The Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Was Significantly Associated with Compositional Patterns of Orointestinal Axis Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Patient Recruitment and Sample Collection
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification and Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Amplicon
2.5. Bioinformatics and Data Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients and Data
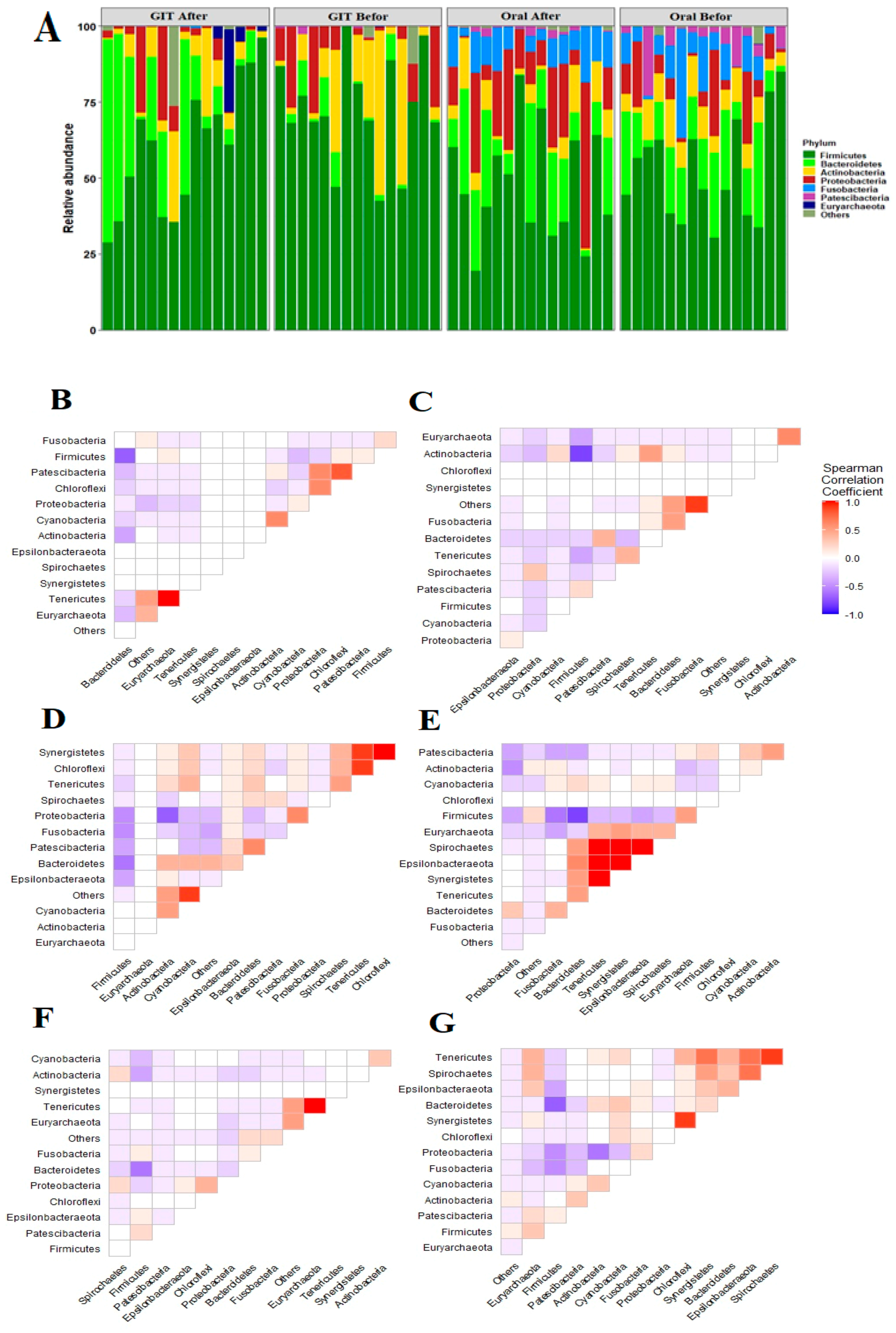
3.2. Distinct Taxonomic Profiles Accompany the Pre/Post-Eradication of H. pylori Infection along the Orointestinal Axis
3.3. H. pylori Infections Are Positively Linked with Diverse Orointestinal axis Microbiomes
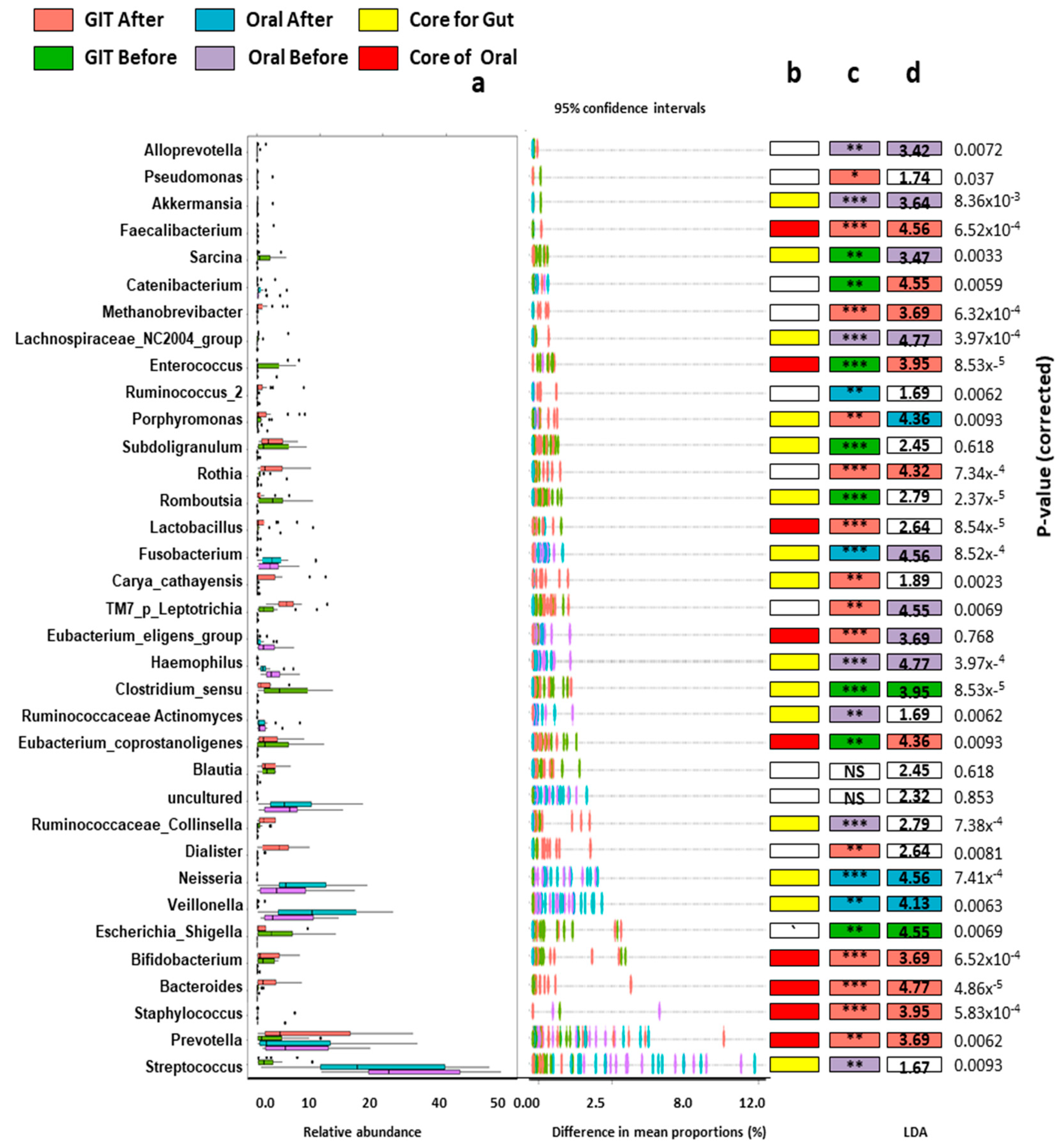
3.4. Orointestinal Axis Microbiomes Have Potential Biomarkers and Microbial Signatures for Pre/Post Eradication of H. pylori
3.5. Enterotype and Orotypes of Pre/Post H. pylori Infection
3.6. Bidirectional Association between Microbiomes, Either Anatomical Sites or the Disease State
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, L.M. Helicobacter pylori: Epidemiology and routes of transmission. Epidemiol. Rev. 2000, 22, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.L.; Chan, W.K.; Shiota, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection and public health implications. Helicobacter 2011, 16 (Suppl. S1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Ebrahimtabar, F.; Zamani, V.; Miller, W.H.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Shokri-Shirvani, J.; Derakhshan, M.H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Adeloye, D.; Luk, T.T.; Huang, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Yi, Q.; Song, P.; Rudan, I. The global prevalence of and factors associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskito, L.A.; Salama, N.R.; Yamaoka, Y. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2018, 23 (Suppl. S1), e12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Cruciani, M.; Mengoli, C.; Pizzolo, G.; Veneri, D. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on platelet count in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.H.; Kim, S.K.; Son, B.K.; Lee, D.H.; Hong, Y.C.; Pai, S.H. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of Helicobacter pylori eradication for iron-deficiency anemia in preadolescent children and adolescents. Helicobacter 1999, 4, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Meng, W.; Wang, B.; Qiao, L. Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation and gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, W.K.; Wong, I.O.L.; Cheung, K.S.; Yeung, K.F.; Chan, E.W.; Wong, A.Y.S.; Chen, L.; Wong, I.C.K.; Graham, D.Y. Effects of Helicobacter pylori Treatment on Incidence of Gastric Cancer in Older Individuals. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorakkers, E.; Lagergren, J. Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment and the risk of gastric adenocarcinoma in a Western population. Gut 2018, 67, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowada, A. Cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori screening followed by eradication treatment for employees in Japan. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.E.; Choi, K.D. The effect of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on gastric cancer prevention in healthy asymptomatic populations. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciric, L.; Pratten, J.; Wilson, M.; Spratt, D. Development of a novel multi-triplex qPCR method for the assessment of bacterial community structure in oral populations. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. Analysis of by high-throughput sequencing: Helicobacter pylori infection and salivary microbiome. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xiao, S. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy, and probiotics intervention on gastric microbiota in young adults. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Gerhard, M.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Zhang, L.; Vieth, M.; Ma, J.-L.; Bajbouj, M.; Suchanek, S.; Liu, W.-D.; et al. Association Between Gut Microbiota and Helicobacter pylori-Related Gastric Lesions in a High-Risk Population of Gastric Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 00202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Peng, C.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N. The eradication of Helicobacter pylori restores rather than disturbs the gastrointestinal microbiota in asymptomatic young adults. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.I.; Pan, C.Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Tsay, F.W.; Peng, N.J.; Kao, S.S.; Wang, H.M.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, D.C. Helicobacter pylori eradication with bismuth quadruple therapy leads to dysbiosis of gut microbiota with an increased relative abundance of Proteobacteria and decreased relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.M.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.M.; Fang, Y.J.; Bair, M.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Long-term changes of gut microbiota, antibiotic resistance, and metabolic parameters after Helicobacter pylori eradication: A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V.; Shokri-Shirvani, J.; Derakhshan, M.H. Worldwide and Regional Efficacy Estimates of First-line Helicobacter pylori Treatments: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Dore, M.P.; Graham, D.Y. Diagnosis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Jernberg, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Short-term antibiotic treatment has differing long-term impacts on the human throat and gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, H.; Tsuda, A.; Matsushima, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ozawa, G.; Koga, Y.; Takagi, A. Changes in the gut microbiota composition and the plasma ghrelin level in patients with Helicobacter pylori-infected patients with eradication therapy. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, W. Application of high-throughput sequencing in understanding human oral microbiome related with health and disease. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Shi, J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y. Long-term changes in the gut microbiota after triple therapy, sequential therapy, bismuth quadruple therapy and concomitant therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in Chinese children. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, S.A.; Azab, M.M.; Ahmed, A.A.A. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing for Preliminary Analysis of Microbiome Causing Primary Endodontic Infections in Egypt. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 2837328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lu, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Long-term changes in the gut microbiota after 14-day bismuth quadruple therapy in penicillin-allergic children. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.; Solyman, S.; Yones, M.; Abdallah, Y.; Halaby, H.; Hanora, A. Skin Microbiome Differences in Atopic Dermatitis and Healthy Controls in Egyptian Children and Adults, and Association with Serum Immunoglobulin E. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2019, 23, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Australas Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E.; Dupont, C.J.R.P.V. Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous; R Package Version; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Volume 3, p. 437. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.-M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, D.; Brown, H.E.; Harris, R.B.; Oren, E. Serologic Evidence for Fecal-Oral Transmission of Helicobacter pylori. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, J.K. Helicobacter pylori colonization of the oral cavity: A milestone discovery. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.; Liou, J.M.; Gisbert, J.P.; O’Morain, C. Review: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection 2019. Helicobacter 2019, 24 (Suppl. S1), e12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y. The status and progress of first-line treatment against Helicobacter pylori infection: A review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1756284821989177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gené, E.; Calvet, X.; Azagra, R.; Gisbert, J.P. Triple vs. quadruple therapy for treating Helicobacter pylori infection: A meta-analysis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 17, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Tang, L.; Huang, C.; Tian, C.; Chen, L.; He, Z.; Yang, G.; Zuo, L.; Zhao, G.; Liu, E.; et al. The Effect of Probiotics Supplementation on Gut Microbiota After Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.M.; Kim, N.; Park, J.H.; Lee, D.H. Changes in Gastric Corpus Microbiota With Age and After Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 621879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.J.Y.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.; Szeto, C.H.; Luk, S.T.Y.; Lau, H.C.H.; Yu, J. Gastric microbes associated with gastric inflammation, atrophy and intestinal metaplasia 1 year after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut 2020, 69, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold, G.L.; Hansen, R. Impact of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease: Co-evolution with the Host Immune System. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 421, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Coin-Aragüez, L.; Roca-Rodríguez, M.D.M.; Muñoz-Garach, A.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Cardona, F.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J. H. pylori eradication with antibiotic treatment causes changes in glucose homeostasis related to modifications in the gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeles, S.R.; Ly, M.; Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Pride, D.T. Effects of Long Term Antibiotic Therapy on Human Oral and Fecal Viromes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishiro, T.; Oka, K.; Kuroki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Saitoh, T.; Tobita, H.; Ishimura, N.; Sato, S.; Ishihara, S.; et al. Oral microbiome alterations of healthy volunteers with proton pump inhibitor. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoda, T.; Takano, C.; Kusano, C.; Suzuki, S.; Ikehara, H.; Hayakawa, S.; Andoh, A. Gut microbiome can be restored without adverse events after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in teenagers. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olekhnovich, E.