Assessment of Comorbidity in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
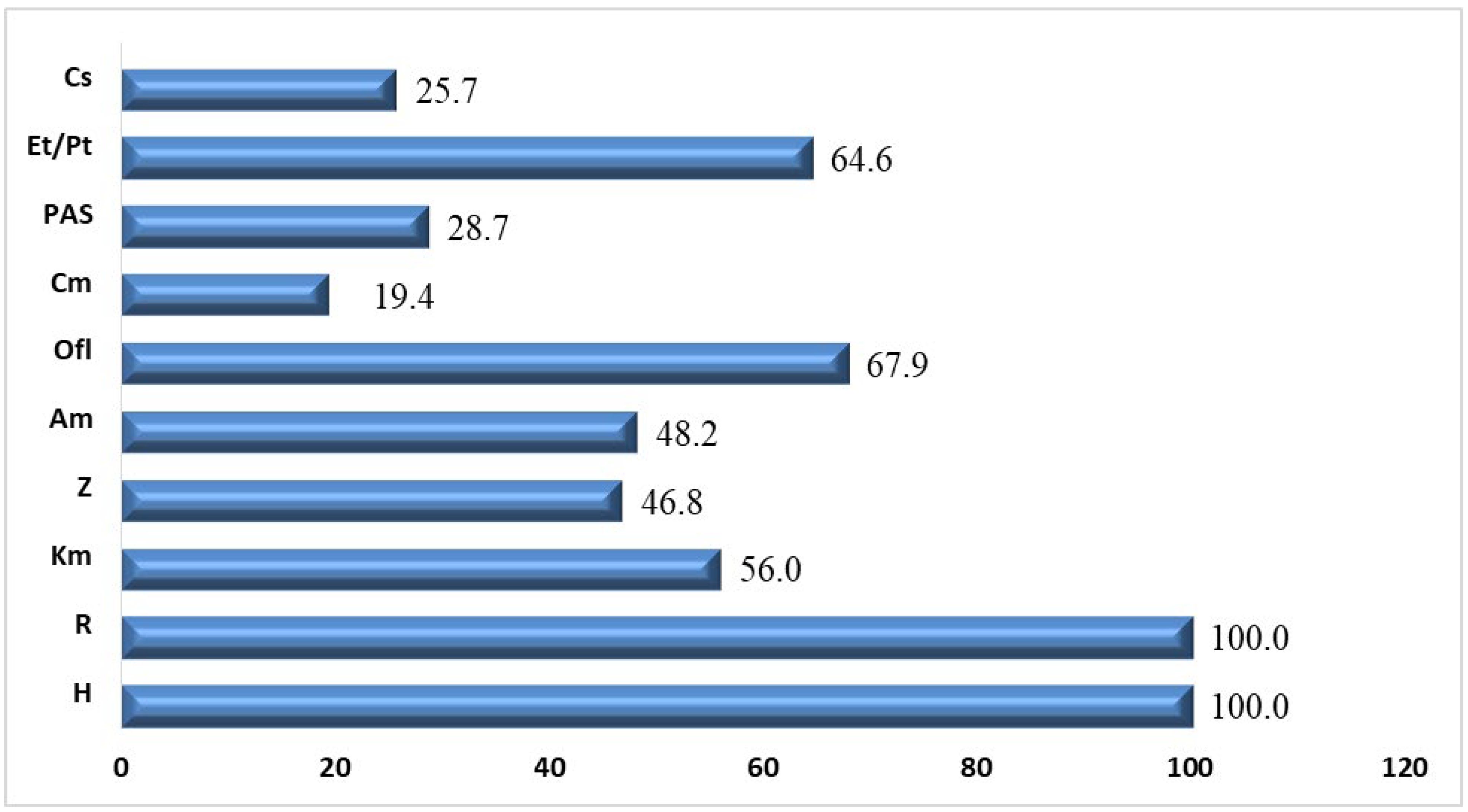
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborative Group for the Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data in MDR-TB treatment–2017; Ahmad, N.; Ahuja, S.D.; Akkerman, O.W.; Alffenaar, J.C.; Anderson, L.F.; Baghaei, P.; Bang, D.; Barry, P.M.; Bastos, M.L.; et al. Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet 2018, 392, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO) GTP. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Harding, E. WHO Global Progress Report on Tuberculosis Elimination. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecai, J.; Mijiti, P.; Chuangyue, H.; Qian, G.; Weiguo, T.; Jihong, C. Treatment outcomes of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients receiving ambulatory treatment in Shenzhen, China: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1134938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrousov, I.; Akhmedova, G.; Molchanov, V.; Fundovnaya, E.; Kozlova, E.; Ostankova, Y.; Semenov, A.; Maslennikova, N.; Leontev, D.; Zhuravlev, V.; et al. Frequent acquisition of bedaquiline resistance by epidemic extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in Russia during long-term treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio-Arques, V.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Moreno-Martinez, A.; Real, J.; Orcau, À.; Mauricio, D.; Mata-Cases, M.; Julve, J.; Navas Mendez, E.; Puig Treserra, R.; et al. Subjects with Diabetes Mellitus Are at Increased Risk for Developing Tuberculosis: A Cohort Study in an Inner-City District of Barcelona (Spain). Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 789952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyaeva, E.N.; Chernokhaeva, I.V.; Sapozhnikova, N.V.; Nazarenko, M.M.; Starshinova, A.A.; Yablonsky, P.K. Factors predisposing to the development of extensive drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Med. Alliance 2017, 4, 51–56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stavitskaya, N.V.; Felker, I.G.; Zhukova, E.M.; Tlif, A.I.; Doktorova, N.P.; Kudlay, D.A. The multivariate analysis of results of bedaquiline use in the therapy of MDR/XDR pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 98, 56–62. