Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
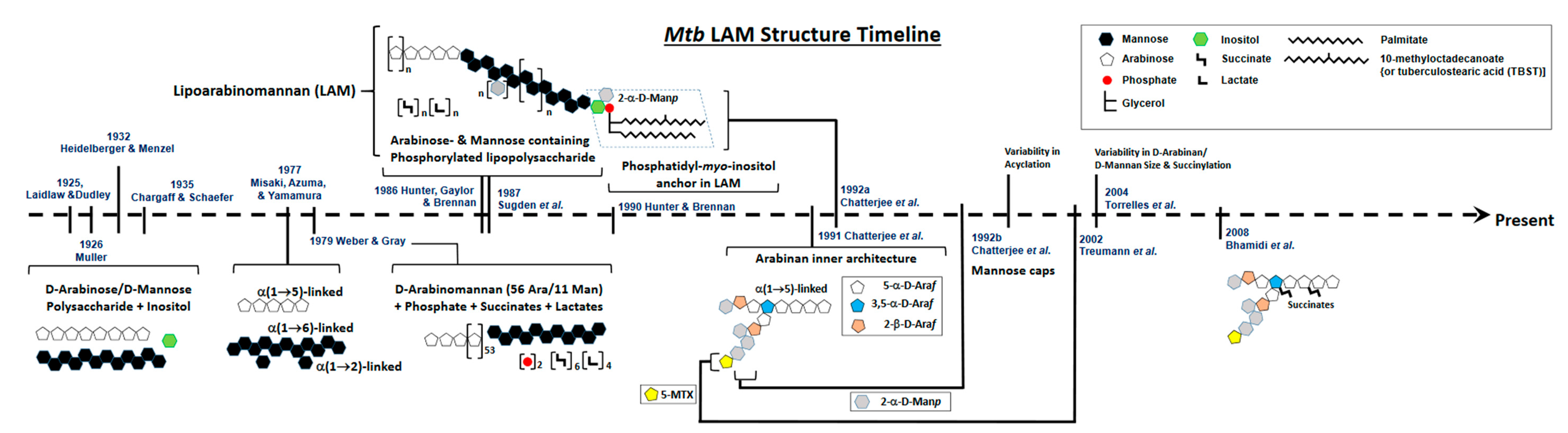
2. Defining the Basic Structure of LAM: A Brief History
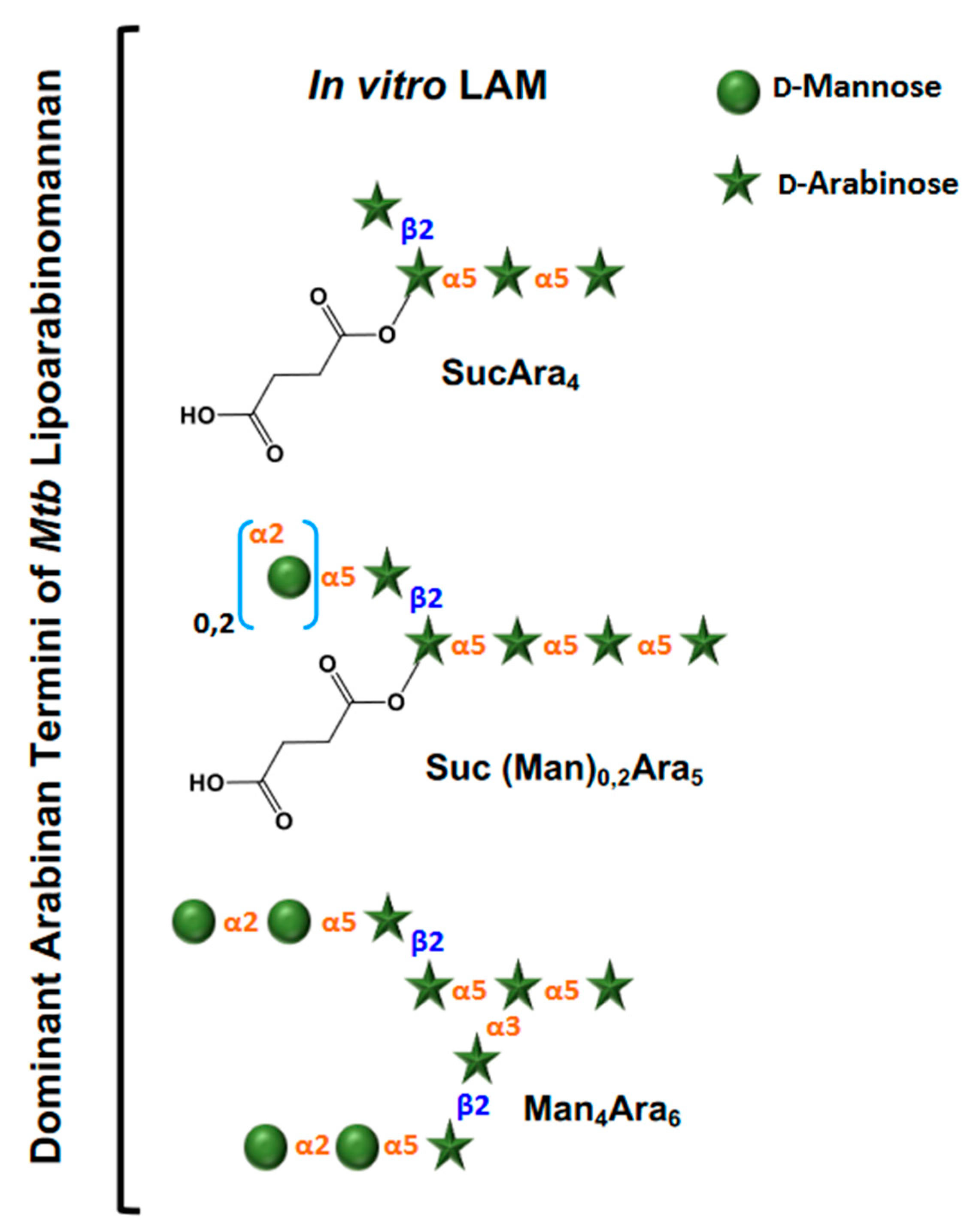
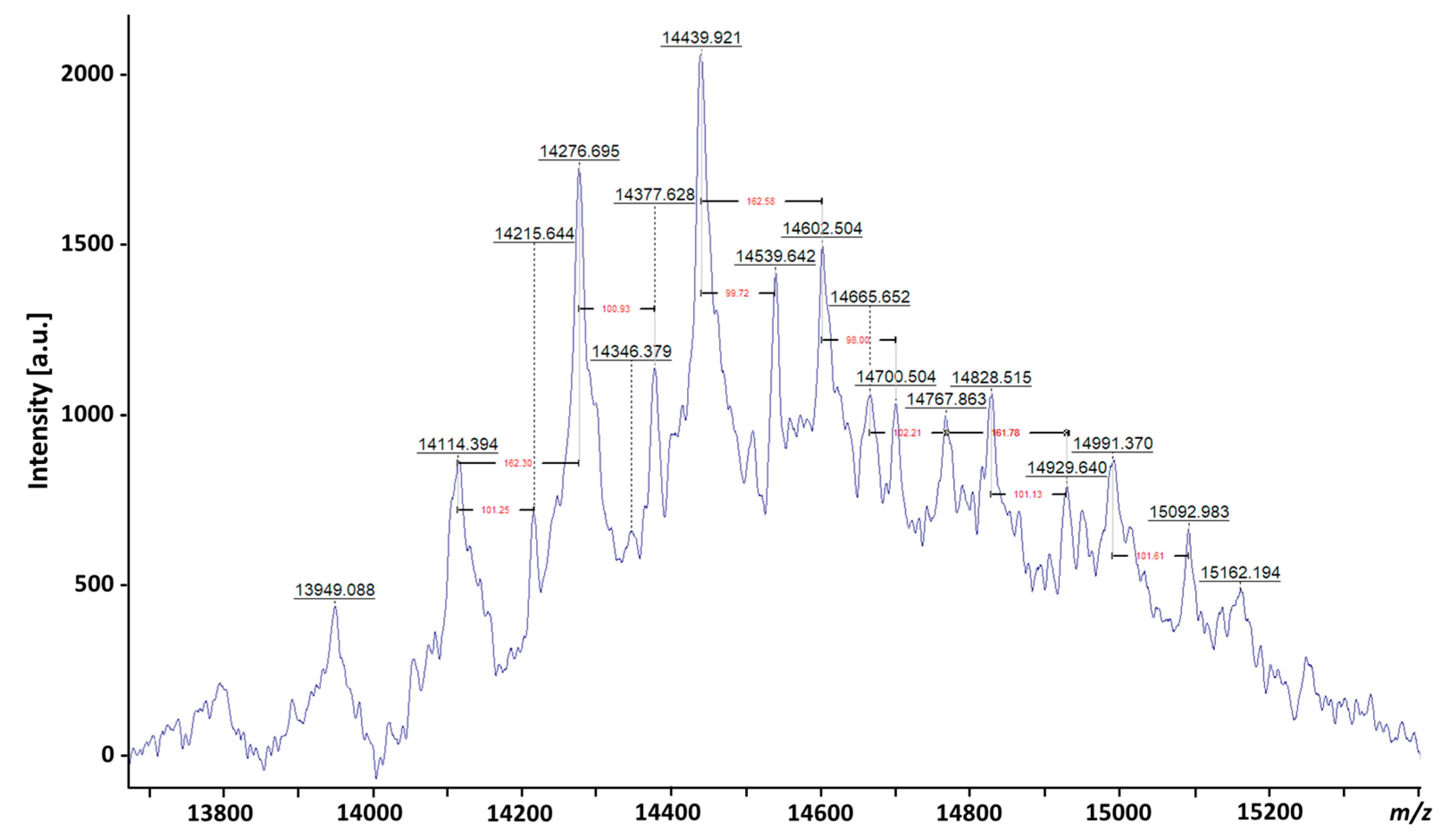
3. Evolution of LAM Structural Studies across Species
4. Biological Properties of Mtb LAM
5. LAM as a Diagnosis Biomarker for TB Disease
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brennan, P.J.; Nikaido, H. The envelope of mycobacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.L. Electron microscopy analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell division. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 240, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, L.; Lefebvre, C.; Parra, J.; Marcoux, J.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Etienne, G.; Tropis, M.; Daffé, M. Dissecting the mycobacterial cell envelope and defining the composition of the native mycomembrane. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffé, M.; Marrakchi, H. Unraveling the Structure of the Mycobacterial Envelope. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulberger, C.L.; Rubin, E.J.; Boutte, C.C. The mycobacterial cell envelope—A moving target. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, H.; Brennan, P.J. Leprosy and the leprosy bacillus: Recent developments in characterization of antigens and immunology of the disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987, 41, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, M.R.; Brennan, P.J. Structure, function and biogenesis of the cell envelope of mycobacteria in relation to bacterial physiology, pathogenesis and drug resistance; some thoughts and possibilities arising from recent structural information. Res. Microbiol. 1991, 142, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Khoo, K.-H. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan: An extraordinary lipoheteroglycan with profound physiological effects. Glycobiology 1998, 8, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.B.; Azad, A.K.; Torrelles, J.B.; Kaufman, T.M.; Beharka, A.; Tibesar, E.; DesJardin, L.E.; Schlesinger, L.S. The human macrophage mannose receptor directs Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan-mediated phagosome biogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hett, E.C.; Rubin, E.J. Bacterial growth and cell division: A mycobacterial perspective. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 126–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrelles, J.B. Broadening our view about the role of Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell envelope components during infection: A battle for survival. In Understanding Tuberculosis—Analyzing the Origin of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pathogenicity; Cardona, P.J., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Torrelles, J.B.; Chatterjee, D. Lipoglycans of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Isolation, purification, and characterization. In Mycobacteria Protocols, 2nd ed.; Parish, T., Brown, A.C., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- Besra, G.S.; Morehouse, C.B.; Rittner, C.M.; Waechter, C.J.; Brennan, P.J. Biosynthesis of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18460–18466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, D.; Guerin, M.E.; Skovierova, H.; Brennan, P.J.; Jackson, M. Chapter 2: Biogenesis of the cell wall and other glycoconjugates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 69, 23–78. [Google Scholar]
