe, E.L.; Foley, J.E. Detection of Babesia odocoilei in humans with babesiosis symptoms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, I.; Ben Mamoun, C. Treatment of human babesiosis: Then and now. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.G.; McElwain, T.F.; Palmer, G.H. Molecular basis for variable expression of merozoite surface antigen gp45 among American isolates of Babesia bigemina. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.J.; Rosenbaum, E.R.; Pritt, B.S.; Haselow, D.T.; Ferren, K.M.; Alzghoul, B.N.; Rico, J.C.; Sloan, L.M.; Ramanan, P.; Purushlthaman, R.; et al. Possible transfusion-transmitted Babesia divergens-like/MO-1 infection in an Arkansas patient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwaldt, B.L.; Linden, J.V.; Bosserman, E.; Young, C.; Olkowska, D.; Wilson, M. Transfusion-associated babesiosis in the United States: A description of cases. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiby, D.A. Transfusion-transmitted Babesia spp.: Bull’s-eye on Babesia microti. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.J.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Branda, J.A.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Lantos, P.M.; Lavergne, V.; Meissner, C.H.; Osani, M.C.; Rips, J.G.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA): 2020 Guideline on diagnosis and management of babesiosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, E.; Krause, P.J. Human babesiosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, P.J.; Spielman, A.; Telford, S.R., 3rd; Sikand, V.K.; McKay, K.; Christianson, D.; Pollack, R.J.; Brassard, P.; Majera, J.; Ryan, R.; et al. Persistent parasitemia after acute babesiosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, P.J.; Gewurz, B.E.; Hill, D.; Marty, F.M.; Vannier, E.; Foppa, I.M.; Furman, R.R.; Neuhaus, E.; Skowron, G.; Gupta, S.; et al. Persistent and relapsing babesiosis in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, E.M.; Kumar, S.; Krause, P.J. Persistence of Babesia microti infection in humans. Pathogens 2019, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Hunfeld, K.P.; Krause, P.J. Management strategies for human babesiosis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffalli, J.; Wormser, G.P. Persistence of babesiosis for >2 years in a patient on rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.R.; Klontz, E.H.; Adams, G.C.; Schnittman, S.R.; Issa, N.C.; Bond, S.A.; Bronda, J.A.; Lemieux, J.E. Babesia microti variant with multiple resistance mutations detected in an immunocompromised patient receiving atovaquone prophylaxis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofado97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.S.; Westblade, F.L.; Dziedziech, A.; Visone, J.E.; Furman, R.R.; Jenkins, S.G.; Schuetz, A.N.; Kirkman, L.A. Clinical and molecular evidence of atovaquone and azithromycin resistance in relapsed Babesia microti infection associated with Rituximab and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormser, G.P.; Prasad, A.; Neuhaus, E.; Joshi, S.; Nowakowski, J.; Nelson, J.; Mittleman, A.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.; Topal, J.; Krause, P.J. Emergence of resistance to azithromycin-atovaquone in immunocompromised patients with Babesia microti infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haston, J.C.; Hwang, J.; Tan, K.R. Guidance for using tafenoquine for prevention and anti-relapse therapy for malaria. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.S.; Hwang, J. Tafenoquine: A toxicity overview. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E. Tafenoquine: First global approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; Abd-Rahman, A.N.; Webster, R.; Potter, A.J.; Llewellyn, S.; Marquart, L.; Sahai, N.; Leelasena, I.; Birrell, G.W.; Edstein, M.D.; et al. Characterizing the blood-stage antimalarial activity of tafenoquine in healthy volunteers experimentally infected With Plasmodium falciparum. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Manzano, J.I.; Castanys, S.; Rivas, L.; Gamarro, F. Tafenoquine, an antiplasmodial 8-aminoquinoline, targets leishmania respiratory complex III and induces apoptosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.A.; Commons, R.J.; Tarning, J.; Simpson, J.A.; Curentas, A.L.; Lacerda, M.V.; Green, J.A.; Koh, G.C.; Chu, C.S.; Nosten, F.H.; et al. The clinical pharmacology of tafenoquine in the radical cure of Plasmodium vivax malaria: An individual patient data meta-analysis. eLife 2022, 11, e83433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alving, C.R. Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR): Fifty years of achievements that impact science and society. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, S.E.; Eberhard, M.L.; Steurer, F.J.; Ellis, W.L.; McGreevy, P.B.; Ruebush, T.K., 2nd. Evaluation of selected antiprotozoal drugs in the Babesia microti-hamster model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordue, D.G.; Wormser, G.P. Could the drug tafenoquine revolutionize treatment of Babesia microti infection? J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ji, S.; Kondoh, D.; Galon, E.M.; Li, J.; Tomihari, M.; Yanagawa, M.; Tagawa, M.; Adachi, M.; Asada, M.; et al. Tafenoquine Is a promising drug candidate for the treatment of babesiosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0020421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.; Krause, P.J.; Norris, A.M.; Ting, M.H.; Nagami, E.H.; Cilley, B.; Vannier, E. Broad antimicrobial resistance in a case of relapsing babesiosis successfully treated with Tafenoquine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, L.A.; Leung, A.; Kirkman, L.; Wormser, G.P. Use of tafenoquine to treat a patient with relapsing babesiosis with clinical and molecular evidence of resistance to azithromycin and atovaquone. IDCases 2022, 27, e01460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.J.; Wormser, G.P. Failure of an approximately six week course of Tafenoquine to completely eradicate Babesia microti infection in an immunocompromised patient. Pathogens 2022, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, N.N.; Healy, G.R.; Western, K.A.; Benson, G.D.; Schultz, M.G. The “Gray” strain of Babesia microti from a human case established in laboratory animals. J. Parasitol. 1970, 56, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; O’Neil, M.; Xie, L.; Caridha, D.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Pybus, B.; Hickman, M.; Melendez, V. Assessment of the prophylactic activity and pharmacokinetic profile of oral tafenoquine compared to primaquine for inhibition of liver stage malaria infections. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novitt-Moreno, A.; Martidis, A.; Gonzalez, V.; Ransom, J.; Scott, C.B.; Dow, G.; Reid, M.; Smith, B.; Zotig, V.E.; Read, L.T.; et al. Long-term safety of the tafenoquine antimalarial chemoprophylaxis regimen: A 12-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 45, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, B.G.; Miller, A.K.; Nasveld, P.E.; Reid, M.G.; Harris, I.E.; Edstein, M.D. Population pharmacokinetics of tafenoquine during malaria prophylaxis in healthy subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.C.; Renard, I.; Singh, P.; Vydyam, P.; Chiu, J.E.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.W.; Dodean, R.; Frueh, L.; Nilsen, A.C.; et al. Babesia duncani as a model organisms to study development, virulence, and drug susceptibility of intraerythrocytic parasites in vitro and in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, L.A.; Wormser, G.P. Relapsing babesiosis with molecular evidence of resistance to certain antimicrobials commonly used to treat Babesia microti infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, A.; Matsuu, A.; Matsuyama, K.; Hikasa, Y. The efficacy of artemisinin, artemether, and lumefantrine against Babesia gibsoni in vitro. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawres, L.A.; Garg, A.; Kumar, V.; Bruzual, I.; Forquer, I.P.; Renard, I.; Virgi, A.Z.; Boulard, P.; Rodriquez, E.X.; Allen, A.L.; et al. Radical cure of experimental babesiosis in immunodeficient mice using a combination of an endochin-like quinolone and atovaquone. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.J.M.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Nugraha, A.B.; Sivakumar, T.; Yokoyama, N. Activities of artesunate-based combinations and tafenoquine against Babesia bovis in vitro and Babesia microti in vivo. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mordue, D.G.; Hale, S.J.; Dennis, W.E.; Vuong, C.V.; Li, X.-M.; Yang, N.; Wormser, G.P. Plasma Blood Levels of Tafenoquine following a Single Oral Dosage in BALBc Mice with Acute Babesia microti Infection That Resulted in Rapid Clearance of Microscopically Detectable Parasitemia. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091113
Mordue DG, Hale SJ, Dennis WE, Vuong CV, Li X-M, Yang N, Wormser GP. Plasma Blood Levels of Tafenoquine following a Single Oral Dosage in BALBc Mice with Acute Babesia microti Infection That Resulted in Rapid Clearance of Microscopically Detectable Parasitemia. Pathogens. 2023; 12(9):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091113
Chicago/Turabian StyleMordue, Dana G., Synthia J. Hale, William E. Dennis, Chau V. Vuong, Xiu-Min Li, Nan Yang, and Gary P. Wormser. 2023. "Plasma Blood Levels of Tafenoquine following a Single Oral Dosage in BALBc Mice with Acute Babesia microti Infection That Resulted in Rapid Clearance of Microscopically Detectable Parasitemia" Pathogens 12, no. 9: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091113
APA StyleMordue, D. G., Hale, S. J., Dennis, W. E., Vuong, C. V., Li, X.-M., Yang, N., & Wormser, G. P. (2023). Plasma Blood Levels of Tafenoquine following a Single Oral Dosage in BALBc Mice with Acute Babesia microti Infection That Resulted in Rapid Clearance of Microscopically Detectable Parasitemia. Pathogens, 12(9), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091113