Relationship between Uveal Inflammation and Viral Detection in 30 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pathotype, Extraocular Lesions and Duration of Clinical Signs in Selected Cases
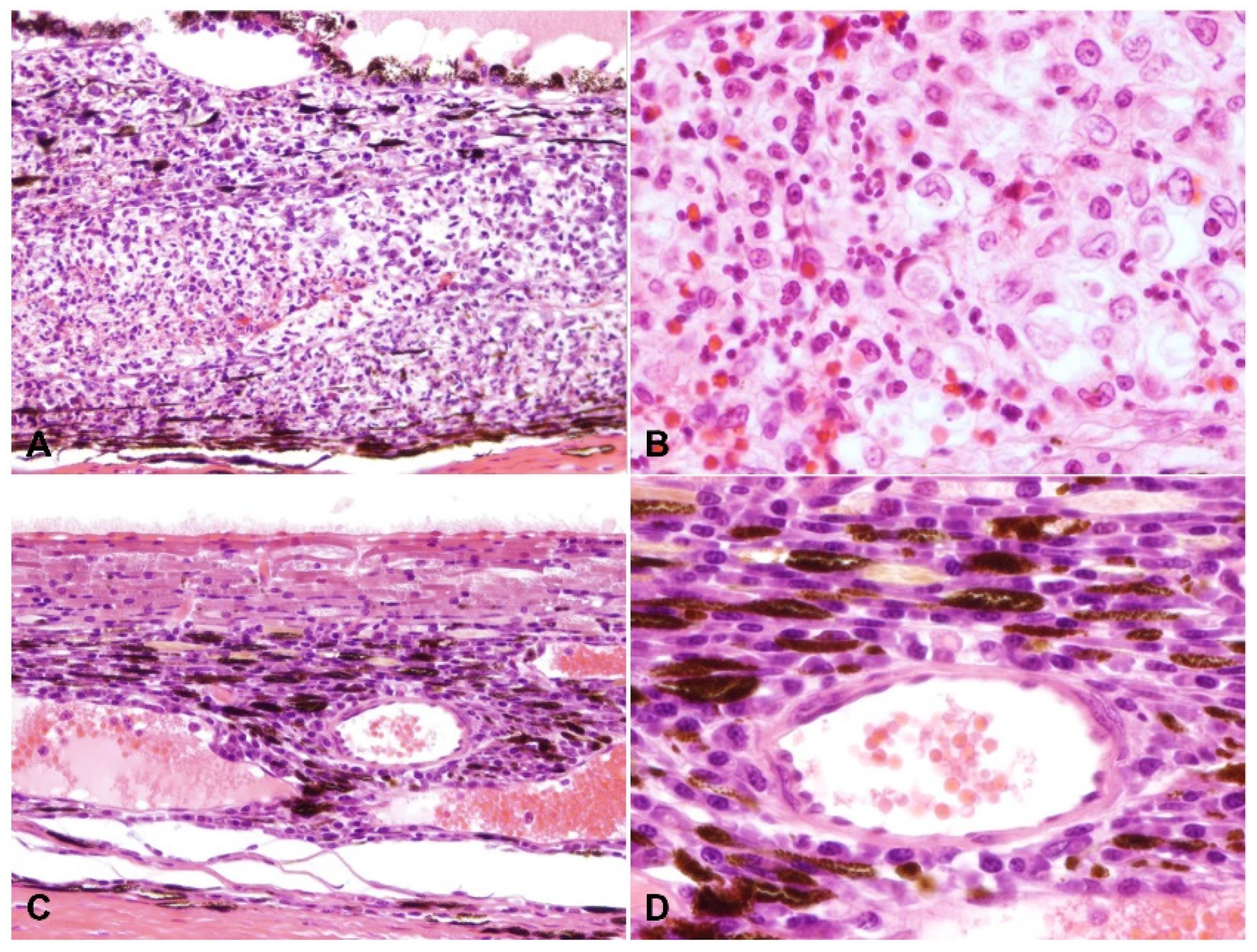
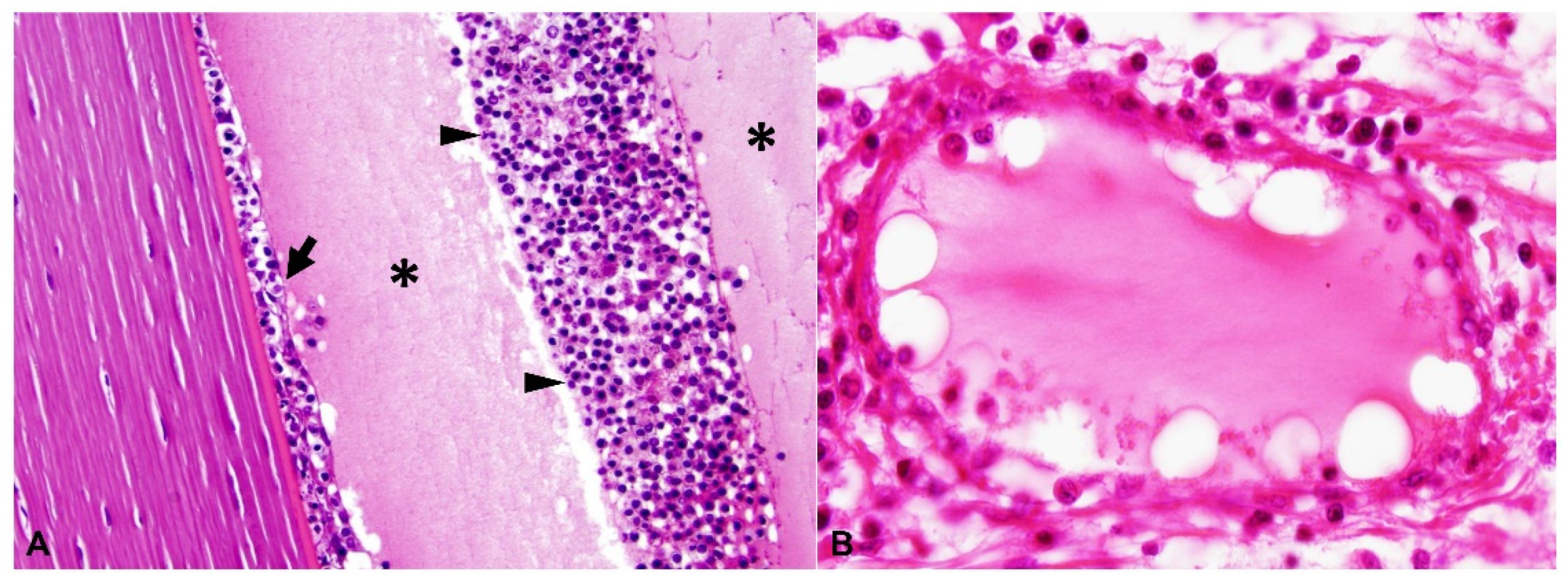
2.2. Ocular Lesions in Cats with FIP-induced Uveitis
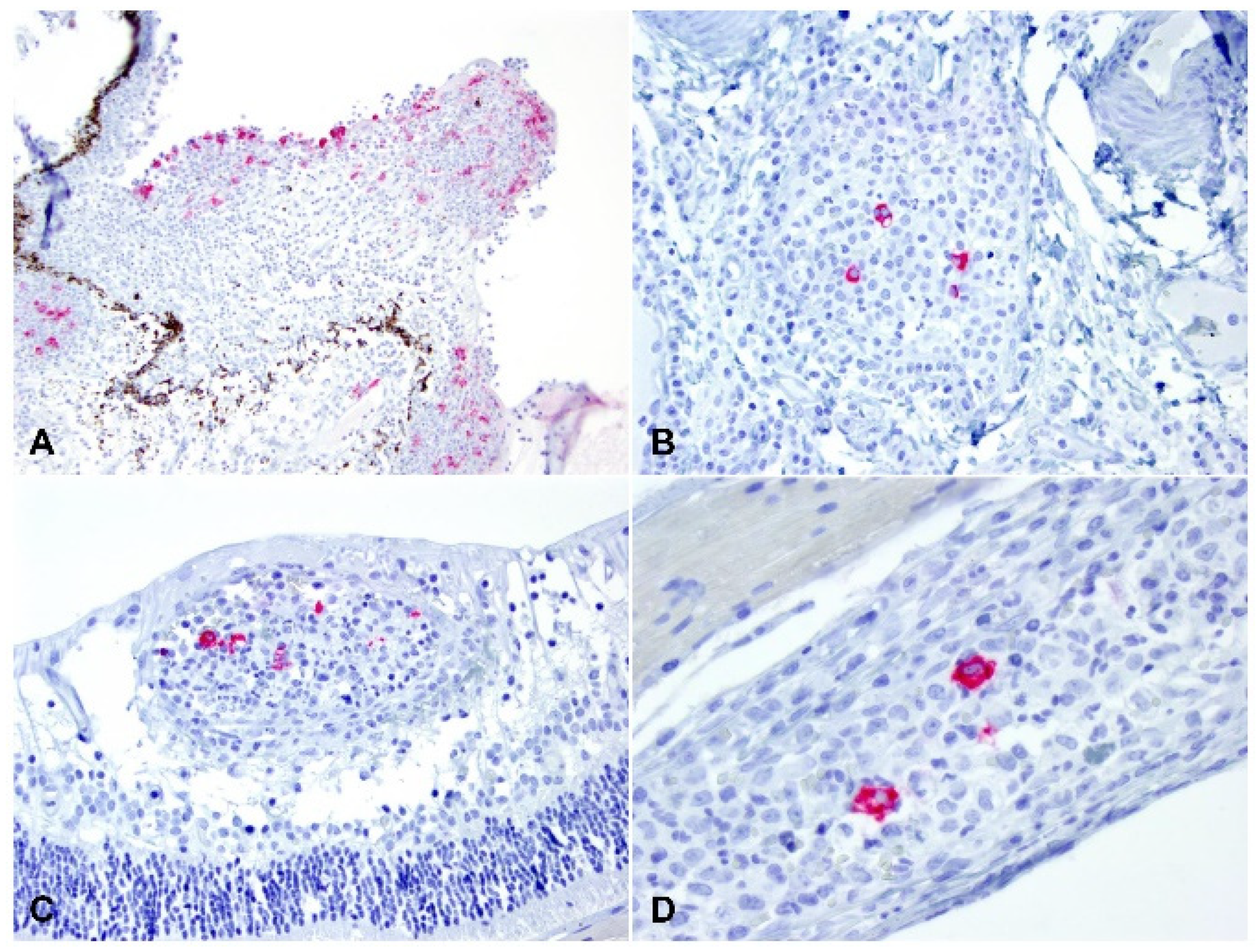
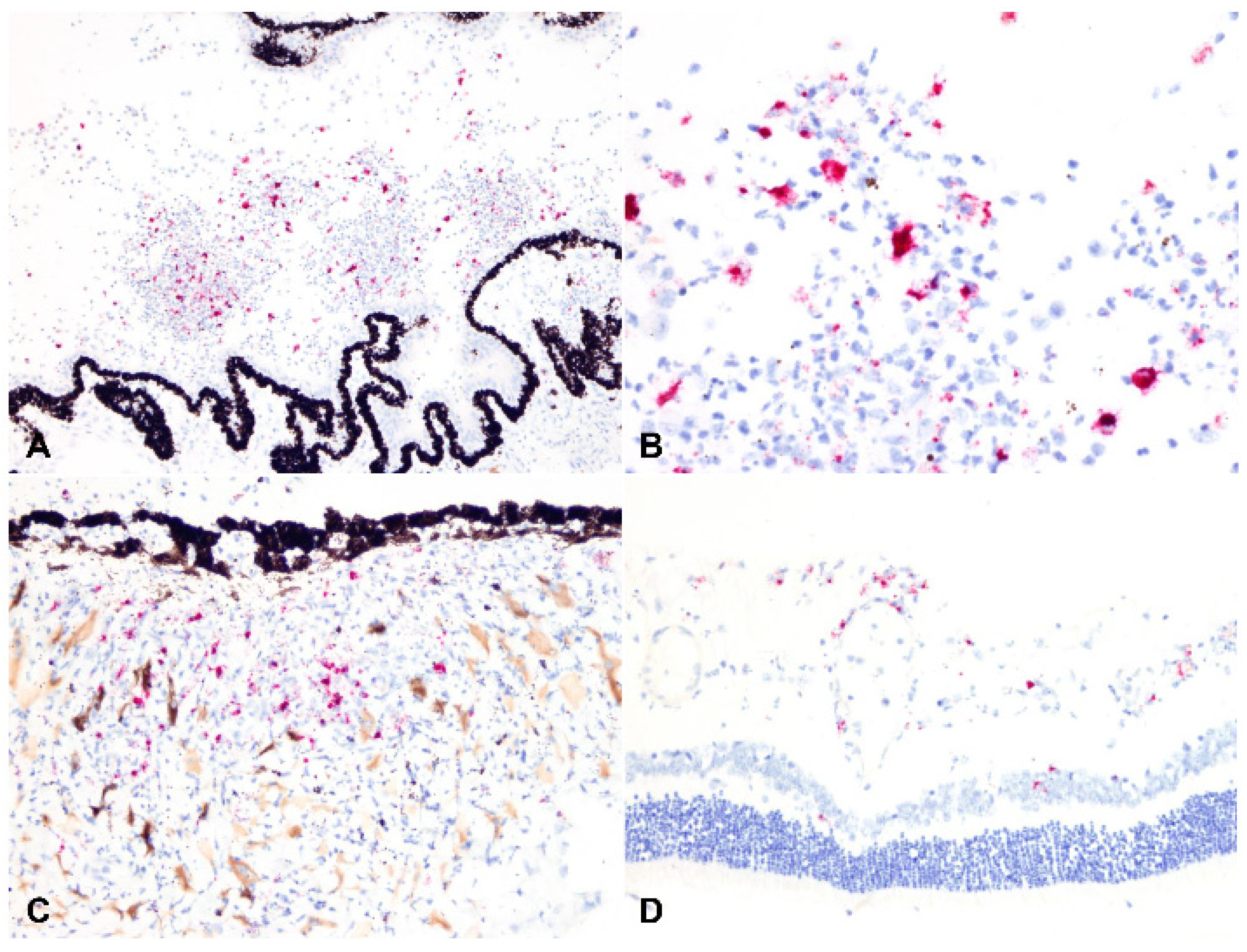
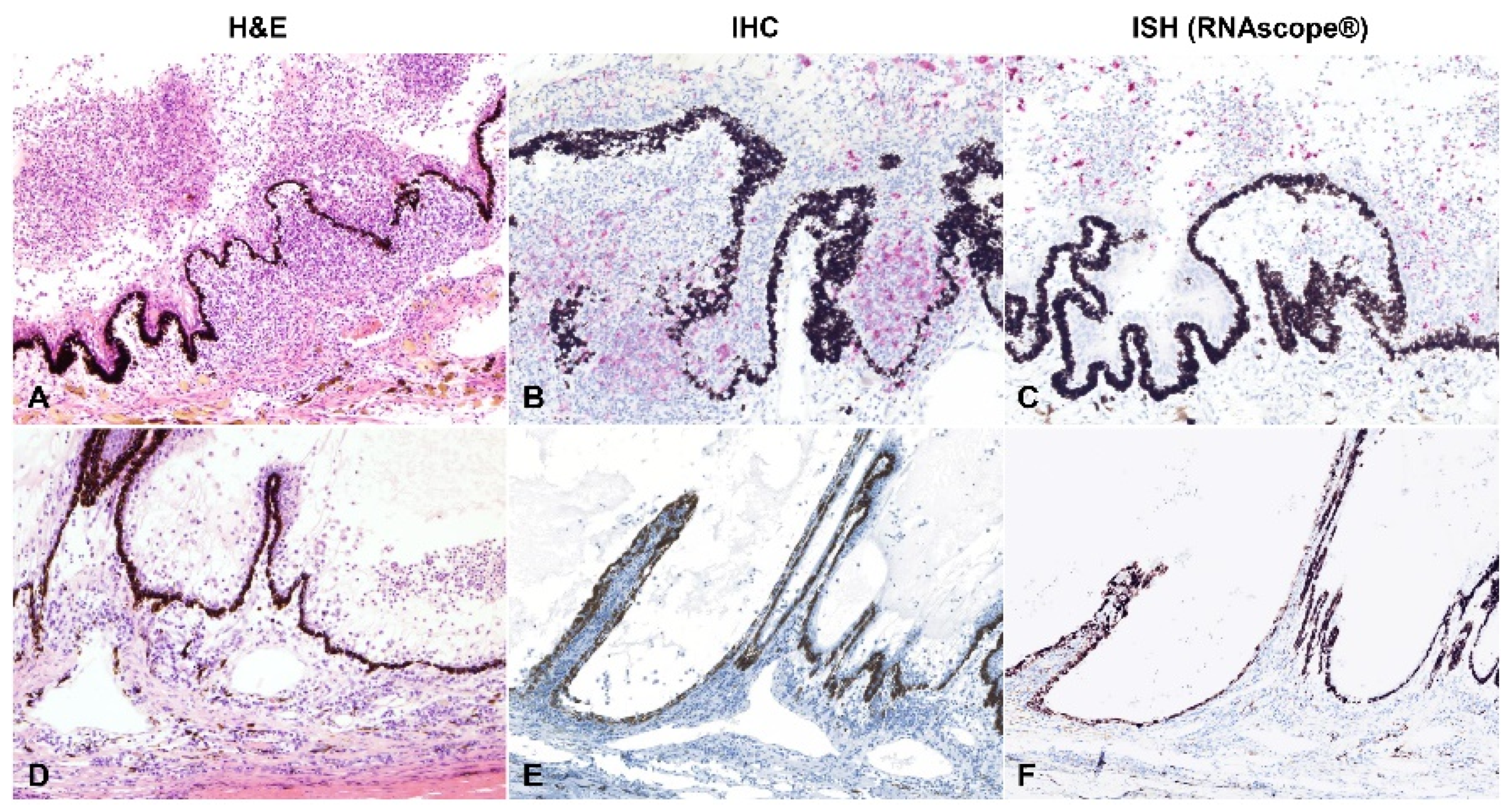
2.3. Detection of Viral Antigen and RNA Via Immunohistochemistry, RNAscope® In Situ Hybridization and RT-qPCR
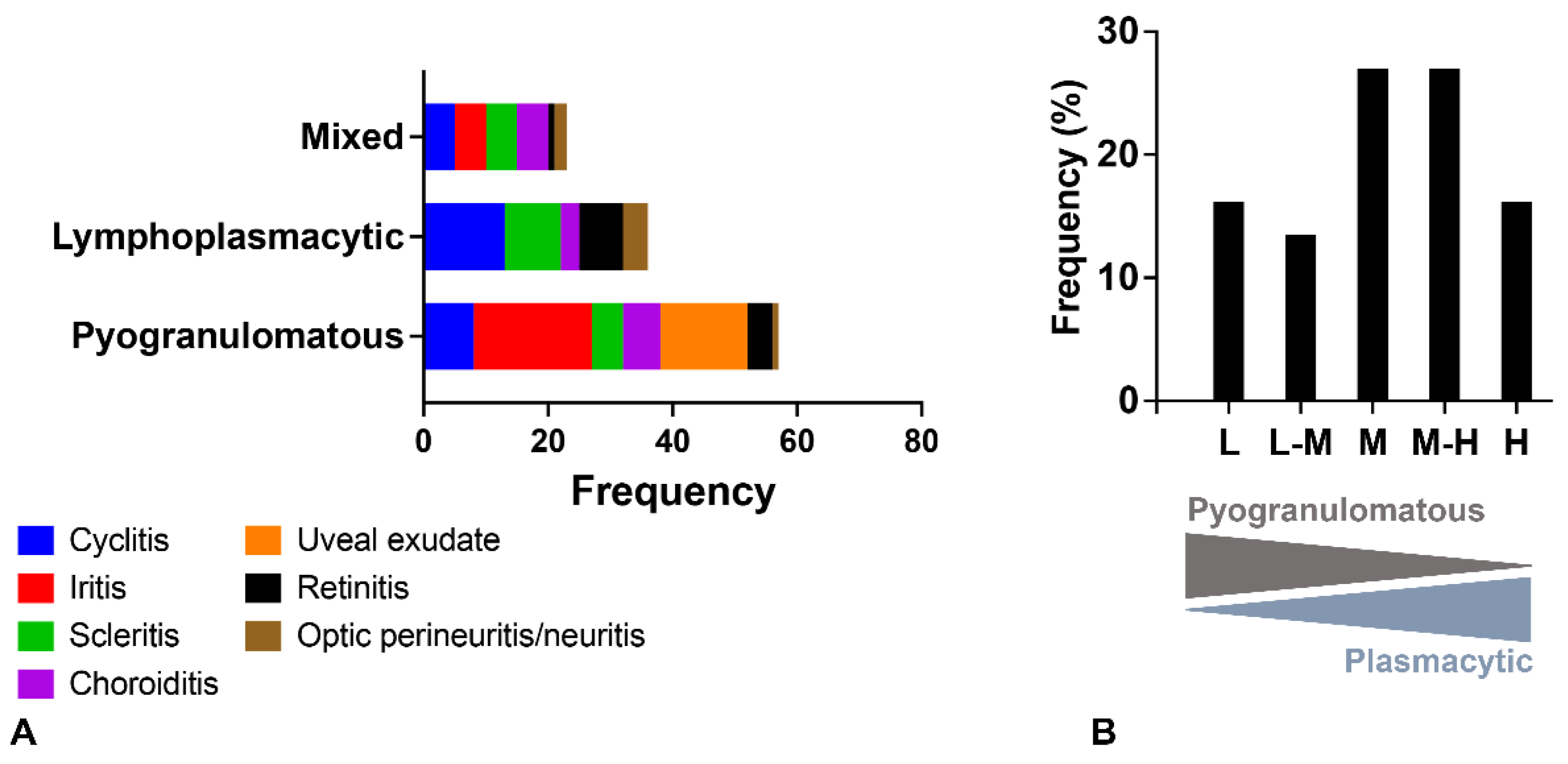
2.4. Relationship between Type of Inflammation and Detection of Viral Antigen and RNA via Immunohistochemistry, RNAscope® In Situ Hybridization and RT-qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Case Selection and Histopathology
4.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.3. RNAscope® In Situ Hybridization (RNAscope® ISH)
4.4. RT-qPCR
4.5. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrew, S.E. Feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 30, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Troyer, J.L.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Roelke, M.E.; O’Brien, S.J. Genetics and pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.W.; de Groot, R.J.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Feline infectious peritonitis: Insights into feline coronavirus pathobiogenesis and epidemiology based on genetic analysis of the viral 3c gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L. Feline infectious peritonitis: Still an enigma? Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Poder, S. Feline and canine coronaviruses: Common genetic and pathobiological features. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 609465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottier, P.J.; Nakamura, K.; Schellen, P.; Volders, H.; Haijema, B.J. Acquisition of macrophage tropism during the pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis is determined by mutations in the feline coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14122–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takano, T.; Tomiyama, Y.; Katoh, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Satoh, R.; Hohdatsu, T. Mutation of neutralizing/antibody-dependent enhancing epitope on spike protein and 7b gene of feline infectious peritonitis virus: Influences of viral replication in monocytes/macrophages and virulence in cats. Virus Res. 2011, 156, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hamme, E.; Desmarets, L.