Abstract
Salmonella is one of the most important zoonotic pathogens that can cause both acute and chronic illnesses in poultry flocks, and can also be transmitted to humans from infected poultry. The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characteristics of Salmonella isolated from diseased and clinically healthy chickens in Anhui, China. In total, 108 Salmonella isolates (5.66%) were successfully recovered from chicken samples (n = 1908), including pathological tissue (57/408, 13.97%) and cloacal swabs (51/1500, 3.40%), and S. Enteritidis (43.52%), S. Typhimurium (23.15%), and S. Pullorum (10.19%) were the three most prevalent isolates. Salmonella isolates showed high rates of resistance to penicillin (61.11%), tetracyclines (47.22% to tetracycline and 45.37% to doxycycline), and sulfonamides (48.89%), and all isolates were susceptible to imipenem and polymyxin B. In total, 43.52% isolates were multidrug-resistant and had complex antimicrobial resistance patterns. The majority of isolates harbored cat1 (77.78%), blaTEM (61.11%), and blaCMY-2 (63.89%) genes, and the antimicrobial resistance genes in the isolates were significantly positively correlated with their corresponding resistance phenotype. Salmonella isolates carry high rates of virulence genes, with some of these reaching 100% (invA, mgtC, and stn). Fifty-seven isolates (52.78%) were biofilm-producing. The 108 isolates were classified into 12 sequence types (STs), whereby ST11 (43.51%) was the most prevalent, followed by ST19 (20.37%) and ST92 (13.89%). In conclusion, Salmonella infection in chicken flocks is still serious in Anhui Province, and not only causes disease in chickens but might also pose a threat to public health security.
1. Introduction
Salmonella enterica is one of the most frequent zoonotic pathogens causing human and animal infections worldwide, comprising a wide variety of serovars, with over 2600 identified [1]. Salmonella is commonly found in both domestic and wild animals, including poultry, pigs, and cattle. Poultry products in particular have been identified as a significant source of human salmonellosis [2]. Foodborne salmonellosis is the most relevant source, with a high global impact on human health, although there are other sources, such as animal/reptile, environmental, or human-to-human sources [3]. Compared with other foodborne microorganisms, Salmonella is the most common cause of hospitalization and death [4]. According to 2018 data, nontyphoid Salmonella infection caused approximately 33 million human deaths worldwide. Although there are various serovars linked to salmonellosis, only a few are accountable for the majority of human infections. The primary serovars responsible for human infections in the EU and USA are S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium [5,6].
The identification of serovars is essential for epidemiological surveillance and disease assessment, as various serovars of Salmonella exhibit distinct host ranges and disease-causing capabilities [7]. Some serovars, for example, S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium, can infect not only poultry but also humans [8]. By contrast, S. Pullorum and S. Gallinarum only induce illness in chickens, causing pullorum disease and fowl typhoid, respectively, leading to considerable economic losses in the poultry industry [9,10]. Therefore, chickens are a prominent source of infection and act as a reservoir for Salmonella. Xu et al. [11] identified 12 serovars of Salmonella from dead embryo samples collected from breeder chicken hatcheries in Henan, China. The dominant serovar was S. Pullorum (75.79%), followed by S. Enteritidis (7.14%). In Zhao et al.’s study [12] in Shandong, China, S. Thompson (37.20%) and S. Infantis (32.60%) were the most prevalent isolates from dead-in-shell chicken embryos. The majority of isolates (66.30%) were resistant to ampicillin, while 55.80% of isolates exhibited multidrug resistance (MDR). Chicken embryos and eggs infected with Salmonella can not only cause the vertical transmission of these bacteria during hatching, but they are also an important cause of human foodborne infection [13]. Another study showed that the most common serovars were S. Kentucky (44.7%) and S. Enteritidis (32.5%) at different chicken-slaughtering stages using whole-genome sequencing in Jiangsu, China [14]. In large-scale breeder farms, S. Enteritidis was found to be the most common serovar, with high rates of antimicrobial resistance to nalidixic acid (100.0%), streptomycin (100.0%), ampicillin (98.4%), and erythromycin (93.7%) [15]. An investigation by Wang et al. on Salmonella contamination of retail meats in Anhui Province markets found that S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium were the most prevalent serovars, with high resistance rates to ampicillin (87.5%), doxycycline (75.0%), and tetracycline (62.5%) [16].
The results of these previous studies provided strong data support for Salmonella infection in poultry, allowing for the prevention and control of its human foodborne infection. However, there have been few studies regarding the prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella isolated from chickens in Anhui Province [17]. The aim of the present work is to study the serovars’ prevalence, phenotypic antimicrobial resistance profile, and molecular characteristics of Salmonella isolated from diseased and clinically healthy chickens in Anhui Province to better understand the epidemiology of Salmonella in chickens in Anhui, China, and to provide a research basis for the prevention and control of this foodborne pathogen.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Culture of Salmonella
From March 2019 to April 2022, 408 pathological tissue samples (liver, spleen, and kidneys) were collected at the Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences’ Veterinary Clinical Diagnosis Guidance Center. These pathological samples were obtained from diseased chickens with bacterial infections in layer and broiler farms, some of which exhibited the histopathological changes suspected of Salmonella infection, such as enlarged liver and spleen, small necrotic spots, and copper-green lesions in the liver. In addition, we collected 1500 cloacal swab samples from clinically healthy chickens from 50 chicken farms (30 cloacal swab samples/farm), including 45 layer farms and 5 broiler farms (19 large-scale, 28 medium-scale, and 3 small-scale). The prevalence of cloacal swab samples is shown in Table S1. This work was a monitoring task of the National Animal Disease Data Center. All samples came from 16 cities in Anhui province: Anqing, Changfeng, Chaohu, Dingyuan, Fanchang, Feidong, Fuyang, Feixi, Guzhen, Hefei, Hexian, Huainan, Huoqiu, Lu’an, Shouxian, and Wuhu.
Salmonella isolates were isolated and identified using previously reported methods [12]. To summarize, 10 g of pathological tissue (mixed sample containing multiple pathological tissues from the same source) or cloacal swab sample was added with 100 mL of buffered peptone water (BPW; Hopebiol, Qingdao, China) and incubated at 37 °C for 12 h. Then, 1 mL of enriched BPW suspension was transferred to 10 mL of selenite cysteine (SC; Hopebiol) at 42 °C for 24 h, which was further streaked on xylose lysine tergitol 4 (XLT4; Hopebiol) agar plates and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h for Salmonella selection. Then, the isolates were subjected to DNA extraction using a bacterial genome extraction kit (Beijing Solarbio Science Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). PCR was performed to amplify the 16S rRNA [18]. The obtained amplicons were sequenced and then aligned using the NCBI database https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 8 June 2022).
