A Virus-like Particle-Based F4 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Is Inhibited by Maternally Derived Antibodies in Piglets but Generates Robust Responses in Sows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
2.1.1. FaeG.Tag Expression and Purification
2.1.2. STb.Tag Expression and Purification
2.1.3. Purification of Catcher.cVLP
2.2. cVLP Vaccine Purification and Quality Assessment
2.3. Monoclonal Antibody Binding to FaeG
2.4. Mouse Immunization Studies
Head-to Head Comparison of Unconjugated FaeG- vs. FaeG.cVLP-Induced Responses
2.5. Pig Immunization Studies
2.5.1. Vaccination of Newly Weaned Pigs from F4-Vaccinated Sows
2.5.2. Vaccination of Piglets from Non-F4 E. coli-Vaccinated Sows
2.5.3. Sow Vaccination
2.6. Fecal Sample Preparation for Immunological Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Vaccine-Induced Antibody Responses
2.8. qPCR and Culturing of Fecal Swabs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Development and Characterization of a cVLP-Based F4 ETEC Vaccine
3.2. cVLP Display Increases the Immunogenicity of Recombinant FaeG
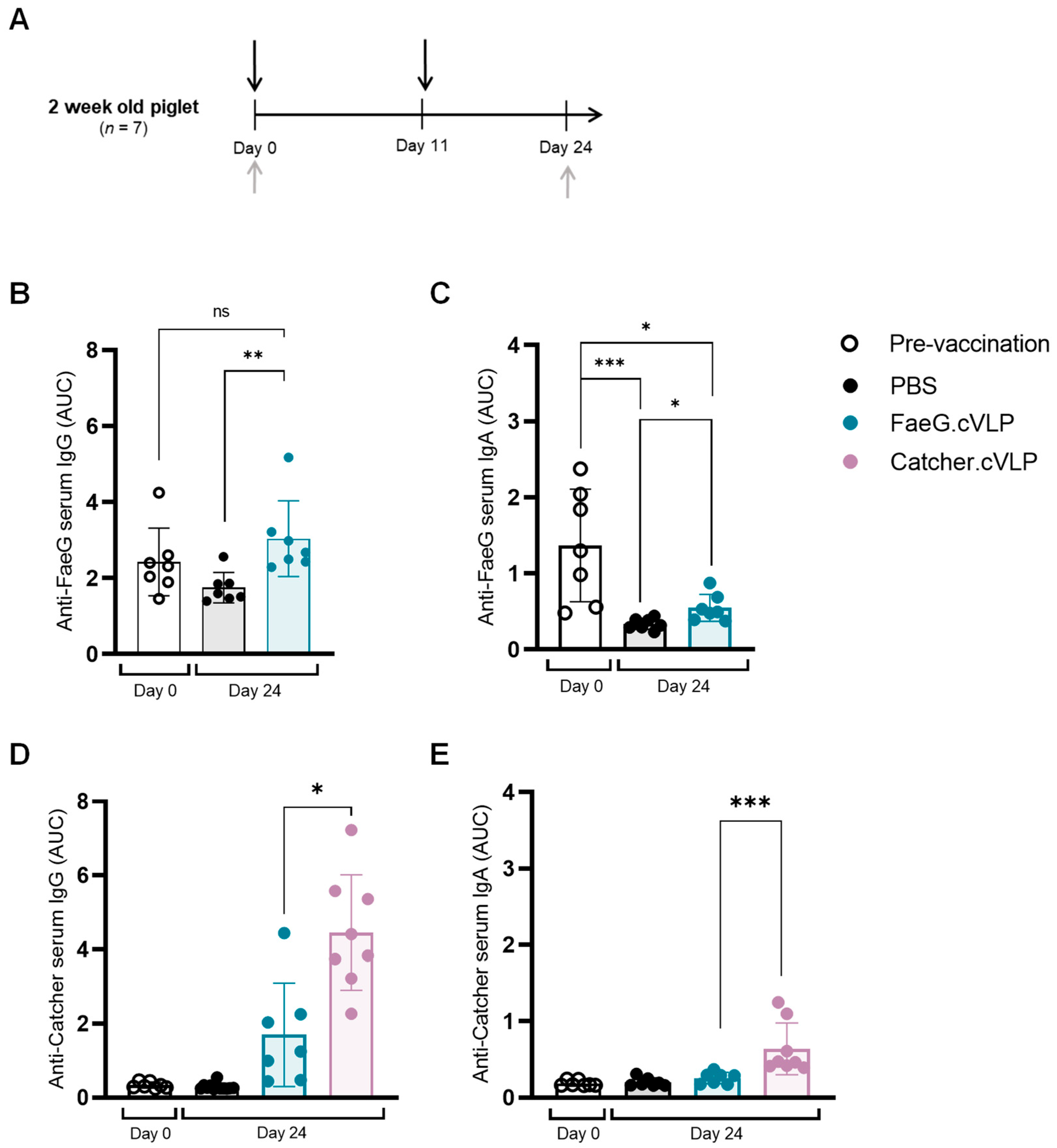
3.3. Induction of FaeG-Specific Humoral Responses in Newly Weaned Pigs Is Hampered by Pre-Existing Maternal Antibodies
3.4. FaeG.cVLP Induces Robust Humoral Responses in Sows
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjolund, M.; Zoric, M.; Wallgren, P. Financial Impact on Pig Production: III. Gastrointestinal Disorders. In Proceedings of the 6th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management, Sorrento, Italy, 7–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, E.; Kudirkiene, E.; Barington, K.; Goecke, N.B.; Blirup-Plum, S.A.; Nielsen, J.P.; Olsen, J.E.; Jensen, H.E.; Pankoke, K.; Larsen, L.E.; et al. An observational field study of porcine post-weaning diarrhea: Clinical and microbiological findings, and fecal pH-measurements as a potential diagnostic tool. Porc. Health Manag. 2023, 9, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Hampson, D.; Wilks, C. Transfer of maternal antibody against group A rotavirus from sows to piglets and serological responses following natural infection. Res. Vet. Sci. 1990, 48, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluske, J.R.; Turpin, D.L.; Kim, J.-C. Gastrointestinal tract (gut) health in the young pig. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, A.; Gibellini, M.; Gin, T.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Bauerfeind, R.; Bonilauri, P.; Labarque, G.; Hidalgo, Á. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Broeck, W.; Cox, E.; Goddeeris, B. Receptor-specific binding of purified F4 to isolated villi. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 68, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías, J.; Berzosa, M.; Pastor, Y.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Maternal Vaccination. Immunization of Sows during Pregnancy against ETEC Infections. Vaccines 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmap 2020. Use of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Food Animals, Food and Humans in Denmark. ISSN 1600-2032. Available online: https://www.danmap.org/reports/2020 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Nielsen, C.L.; Kongsted, H.; Sørensen, J.T.; Krogh, M.A. Antibiotic and medical zinc oxide usage in Danish conventional and welfare-label pig herds in 2016–2018. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 189, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.; Jørgensen, L.; Schultz, M.S. Effect of Zinc and Organic Acids on Diarrhoea in the Weaner Period; SEGES: Aarhus, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bonetti, A.; Tugnoli, B.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. Towards Zero Zinc Oxide: Feeding Strategies to Manage Post-Weaning Diarrhea in Piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slifierz, M.J.; Friendship, R.; Weese, J.S. Zinc Oxide Therapy Increases Prevalence and Persistence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Pigs: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA; CVMP. Zinc Oxide Article-35 Referral-Annex I, II. 2017. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/veterinary/referrals/zinc-oxide (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Van Den Broeck, W.; Cox, E.; Oudega, B.; Goddeeris, B. The F4 fimbrial antigen of Escherichia coli and its receptors. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 71, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdonck, F.; Cox, E.; Van Der Stede, Y.; Goddeeris, B.M. Oral immunization of piglets with recombinant F4 fimbrial adhesin FaeG monomers induces a mucosal and systemic F4-specific immune response. Vaccine 2004, 22, 4291–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdonck, F.; Snoeck, V.; Goddeeris, B.; Cox, E. Cholera toxin improves the F4(K88)-specific immune response following oral immunization of pigs with recombinant FaeG. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 103, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Molle, I.; Joensuu, J.J.; Buts, L.; Panjikar, S.; Kotiaho, M.; Bouckaert, J.; Wyns, L.; Niklander-Teeri, V.; De Greve, H. Chloroplasts Assemble the Major Subunit FaeG of Escherichia coli F4 (K88) Fimbriae to Strand-swapped Dimers. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Qi, R.; Chen, C.; Yin, J.; Ma, S.; Shi, W.; Wu, Y.; Ge, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, L.; et al. Immunogenicity of recombinant Lactobacillus casei-expressing F4 (K88) fimbrial adhesin FaeG in conjunction with a heat-labile enterotoxin A (LTAK63) and heat-labile enterotoxin B (LTB) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as an oral adjuvant in mic. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 122, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, U.V.; Melkebeek, V.; Devriendt, B.; Goetstouwers, T.; Van Poucke, M.; Peelman, L.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Cox, E. Maternal immunity enhances systemic recall immune responses upon oral immunization of piglets with F4 fimbriae. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frietze, K.M.; Peabody, D.S.; Chackerian, B. Engineering virus-like particles as vaccine platforms. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Seong, B.L. Exploiting virus-like particles as innovative vaccines against emerging viral infections. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.D.; Howarth, M. New Routes and Opportunities for Modular Construction of Particulate Vaccines: Stick, Click, and Glue. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, A.; Zabel, F.; Schnetzler, Y.; Titz, A.; Brombacher, F.; Bachmann, M.F. Innate Immunity Mediates Follicular Transport of Particulate but Not Soluble Protein Antigen. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3724–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F. Interaction of Viral Capsid-Derived Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) with the Innate Immune System. Vaccines 2018, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Zinkernagel, R.M. Neutrilizing antiviral B cell responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 235–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Jennings, G.T. Vaccine delivery: A matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrane, S.; Janitzek, C.M.; Matondo, S.; Resende, M.; Gustavsson, T.; de Jongh, W.A.; Clemmensen, S.; Roeffen, W.; van de Vegte-Bolmer, M.; van Gemert, G.J.; et al. Bacterial superglue enables easy development of efficient virus-like particle based vaccines. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aves, K.-L.; Goksøyr, L.; Sander, A.F. Advantages and Prospects of Tag/Catcher Mediated Antigen Display on Capsid-like Particle-Based Vaccines. Viruses 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisci, E.; Bárcena, J.; Montoya, M. Virus-like particle-based vaccines for animal viral infections. Inmunologia 2012, 32, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Ju, C.; Tong, T.; Huang, H.; Lv, J.; Chen, H. Immunogenicity of Empty Capsids of Porcine Circovius Type 2 Produced in Insect Cells. Vet. Res. Commun. 2007, 31, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoms, F.; Jennings, G.T.; Maudrich, M.; Vogel, M.; Haas, S.; Zeltins, A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Riond, B.; Grossmann, J.; Hunziker, P.; et al. Immunization of cats to induce neutralizing antibodies against Fel d 1, the major feline allergen in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Zeltins, A.; Kalnins, G.; Balke, I.; Fischer, N.; Rostaher, A.; Tars, K.; Favrot, C. Vaccination against IL-31 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in dogs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 279–281.