Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Neuropeptide Transcript Levels in the Synganglion of Ixodes ricinus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Ticks
2.2. Irradiation Procedure
2.3. Dissection Protocol
2.4. RNA Isolation of Tick Synganglia and Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
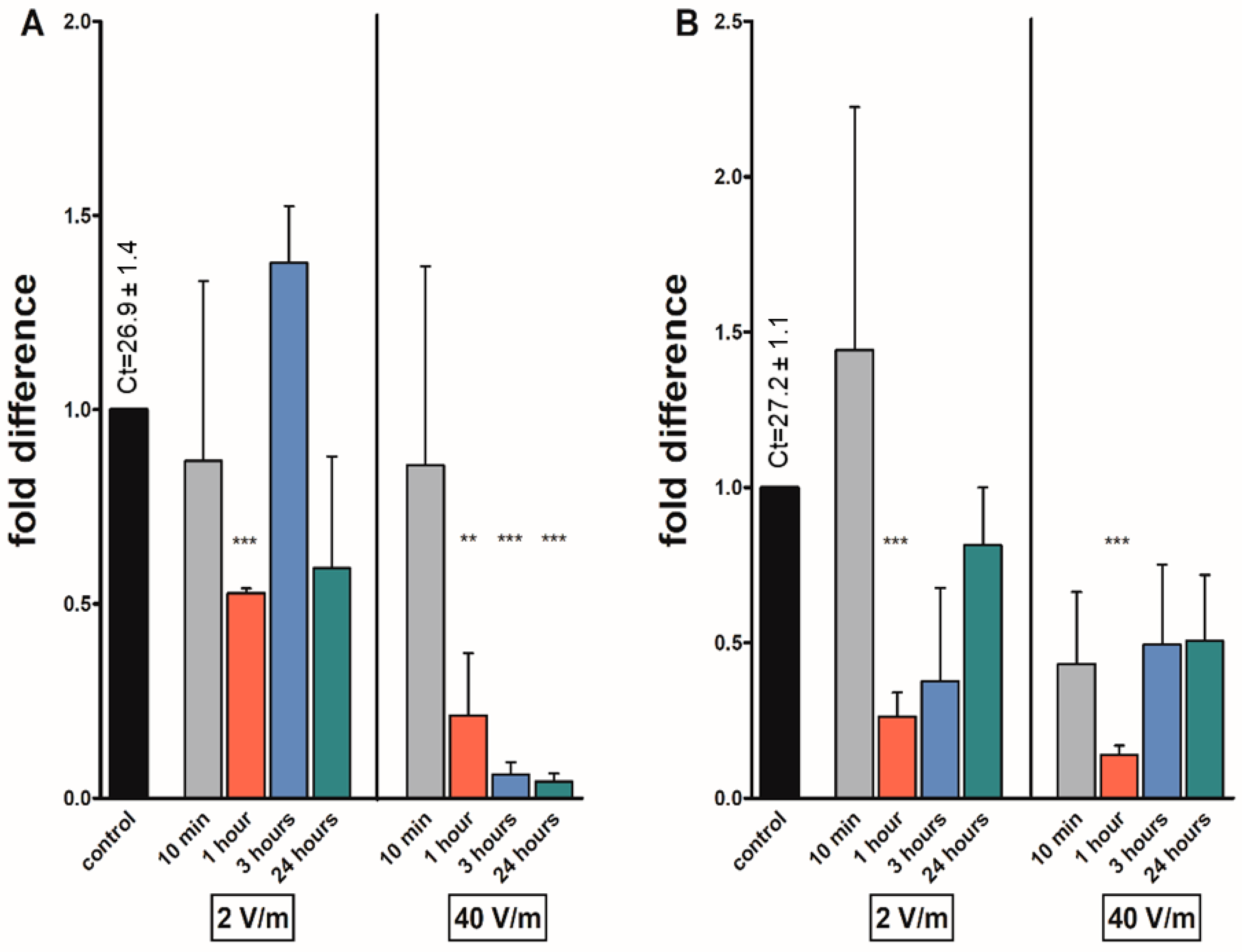
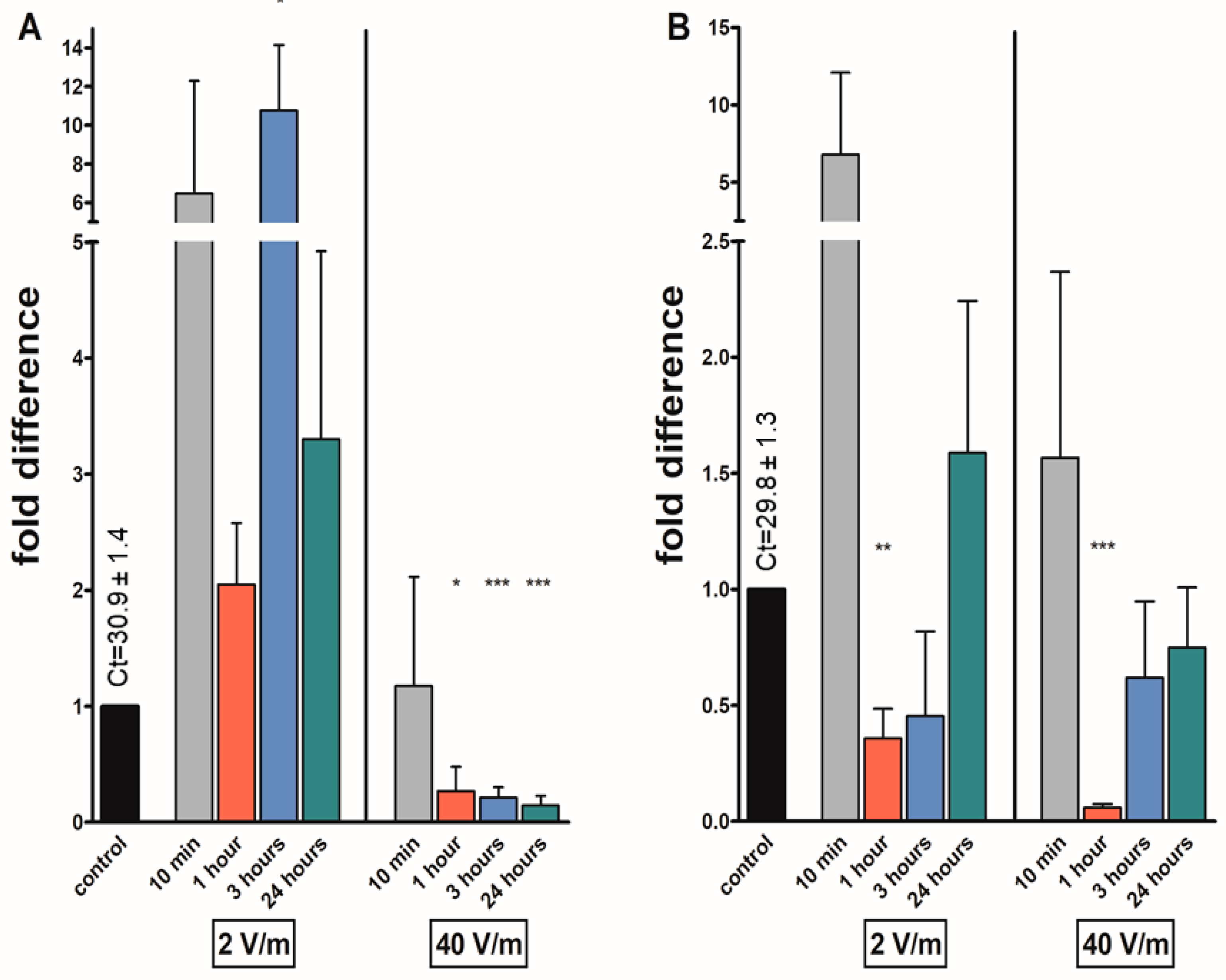
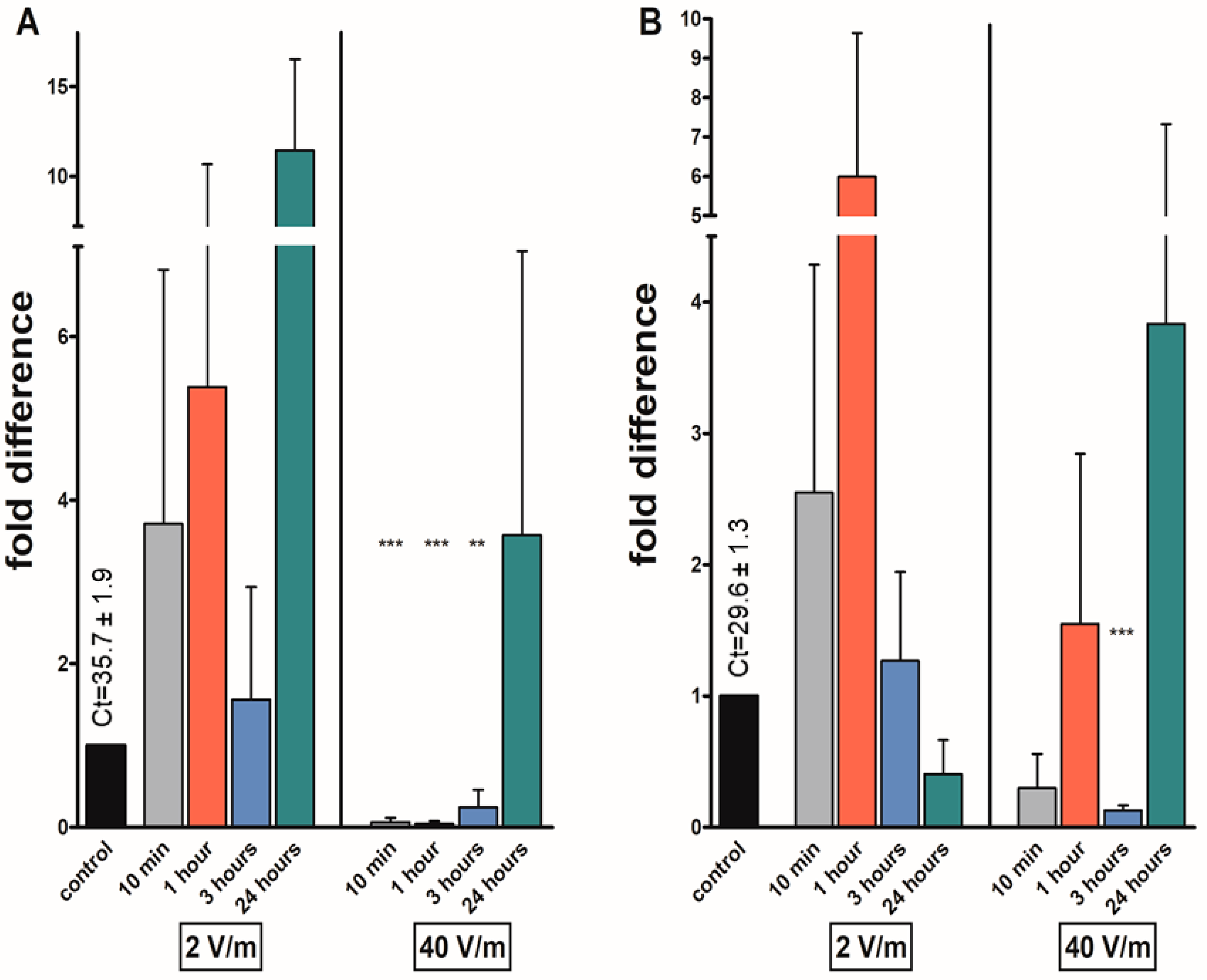
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balmori, A. Electromagnetic Radiation as an Emerging Driver Factor for the Decline of Insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Kaur, R. Electromagnetic Fields: Biological Implications on Various Life Forms. Int. J. Bioassays 2014, 3, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar]
- De Iuliis, G.N.; Newey, R.J.; King, B.V.; Aitken, R.J. Mobile Phone Radiation Induces Reactive Oxygen Species Production and DNA Damage in Human Spermatozoa in Vitro. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubay, M.; Yahyazadeh, A.; Deniz, Ö.G.; Kıvrak, E.G.; Altunkaynak, B.Z.; Erdem, G.; Kaplan, S. Effects of Prenatal 900 MHz Electromagnetic Field Exposures on the Histology of Rat Kidney. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Montenegro, M.A.; Acuña-Rodríguez, I.S.; Ballesteros, G.I.; Baldelomar, M.; Torres-Díaz, C.; Broitman, B.R.; Vázquez, D.P. Electromagnetic Fields Disrupt the Pollination Service by Honeybees. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; Hwang, Y.R.; Park, H.R.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.-G.; Kim, H.R. Exposure to RF-EMF Alters Postsynaptic Structure and Hinders Neurite Outgrowth in Developing Hippocampal Neurons of Early Postnatal Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J.; Chavdoula, E.D.; Nezis, I.P.; Margaritis, L.H. Cell Death Induced by GSM 900-MHz and DCS 1800-MHz Mobile Telephony Radiation. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 626, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Shepherd, S.; Sharkh, S.; Jackson, C.W.; Newland, P.L. Exposure to Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Alters the Behaviour, Physiology and Stress Protein Levels of Desert Locusts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, E.M.; Sharpe, P.T.; Greenebaum, B.; Marron, M.T. Pulsed Magnetic Fields Alter the Cell Surface. FEBS Lett. 1986, 199, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.J.; Prato, F.S.; Drost, D.J.; Diesbourg, L.D.; Dixon, S.J. Time-Varying Magnetic Fields Increase Cytosolic Free Ca2+ in HL-60 Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1990, 259, C687–C692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindströum, E.; Lindströum, P.; Berglund, A.; Mild, K.H.; Lundgren, E. Intracellular Calcium Oscillations Induced in a T-Cell Line by a Weak 50 Hz Magnetic Field. J. Cell. Physiol. 