Abstract
The present context is a pioneer attempt to verify the ability of copepod, Lernanthropus kroyeri (L. kroyeri), to uptake and accumulate heavy metals. We primarily assess the prevalence of the parasite in various seasons and its clinical signs, as well as post-mortem changes in sea bass (Moron labrax). The morphological features of the parasite using a light microscope, the bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the tissues of both L. kroyeri and M. labrax (gills, muscles) using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, and the histopathological alterations were monitored. Fish (n = 200) were obtained from Ezbet Elborg and examined for the parasite, L. kroyeri. The results revealed that the total infection was recorded at 86%. The infested fish exhibited excessive mucous and ulceration at the site of attachment. The post-mortem lesion in the gills revealed a marbling appearance with destructed filaments. Various heavy metals (Zn, Co, Cu, and Cd) were detected in the tissues of L. kroyeri and M. labrax and, surprisingly, L. kroyeri had the ability to uptake and accumulate a high amount of Zn in its tissues. Infested fish accumulated a lower concentration of Zn in their tissue compared with the non-infested ones. Within the host tissue, the accumulation of Zn was higher in the gills compared with the muscles. The histopathological findings demonstrated scattered parasitic elements with the destruction of the gill lamellae. Taken together, we highlight the potential role of L. kroyeri to eliminate Zn and it can be utilized as a bio-indicator for metal monitoring studies for sustaining aquaculture.
1. Introduction
Recently, parasitic infestations have induced serious hazards, including higher mortalities and diseases, to the freshwater fish in Egypt [1,2]. Parasitic copepods are commonly present in wild and cultured marine fish [3]. Lernanthropus is the most common genus of copepods and there are more than 100 species isolated from the gills of different species of marine fish [4,5]. Lernanthropus causes the erosion and necrosis of gill filaments [6] with severe desquamation and necrosis of the secondary lamellae and leukocytic infiltration [7]. At the site of parasite attachment, there is complete superficial tissue erosion with exposure of the primary lamellar cartilage, exposure of the blood vessels, and hemorrhage resulting from the grasping action of the mandibles and the maxillae of the parasite [6].
Pollution with heavy metals or toxic pollutants in the aquatic ecosystem is a global problem, with potential concern as it can negatively affect fish with health-inducing physiological, biochemical, molecular, and histopathological alterations [8,9,10]. Fish absorb heavy metals from the surrounding water and accumulate in different tissues in various amounts [11]. The metals can enter the bloodstream of fish and gradually accumulate in their tissues [12,13], particularly in the hepatic tissue, where they reach the consumers through the food chain or are bio-transformed and excreted [14].
Hence, parasites, as well as heavy metals, induce serious damage to the biochemical and physiological processes that in turn induce severe impairments to the health and physiology status of fish [15]. Recent reports have addressed various methods for heavy metal chelation such as natural extracts, probiotics, and nanoparticles [13,16,17]. Fish parasites are considered extra sensitive to pollution with heavy metals, as they not only uptake and accumulate toxicants in their tissues, but also produce a physiological response to them [18]. Parasites can be used either as effective indicators or as accumulation indicators, because of the different ways in which they react to anthropogenic pollution [19,20]. There is a relationship between parasitism and pollution, and the role of parasites as bio-indicators of heavy metals pollution [21]. Previous reports have addressed the ability of some parasites to accumulate heavy metal concentrations, such as Acanthocephalans, Cestodes [22], and parasitic nematodes [23,24].
Therefore, the current investigation was carried out to assess the impacts of L. kroyeri infestation. We addressed the prevalence of the parasite in the different seasons, the clinical signs, and the post-mortem changes. The body surface of L. kroyeri using a light microscope was illustrated, besides the bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the tissues of both L. kroyeri and M. labrax. Furthermore, histopathological alterations on the gills and muscles of infected M. labrax were detected.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Ethics
The protocol of the current study complies with the guidelines and was carried out according to the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986, and the associated guidelines of the EU Directive for Animal Experiments. The experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Aquatic Animal Care and Use Committee (IAACUC), Faculty of Aquatic and Fisheries Sciences, Kafrelsheikh University, Kafrelsheikh, Egypt. Approval Code: IAACUC-KSU-038-2022
2.2. Fish Samples
A total number of 200 sea bass (Moron labrax) fish samples were collected alive or freshly dead from the market of the Ezbet-El Borg area, Damietta Province, Egypt, during the period between March 2019 until February 2020. The collected fish were transported on thick ice polyethylene bags to the laboratory of the Animal Health Research Institute, El-Mansoura Branch, where they were examined immediately.