2.2. Serotyping of Salmonella Isolates
The Salmonella isolates were subcultured and serotyped using commercial O and H antisera through slide agglutination, following the manufacturer’s guidelines (Tianrun Bio Pharmaceutical, Ningbo, China). All identified Salmonella isolates were added to the lyophilization protectant and stored at −80 °C for further use.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Salmonella sensitivity to 24 different common antimicrobials from 14 classes of antimicrobials (Hangzhou microbial reagent Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) was evaluated using a Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion approach, following the protocols of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) [19]. The selected antimicrobials are frequently utilized to manage bacterial infections in animals and humans. The antimicrobials used for these tests comprised ampicillin (AMP), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AMC), ceftriaxone (CRO), cefotaxime (CTX), cephalexin (CN), gentamicin (GEN), amikacin (AMK), neomycin (NEO), tetracycline (TET), doxycycline (DOX), ciprofloxacin (CIP), enrofloxacin (ENR), levofloxacin (LEV), norfloxacin (NOR), chloramphenicol (CHL), florfenicol (FLO), sulfamethoxazole (SXT), trimethoprim (TMP), azithromycin (AZM), furazolidone (FUR), imipenem (IPM), polymyxin B (PB), fosfomycin (FOS), and aztreonam (AZT). The ATCC 25,922 Escherichia coli strain was used as the quality control (Hopebiol). All Salmonella isolates that were found to be resistant to more than three antimicrobials classes were defined as being MDR isolates.
2.4. Prevalence of Drug Resistance and Virulence Genes in Salmonella Isolates
Briefly, all Salmonella isolates preserved at −80 °C were streaked onto tryptic soy agar and incubated at 37 °C for 12 h. Subsequently, one colony was selected, inoculated into BPW, and incubated at 37 °C overnight. The next day, 1 mL of bacterial solution was collected and centrifuged at 5000× g for 5 min, and then commercial kits (Beijing Solarbio Science Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) were used to extract DNA from the isolates. We used conventional PCR methods to identify 14 drug resistance genes and 7 virulence genes in all the isolates. Resistance genes included blaTEM, blaCMY-2, aadA1, strA, aph(3′)-IIa, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, qnrB, qnrS, sul1, sul2, tetA, tetB, cat1, and floR. Virulence genes included invA, sseL, mgtC, siiE, sopB, spvB, and stn. The sequences of the PCR primers for all the genes are shown in Table 1. The primers were obtained from Anhui General Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Anhui, China), and the PCR reaction was conducted with a Takara Premix Taq kit (Takara Bio Inc., Dalian, China) in a total volume of 20 µL. PCR products were identified using a gel imaging system after treatment with GoldView nucleic acid stain (Beijing Solarbio Science Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).

Table 1.
Primers for antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of Salmonella.
2.5. Biofilm Assay
The amount of biofilm formed by Salmonella isolates was measured using the 96-well polystyrene microtiter plate test method described by Yin et al. [24]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27,853 (Hopebiol, Qingdao, China) was utilized as a positive control, while negative control wells were filled with 200 µL of TSB only. Six replicate wells were used to test each isolate as well as the negative control wells. The amount of biofilm formed by each tested isolate was determined by calculating the average optical density at 570 nm (OD570) using the absorbance of six wells measured by INFINITE 200PRO (Tecan Austria GmbH, Grödig, Austria). The biofilm-forming abilities of the Salmonella isolates were classified into four groups based on a comparison of the optical density (OD) of the test wells and the negative control wells (ODc): (i) no biofilm producer: OD ≤ ODc; (ii) weak biofilm producer: ODc < OD ≤ (2 × ODc); (iii) moderate biofilm producer: (2 × ODc) < OD ≤ (4 × ODc); and (iv) strong biofilm producer: (4 × ODc) < OD.
2.6. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
The Salmonella isolates were analyzed by MLST, which involved amplifying seven housekeeping genes (aroC, dnaN, hemD, hisD, purE, sucA, and thrA) according to previously described protocols [25]. PCR amplifications were conducted in a 25 µL volume containing 12.5 µL of 2 × Taq PCR Mix (Takara Bio Inc.), 2 µL of template, 1 µL of each 20 µM primer, and 8.5 µL of sterile ddH2O. The conditions for PCR reactions were obtained from the Salmonella MLST website and database http://mlst.warwick.ac.uk/mlst/dbs/Senterica/ (accessed on 25 August 2022). The PCR samples were purified using gel electrophoresis and sent for bidirectional DNA sequencing at Anhui General Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Each gene sequence was submitted to the Salmonella MLST database for comparison to obtain the specific Salmonella sequence type. The MUSCLE alignment program was utilized to align all sequences [26], and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA 7.0 [27].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data were preliminarily processed using Excel 2010 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). The Salmonella serovar distribution, cluster heat map, and correlation analysis were drawn using Excel 2010 and GraphPad Prism 7 software (GraphPad Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA), respectively. The determination results of the Salmonella isolates’ biofilm-forming abilities were processed by Excel 2010 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) and the experiments were repeated three times.
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Serotyping of Salmonella
In this study, 1908 samples were collected, including 1500 cloacal swab samples and 408 pathological tissue samples. In total, 108 strains of Salmonella were isolated and identified from all the samples by isolation culture and PCR 16S rRNA amplification sequencing, with an overall salmonella isolation rate of 5.66% (Table 2). Among them, 51 isolates were from cloacal swab samples, with an isolation rate of 3.40%, and 57 isolates were from pathological tissue samples, with an isolation rate of 13.97%. The pathological tissue samples had a higher Salmonella isolation rate than the cloacal swab samples, and the prevalence information for all Salmonella isolates is shown in Table S2. A total of 9 different serovars were identified among the 108 Salmonella isolates, and S. Enteritidis (43.52%), S. Typhimurium (23.15%), and S. Pullorum (10.19%) were the most frequent serovars in the chicken samples (Figure 1a). The prevalence of Salmonella serovars in different samples varied; for example, the proportions of S. Pullorum (9/51, 17.65%) and S. Gallinarum (4/51, 7.84%) in cloacal swab samples were higher than in the pathological tissue samples (both 2/57, 3.51%), and S. Thompson was isolated only from tissue samples from diseased chickens (Figure 1b).

Table 2.
Prevalence of Salmonella isolates among type and number of samples.
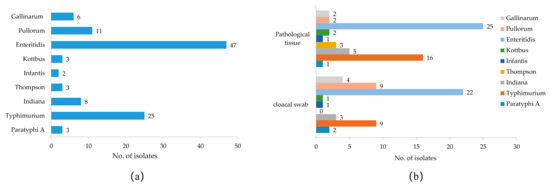
Figure 1.
Serovar prevalence of Salmonella isolates isolated from chickens in Anhui. (a) Serovar distribution of all Salmonella isolates. (b) Serovar distribution of Salmonella from different sample sources.
3.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
The susceptibilities of the 108 Salmonella isolatesfrom chickens to 24 antibiotics are shown in Table 3. The results revealed high rates of resistance to ampicillin (61.11%), tetracycline (47.22%), doxycycline (45.37%), sulfamethoxazole (48.89%), trimethoprim (48.89%), and aztreonam (34.26%). About 30% of Salmonella isolates were resistant to cephems, namely ceftriaxone (33.33%), cefotaxime (27.78%), and cephalexin (33.33%); and 22.22% of Salmonella isolates were resistant to chloramphenicols (chloramphenicol and florfenicol). Salmonella isolates showed low resistance rates to aminoglycoside, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics; however, all isolates were susceptible to imipenem and polymyxin B. Regarding serovars (Figure 2a), the antibiotic resistance rates of S. Paratyphi A, S. Typhimurium, S. Indiana, and S. Thompson were higher than those of S. Kottbus, S. Enteritidis, S. Pullorum, and S. Gallinarum.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from chickens.