1993, 156, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, M.H.; Abd El Halim, N.; Khalil, W.A. Effect of Microwave Radiation on the Biophysical Properties of Liposomes. Bioelectromagnetics 2005, 26, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabi, N.; Mobasheri, H.; Faraji-Dana, R. Electromagnetic Fields (UHF) Increase Voltage Sensitivity of Membrane Ion Channels; Possible Indication of Cell Phone Effect on Living Cells. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunkaynak, B.Z.; Altun, G.; Yahyazadeh, A.; Kaplan, A.A.; Deniz, O.G.; Türkmen, A.P.; Önger, M.E.; Kaplan, S. Different Methods for Evaluating the Effects of Microwave Radiation Exposure on the Nervous System. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J.; Karabarbounis, A.; Yakymenko, I.; Chrousos, G.P. Human-made Electromagnetic Fields: Ion Forced-oscillation and Voltage-gated Ion Channel Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, C.; Haudek, V.; Schandl, U.; Bayer, E.; Gundacker, N.; Hutter, H.P.; Mosgoeller, W. Increased Protein Synthesis by Cells Exposed to a 1800-MHz Radio-Frequency Mobile Phone Electromagnetic Field, Detected by Proteome Profiling. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. 2010, 83, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Blank, M.; Goodman, R. A Magnetic Field-Responsive Domain in the Human HSP70 Promoter. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 75, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyz, J.; Guan, K.; Zeng, Q.; Nikolova, T.; Meister, A.; Schönborn, F.; Schuderer, J.; Kuster, N.; Wobus, A.M. High Frequency Electromagnetic Fields (GSM Signals) Affect Gene Expression Levels in Tumor Suppressor P53-Deficient Embryonic Stem Cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2004, 25, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.-Y.; Zou, S.-P.; Knapp, P.E. Exposure to Cell Phone Radiation Up-Regulates Apoptosis Genes in Primary Cultures of Neurons and Astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, A.; Pesce, M.; Grilli, A.; Speranza, L.; Franceschelli, S.; De Lutiis, M.A.; Vianale, G.; Costantini, E.; Amerio, P.; Muraro, R.; et al. MTOR Activation by PI3K/Akt and ERK Signaling in Short ELF-EMF Exposed Human Keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; Goodman, R. Electromagnetic Fields Stress Living Cells. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, S.; Erdem, G. Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 3933–3941. [Google Scholar]