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonskiy, P.K.; Starshinova, A.A.; Nazarenko, M.M.; Beliaeva, E.N.; Chuzhov, A.L.; Alekseev, D.Y.; Pavlova, M.V. Efficacy of new treatment regimes of patients with extensive drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bull. Contemp. Clin. Med. 2022, 15, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Harries, A.; Jeon, C.; Hart, J.; Kapur, A.; Lonnroth, K.; Ottmani, S.E.; Goonesekera, S.; Murray, M. The impact of diabetes on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riza, A.L.; Pearson, F.; Ugarte-Gil, C.; Alisjahbana, B.; van de Vijver, S.; Panduru, N.M.; Hill, P.C.; Ruslami, R.; Moore, D.; Aarnoutse, R.; et al. Clinical management of concurrent diabetes and tuberculosis and the implications for patient services. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, F.; Diaco, H.A.; Ngubane, N.; Howell, P.; Everitt, D.; Crook, A.M.; Mendel, C.M.; Egizi, E.; Moreira, J.; Timm, J.; et al. Treatment of Highly Drug-Resistant Pulmonary Tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolenko, N.Y.; Kudlay, D.A.; Doktorova, N.P. Pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics of multidrug and extensively drug resistant tuberculosis. Pharmacoeconom. Mod. Pharmacoeconom. Pharmacoepidemiol. 2021, 14, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, L.; Veziris, N.; Aubry, A.; Brossier, F.; Bernard, C.; Sougakoff, W.; Jarlier, V.; Robert, J. Risk factors for extensive drug resistance in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis cases: A case-case study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yi, H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, S. Incidence and Temporal Trend of Antituberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Trop. Med. 2022, 2022, 8266878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, D.A.; Borisov, S.E. Profile and risk factors of adverse reactions in new tuberculosis cases receiving treatment. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2017, 95, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis; Module 4: Treatment—drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; 96p, ISBN 978-92-4-155052-9.
- Federal Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Extensively Drug-Resistant Respiratory Tuberculosis. ROF M. 2015. Available online: http://roftb.ru/netcat_files/doks2015/rec2018.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2015).
- WHO. Definitions and Reporting Framework for Tuberculosis—2013 Revision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN -9789241505345.
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines Ontuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment-Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-92-4-000704-8.
