rMELEISH: A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope-Based Protein Applied to the Serodiagnosis of Both Canine and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites
2.2. Canine Sera
2.3. Human Samples
2.4. Design of the Synthetic Gene, Cloning, and Expression
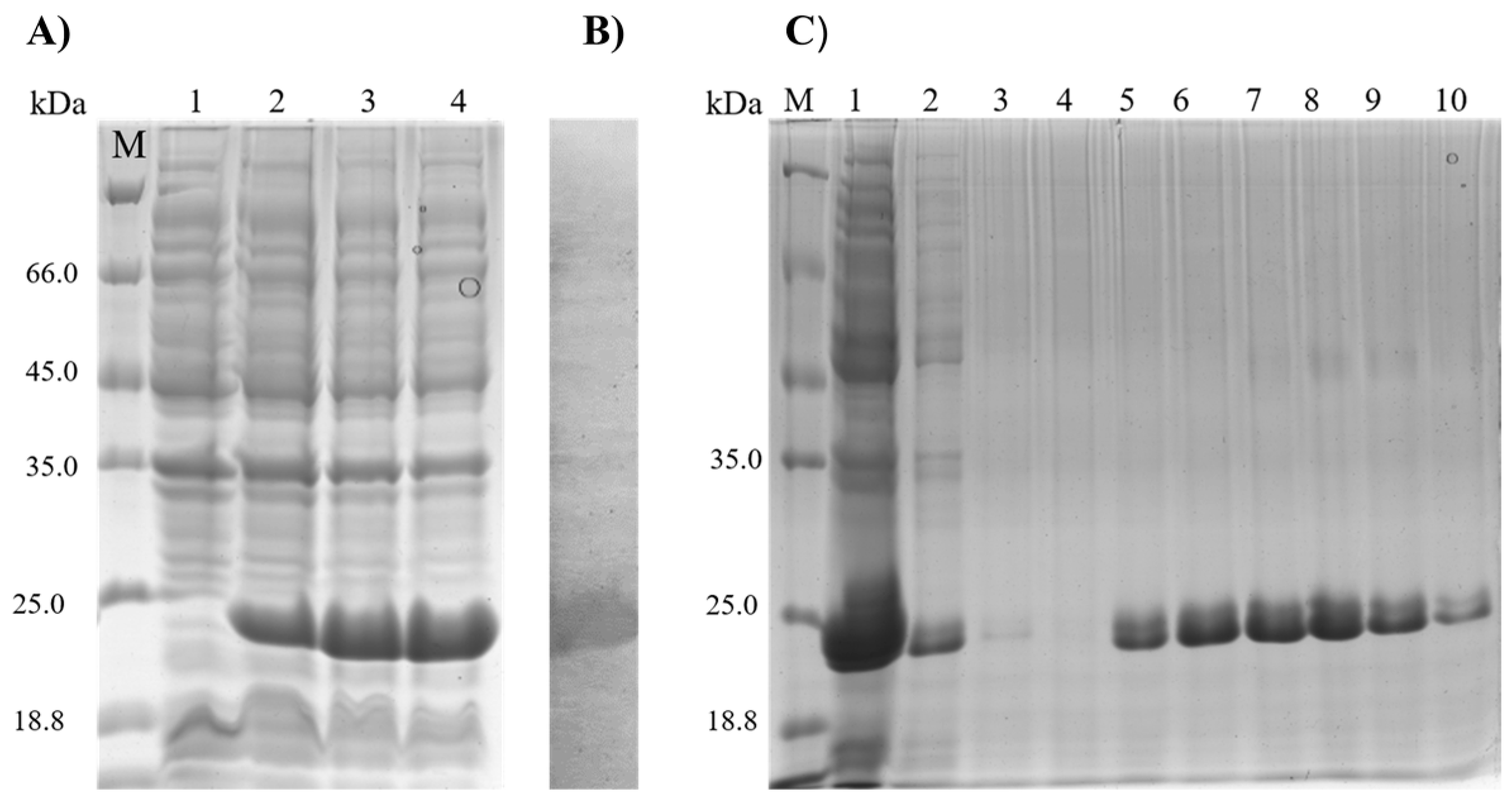
2.5. Purification of the rMELEISH Protein
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
2.7. ELISA Assay
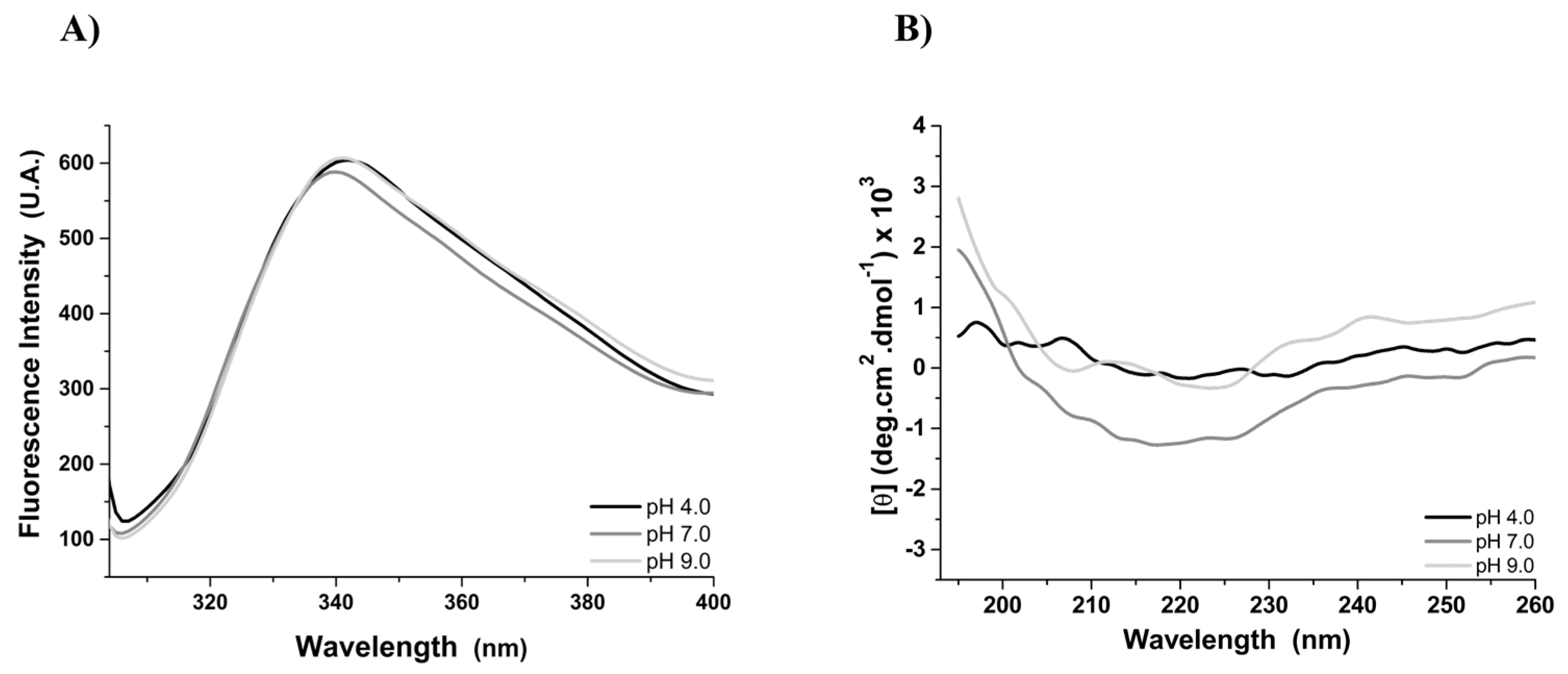
2.8. Fluorescence and Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization and Purification of the rMELEISH Protein
3.2. Tertiary and Secondary Structure of the rMELEISH Protein
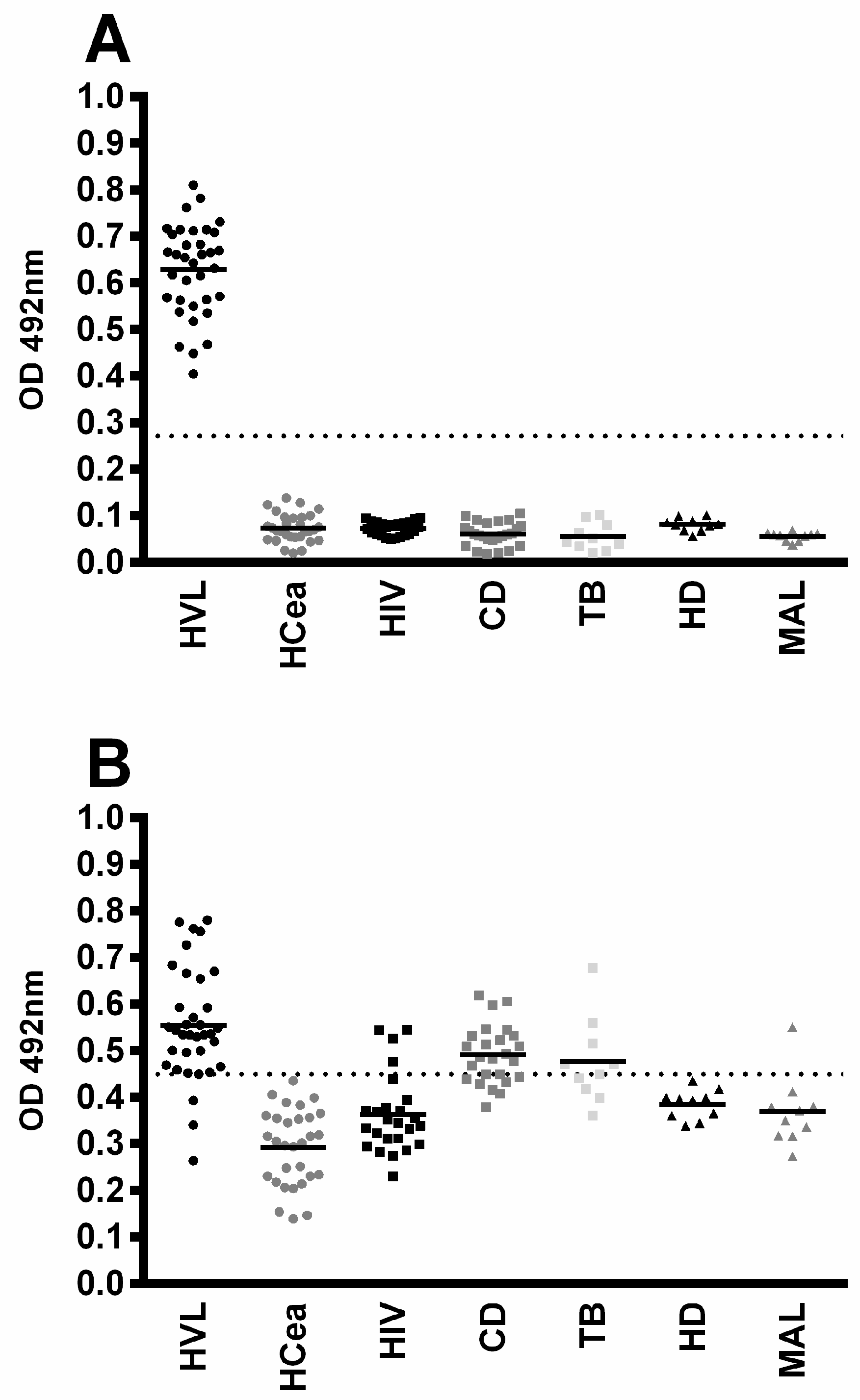
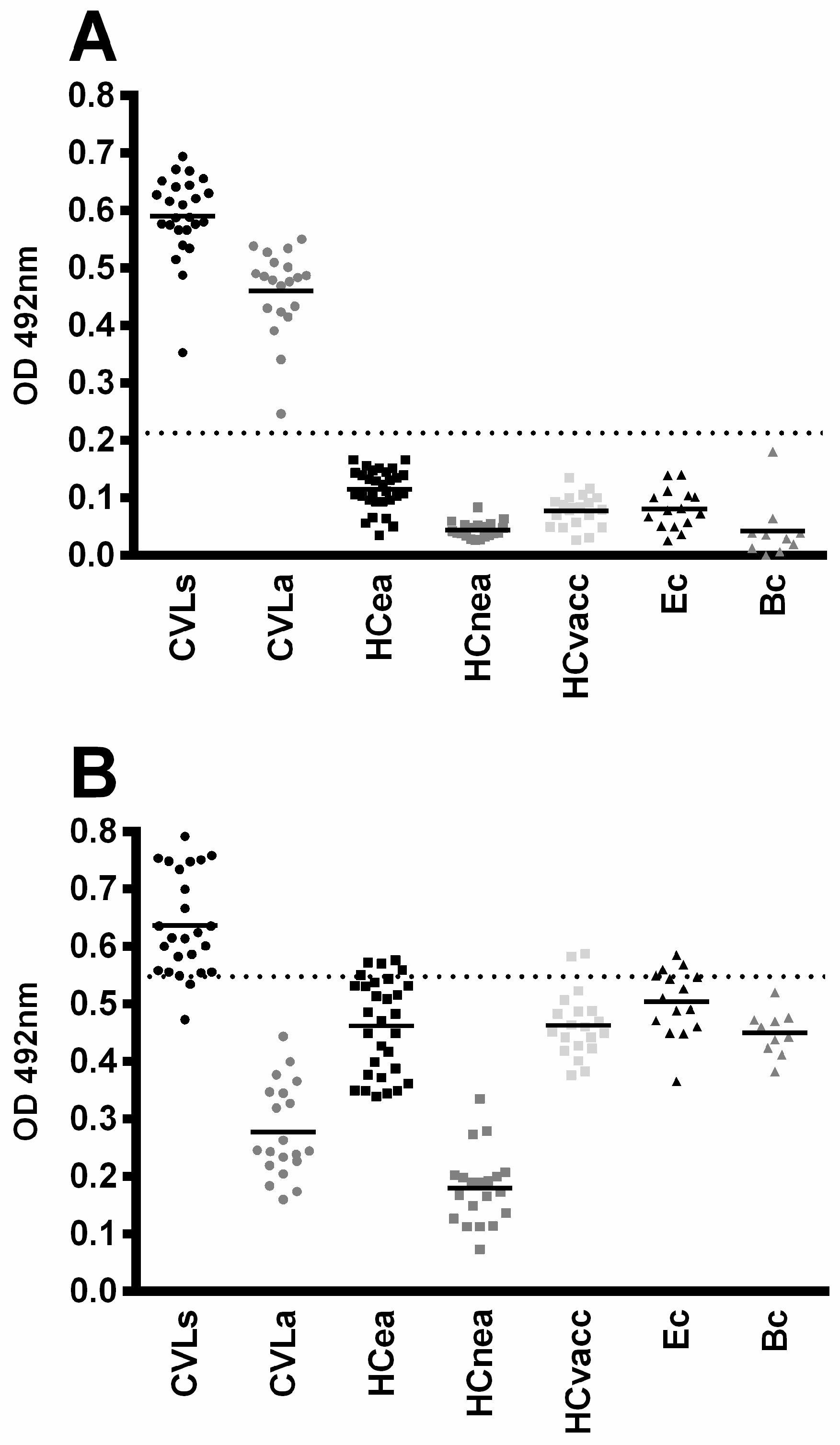
3.3. Diagnostic Evaluation of rMELEISH for Human VL
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis, 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/topic-details/GHO/leishmaniasis (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Alvar, J.; Vélez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; Boer, M. den Leishmaniasis Worldwide and Global Estimates of Its Incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, F.R.P.; Morais, M.H.F.; Cardoso, D.L.; Bruhn, N.C.P.; Ferreira, F.; Rocha, C.M.B.M. Spatial and Temporal Relationships between Human and Canine Visceral Leishmaniases in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, 2006–2013. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenti, M.D.; Rossi, C.N.; Matta, V.L.R.D.; Tomokane, T.Y.; Corbett, C.E.P.; Secundino, N.F.C.; Pimenta, P.F.P.; Marcondes, M. Asymptomatic Dogs Are Highly Competent to Transmit Leishmania (Leishmania) Infantum Chagasi to the Natural Vector. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.R.; de Castro Veloso, L.; Coura-Vital, W.; Reis, A.B.; Damasceno, L.M.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Andrade, H.M. Novel Recombinant Multiepitope Proteins for the Diagnosis of Asymptomatic Leishmania Infantum-Infected Dogs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, M.H.F.; Sabroza, P.C.; Pessanha, J.E.; Sobral, A. Visceral Leishmaniasis Control Actions: Epidemiological Indicators for Its Effectiveness Evaluation in a Brazilian Urban Area. Cad Saude Publica 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podaliri Vulpiani, M.; Iannetti, L.; Paganico, D.; Iannino, F.; Ferri, N. Methods of Control of the Leishmania Infantum Dog Reservoir: State of the Art. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 215964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özbel, Y.; Turgay, N.; Özensoy, S.; Özbilgin, A.; Alkan, M.Z.; Özcel, M.A.; Jaffe, C.L.; Schnur, L.; Oskam, L.; Abranches, P. Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Control of Leishmaniasis in the Mediterranean Region. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1995, 89, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, R.B. Control of Zoonotic Visceral Leishmaniasis: Is It Time to Change Strategies? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 52, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, C. The Logic of Visceral Leishmaniasis Control. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Ghalehbin, B.; Reza Hatam, G.; Sarkari, B.; Mohebali, M.; Zarei, Z.; Jaberipour, M.; Bohlouli, S. A Leishmania infantum FML-ELISA for the Detection of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis in an Endemic Area of Iran. Iran. J. Immunol. 2011, 8, 244–250. [Google Scholar]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Villanueva-Saz, S.; Carbonell, M.; Trotta, M.; Furlanello, T.; Natale, A. Serological Diagnosis of Canine Leishmaniosis: Comparison of Three Commercial ELISA Tests (Leiscan®, ID Screen® and Leishmania 96®), a Rapid Test (Speed Leish K®) and an in-House IFAT. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Arruda, M.M.; Figueiredo, F.B.; Cardoso, F.A.; Hiamamoto, R.M.; Brazuna, J.C.M.; de Oliveira, M.R.F.; Noronha, E.F.; Romero, G.A.S. Validity and Reliability of Enzyme Immunoassays Using Leishmania major or L. Infantum Antigens for the Diagnosis of Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, M.L.; Machado de Assis, T.; Oliveira, E.; Moreira de Avelar, D.; Siqueira, I.C.; Barral, A.; Rabello, A.; Cota, G. Performance of Serological Tests Available in Brazil for the Diagnosis of Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.L.; de Souza, A.; Cota, G.; Rabello, A.; Machado de Assis, T. Cost-Effectiveness of Serological Tests for Human Visceral Leishmaniasis in the Brazilian Scenario. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, G.; Teva, A.; Ferreira, A.L.; dos Santos, C.B.; Pinto, I. de-S.; de-Azevedo, C.T.; Falqueto, A. Evaluation of a Novel Chromatographic Immunoassay Based on Dual-Path Platform Technology (DPP® CVL Rapid Test) for the Serodiagnosis of Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 106, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.R.; Costa, M.M.; Giusta, M.S.; Grimaldi, G.; Penido, M.L.O.