The Immunological Changes in the Skin of BALC/c Mice with Disseminated Acanthamoebiasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
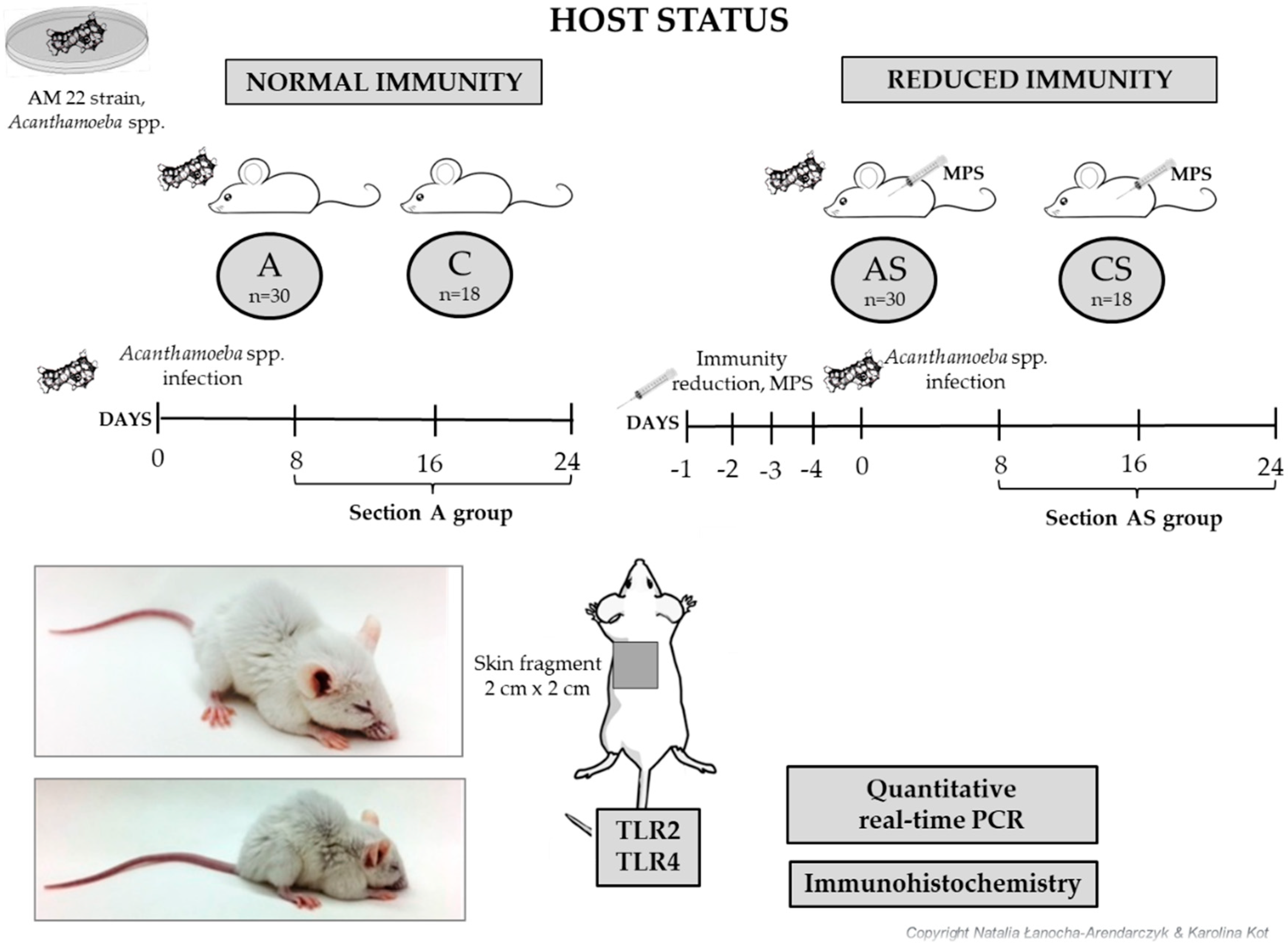
2.1. The Design of Experimental Model of Disseminate Acanthamoebiasis
2.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
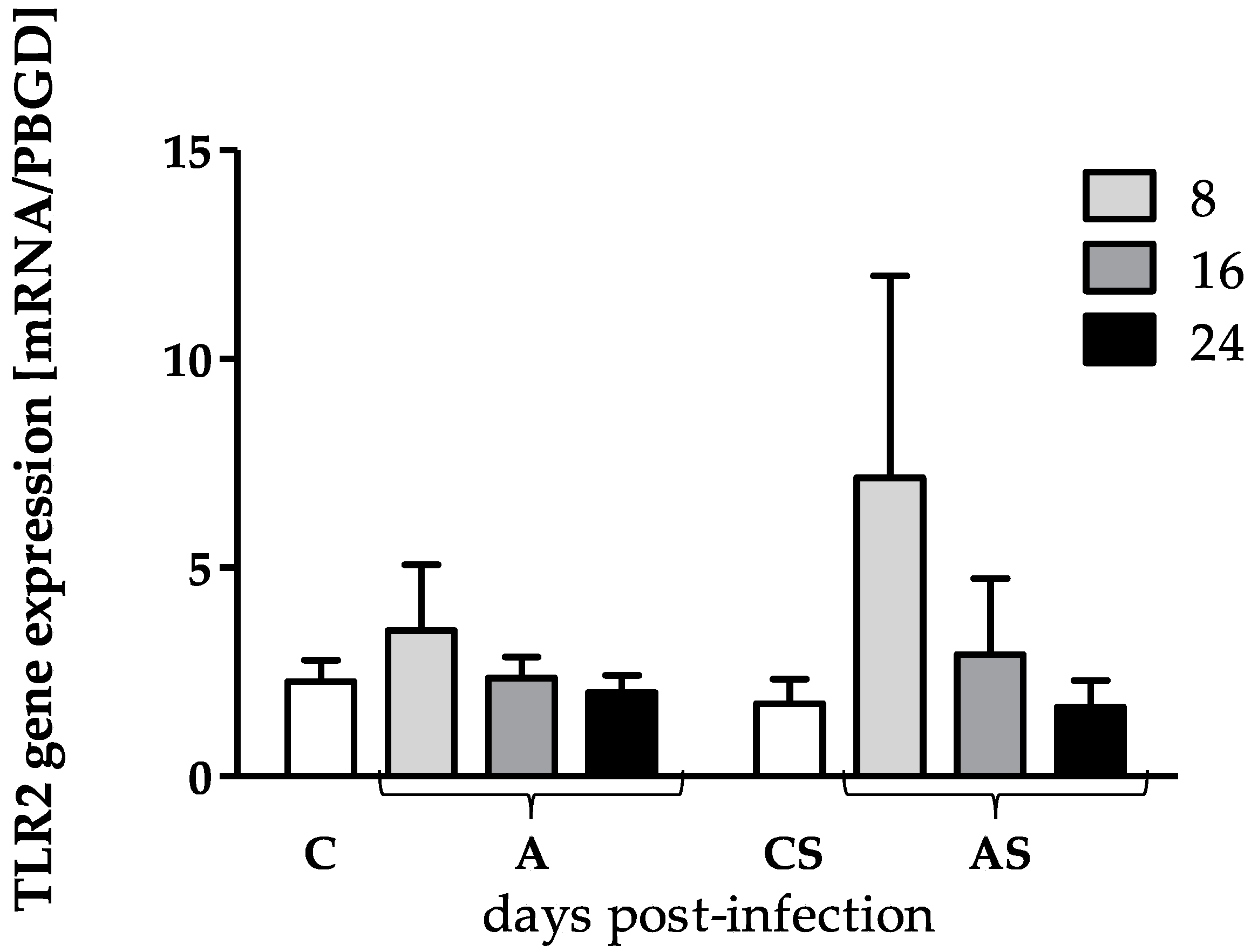
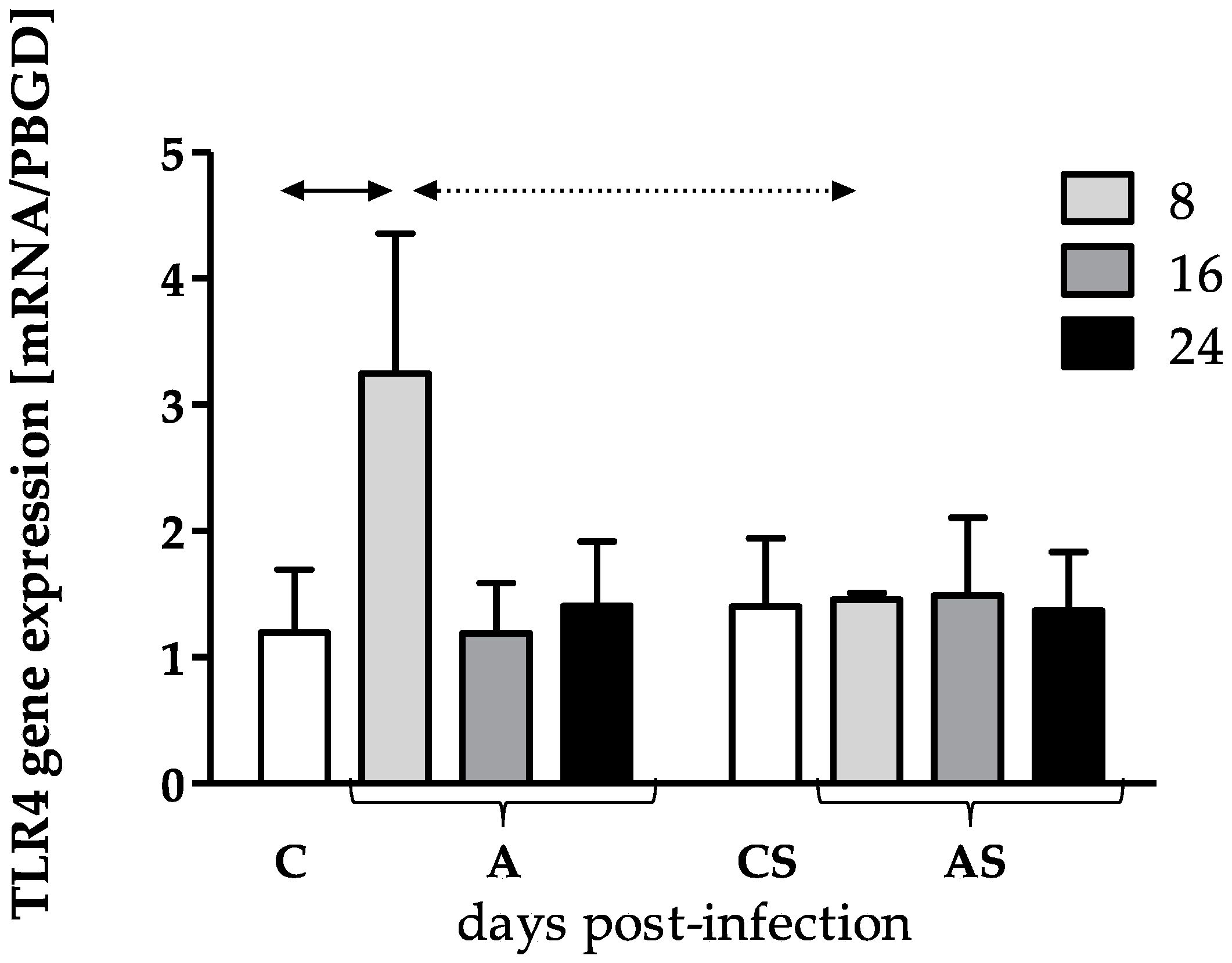
3.1. TLR2 and TLR4 Genes Expression
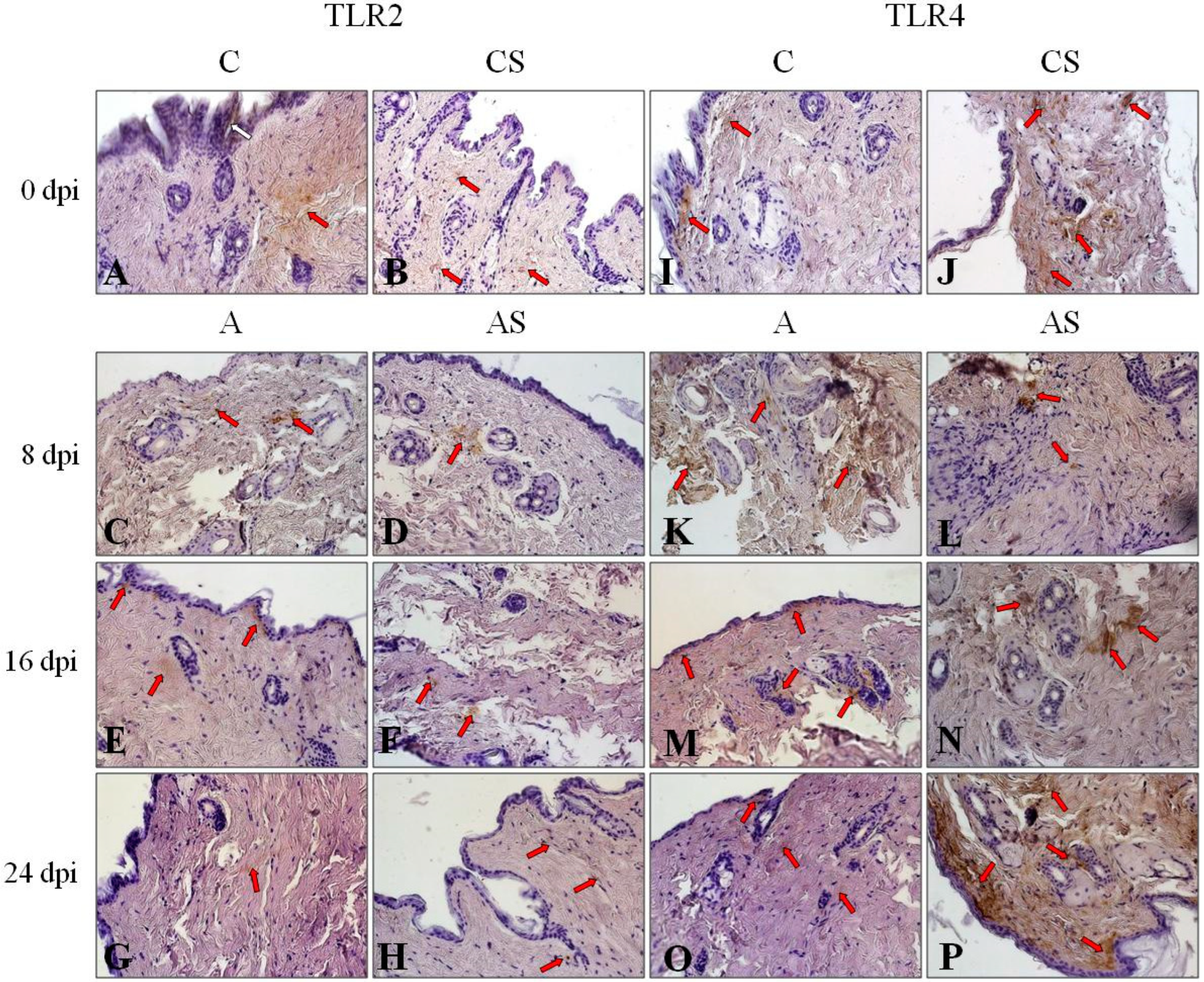
3.2. Results of Immunohistochemistry
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, D.L.; van den Berg, E.; Grayson, W.; Mphahlele, M.; Frean, J. Clinical improvement of disseminated Acanthamoeba infection in a patient with advanced HIV using a non-miltefosine-based treatment regimen in a low-resource setting. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, C.; Ramos, W.; Gutierrez, E.L.; Ronceros, G.; Teran, M.; Uribe, M.; Ñavincopa, M.; Ortega-Loayza, A.G. Cutaneous acanthamebiasis infection in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Int. J. Dermatol. 2009, 48, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król-Turmińska, K.; Olender, A. Human infections caused by free-living amoebae. Ann Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Jasso, M.; Hernández-Martínez, D.; Avila-Acevedo, J.G.; Benítez-Flores, J.D.C.; Gallegos-Hernández, I.A.; García-Bores, A.M.; Espinosa-González, A.M.; Villamar-Duque, T.E.; Castelan-Ramírez, I.; González-Valle, M.D.R.; et al. Morphological description of the early events during the invasion of Acanthamoeba castellanii trophozoites in a murine model of skin irradiated under UV-B Light. Pathogens 2020, 27, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padzik, M.; Hendiger, E.B.; Szaflik, J.P.; Chomicz, L. Pełzaki z rodzaju Acanthamoeba-czynniki etiologiczne stanów patologicznych ludzkiego organizmu. Post. Mikrobiol. 