- Newland, P.L.; Al Ghamdi, M.S.; Sharkh, S.; Aonuma, H.; Jackson, C.W. Exposure to Static Electric Fields Leads to Changes in Biogenic Amine Levels in the Brains of Drosophila. Proc. R. Soc. 2015, 282, 20151198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkov, I.; Burenkov, M.; Burenkova, L.; Pichugin, V.I.; Chunikhin, S.; Engovatov, V. The Reaction of the Tick Hyalomma Asiaticum (Acarina, Ixodidae) to 1-to 4-GHz Microwaves. Med. Parazitol. 1996, 4, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkov, I.S.; Burenkova, L.; Burenkov, M.; Pichugin, V.I. The Impact of Electromagnetic Radiation at Microwave Frequency (9.8 HhZ) on the Embryonic and Postembryonic Development of the Tick Hyalomma Asiaticum (Acarina, Ixodidae). Med. Parazitol. 2000, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vargová, B.; Majlath, I.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Pipova, N.; Živčák, J.; Tryjanowski, P.; Peťko, B.; Džmura, J.; Ižariková, G.; et al. Morphometric Analysis–Effect of the Radiofrequency Interface of Electromagnetic Field on the Size of Hatched Dermacentor Reticulatus Larvae. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargová, B.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Kosterec, M.; Majláth, I.; Pipová, N.; Tryjanowski, P.; Jankowiak, Ł.; Majláthová, V. Ticks and Radio-Frequency Signals: Behavioural Response of Ticks (Dermacentorreticulatus) in a 900 MHz Electromagnetic Field. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 22, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargová, B.; Majláth, I.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Kosterec, M.; Tryjanowski, P.; Jankowiak, Ł.; Raši, T.; Majláthová, V. Electromagnetic Radiation and Behavioural Response of Ticks: An Experimental Test. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 75, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frątczak, M.; Vargová, B.; Tryjanowski, P.; Majláth, I.; Jerzak, L.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Jankowiak, Ł.; Conka, Z.; Majláthová, V. Infected Ixodes Ricinus Ticks Are Attracted by Electromagnetic Radiation of 900 MHz. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nässel, D.R. Neuropeptides in the Nervous System of Drosophila and Other Insects: Multiple Roles as Neuromodulators and Neurohormones. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 68, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, J.G.C.; Pandit, A.A.; Zandawala, M.; Nässel, D.R.; Davies, S.