2.3. Clinical Examination
The fish were examined for the detection of any clinical abnormalities and external parasites according to Eissa [25].
2.4. Parasitological Examination
Examination of the external surface of the fish body was carried out with naked eyes and a hand lens to detect any abnormalities, the gill opercula were removed using scissors, and the gill filaments were transferred to slides with some normal saline and then covered by a cover slide and examined microscopically [26]. The detected crustacean parasites were carefully collected using a fine brush and special needle, transferred into Petri-dish, and washed several times in distilled water then preserved in 70% ethanol and cleared in lactophenol, and then mounted with polyvol [27].
2.5. Heavy Metals Analysis
The samples were dried at 60 °C for 48 h. Then, the samples were ground to a fine powder and stored in plastic bags until analysis. One gram of each sample was dry-ashed in a muffle furnace at 450 °C for 5 h, and extracted with 20% hydrochloric acid. The samples were measured by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry FAAS (GBC Avanta E, Victoria, Australia; Ser. No. A5616). All of the equipment used was calibrated and uncertainties were calculated. Internal and external quality assurance systems were applied in the Central Laboratory of Environmental Studies at Kafr-Elsheikh University according to ISO/IEC 17025 (2005). All of the measurements, blanks, triplicate measurements of elements in the extracts, and analysis of certified reference materials for each metal (Merck) were routinely included for quality control.
2.6. Histopathological Examination
Tissue specimens were collected from the gills and immediately fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution for at least 24 h, then processed using the conventional paraffin embedding technique. Five-micron sections were prepared and then routinely stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) according to Suvarna et al. [28], and then examined microscopically.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Examination of Infected Fish
The clinical signs of the infected fish were hemorrhagic areas on different parts of the body surface (Figure 1, red arrows) and the gills showed a marbling appearance (area of redness and paleness) (Figure 1, white arrows). The gill tips were attached in some areas with mucous secretion and L. kroyeri was seen macroscopically as black filaments (Figure 1, black arrows).
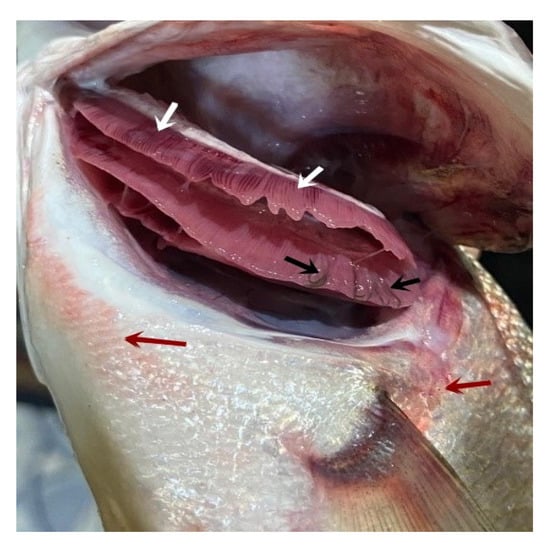
Figure 1.
Moron labrax showing hemorrhagic areas on different parts of the body surface (red arrows), a marbling appearance (white arrows), and gill tips that were attached in some areas with mucous secretion, and the parasites were seen by naked eyes as black filaments (black arrows).
3.2. Parasitological Examination
3.2.1. Morphological Description of L. kroyeri Van Beneden, 1851
The parasite was found to be attached to the gills of M. labrax. It appeared to have a white to yellowish color in the fresh samples. The female was easily recognized by the presence of the two egg-sacs, which were clearly seen by the naked eyes (Figure 2). The bodies of isolated copepods appeared elongated in both sexes.
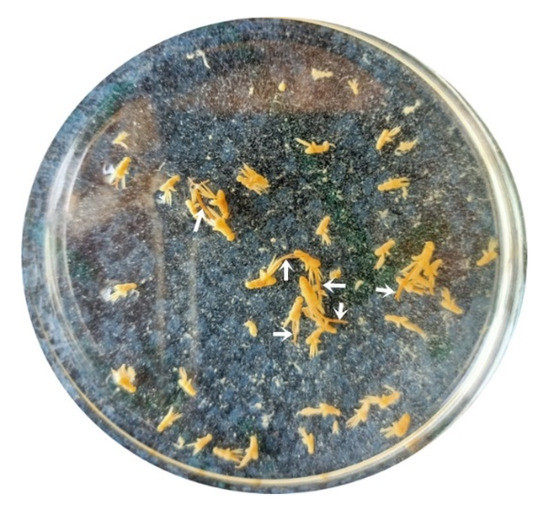

Figure 2.