- Sarsenbayeva, G.I.; Tursynbekova, A.E. Modern approaches to assessing comorbidity in patients. Cardio Somat. 2019, 10, 19–23. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguti, V.; Rijo, R.; Crepaldi, N.; Ruffino-Netto, A.; Carvalho, I.; Alves, D. Charlson Comorbidities Index importance evaluation as a predictor to tuberculosis treatments outcome in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 138, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Fan, H. Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Analysis of Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Type 2 Diabetes Comorbidity in China: A Retrospective Analysis. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 710981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, J.F.; Harley, C.R.; Devine, J.W. A comparison of comorbidity measurements to predict healthcare expenditures. Am. J. Manag. Care 2006, 12, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, S.; Danila, E.; Maryandyshev, A.; Dalcolmo, M.; Miliauskas, S.; Kuksa, L.; Manga, S.; Skrahina, A.; Diktanas, S.; Codecasa, L.R.; et al. Surveillance of adverse events in the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis: First global report. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1901522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, S.E.; Dheda, K.; Enwerem, M.; Leyet, R.R.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Sotgiu, G.; Tiberi, S.; Alffenaar, J.-W.; Maryandyshev, A.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of bedaquiline-containing regimens in the treatment of MDR- and XDR-TB: A multicentre study. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1700387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Baghaei, P.; Barkane, L.; Benedetti, A.; Brode, S.K.; Brust, J.C.M.; Campbell, J.R.; Chang, V.W.L.; Falzon, D.; et al. Collaborative Group for the Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data in MDR-TB treatment 2017. Drug-associated adverse events in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.T.; Du, J.; Wu, G.H.; Pei, Y.; Gao, M.Q.; Martinez, L.; Fan, L.; Chen, W.; Xie, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Bedaquiline-containing regimens in patients with pulmonary multidrug--resistant tuberculosis in China: Focus on the safety. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, D.A.; Borisov, S.E.; Rodina, O.V.; Filippov, A.V.; Ivanushkina, T.N.; Litvinova, N.V. Safety of treatment regimens in multiple drug resistant tuberculosis patients compiled as per the new WHO recommendations as of 2019. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 98, 5–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, L.; Tiberi, S.; Burman, M.; Kunst, H.; Wejse, C.; Togonidze, T.; Bothamley, G.; Lange, C. QT prolongation and cardiac toxicity of new tuberculosis drugs in Europe: A Tuberculosis Network European Trialsgroup (TBnet) study. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, D.V.; Muniz, T.P.; Yang, A.; Keshavarzi, S.; Sorotsky, H.; Butler, M.O.; Saibil, S.; Spreafico, A.; Hogg, D. Real World Outcomes and Hepatotoxicity of Infliximab in the Treatment of Steroid-Refractory Immune-Related Adverse Events. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, K. Tuberculosis non-communicable disease comorbidity and multimorbidity in public primary care patients in South Africa. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2018, 10, a1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, G.; Su, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, R.; Jia, J.; Wang, P. Effects of smoking on the severity and transmission of pulmonary tuberculosis: A hospital-based case control study. Front. Public Health 2023, 26, 1017967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fløe, A.; Hilberg, O.; Wejse, C.; Ibsen, R.; Løkke, A. Comorbidities, mortality and causes of death among patients with tuberculosis in Denmark 1998–2010: A nationwide, register-based case–control study. Thorax 2018, 73, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridson, T.; Matthiesson, A.; Owens, L. Diabetes: A Contributor to tuberculosis in Tropical Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Fu, H.; Lee, M.R.; Magee, M.; Lin, H.H. Tuberculosis and diabetes in low and moderate tuberculosis incidence countries. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xie, W.; Gong, L.; Ren, M.; Pan, P.; Luo, B. The relationship between HbA1c control levels and antituberculosis treatment effects: A meta-analysis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.R.; Njie, G.; Zenner, D.; Cohn, D.L.; Reves, R.; Ahmed, A.; Menzies, D.; Horsburgh, R.C.; Crane, M.C.; Burgos, M.; et al. Guidelines for the Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Recommendations from the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association and CDC, 2020. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2020, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.M.; Ortmann, J.; Rostig, S.; Schiffl, H. Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates hepatotoxicity of multidrug treatment of mycobacterial infections: A prospective pilot study. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2019, 8, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, C.; Liu, K.G.; Wu, W.; Tian, Y.X. Is the Prophylactic Use of Hepatoprotectants Necessary in Anti-Tuberculosis Treatment? Chemotherapy 2017, 62, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.X. Prophylactic Therapy of Silymarin (Milk Thistle) on Antituberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 3192351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkina, I.A.; Maevskaya, M.V.; Tikhonov, I.N.; Zozulya, V.N.; Leshchenko, V.I. Infusion therapy in chronic liver diseases. Ros. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Coloproctol. 2018, 28, 81–87. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balukova, E.V.; Uspensky, Y.P.; Fominykh, Y.A. Liver lesions of various origins (toxic, medicinal, dysmetabolic): From etiological heterogeneity to a single unified therapy for patients. breast cancer. Med. Rev. 2018, 1, 35–40. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkin, V.T.; Baranovsky, A.Y.; Raykhelson, K.L.; Palgova, L.K.; Maevskaya, M.V.; Kondrashina, E.A.; Marchenko, N.V.; Nekrasova, T.P.; Nikitin, I.G. Drug-induced liver injury (clinical guidelines for physicians). Russ. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Coloproctol. 2019, 29, 101–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilchenko, L.Y.; Okovity, S.V. Remaxol: Mechanisms of action and application in clinical practice. Arch. Intern. Med. 2016, 2, 16–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberi, S.; Pontali, E.; Tadolini, M.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Migliori, G.B. Challenging MDR-TB clinical problems—The case for a new Global TB Consilium supporting the compassionate use of new anti-TB drugs. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 80, S68–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakimova, M.A.; Karpina, N.; Gordeeva, O.; Asanov, R. Comorbidity: Pulmonary tuberculosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Carrozzino, D.; Guidi, J.; Patierno, C. Charlson comorbidity index: A critical review of clinimetric properties. Psychother. Psychosom. 2022, 91, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudlay, D.A. Development and introduction into clinical practice of a new pharmacological substance from the class of diarylquinolines. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 84, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Hu, X.M.; Jin, W.; Cheng, C.H.; Xiong, L.Q.; Hu, R.H.; Jin, Q.; Liu, Y. Sixty-seven MDR-,and XDR-PTB cases with sputum culture conversion then treated with bedaquiline-containing regimens: A singal arm, single center observational study. Chin. J. Antituberc. 2021, 43, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontali, E.; Sotgiu, G.; Tiberi, S.; Tadolini, M.; Visca, D.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Spanevello, A.; Migliori, G.B. Combined treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis with bedaquiline and delamanid: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starshinova, A.; Dovgalyk, I.; Belyaeva, E.; Glushkova, A.; Osipov, N.; Kudlay, D. Efficacy of Tuberculosis Treatment in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis with the Use of Bedaquiline: The Experience of the Russian Federation. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, L.J.; Walker, A.; Hettle, R.; Lu, X.; Kambili, C.; Murungi, A. Cost Effectiveness of Adding Bedaquiline to Drug Regimens for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in the UK. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, N.Y.; Kudlay, D.A.; Borisov, S.E.; Sannikova, T.E.; Doktorova, N.P. Evaluation of the clinical and economic efficiency of various regimens of etiotropic chemotherapy in patients with respiratory tuberculosis with multiple and extensive drug resistance. Pharmacoeconomics Mod. Pharmacoeconomics Pharmacoepidemiol. 2023, 16, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.M.; Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Hsieh, N.H.; Huang, T.L.; Chio, C.P. A probabilistic transmission and population dynamic model to assess tuberculosis infection risk. Risk Anal. 2012, 32, 1420–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics of Patients | Patients with Tuberculosis (n = 307) |
|---|---|
| Males (n (%)) | 218 (71.1) |
| Females (n (%)) | 89 (28.9) |
| Mean age (M ± m) | 40.8 ± 11.2 |
| Infiltrative lung TB (n (%)) | 148 (48.3) |
| Fibrotic cavernous lung TB (n (%)) | 95 (30.9) |
| Disseminated lung TB (n (%)) | 64 (20.8) |
| Comorbid pathology (n (%)) | 230 (74.9) |
| Treatment duration (years) (M ± m) | 4.3 ± 2.5 |
| Chronic alcoholism (n (%)) | 34 (11.1) |
| Smoking (n (%)) | 112 (36.5) |
| Group of Patients | Group I—MDR-TB (n = 157) | Group II—XDR-TB(n = 150) | 95% Cl | p, χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/% | ||||
| Length of therapy | 3.1 ± 1.3 years | 3.5 ± 1.5 years | ||
| Previous anti-TB treatment | 37 (23.6) | 98 (65.3) | 0.099; 0.269 | p < 0.05; 0.54 |
| Comorbidity | 89 (58.2) | 139 (92.6) | 0.052; 0.207 | p < 0.05; 0.53 |
| Group of Patients | Treatment Success (Cured + Treatment Completed) | Treatment Failure | Lost to Follow-Up | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n (%)) | ||||
| Group I—MDR-TB (n = 157) | 105 * (66.8) | 45 (28.7) | 6 (3.8) | 0 |
| Group II—XDR-TB (n = 150) | 61 (40.7) | 57 (38.0) | 25 * (16.7) | 7 * (4.6) |
| Patients with Comorbidities | Score (n, %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1–2 | 3–4 | 5–6 | |
| Group I—MDR-TB (n = 89) | 37 * (41.6) | 30 (33.7) | 22 (24.7) | 0 |
| Group II—XDR-TB (n = 139) | 29 (20.9) | 34 (24.5) | 61 * (43.9) | 15 * (10.7) |
| Comparison Groups | Treatment Success (Cured + Treatment Completed) (n/%) | Treatment Failure (n/%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 | 3–4 | 5–6 | 1–2 | 3–4 | 5–6 | |
| Score | Score | |||||
| Group I—MDR-TB (n = 89) | 20 (38.5) | 8 (15.4) | 0 | 10 * (19.2) | 14 (26.9) | 0 |
| Group II—XDR-TB (n = 139) | 32 (29.1) | 25 (22.7) | 1 (0.9) | 5 (4.5) | 36 (32.7) | 11 ** (10.0) |
| Analyzed Relation | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity (CCI > 0) affects treatment success in entire sample | 0.33 (0.16–0.67) | 0.0019 ** |
| Comorbidity (CCI > 0) affects treatment success in MDR-TB patients | 0.3 (0.11–0.84) | 0.018 * |
| High comorbidity index (CCI > 2) affects treatment success in XDR-TB patients | 0.35 (0.13–0.95) | 0.038 * |
| Effectiveness of TB treatment tending to decrease along with rise in comorbidity index in XDR-TB patients | Unapplicable | 0.033 * |
| Patients with TB Treatment Failure | Comorbidity Pathology (n (%)) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | COPD | PGIT and Viral Hepatitis | Chronic Alcoholism | |
| XDR-TB (n = 42) | 3 (7.1) | 2(4.7) | 32 (76.2) * | 3 (9.1) |
| χ2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 18.42 | 1.8 |
| p | p > 0.05 | p > 0.05 | p < 0.001 | p > 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Starshinova, A.; Nazarenko, M.; Belyaeva, E.; Chuzhov, A.; Osipov, N.; Kudlay, D. Assessment of Comorbidity in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121394
Starshinova A, Nazarenko M, Belyaeva E, Chuzhov A, Osipov N, Kudlay D. Assessment of Comorbidity in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121394
Chicago/Turabian StyleStarshinova, Anna, Michail Nazarenko, Ekaterina Belyaeva, Alexander Chuzhov, Nikolay Osipov, and Dmitry Kudlay. 2023. "Assessment of Comorbidity in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121394
APA StyleStarshinova, A., Nazarenko, M., Belyaeva, E., Chuzhov, A., Osipov, N., & Kudlay, D. (2023). Assessment of Comorbidity in Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Pathogens, 12(12), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121394