-A.; Dow, J.A.T. DINeR: Database for Insect Neuropeptide Research. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 86, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Hernández, L.; Pipová, N.; Allain, E.; Henry, C.; Rouxel, C.; Lagrée, A.-C.; Haddad, N.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Valdés, J.J.; Alberdi, P.; et al. Enlisting the Ixodes Scapularis Embryonic ISE6 Cell Line to Investigate the Neuronal Basis of Tick—Pathogen Interactions. Pathogens 2021, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; de la Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genomic Insights into the Ixodes Scapularis Tick Vector of Lyme Disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimo, L.; Slovák, M.; Park, Y.; Žitňan, D. Identification of a Complex Peptidergic Neuroendocrine Network in the Hard Tick, Rhipicephalus Appendiculatus. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 335, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Šimo, L.; Park, Y. Molecular Characterization of Neuropeptide Elevenin and Two Elevenin Receptors, IsElevR1 and IsElevR2, from the Blacklegged Tick, Ixodes Scapularis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 101, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimo, L.; Park, Y. Neuropeptidergic Control of the Hindgut in the Black-Legged Tick Ixodes Scapularis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimo, L.; Žitňan, D.; Park, Y. Two Novel Neuropeptides in Innervation of the Salivary Glands of the Black-Legged Tick, Ixodes Scapularis: Myoinhibitory Peptide and SIFamide. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 517, spc1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- © Voxo 2011–2023 Mapa Vysielačov v SR. Available online: https://elektrosmog-info.voxo.eu/mapa-vysielacov (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Electrical Power Engeneering Department, Technical University in Košice; VUJE, Inc. Maps of Electromagnetic Fields. Available online: http://www.emp.vuje.sk/EN4/# (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Coast, G.M.; Schooley, D.A. Toward a Consensus Nomenclature for Insect Neuropeptides and Peptide Hormones. Peptides 2011, 32, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koči, J.; Šimo, L.; Park, Y. Validation of Internal Reference Genes for Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Studies in the Tick, Ixodes Scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromníková, D. Use of Molecular and Transgenic Methods in Identification and Functional Analysis of Receptors. Ph.D. Thesis, Comenius University Bratislava, Bratislava, Slovakia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J.; Chavdoula, E.D.; Karabarbounis, A.; Margaritis, L.H. Comparison of Bioactivity Between GSM 900 MHz and DCS 1800 MHz Mobile Telephony Radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2007, 26, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargová, B.; Majláth, I.