Fresh samples of the parasite, L. kroyeri, appeared white to yellowish color in the Petri dish. The female was easily recognized by the presence of the two egg-sacs (arrows).
The cephalothorax had a dorsal shield narrower anteriorly, and was slightly concave on the posterior margin, with rounded posterolateral corners and the anterolateral extended ventrally as prominent, rounded lobes. A deep constriction was found between the cephalothorax and pregenital trunk. There were four pairs of thoracic legs, the first one was biramous (Figure 3).
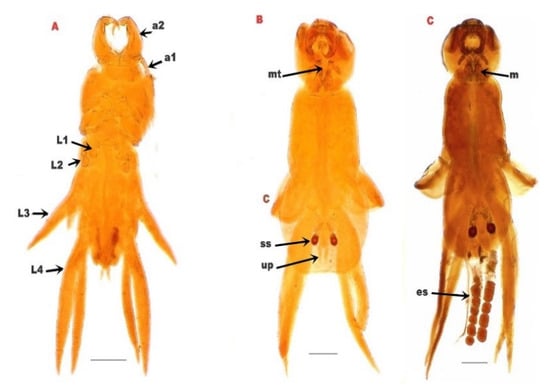
Figure 3.
(A): L. kroyeri premature stage. (B): male L. kroyeri. (C): female L. kroyeri. a1; 1st antenna. a2; 2nd antenna. L1; 1st thoracic leg. L2; 2nd thoracic leg. L3; 3rd thoracic leg. L4; 4th thoracic leg. m; maxilliped. mt; mouth tube. es; egg sac. ss; spermatophore sac. up; uropod. Scale bars = 500 μm.
3.2.2. Prevalence of L. kroyeri in Infected M. labrax
One hundred sixty-two out of two hundred examined M. labrax were infected with L. kroyeri (81%). The highest infection was recorded during spring (94%), followed by summer (90%) and then autumn (78%), and the lowest infections were recorded in winter (31%), as depicted in Table 1 and Figure 4.

Table 1.
Prevalence of L. kroyeri among examined M. labrax along the monitored season.
Table 1.
Prevalence of L. kroyeri among examined M. labrax along the monitored season.
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Total | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nu Ex | Nu In | % | Nu Ex | Nu In | % | Nu Ex | Nu In | % | Nu Ex | Nu In | % | Nu Ex | Nu In | % |
| 50 | 31 | 62 | 50 | 47 | 94 | 50 | 45 | 90 | 50 | 39 | 78 | 200 | 162 | 81 |
Nu.Ex: number of examined M. labrax. Nu.In: number of infected M. labrax. %: Percentage of infection.
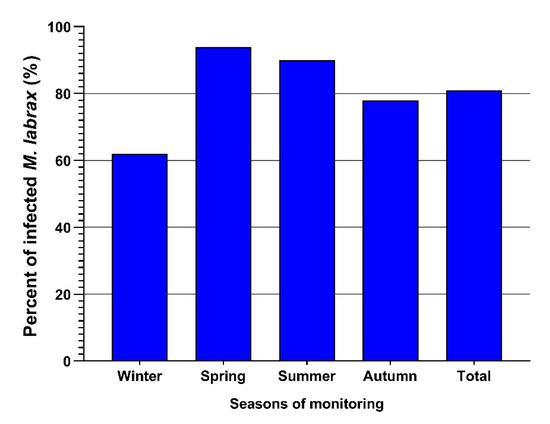
Figure 4.
Seasonal prevalence of L. kroyeri infestation among the examined M. lebrax fish along the monitored seasons. Bars demonstrate the percentage of infested fish in each season.
3.2.3. Heavy Metal Accumulation by L. kroyeri and Fish Host
Mean ± SEM of heavy metal concentrations in the gills and muscle of both infected and non-infected fish, as well as in parasitic tissue, are illustrated in Table 2 and Figure 5. Zinc was accumulated in higher levels in the gills (374.0 ± 2.51 mg/kg) and muscles (270.5 ± 3.03 mg/kg) of non-infested fish compared with the gills (275.0 ± 3.11 mg/kg) and muscles (124.8 ± 2.15 mg/kg) of infested fish. Surprisingly, the parasite accumulated Zn in its tissue (237.5 ± 2.86 mg/kg). The differential concentration of Zn in the gills, muscle, and parasitic tissue were analyzed by an unpaired t-test, while the concentrations of other elements were recorded under the detection limit (UDL; <0.3 mg/kg for Co and Cu or <0.03 mg/kg for Cd).

Table 2.