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. Intriguing interplay between feline infectious peritonitis virus and its receptors during entry in primary feline monocytes. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrrha, L.W.; Silva, F.M.; Peternelli, E.F.; Junior, A.S.; Resende, M.; de Almeida, M.R. The paradox of feline coronavirus pathogenesis: A review. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, Y.; Alcaraz, A.; Bossong, F.J.; Collisson, E.W.; Diniz, P.P. Feline coronavirus in multicat environments. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 1133–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colitz, C.M. Feline uveitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 20, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.J. Ocular manifestations of feline infectious peritonitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1971, 159, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Jinks, M.R.; English, R.V.; Gilger, B.C. Causes of endogenous uveitis in cats presented to referral clinics in North Carolina. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2016, 19 (Suppl. S1), 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, R.L., Jr.; Wilcock, B.P. Histopathologic study of uveitis in cats: 139 cases (1978–1988). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1991, 198, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes, A.H.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; Harbour, D.A. Feline infectious peritonitis: A review of clinicopathological changes in 65 cases, and a critical assessment of their diagnostic value. Vet. Rec. 1991, 129, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Chueh, L.L.; Lin, C.N.; Su, B.L. Clinicopathological findings and disease staging of feline infectious peritonitis: 51 cases from 2003 to 2009 in Taiwan. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowska, N.; Pazdzior-Czapula, K.; Lewczuk, B.; Mikulska-Skupien, E.; Przybylska-Gornowicz, B.; Kwiecinska, K.; Ziolkowski, H. Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Immunohistochemical Features of Ocular Inflammation and the Distribution of Viral Antigens in Structures of the Eye. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissi, D.R. A retrospective study of the neuropathology and diagnosis of naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangl, L.; Matiasek, K.; Felten, S.; Grundl, S.; Bergmann, M.; Balzer, H.J.; Pantchev, N.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hartmann, K. Detection of feline coronavirus mutations in paraffin-embedded tissues in cats with feline infectious peritonitis and controls. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stranieri, A.; Giordano, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Giudice, C.; Cannito, V.; Lauzi, S. Comparison of the performance of laboratory tests in the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stranieri, A.; Scavone, D.; Paltrinieri, S.; Giordano, A.; Bonsembiante, F.; Ferro, S.; Gelain, M.E.; Meazzi, S.; Lauzi, S. Concordance between Histology, Immunohistochemistry, and RT-PCR in the Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, S. Diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis: Update on evidence supporting available tests. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubielzig, R.R.; Ketring, K.; McLellan, G.J.; Albert, D.M. The uvea. In Veterinary Ocular Pathology: A Comparative Review; Dubielzig, R.R., Ketring, K., McLellan, G.J., Albert, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 245–322. [Google Scholar]
- Corapi, W.V.; Olsen, C.W.; Scott, F.W. Monoclonal antibody analysis of neutralization and antibody-dependent enhancement of feline infectious peritonitis virus. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6695–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, M.A. Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Update on Pathogenesis, Diagnostics, and Treatment. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.W.; Corapi, W.V.; Jacobson, R.H.; Simkins, R.A.; Saif, L.J.; Scott, F.W. Identification of antigenic sites mediating antibody-dependent enhancement of feline infectious peritonitis virus infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74 Pt 4, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.W.; Corapi, W.V.; Ngichabe, C.K.; Baines, J.D.; Scott, F.W. Monoclonal antibodies to the spike protein of feline infectious peritonitis virus mediate antibody-dependent enhancement of infection of feline macrophages. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Scarlett, J.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Golovko, L.; Kennedy, H.; Kamal, F.M. Feline infectious peritonitis: Role of the feline coronavirus 3c gene in intestinal tropism and pathogenicity based upon isolates from resident and adopted shelter cats. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Azuma, N.; Satoh, M.; Toda, A.; Hashida, Y.; Satoh, R.; Hohdatsu, T. Neutrophil survival factors (TNF-alpha, GM-CSF, and G-CSF) produced by macrophages in cats infected with feline infectious peritonitis virus contribute to the pathogenesis of granulomatous lesions. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Ohyama, T.; Kokumoto, A.; Satoh, R.; Hohdatsu, T. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), produced by feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus-infected monocytes and macrophages, induces vascular permeability and effusion in cats with FIP. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slauson, D.O.; Finn, J.P. Meningoencephalitis and panophthalmitis in feline infectious peritonitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1972, 160, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.E.; Lapointe, J.M.; Koblik, P.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C. Diagnostic features of clinical neurologic feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammer, R.; Evensen, O.; Lutz, H.; Reinacher, M. Immunohistological demonstration of feline infectious peritonitis virus antigen in paraffin-embedded tissues using feline ascites or murine monoclonal antibodies. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 49, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Miller, M.A. When tissue antigens and antibodies get along: Revisiting the technical aspects of immunohistochemistry--the red, brown, and blue technique. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 42–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carossino, M.; Ip, H.S.; Richt, J.A.; Shultz, K.; Harper, K.; Loynachan, A.T.; Del Piero, F.; Balasuriya, U.B.R. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by RNAscope(I) in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry techniques. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2373–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carossino, M.; Loynachan, A.T.; James MacLachlan, N.; Drew, C.; Shuck, K.M.; Timoney, P.J.; Del Piero, F.; Balasuriya, U.B. Detection of equine arteritis virus by two chromogenic RNA in situ hybridization assays (conventional and RNAscoI(R))) and assessment of their performance in tissues from aborted equine fetuses. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3125–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denes, L.; Horvath, D.G.; Duran, O.; Ratkhjen, P.H.; Kraft, C.; Acs, B.; Szasz, A.M.; Rumenapf, T.; Papp, M.; Ladinig, A.; et al. In Situ Hybridization of PRRSV-1 Combined with Digital Image Analysis in Lung Tissues of Pigs Challenged with PRRSV-1. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Trujillo, J.D.; Carossino, M.; Meekins, D.A.; Morozov, I.; Madden, D.W.; Indran, S.V.; Bold, D.; Balaraman, V.; Kwon, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease and transmission in domestic cats. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, A.M.; Zhu, K.W.; Dela Cruz, F.N., Jr.; Affolter, V.K.; Pesavento, P.A. Localization of Bovine Papillomavirus Nucleic Acid in Equine Sarcoids. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.; Hunter, L.; Emery, K.; Hewson, R.; Fooks, A.R.; Horton, D.L.; Johnson, N. Detection of Rift Valley Fever Virus RNA in Formalin-Fixed Mosquitoes by In Situ Hybridization (RNAIpe((R))). Viruses 2021, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Vascellari, M.; Zanardello, C.; Melchiotti, E.; Vannini, S.; Forzan, M.; Marchetti, V.; Albanese, F.; Abramo, F. Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and RNAscope in situ hybridization (RNA-ISH) as effective tools to diagnose feline herpesvirus-1-associated dermatitis. Vet. Dermatol. 2019, 30, 491-e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, P.A.; Cunha, C.W.; Li, H.; Jackson, K.; O’Toole, D. In Situ Hybridization for Localization of Ovine Herpesvirus 2, the Agent of Sheep-Associated Malignant Catarrhal Fever, in Formalin-Fixed Tissues. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, C.J.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Lawson, D.; Cohen, C. RNA In Situ Hybridization for Epstein-Barr Virus and Cytomegalovirus: Comparison With In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilasi, A.; Denes, L.; Jakab, C.; Erdelyi, I.; Resende, T.; Vannucci, F.; Csomor, J.; Mandoki, M.; Balka, G. In situ hybridization of feline leukemia virus in a primary neural B-cell lymphoma. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Bellmann, S.; Kremendahl, J.; Kohler, K.; Reinacher, M. Cellular composition, coronavirus antigen expression and production of specific antibodies in lesions in feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 65, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Kremendahl, J.; Addie, D.D.; Leukert, W.; Grant, C.K.; Reinacher, M. Fatal enteritis associated with coronavirus infection in cats. J. Comp. Pathol. 1998, 119, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Carossino, M.; Morozov, I.; Trujillo, J.D.; Meekins, D.A.; Madden, D.W.; Cool, K.; Artiaga, B.L.; McDowell, C.; Bold, D.; et al. Experimental re-infected cats do not transmit SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Animal Identification | Pathotype | Duration (Weeks) | Extraocular Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wet | 4 | Fibrinous peritonitis |
| 2a | Dry | 1 | Pyogranulomatous and fibrinous meningoencephalitis |
| 2b | |||
| 3 | Wet | 1 | Granulomatous peritonitis; lymphoplasmacytic pancreatitis |
| 4 | Wet | 2 | Necrotizing and plasmacytic pleuritis and peritonitis; fibrinosuppurative and plasmacytic hepatitis; necrotizing and plasmacytic interstitial nephritis; pyogranulomatous pancreatitis |
| 5a | Wet | 3 | Nonsuppurative epicarditis; granulomatous meningitis; fibrinous and pyogranulomatous pleuritis and peritonitis; granulomatous nephritis |
| 5b | |||
| 6 | Dry | 1 | Pyogranulomatous nephritis, hepatitis, mesenteric lymphadenitis, and meningitis; nonsuppurative interstitial pneumonia |
| 7 | Dry | 7 | Granulomatous peritonitis, meningitis, polyradiculoneuritis, and nephritis |
| 8 | Dry | 24 | Suppurative lymphadenitis |
| 9 | Dry | 3 | Pyogranulomatous nephritis, hepatitis, meningitis |
| 10 | Dry | 3 | Chronic cholangitis; fibrinous splenitis; peripancreatic necrosis; eosinophilic and granulomatous pancreatic lymphadenitis; eosinophilic osteomyelitis (carpi) |
| 11 | Wet | NA | Chronic interstitial pneumonia; fibrinous, pyogranulomatous peritonitis; pyogranulomatous cholangiohepatitis |
| 12 | Mixed | NA | Nonsuppurative meningoencephalitis; necrotizing adrenalitis; nonsuppurative renal vasculitis; mesenteric lymphadenitis |