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Samoilov, A.E.; Prianichnikov, N.A.; Malakhova, M.V.; Tyakht, A.V.; Pavlenko, A.V.; Babenko, V.V.; Larin, A.K.; Kovarsky, B.A.; et al. Shifts in the Human Gut Microbiota Structure Caused by Quadruple Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, G.; Peng, L.; Lu, Z.; Yan, B.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y. Effects of anti-H. pylori triple therapy and a probiotic complex on intestinal microbiota in duodenal ulcer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.I.; Pan, C.Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Tsay, F.W.; Peng, N.J.; Kao, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, D.C.; Tsai, K.W. Short-term and long-term impacts of Helicobacter pylori eradication with reverse hybrid therapy on the gut microbiota. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. The interactions between oral-gut axis microbiota and Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 914418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, A.; Kinnevey, P.; Shore, A.; Earls, M.; Poovelikunnel, T.T.; Brennan, G.; Humphreys, H.; Coleman, D.C. The oral cavity revealed as a significant reservoir of Staphylococcus aureus in an acute hospital by extensive patient, healthcare worker and environmental sampling. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, P396–P589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaatout, N. Presence of non-oral bacteria in the oral cavity. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2747–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, S.; Leonhardt, Å.; Arirachakaran, P.; Carlen, A.; Dahlén, G. Phenotype, genotype, and antibiotic susceptibility of Swedish and Thai oral isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Oral Microbiol. 2015, 7, 26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghni, A.; Ben Nejma, M.; Hentati, H.; Mahjoub, A.; Mastouri, M. Adhesive properties and extracellular enzymatic activity of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from oral cavity. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 73, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Silva, L.; Ferreira, S.; Santos-Araujo, C.; Tabaio, M.; Pestana, M. Oral Colonization of Staphylococcus Species in a Peritoneal Dialysis Population: A Possible Reservoir for PD-Related Infections? Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 5789094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuanazzi, D.; Souto, R.; Mattos, M.B.; Zuanazzi, M.R.; Tura, B.R.; Sansone, C.; Colombo, A.P. Prevalence of potential bacterial respiratory pathogens in the oral cavity of hospitalised individuals. Arch. Oral Biol. 2010, 55, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.; Wray, D.; Bagg, J. Oral staphylococcal mucositis: A new clinical entity in orofacial granulomatosis and Crohn’s disease. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 89, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, I.T.; Diz Dios, P.; Scully, C. An update on the controversies in bacterial endocarditis of oral origin. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 93, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, A.; Cocuzzi, R. Streptococcus thermophilus: To Survive, or Not to Survive the Gastrointestinal Tract, That Is the Question! Nutrients 2020, 12, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Ho, C.L. Recent Development of Probiotic Bifidobacteria for Treating Human Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 770248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S. Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: An overview of recent literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4745–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Cho, I.K.; Lee, C.H.; Song, G.G.; Lim, J.H. Clinical Outcomes of Standard Triple Therapy Plus Probiotics or Concomitant Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazireh, H.; Shariati, P.; Azimzadeh Jamalkandi, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Boroumand, M.A. Isolation of Novel Probiotic Lactobacillus and Enterococcus Strains From Human Salivary and Fecal Sources. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 597946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Koh, S.J.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Chun, J. The Effect of Probiotics on Gut Microbiota during the Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Randomized Controlled Trial. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Li, Y.C.; Deng, J.; Tu, J.; Song, Z.Q.; Zou, Q.H. Effects of anti-Helicobacter pylori concomitant therapy and probiotic supplementation on the throat and gut microbiota in humans. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between gut microbiota and diet in cardio-metabolic health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.W.; Gan, H.M.; Lee, Y.P.; Leow, A.H.; Azmi, A.N.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Loke, M.F.; Goh, K.L.; Vadivelu, J. Helicobacter pylori Eradication Causes Perturbation of the Human Gut Microbiome in Young Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, A.; Selak, M.; Lantin, D.; Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Bifidobacteria and Butyrate-Producing Colon Bacteria: Importance and Strategies for Their Stimulation in the Human Gut. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.V.; Frassetto, A.; Kowalik, E.J., Jr.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Lu, M.M.; Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.A.; Szeto, D.; Yao, X.; Forrest, G.; et al. Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.H.; Qin, Y.; Sham, P.C.; Lau, K.S.; Chu, K.M.; Leung, W.K. Alterations in Gastric Microbiota After H. Pylori Eradication and in Different Histological Stages of Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Chatel, J.M.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.D.; Sun, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, V.; Pozuelo, M.; Borruel, N.; Casellas, F.; Campos, D.; Santiago, A.; Martinez, X.; Varela, E.; Sarrabayrouse, G.; Machiels, K.; et al. A microbial signature for Crohn’s disease. Gut 2017, 66, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Fatima, J.; Shakil, S.; Rizvi, S.M.; Kamal, M.A. Antibiotic resistance and extended spectrum beta-lactamases: Types, epidemiology and treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, U.K. Oral Prevotella Species and Their Connection to Events of Clinical Relevance in Gastrointestinal and Respiratory Tracts. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 798763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Niu, X.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.; Bao, M.; Mohyuddin, S.G.; Yong, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Yu, Z.; et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Colonic Flora Diversity, Short Chain Fatty Acid Metabolism, Transcripts, and Biochemical Indexes in Heat-Stressed Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Haemophilus and Aggregatibacter species with host specificity for humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 214–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaucer, B.; Smith, N.; Beatty, D.; Yadav, M. Multiple Hepatic Abscess from Parvimonas micra: An Emerging Gastrointestinal Microbe. ACG Case Rep. J. 2018, 5, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlvanna, E.; Linden, G.J.; Craig, S.G.; Lundy, F.T.; James, J.A. Fusobacterium nucleatum and oral cancer: A critical review. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.Y.; Tung, S.Y.; Pan, H.Y.; Chang, T.S.; Wei, K.L.; Chen, W.M.; Deng, Y.F.; Lu, C.K.; Lai, Y.H.; Wu, C.S.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum colonization is associated with decreased survival of helicobacter pylori-positive gastric cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7311–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, A.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hong, X.L.; Sun, T.T.; Huang, X.W.; Wang, J.L.; Xiong, H. Fusobacterium nucleatum exacerbates colitis by damaging epithelial barriers and inducing aberrant inflammation. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashima, I.; Nakazawa, F. The interaction between Streptococcus spp. and Veillonella tobetsuensis in the early stages of oral biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Oral Before | Oral After | Gut Before | Gut After | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | G1 | G2 |
| Streptococcus | Streptococcus | Streptococcus | Neisseria | Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 | Prevotella |
| Neisseria | Fusobacterium | Neisseria | Prevotella | Escherichia_Shigella | Bacteroides |
| Ruminococcaceae Actinomyces | Haemophilus | Fusobacterium | Veillonella | Bifidobacterium | Bifidobacterium |
| Eubacterium_eligens_group | Enterococcus | Prevotella | Fusobacterium | Enterococcus | Lactobacillus |
| Porphyromonas | Neisseria | Rothia | Streptococcus | Subdoligranulum | Romboutsia |
| Prevotella | Prevotella | Ruminococcaceae Actinomyces | Ruminococcaceae Actinomyces | Ruminococcaceae_Collinsella | Sarcina |
| Bifidobacterium | Veillonella | Streptococcus | Staphylococcus | Prevotella | Escherichia_Shigella |
| Veillonella | Staphylococcus | Haemophilus | Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes | Blautia | |
| Staphylococcus | Romboutsia | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawfik, S.A.; Azab, M.; Ramadan, M.; Shabayek, S.; Abdellah, A.; Al Thagfan, S.S.; Salah, M. The Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Was Significantly Associated with Compositional Patterns of Orointestinal Axis Microbiota. Pathogens 2023, 12, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060832
Tawfik SA, Azab M, Ramadan M, Shabayek S, Abdellah A, Al Thagfan SS, Salah M. The Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Was Significantly Associated with Compositional Patterns of Orointestinal Axis Microbiota. Pathogens. 2023; 12(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawfik, Sally Ali, Marwa Azab, Mohammed Ramadan, Sarah Shabayek, Ali Abdellah, Sultan S. Al Thagfan, and Mohammed Salah. 2023. "The Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Was Significantly Associated with Compositional Patterns of Orointestinal Axis Microbiota" Pathogens 12, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060832
APA StyleTawfik, S. A., Azab, M., Ramadan, M., Shabayek, S., Abdellah, A., Al Thagfan, S. S., & Salah, M. (2023). The Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Was Significantly Associated with Compositional Patterns of Orointestinal Axis Microbiota. Pathogens, 12(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060832