Mean of heavy metal concentration in fish tissues and parasites.
Table 2.
Mean of heavy metal concentration in fish tissues and parasites.
| Element | Organ | Non-Infected | Infected | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Fish | Gills | 374.0 ± 2.51 | 275.0 ± 3.11 | <0.0001 |
| Muscle | 270.5 ± 3.03 | 124.8 ± 2.15 | <0.0001 | ||
| Parasite | 237.5 ± 2.86 | ||||
| Co | Fish | Gills | UDL | UDL | - |
| Muscle | UDL | UDL | - | ||
| Parasite | UDL | ||||
| Cd | Fish | Gills | UDL | UDL | - |
| Muscle | UDL | UDL | - | ||
| Parasite | UDL | ||||
| Cu | Fish | Gills | UDL | UDL | - |
| Muscle | UDL | UDL | - | ||
| Parasite | UDL | ||||
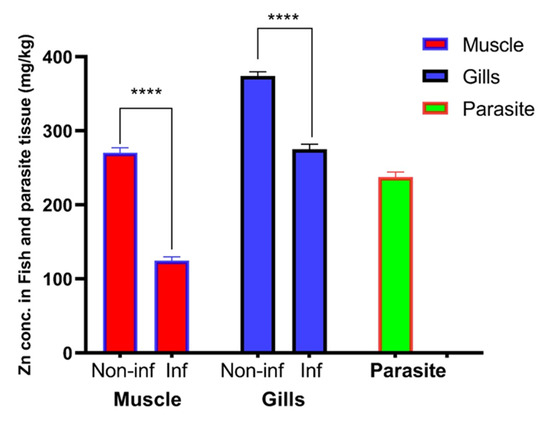
Figure 5.
Mean ± SEM concentration of Zn in the gills, muscle, and parasitic tissue. (****) indicates significant differences at p value > 0.0001 as reported via t-test.
3.3. Histopathological Results
Various sections from crustacean parasitic elements randomly distributed in the gills were noticed (Figure 6A,B). The adjacent primary filaments were bent, stunted, and disorganized with the partial or complete destruction of the secondary lamellar epithelium (Figure 6A,B). Metaplasia of some surface epithelium to goblet cells was evident. Sometimes, intense hemorrhage on the gill surface, excess mucous exudate, and parasites were also observed (Figure 6C). Moreover, complete destruction of the secondary lamellar epithelium from both sides of the gill filaments leaving the primary filaments denuded could be seen (Figure 6D).
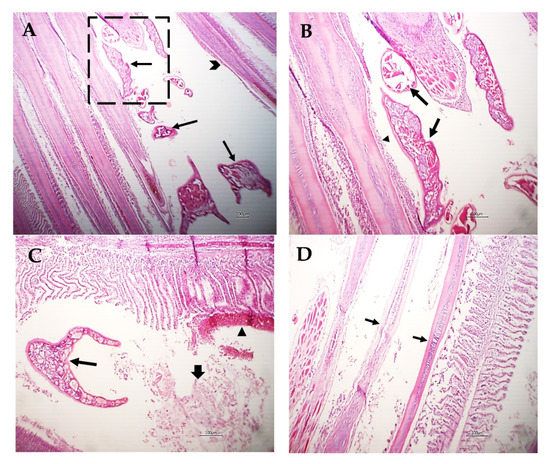
Figure 6.
Photomicrograph of M. labrax gills stained with H&E. (A) Parasitic elements embedded between gill filaments (arrows) with stunted, bent, and disorganized primary filaments (arrowhead). (B) High power of the previous picture showing parasitic sections (arrows) with partial destruction of the lamellar epithelium (arrowhead) or metaplasia to mucus-secreting cells. (C) Gills showing parasitic sections (thin arrow), intense hemorrhage on the gill surface (arrowhead), and mucous exudate (thick arrow). (D) Gills showing denuded of primary filaments (arrow) with complete destruction of the secondary lamellae of some filaments. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Other gill filaments showed compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the secondary lamellar epithelium, which resulted in their fusion (Figure 7A). The blood vessels of the gill filaments and arches revealed telangiectasis beside edema in the surrounding tissue (Figure 7B). Sometimes, lymphocytes and eosinophils granular cells besides melanomacrophage cells were focally scattered in the gill filaments and arches and the sloughing of epidermal tissue of the gill arch in addition to metaplasia to the mucus secretory cells were common (Figure 7C). The gill raker had erosion of its covering epithelium besides necrosis and hyalinization of the muscles (Figure 7D).