2017, 56, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Winsett, F.; Dietert, J.; Tschen, J.; Swaby, M.; Bangert, C.A. A rare case of cutaneous acanthamoebiasis in a renal transplant patient. Dermatol. Online J. 2017, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.Y.; Wu, X.Y. Toll-like receptor 4 signalling pathway activation in a rat model of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Parasite Immunol. 2011, 33, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, X.; Lv, S. A rabbit model of acanthamoeba keratitis that better reflects the natural human infection. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füst, Á.J.; Tóth, J.; Simon, G.; Imre, L.; Nagy, Z.Z. Specificity of in vivo confocal cornea microscopy in Acanthamoeba keratitis. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 27, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N. The expression of TLR2 and TLR4 in the kidneys and heart of mice infected with Acanthamoeba spp. Parasit. Vectors. 2020, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A. Expression of Toll-like receptors (TLR2 and TLR4) in the eyes of mice with disseminated acanthamoebiasis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 14001894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Derda, M.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Hadaś, E.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Solarczuk, P.; Jagodziński, P.P.; Wandurska-Nowak, E. Toll-like receptors in the brain of mice following infection with Acanthamoeba spp. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4335–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derda, M.; Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Hadaś, E.; Jagodziński, P.P.; Wandurska-Nowak, E. Acanthamoeba infection in lungs of mice expressed by toll-like receptors (TLR2 and TLR4). Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 165, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, H.; Tripathi, T.; Abdi, M.; Smith, A.D. Pathogenic strains of Acanthamoeba are recognized by TLR4 and initiated inflammatory responses in the cornea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Gao, L.; Wu, X. TLR4: The receptor bridging Acanthamoeba challenge and intracellular inflammatory responses in human corneal cell lines. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygorowicz, M.A.; Kozłowska, E. Involvement of receptors recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns—TLRs in modulation of regulatory T cell CD4 +CD25 +FoxP3 + activity. Postepy Mikrobiologii 2011, 50, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.C.; Glusman, G.; Rowen, L.; Kaur, A.; Purcell, M.K.; Smith, K.D.; Hood, L.E.; Aderem, A. The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9577–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnegowda, G.; Hajjar, A.M.; Zhu, J.; Douglass, E.J.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Woods, A.S.; Gowda, D.C. Induction of proinflammatory responses in macrophages by the glycosylphosphatidylinositols of Plasmodium falciparum: Cell signaling receptors, glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) structural requirement, and regulation of GPI activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8606–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debierre-Grockiego, F.; Campos, M.A.; Azzouz, N.; Schmidt, J.; Bieker, U.; Resende, M.G.; Mansur, D.S.; Weingart, R.; Schmidt, R.R.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by glycosylphosphatidylinositols derived from Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, D.; Naik, S. Leishmania donovani infection down-regulates TLR2-stimulated IL-12p40 and activates IL-10 in cells of macrophage/monocytic lineale by modylating MAPK pathways through a contact-dependent mechanizm. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, C.E.; Sukhumavasi, W.; Butcher, B.A.; Denkers, E.Y. Functional aspekt of Toll-like receptor/myd88 signalling turing protozoan iInfection: Focus on Toxoplasma gondii. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, D.N.; Vodnala, S.K.; Masocha, W.; Sun, B.; Kristensson, K.; Rottenberg, M.E. Distinct Toll-like receptor signals regulate cerebral parasite load and Interferon α/ß and tumor necrosis factor α-dependent T-cell infiltration in the brains of Trypanosoma brucei—Infected mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartey, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and Toll-like receptor targeted therapeutics in innate immune cells. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 36, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A. Signal transduction by lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunolog. 2004, 113, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuon, F.F.; Amato, V.S.; Bacha, H.A.; Almusawi, T.; Duerte, M.I.; Neto, V.A. Toll-like receptors and leishmaniasis. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kleij, D.; Latz, E.T.N.F.; Brouwers, J.F.; Kruize, Y.C.; Schmitz, M.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Espevik, T.; de Jong, E.C.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. A Novel host-parasite lipid cross-talk. schistosomal lyso-phosphatidylserine activates Toll-like receptor 2 and affects immune polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48122–48129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layland, L.E.; Rad, R.R.; Wagner, H.; da Costa, C.U. Immunopathology in Schistosomiasis is controlled by antygen-specific regulatory T-cells primed in the presence of TLR2. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kleij, D.; van den Biggelaar, A.H.; Kruize, Y.C.; Retra, K.; Fillie, Y.; Schmitz, M.; Kremsner, P.G.; Tielens, A.G.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Responses to Toll-like receptor ligands in children living in areas where Schistosome infections are endemic. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Karmakar, S.; Babu, S.P. TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: A review. Braz. J. infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptor signaling and its inducible proteins. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jończyk, M.; Kuliczkowska-Płaksej, J.; Mierzwicka, A.; Bolanowski, M. The polycystic oovaria syndrome and chronic inflommation: The role of Toll-like receptors. Postepy High. Med. Dosw. 2018, 72, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the immune response in the human gut. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gołąb, J.; Jakubisiak, M.; Lasek, W. Immunologia; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Czerkies, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. Receptory Toll-podobne (TLR) i ich udział we wrodzonej odpowiedzi odpornościowej na przykładzie aktywacji TLR4 przez lipopolisacharyd. Postępy Biol. Komórki. 2013, 40, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Majewska, M.; Szczepanik, M. The role of toll-like receptors (TLR) in innate and adaptive immune responses and their function in immune response regulation. Postępy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2006, 60, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Kot, K.; Gutowska, I.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Chlubek, D.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Expression and activity of COX-1 and COX-2 in Acanthamoeba sp.-infected lungs according to the host immunological status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łanocha, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Kuźna-Grygiel, W. Rola pełzaków wolno-żyjących w wywoływaniu i transmisji chorób u ludzi i zwierząt. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2009, 90, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, S.M.; Sobieski, T.; Martinez, A.J.; Duma, R.J. Experimental Acanthamoeba infections in mice pretreated with methylprednisolone or tetracycline. Am. J. Pathol. 1978, 92, 733–744. [Google Scholar]
- Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Ptak, M.; Roszkowska, P.; Kram, A. Histological changes in the kidneys and heart in experimental acanthamoebiasis in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed hosts. Folia Biol. 2021, 69, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordeix, L.; Silva, J.E.D.S.; Llull, J.; Quirola, P.; Montserrat-Sangra, S.; Martinez-Orellana, P.; Solano-Gallego, L. Histological and immunological description of the leishmanian skin test in Ibizan hounds. J. Comp. Pathol. 2018, 158, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Fonseca, D.C.M.; Oliviera-Rovai, F.M.; Rodas, L.A.C.; Beloti, C.A.C.; Torrecilha, R.B.P.; Ito, P.K.R.K.; Avanco, S.V.; Cipriano, R.S.; Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Hiramoto, R.M.; et al. Dog skin parasite load, TLR-2. IL-10 and TNF-α expression an infectiousness. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polari, L.P.; Carneiro, P.P.; Macedo, M.; Machado, P.R.L.; Scott, P.; Carvalho, E.M.; Bacellar, O. Leishmania braziliensis enhances Toll-like recptors 2 and 4 expression and triggers TNF-α and IL-10 production in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.B.; Lima, L.V.D.R.; de Lima, A.C.S.; Vasconcelos Dos Santos, T.; Ramos, P.K.S.; Gomes, C.M.C.; Silveira, F.T. Toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 9 expressions over the en tire clinical and immunopathological spectrum of American cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania (V.) braziliensis and Leishmania (L.) amazonensis. PloS ONE 2018, 13, e0194383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromczyńska, G.; Szymańska-Pomorska, G.; Pytel, A. Pełzakowate zapalenie rogówki jako powikłanie nieprawidłowego używania soczewek kontaktowych. Kosmetologia Estetyczna. 2015, 5, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Bossowska, M.; Dembele, K.; Toka, F.N. Udział receptorów Toll-podobnych w patogenezie atopowego zapalenia skóry u ludzi i zwierząt. Część II. Atopowe zapalenie skóry—Charakterystyka, występowanie i objawy choroby. Życie Wet. 2016, 91, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.S. Toll-like receptors in skin. Adv. Dermatol. 