- Laidlaw, P.P.; Dudley, H.W. A specific pre-cipitating substance from tubercle bacilli. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1925, 6, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger, M.; Menzel, A.E. Specific and non-specific cell polysaccharides of the humantype of tubercle bacillus, H37. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1932, 29, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.H. A chemical study of the specific elements of tuberculin: II. The preparation of resi¬due antigen from old tuberculin. J. Exp. Med. 1926, 43, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, A.E.; Heidelberger, M. Specific and non-specific cell polysaccharides of an avian strain of tubercle bacillus. J. Biol. Chem. 1939, 127, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chargaff, E.; Schaefer, W. A specific polysaccharide from the Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG). J. Biol. Chem. 1935, 112, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, A.; Azuma, I.; Yamamura, Y. Structural and immunochemical studies on D-arabino-D-mannans and D-mannans of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other Mycobacterium species. J. Biochem. 1977, 82, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.L.; Gray, G.R. Structural and immunochemical characterization of the acidic arabinomannan of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 74, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.W.; Gaylord, H.; Brennan, P.J. Structure and antigenicity of the phosphorylated lipopolysaccharide antigens from the leprosy and tubercle bacilli. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 12345–12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, E.A.; Samagh, B.S.; Bundle, D.R.; Duncan, J.R. Lipoarbinomannan and Lipid-free arabinomannan antigens of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.; Ballou, C.E. Biosynthesis of mannophosphoinositides by Mycobacterium phlei: Enzymatic acylation of the dimannophosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, P.J.; Ballou, C.E. Biosynthesis of Mannophosphoinositides by Mycobacterium phlei: The family of dimannosylphosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 3046–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.W.; Brennan, P.J. Evidence for the presence of a phosphatidylinositol anchor on the lipoarabinomannan and lipomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 9272–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Bozic, C.M.; McNeil, M.; Brennan, P.J. Structural features of the arabinan component of the lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9652–9660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Hunter, S.W.; McNeil, M.; Brennan, P.J. Lipoarabinomannan. Multiglycosylated form of the mycobacterial mannosylphophatidylinositols. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6228–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzis, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Brennan, P.J. Structure and antigenicity of lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1993, 139, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrelles, J.B.; Khoo, K.H.; Sieling, P.A.; Modlin, R.L.; Zhang, N.; Marques, A.M.; Treumann, A.; Rithner, C.D.; Brennan, P.J.; Chatterjee, D. Truncated Structural Variants of Lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium leprae and an Ethambutol-resistant Strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41227–41239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrelles, J.B.; Sieling, P.A.; Zhang, N.; Keen, M.A.; McNeil, M.R.; Belisle, J.T.; Modlin, R.L.; Brennan, P.J.; Chatterjee, D. Isolation of a distinct Mycobacterium tuberculosis mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan isoform responsible for recognition by CD1b-restricted T cells. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.-H.; Dell, A.; Morris, H.R.; Brennan, P.J.; Chatterjee, D. Inositol phosphate capping of the nonreducing termini of lipoarabinomannan from rapidly growing strains of Mycobacterium. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12380–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, C.J.; Stanton, L.H.; Leary, J.A. Structural characterization of Lipoarabinomannans from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis by ESI mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, P.; Shi, L.; Boot, C.; Ordway, D.; McNeil, M.; Chatterjee, D. Comparative Structural Study of Terminal Ends of Lipoarabinomannan from Mice Infected Lung Tissues and Urine of a Tuberculosis Positive Patient. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treumann, A.; Xidong, F.; McDonnell, L.; Derrick, P.J.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Chatterjee, D.; Homans, S.W. 5-Methylthiopentose: A new substituent on lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 316, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, W.B.; Shimizu, K.H.; Chatterjee, D.; Homans, S.W.; Treumann, A. Identification of the 5-methylthiopentosyl substituent in Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 3918–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrelles, J.B.; Knaup, R.; Kolareth, A.; Slepushkina, T.; Kaufman, T.M.; Kang, P.B.; Hill, P.; Brennan, P.J.; Chatterjee, D.; Belisle, J.T.; et al. Identification of mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates with altered phagocytosis by human macrophages due to a truncated lipoarabinomannan. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31417–31428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Torrelles, J.B.; McNeil, M.R.; Escuyer, V.E.; Khoo, K.H.; Brennan, P.J.; Chatterjee, D. The Emb proteins of mycobacteria direct arabinosylation of lipoarabinomannan and arabinogalactan via an N-terminal recognition region and a C-terminal synthetic region. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jourani, O.; Benedict, S.T.; Ross, J.; Layton, A.J.; van der Peet, P.; Marando, V.M.; Bailey, N.P.; Heunis, T.; Manion, J.; Mensitieri, F.; et al. Identification of D-arabinan-degrading enzymes in mycobacteria. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.G.; De, P.; Spencer, J.S.; Brennan, P.J.; Daum, J.; Andre, B.G.; Joe, M.; Bai, Y.; Laurentius, L.; Porter, M.D.; et al. Detection of lipoarabinomannan in urine and serum of HIV-positive and HIV-negative TB suspects using an improved capture-enzyme linked immuno absorbent assay and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Tuberculosis 2018, 111, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Amin, A.G.; Flores, D.; Simpson, A.; Dobos, K.; Chatterjee, D. Structural implications of lipoarabinomannan glycans from global clinical isolates in diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angala, S.; Li, W.; Boot, C.M.; Jackson, M.; McNeil, M.R. Secondary Extended Mannan Side Chains and Attachment of the