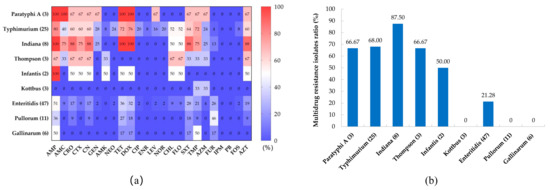
Figure 2.
The prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among different serovars of Salmonella. (a) Heat map of antibiotic resistance distribution among different serovars of Salmonella. (b) Distribution of multidrug-resistant isolates among different serovars of Salmonella.
The antimicrobial resistance spectrum of the isolates is shown in Table S3. Chicken-derived Salmonella isolates in Anhui have a complex antibiotic resistance spectrum, among which 43.52% (47 isolates) were MDR isolates; however, 18.52% (20 isolates) were still sensitive to all antibiotics. Strikingly, one S. Typhimurium isolate was resistant to 20 antibiotics. The proportion of MDR isolates among S. Indiana isolates was the highest, at 87.50%, followed by S. Typhimurium (68.00%), S. Thompson (66.67%), and S. Paratyphi A (66.67%). Only 21.28% of S. Enteritidis isolates were MDR isolates, while no MDR isolates appeared among S. Pullorum, S. Gallinarum, and S. Kottbus isolates (Figure 2b). There is a certain correlation between the resistance phenotypes of isolates to different classes of antimicrobials (Figure S1). The resistance phenotypes of aminoglycosides and quinolone antimicrobials show a significantly positive correlation, as well as a positive correlation between tetracyclines and chloramphenicol-resistant phenotypes. In total, 95.83% (23/24) of chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella isolates exhibited co-resistance to chloramphenicol and cefotaxime, and all ciprofloxacin-resistant isolates were resistant to both gentamicin and neomycin.
3.3. Prevalence of Antimicrobial-Resistance-Related Genes in Salmonella Isolates
The results of the PCR analysis for antimicrobial resistance genes are shown in Figure 3a. The carrier rates of the two β-lactamase genes, blaTEM and blaCMY-2, were 61.11% and 63.89%, respectively; the carrier rates of aminoglycoside-resistance-related genes aadA, strA, and aph(3′)-IIa were 12.40%, 36.11%, and 18.52%, respectively; the carrier rates of quinolone-resistance-related genes aac(6′)-Ib-cr, qnrB, and qnrS were 39.81%, 23.15% and 27.78%, respectively; the carrier rates of sulfonamide-resistance-related genes sul1 and sul2 were both 42.59%; and the carrier rates of the tetracycline resistance genes tetA and tetB were 49.07% and 37.96%, respectively. All isolates had high carrying rates of chloramphenicol-resistance-related genes, with 77.78% (catA1) and 54.71% (floR), respectively.
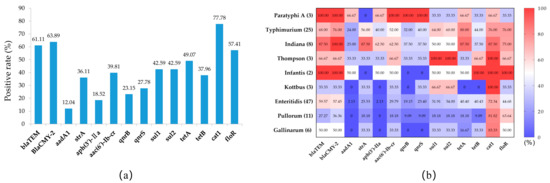
Figure 3.
The prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella isolates. (a) Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in all Salmonella isolates. (b) Heat map of the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes among different Salmonella serovars.
There were some differences in the carrier rates of drug-resistance-related genes among different serovars (Figure 3b). Overall, the carrier rate of the drug-resistance-related genes of S. Paratyphi A, S. Typhimurium, S. Indiana, S. Thompson, and S. Infantis were higher than those of S. Enteritidis, S. Pullorum, and S. Gallinarum. However, the chloramphenicol-resistance-related genes cat1 and floR had higher positive rates in S. Enteritidis, S. Pullorum, and S. Gallinarum than in the other serovars. Furthermore, these resistance-related genes showed higher carrier rates in isolates with corresponding resistance phenotypes (Table 4), e.g., the carrier rates of aac(6’) Ib-cr, qnrB, and qnrS were 100% in quinolone-resistant isolates, while the carrier rates aadA and aph(3′)-IIa were both 93.33% in isolates that were resistant to aminoglycoside antibiotics.

Table 4.
Genotypic drug resistance characteristics of Salmonella Isolates.
The results of the correlation analysis between the drug-resistance-phenotype- and drug- resistance-gene-carrying Salmonella isolates are shown in Figure 4. The carrier rates of β-lactamase genes (blaTEM and blaCMY-2) in isolates are significantly correlated with their resistance to penicillin and cephalosporins (Figure 4a). The carrier rates of quinolone (aac(6’) Ib-cr, qnrB, and qnrS)- and sulfonamide (sul1 and sul2)-resistance-related genes in isolates are significantly correlated with their resistance to quinolones and sulfonamide antimicrobials (Figure 4b,f). However, some aminoglycoside (Figure 4c)-, tetracycline (Figure 4d)- and chloramphenicol-resistance-related genes (Figure 4e) carried in isolates were not correlated to their resistance phenotypes, such as strA, tetB, and cat A1.
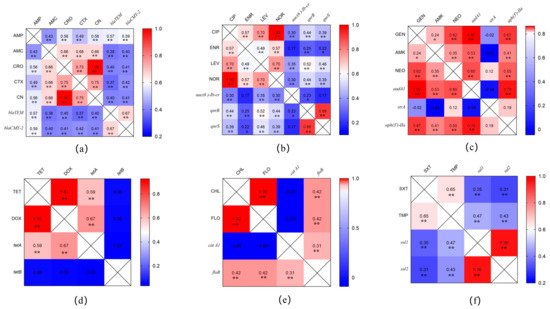
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis between the antimicrobial-resistance-phenotype- and their resistance−gene−carrying Salmonella isolates. (a) Correlation analysis of β-lactamase−resistance−genes with their resistance to penicillins and cephalosporins. (b) Correlation analysis of quinolone−resistance−genes with their resistance to quinolones. (c) Correlation analysis of aminoglycoside−resistance−genes with their resistance to aminoglycosides. (d) Correlation analysis of tetracycline−resistance−genes with their resistance to tetracyclines. (e) Correlation analysis of chloramphenicol−resistance−genes with their resistance to chloramphenicols. (f) Correlation analysis of sulfonamide−resistance−genes with their resistance to sulfonamides. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, correlation analysis by pearson method.
3.4. The Prevalence of Virulence Genes and the Biofilm-Producing Ability of Salmonella Isolates
The prevalence of virulence genes in the Salmonella isolates is shown in Figure 5a. The virulence genes invA, mgtC, and stn were present in all isolates. The carrier rates of siiE, sopB, and spvB were 99.07%, 94.44%, and 75.93, respectively, whereas that of the sseL gene was lower, at 65.2%. In the serovars, the positive carrier rates of sseL and sopB genes in S. Enteritidis, S. Pullorum, and S. Gallinarum isolates were lower than those in the other serovars, while the prevalence of the spvB gene in different serovars showed the opposite pattern (Figure 5b).