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Andrade, H.M.; Andrade, H.M. High-Throughput Analysis of Synthetic Peptides for the Immunodiagnosis of Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.G.; Sevá, A.P.; Ferreira, F.; Nunes, C.M.; Keid, L.B.; Hiramoto, R.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Oliveira, T.M.F.S.; Bigotto, M.F.D.; Galvis-Ovallos, F.; et al. Serological and Molecular Diagnostic Tests for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis in Brazilian Endemic Area: One out of Five Seronegative Dogs Are Infected. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2436–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa-e-Silva, R.; Vaitkevicius-Antão, V.; de Andrade, T.A.S.; de Oliveira Silva, A.C.; de Oliveira, G.A.; Trajano-Silva, L.A.M.; Nakasone, E.K.N.; de Paiva-Cavalcanti, M. The Diagnosis of Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis in Brazil: Confronting Old Problems. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 199, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Rai, M. Laboratory Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2002, 9, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, M.; Nahrevanian, H. Application of Recombinant Proteins for Serodiagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Humans and Dogs. Iran. Biomed. J. 2016, 20, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameie, F.; Dalimi, A.; Pirestani, M.; Mohebali, M. Development of a Multi-Epitope Recombinant Protein for the Diagnosis of Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. Iran J. Parasitol. 2021, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, P.; Bandehpour, M.; Mohebali, M.; Akhoundi, B.; Kazemi, B. Designing and Evaluation of a Recombinant Multiepitope Protein by Using ELISA for Diagnosis of Leishmania Infantum Infected in Dogs. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2021, 16, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengo, B.N.; Shintouo, C.M.; Hotterbeekx, A.; Yaah, N.E.; Shey, R.A.; Quanico, J.; Baggerman, G.; Ayong, L.; Vanhamme, L.; Njemini, R.; et al. Immunoinformatics Design and Assessment of a Multiepitope Antigen (OvMCBL02) for Onchocerciasis Diagnosis and Monitoring. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameie, F.; Dalimi, A.; Pirestani, M.; Mohebali, M. Detection of Leishmania Infantum Infection in Reservoir Dogs Using a Multiepitope Recombinant Protein (PQ10). Arch. Razi Inst. 2020, 75, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, T.H.S.; Faria, A.R.; Leite, H.M.; da Silveira, J.A.G.; Carneiro, C.M.; Andrade, H.M. Chemiluminescent ELISA with Multi-Epitope Proteins to Improve the Diagnosis of Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. Vet. J. 2019, 253, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomasini, R.L.; Souza, H.G.A.; Bruna-Romero, O.; Totola, A.H.; Gonçales, N.S.L.; Lima, C.X.; Teixeira, M.M. Evaluation of a Recombinant Multiepitope Antigen for Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Virus: A Lower Cost Alternative for Antigen Production. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, A.S.; Santos, J.C.; Souza, M.Q.; Nóbrega, Y.K.M.; Xavier, M.-A.E.; Felipe, M.S.S.; Freitas, S.M.; Torres, F.A.G. A Novel Structurally Stable Multiepitope Protein for Detection of HCV. Hepat. Res. Treat. 2016, 2016, 6592143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, D.P.; Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Dias, D.S.; Mendonça, D.V.C.; Ramos, F.F.; Carvalho, L.M.; de Oliveira, D.; Steiner, B.T.; Martins, V.T.; Perin, L.; et al. A Candidate Vaccine for Human Visceral Leishmaniasis Based on a Specific T Cell Epitope-Containing Chimeric Protein Protects Mice against Leishmania infantum Infection. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi, A.; Kefayat, A.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Salehi, M.; Modarressi, M.H. Production, Purification, and in Vivo Evaluation of a Novel Multiepitope Peptide Vaccine Consisted of Immunodominant Epitopes of SYCP1 and ACRBP Antigens as a Prophylactic Melanoma Vaccine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Bai, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, J. Study on Immunogenicity and Antigenicity of a Novel Brucella Multiepitope Recombined Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 540, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, E.A.F.; Tavares, C.A.P.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Chaves, K.F.; Teixeira, K.N.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Charest, H.; Matlashewski, G.