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, S.; Fettelschoss, V.; Olomski, F.; Talker, S.C.; Mirkovitch, J.; Rhiner, T.; Birkmann, K.; Thoms, F.; Wagner, B.; Bachmann, M.F.; et al. Safety Profile of a Virus-Like Particle-Based Vaccine Targeting Self-Protein Interleukin-5 in Horses. Vaccines 2020, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, Y.; Pabst, M.J. Removal of endotoxin from protein solutions by phase separation using triton X-114. J. Immunol. Methods 1990, 132, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecke, N.B.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Krog, J.S.; Skovgaard, K.; Larsen, L.E. Development of a high-throughput real-time PCR system for detection of enzootic pathogens in pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Ruesch, L.; Omot, A.; Francis, D. Prevalence of virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains recently isolated from young pigs with diarrhea in the US. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 123, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.; Bourne, F.J. Half-lives of immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM in the serum of new-born pigs. Immunology 1973, 24, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Luppi, A. Swine enteric colibacillosis: Diagnosis, therapy and antimicrobial resistance. Porc. Health Manag. 2017, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiesk, S. Maternal Antibodies: Clinical Significance, Mechanism of Interference with Immune Responses, and Possible Vaccination Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras, E.; Urbiztondo, L.; Costa, J.; Batalla, J.; Torner, N.; Plasencia, A.; Salleras, L.; Dominguez, A.; Working Group for the Study of Measles Immunity in Children. Measles antibodies and response to vaccination in children aged less than 14 months: Implications for age of vaccination. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 140, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.-H. Influence of maternal antibody against hepatitis B surface antigen on active immune response to hepatitis B vaccine in infants. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6064–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, E.A.F.; Padmini, B.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Jadhav, M.; John, T.J. Antibody Response of Infants to Two Doses of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine of Enhanced Potency. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1985, 139, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska-Daniel, I.; Pomorska-Mól, M.; Pejsak, Z. The influence of age and maternal antibodies on the postvaccinal response against swine influenza viruses in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 142, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.A.; Gow, S.P.; Goji, N. Response to experimentally induced infection with bovine respiratory syncytial virus following intranasal vaccination of seropositive and seronegative calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 236, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkenberg, D.; Moormann, R.J.M.; de Smit, A.; Bouma, A.; de Jong, M. Influence of maternal antibodies on efficacy of a subunit vaccine: Transmission of classical swine fever virus between pigs vaccinated at 2 weeks of age. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, C.C.; Thoms, F.; Keller, E.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F. Virus-Specific Secondary Plasma Cells Produce Elevated Levels of High-Avidity Antibodies but Are Functionally Short Lived. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melkebeek, V.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Cox, E. ETEC vaccination in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangroenweghe, F.A.C.J.; Boone, M. Vaccination with an Escherichia coli F4/F18 vaccine improves piglet performance combined with a reduction in antimicrobial use and secondary infections due to Streptococcus suis. Animals 2022, 12, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E.; Vidarsson, G. Antibodies and Their Receptors: Different Potential Roles in Mucosal Defense. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruane, D.; Chorny, A.; Lee, H.; Faith, J.; Pandey, G.; Shan, M.; Simchoni, N.; Rahman, A.; Garg, A.; Weinstein, E.G.; et al. Microbiota regulate the ability of lung dendritic cells to induce IgA class-switch recombination and generate protective gastrointestinal immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuercher, A.W.; Coffin, S.E.; Thurnheer, M.C.; Fundova, P.; Cebra, J.J. Nasal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Is a Mucosal Inductive Site for Virus-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromantin, C.; Jamot, B.; Cohen, J.; Piroth, L.; Pothier, P.; Kohli, E. Rotavirus 2/6 virus-like particles administered intranasally in mice, with or without the mucosal adjuvants cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin, induce a Th1/Th2-like immune response. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11010–11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kamary, S.S.; Pasetti, M.F.; Mendelman, P.M.; Frey, S.E.; Bernstein, D.I.; Treanor, J.J.; Ferreira, J.; Chen, W.H.; Sublett, R.; Richardson, C.; et al. Adjuvanted Intranasal Norwalk Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits Antibodies and Antibody-Secreting Cells That Express Homing Receptors for Mucosal and Peripheral Lymphoid Tissues. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q. Comparison of oral and nasal immunization with inactivated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus on intestinal immunity in piglets. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, E.A.; Buterbaugh, R.E.; Rinehart, C.L.; Ensley, D.; Perry, G.A.; Abdelsalam, K.W.; Chase, C.C. Protection against bovine respiratory syncytial virus in calves vaccinated with adjuvanted modified live vaccine administered in the face of maternal antibody. Vaccine 2020, 38, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, B.; Chang, H.; Zhang, R.; Lu, F.; Wang, F.; Fang, F.; Chen, Z. Intranasal Immunization of Mice to Avoid Interference of Maternal Antibody against H5N1 Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, H.; Cui, Z. Factors Limiting the Translatability of Rodent Model–Based Intranasal Vaccine Research to Humans. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renu, S.; Dhakal, S.; Kim, E.; Goodman, J.; Lakshmanappa, Y.S.; Wannemuehler, M.J.; Narasimhan, B.; Boyaka, P.N.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Intranasal delivery of influenza antigen by nanoparticles, but not NKT-cell adjuvant differentially induces the expression of B-cell activation factors in mice and swine. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 329, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, H.; Berri, M.; Gerdts, V.; Meurens, F. Humoral and cellular factors of maternal immunity in swine. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aves, K.-L.; Guerra, P.R.; Fresno, A.H.; Saraiva, M.M.S.; Cox, E.; Bækbo, P.J.; Nielsen, M.A.; Sander, A.F.; Olsen, J.E. A Virus-like Particle-Based F4 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Is Inhibited by Maternally Derived Antibodies in Piglets but Generates Robust Responses in Sows. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121388
Aves K-L, Guerra PR, Fresno AH, Saraiva MMS, Cox E, Bækbo PJ, Nielsen MA, Sander AF, Olsen JE. A Virus-like Particle-Based F4 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Is Inhibited by Maternally Derived Antibodies in Piglets but Generates Robust Responses in Sows. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121388
Chicago/Turabian StyleAves, Kara-Lee, Priscila R. Guerra, Ana H. Fresno, Mauro M. S. Saraiva, Eric Cox, Poul J. Bækbo, Morten A. Nielsen, Adam F. Sander, and John E. Olsen. 2023. "A Virus-like Particle-Based F4 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Is Inhibited by Maternally Derived Antibodies in Piglets but Generates Robust Responses in Sows" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121388
APA StyleAves, K.-L., Guerra, P. R., Fresno, A. H., Saraiva, M. M. S., Cox, E., Bækbo, P. J., Nielsen, M. A., Sander, A. F., & Olsen, J. E. (2023). A Virus-like Particle-Based F4 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Is Inhibited by Maternally Derived Antibodies in Piglets but Generates Robust Responses in Sows. Pathogens, 12(12), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121388