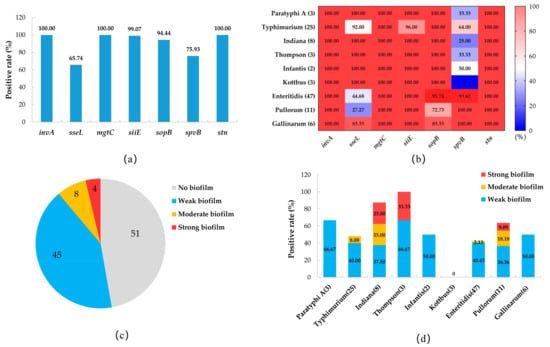
Figure 5.
Prevalence of virulence genes and characteristics of biofilm-producing Salmonella isolates. (a) Prevalence of virulence genes of all Salmonella isolates. (b) Heat map of the prevalence of virulence genes among different serovars of Salmonella isolates. (c) Number of Salmonella isolates with different biofilm-producing abilities. (d) Prevalence of isolates with different biofilm-producing abilities among different Salmonella serovars.
The biofilm assay results of the Salmonella isolates showed that 57 isolates (52.78%) had the ability to form biofilms, among which 45 isolates (41.67%) were a weak biofilm producer, 8 isolates (7.41%) were a moderate biofilm producer, and 4 isolates (3.70%) were a strong biofilm producer (Figure 5c). Among the serovars, all serovars of Salmonella except S. Kottbus had biofilm-producing isolates, among which S. Thompson had a higher proportion (3/3, 100%), followed by S. Indiana (7/8, 87.50%), S. Paratyphi A (2/3, 66.67%), and S. Pullorum (7/11, 63.64%). Three serovars (S. Paratyphi A, S. Infantis, and S. Gallinarum) only had weak biofilm-producing isolates, and the moderate and strong biofilm-producing isolates appeared in S. Typhimurium (two moderate isolates), S. Thompson (one strong and two moderate isolates), S. Indiana (two strong and two moderate isolates), and S. Pullorum (one strong and two moderate isolates) (Figure 5d).
3.5. MLST Analysis
In the MLST analysis (Figure 6), the 108 Salmonella isolates were classified into 12 ST types: ST11, ST17, ST19, ST26, ST32, ST34, ST78, ST85, ST92, ST1251, ST1544, and ST1960. ST11 was the most common ST in this study (47/108, 43.51%), followed by ST19 (20.37%), ST92 (13.89%), and ST17 (7.41%). ST11 had a wide distribution in several regions of Anhui and was the dominant ST type in Lu’an, Huainan, Fuyang, and Wuhu (Figure 7). ST19 was the most prevalent ST in S. typhimurium isolates (23/25, 92.00%), and was widely distributed in Changfeng, Hefei, Feidong, and Chaohu. ST92 isolates were mainly from Hefei, Guzhen, and Fuyang, and most of the isolates were isolated from cloacal swab samples of clinically healthy chickens. Furthermore, we observed that the majority of isolates sharing the same sequence types (STs) were also of the same serovars. For instance, strains with ST11 were identified as S. Enteritidis, while ST19, ST34, and 1544 were associated with S. Typhimurium, ST17 with S. Indiana, and ST1960 with S. Kottbus. However, ST92 corresponded to two serovars: S. Pullorum and S. Gallinarum.
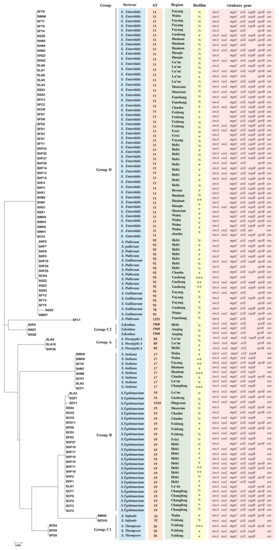
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic tree of Salmonella isolate-based multilocus sequence typing. Markers include serovar group, serovars, ST-types, region, biofilm (“N” represent non-biofilm producer, “+” represent weak biofilm producer, “++” represent moderate biofilm producer, and “+++” represent strong biofilm producer), and virulence genes (invA, sseL, mgtC, siiE, sopB, spvB and stn; blank indicates that gene detection was negative) of Salmonella isolates.
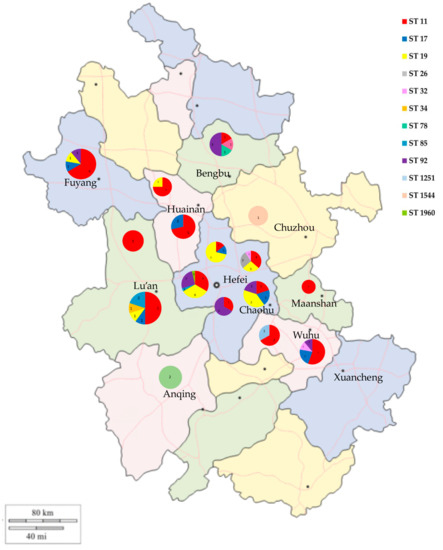
Figure 7.
Geographical distribution of ST-type Salmonella isolates in Anhui Province.
4. Discussion
In this study, a total of 108 Salmonella isolates were identified from pathological tissue samples from diseased chickens and cloacal swab samples from clinically healthy chickens collected in 16 cities in Anhui. The overall isolation rate of Salmonella was 5.66%, similar to that reported by Zhao et al. [12] and Li et al. [28] from chicken farms and hatchery samples in Shandong and Shaanxi, respectively. However, it was lower than the isolation rates reported from commercial chicken farms in Henan [11] and Qingdao [29], China. The Salmonella isolation rate from clinically diseased chickens in the present study was higher than that reported by Wang et al. [25] in a clinical investigation of diseased chickens in north China. In any case, the isolation rate of Salmonella in slaughterhouses and chicken products was higher than in farms, which is an important Salmonella link between chicken production and food [30]. The variations in Salmonella isolation rates could be due to differences in region or season, or differences in the sampling techniques used across studies [31]. The poultry farming industry in Anhui Province is large, and according to statistics, there was an average annual stock of 70–80 million egg-laying hens and an average annual slaughter of 180–200 million broiler chickens in 2020–2022 (unofficial data). In this study, samples from laying and broiler farms with different breeding modes and scales in 16 cities in Anhui Province were used for an epidemiological study of Salmonella infection in chickens, and the results were representative. However, the sample isolation rates of Salmonella indicate that the Salmonella infection situation in chickens in Anhui remains serious, leading to the clinical morbidity of chickens, and more importantly, an invisible infection of Salmonella in clinically healthy chickens, which is a considerable mediator of horizontal and vertical Salmonella transmission in chickens.