| 13a | Dry | 0.14 | Granulomatous and necrotizing peritonitis, nephritis, splenitis, hepatitis, pneumonia, enterocolitis, lymphadenitis, pituitary adenitis, and encephalitis |
| 13b | |||
| 14a | Dry | 6 | Granulomatous nephritis, hepatitis, encephalomyelitis; fibrinous peritonitis |
| 14b | |||
| 15a | Dry | 1 | Granulomatous nephritis, hepatitis, encephalitis |
| 15b | |||
| 16 | Dry | 3.5 | Pyogranulomatous nephritis, hepatitis, peritonitis, pleuritis, pericarditis, and pneumonia |
| 17 | Dry | 4 | Pyogranulomatous pleurtitis, epicarditis, pulmonary vasculitis, meningitis, neuritis, nephritis, and splenitis |
| 18 | Wet | 1 | Granulomatous peritonitis, nephritis and mesenteric lymphadenitis |
| 19 | Dry | 1 | Nonsuppurative meningoencephalitis and perivascular nephritis; purulent rhinitis |
| 20 | Dry | 3 | Lymphocytic nephritis and periportal hepatitis |
| 21 | Dry | 5 | Granulomatous and necrotizing meningoencephalomyelitis; pyogranulomatous nephritis |
| 22 | Dry | 2 | Granulomatous nephritis; lymphoma |
| 23a | Mixed | 6 | Pyogranulomatous meningoencephalitis; subacute purulent pneumonia; pyogranulomatous nephritis |
| 23b | |||
| 24 | Dry | 0.28 | Pyogranulomatous serositis and nephritis, bronchointerstitial pneumonia, hepatitis |
| 25 | Dry | NA | NA |
| 26a | Dry | NA | NA |
| 26b | |||
| 27 | Dry | 16 | NA |
| 28 | Dry | 3 | Pyogranulomatous nephritis and hepatitis |
| 29 | Dry | NA | Meningoencephalitis |
| 30a | Dry | 0.7 | Pyogranulomatous and plasmacytic meningitis, pneumonia, peritonitis, nephritis |
| 30b |
| Animal Identification | Cellular Composition | Grade–Severity | RT-qPCR | IHC | ISH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 2a | M | 3 | + | + | + |
| 2b | M | 3 | + | + | + |
| 3 | L | 2 | + | + | + |
| 4 | L | 1 | - | - | - |
| 5a | M-H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 5b | M | 3 | - | - | NA |
| 6 | L-M | 3 | - | - | - |
| 7 | M-H | 2 | - | - | + |
| 8 | H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 9 | H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 10 | L | 2 | - | - | - |
| 11 | L | 2 | - | - | - |
| 12 | M | 1 | - | - | - |
| 13a | L-M | 2 | + | + | + |
| 13b | L-M | 1 | + | - | - |
| 14a | M | 3 | + | + | + |
| 14b | M | 3 | + | + | NA |
| 15a | M-H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 15b | H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 16 | M | 3 | - | + | - |
| 17 | L | 2 | - | + | + |