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Fernandes, A.P. Immune Responses Induced by the Leishmania (Leishmania) donovani A2 Antigen, but Not by the LACK Antigen, Are Protective against Experimental Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis Infection. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3988–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 Web Portal for Protein Modeling, Prediction and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera. A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.J.; Greenfield, N.J.; Fasman, G.D. Circular Dichroism and Optical Rotatory Dispersion of Proteins and Polypeptides. Methods Enzym. 1973, 27, 675–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, B.; Alemayehu, M. Leishmaniasis: A Review on Parasite, Vector and Reservoir Host. Health Sci. J. 2017, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis, 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Taherzadeh, M.; Fouladvand, M.; Kazemi, B. Evaluation of a New Multi-Epitope Sequence of Eight Known Leishmania Infantum Antigens for HVL Diagnosis by ELISA and Western Blot. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2021, 58, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driemeier, M.; de Oliveira, P.A.; Druzian, A.F.; Lopes Brum, L.F.; Pontes, E.R.J.C.; Dorval, M.E.C.; Paniago, A.M.M. Late Diagnosis: A Factor Associated with Death from Visceral Leishmaniasis in Elderly Patients. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipti, C.A.; Jain, S.K.; Navin, K. A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope Protein as a Hepatitis C Diagnostic Intermediate of High Sensitivity and Specificity. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Souza, M.Q.; Dias, D.S.; Álvares, A.C.M.; Nogueira, L.M.; Machado, J.M.; dos Santos, J.C.; Godoi, R.R.; Nobrega, Y.K.M.; Campos-da-Paz, M.; et al. A Custom-Designed Recombinant Multiepitope Protein for Human Cytomegalovirus Diagnosis. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2019, 13, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.K.; Gull, K.; Miles, M.A. Antibodies to Tubulin in Patients with Parasitic Infections. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1987, 68, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Badaro, R.; Benson, D.; Eulalio, M.C.; Freire, M.; Cunha, S.; Netto, E.M.; Pedral-Sampaio, D.; Madureira, C.; Burns, J.M.; Houghton, R.L.; et al. RK39: A Cloned Antigen of Leishmania chagasi That Predicts Active Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.M.; Shreffler, W.G.; Benson, D.R.; Ghalib, H.W.; Badaro, R.; Reed, S.G. Molecular Characterization of a Kinesin-Related Antigen of Leishmania chagasi That Detects Specific Antibody in African and American Visceral Leishmaniasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.-Q.; Zhong, L.; Masoom-Yasinzai, M.; Abdur-Rab, M.; Aksu, H.S.Z.; Reed, S.G.; Chang, K.-P.; Gilman-Sachs, A. Serodiagnosis of Asian Leishmaniasis with a Recombinant Antigen from the Repetitive Domain of a Leishmania Kinesin. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 88, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Gilman-Sachs, A.; Chang, K.-P.; Reed, S.G. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of K39 Recombinant Antigen in Indian Leishmaniasis. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, E.E.; Daifalla, N.S.; Kager, P.A.; Khalil, E.A.G.; El-Hassan, A.M.; Reed, S.G.; Ghalib, H.W. RK39 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Leishmania donovani Infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerpa, O.; Ulrich, M.; Negrón, E.; Rodríguez, N.; Centeno, M.; Rodríguez, V.; Barrios, R.M.; Belizario, D.; Reed, S.; Convit, J. Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis on Margarita Island (Nueva Esparta, Venezuela). Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 94, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalone, A.; de Luna, R.; Oliva, G.; Baldi, L.; Satta, G.; Vesco, G.; Mignone, W.; Turilli, C.; Mondesire, R.R.; Simpson, D.; et al. Evaluation of the Leishmania Recombinant K39 Antigen as a Diagnostic Marker for Canine Leishmaniasis and Validation of a Standardized Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 104, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, M.; Zavaran Hoseini, A.; Kazemi, B.; Alborzi, A.; Kiany, S. Expression of Recombinant Heat-Shock Protein 70 of MCAN/IR/96/LON-49, a Tool for Diagnosis and Future Vaccine Research. Iran J. Immunol. 2009, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Vergnes, B.; Gourbal, B.; Girard, I.; Sundar, S.; Drummelsmith, J.; Ouellette, M. A Proteomics Screen Implicates HSP83 and a Small Kinetoplastid Calpain-Related Protein in Drug Resistance in Leishmania donovani Clinical Field Isolates by Modulating Drug-Induced Programmed Cell Death. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, A.I.; Gironès, N.; Fresno, M.; Alonso, C.; Requena, J.M. The Heat Shock Proteins, Hsp70 and Hsp83, of Leishmania Infantum Are Mitogens for Mouse B Cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2002, 7, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, P.; Dran, G.; Pereda, G.; Rico, A.I.; Requena, J.M.; Alonso, C.; Guarnera, E.; Angel, S.O. Analysis of the Adjuvant Effect of Recombinant Leishmania infantum Hsp83 Protein as a Tool for Vaccination. Immunol. Lett. 2001, 76, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada, L.; Requena, J.M.; Soto, M.; Gómez, L.C.; Guzman, F.; Patarroyo, M.E.; Alonso, C. Mapping of the Linear Antigenic Determinants of the Leishmania infantum Hsp70 Recognized by Leishmaniasis Sera. Immunol. Lett. 1996, 52, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada, L. Analysis of the Antigenic Properties of the L. Infantum Hsp70: Design of Synthetic Peptides for Specific Serodiagnosis of Human Leishmaniasis. Immunol. Lett. 1998, 63, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeiky, Y.A.; Benson, D.R.; Guderian, J.A.; Whittle, J.A.; Bacelar, O.; Carvalho, E.M.; Reed, S.G. Immune Responses of Leishmaniasis Patients to Heat Shock Proteins of Leishmania Species and Humans. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4105–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, D.L.; Lage, D.P.; Machado, A.S.; Freitas, C.S.; de Oliveira, D.; Galvani, N.C.; Fernandes, B.B.; Luiz, G.P.; Oliveira, J.S.; Oliveira-da-Silva, J.A.; et al. Serodiagnosis of Canine Leishmaniasis Using a Novel Recombinant Chimeric Protein Constructed with Distinct B-Cell Epitopes from Antigenic Leishmania Infantum Proteins. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 296, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.Q.; Galdino, A.S.; dos Santos, J.C.; Soares, M.V.; Nóbrega, Y.C.D.; Álvares, A.D.C.M.; de Freitas, S.M.; Torres, F.A.G.; Felipe, M.S.S. A Recombinant Multiepitope Protein for Hepatitis B Diagnosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 148317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Canine Sera | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen | AUC | p-Value | Cut-Off | Se | 95%CI | Sp | 95%CI | J |
| rMELEISH | 1.0 | <0.0001 | >0.2130 | 100 | 92.13–100 | 100 | 96.19–100 | 1.0 |