Serotyping can be used as an effective method to assess the means of transmission and develop strategies for preventing the spread of disease within poultry facilities. [32]. Among the isolates, we identified nine serovars, of which S. Enteritidis was the most frequent, followed by S. Typhimurium and S. Pullorum. This is consistent with studies of commercial chicken farms in Shanghai and Sichuan [33,34], while S. Gallinarum-pullorum was found to be dominant in Henan [11]. Another study found that S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium were the most common serovars isolated from diseased poultry in northern China [25]. S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium are the most common serovars of Salmonella that cause human infection, resulting in severe gastrointestinal disease [35,36,37]. According to the China National Foodborne Diseases Surveillance Network, over the past decade (2010–2019), the most prevalent serovars in nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in Zhejiang Province were S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium [13]. Our findings suggested that the widespread distribution of foodborne Salmonella serovars in chicken flocks might pose a threat to food safety, and this conclusion was also confirmed by the literature [38,39]. Differences in the distribution of Salmonella serovars in different studies are related to regional differences and, in addition, might be related to the source and type of samples selected. For example, S. Pullorum and S. Enteritidis were the most common Salmonella serovars isolated from dead chicken embryos [11,25], while the more common serovars found in the slaughterhouse and chicken meat samples were S. Indiana [40], S. Typhimurium [41], or S. Enteritidis [42]. In the present study, the isolation rates of S. Pullorum and S. Gallinarum were higher in cloacal swabs than in pathological tissue samples. Although adult chickens infected with S. Pullorum may appear asymptomatic, the bacteria can persist for several months in the spleen and reproductive tract, leading to vertical transmission to eggs and progeny [43], which might also explain the high isolation rate of S. Pullorum in dead chicken embryos. However, the elimination of S. Pullorum has been carried out in many large breeder farms in China, and remarkable results have been achieved.
Animals are administered antimicrobials for various purposes, such as disease treatment, prevention, control, and growth/feed efficiency promotion [44]. Resistance to antibiotics has emerged as a significant global public health concern, with reports of bacteria isolated from animals displaying resistance to different antibiotics [45]. Despite efforts to limit antibiotic use in animal feeding, this study found that Salmonella isolates exhibited high rates of resistance to ampicillin, tetracycline, doxycycline, sulfamethoxazole, and trimethoprim. These resistance rates agree with reports on poultry Salmonella isolates in northern China [25], Shandong [12], and Guangdong [46], but are generally lower than those of Henan [11]. There were low resistance rates to aminoglycoside, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics and no resistance to imipenem and polymyxin B, which contrasted with Zhao et al.’s report [7], in which the Salmonella isolates isolated from broiler chickens were 100% resistant to polymyxin B. These high resistance rates in Salmonella isolated from chickens might be attributed to the widespread use of antibiotics for animal breeding and disease control [47]. In addition, different serovars of Salmonella showed different antibiotic resistance patterns in our study, such as the antibiotic resistance rates of S. Typhimurium and S. Indiana, which were higher than those of S. Enteritidis and S. Pullorum. While certain serovars may not be currently dominant, their prevalence may shift over time, and they could potentially become the primary serovars in a given region due to exposure to multiple antimicrobial selection pressures [48].
In this study, a high prevalence of MDR patterns among the Salmonella isolates was detected, and 43.52% of Salmonella isolates presented resistance to more than three antibiotic classes, which was lower than that previously reported in Shandong (53.7%), Henan (69.64%), Guangdong (59.5%), and northern China (69.64%). Yang et al. [49] also showed that 86.7% of Salmonella isolates from Shanghai exhibited an MDR phenotype. There are some differences in the prevalence of MDR isolates in different serovars of Salmonella. In addition, S. Indiana showed the highest proportion of MDR isolates (87.50%), which was consistent with Zhang et al.’s report [50]. However, one study found different results from ours, namely that S. Enteritidis showed a high MDR rate [7]. We also found a certain correlation between the resistance phenotypes of different types of antibiotics among MDR isolates, such as 95.83% (23/24) of chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella isolates exhibiting co-resistance to chloramphenicol and cefotaxime. According to Abd El-Aziz et al. [51], there are many XDR Salmonella isolates in livestock animals exhibiting co-resistance to ciprofloxacin (CIP) and tigecycline (TIG), and this co-resistance is facilitated by the overexpression of acrAB, which enhances efflux-mediated resistance to CIP/TIG. The phenomenon of co-resistance is prevalent in MDR pathogenic bacteria isolated from animals, such as amoxicillin and tetracycline co-resistance in Escherichia coli [52], and co-resistance to macrolides and fluoroquinolones in Campylobacter [53]. Therefore, the molecular mechanism of co-resistance remains to be further studied. Our findings indicated that it is necessary to continue monitoring antibacterial agents using them prudently in clinically, veterinary, and agricultural settings to avoid the development of cross-resistance.
The presence of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) is the origin and molecular basis of bacterial resistance [54]. The abundance of ARGs showed a significant statistical effect with antibiotic pressure, even at very low levels [55]. The extended-spectrum β lactamases are bacterial enzymes capable of hydrolyzing extended-spectrum cephalosporins and rendering beta-lactam antibiotics ineffective [56]. In this study, two β-lactamase genes, blaTEM and blaCMY-2, were found in 61.11% and 63.89% of the Salmonella isolates, respectively, which was similar to the proportions detected in Salmonella isolated from Shandong chicken flocks by Zhao et al. [12] and Alam et al. [8], indicating the high proportion of Salmonella isolates carrying β-lactamase genes in different cities or provinces. We found that the chloramphenicol-resistance-related genes cat1 and floR were very common among the isolates. Florfenicol is a commonly used antibiotic in veterinary medicine; therefore, the emergence of these resistance genes might be related to the long-term use of this antibiotic [57]. Hence, further attention should be paid to the changes in the resistance of Salmonella to florfenicol. The rate of carrying aminoglycoside- and quinolone-resistance-related genes was low in the isolates from Anhui. This finding is consistent with the results for Salmonella isolated from Shandong [12] and Henan [11]. There is a certain correlation between the presence of drug-resistance genes in isolates and their drug susceptibility [58]. These resistance-related genes showed higher carrier rates in isolates with corresponding resistance phenotypes, e.g., the carrier rates of aac(6’)-Ib-cr, qnrB, and qnrS were 100% in quinolone-resistant isolates, and aadA and aph(3′)-IIa were present in 93.33% of isolates that were resistant to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Correlation analysis found that most of the resistance genes in the isolates were significantly positively correlated with their resistance phenotypes. However, the carrying of drug resistance genes is not completely consistent with the drug resistance of the isolate because bacteria have multiple drug resistance mechanisms, such as efflux pumps, drug resistance gene mutations, and biofilms formation [59]. Some isolates also carry resistance-related genes but do not show corresponding resistance phenotypes, which might be related to the selective silencing of some genes under specific conditions [59]. To clarify the mechanism, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the biological characteristics and genomic information of the isolates. However, the presence of drug resistance genes in an isolate indicated that it is likely to mutate into the corresponding antibiotic-resistant isolate [60].