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Zbojovský, J.; Tryjanowski, P.; Majláthová, V. Locomotor Activity of Ixodes Ricinus Females in 900 MHz Electromagnetic Field. Life 2022, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J. Comparing DNA Damage Induced by Mobile Telephony and Other Types of Man-Made Electromagnetic Fields. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2019, 781, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilić, M.; Tlak Gajger, I.; Tucak, P.; Štambuk, A.; Šrut, M.; Klobučar, G.; Malarić, K.; Žura Žaja, I.; Pavelić, A.; Manger, M.; et al. Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Mobile Phone Radiofrequency (900 MHz) on the Oxidative Response and Genotoxicity in Honey Bee Larvae. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdal, P.; Bieńkowski, P.; Cebrat, M.; Berbeć, E.; Plotnik, M.; Murawska, A.; Sobkiewicz, P.; Łaszkiewicz, A.; Latarowski, K. Exposure to a 900 MHz Electromagnetic Field Induces a Response of the Honey Bee Organism on the Level of Enzyme Activity and the Expression of Stress-Related Genes. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J.; Chavdoula, E.D.; Margaritis, L.H. Bioeffects of Mobile Telephony Radiation in Relation to Its Intensity or Distance from the Antenna. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Cai, P. 3.5-GHz Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation Promotes the Development of Drosophila Melanogaster. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbojovský, J.; Pavlík, M.; Cimbala, R.; Kurimský, J. Merania elektromagnetických polí v okolí vybraných telekomunikačných vysielačov v lokalitách Košice a okolie. In Proceedings of the Zborník Príspevkov Prednesených na Vedeckom Seminári EMITICK22; Technická Univerzita v Košiciach: Stará Lesná, Slovakia, 2022; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Act No. 355/2007 Z. z. on the Protection, Promotion and Development of Public Health and Amending Certain Acts, as Amended. Available online: https://www.epi.sk/zz/2007-534 (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Tan, A.W.L.; Francischetti, I.M.B.; Slovak, M.; Kini, R.M.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Sexual Differences in the Sialomes of the Zebra Tick, Rhipicephalus Pulchellus. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 120–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaoud, C.; Nishiyama, M.Y.; Ben Hamda, C.; Lichtenstein, F.; Castro de Oliveira, U.; Faria, F.; Loiola Meirelles Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; Ghedira, K.; Bouattour, A.; M’Ghirbi, Y.; et al. De Novo Assembly and Annotation of Hyalomma Dromedarii Tick (Acari: Ixodidae) Sialotranscriptome with Regard to Gender Differences in Gene Expression. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Kobak, J.; Aonuma, H. Electromagnetic Field Exposure Affects the Calling Song, Phonotaxis, and Level of Biogenic Amines in Crickets. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 93255–93268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sormunen, J.J.; Kulha, N.; Klemola, T.; Mäkelä, S.; Vesilahti, E.-M.; Vesterinen, E.J. Enhanced Threat of Tick-Borne Infections within Cities? Assessing Public Health Risks Due to Ticks in Urban Green Spaces in Helsinki, Finland. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heylen, D.; Lasters, R.; Adriaensen, F.; Fonville, M.; Sprong, H.; Matthysen, E. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases in the City: Role of Landscape Connectivity and Green Space Characteristics in a Metropolitan Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, S.J.; Lihou, K.; Robert, D. Static Electricity Passively Attracts Ticks onto Hosts. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 3041–3047.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.D.; Zhu, J.; Carr, A.L.; Dhammi, A.; Cave, G.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Infrared Light Detection by the Haller’s Organ of Adult American Dog Ticks, Dermacentor Variabilis (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Avalos, D.; Wajnberg, E.; Oliveira, P.S.; Leal, I.; Farina, M.; Esquivel, D.M.S. Isolation of Magnetic Nanoparticles from Pachycondyla Marginata Ants. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambinet, V.; Hayden, M.E.; Reigl, K.; Gomis, S.; Gries, G. Linking Magnetite in the Abdomen of Honey Bees to a Magnetoreceptive Function. Proc. Royal Soc. B 2017, 284, 20162873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Radiation Intensity | Biological Replications | Sex | Exposure Time | Number of Individuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 V/m | 3 | ♀ | 10 min | 5 |
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 | |||
| ♂ | 10 min | 5 | ||
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 | |||
| 2 V/m | 3 | ♀ | 10 min | 5 |
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 | |||
| ♂ | 10 min | 5 | ||