| SLA | 0.63 | 0.017 | >0.5480 | 51.11 | 35.77–66.30 | 88.42 | 80.23–94.08 | 0.39 |
| Human Sera | ||||||||
| Antigen | AUC | p-Value | Cut-Off | Se | 95%CI | Sp | 95%CI | J |
| rMELEISH | 1.0 | <0.0001 | >0.2712 | 100 | 90.00–100 | 100 | 96.70–100 | 1.0 |
| SLA | 0.86 | <0.0001 | >0.4493 | 91.43 | 76.94–98.20 | 76.36 | 67.32–83.94 | 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, D.S.; Machado, J.M.; Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Machado, A.S.; Ramos, F.F.; Nogueira, L.M.; Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Ramos, L.d.S.; Gandra, I.B.; Coutinho, F.S.; et al. rMELEISH: A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope-Based Protein Applied to the Serodiagnosis of Both Canine and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020302
Dias DS, Machado JM, Ribeiro PAF, Machado AS, Ramos FF, Nogueira LM, Gonçalves AAM, Ramos LdS, Gandra IB, Coutinho FS, et al. rMELEISH: A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope-Based Protein Applied to the Serodiagnosis of Both Canine and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens. 2023; 12(2):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020302
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Daniel Silva, Juliana Martins Machado, Patrícia Aparecida Fernandes Ribeiro, Amanda Sanchez Machado, Fernanda Fonseca Ramos, Lais Moreira Nogueira, Ana Alice Maia Gonçalves, Luana de Sousa Ramos, Isadora Braga Gandra, Flaviane Silva Coutinho, and et al. 2023. "rMELEISH: A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope-Based Protein Applied to the Serodiagnosis of Both Canine and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis" Pathogens 12, no. 2: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020302
APA StyleDias, D. S., Machado, J. M., Ribeiro, P. A. F., Machado, A. S., Ramos, F. F., Nogueira, L. M., Gonçalves, A. A. M., Ramos, L. d. S., Gandra, I. B., Coutinho, F. S., Santos, M. d., Silva, J. O. d., Chávez-Fumagalli, M. A., Teixeira-Neto, R. G., Chaves, A. T., Campos-da-Paz, M., Souza, A. A., Giunchetti, R. C., Freitas, S. M., ... Galdino, A. S. (2023). rMELEISH: A Novel Recombinant Multiepitope-Based Protein Applied to the Serodiagnosis of Both Canine and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens, 12(2), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020302