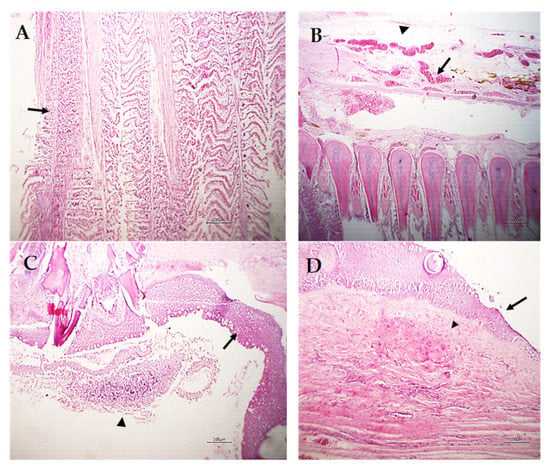
Figure 7.
Photomicrograph of M. labrax gills stained with H&E. (A) Showing compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the secondary lamellar epithelium (arrow) of some adjacent gill filaments. (B) Gill arch showing telangiectasis of blood vessels (arrow) and edema (arrowhead). (C) Gill arch showing partial sloughing of the epidermal covering (arrowhead) and metaplasia of the mucus secretory cells (goblet cells) in superficial cells (arrow). (D) Gill raker showing erosion of the covering epithelium (arrow) with necrosis and partial hyalinization of muscles (arrowhead). Scale bar = 100 µm.
4. Discussion
Lernanthropus is the most common genus of parasitic copepods. There are more than 100 species described from the gills of different marine fish [5]. The current investigation revealed hemorrhagic areas on the body surface with excessive mucous secretion and a marbling appearance of the gills of infected M. labrax with L. kroyeri. These lesions could be attributed to the attachment of the parasites by their rigid claws, feeding activity, severe irritation caused by parasitic movement, and mucous increase as a defense mechanism from the host to overcome the infection, as reported by Abdel-Mawla et al. [29].
The present study recorded the isolation of L. kroyeri from the gills of M. labrax. Likewise, Toksen et al. [30], Henry et al. [31], and Eissa et al. [32] isolated the same parasite from the same host and the same site. Meanwhile, El-Deen et al. [33] and Hassanin [34] isolated L. kroyeri from the gills of other fish species such as Mugil cephalus and Moolgarda seheli.
In the current prospective study, the prevalence of L. kroyeri was 81%, concurrent with a previous study by Aneesh et al. [35] that recorded 81.4% infection of Strongylura strongylura by L. kroyeri. Additionally, Toksen [5] reported a higher infection rate (100%) by L. kroyeri in Dicentrarchus labrax. Nevertheless, Manera and Dezfuli [6] obtained a lower infection rate (35%) with L. kroyeri in D. labrax. Our paper reports that L. kroyeri infection was the highest during spring (94%), followed by summer (90%), then autumn (78%), and finally winter (31%). This sequence is nearly in agreement with Eissa [25], who also reported that the infection rate with L. kroyeri reached its maximum rate during spring and summer, while the lowest infection was recorded during autumn. These results were inconsistent with Samak and Said [36], who reported that the infection rates with the same parasite reached their maximum rates in autumn and winter (42.5% and 35%), respectively, while their minimum value was 7.5% in spring. These variances in the total infection and seasonal dynamics could be a result of the difference in fish species and the difference in the locality of fish collection.
Zn is an essential heavy metal with a permissible limit in the fish muscle of 40 mg/kg [37] or 100 mg/kg [38]. The toxic effect of zinc on aquatic animals depends on several environmental factors, especially temperature, water hardness, and dissolved oxygen concentration. An acute toxic concentration of zinc kills fish by destroying gill tissue and at a chronic toxic level, it induces stress that results in the death of fish [39]. Certain fish parasites can accumulate heavy metals at concentrations significantly higher than those in host tissues or the environment [40,41,42,43,44]. The data of our study revealed that there was a high concentration of Zn in the collected samples, while the concentrations of Cu, Cd, and Co were under the detection limit. In general, the accumulation of Zn was significantly higher in the non-infested tissue in comparison with the infested tissue samples. It is thought that L. kroyeri can absorb Zn from the fish tissue through its alimentary canal and that it accumulates in the parasite tissue, and this finding was verified by analysis of Zn in the parasite tissue. In the same manner, a recent study by Hassanine and Al-Hasawi [45] reported that acanthocephalan accumulates higher concentrations of heavy metals. Concurrent with another study, Szefer et al. [46] suggested that the bioaccumulation of parasites may reflect the higher ability of the host to clear heavy metals. In addition, Thielen et al. [44], Sures and Siddall [47], and Malek et al. [48] considered the parasites beneficial and that they could act as a heavy metal sanitizer for the host. Gills accumulated a higher Zn value compared with the edible part of its fish host. The low ratio of Zn concentration in the host muscle could be a result of the longer exposure time as metal uptake occurs faster in parasites, as stated by Sures [40].