Salmonella virulence-factor-encoding genes are primarily situated in discrete genomic regions distributed throughout the chromosome, known as Salmonella pathogenicity islands (SPIs), which help pathogens evade the host immune system while exerting their pathogenicity [61]. Among them, SPI1, SPI2, SPI3, SPI4, and SPI5 have been studied systematically [62]. In this study, certain virulence genes, including invA, mgtC, and stn, were detected in all Salmonella isolates, while siiE and sopB exhibited notably high carrier rates, suggesting their potential significance in Salmonella pathogenesis, which is consistent with previous findings in chickens and ducks reported by Zhang et al. [63] and Yang et al. [64]. The sseL gene significantly enhanced the virulence of S. Pullorum in chickens and suppressed the activation of cellular inflammatory response [65]. The spvB gene, a crucial effector encoded within this locus, is strongly linked to Salmonella pathogenicity, for example, by interfering with autophagy and iron homeostasis [66]. Previous investigations identified spvB as a potential plasmid-encoded virulence gene in S. Pullorum, with detection rates as high as 98.0%. [63], which differed from another study reporting that spvB was found in 10% of isolates of Salmonella spp. [23]. Another study showed that spvB is not present in S. Typhimurium [67]. In this study, the positive carrier rate of sseL and spvB genes showed different distribution patterns among Salmonella serovars, which might be closely related to bacterial invasion and the cellular immune response triggered by invasion [68]. These findings indicate that virulence genes are extensively present in Salmonella isolates from chickens in Anhui.
Bacterial biofilm is an extracellular matrix composed of polysaccharides, lipids, proteins, and extracellular DNA secreted by bacteria and carbohydrates in the environment, which, as one of the most important antistress mechanisms of bacteria, can endow biofilm bacteria with strong drug resistance and immune escape, resulting in persistent infection [69]. Previous research has shown that biofilm formation by Salmonella plays a significant role in its pathogenicity [70] and high potential on common contact surfaces with chicken products [71]. In this study, 52.78% of Salmonella isolates could produce a biofilm, most of which were weak biofilm-producing isolates. Further analysis revealed that the proportions of moderate and strong biofilm-producing isolates among S. Typhimurium, S. Thompson, S. Indiana, and S. Pullorum were higher than in the other serovars. Similar to our results, 62% of S. Enteritidis and 73.8% of S. Typhimurium isolates from avian sources exhibited the ability to form biofilms, with S. Enteritidis demonstrating a strong capacity for adhesion [72]. Among Salmonella isolated from chickens in South Africa, the proportion of isolates producing biofilms at different temperatures reached 86.44–88.14%, and S. Heidelberg and S. Weltevreden were the serovars with the highest biofilm-forming capacities [73]. Another study found that all of the Salmonella serovars were isolated from meat, with 75.86% exhibiting moderate biofilm formation and 24.14% displaying strong biofilm formation. S. Enteritidis was identified as the most potent biofilm producer. [74]. Silva et al. [75] believed that S. Gallinarum and S. Minnesota had stronger biofilm production abilities than the S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, and S. Heidelberg serovars. However, the impact of incubation temperature on biofilm formation was found to be more significant than that of the serovar [72,73]. The results of different studies indicated that the differences in biofilm production ability might be more related to the source, region, and characteristics of the isolates themselves.
MLST has emerged as a fundamental method for bacterial isolate classification into strains, and is being increasingly utilized by both reference and diagnostic laboratories for epidemiological investigations and outbreak studies [76,77]. In this study, sequence analysis revealed ST11, ST19, and ST92 to be the most prevalent sequence types (STs). All 47 S. Enteritidis isolates were assigned into ST11, which was consistent with a previous study on S. Enteritidis in China spanning from 2011 to 2016 [78]. The results of two independent studies of Salmonella isolated from chickens in Shandong were also consistent with our results, finding that ST11 had the highest isolation rates in both breeder farms and free-range flocks [15,79]. In addition, ST11 has been detected in various hosts, including humans, poultry, food sources, and numerous wild animal species, such as reptiles, with a wide geographic distribution spanning Asia, Africa, South America, and Europe [80]. In the present study, ST19 was the most prevalent ST in S. Typhimurium isolates, and S. Typhimurium isolates also contained ST34 and ST1544. ST19 is very common in S. Typhimurium isolated from chicken flocks [25], and is the most common ST isolated from humans and animal-based food products across the world [81,82]. Moreover, ST34 and ST1544 have been identified from human and animal samples in China [83,84]. A study found that ST34 was associated with a higher MDR rate and more complex MDR patterns than ST19 [82]. Although there were only two isolates of ST34 in our study, they were both MDR isolates, which supported the MDR status of ST34 [85].
ST92 contains S. Pullorum and S. Gallinarum isolates, which are the etiological agents of pullorum disease (PD) and fowl typhoid (FT), respectively, causing huge economic losses to the poultry industry, especially in developing countries [86]. In China, ST92 is widely present in chicken flocks, and was the most common ST in some studies [17,78]. Despite the limited data from this study, we found differences in the prevalence of Salmonella STs in different regions of Anhui Province. These results showed that there are a variety of ST Salmonella epidemics in chicken flocks in Anhui, and further measures should be taken to prevent Salmonella from causing harm to the health of chicken flocks and compromising public health.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we explored the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characteristics of Salmonella isolated from diseased and clinically healthy chickens in Anhui, China. We found that the dominant Salmonella serovars among the isolates were clinically significant S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, and S. Pullorum, and the majority of other isolates were also associated with salmonellosis in animals and humans. The determination of the drug resistance of Salmonella isolates and the distribution of drug-resistance-related genes provide basic data for the rational use of antibiotics and monitoring of changes in Salmonella drug resistance. The determination of virulence genes and biofilms enriched our knowledge regarding the molecular pathogenic properties of the isolates. MLST analysis showed the prevalence of various ST-type Salmonella in Anhui Province, among which ST11, ST19, and ST92 are dominant isolates. This study will aid in the continuous monitoring of the genetic diversity of Salmonella isolated from chickens in Anhui and might reveal differences in the epidemiology, evolution, and genetic traits that influence control and treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens12030465/s1, Figure S1: Correlation analysis among different classes of antimicrobials resistance phenotypes of Salmonella isolates in Anhui, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, correlation analysis by pearson method; Table S1: Salmonella isolation results from cloacal swab samples from 50 chicken farms; Table S2: Prevalence of Salmonella isolated from chicken in Anhui; Table S3: Antimicrobial resistance spectrum of the Salmonella isolates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.P. and Y.L.; methodology, A.Z. and X.S.; software, L.Y.; validation, D.Y. and J.W.; formal analysis, Y.D.; investigation, X.H. and H.H.; resources, R.Z.; data curation, X.S. and L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; visualization, D.Y. and X.S.; supervision, X.P.; project administration, Y.L. and X.P.; funding acquisition, D.Z. and X.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Key Research and Development Project of Anhui Province, grant number 202204c06020039; Jiangsu Province Key Research and Development Program (Modern Agriculture) Project, grant number BE2022329; Major Science and Technology Special Project in Anhui Province, grant number 20203b06020006, 2020003a06020012; The China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, Grant number CARS-40; Key Research and Development Project of Anhui Province, grant number 202204c06020009; Anhui Poultry Industry Technical System Project grant number ahcyjstx-06 and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, National Data Center of Animal Health. The APC was funded by Platform Project of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Science, grant number 2023YL013.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information Files).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Changwei Lei (College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University) and Daxing Peng (College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University) for their excellent support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Takaya, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Tokoyoda, K. Humoral immunity vs. Salmonella. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Moreno, L.Z.; Castellanos, L.R.; Chattaway, M.A.; McLauchlin, J.; Lodge, M.; O’Grady, J.; Zamudio, R.; Doughty, E.; Petrovska, L.; et al. Dynamics of Salmonella enterica and antimicrobial resistance in the Brazilian poultry industry and global impacts on public health. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello, H.; Guerra, B.; Rodríguez, I.; Rubio, P.; Carvajal, A. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance determinants and class 1 and class 2 integrons in Salmonella enterica spp., multidrug-resistant isolates from pigs. Genes 2018, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Dewey-Mattia, D.; Subramhanya, S.; Cui, Z.; Griffin, P.M.; Lance, S.; Lanier, W.; Wise, M.E.; Crowe, S.J. Food recalls associated with foodborne disease outbreaks, United States, 2006–2016. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 149, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Mourão, J.; Campos, J.; Peixe, L. Salmonellosis: The role of poultry meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efsa. The European Union Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents and Food-borne Outbreaks in 2011. EFSA J. 2011, 11, 19–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Y. Characterization of integrons and antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella from broilers in Shandong, China. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 7046–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.B.; Mahmud, M.; Akter, R.; Hasan, M.; Sobur, A.; Nazir, K.N.H.; Noreddin, A.; Rahman, T.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, M. Molecular Detection of Multidrug Resistant Salmonella Species Isolated from Broiler Farm in Bangladesh. Pathogens 2020, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Geng, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Induction of arthritis in chickens by infection with novel virulent Salmonella Pullorum strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 228, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.C.; Soria, M.A.; Bueno, D.J. Comparison of 2 culture methods and PCR assays for Salmonella detection in poultry feces. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Ed-Dra, A.; Yue, M. Epidemiological investigation and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella isolated from breeder chicken hatcheries in Henan, China. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ju, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Tang, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, S. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from dead-in-shell chicken embryos in Shandong, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 581946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Qi, X.; Zhang, R. Epidemiology of foodborne disease outbreaks caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella in Zhejiang Province, China, 2010-2019. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Kang, X.; Meng, C.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Prevalence of Salmonella isolates and their distribution based on whole-genome sequence in a chicken slaughterhouse in Jiangsu, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Chang, Y.; Su, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S. Occurrence and characterization of Salmonella isolated from large-scale breeder farms in Shandong Province, China. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8159567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Shao, X.; Huang, P.; Zha, J.; Ye, Y. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from retail meats in Anhui, China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4701–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Gu, X.; Sun, S. Occurrence and characterization of Salmonella isolated from chicken breeder flocks in nine chinese provinces. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K. CLSI methods development and standardization working group best practices for evaluation of antimicrobial susceptibility tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01934-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, S.; White, D.G.; Schroeder, C.M.; Lu, R.; Yang, H.; McDermott, P.F.; Ayers, S.; Meng, J. Characterization of multiple-antimicrobial-resistant salmonella serovars isolated from retail meats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Lertworapreecha, M.; Evans, M.C.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; Chalermchaikit, T.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Wegener, H.C. Antimicrobial susceptibility and occurrence of resistance genes among Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden from different countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, D.; Yin, X.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Zhao, H.; Bie, X. Occurrence, drug resistance, and virulence genes of Salmonella isolated from chicken and eggs. Food Control. 2020, 113, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyberg, J.A.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K. Virulence genotyping of Salmonella spp. with multiplex PCR. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P.; Mao, Y.; Liang, R.; Niu, L.; Luo, X. The Characterization of biofilm formation and detection of biofilm-related genes in Salmonella isolated from beef processing plants. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Su, J. Characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from diseased poultry in northern China between 2014 and 2018. Pathogens 2020, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, X.; Niu, Q.; Yang, B. Prevalence, serotype, antibiotic susceptibility, and genotype of Salmonella in eggs from poultry farms and marketplaces in Yangling, Shaanxi province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Xie, M.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Wu, C. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from an integrated broiler chicken supply chain in Qingdao, China. Food Control 2016, 62, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, K.; Ren, D.; Xiao, Y. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella from meat in slaughterhouses in Hangzhou, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 371, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasamsetti, S.; Berrang, M.E.; Cox, N.A.; Shariat, N.W. Assessing Salmonella prevalence and complexity through processing using different culture methods. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Elbediwi, M.; Zhou, X.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Yue, M. Characterization of Salmonella Dublin isolated from bovine and human hosts. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, J.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella species isolated from pigs, ducks and chickens in Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.B.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, B.; Shi, X.M. Serotype, genotype, and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Salmonella from chicken farms in Shanghai. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quino, W.; Caro-Castro, J.; Mestanza, O.; Hurtado, C.V.; Zamudio, M.L.; Gavilan, R.G. Phylogenetic structure of Salmonella Enteritidis provides context for a foodborne outbreak in Peru. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.K.; Chen, S.Y.; Wong, M.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Chu, C. Pathogenicity differences of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium, Enteritidis, and Choleraesuis-specific virulence plasmids and clinical S. Choleraesuis strains with large plasmids to the human THP-1 cell death. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, F.; McLauchlin, J.; Verlander, N.Q.; Aird, H.; Balasegaram, S.; Chattaway, M.A.; Dallman, T.; Herdman, M.T.; Hoban, A.; Lai, S.; et al. Levels and genotypes of Salmonella and levels of Escherichia coli in frozen ready-to-cook chicken and turkey products in England tested in 2020 in relation to an outbreak of S. Enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 369, 109609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari-Lari, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Manzari, M.; Khaledian, S. Survey of Salmonella in commercial broiler farms in Shiraz, southern Iran. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 198, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramtahal, M.A.; Amoako, D.G.; Akebe, A.L.K.; Somboro, A.M.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. A public health insight into Salmonella in poultry in Africa: A review of the past decade: 2010–2020. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 710–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Song, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of fluoroquinolone resistant Salmonella isolated from an integrated broiler chicken supply chain. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, B.; Wang, H. Antimicrobial resistance and CRISPR typing among Salmonella isolates from poultry farms in China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, N.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y. Genomic characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from retail meat in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigley, P.; Jones, M.A.; Barrow, P.A. Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum requires the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system for virulence and carriage in the chicken. Avian Pathol. 2002, 31, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Cuadrado, D.; Moreno, M.A.; Ugarte-Ruíz, M.; Domínguez, L. Antimicrobial resistance in the food chain in the European Union. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 86, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, D.R. Antibiotic resistance: A current epilogue. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 134, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wu, G.; He, X.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity of Salmonella enterica from eggs. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2847–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, M.; El-Hadidi, M.; Huson, D.H.; Schütz, M.; Weidenmaier, C.