2008, 24, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Walton, S.F.; Ventura, T.; Liu, X.; McCarthy, J.S.; Burgess, S.T.G.; Mounsey, K.E. Early immune suppression leads to uncontrolled mite proliferation and potent host inflammatory responses in a porcine model of crusted versus ordinary scabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 4, e000860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.O.; Morris, R.; Shannon, A.; Lauer, S.R.; Guarner, J.; Kraft, C.S. Disseminated Acanthamoeba infection presenting with cutaneous lesions in an immunocompromised patient: A case report, review of histomorphologic findings, and potential diagnostic pitfalls. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Derda, M.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kolasa, A.; Kot, K.; Walczykiewicz, J.; Solarczyk, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. The Immunological Changes in the Skin of BALC/c Mice with Disseminated Acanthamoebiasis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050631
Wojtkowiak-Giera A, Derda M, Łanocha-Arendarczyk N, Kolasa A, Kot K, Walczykiewicz J, Solarczyk P, Kosik-Bogacka D. The Immunological Changes in the Skin of BALC/c Mice with Disseminated Acanthamoebiasis. Pathogens. 2023; 12(5):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050631
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtkowiak-Giera, Agnieszka, Monika Derda, Natalia Łanocha-Arendarczyk, Agnieszka Kolasa, Karolina Kot, Joanna Walczykiewicz, Piotr Solarczyk, and Danuta Kosik-Bogacka. 2023. "The Immunological Changes in the Skin of BALC/c Mice with Disseminated Acanthamoebiasis" Pathogens 12, no. 5: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050631
APA StyleWojtkowiak-Giera, A., Derda, M., Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N., Kolasa, A., Kot, K., Walczykiewicz, J., Solarczyk, P., & Kosik-Bogacka, D. (2023). The Immunological Changes in the Skin of BALC/c Mice with Disseminated Acanthamoebiasis. Pathogens, 12(5), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050631