Considering the histopathological findings, we illustrated sections of L. kroyeri were distributed in the gills. Similarly, a recent study by Eissa et al. [7] reported the occurrence of L. kroyeri fragments in the gills of D. labrax. The destruction of the secondary lamellar epithelium, goblet cell metaplasia with hemorrhage, and excess mucous secretion could be induced as a tissue reaction to decrease the irritation against the infestation. Concurrent with previous studies, Abdel-Mawla et al. [29], Lester and Hayward [49], Manera and Dezfuli [6], and Ragias et al. [50] reported extensive hemorrhage due to the feeding activity of this parasite. Lymphocytes and eosinophils were found in the gill filaments and arches, and these outcomes have been previously reported [4,5,6,51,52]. In addition, erosion of the gill raker as well as necrosis of the muscles was seen; likewise, Vinoth et al. [53] reported pale gills induced by copepod parasites due to the loss of the gill raker.
Our investigation concluded that, although L. kroyeri has a negative effect on the infected M. labrax, it also plays an important role in the elimination of heavy metals from the tissue of the infected fish through its ability to accumulate heavy metals in its body, which can be advantageous for the infected hosts, allowing them to tolerate much higher concentrations of certain metals. The present results also confirm that L. kroyeri seems to be a good indicator of environmental pollution.
5. Conclusions
To date, our perspective study represents a premier work to report on the efficacy of L. kroyeri to uptake and accumulate heavy metals (zinc). However, L. kroyeri infests M. labrax with a high prevalence in spring and summer and demonstrates excessive mucous secretion, ulceration, marbling appearance of gills, and various histopathological changes in the gills of the infested fish. By detecting various heavy metals (Zn, Co, Cu, and Cd) in the tissues of L. kroyeri and M. labrax, surprisingly, L. kroyeri was found to uptake the highest concentration of Zn in its tissues. Conclusively, the parasitic infestation is an eco-friendly method to uptake heavy metals, and L. kroyeri can be utilized as a natural antitoxic agent, as well as be considered a bio-indicator of toxicity with heavy metals and to lessen the hazardous impact on the aquatic environment for sustaining aquaculture. Future studies are needed to test the activity of other parasites to chelate heavy metals, as well as studies on various fish species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; methodology, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; formal analysis, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; investigation, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; resources, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.A.Z., R.R.A.E.M., N.R., D.M.M., and H.H.M.; editing and responding to reviewers’ comments, H.M.A.E.-L., J.-M.S., H.M.S., G.E.-S.B., and M.D.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.D.W. thanks the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche and the Région Pays de la Loire for financial support on COVID-19 research (ANR Flash COVID 19 call—name: CoV2-E-TARGET—grant number: 2020 07132).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Aquatic Animal Care and Use Committee (IAACUC), Faculty of Aquatic and Fisheries Sciences, Kafrelsheikh University, Kafrelsheikh, Egypt. Approval Code: IAACUC-KSU-038-2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement:
All data available in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research at King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia, for financial support under the annual funding track (GRANT 2136).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mahboub, H.H.; Shaheen, A. Prevalence, diagnosis and experimental challenge of Dermocystidium sp. infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H. Mycological and histopathological identification of potential fish pathogens in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, G.; Ravichandran, S. Lernaeenicus sprattae (Crustacea: Copepoda) on Hemiramphus far. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 11, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar]
- KORUN, J.; TEPECİK, R. Gill lesions caused by infection of Lernanthropus spp. Blainville, 1822 on cultured sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). İstanbul Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2005, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Toksen, E. Lernanthropus kroyeri van Beneden, 1851 (Crustacea: Copepoda) infections of cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2007, 27, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Manera, M.; Dezfuli, B.S. Lernanthropus kroyeri infections in farmed sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax: Pathological features. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 57, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.; Dessouki, A.; Abdel-Mawla, H.; Qorany, A. Prevalence of Lernanthropus Kroyeri in Seabass (Dicentrarchus Labrax) and spotted seabass (Dicentrarchus Punctatus) from Suez Canal, Egypt. Int. J. Fisher. Aquat. Res 2020, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mbeh, G.M.; Kamga, F.T.; Kengap, A.K.; Atem, W.E.; Mbeng, L.O. Quantification of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Fe, Mg, Cu, and Zn) in seafood (fishes and crabs) and evaluation of health risks to consumers in Limbe, Cameroon. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2019, 10, 948–957. [Google Scholar]