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 | |||
| 0 V/m | 3 | ♀ | 10 min | 5 |
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 | |||
| ♂ | 10 min | 5 | ||
| 1 h | 5 | |||
| 3 h | 5 | |||
| 24 h | 5 |
| Protein | Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGLa-related allatostatins | fgla/ast | AGCGGAGGTACAACTTTGGC | CTCCTCTTCCAGCGCTCG | [42] |
| Allatotropin | at | GGCTTTGGCAAGAGAATGAG | GGCTATTTCCTCCGCTAACC | [42] |
| Arginine-vasopressin like peptide | avpl | TCTCACACATGCTGCTCCTG | GCATCGTTGAGGATGCACAT | This study |
| Kinin | kinin | ACCACGTTCCTGATGAGCAT | ATGTTCCAGCGAATGAAGCT | This study |
| Ribosomal protein S4 | rsp4 | GGTGAAGAAGATTGTCAAGCAGAG | TGAAGCCAGCAGGGTAGTTTG | [41] |
| ♀ | 2 V/m | 40 V/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | 10 min | 1 h | 3 h | 24 h | 10 min | 1 h | 3 h | 24 h |
| kinin | *** | *** | ** | |||||
| avpl | * | * | *** | *** | ||||
| at | *** | ** | *** | *** | ||||
| fgla/ast | * | * | *** | *** | ||||
| ♂ | 2 V/m | 40 V/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | 10 min | 1 h | 3 h | 24 h | 10 min | 1 h | 3 h | 24 h |
| kinin | *** | |||||||
| avpl | * | |||||||
| at | *** | *** | ||||||
| fgla/ast | *** | * | *** | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šofranková, L.; Baňas, M.; Pipová, N.; Majláth, I.; Kurimský, J.; Cimbala, R.; Pavlík, M.; Mateos-Hernández, L.; Šimo, L.; Majláthová, V. Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Neuropeptide Transcript Levels in the Synganglion of Ixodes ricinus. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121398
Šofranková L, Baňas M, Pipová N, Majláth I, Kurimský J, Cimbala R, Pavlík M, Mateos-Hernández L, Šimo L, Majláthová V. Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Neuropeptide Transcript Levels in the Synganglion of Ixodes ricinus. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121398
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠofranková, Lívia, Miroslav Baňas, Natália Pipová, Igor Majláth, Juraj Kurimský, Roman Cimbala, Marek Pavlík, Lourdes Mateos-Hernández, Ladislav Šimo, and Viktória Majláthová. 2023. "Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Neuropeptide Transcript Levels in the Synganglion of Ixodes ricinus" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121398
APA StyleŠofranková, L., Baňas, M., Pipová, N., Majláth, I., Kurimský, J., Cimbala, R., Pavlík, M., Mateos-Hernández, L., Šimo, L., & Majláthová, V. (2023). Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Neuropeptide Transcript Levels in the Synganglion of Ixodes ricinus. Pathogens, 12(12), 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121398