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Peter, S. Antibiotic selection pressure determination through sequence-based metagenomics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7335–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Prevalence and characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica isolates from retail foods in Shanghai, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Co-existence of mphA, oqxAB and blaCTX-M-65 on the IncHI2 Plasmid in highly drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana ST17 isolated from retail foods and humans in China. Food Control 2020, 118, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Tartor, Y.H.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; Erfan, A.M.; Khalifa, E.; Said, M.A.; Ammar, A.M.; Samir, M. Extensive drug-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and humans: Prevalence and molecular determinants behind the co-resistance to ciprofloxacin and tigecycline. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 738784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourély, C.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Jouy, E.; Haenni, M.; Lupo, A.; Madec, J.Y.; Leblond, A.; Gay, E. Co-resistance to amoxicillin and tetracycline as an indicator of multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from animals. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.G.; de Melo, R.T.; Dumont, C.F.; Peixoto, J.L.M.; Ferreira, G.R.A.; Chueiri, M.C.; Iasbeck, J.R.; Timóteo, M.F.; de Araújo Brum, B.; Rossi, D.A. Agents of campylobacteriosis in different meat matrices in Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xu, T.; Sun, S.; Yan, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jia, J.; Dou, T. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria: Occurrence, spread, and control. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.J.; Oldenkamp, R.; Ragas, A.M.J. Modelling environmental antibiotic-resistance gene abundance: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafourian, S.; Sadeghifard, N.; Soheili, S.; Sekawi, Z. Extended spectrum beta-lactamases: Definition, classification and epidemiology. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2015, 17, 11–21. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24821872/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Mei, X.; Ma, B.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, A.; Lei, C.; Zuo, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. Florfenicol enhances colonization of a Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis floR mutant with major alterations to the intestinal microbiota and metabolome in neonatal chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0168121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sinha, P.; Nema, V.; Gupta, P.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Kulkarni, S.; Rastogi, N.; Anupurba, S. Detection of Beijing strains of MDR M. tuberculosis and their association with drug resistance mutations in katG, rpoB, and embB genes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yin, L.; Ma, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, R.; Dai, Y.; Hou, H.; Hu, X. Comprehensive genomic analysis and characterization of a new ST 174 type Klebsiella variicola strain isolated from chicken embryos. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 90, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, A.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Broere, F.; Rutten, V.; Jansen, C.A. The interplay between Salmonella and intestinal innate immune cells in chickens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andesfha, E.; Indrawati, A.; Mayasari, N.; Rahayuningtyas, I.; Jusa, I. Detection of Salmonella pathogenicity island and Salmonella plasmid virulence genes in Salmonella Enteritidis originated from layer and broiler farms in Java Island. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, T.; Shao, H.; Han, X.; Gong, J. Virulence gene distribution of Salmonella Pullorum isolates recovered from chickens in China (1953–2015). Avian Dis. 2018, 62, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ju, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, S. Serotype, antimicrobial susceptibility and genotype profiles of Salmonella isolated from duck farms and a slaughterhouse in Shandong province, China. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Barrow, P.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. The SseL protein inhibits the intracellular NF-κB pathway to enhance the virulence of Salmonella Pullorum in a chicken model. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, S.; Deng, Q.; Dong, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, R. Salmonella effector SpvB disrupts intestinal epithelial barrier integrity for bacterial translocation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 606541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemfareji, O.I.; Thong, K.L. Comparative virulotyping of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella enteritidis. Indian J. Microbiol. 2013, 53, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanguiné, A.Y.; D’Alessandro, B.; Langleib, M.; Traglia, G.M.; Mónaco, A.; Durán, R.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Betancor, L.; Yim, L. Salmonella enterica Serovars Dublin and Enteritidis comparative proteomics reveals differential expression of proteins involved in stress resistance, virulence, and anaerobic Metabolism. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00606-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Agarwal, R.K.; Bhilegaonkar, K.N.; Kumar, A.; Nambiar, P.; Rawat, S.; Singh, M. Cloning and sequencing of biofilm-associated protein (bapA) gene and its occurrence in different serotypes of Salmonella. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; King, D.A.; Kalchayanand, N. Evaluation of Salmonella biofilm cell transfer from common food contact surfaces to beef products. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, K.A.; Furian, T.Q.; de Souza, S.N.; Menezes, R.; de Lima, D.A.; Fortes, F.B.B.; Salle, C.T.P.; Moraes, H.L.S.; Nascimento, V.P. Biofilm formation by Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from avian sources is partially related with their in vivo pathogenicity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, S.A.; Tshimpamba, M.E.; Mwanza, M.; Ateba, C.N. Biofilm production potential of Salmonella Serovars isolated from chickens in north west province, South Africa. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, L.; Aliakbarlu, J.; Dastmalchi Saei, H. Antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation ability of Salmonella serotypes isolated from beef, mutton, and meat contact surfaces at retail. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2516–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Goulart, L.R.; Reis, T.F.M.; Mendonça, E.P.; Melo, R.T.; Penha, V.A.S.; Peres, P.; Hoepers, P.G.; Beletti, M.E.; Fonseca, B.B. Biofilm formation in different Salmonella serotypes isolated from poultry. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougue, A.N.; El-Kholy, M.A.; Giuffrè, L.; Galeano, G.; D′Aleo, F.; Kountchou, C.L.; Nangwat, C.; Dzoyem, J.P.; Giosa, D.; Pernice, I.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) analysis reveals many novel genotypes and a high level of genetic diversity in Candida tropicalis isolates from Italy and Africa. Mycoses 2022, 65, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, T.; Roasto, M.; Mäesaar, M.; Kisand, V.; Ivanova, M.; Meremäe, K. The prevalence, counts, and MLST genotypes of Campylobacter in poultry meat and genomic comparison with clinical isolates. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Q.; Wen, G.; Wang, G.; Shao, H.; Zhang, T. Quinolone resistance phenotype and genetic characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum isolates in China, during 2011 to 2016. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Chang, W. Prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella isolated from free-range chickens in Shandong Province, China. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8183931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L.; Sharif, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, R.M.; Husin, S.A.; Hazis, N.; Sohaimi, N.F.M.; Bakar, S.A.; Garba, B. Analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates from chickens and chicken meat products in Malaysia using PFGE, and MLST. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ktari, S.; Ksibi, B.; Gharsallah, H.; Mnif, B.; Maalej, S.; Rhimi, F.; Hammami, A. Molecular epidemiological characteristics of Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis, Typhimurium and Livingstone strains isolated in a Tunisian university hospital. Apmis 2016, 124, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ge, H.; He, J.; Hu, M.; Xu, Z.; Jiao, X.; Chen, X. Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 isolate was more resistant than the ST19 isolate in China, 2007– 2019. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ke, B.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C. The molecular epidemiological characteristics and genetic diversity of Salmonella typhimurium in Guangdong, China, 2007–2011. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C.; Zeng, H.; Wei, X.; Gu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Prevalence, abundance, serovars and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from retail raw poultry meat in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fanning, S.; Nguyen, S.V.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Cui, X.; Dong, Y.; Gan, X.; Xu, J.; Li, F. Emergence of a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST34 isolate, CFSA629, carrying a novel mcr-1.19 variant cultured from egg in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, R.K.; Thakur, Z.; Anand, T.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, B.N. Comparative genome analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum decodes strain specific genes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).