- Abiona, O.O.; Anifowose, A.J.; Awojide, S.H.; Adebisi, O.C.; Adesina, B.T.; Ipinmoroti, M.O. Histopathological biomarking changes in the internal organs of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and catfish (Clarias gariepinus) exposed to heavy metals contamination from Dandaru pond, Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2019, 13, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhiee, E.Y.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Saad, A.H.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Aboubakr, M.; El-Nagar, S.H.; El-Diasty, E.M.; Salah, A.S.; Saad, H.M.; Fadl, S.E. The impact of Moringa oleifera on the health status of Nile tilapia exposed to aflatoxicosis. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.E.; Alhindy, M.K.; Fahmy, M. Trypanorhynch cestodes infecting Mediterranean Sea fishes, Egypt: Callitetrarhynchus gracilis larvae (Pintner, 1931) as a bio-indicator of heavy metals pollution. Oceanography 2015, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, H.T.H.; Mahboub, H.H.H. Effect of acute exposure to nonylphenol on biochemical, hormonal, and hematological parameters and muscle tissues residues of Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Vet. World 2016, 9, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Beheiry, R.R.; Shahin, S.E.; Behairy, A.; Khedr, M.H.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Daoush, W.M.; Altohamy, D.E.; Ismail, T.A. Adsorptivity of mercury on magnetite nano-particles and their influences on growth, economical, hemato-biochemical, histological parameters and bioaccumulation in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 235, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Z.; Pazooki, J.; Abtahi, B.; Shokri, M.R. Bioaccumulation of Zn and Cu in Chasar bathybius (Gobiidae) tissue and its nematode parasite Dichelyne minutus, southeast of the Caspian Sea, Iran. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2013, 42, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sabra, F.S.; Mehana, E.-S.E.-D. Pesticides toxicity in fish with particular reference to insecticides. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2015, 3. Available online: https://www.ajouronline.com/index.php/AJAFS/article/view/2156 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- El-Bouhy, Z.M.; Reda, R.M.; Mahboub, H.H.; Gomaa, F.N. Bioremediation effect of pomegranate peel on subchronic mercury immunotoxicity on African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 2219–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bouhy, Z.M.; Reda, R.M.; Mahboub, H.H.; Gomaa, F.N. Chelation of mercury intoxication and testing different protective aspects of Lactococcus lactis probiotic in African catfish. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3815–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, A. Ecology of the acanthocephalan Sclerocollum rubrimaris Schmidt and Paperna, 1978 (Rhadinorhynchidae: Gorgorhynchinae) from wild populations of rabbitfish (genus Siganus) in the northern Red Sea. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 34, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Dezfuli, B.S.; Krug, H.F. The intestinal parasite Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) interferes with the uptake and accumulation of lead (210Pb) in its fish host chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckenbach, T.; Triebskorn, R.; Müller, E.; Oberemm, A. Toxicity of waters from two streams to early life stages of brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario L.), tested under semi-field conditions. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B. How parasitism and pollution affect the physiological homeostasis of aquatic hosts. J. Helminthol. 2006, 80, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najm, M.; Fakhar, M. Helminthic parasites as heavy metal bioindicators in aquatic ecosystems. Med. Lab. J. 2015, 9, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar, H.; Malek, M.; McKenzie, K. The parasitic nematodes Hysterothylacium sp. type MB larvae as bioindicators of lead and cadmium: A comparative study of parasite and host tissues. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachev, M.; Schertzinger, G.; Sures, B. Comparison of the metal accumulation capacity between the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis and larval nematodes of the genus Eustrongylides sp. infecting barbel (Barbus barbus). Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.E. Clinical and Laboratory Manual of Fish Diseases; Lap Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lucky, Z.; Lucký, Z.k. Methods for the diagnosis of fish diseases. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 1977, 1, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Raef, A.; El-Ashram, A.; El-Sayed, N. Crustacean parasites of some cultured freshwater fish and their control in Sharkia. Egypt. Vet. J. 2000, 28, 180–191. [Google Scholar]