| 18 | M-H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 19 | H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 20 | M-H | 3 | - | - | - |
| 21 | M-H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 22 | L-M | 3 | - | - | - |
| 23a | M-H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 23b | H | 1 | - | - | - |
| 24 | L-M | 3 | + | + | + |
| 25 | L | 3 | + | + | + |
| 26a | M-H | 2 | - | - | - |
| 26b | NA | NA | - | - | NA |
| 27 | M-H | 3 | - | - | - |
| 28 | M | 2 | - | - | - |
| 29 | M-H | 2 | + | - | + |
| 30a | M | 3 | + | + | + |
| 30b | M | 3 | + | + | + |
| IHC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| RT-qPCR | Positive | 7 | 1 | 8 |
| Negative | 2 | 20 | 22 | |
| Total | 9 | 21 | 30 | |
| ISH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| RT-qPCR | Positive | 8 | 0 | 8 |
| Negative | 2 | 20 | 22 | |
| Total | 10 | 20 | 30 | |
| ISH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| IHC | Positive | 8 | 1 | 9 |
| Negative | 2 | 19 | 21 | |
| Total | 10 | 20 | 30 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carossino, M.; Del Piero, F.; Lee, J.; Needle, D.B.; Levine, J.M.; Riis, R.R.; Maes, R.; Wise, A.G.; Mullaney, K.; Ferracone, J.; et al. Relationship between Uveal Inflammation and Viral Detection in 30 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080883
Carossino M, Del Piero F, Lee J, Needle DB, Levine JM, Riis RR, Maes R, Wise AG, Mullaney K, Ferracone J, et al. Relationship between Uveal Inflammation and Viral Detection in 30 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080883
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarossino, Mariano, Fabio Del Piero, Jeongha Lee, David B. Needle, Jonathan M. Levine, Ronald R. Riis, Roger Maes, Annabel G. Wise, Keenan Mullaney, Jacqueline Ferracone, and et al. 2022. "Relationship between Uveal Inflammation and Viral Detection in 30 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis" Pathogens 11, no. 8: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080883
APA StyleCarossino, M., Del Piero, F., Lee, J., Needle, D. B., Levine, J. M., Riis, R. R., Maes, R., Wise, A. G., Mullaney, K., Ferracone, J., & Langohr, I. M. (2022). Relationship between Uveal Inflammation and Viral Detection in 30 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens, 11(8), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080883