Arabinan in Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Torrelles, J.B. Mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigou, J.; Gilleron, M.; Puzo, G. Lipoarabinomannans: From structure to biosynthesis. Biochimie 2003, 85, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcekova, Z.; Angala, S.K.; Belardinelli, J.M.; Eskandarian, H.A.; Joe, M.; Brunton, R.; Rithner, C.; Jones, V.; Nigou, J.; Lowary, T.L.; et al. Disruption of the SucT acyltransferase in Mycobacterium smegmatis abrogates succinylation of cell envelope polysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10325–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Lowell, K.; Rivoire, B.; McNeil, M.R.; Brennan, P.J. Lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Capping with mannosyl residues in some strains. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6234–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Khoo, K.H.; McNeil, M.R.; Dell, A.; Morris, H.R.; Brennan, P.J. Structural definition of the non-reducing termini of mannose-capped LAM from Mycobacterium tuberculosis through selective enzymatic degradation and fast atom bombardment-mass spectrometry. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.-H.; Tang, J.-B.; Chatterjee, D. Variation in mannose-capped terminal arabinan motifs of lipoarabinomannans from clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3863–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angala, S.K.; McNeil, M.R.; Shi, L.; Joe, M.; Pham, H.; Zuberogoitia, S.; Nigou, J.; Boot, C.M.; Lowary, T.L.; Gilleron, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of the Methylthioxylose Capping Motif of Lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angala, S.K.; Palcekova, Z.; Belardinelli, J.M.; Jackson, M. Covalent modifications of polysaccharides in mycobacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcekova, Z.; Obregon-Henao, A.; De, K.; Walz, A.; Lam, H.; Philp, J.; Angala, S.K.; Patterson, J.; Pearce, C.; Zuberogoitia, S.; et al. Role of succinyl substituents in the mannose-capping of lipoarabinomannan and control of inflammation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venisse, A.; Berjeaud, J.M.; Chaurand, P.; Gilleron, M.; Puzo, G. Structural features of lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Determination of molecular mass by laser desorption mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 12401–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, E.; Brennan, P.J.; Herrera, T.; Torres, M. Evaluation of lipoarabinomannan for the serological diagnosis of tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.N.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, J.D.; Chong, Y. Production of monoclonal antibodies to lipoarabinomannan-B and use in the detection of mycobacterial antigens in sputum. Yonsei Med. J. 1990, 31, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Adams, L.B.; Krahenbuhl, J.L. Inhibition of interferon-gamma-mediated activation in mouse macrophages treated with lipoarabinomannan. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 80, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Hunter, S.W.; Brennan, P.J.; Krahenbuhl, J.L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan inhibits gamma interferon-mediated activation of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Gandhi, R.R.; Weinstein, D.E.; Levis, W.R.; Patarroyo, M.E.; Brennan, P.J.; Cohn, Z.A. Mycobacterium leprae antigen-induced suppression of T cell proliferation in vitro. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 3028–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Fan, X.; Hunter, S.W.; Brennan, P.J.; Bloom, B.R. Lipoarabinomannan, a possible virulence factor involved in persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Mehlert, A.; Lamb, J. The inhibitory effects of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan and polysaccharides upon polyclonal and monoclonal human T cell proliferation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1988, 74, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, C.; Taverne, J.; Mehlert, A.; Bate, C.A.W.; Brealey, R.J.; Meager, A.; Rook, G.A.W.; Playfair, J.H.L. Lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the production of tumor necrosis factor from human and murine macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1989, 76, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.F.; Chatterjee, D.; Brennan, P.J.; Rea, T.H.; Modlin, R.L. Tumor necrosis factor production in patients with leprosy. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Roberts, A.D.; Lowell, K.; Brennan, P.J.; Orme, I.M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.B.; Fukutomi, Y.; Krahenbuhl, J.L. Regulation of murine macrophage effector functions by lipoarabinomannan from mycobacterial strains with different degrees of virulence. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.F.; Chatterjee, D.; Abrams, J.S.; Lu, S.; Wang, E.; Yamamura, M.; Brennan, P.J.; Modlin, R.L. Cytokine production induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan: Relationship to chemical structure. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rom, W.N. Regulation of the interleukin-1b (IL-1b) gene by mycobacterial components and lipopolysaccharide is mediated by two nuclear factor-IL6 motifs. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 3831–3837. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, N.; Nigou, J.; Herrmann, J.L.; Jackson, M.; Amara, A.; Lagrange, P.H.; Puzo, G.; Gicquel, B.; Neyrolles, O. The cell surface receptor DC-SIGN discriminates between Mycobacterium species through selective recognition of the mannose caps on lipoarabinomannan. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5513–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, L.S.; Hull, S.R.; Kaufman, T.M. Binding of the Terminal Mannosyl Units of Lipoarabinomannan from a Virulent Strain of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis to Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 4070–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venisse, A.; Fournié, J.-J.; Puzo, G. Mannosylated lipoarabinomannan interacts with phagocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratti, R.A.; Chua, J.; Vergne, I.; Deretic, V. Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycosylated phosphatidylinositol causes phagosome maturation arrest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5437–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, L.S.; Kaufman, T.M.; Iyer, S.; Hull, S.R.; Marchiando, L.K. Differences in mannose receptor-mediated uptake of lipoarabinomannan from virulent and attenuated strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by human macrophages. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 4568–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieling, P.A.; Chatterjee, D.; Porcelli, S.A.; Prigozy, T.I.; Mazzaccaro, R.J.; Soriano, T.; Bloom, B.R.; Brenner, M.B.; Kronenberg, M.; Brennan, P.J.; et al. CD1-restricted T cell recognition of microbial lipoglycan antigens. Science 1995, 269, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigozy, T.I.; Sieling, P.A.; Clemens, D.; Stewart, P.L.; Behar, S.M.; Porcelli, S.A.; Brenner, M.B.; Modlin, R.L.; Kronenberg, M. The mannose receptor delivers lipoglycan antigens to endosomes for presentation to T cells by CD1b molecules. Immunity 1997, 6, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallert, S.; Zenk, S.F.; Walther, P.; Grieshober, M.; Weil, T.; Stenger, S. Liposomal delivery of lipoarabinomannan triggers Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific T-cells. Tuberculosis 2015, 95, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Obregon-Henao, A.; Pham, H.; Chatterjee, D.; Brennan, P.J.; Jackson, M. Lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium: Mannose capping by a multifunctional terminal mannosyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17973–17977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderwick, L.J.; Birch, H.L.; Mishra, A.K.; Eggeling, L.; Besra, G.S. Structure, function and biosynthesis of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall: Arabinogalactan and lipoarabinomannan assembly with a view to discovering new drug targets. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Brennan, P.J. Glycosylated components of the mycobacterial cell wall;structure and function. In Microbial Glycobiology: Structures, Relevance and Applications, 1st ed.; Holst, O., Brennan, P.J., Itzstein, V.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Briken, V.; Porcelli, S.A.; Besra, G.S.; Kremer, L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan and related lipoglycans: From biogenesis to modulation of the immune response. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivoire, B.; Ranchoff, B.; Chatterjee, D.; Gaylord, H.; Tsang, A.; Kolk, A.H.J.; Aspinall, G.O.; Brennan, P.J. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to the specific sugar epitopes of Mycobacterium avium complex serovars. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Xie, L.; Pyle, M.; Suarez, M.F.; Broger, T.; Steinberg, D.; Ame, S.M.; Lucero, M.G.; Szucs, M.J.; MacMullan, M.; et al. A rapid triage test for active pulmonary tuberculosis in adult patients with persistent cough. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Patel, D.; Honnen, W.; Lai, Z.; Prattipati, R.S.; Zheng, R.B.; Hsueh, Y.C.; Gennaro, M.L.; Lardizabal, A.; Restrepo, B.I.; et al. Characterization of the Antigenic Heterogeneity of Lipoarabinomannan, the Major Surface Glycolipid of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Complexity of Antibody Specificities toward this Antigen. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3053–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, D.T.; Ishida, E.; Chatterjee, D.; Lowary, T.L.; Achkar, J.M. Monoclonal antibodies to lipoarabinomannan/arabinomannan—Characteristics and implications for tuberculosis research and diagnostics. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, S.D.; Gupta-Wright, A. Detection of lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in urine is indicative of disseminated TB with renal involvement in patients living with HIV and advanced immunodeficiency: Evidence and implications. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta-Wright, A.; Peters, J.A.; Flach, C.; Lawn, S.D. Detection of lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in urine is an independent predictor of mortality risk in patients receiving treatment for HIV-associated tuberculosis in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Hanrahan, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Dendukuri, N.; Lawn, S.D.; Denkinger, C.M.; Steingart, K.R. Lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan assay for detecting active tuberculosis in HIV-positive adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, CD011420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.G.; De, P.; Graham, B.; Calderon, R.I.; Franke, M.F.; Chatterjee, D. Urine lipoarabinomannan in HIV uninfected, smear negative, symptomatic TB patients: Effective sample pretreatment for a sensitive immunoassay and mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.G.; De, P.; Graham, B.; Jensen, B.L.; Moreau, E.; Chatterjee, D. Overcome low levels of detection limit and choice of antibody affects detection of lipoarabinomannan in pediatric tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, G.B.; Pinter, A.; Lowary, T.L.; Kawasaki, M.; Li, A.; Mathew, A.; Tsionsky, M.; Zheng, R.B.; Plisova, T.; Shen, K.; et al. A Novel Sensitive Immunoassay Targeting the 5-Methylthio-d-Xylofuranose-Lipoarabinomannan Epitope Meets the WHO’s Performance Target for Tuberculosis Diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01338-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Jumbe, E.; Krysiak, R.; Sidiki, S.; Kelley, H.V.; Chemey, E.K.; Kamba, C.; Mwapasa, V.; Garcia, J.I.; Norris, A.; et al. Low-cost diagnostic test for susceptible and drug-resistant tuberculosis in rural Malawi. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 2018, 7, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, S.D.; Kerkhoff, A.D.; Nicol, M.P.; Meintjes, G. Underestimation of the true specificity of the urine lipoarabinomannan (LAM) point-of-care diagnostic assay for HIV-associated tuberculosis. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2015, 69, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, L.; Magni, R.; Zaidi, F.; Araujo, R.; Saini, N.; Harpole, M.; Coronel, J.; Kirwan, D.E.; Steinberg, H.; Gilman, R.H.; et al. Urine lipoarabinomannan glycan in HIV-negative patients with pulmonary tuberculosis correlates with disease severity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeemeeah, F.; Sabet, R.; Moloantoa, T.; Waja, Z.; Pretorius, Z.; Majoro, K.; Letutu-Xaba, M.; Vilaplana, C.; Nigou, J.; Martinson, N. Exhaled breath specimens subjected to point-of-care lipoarabinomannan testing. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2023, 27, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Restrepo, S.F.; Zuberogoïtia, S.; Gouxette, L.; Layre, E.; Gilleron, M.; Stella, A.; Rengel, D.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Caro, A.C.; Garcia, L.; et al. A Mycobacterium tuberculosis fingerprint in human breath allows tuberculosis detection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broger, T.; Tsionksy, M.; Mathew, A.; Lowary, T.L.; Pinter, A.; Plisova, T.; Bartlett, D.; Barbero, S.; Denkinger, C.M.; Moreau, E.; et al. Sensitive electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunoassays for detecting lipoarabinomannan (LAM) and ESAT-6 in urine and serum from tuberculosis patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Amin, A.G.; Graham, B.; Martiniano, S.L.; Caceres, S.M.; Poch, K.R.; Jones, M.C.; Saavedra, M.T.; Malcolm, K.C.; Nick, J.A.; et al. Urine lipoarabinomannan as a marker for low-risk of NTM infection in the CF airway. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qvist, T.; Johansen, I.S.; Pressler, T.; Hoiby, N.; Andersen, A.B.; Katzenstein, T.L.; Bjerrum, S. Urine lipoarabinomannan point-of-care testing in patients affected by pulmonary nontuberculous mycobacteria--experiences from the Danish Cystic Fibrosis cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, J.A.; Dedrick, R.M.; Gray, A.L.; Vladar, E.K.; Smith, B.E.; Freeman, K.G.; Malcolm, K.C.; Epperson, L.E.; Hasan, N.A.; Hendrix, J.; et al. Host and pathogen response to bacteriophage engineered against Mycobacterium abscessus lung infection. Cell 2022, 185, 1860–1874.e1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerardel, Y.; Maes, E.; Briken, V.; Chirat, F.; Leroy, Y.; Locht, C.; Strecker, G.; Kremer, L. Lipomannan and lipoarabinomannan from a clinical isolate of Mycobacterium kansasii: Novel structural features and apoptosis-inducing properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36637–36651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, L.N.; Swapna, G.; Chavadi, S.S.; Tufariello, J.M.; Mi, K.; Drumm, J.E.; Lam, T.T.; Zhu, G.; Zhan, C.; Vilcheze, C.; et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis universal stress protein Rv2623 interacts with the putative ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter Rv1747 to regulate mycobacterial growth. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscolla, M.; Gagneux, S. Consequences of genomic diversity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneux, S.; DeRiemer, K.; Van, T.; Kato-Maeda, M.; de Jong, B.C.; Narayanan, S.; Nicol, M.; Niemann, S.; Kremer, K.; Gutierrez, M.C.; et al. Variable host-pathogen compatibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2869–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikusova, K.; Huang, H.; Yagi, T.; Holsters, M.; Vereecke, D.; D’Haeze, W.; Scherman, M.S.; Brennan, P.J.; McNeil, M.R.; Crick, D.C. Decaprenylphosphoryl arabinofuranose, the donor of the D-arabinofuranosyl residues of mycobacterial arabinan, is formed via a two-step epimerization of decaprenylphosphoryl ribose. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8020–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, M.; Hanlon, D.; Zhao, M.; Pollock, N.R. Detection of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan in serum for diagnosis of active tuberculosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, J.; Sasindran, S.J.; Fujiwara, N.; Turner, J.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Torrelles, J.B. Human lung hydrolases delineate Mycobacterium tuberculosis-macrophage interactions and the capacity to control infection. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torrelles, J.B.; Chatterjee, D. Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12111281
Torrelles JB, Chatterjee D. Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan. Pathogens. 2023; 12(11):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12111281
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorrelles, Jordi B., and Delphi Chatterjee. 2023. "Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan" Pathogens 12, no. 11: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12111281
APA StyleTorrelles, J. B., & Chatterjee, D. (2023). Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan. Pathogens, 12(11), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12111281