- Suvarna, K.S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Mawla, H.I.; El-Lamie, M.M.; Dessouki, A.A. Investigation on ectoparasitic crustacean diseases in some Red sea fishes and their associated pathological lesions. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2015, 28, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Toksen, E.; Nemli, E.; Degirmenci, U. The morphology of Lernanthropus kroyeri van Beneden, 1851 (Copepoda: Lernanthropidae) parasitic on sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L., 1758), from the Aegean Sea, Turkey. Turk. Soc. Parasitol. 2008, 32, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Alexis, M.; Fountoulaki, E.; Nengas, I.; Rigos, G. Effects of a natural parasitical infection (Lernanthropus kroyeri) on the immune system of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.; El-Lamie, M.; Zakai, M. Studies on Crustacean Diseases of Seabass, Morone Labrax, in Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 512–518. [Google Scholar]
- El-Deen, A.N.; Mahmoud, A.; Hassan, A. Field studies of caligus parasitic infections among cultured seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and mullet (Mugil cephalus) in marine fish farms with emphasis on treatment trials. Glob. Vet. 2013, 11, 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanin, D.A. Studies on prevailing problems affecting cultured marine fishes at port-said governorate. M. Sc. Fac. Vet. Med. (Dept. Fish Dis. Manag.) Suez. Canal. Univ. 2016, 22, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneesh, P.-T.; Sudha, K.; Helna, A.K.; Anilkumar, G.; Trilles, J.-P. Multiple parasitic crustacean infestation on belonid fish Strongylura strongylura. ZooKeys 2014, 457, 339–353. [Google Scholar]
- Samak, O.A.A.; Said, A.E. Population Dynamics of the Monogeneans, Diplectanum Aequans and d. Laubieri and the Copepod, Lernanthropus Kroyeri Infesting the Gills of the Sea Bass, Dicentrarchus labrax in Egypt. Res. Gate 2008, 56, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. In Proceedings of the Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Thirty-Third Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, Geneva, Switzerland, 21–30 March 1989. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/39252 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- World Health Organization. Lead: Environmental Aspects-Environmental Health Criteria 85; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore, J. Toxicity of zinc compounds to aquatic animals, with special reference to fish. Q. Rev. Biol. 1964, 39, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B. The use of fish parasites as bioindicators of heavy metals in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2001, 35, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B. Accumulation of heavy metals by intestinal helminths in fish: An overview and perspective. Parasitology 2003, 126, S53–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schludermann, C.; Konecny, R.; Laimgruber, S.; Lewis, J.; Schiemer, F.; Chovanec, A.; Sures, B. Fish macroparasites as indicators of heavy metal pollution in river sites in Austria. Parasitology 2003, 126, S61–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin-Özan, S.; Kir, İ. Comparative study on the accumulation of heavy metals in different organs of tench (Tinca tinca L. 1758) and plerocercoids of its endoparasite Ligula intestinalis. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 97, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, F.; Zimmermann, S.; Baska, F.; Taraschewski, H.; Sures, B. The intestinal parasite Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) from barbel as a bioindicator for metal pollution in the Danube River near Budapest, Hungary. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanine, R.; Al-Hasawi, Z. Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts. Fishes 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P.; Rokicki, J.; Frelek, K.; Skóra, K.; Malinga, M. Bioaccumulation of selected trace elements in lung nematodes, Pseudalius inflexus, of harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) in a Polish zone of the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 220, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B.; Siddall, R. Pomphorhynchus laevis: The intestinal acanthocephalan as a lead sink for its fish host, chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Exp. Parasitol. 1999, 93, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Haseli, M.; Mobedi, I.; Ganjali, M.; MacKenzie, K. Parasites as heavy metal bioindicators in the shark Carcharhinus dussumieri from the Persian Gulf. Parasitology 2007, 134, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, R.J.; Hayward, C.J. Phylum arthropoda. In Fish Diseases and Disorders. Volume 1: Protozoan and Metazoan Infections; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2006; pp. 466–565. [Google Scholar]
- Ragias, V.; Tontis, D.; Athanassopoulou, F. Incidence of an intense Caligus minimus Otto 1821, C. pageti Russel, 1925, C. mugilis Brian, 1935 and C. apodus Brian, 1924 infection in lagoon cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) in Greece. Aquaculture 2004, 242, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithendran, K.; Natarajan, M.; Azad, I. Crustacean parasites and their management in brackishwater fi nfi sh culture. Aquac. Asia 2008, 13, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yardimci, B.; Pekmezci, G.Z. Gill histopathology in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax (L.) coinfected by Diplectanum aequans (Wagener, 1857) and Lernanthropus kroyeri (van Beneden, 1851). Ank. Üniv. Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2012, 59, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth, R.; Kumar, T.A.; Ravichandran, S.; Gopi, M.; Rameshkumar, G. Infestation of Copepod parasites in the food fishes of Vellar estuary, Southeast coast of India. Acta Parasitol. Glob. 2010, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).